Abstract
This article presents RuPro, a new corpus resource of prosodically annotated speech by Russian heritage speakers in the U.S. and monolingually raised Russian speakers. The corpus contains data elicited in formal and informal communicative situations, by male/female and adolescent/adult speakers. The resource is presented with its architecture and annotation, and it is shown how it is used for the analysis of intonational features of spontaneous mono- and bilingual Russian speech. The analyses investigate the length of intonation phrases, types and number of pitch accents, and boundary tones. It emerges that the speaker groups do not differ in the inventory of pitch accents and boundary tones or in the relative frequency of these tonal events. However, they do differ in the length of intonation phrases (IPs), with heritage speakers showing shorter IPs also in the informal communicative situation. Both groups also differ concerning the number of pitch accents used on content words, with heritage speakers using more pitch accents than monolingually raised speakers. The results are discussed with respect to register differentiation and differences in prosodic density across both speaker groups.
1. Introduction
Speakers of heritage languages (heritage speakers, henceforth HSs) form a unique group of bilinguals who grow up with a language at home (heritage language, henceforth HL) that differs from the majority language (language of the larger society, ML) and who are often more fluent in their ML than in the HL (Polinsky 2018). HSs have been shown to perform close to monolinguals in some linguistic areas (e.g., good overall comprehension). Other aspects, however, were found to differ in HSs compared to monolinguals (e.g., morphosyntax) (Aalberse et al. 2019; Montrul 2016; Polinsky 2018).
Prosody in HLs has so far mostly been investigated in specific linguistic structures, such as question intonation (Dehé 2018; Zuban et al. 2023) or nuclear contours (Rao 2016), which have been elicited in experimental settings.
The current article presents a corpus on spoken Russian (RuPro), containing speech by both monolingually raised speakers in Russia and HSs of Russian in the U.S., representing speakers of different age groups (adult/adolescent) and genders (male/female) and containing spontaneous speech in two communicative situations (formal/informal). The corpus has been annotated for prosody, namely, boundary tones, intonational phrasing, and types of pitch accent. It thus allows for a quantitative exploration and comparison of overall intonational features among these speakers. Due to the multilayered structure of the corpus, connections to parts of speech can be drawn and analyzed. The corpus confirms earlier impressions on and provides evidence for a higher prosodic density in HSs, i.e., a more rapid succession of intonational cues, caused by shorter intonational phrases and more pitch accents.
The analysis of the RuPro corpus contributes to research on variation due to bilingualism and due to communicative situation. The corpus can further be explored for gender and age, which remains a topic for further research.
The article is structured as follows: Section 1.1 presents the necessary background on Russian intonation and attested variation (Section 1.2). It also presents a brief review of existing corpora of spoken Russian (Section 1.3) and describes in how far the corpus analyzed here differs from these. Lastly, it reviews previous studies on intonation in HLs (Section 1.4). Section 2 presents the corpus in detail, with its architecture and annotation. The guidelines for the prosodic annotation of our data, which follows an AM-like representation of discrete tonal events over the course of an utterance, are laid out in Section 2.3. Section 3 presents the analyses and results. The results are summarized and discussed in Section 4.
1.1. Intonation in Russian
Russian is a stress language, and word-level stress in Russian is claimed to be free: it can fall on any syllable of the word or any morpheme (e.g., /babočka ’butterfly’, ri/sunok ’drawing’, bara/ban ’drum’; Mołczanow et al. 2013).
Sentence-level intonation plays an important role in Russian due to its flexible word order and its marking of information structure (e.g., theme/rheme) through prosody, in addition to lexical or syntactic means. Polar questions are distinguished from declaratives only by prosodic means (Svetozarova 1998, pp. 268–69).
One influential approach analyzes Russian intonation in terms of seven intonational categories or so-called “intonational constructions” (intonacionnye konstrukcii, henceforth IKs) (Bryzgunova 1963, 1980). The IK model primarily had the didactic purpose of teaching Russian intonation to non-native speakers of Russian. IKs differ with respect to the level and position of pitch in a syllable, which is important for distinguishing different meanings of a sentence (e.g., affirmation, wh-question, exclamation). An IK has an obligatory center (stressed syllable on which the nuclear pitch accent falls) and an optional part/parts that are located right before or right after the center and can be composed of one or more syllables (Bryzgunova 1980, pp. 97–101). There are seven IKs that are distinguished by Bryzgunova (1980). The IKs have a basic neutral meaning and additional modal meanings that express the personal attitude or emotions of a speaker (e.g., anger, fear, surprise).
Bryzgunova’s (1980) theory received criticism in the literature on Russian intonation. For instance, Zybatow and Mehlhorn (2000, p. 415) point out that IKs only describe the local F0 contours, namely, the placement of the nuclear pitch accent and the syllables that immediately precede and follow it. Thus, it is not possible to describe the intonational contour of an entire utterance with them.
Other studies on Russian intonation describe the intonation of specific sentence types and syntactic categories (e.g., interrogatives, exclamations) (e.g., Svetozarova 1998). A typical intonation contour of an SVO declarative sentence with broad focus has a sequence of rising and falling pitch accents, with a rising (L+H*) accent on the clause-initial topic and a falling H+L* nuclear pitch accent on the final constituent, (Jasinskaja 2014, p. 711; Svetozarova 1998, p. 270; Yokoyama 1987, pp. 182–91). In addition, every content word is expected to receive an accent, and downstepped accents are expected on content words following the first one (Jasinskaja 2014, p. 711). In general, content words are typically accented in monolingual Russian, and function words are not (Svetozarova 1998, pp. 266–67).
In utterances with narrow focus, any word in an utterance can be focused and is usually marked with an H*+L accent. Prenuclear accents are either rare or absent, and all constituents that follow the focused one are unaccented (Jasinskaja 2014, pp. 711, 713).
Regarding sentence types other than declaratives, yes-no questions are particularly interesting, since they do not differ from the declarative sentences in Russian in terms of their morphosyntax but only in terms of their intonation pattern (e.g., Rathcke 2006a; Svetozarova 1998). In non-contrastive SVO yes-no questions, the verb receives a rising nuclear pitch accent, and other constituents are expected to be deaccented. However, Zuban et al. (2023) found that monolingual speakers of Russian do not always deaccent subjects and objects in this context. In addition, the final boundary tone of yes-no questions is typically low (Igarashi 2008; Rathcke 2006b; Svetozarova 1998).
One of the current approaches to intonation is the Autosegmental-Metrical approach (Pierrehumbert 1980; Ladd 2008; abbreviated as AM). According to this approach, intonation is analyzed as sequences of discrete intonational events. The emerging pitch contour can be seen as a transition from one tonal event to the next. There are two main types of tonal events, namely, pitch accents and edge tones. Pitch accents are prominence-lending pitch excursions associated with metrically strong syllables. All pitch accents consist of a single H (high) or L (low) tone or a combination of two tones. In bitonal accents, one of two tones is central, i.e., it is linked to the stressed syllable and is marked with an asterisk (H* or L*) (Ladd 2008).
Edge tones are tones “that are associated with the periphery of a prosodic domain” (Ladd 2008, p. 47). Each edge can be of two types: phrase accents (notated as L-, H-) or boundary tones (notated as H%, L%). The phrase accent is a tone that appears “after the nuclear pitch accent and before the boundary tone”. Boundary tones are tones that are associated with the very end of an intonational phrase (or the very beginning, in some languages) (Pierrehumbert 1980, p. 84).
The AM model of intonation has not received a lot of attention in research on monolingual Russian. Studies on Russian intonation that have been carried out following the AM framework present the results of some specific case studies (e.g., Igarashi 2006 on intonation of questions; Rathcke 2006a on differences between yes-no questions and declarative utterances; Meyer and Mleinek 2006 on pitch accents in yes-no questions; Zuban et al. 2023 on yes-no questions in monolingual and bilingual speakers of Russian). ToRI (Transcription of Russian Intonation) does not fully follow some tenets of the AM framework, e.g., it recognizes a middle tone M that is not assumed in the standard AM theory (Odé 2008).
Rathcke (2009, p. 37) summarizes the existing work on Russian intonation in the AM framework, specifying the frequent nuclear pitch accent types together with the boundary tones and their meaning. Her overview is given in Table 1.

Table 1.
Frequent nuclear F0 contours, their AM analysis and semantic interpretation in Russian (from Rathcke 2009, p. 37).
The summary in Table 1 serves as a starting point for the analysis of Russian intonation within the AM framework, but it leaves some questions for further clarification, such as the meaning of the H+L* LH% tune (as indicated by the question marks in Table 1). Also, the status of monotonal pitch accents is not clear. Although Table 1 postulates the existence of a monotonal H* accent in monolingual Russian, it is also stated that it is probably a bitonal H*+L rather than an H* accent. In other work, the H* accent does not form part of the inventory of Russian intonation. For instance, Odé (2008) proposes the following inventory of pitch accents in monolingual Russian: H*L, H*H, H*M, L*, HL*, and L*H. Yokoyama (2001) suggests that there are no monotonal accents in Russian at all, but only rising and falling accents. Jasinskaja (2014), on the other hand, assumes that monotonal H* accents do occur in Russian (e.g., in prenuclear positions or on verbs of SVO utterances with broad focus).
