Abstract
Recent research found that the languages of bilingual listeners are active and interact, such that both lexical representations are activated by the spoken input with which they are compatible. However, the time course of bilingual activation and whether suprasegmental information further modulates this cross-language competition are still not well understood. This study investigates the effect of stress placement on the processing of English–Spanish cognates by beginner-to-intermediate Spanish-speaking second-language (L2) learners of English and intermediate-to-advanced English-speaking L2 learners of Spanish using the visual-world eye-tracking paradigm. In each trial, participants saw a target (asado, ‘roast’), one of two competitors (stress match: asados, ‘roast (pl)’; stress mismatch: asador, ‘rotisserie’), and two unrelated distracters, while hearing the target word. The experiment included a non-cognate condition (asado-asados-asador) and a cognate condition, where the stress pattern of the English word corresponding to the Spanish competitor in the stress-mismatch condition (inventor) instead matched that of the Spanish target (invento, ‘invent’). Growth-curve analyses revealed cognate-status and stress-mismatch effects for Spanish-speaking L2 learners of English, and cognate-status and stress-mismatch effects, and an interaction for English-speaking L2 learners of Spanish. This suggests that both groups use stress for word recognition, but the English stress pattern only affects the processing of Spanish words in the English-speaking L2 learners of Spanish.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, bilingualism is becoming the norm, rather than being considered an exception. It is estimated that half of the world’s population, if not more, is bilingual (Grosjean 2010). Research done in the past 25 years has shown that bilinguals, including simultaneous bilinguals as well as early and late second-language (L2) learners, activate words in both of their languages even when they consciously intend to use only one language (e.g., Blumenfeld and Marian 2011; Canseco-Gonzalez et al. 2010; Desmet and Duyck 2007; Dijkstra 2005; Marian and Spivey 2003a, 2003b; Schulpen et al. 2003; Weber and Cutler 2004). So, for bilinguals, as a spoken word in the speech signal unfolds, not only lexical candidates that most closely match the input in the intended language, but also words in the unintended language, become partially activated and compete for recognition. A word is described as being “partially activated” before it has been successfully identified (when it becomes “fully activated”). For example, when listening to the word “material” (in English), and before it becomes fully activated, the listener is going to partially activate all those words consistent with the acoustic input in an incremental way (e.g., the listener may partially activate “mister, “model”, “material”, etc. after processing /m-/, and words such as “mathematics”, “material”, “materialistic”, as more acoustic information unfolds, etc.). Of course, this is a really simple example, which is not taking into account other factors such as coarticulation effects in the production of the individual phonemes or suprasegmental information. That is, while research has found that both monolingual and bilingual speakers activate lexical candidates that are phonologically similar to the speech signal in the target language, bilinguals have also been found to partially activate words in their other language (for a review, see Marian et al. 2008). Successful recognition of the speech signal, then, involves inhibiting not only the non-intended word, but also the non-intended language. Notice, though, that while there is now abundant evidence from psycholinguistic research suggesting that bilinguals are not able to selectively turn off one of their languages (for a review, see Bonfieni et al. 2019), there is also some evidence suggesting the opposite pattern. That is, while most of the evidence suggests that both languages in bilingual’s brain are continuously activated, some research claims that factors such as language dominance, frequency of language use, or task effects may impact how selective language activation is (e.g., Colomé 2001).
Several factors have been proposed to modulate the level of cross-language activation discussed in the bilingual language comprehension literature, among which language proficiency or language dominance and language bias (or language mode) have been consistently reported (e.g., Grosjean 1997; Guo and Peng 2006; Ju and Luce 2004; Marian and Spivey 2003a; Soares and Grosjean 1984; Spivey and Marian 1999; Weber and Cutler 2004). Recently, other factors, such as daily exposure to the language (Chen et al. 2017), have also been reported. However, even though most studies show support for these factors to be critical to the understanding of bilingual activation, there are other factors that are not so well understood. For example, Ju and Luce (2004) proposed that the degree of cross-language competition depends, at least in part, on the precise match between the input and the bilingual’s mental representation of the words. In their study, they found an effect in the degree of activation with those items in which the voice onset time (VOT) was manipulated to be “more” or “less” native-like. However, this study (as well as others discussed in the next section) focused on subtle acoustic differences at the segmental level, leaving open the question of whether differences at the suprasegmental level would have the same effect on bilingual activation. This is, while Ju and Luce (2004)’s study sheds light on how VOT differences affect bilingual activation, we still do not know what can happen when looking at, for example, differences in lexical stress placement.
Research has shown that in languages that have word-level stress, greater activation of words that match the signal both segmentally and suprasegmentally is observed, as compared to words that only match the signal segmentally, for both native speakers (e.g., Cooper et al. 2002; Soto-Faraco et al. 2001) and, to some extent, L2 learners (e.g., Tremblay 2008; Van Anne et al. 2014). However, it is unclear whether stress placement that differs between two languages can interfere with the recognition of cognate words, as compared to non-cognate, control words and cognate words with non-interfering stress placement.
This study, then, examines the degree of lexical competition that cognates with different stress patterns in Spanish and English created for bilingual English–Spanish bilinguals. It does so by using the visual world eye-tracking paradigm and testing L1-Spanish, L2-English bilinguals at a mid-proficiency level in English and L1-English, L2-Spanish bilinguals at a mid-to-high level of proficiency in Spanish. This paper continues with a more detailed review of the bilingual activation literature, which uses cognate words and lexical stress with an outline of the research questions of this study (Section 1.1); the description of the visual world eye-tracking experiment (Section 2); and a discussion of how the results can be interpreted in relation to the research questions (Section 3).
1.1. Bilingual Activation and the Visual World Eye-Tracking Paradigm
Research on cross-language activation in language comprehension generally shows that lexical activation is not language selective: Bilinguals activate their two languages in parallel during language comprehension (e.g., Ju and Luce 2004; Marian and Spivey 2003b; Schulpen et al. 2003; Spivey and Marian 1999; Weber and Cutler 2004).
One common paradigm that has been used to investigate bilingual activation is the visual world eye-tracking paradigm. This methodology provides good temporal resolution of the activation of words that closely match the acoustic input (Allopenna et al. 1998). Spivey and Marian (1999) were among the first to implement this paradigm to better understand the time course of bilingual activation during spoken word comprehension. In their study, Spivey and Marian (1999) (see also Marian and Spivey 2003a, 2003b) presented Russian–English bilinguals with a visual display consisting of four objects, and asked participants to manipulate one of the objects (the target) while performing the task in either English or Russian in different blocks. This manipulation consisted of an English target word (e.g., marker) that shared an onset with and would be phonetically similar to the Russian name of one of the other objects in the display (e.g., marku, ‘stamp’). The authors found that upon hearing the target word marker, Russian–English bilinguals made eye-movements to the between-language competitor (marku). These results clearly indicate that bilinguals automatically activated both the English and the Russian lexicons when processing English words. Similar results were found in a block in which participants completed the task in Russian: Upon hearing “marku” (‘stamp’), Russian–English bilinguals also looked at the marker.
This pattern of parallel activation has since been replicated with other combinations of languages: with Dutch–English bilinguals (Weber and Cutler 2004), Spanish–English bilinguals (Canseco-Gonzalez et al. 2010; Ju and Luce 2004), French–English bilinguals (Pivneva et al. 2014), and Japanese–English bilinguals (Cutler et al. 2006). Importantly, the size of this cross-language activation effect has been shown to vary based on several factors, including whether the task is conducted in the L1 or the L2 (e.g., Marian and Spivey 2003a), how proficient bilingual listeners are in the L2 (e.g., Mishra and Singh 2016; Silverberg and Samuel 2004), whether the input and bilingual listeners’ lexical representation closely matched (Ju and Luce 2004), and whether bilingual listeners expect to hear only one or both of their languages (Grosjean 1997; Marian and Spivey 2003a).
Also using a visual world eye-tracking experiment, the role of the precise match between the input and the bilingual’s mental representation of the words in determining the degree of bilinguals’ activation have been explored. Ju and Luce (2004) manipulated the VOT of Spanish words to make them consistent with stops in either Spanish or English, the two languages of the bilinguals tested. Their study included competitor pictures whose English names were phonologically similar to the Spanish targets (e.g., playa ‘beach’ and pliers). Their results indicated that Spanish–English bilinguals showed greater evidence of cross-language competition (i.e., more fixations to the picture with the phonologically similar English name) when the target words contained English-appropriate VOTs. These findings are in line with those reported in previous bilingual cross-language phone perception studies, suggesting that bilinguals are sensitive to subtle acoustic-phonetic differences (e.g., Flege 1984, 1991; Flege and Hammond 1982), with this information reducing cross-language interference in word recognition. However, while the role of segmental information has been explored in previous studies (e.g., VOT in Ju and Luce (2004)’s study), we still do not know how differences in suprasegmental information may affect bilingual activation.