As for bitonal pitch accents, they are frequent in Russian. Rising pitch accents are typical at the beginning of a phrase (especially with the SVO order), whereas falling accents are typical in nuclear position (Comstock 2018; Jasinskaja 2014). Furthermore, combinations of falling and rising pitch accents are common in Russian, and they are referred to as a “harmonica pattern” and a “sawtooth pattern” (in the latter, a sequence of rising and falling accents have a small excursion) (Odé 2008).
1.2. Variation in Russian Intonation
In general, when analyzing intonation in the speech of mono- and bilingual speakers, variation can be expected due to a variety of reasons, least of which lies in the different linguistic biographies of the speakers. Sociolinguistic and dialectal variation in prosody has recently received more attention (see Armstrong et al. 2022) and is also increasingly being documented for intonation in Russian (see Post 2017 for a motivation), as will be reviewed in this section.
Socially determined variation has been found by Kachkovskaia et al. (2022) based on analyses of data from the SibLing corpus. They found that peak alignment in Russian rise-fall tunes varies with the social factors of age and gender.
Dialectal variation has been attested in an experimental study by Duryagin and Knyazev (2022) that investigates the phonetic realization of the falling nuclear pitch accent in Russian (in AM H*L), reported to be used in narrow focus constructions, wh-questions, and exclamations. Speakers of Northern Standard Russian spoken in urban areas of the Vologda region tend to align the high turning point significantly later than speakers of Central Standard Russian from Moscow. Post (2022) documents dialectal differences in polar question intonation in spontaneous speech in Russian speakers from Moscow and Perm.
Variation due to bilingualism has been reported by Visson (1989) and Andrews (1993) for heritage speakers (called émigré speakers in these publications). Andrews (1993, p. 162) reports the “strange intonation” that is noticed in heritage language speakers; Visson states that they lose “the sharply rising and falling cadences” of Russian (Visson 1989, p. 186). Andrews (1993) bases his descriptions on interviews with 12 young adults (20 to 34 years old) who were either born in the former Soviet Union and left during early childhood (between 6 and 12 years old) or were born in the U.S. to Russian-speaking parents. Most identified themselves as native speakers of both Russian and English.
1.3. Corpus Studies on Russian Intonation
Dobrushina and Sokur (2022) have recently reviewed and categorized existing spoken corpora for Slavic languages. For Russian, 30 spoken corpora of different varieties have been reviewed. The authors categorize the spoken corpora according to the type of lect, namely, “corpora of standard languages (which are spoken mainly in cities and exist in written as well as in oral form), dialects (spoken mainly in villages and not written), and bilingual varieties (this includes varieties spoken as L2 by people with a different language as L1 and all varieties that evolved in a multilingual environment)” (p. 80). Furthermore, the corpora are differentiated according to type of text or register (p. 82), such as public and private, prepared and spontaneous texts, and monologues and dialogues.
Following their categorization, the RuPro corpus that we present in this article can be described as containing data of “standard language” by monolingually raised speakers of Russian in urban areas as well as data of a bilingual variety, namely, heritage Russian in the U.S., which evolved in a multilingual environment. It contains spoken data elicited both in formal and informal communicative situations. For further details, see Section 2.
As for annotations, most spoken corpora reviewed by Dobrushina and Sokur (2022) contain morphological annotations, whereas syntactic and/or prosodic annotation are reported to be very rare (p. 86). RuRro is unique in that it contains all three, i.e., morphological, syntactic, and prosodic annotations. The corpora of spoken Russian are briefly reviewed in the following, which also provide prosodic annotations.
CoRuSS (Kachkovskaia et al. 2016; Volskaya and Kachkovskaia 2016) is a corpus of 14 h of Russian spontaneous speech by 60 speakers of three age groups, balanced for gender. Interactive dialogues on free topics were manually transcribed for their prosody, differentiating between 13 basic melodic types (largely following the intonational constructions postulated in Bryzgunova 1980, see Section 1.1). The prosodic annotation in CoRuSS includes phrasing (IPs), prosodic prominence, and tonal events. Annotations were created based on perceptual impression and acoustic measures.
In Skrelin et al. (2010), the results of prosodic annotations of spontaneous speech in CoRuSS are compared with prosodic annotations in CORPRES, a prosodically annotated corpus of Russian Professionally Read Speech of different genres to be used for text-to-speech synthesis. It contains 60 h of speech from eight speakers (4m, 4f), i.e., up to 7.5 h per speaker.
SibLing (Kachkovskaia et al. 2020) is a recently created corpus of Russian dialogue speech, designed for the scientific study of entrainment. It contains 90 dialogues by 100 speakers, playing a card game and a map task. It is balanced for gender and degree of familiarity of the interlocutors. The prosodic annotations of the corpus include automatically detected turn boundaries and inter-pausal units. Further prosodic annotations are partially available (following the approach by Volskaya and Kachkovskaia 2016).
Lastly, the Russian Intonation Corpus (RINCO) (Arkhipov et al. 2012; Kodzasov et al. 2011) was designed to contain descriptions of prosodic characteristics, such as tones, loudness, phonation types a.o. for quasi-natural dialog utterances, as well as for a selection of spontaneous and prepared spoken narrative texts of different genres.
The RuPro presented here provides prosodic annotations relating to phrasing (intonation phrases), pitch accent (PA) type, and boundary tones (BT). The creation of (spoken) corpora is technically challenging and requires many well-grounded decisions concerning transcription and annotation (see Shadrova et al., forthcoming). More details on the annotations created for this corpus are provided in Section 2.4.
1.4. Intonation in Heritage Languages
Studies on variation in Russian intonation due to bilingualism were reviewed in Section 1.2. In the field of HL research, an increasing number of case studies have investigated intonational features of bilingual heritage speakers, a selection of which will be revised in this section.
Bullock (2009) found for Pennsylvanian French, a moribund HL in the U.S., that high pitch accents were used to express focus on clitics. Focus is usually expressed through syntactic dislocation and phrasing in Standard French. High pitch accents are a common focus strategy in English though. Her research showed that intonational features typical of the ML have been transferred to the HL.
Rao (2016) investigated nuclear contours in statement and question intonation in HSs of Mexican Spanish. For statements, HSs were found to use fewer tunes for different pragmatic meanings as compared to monolingual speakers. For questions, the nuclear contours are varied and different from monolingual speakers. Together, the results suggest that intonation and meaning are linked differently in heritage and monolingual speakers. Rao (2016) attributes these differences to exposure to diverse forms of intonational input, either from the input varieties of, e.g., the parents, or from the ML.
Dehé (2018) investigated the intonation of yes-no questions in North American heritage Icelandic and compared it to Icelandic spoken in Iceland and to English spoken in Canada. It was found that HSs of North American heritage Icelandic had a lower percentage of falling terminals in Icelandic compared to Icelandic monolinguals and a slightly lower percentage of rising terminals in yes-no questions in English compared to English monolinguals. These results give evidence for bidirectional prosodic influence between an HL and an ML.
In a cross-generational, inter-familial study, Aziz et al. (2022) followed up on Rao (2016) and investigated pitch accents, boundary tones, and overall nuclear contour in yes/no questions in Spanish HSs, with the aim to differentiate parental influence and influence from the ML. They found evidence that influence can be attested from both, although differently for the tonal elements investigated.
In an interactional task collecting spontaneous speech, Kim (2023) investigated uptalk and IP-final deaccenting in HSs Spanish and English. She found that uptalk and IP-final deaccenting occurred in both HSs’ languages, but that cross-linguistic influence affected the realization and the frequency of these prosodic phenomena differently. She interprets the results in that if languages are in competition as they are in bilinguals, phonological distinctions are kept, whereas phonetic distinctions that do not alter meaning are more susceptible to be changed to reduce processing costs.
For a heritage setting involving Russian, Comstock (2018) investigated the intonation by two monolingual Russian-speaking journalists and one HS of Russian in the U.S. in two different interview situations. Comstock (2018) reports that the HS was similar to the monolingual interviewers regarding some intonational patterns, e.g., by producing a comparable number of nuclear H+L* accents or IP-initial rising accents or by producing a comparable number of one-word IPs. However, the HS also differed from the monolingual speakers, e.g., by producing monotonal pitch accents and fewer bitonal accents than the monolingual interviewers (Comstock 2018, pp. 240–65).
A study on the intonation patterns of yes-no questions produced by monolingual Russian speakers and Russian HSs living in the U.S. and in Germany could not find evidence for an influence of the ML on the HL (Zuban et al. 2023). However, intonation patterns still differed between the groups, as HSs generally produced more pitch accents on syntactic constituents compared to monolinguals.
Thus, previous research on intonation in HLs has provided varied evidence for emerging differences, which can sometimes be traced back to the mutual influence of a speaker’s languages. The data from RuPro presented here focus on the distribution of intonational features across spoken productions.
2. Material and Methods: Corpus
2.1. Data
As the database for our analysis, we used the prosodically annotated corpus of heritage Russian (RuPro; spoken in the U.S.), which allows us to investigate overall intonational features and compare them with comparable data from monolingually raised speakers.1
RuPro extends a subcorpus of the RUEG corpus (Wiese et al. 2021), collected and annotated by the collaborative research unit «Emerging Grammars». Naturalistic repertoire data were elicited by means of presenting participants with a fictional incident. Participants were instructed to describe a minor car accident, acting out different communicative situations that covered different modes and settings (spoken/written x formal/informal) (for details on methodology, see Wiese 2020). The overall corpus contains data from bilingual speakers of heritage Russian, heritage Greek, and heritage Turkish and majority English and majority German as well as data from bilingual speakers of heritage German and majority English. Data by monolingually raised speakers of German, English, Russian, Greek, and Turkish were elicited to enable comparisons.
Each speaker provided narrations that reported on the accident in a formal communicative situation (i.e., talking to a policeman or writing a police report) and in an informal communicative situation (i.e., leaving a voice message to a friend or leaving a written WhatsApp message to a friend). RuPro contains the data from the spoken communicative situations (formal/informal).
2.2. Speakers
The RuPro corpus contains the spoken data of 53 HSs of Russian in the U.S. and 40 monolingual Russian speakers. The speakers fall into two age groups, i.e., adolescents (14–18 years; 20 monolingually raised, 22 bilingual) and adults (22–35 years; 20 mono-, 31 bilingual). The data of all HSs were gathered in the greater Washington area (Virginia, Maryland, DC), and the data of monolinguals were collected in Saint Petersburg. The corpus data of each participant is enriched with extensive metadata on their language background, socio-economic status, and personality traits.2
HSs providing the data for the corpus were second-generation speakers who were either born in the U.S. or moved there before the age of five. Nearly all HSs were exposed to Russian from birth at home. A small number of HSs also learned Russian as a foreign language in a formal school setting for different periods of time. Some HSs were additionally engaged in activities in Russian (e.g., music lessons, dance classes). Very many HSs could write in Cyrillic script and reported that they felt like native speakers of Russian. HSs self-assessed their language skills in understanding, speaking, reading, and writing Russian on a five-point scale from “very easy”, “easy”, “neither easy nor difficult”, “difficult”, to “very difficult”. In order to gain information on language input, speakers further self-assessed how often they conversed in Russian and/or used various media on a three-point scale from “never”, “sometimes” to “often”.
From the information provided, it emerged that Russian HSs were quite actively involved with the Russian language, though less so than Russian monolingually raised speakers.
2.3. Corpus Annotation/Preprocessing
For the original RUEG corpus, all Russian data3 were transcribed, normalized, and annotated for part-of-speech (PoS) and communicative unit, the latter being a substitute unit for sentence that is more easily applicable across production modes (CU, Hughes et al. 1997; Loban 1976). Many annotations in the corpus have been created manually; PoS tags and lemmas are manual corrections of automatic annotations created with UDPipe (Straka et al. 2016) and MyStem analyzer (Segalovich 2003). The annotated corpus data are stored in two formats, EXMARaLDA (Schmidt and Wörner 2014) for morphological and lexical annotations as sourced from the original RUEG corpus, and PRAAT (Boersma and Weenink 2007) for the additional prosodic annotations for RuPro. For the final RuPro corpus that only features spoken data, both sources are merged using Pepper (Zipser and Romary 2010), aligning the annotated tokens from the EXMARaLDA and the PRAAT data. This way, morphological and prosodic information can be combined when querying the compiled corpus in ANNIS (Krause and Zeldes 2016; Krause 2019).
The prosodic annotations are based on the diplomatic tokenization of the RUEG corpus, a segmentation into words of the original transcriptions. The diplomatic token layer is as close to the speaker’s utterance as possible, e.g., disfluencies are represented or potential grammatical disagreement with a standard grammar is not assimilated. Those tokens are aligned with the audio signal using WebMAUS (Kisler et al. 2017; Schiel 1999); the alignments were manually checked and corrected if necessary. Syllables were manually annotated for all tokens that carry relevant phonetic events (pitch accents or boundary tones), providing a partial baseline tokenization for prosodic annotations. The data have been annotated by two linguistically trained annotators, and three prosodic layers for pitch accents (see Section 2.4.1 and Section 2.4.2) and boundary tones (see Section 2.4.3 and Section 2.4.4) were assigned to the syllable on which they were observed. Intonation phrases were annotated on a fourth annotation layer, grouping all the speech material into larger units (following guidelines in Himmelmann et al. 2018, see below). Intonation phrases are competing sentential units to CU, which are more useful to phonetic analyses.
2.4. Criteria for Prosodic Annotation
Given that the RuPro corpus on spoken Russian comprises data from both monolingual and bilingual speakers of Russian, it had to be decided which annotation system to use for non-standard or bilingual prosody. The well-established system of Bryzgunova (1980), with its close tie of intonational form and function, did not seem to be suitable, as it is debatable whether the same forms are used with the same functions by bilingual speakers. Decoupling form and function seemed to be mandatory for our work.
The autosegmental-metrical framework to intonation (AM-theory; see Section 1.1) distinguishes between form and function of tonal events and contours. Research on Russian intonation that has been carried out in the AM framework investigates the intonation in specific linguistic structures (e.g., Igarashi 2008 on question intonation, Rathcke 2006a on yes-no questions and contrastive emphasis). However, in bilingual speech, we cannot assume a priori that the same inventory exists in both speaker groups.
For bilingual speech, Gut (2009, p. 70) used a modified version of ToBI in her corpus-based analysis of phonological and phonetic properties of L2 English and German by speakers with varying L1s. Across all interlanguages, her annotation system is comprised of 12 different types of pitch accents and eight edge tone combinations.
For our corpus, a phonetic-auditory approach was taken for annotation of both monolingual and heritage speakers’ intonation: pitch accent location, pitch accent type, and boundary tone were determined based on auditory impression and F0 examination (such as low and high turning points). A ToBI-style label was assigned that mirrored the phonetic-auditory impression closest, resulting in the inventory of pitch accents and boundary tones shown below. The prosodic annotations were carried out by two annotators who are both speakers of Russian.
2.4.1. Pitch Accent Location
Pitch accent placement was determined auditorily and phonetically. The presence of a pitch accent was identified by increased duration and higher intensity of the stressed syllable and further analyzed with regard to the local F0 changes (low and high turning points).
2.4.2. Pitch Accent Type
Six types of pitch accents (L*, H*, L*+H, L+H*, H+L*, and H*+L) and two phrase-final boundary tones (L%, H%) emerged as relevant in the data. Pitch accent types were annotated according to the following principles:
- H*: an accent with a high tonal target in the accented syllable without any sharp low target nearby.
- L*: an accent with a low tonal target in the accented syllable without any sharp high target nearby.
- H+L*: a falling accent that starts at a high pitch level and falls to a low target in the accented syllable.
- H*+L: a falling accent with a high target in the accented syllable, followed by the falling pitch.
- L*+H: a rising accent with a low tonal target in the accented syllable, followed by a sharp rise to high pitch (the F0 peak is realized after the accented syllable).
- L+H*: a rising accent with a high tonal target in the accented syllable, which is preceded by a sharp rise from a low target (the F0 peak is realized in the accented syllable).
All H tones could be additionally upstepped (i.e., pitch range is expanded compared to a preceding high tone, indicated by ^) or downstepped (i.e., pitch range is compressed compared to a preceding high tone, indicated by !). Upstepped and downstepped tones are considered to constitute one category, whose phonetic realization solely depends on the tonal context (only occurring when a previous H is present; downstepped if previous H is higher, upstepped if previous H is lower). Figure 1 exemplifies the pitch accent types described.
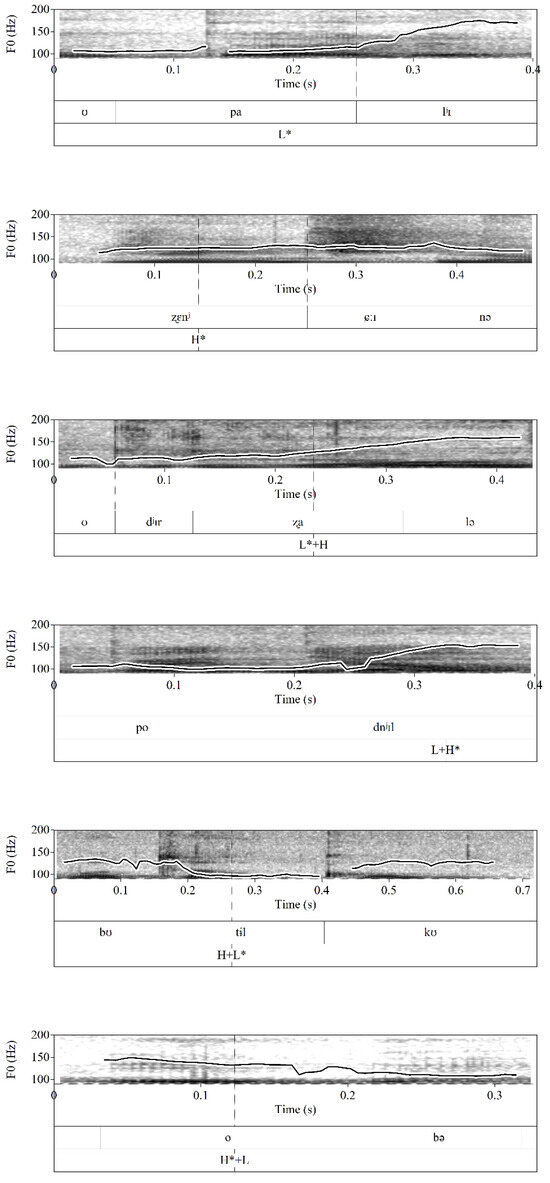

Figure 1.
Examples of pitch accents annotated in RuPro.
2.4.3. IP Boundaries
Phonetic IP boundaries were annotated based on prosodic cues, following the annotation guidelines stated in Himmelmann et al. (2018). In their cross-linguistic interrater study, they provide empirical evidence for their claim that in spontaneous speech, IPs are robustly identifiable by naive annotators across familiar and unfamiliar languages (in their study, German and three languages of Indonesia unknown to the annotators). Their method thus seems particularly suited to be applied to spontaneous monolingual and bilingual speech.