The speech processing system is extremely efficient: In order to recognize words successfully, it uses all available information in the signal to activate the intended target word and inhibit the unintended lexical competitors. One such type of information is word-level stress. Several studies have shown that in languages that have word-level stress (e.g., Spanish, Dutch, and English), stress constrains lexical access in native speakers (e.g., Cooper et al. 2002; Cutler and Pasveer 2006; Cutler et al. 2007; Soto-Faraco et al. 2001) and, to some extent, L2 learners (e.g., Tremblay 2008; Van Anne et al. 2014). During online word recognition, as a spoken word unfolds, lexical candidates that most closely match the input segmentally become partially activated and compete most strongly with the target word for recognition (e.g., Luce and Pisoni 1998; Luce 1986; Marslen-Wilson and Warren 1994). In languages that have word-level stress, greater activation of words that match the signal both segmentally and suprasegmentally is observed as compared to words that only match the signal segmentally (e.g., Cooper et al. 2002; Soto-Faraco et al. 2001).
However, it is unclear how a difference in the stress placement of cognate words in bilingual’s two languages may affect the degree of bilingual activation, as compared with control words and cognate words with non-interfering stress placement. Stress provides an interesting test for examining bilingual activation because Spanish and English have a number of words that share the same (orthographic) segments (i.e., cognates) but do not have the same stress pattern. For instance, the word material, with the same meaning in both languages, has second-syllable stress in English but final stress in Spanish. In this case, the segmental similarity between the two languages is expected to make the words be highly activated in both Spanish and English. Bilingual listeners’ ability to use stress to recognize Spanish words should thus be contingent on their ability to use Spanish stress to inhibit the English competitor.
In summary, parallel activation of bilinguals’ two languages during comprehension has been consistently reported in the literature on bilingual activation. Moreover, this cross-language activation can be influenced by many factors, most of which still need to be further explored, such as the role of suprasegmental features. That is, it is possible to compare the use of lexical stress (by comparing a stress match vs. a stress mismatch condition) and to look at its effects depending on the presence of a stress mismatching cognate such as material (comparing a cognate vs. non-cognate condition). In such a scenario and taking into account the findings regarding bilinguals’ parallel activation, it could be predicted that the effect of stress would be stronger in the non-cognate condition, and that the cognate status would emerge more strongly in the stress mismatch condition than in the stress match condition. The current study intends to address these specific research questions:
- Does lexical stress modulate cross-language activation in L1 Spanish L2 English bilinguals with a mid-proficiency level in English’s comprehension of Spanish–English cognate words in a Spanish monolingual language mode?
- Does lexical stress modulate cross-language activation in L1 English L2 Spanish with a mid-to-high-proficiency in Spanish’s comprehension of Spanish–English cognate words in a Spanish monolingual language mode?
The next sections describe the experimental design, the results obtained, and how the results can be used to address these questions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
Two experimental groups of participants were tested. The first group, referred to as L1 Spanish-L2 English, consisted of 48 native speakers of Spanish (34 women, mean age 25) with a mid-proficiency level in English, who were tested in Spain. Their proficiency in English was assessed using a cloze test (Brown 1980) and the LexTALE task (Lemhöfer and Broersma 2012). The second group, referred to as L1 English-L2 Spanish, consisted of 40 mid-to-high-proficiency English-speaking L2 learners of Spanish (19 women, mean age 26), and was tested in a Midwestern university in the US. Their proficiency in Spanish was assessed with a 50-item test, which was a combination of the MLA cooperative language text (Spanish Embassy, Washington, DC, USA), the Diploma de Español como Lengua Extranjera (Educational Testing Service, Princeton, NJ, USA), and a version of the LexTALE task. The scores reported in the literature were followed to decide the proficiency level of the participants based on their scores. However, it was impossible to use the same exact tests in both languages, as they did not exist at the time in which this experiment was conducted. More information regarding their language background can be found in Table 1.

Table 1.
Participants’ language background and proficiency information.
These two groups were included to further explore the influence of the L1 vs. the L2 on bilingual activation. All participants were compensated for their time ($30 or its equivalent in Euros). This experiment was part of a larger project, in which participants had to commit to attend 3 experimental sessions in 3 different days.
2.2. Materials
This study used the visual world eye-tracking paradigm, including in each visual display a target word, a competitor word, and two distracter items.