Himmelmann et al. (2018) instructed naive annotators to segment narratives “into sequences that are perceivable as a distinct unit by means of a coherent melody” (p. 1 supplement). They further specified that intonation phrase boundaries are typically characterized by two features (also supplement): “(i) the interruption of the rhythmic delivery by, inter alia, a pause or final lengthening, and (ii) the disruption of the pitch contour by a jump in pitch (up or down) between the end of one unit and the beginning of the next”. They specifically point out that in cases when an IP is followed by a hesitation pause and the pitch stays at the same level afterwards, the material after the hesitation should be included into the same IP.
2.4.4. Boundary Tones
Final boundary tones were annotated according to the following principles: The label L% was assigned at a boundary with a low pitch level in the speaker’s range at the end of an IP. The label H% was assigned at a boundary with a high pitch level in the speaker’s range at the end of an IP. The H% could be further upstepped or downstepped depending on a preceding high pitch accent. An upstepped ^H% represents a higher target at the boundary than any preceding H-toned pitch. A downstepped !H% represents a high pitch level at the boundary, which is lower than a preceding H-toned pitch. Figure 2 exemplifies the boundary tones described.
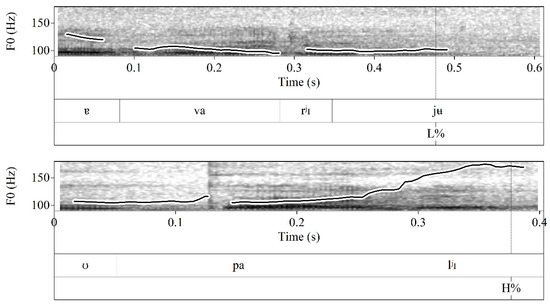
Figure 2.
Examples of boundary tones annotated in RuPro.
2.5. Interrater Agreement
In the initial phase of the prosodic annotation, interrater agreement between the two annotators was calculated for intonation phrases on a small sample of eight speech recordings (2 male, 2 female; 4 formal, 4 informal). The descriptive statistics for the sample are given in Table 2 by the annotator.

Table 2.
Rater measures on subsample.
Himmelmann et al. (2018, p. 220) found that the mean length of an IP varies from 3.29 to 5.35 words depending on the annotator, with a grand mean of 4.09 words per IP. The results from our small sample fall within this range and also confirm that differences depending on annotator exist. A closer look at the individual annotations reveals that annotators differ rather consistently from each other in their tendency to either assume more or fewer IPs in a given stretch of speech. Annotator 2 posits more IPs than annotator 1, resulting in shorter IPs on average. Such inter-individual differences have also been noted in Himmelmann et al. (2018, p. 221).
Table 3 shows the agreement between the two raters on individual speech files as well as the overall agreement. As the start of the first IP and the end of the last IP in a narrative always coincide with the first and last words and are thus given by definition, they were excluded from evaluation. We therefore have to consider 3116 potential IP boundaries, respectively (one less than the number of words for each subcorpus (and speech file, respectively)).

Table 3.
Interrater agreement (kappa scores).
Overall, we obtained a kappa score of 0.65, which represents substantial agreement according to Landis and Koch (1977).
As will be seen in Section 3.2, the mean length of IPs across the entire RuPro corpus turns out to be lower, with 2.4 to 3 words per IP. This difference might be due to differences in elicitation: whereas in Himmelmann et al. (2018) spontaneous productions were elicited by means of retellings of the Pear Film, which is a six-minute film, the productions in the RUEG corpus are oral reports on a car accident to a friend and the police via voice messages, prompted by a 42 seconds’ video. The narrations in RUEG are thus a priori shorter and contain discourse openings and closings, which will lead to overall shorter utterances on average.
2.6. Corpus Integration
Next to prosodic annotations, the RuPro subcorpus also contains the annotations from the original RUEG corpus for the selected speakers, i.e., morphological annotations (lemma, PoS, morphological features), annotations on referent introduction, and metadata related to the speakers represented in the corpus.
In the original RUEG database, their morphological and lexical annotations are based on a normalization of the diplomatic tokens, whereas the prosodic annotations are based on syllables. Both normalization and division into syllables reinterpret the diplomatic tokens in different ways by edition, merge, and subdivision. Thus, the diplomatic tokenization is the entry point for merging the two sets of annotations. Unfortunately, association between syllable segmentation and diplomatic text in the prosodic data, on the one hand, and normalized tokens and diplomatic tokens, on the other hand, are modeled by text coverage rather than explicit association edges (i.e., as overlapping table cells). This implicit association makes mapping normalized tokens and syllables to each other correctly a complex and expensive task. To avoid this and to fully and automatically merge the two sources without misrepresenting the data through invalid associations between morphological and prosodic information, the diplomatic tokens of the prosodic data and the diplomatic tokens of the RUEG corpus are linked via explicit correspondence edges in a parallel corpus fashion. This way, prosody can be analyzed incorporating morphological or referential information, and vice versa (see Sharova et al. accepted for illustration).
3. Analyses and Results
The RuPro subcorpus is used to address research questions on overall intonational features in the speech of HSs of Russian in the U.S. and monolingually raised Russian speakers, concerning the tonal inventory of pitch accents and boundary tones and their frequency, as well as the size of intonational phrases.4
3.1. Tonal Inventory
Prominences representing pitch accents were detected auditorily, and tonal labels were assigned according to the guidelines stated in Section 2.4.2. The occurrences and frequencies of pitch accent types that emerged across the two groups are given in Table 4. Note that upstepped and downstepped tones are grouped together, as they can be considered to constitute one category whose phonetic realization depends on the tonal context, see also Section 2.4.2.

Table 4.
Number of occurrences of the different PA types across groups.
Table 4 and Figure 3 reveal an overall similar distribution in the types of pitch accents used by both speaker groups. Thus, contrary to Rao (2016), we do not find evidence for a reduced inventory in HSs. Despite the attested occurrence of all pitch accent variants in both groups, however, we cannot exclude systemic differences in the tonal inventories, given that the labels are based on a phonetic approach. However, individual pitch accents could be further investigated for their phonetic realization, which is beyond the scope of the current paper.
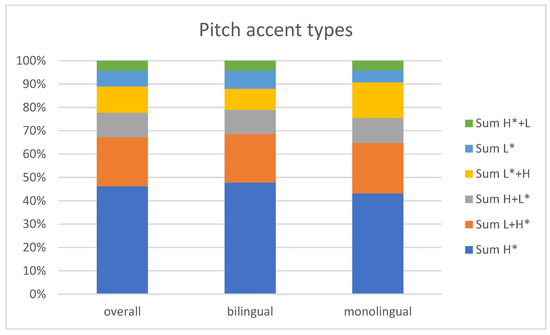
Figure 3.
Visualization of the relative distribution of pitch accent types in both speaker groups.
What seems noteworthy considering the literature on Russian prosody is the very high number of monotonal H* accents across both groups, which have been claimed by some scholars to not or only rarely occur in Standard Russian (see discussion in Section 1.1). We attribute this to our phonetic approach to pitch accent annotation and the fact that we annotated unprepared spontaneous speech as opposed to read and prepared speech. Intonational variance has been observed across these two speaking styles: De Ruiter (2015) found for German intonation that speaking mode (i.e., spontaneous versus read speech) was highly relevant. In spontaneous speech, more pitch accents and less pitch accent variation could be found in the marking of information status than in read speech. In spontaneous speech, pitch variation might also be less pronounced, and thus bitonal pitch accents are less easily detectable. However, the overall high number of bitonal pitch accents across both groups (44.4% in HSs, 51.8% in monolingual speakers) is still remarkable.
Across the groups, there seem to be slightly more monotonal accents annotated for HSs (55.6% of all pitch accents in this group are monotonal) than for monolingual speakers (48.2% of all pitch accents are monotonal). This might be due to a reduction or simplification of tones in bilingual speakers (see Trudgill 2010, p. 4 for simplification and reduction as major processes in language contact and language change), or it can be due to other differences in the intonation system, e.g., related to the size of intonational phrases, which might lead to increased time pressure to realize tonal targets.
It remains a topic for future research whether mono- versus bitonal accents undergo language change. A future study would need to look at adolescents and adults to check for evidence of language change in monolingual Russian. We would expect more monotonal accents in adolescents than in adults if the emergence of monotonal accents was a recent development.
3.2. Intonation Phrases
IPs were extracted from the data per speaker group and formality in order to find out whether speaker groups differed in the length of IPs (in words).
Words are defined as units tagged for PoS. Hesitations might have constituted an “IP”, but IPs containing only hesitations were not annotated for PA placement, PA type, or boundary tone. However, if hesitations were continuously integrated into an IP (see criteria in Section 2.4.3), they formed part of it. For the analysis, the number of IPs containing the prosodic labels of boundary tones (BTs) were extracted from the data, thus excluding IPs only containing hesitations. The results concerning the length of IPs are reported in Table 5 and Figure 4.

Table 5.
Length of IPs across speaker groups by formality.
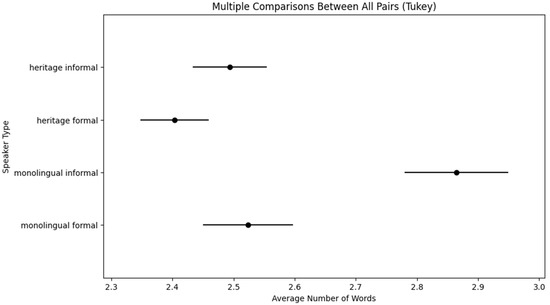
Figure 4.