To determine whether participants were influenced by the presence of a Spanish–English cognate word, two conditions were compared: A non-cognate condition (in which the competitor word was a non-cognate control word, as in Table 2) and a cognate condition (in which the competitor word was a Spanish–English cognate, as in Table 3). Critically, in the cognate condition, the English stress of the competitor word matched that of the Spanish target. For example, the stress patterns of the target words materia (‘matter/subject’) and competitor material differ in Spanish (with the stressed syllable underlined). In Spanish, then, the word material has third syllable stress, while in English, the same word has second syllable stress (material). Thus, the English pronunciation of the competitor word and the Spanish pronunciation of the target word (materia) have the stress located in the same position. It was, thus, expected that these orthographic cognates would activate both Spanish and English pronunciations and, thus, both stress patterns (third syllable in Spanish, second syllable in English), with participants needing to inhibit the non-target stress pattern (i.e., the English stress pattern) to correctly recognize the Spanish target word as early as in the second syllable.

Table 2.
Example stimuli in the non-cognate condition.

Table 3.
Example stimuli in the cognate condition.
However, finding an effect of cognate condition could still be related to factors other than lexical stress (e.g., a facilitatory effect of the cognate word). In order to determine the real effect of lexical stress, two further conditions were created. One of these conditions (the mismatched-stress condition) would show a different stress placement between target and competitor (e.g., asado ‘roasted’ vs. asador ‘rotisserie’) and, thus, should be easier to disambiguate, as there would be suprasegmental information at the second syllable to help the listener disambiguate between these two words. Critically, in the stress-match condition, the target and the competitor had the same stress placement (e.g., asado ‘roasted’ vs. asados ‘roasted, pl.’) and could only be disambiguated at the end of the last syllable, when reaching the last segment of the word.
In summary, the study included a total of 32 Spanish trisyllabic target nouns with regular stress placement. The stress match and mismatch conditions served the purpose of evaluating the degree to which listeners use stress in lexical access. The non-cognate and cognate conditions served the purpose of evaluating whether cognates, whose stress pattern in English matched the Spanish target, cause an increase in lexical competition. All four conditions were necessary to answer the research questions because we evaluate the difference in competition between the stress-match and stress-mismatch conditions (match—mismatch) to see whether this difference is smaller in the cognate condition than in the non-cognate condition. This would indicate that the stress-mismatch condition in the cognate condition behaved more similarly to the stress-match, as compared with the non-cognate condition, due to the influence of English. Between conditions, words were matched in terms of part of speech, average lemma frequency, and average orthographic length1.
Target, competitor, and distracter words were matched in terms of length and frequency within and between cognate conditions. In all cases, the target word was more frequent than the rest of the words in the experimental trial, but targets among conditions (cognate and non-cognate) were matched with respect to this factor. The complete list of stimuli used in the experiment can be found in Appendix A and Appendix B for the non-cognate and cognate conditions, respectively.
Two different lists were used such that each participant would see each target with only one competitor type. For example, participants assigned to List 1 saw asado-asados ‘roast (singular and plural)’; participants in List 2 saw asado-asador ‘roast-rotisserie’) in a counterbalanced way, so that all participants saw the same number of experimental trials in each condition.
This experiment also included 96 filler trials. Appendix C includes a list with all the filler trials. The filler items followed the same design as that described for the experimental items, but the target word was always a word other than the singular word with the final light (Consonant + Vowel) syllable (e.g., in a pair of target-competitor word such as mejillón ‘mussel’—mejilla ‘cheek’, the target would be mejillón). Among the fillers, some English–Spanish cognate and pseudo-cognates words were included to make sure the cognate competitors did not stand out within the experiment.
2.3. Procedure
Participants had their eye movements recorded by a head-mounted Eyelink II at a sampling rate of 250 Hz. The experiment began with a calibration of the eye tracker using the participants’ right eye, or left eye if the right eye could not be tracked sufficiently well. This initial calibration was followed by a practice session of four trials and by the main experiment, divided into 4 blocks (to give time to the participant to rest and to recalibrate the eye-tracker whenever necessary). Each block contained 8 experimental trials (four in the non-cognate condition and four in the cognate condition) and 24 filler trials.