Visualization of the Tukey HSD.
In order to test for statistically significant differences between speaker groups and formality, we ran a linear mixed model in Python with words/IP as the dependent variable and speaker group (HS/monolingual) and formality (formal/informal) as independent variables, also testing the interaction between the variables of speaker group and formality. Speaker was added as a random effect. The model revealed a significant effect of formality (z = 5.97, p < 0.001) and a significant interaction of formality and speaker group (z = −3.52, p < 0.001). A post-hoc pairwise comparison, using Tukey HSD, revealed a significant difference between monolingual formal and informal (p < 0.001) and between monolingual informal and heritage informal (p < 0.001), as shown in Figure 4.
We thus find that IPs are generally shorter in formal communicative situations than in informal ones. However, only monolingually raised speakers of Russian show a register effect, in that they produce longer IPs in the informal than in the formal communicative situation. This is also where the two speaker groups differ: in informal communicative situations, monolinguals produce longer IPs than HSs. HSs do not show any difference between formal vs. informal communicative situation. In formal communicative situations, the two speaker groups do not differ from each other.
Our results on average IP size are roughly in line with the work by Volskaya and Kachkovskaia (2016), who found the average length of IPs to be 3.58 lexical words, or 2.31 prosodic words in CoRuSS.
3.3. Pitch Accents
3.3.1. Number of Pitch Accents on Content Words
In a first step, the number of PAs was extracted per speaker group and per formality and normalized against the overall number of words (i.e., PoS-tagged entities) in order to see whether the two groups differ in the frequency of use of PAs. If all PoS-tagged entities are taken as the basis, PAs on function words, connectors, conjunctions, and interjections would also be considered. PAs are structurally not expected on these words and might be a consequence of speech planning or processing issues in unprepared speech.
As we were interested in the question as to whether there is a difference in the frequency of use of structurally licit PAs, i.e., on content words, we reran the calculation with PAs on content words, i.e., noun, proper noun, adjective, adverb, verb, or numeral and normalized them by the overall number of words in these categories. The corpus architecture and annotation allowed for the combined query of the co-occurrence of prosodic and morphosyntactic information. Both analyses yielded similar results, and we only report on the occurrence of PAs on content words in Table 6.

Table 6.
Number of pitch accents on content words across speaker groups by formality.
For statistical modeling, we ran a binomial generalized linear mixed-effects model in R (R Core Team 2020) using lme4 (Bates et al. 2015), sjPlot (Lüdecke 2020), and tidyverse (Wickham et al. 2019) packages for data preparation and visualization. The dependent variable was the presence (1) or absence (0) of a pitch accent on a content word. The independent variables were speaker group (HS/monolingual) and formality (formal/informal). The interaction of speaker group and formality was included. The motivation was to see whether the group itself had an influence on the occurrence of PAs. or whether it influenced the aforementioned variable together with formality. The independent variables were contrast-coded as either −0.5 or 0.5. This is essential to allow for analysis of their interactions. Speaker was added as a random effect.
The model revealed one main effect of speaker group, which is plotted in Figure 5. Accordingly, HSs produced more PAs on content words than monolingual speakers (z = 6.53, p < 0.001).
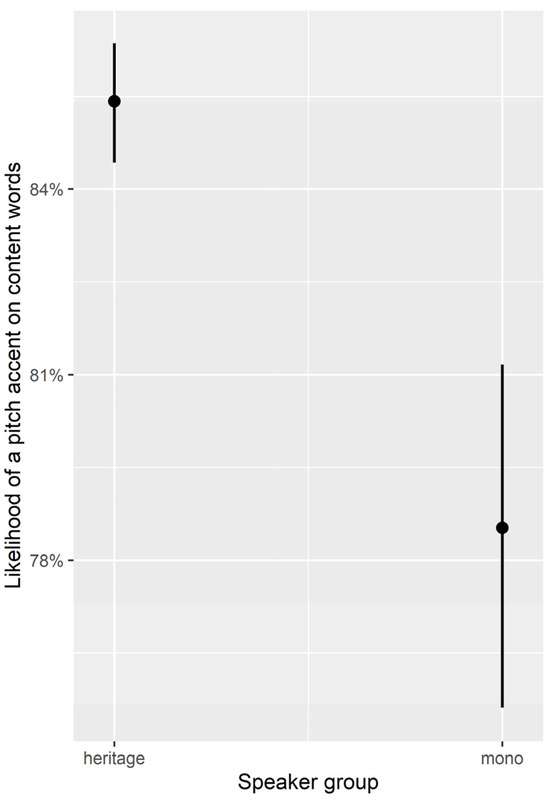
Figure 5.
Visualization of the likelihood of a pitch accent on content words by speaker group.
A higher number of PAs has also been found in other studies, referring to speakers or data in the RUEG corpus. In their work on yes/no questions in heritage and monolingual Russian, Zuban et al. (2023) found that HSs realize more PAs on subjects and objects as compared to monolingual speakers. In their work on narrowly focused adjectives, Zerbian et al. (2022) likewise found that HSs produce more PAs in modified noun phrases.
3.3.2. Number of Pitch Accents on Verbs
Exploiting the annotations of the corpus in different linguistic domains, we further checked the number of PAs on verbs (“V”) across both speaker groups. Verbs in Russian frequently receive a PA, possibly more often than in English (e.g., Jasinskaja 2014, p. 711 on PAs on verbs in SVO sentences with broad focus; Zuban et al. 2023 on PAs on verbs in yes-no questions). Therefore, we were interested to explore whether cross-linguistic influence shows itself in the frequency of PAs on verbs, being predicted to be lower for HSs. The results are shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
Number of pitch accents on verbs across speaker groups.
Again, we ran a binomial generalized linear mixed-effects model (for details, see Section 3.3.1) with the presence (1) or absence (0) of a pitch accent on the verb as the dependent variable, speaker group (HS/monolingual) and formality (formal/informal) as independent variables, and an interaction of speaker group and formality. The independent variables were again contrast-coded. We added speaker as a random effect.
The model revealed two main effects for PA placement on verbs. First, there was a main effect of speaker group, i.e., HSs produced more PAs on verbs than monolinguals (z = 3.93, p < 0.001). Second, there was a main effect of formality, i.e., both speaker groups produced more PAs on verbs in informal communicative situations (z = −2.33, p = 0.02). The models’ estimates are shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7.
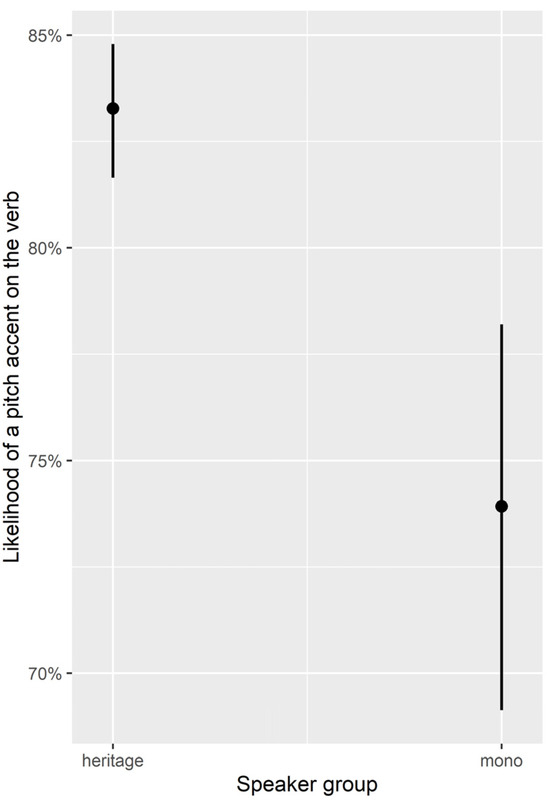
Figure 6.
Likelihood of PAs (on verb) per speaker group.
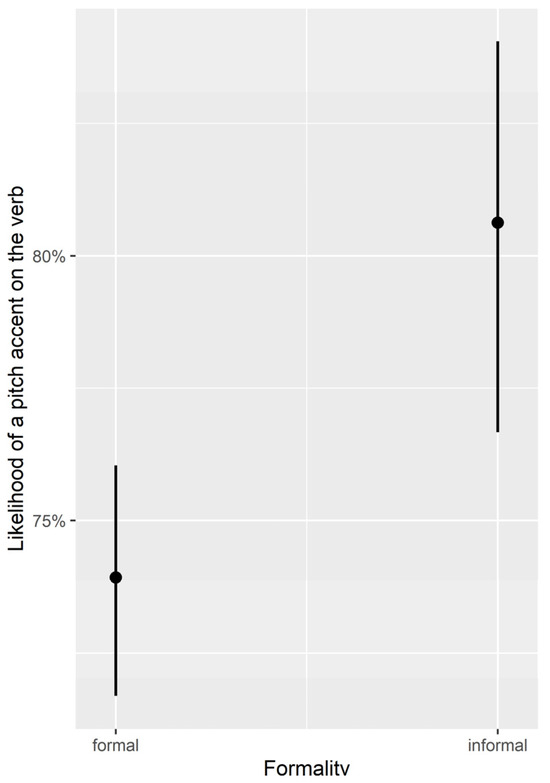
Figure 7.
Likelihood of PAs (on verb) per formality.
Contrary to predictions, HSs did not show cross-linguistic influence from English by accenting verbs less often than monolingual speakers. On the contrary, in line with all other content words, verbs were accented more frequently by HSs than by monolingual speakers.
3.4. Boundary Tones
Boundary tones were extracted at right IP boundaries. H%, !H%, and ^H% are grouped together, as their realization depends on previous tone, as described in Section 2.4.4. Thirty-eight utterances were excluded due to mistakes in the labels. Table 8 shows the results per speaker group.

Table 8.
Number of boundary tones across speakers.
Again, we ran a binomial generalized linear mixed-effects model (for more details, see Section 3.3.1) with the choice of a final boundary tone (H% or L%)5 as the dependent variable and speaker group (HSs/monolinguals) and formality (formal/informal) as independent variables as well as an interaction of speaker group and formality. The independent variables were contrast-coded. We added speaker as a random effect.
The model of the final boundary tones revealed one main effect of formality, i.e., both speaker groups produced more H% in formal communicative situations compared to informal ones (z = 2.35, p = 0.02). The model estimates are shown in Figure 8.
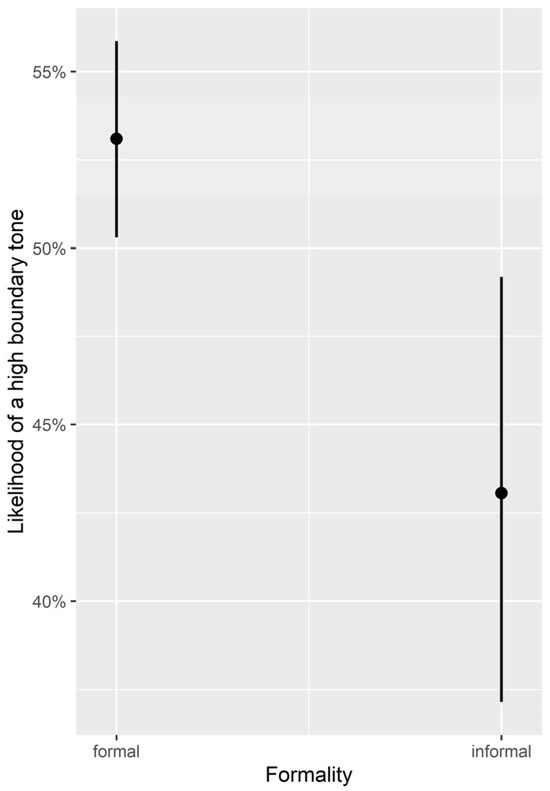
Figure 8.
Visualization of the likelihood of high boundary tone.
Both speaker groups thus did not differ in their frequency of use of boundary tones (the quantitative study cannot say anything about the meaning with which the boundary tones were used).
The highly frequent use of H% might be somewhat surprising initially. However, given that one of the functions of H% is to mark continuation, a high frequency of H% in narrations is not unexpected. It also needs to be remembered that the annotation of IPs is based on prosodic and not syntactic information. This means that boundary tones in RuPro are not only annotated at the end of sentences or clauses but might also occur internally within a clause (see Section 2.4.3). But even in syntactically determined intonation phrases, in a sequence of two clauses A + B, an L% is expected on A only in the case of two main clauses. In all other instances (main clause followed by embedded clause, embedded clause followed by main clause, and two embedded clauses following each other), an H% is expected on A, marking the sentential connection with the following clause. Fully exploiting the rich annotations of RuPro, we would predict that H% occurs more often when the punctuation mark “,” follows, whereas L% occurs when the punctuation mark “.” follows. However, this remains a topic for future research.
The high frequency of H% is mirrored in other studies too. Volskaya and Kachkovskaia (2016) also found neutral rising (falling) intonation the most frequent. They claim that these Hs are characteristic of spontaneous speech. Andrews (1993, p. 166) observes that “falling tones are statistically less frequent in [his] interviews than rising ones”.
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of the Results
Our analysis of overall intonational features in spontaneous narrations of heritage speakers and monolingually raised speakers of Russian has brought to light interesting insights with respect to tonal inventory, the length of intonation phrases, the frequency of pitch accents, and the frequency of boundary tones.
As for tonal inventory (Section 3.1), it emerges that both HSs and monolingually raised speakers frequently use a parallel inventory of tones similarly. There seem to be only slight differences in distribution across groups, with slightly more monotonal pitch accents in HSs.
As for intonation phrases (Section 3.2), it emerges that formality is a decisive factor for the length of intonation phrases for monolingual speakers: in informal speech, IPs are longer. However, no register difference emerges in HSs concerning the length of IPs. In formal communicative situations, HSs and monolingual speakers are similar in producing shorter IPs.
As for pitch accents (Section 3.3), HSs accent content words more frequently than monolingually raised speakers.
Lastly, for boundary tones (Section 3.4), we find an equal distribution of H% and L% boundary tones across both speaker groups.
4.2. Discussion
The RuPro corpus presents spontaneous speech annotated for intonational phrasing, pitch accent location, pitch accent type, and boundary tone type. It differs from existing corpora reviewed in Section 1.3 not only by providing comparable data from mono- and bilingual speakers but also by its rich annotation. Given its multi-layered structure, morphosyntactic and prosodic queries can be posed in tandem (for challenges of such complex corpora, see Shadrova et al., forthcoming).
The current article not only presents a corpus resource with a huge potential for future research. Our work also provides empirical insights into general features of Russian heritage intonation. With its comparative set-up, it provides quantitative evidence against some of the impressionistic claims made in the literature. Polinsky (2018, pp. 120–21) gave the high boundary tone as one of the salient prosodic features of Russian HSs. Our study confirms the frequent use of H% by HSs. At the same time, we show that this is not a feature unique to HSs, as monolingually raised speakers use it as frequently. Obviously, further investigations into the functions of the H%s in both speaker groups are necessary.
In the following subsections, we address two overarching topics further, namely, the relevance of register for intonation and overall prosodic density.
4.2.1. Register Differences in Intonation?
Our results provide mixed results with respect to register differentiation in intonation: on the one hand, there is an effect of communicative situation (formal/informal) that is similar for both speaker groups, namely, more PAs on verbs in informal communicative situations and more H% in formal communicative situations. The differences in PAs and H% in HSs might indicate register awareness and are thereby contrary to Comstock (2018) or studies on other linguistic domains that report register-leveling in HSs (e.g., Alexiadou et al. 2022; Schroeder et al., forthcoming). However, one might question whether the intonational differences are a direct phenomenon of register or whether they result from some other linguistic or non-linguistic differences.
The attested increased frequency of accents on verbs in informal communicative situations might be a consequence of word order differences across the two communicative situations. Zuban (2023) investigated the choice of different word orders by HSs of Russian in the U.S. using the RUEG corpus. One of the findings is a more frequent use of SOV order in informal situations by HSs and monolinguals. Furthermore, SVO order was found to be preferred in formal situations by both speaker groups. SOV word order is usually produced when the subject and the object are both referentially given and when the object is pronominal. Importantly, in this case, the main prominence is expected to be on the verb (Kallestinova 2007, p. 113; Dyakonova 2009, p. 56). Thus, register-dependent differences in word order that lead to differences in accent placement might be responsible for this observed “register” effect of an intonational feature.
However, the increased use of H% in the formal communicative situations might indeed be directly due to the formal communicative situation, expressing politeness and/or floor holding. A closer analysis of the function of the tones is necessary to shed more light on this.
On the other hand, we find effects that show that HSs do not change their intonation in different communicative situations. This is the case concerning IP length, where monolingually raised speakers produce shorter IPs in formal speech than in informal speech, but HSs produce IPs of equal length in both communicative situations. Again, IP length might not be an intonational feature that directly mirrors register but relates to register indirectly through differences in processing and planning. If IPs are (also) considered as planning units, and if formal register and bilingualism are associated with higher processing and/or planning costs, then our results of IP length in monolingual and heritage speakers are fully in line with that. Interestingly, work on filled pauses in the RUEG corpus has found the same distribution: more filled pauses in HSs across registers and in the formal communicative situation by monolingual speakers (Boettcher et al. 2023).
4.2.2. Prosodic Density
Our study gives a quantitative measure on the reported higher use of pitch accents in bilinguals (e.g., Gut 2009; Jilka 2000). The increased use cannot be attributed to cross-linguistic transfer from the ML English, as English does not necessarily accent every content word. Instead, accent placement in English also depends on information status and information structure, and deaccentuation is commonly observed.
Next to an increased number of PAs, our work has also provided evidence for shorter IPs in HSs in informal communicative situations. Again, this difference cannot be attributed to cross-linguistic transfer because of language contact with the ML English. First, we are not aware that IPs in English are shorter than in Russian in informal communicative situations. And second, differences in IP length are also attested for monolingually raised speakers, namely, across registers. As mentioned above, we assume that they are a consequence of higher processing and planning in HSs in both communicative situations.
However, by considering these two aspects together (number of PAs and length of IPs), we can constate a higher prosodic density in HSs’ speech. On the one hand, shorter IPs lead to a more rapid succession of phrase boundaries, which are signaled by durational and pitch-related boundary cues (see e.g., Schubö and Zerbian 2023 on German). On the other hand, due to more PAs, there are more pitch targets to be realized. Together, this might lead to what has been described as a “harmonica pattern” and a “sawtooth pattern” (e.g., Odé 2008).
It might be this higher prosodic density (next to any systemic, semantic, and/or realizational differences that also exist) that contributes to the perceived overall accent that HSs show, as evidenced in perception studies (e.g., Kupisch et al. 2014; Polinsky 2018, pp. 118–21). These studies investigated whether an overall impression of accent was attested in HSs but not the sources of the accent. Syntactic and morphosyntactic cues were excluded from the sound samples to be rated. Whereas segmental differences might have contributed, prosodic features such as overall prosodic density might have too.
4.3. Outlook
The specific architecture of the corpus allows for a combination of the investigation of prosodic and (morpho)syntactic features, as was done for PAs on content words and on verbs above. It opens the door to other queries such as the distribution of boundary tones in connection to clause type (main versus embedded) and the functions of H%s across utterances and speaker groups. One of the limitations of the current study is its quantitative nature. As a result, it does not address the functional aspects of prosody in specific contexts. For instance, the pitch accent types whose frequency of occurrence was presented in Section 3.1 should be further investigated for their phonetic realization, as previous work on Russian has provided evidence for social variation depending on age and gender (see Section 1.2). All these topics remain questions for further research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.Z., Y.Z.; methodology, S.Z., Y.Z., M.K.; software, M.K.; validation, S.Z., Y.Z., M.K.; formal analysis, Y.Z., M.K.; investigation, S.Z., Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, S.Z., Y.Z., M.K.; writing—review & editing, S.Z., Y.Z., M.K.; visualization, Y.Z., S.Z.; project administration, S.Z.; funding acquisition, S.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) as part of the research unit Emerging grammars in language contact situations: a comparative approach (FOR 2537) in projects P8 and Pc (project no. 313607803, GZ ZE940/4-1 and GZ LU 856/16-1).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the DGfS Ethics Committee of the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Sprachwissenschaft (German Society for Linguistics) (Corpus study: Protocol Code: #2017-06-171120, Date of approval: 20 November 2017).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants involved in the study. In case of minors, their guardians provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Data Availability Statement
All data sheets and analyses are available here: https://osf.io/rfyde/ (accessed on 13 December 2023). All spoken productions of the participants can be found here: https://korpling.org/annis/#_c=UlVFRy1SdVBybw (accessed on 13 December 2023).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to three anonymous reviewers for constructive feedback. We would like to thank Yuliia Ivashchyk for her contribution to the prosodic annotation of the data and Nash Whaley for assistance with data extraction and analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Notes
| 1 | The RuPro corpus can be accessed here: https://korpling.org/annis/#_c=UlVFRy1SdVBybw (accessed on 4 December 2023). |
| 2 | The questionnaires used by the RUEG group can be found here: https://osf.io/qhupg/ (accessed on 13 December 2023). |
| 3 | English, German, Greek, and Turkish data were preprocessed in a comparable way. |
| 4 | Files with extracted data and the code used in the analyses can be accessed here: https://osf.io/rfyde/ (accessed on 4 December 2023). |
| 5 | Since there are only two final boundary tones in the data, either H% or L%, only one of them was modeled as a dependent variable via the glmer function. H% was chosen as a dependent variable (the upstepped and downstepped variants of the H% were included into the category H%). |
References
- Aalberse, Suzanne, Ad Backus, and Pieter Muysken. 2019. Heritage Languages: A Language Contact Approach, Studies in Bilingualism. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiadou, Artemis, Vasiliki Rizou, and Foteini Karkaletsou. 2022. A Plural Indefinite Article in Heritage Greek: The Role of Register. Languages 7: 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, David R. 1993. American Intonational Interference in Emigre Russian: A Comparative Analysis of Elicited Speech Samples. Slavic and East European Journal 37: 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkhipov, Alexandre V., Leonid M. Zakharov, Olga F. Krivnova, Sandro V. Kodzasov, and Andrey A. Lebedev. 2012. Russian Intonation Corpus: A preliminary report. In Computational Linguistics and Intellectual Technologies: Annual International Conference “Dialogue”, Moscow, Russia, May 30–June 3. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/8119409 (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Armstrong, Meghan, Mara Breen, Shelome Gooden, Erez Levon, and Kristine M. Yu. 2022. Sociolectal and Dialectal Variation in Prosody. Language and Speech 65: 783–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, Jacob, Vanina Machado Araujo, Natasha Swiderski, Celina Valdivia, Ryan Stevenson, Yasaman Rafat, and Rajiv Rao. 2022. Intonation Patterns in Argentinean- and Venezuelan-Canadian Heritage Speakers of Spanish—Investigating Parental and English Influences. Spanish as a Heritage Language 2: 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, Douglas, Martin Mächler, Ben Bolker, and Steve Walker. 2015. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Softwar 67: 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Boersma, Paul, and David Weenink. 2007. Praat: Doing Phonetics by Computer. Available online: https://www.fon.hum.uva.nl/praat/ (accessed on 13 December 2023).
- Boettcher, Marlene, Annika Labrenz, Franziska Groth, Kateryna Iefremenko, and Kalliopi Katsika. 2023. Using discourse markers and filler particles to mark discourse boundaries: A corpus study across speaker groups and communicative situations. Paper presented at the RUEG Conference, Berlin, Germany, September 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Bryzgunova, Elena A. 1963. Praktičeskaja Fonetika i Intonacija Russkogo Jazyka: Posobie Dlja Prepodavatelej, Zanimajuščixsja s Inostrancami [Practical Phonetics and Intonation of the Russian Language: A Guide for Teachers Dealing with Foreigners]. Moscow: Izdatel’stvo Moskovskogo Universiteta. [Google Scholar]
- Bryzgunova, Elena A. 1980. Intonacija [Intonation]. In Russkaja Grammatika. Moscow: Nauka, pp. 96–122. [Google Scholar]
- Bullock, Barbara E. 2009. Prosody in contact in French: A case study from a heritage variety in the USA. International Journal of Bilingualism 13: 165–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comstock, Lindy Burden. 2018. Pragmatic Accommodation and Linguistic Salience in U.S.-Russian Political Discourse. Ph.D. thesis, University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Dehé, Nicole. 2018. The Intonation of Polar Questions in North American (“Heritage”) Icelandic. Journal of Germanic Linguistics 30: 213–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruiter, Laura E. 2015. Information status marking in spontaneous vs. read speech in story-telling tasks—Evidence from intonation analysis using GToBI. Journal of Phonetics 48: 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrushina, Nina, and Elena Sokur. 2022. Spoken Corpora of Slavic Languages. Russian Linguistics 46: 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duryagin, Pavel, and Sergey Knyazev. 2022. Prosodic diversity in Standard Russian: Pitch alignment in Central and Northern varieties. Russian Linguistics 46: 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyakonova, Marina. 2009. A phase-Based Approach to Russian Free Word Order. Ph.D. thesis, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. [Google Scholar]
- Gut, Ulrike. 2009. Non-Native Speech—A Corpus-Based Analysis of Phonological and Phonetic Properties of L2 English and German. Frankfurt am Main: Peter Lang. [Google Scholar]
- Himmelmann, Nikolaus P., Meytal Sandler, Jan Strunk, and Volker Unterladstetter. 2018. On the universality of intonational phrases: A cross-linguistic interrater study. Phonology 35: 207–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, Diana, LaRae McGillivray, and Mark Schmidek. 1997. Guide to Narrative Language: Procedures for Assessment. Eau Claire: Thinking Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi, Yosuke. 2006. Intonational Patterns in Russian Interrogatives: Phonetic Analyses and Phonological Interpretations. In Usage-Based Linguistic Informatics. Edited by Yuji Kawaguchi, Ivan Fónagy and Tsunekazu Moriguchi. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company, p. 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, Yosuke. 2008. Russian Interrogatives and Intonational Categories. In The Discourse Potential of Underspecified Structures. Edited by Anita Steube. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter, pp. 227–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasinskaja, Katja. 2014. Information Structure in Slavic. In The Oxford Handbook of Information Structure. Edited by Caroline Féry and Shin Ishihara. Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 709–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilka, Matthias. 2000. The Contribution of Intonation to the Perception of Foreign Accent. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany. [Google Scholar]
- Kachkovskaia, Tatiana, Daniil Kocharov, Pavel Skrelin, and Nina Volskaya. 2016. CoRuSS—A New Prosodically Annotated Corpus of Russian Spontaneous Speech. Paper presented at Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’16), Portorož, Slovenia, May 23–28; pp. 1949–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kachkovskaia, Tatiana, Svetlana Zimina, Alena Portnova, and Daniil Kocharov. 2022. Social variability of peak alignment in Russian rise-fall tunes. Paper presented at the Eleventh International Conference on Speech Prosody, Lisbon, Portugal, May 23–26; pp. 862–66. [Google Scholar]
- Kachkovskaia, Tatiana, Tatiana Chukaeva, Vera Evdokimova, Pavel Kholiavin, Natalia Kriakina, Daniil Kocharov, Anna Mamushina, Alla Menshikova, and Svetlana Zimina. 2020. SibLing corpus of Russian dialogue speech designed for research on speech entrainment. Paper presented at the 12th Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, Marseille, France, May 11–16; pp. 6556–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kallestinova, Elena D. 2007. Aspects of Word Order in Russian. Ph.D. thesis, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Ji Young. 2023. Spanish-English Cross-Linguistic Influence on Heritage Bilinguals’ Production of Uptalk. Languages 8: 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisler, Thomas, Uwe Reichel, and Florian Schiel. 2017. Multilingual processing of speech via web services. Computer Speech and Language 45: 326–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodzasov, Sandro V., Olga F. Krivnova, Leonid M. Zakharov, Alexandre V. Arkhipov, Anastasia A. Bonch-Osmolovskaya, Irina M. Kobozeva, and Andrey A. Lebedev. 2011. RINCO—Russian Intonation Corpus. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/8119302 (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- Krause, Thomas. 2019. ANNIS: A Graph-Based Query System for Deeply Annotated Text Corpora. Ph.D. dissertation, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, Thomas, and Amir Zeldes. 2016. ANNIS3: A new architecture for generic corpus query and visualization. Digital Scholarship in the Humanities 31: 118–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupisch, Tanja, Dagmar Barton, Katja Hailer, Ewgenia Klaschik, Ilse Stangen, Tatjana Lein, and Joost van de Weijer. 2014. Foreign Accent in Adult Simultaneous Bilinguals. Heritage Language Journal 11: 123–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladd, D. Robert. 2008. Intonational Phonology, 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J. Richard, and Gary G. Koch. 1977. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 33: 159–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loban, Walter. 1976. Language Development: Kindergarten through Grade Twelve. Champaign: NCTE. [Google Scholar]
- Lüdecke, Daniel. 2020. Data Visualization for Statistics in Social Science. R Package Version 2.8.4. Available online: https://strengejacke.github.io/sjPlot/ (accessed on 4 December 2013).
- Meyer, Ronald, and Ina Mleinek. 2006. How prosody signals force and focus—A study of pitch accents in Russian yes-no questions. Journal of Pragmatics 38: 1615–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mołczanow, Janina, Ulrike Domahs, Johannes Knaus, and Richard Wiese. 2013. The lexical representation of word stress in Russian: Evidence from event-related potentials. The Mental Lexicon 8: 164–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrul, Silvina. 2016. The Acquisition of Heritage Languages, 1st ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odé, Cecilia. 2008. Transcription of Russian intonation, ToRI, an interactive research tool and learning module on the internet. In Dutch Contributions to the Fourteenth International Congress of Slavists, Ohrid, September 10–16. Edited by Peter Houtzagers, Janneke Kalsbeek and Jos Schaeken. Leiden: Brill, pp. 431–49. [Google Scholar]
- Pierrehumbert, Janet B. 1980. The Phonology and Phonetics of English Intonation. Cambridge: MIT. [Google Scholar]
- Polinsky, Maria. 2018. Heritage Languages and Their Speakers, 1st ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, Margie. 2017. Why Regional Prosodic Variation is Worth Studying: An Example from Russian. Bergen Language and Linguistics Studies 7: 164–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Post, Margie. 2022. Spoken corpora of spontaneous speech as a source to study polar question intonation in Russian dialects. Paper presented at Computational Linguistics and Intellectual Technologies: Proceedings of the International Conference “Dialogue 2022”, Moscow, Russia, June 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Rajiv. 2016. On the nuclear intonational phonology of heritage speakers of Spanish. In Advances in Spanish as a Heritage Language. Edited by Diego Pascualy y Cabo. Amsterdam: John Benjamins, pp. 51–80. [Google Scholar]
- Rathcke, Tamara. 2006a. A perceptual study on Russian questions and statements. In Arbeitsberichte des Instituts für Phonetik und Digitale Sprachverarbeitung (AIPUK 37). Edited by Jonathan Harrington, Christine Mooshammer and Felicitas Kleber. Kiel: University of Kiel, pp. 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Rathcke, Tamara. 2006b. Relevance of F0 peak shape and alignment for the perception of a functional contrast in Russian. Paper presented at the 3rd Conference on Speech Prosody, Dresden, Germany, May 2–5; pp. 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Rathcke, Tamara. 2009. Komparative Phonetik und Phonologie der Intonationssysteme des Deutschen und Russischen [Comparative phonetics and phonology of the intonation systems of German and Russian]. Munich: Herbert Utz Verlag. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. 2020. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.gbif.org/tool/81287/r-a-language-and-environment-for-statistical-computing (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- Schiel, Florian. 1999. Automatic Phonetic Transcription of Non-Prompted Speech. Paper presented at the XIVth International Congress of Phonetic Sciences, San Francisco, CA, USA, August 1–7; pp. 607–10. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, Thomas, and Kai Wörner. 2014. EXMARaLDA. In The Oxford Handbook of Corpus Phonology. Edited by Jacques Durand, Ulrike Gut and Gjert Kristoffersen. Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 402–19. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, Christoph, Kateryna Iefremenko, and Mehmet Öncü. Forthcoming. The post-verbal position in heritage Turkish. A comparative approach with a focus on non-clausal elements. In Zweisprachigkeit Deutsch-Türkisch. Edited by Zeynep Kalkavan-Aydın and Yazgül Şimşek. Münster: Waxmann.
- Schubö, Fabian, and Sabine Zerbian. 2023. The patterns of pre-boundary lengthening in German. In Prosodic Boundary Phenomena. Edited by Fabian Schubö, Sabine Zerbian, Sandra Hanne and Isabel Wartenburger. Berlin: Language Science Press, pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segalovich, Ilya. 2003. A fast morphological algorithm with unknown word guessing induced by a dictionary for a web search engine. Paper presented at the International Conference on Machine Learning; Models, Technologies and Applications, Las Vegas, NV, USA, June 23–26; pp. 273–80. [Google Scholar]
- Shadrova, Anna, Martin Klotz, Rahel Gajaneh Hartz, and Anke Lüdeling. Forthcoming. Mapping the Mappings and then Containing them all: Quality Assurance, Interface Modeling, and Epistemology in Complex Corpus Projects. In Linguistic Dynamics in Heritage Speakers. Edited by Shanley Allen, Mareike Keller, Artemis Alexiadou and Heike Wiese.
- Skrelin, Pavel, Nina Volskaya, Daniil Kocharov, Karina Evgrafova, Olga Glotova, and Vera Evdokimova. 2010. CORPRES—Corpus of Russian Professionally Read Speech. Paper presented at the 13th International Conference on Text, Speech and Dialogue, Brno, Czech Republic, September 6–10; pp. 392–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straka, Milan, Jan Hajič, and Jana Straková. 2016. UDPipe: Trainable Pipeline for Processing CoNLL-U Files Performing Tokenization, Morphological Analysis, POS Tagging and Parsing. Paper presented at the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, Portorož, Slovenia, May 23–28; pp. 4290–97. [Google Scholar]
- Svetozarova, Natalija. 1998. Intonation in Russian. In Intonation Systems: A Survey of Twenty Languages. Edited by D. Hirst and A. Di Cristo. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 264–77. [Google Scholar]
- Trudgill, Peter. 2010. Investigations in Sociohistorical Linguistics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Visson, Lynn. 1989. Russian in America: Notes on the Russian Spoken by Émigrés. Russian Language Journal 43: 185–91. [Google Scholar]
- Volskaya, Nina, and Tatiana Kachkovskaia. 2016. Prosodic annotation in the new corpus of Russian spontaneous speech CoRuSS. Paper presented at the Speech Prosody, Boston, MA, USA, May 31–June 3; pp. 917–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, Hadley, Mara Averick, Jennifer Bryan, Winston Chang, Lucy D’Agostino McGowan, Romain François, Garrett Grolemund, Alex Hayes, Lionel Henry, Jim Hester, and et al. 2019. Welcome to the Tidyverse. Journal of Open Source Software 4: 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, Heike. 2020. Language Situations: A method for capturing variation within speakers’ repertoires. In Methods in Dialectology XVI. Bamberg Studies in English Linguistics. Frankfurt am Main: Peter Lang, pp. 105–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wiese, Heike, Artemis Alexiadou, Shanley Allen, Oliver Bunk, Natalia Gagarina, Kateryna Iefremenko, Esther Jahns, Martin Klotz, Thomas Krause, Annika Labrenz, and et al. 2021. RUEG Corpus. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/5808870 (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- Yokoyama, Olga T. 1987. Discourse and Word Order, Pragmatics & Beyond. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, Olga T. 2001. Neutral and Non-Neutral Intonation in Russian. A Reinterpretation of the IK System. Die Welt der Slaven XLVI 1: 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zerbian, Sabine, Marlene Böttcher, and Yulia Zuban. 2022. Prosody of contrastive adjectives in mono- and bilingual speakers of English and Russian: A corpus study. Paper presented at the 11th Speech Prosody, Lisbon, Portugal, May 23–26; pp. 812–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zipser, Florian, and Laurent Romary. 2010. A model oriented approach to the mapping of annotation formats using standards. Paper presented at the Workshop on Language Resource and Language Technology Standards, Valetta, Malta, May 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zuban, Yulia. 2023. The role of communicative situations in word order choice in heritage Russian. Paper presented at the Heritage Languages at the Crossroads, Instanbul, Turkey, May 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zuban, Yulia, Tamara Rathcke, and Sabine Zerbian. 2023. Do Different Majority Languages Lead to Different Intonational Grammars? A Case Study of Yes/No-Questions in Heritage Russian. Heritage Language Journal 20: 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zybatow, Gerhild, and Grit Mehlhorn. 2000. Experimental Evidence for Focus Structure in Russian. In Annual Workshop on Formal Approaches to Slavic Linguistics. The Philadelphia Meeting 1999. Edited by Tracy H. King and Irina Sekerina. Ann Arbor: Michigan Slavic Publications, pp. 414–34. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).