In each trial, participants first saw the four orthographic words located in the four corners of the screen for 4000 ms, which they were instructed to silently read. The words then disappeared, and a fixation cross appeared and stayed on the screen for 500 ms. As the fixation point disappeared, the same four words reappeared on the screen and participants simultaneously heard the target word. Participants were asked to click on the word that matched the acoustic input as accurately as possible. Orthographic words were included (rather than pictures as in previous studies) because not all stimuli were concrete objects. Moreover, the orthographic representation of words has been found to be more sensitive to phonological manipulations than the traditional version using pictures (e.g., Huettig and McQueen 2007; Weber et al. 2007). The position of the target and competitor words in the display and the order of the test items (experimental, filler) were completely randomized. The target words appeared an equal number of times in each position on the screen, thus, avoiding any possible bias on the results reported.
2.4. Data Analysis
Growth curve analysis (GCA) was used to model listeners’ differential proportions of fixations (Mirman et al. 2008), which models the curvilinear relationship between proportions of eye fixations over time. This statistical method allows modeling the shape of participants’ overall fixation line rather than their average fixations at arbitrary points in time. Thus, his method is less subjective than other statistical approaches, such as running a time-window analysis.2 To conclude that stress of the English cognate competitor word had an effect on participants’ fixations, the GCA outcome results must reveal an interaction between this variable and at least one of the time polynomials. Such interactions would indicate that the shape of participants’ fixation line differs between conditions, which would reflect their intake of the speech signal.
The GCAs were run on participants’ differential proportions of fixations using the lme4 package in R (Bates et al. 2015) from 0 to 1500 ms, with a delay of 200 ms. The analysis included group (L1 Spanish vs. L1 English, with L1 Spanish as the baseline), cognate status (cognate condition vs. non-cognate condition, with the non-cognate condition as the baseline), and stress (match vs. mismatch, with the match as the baseline) as fixed effects, as well as all two- and three-way interactions. Analyses yielding significant interactions between cognate status and stress were followed up by subsequent GCAs conducted on the two cognate conditions separately, with the alpha level being adjusted. All analyses included participant and item as random intercepts, and the time polynomials as random slopes for the participant variable, thus modelling a different line shape for each participant.
3. Results
Figure 1 shows the predicted values for the two cognate conditions (the non-cognate condition in the left panels and represented with solid lines and the cognate condition in the right panels and represented with doted lines). In each case, the red lines represent the stress-match (e.g., asado-asados or materia-materias) and the black lines represent the stress-mismatch conditions (e.g., asado-asador or materia-material). The first row represents the L1-Spanish, L2-English group and the second row the L1-English, L2-Spanish group. A four-way interaction emerged (Estimate = −0.058, SE = 0.019, p < 0.01), indicating that the two groups patterned differently. Follow-up analyses were done on the groups separately.
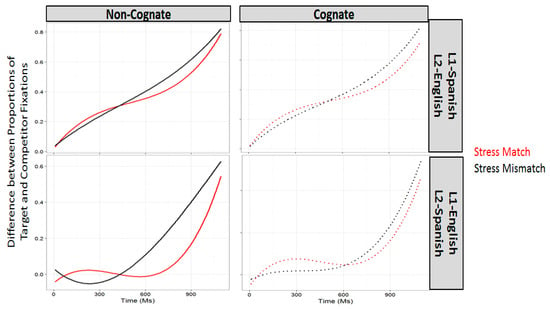
Figure 1.
Growth curve analysis results.
The results of the GCA with the best fit on native Spanish participants’ differential proportions of fixations in all conditions showed a three-way interaction between stress, cognate status, and the linear polynomial (Estimate = −0.163, SE = 0.059, p < 0.01) as well as a three-way interaction between stress, cognate status, and the quadratic polynomial (Estimate = −0.176, SE = 0.059, p < 0.01), so follow-up analyses were run on the two cognate conditions separately. The main difference between them emerged with respect to the cubic polynomial. Only the interaction between stress and the cubic polynomial was significant in the non-cognate condition (Estimate = −0.252, SE = 0.037, p < 0.001), while the interaction between stress and the quadratic (Estimate = 0.127, SE = 0.039, p < 0.001) and the cubic (Estimate = −0.171, SE = 0.039, p < 0.001) polynomials is significant in the cognate condition. The fact that at least an interaction is found in both conditions indicates that both conditions patterned similarly, although the strength of the interaction in each case differed. Thus, no effect of the presence of a cognate word with interfering stress pattern is observed in this group.
The results of the GCA with the best fit on L1-English L2-Spanish bilinguals’ differential proportions of fixations in all conditions showed a three-way interaction between stress, cognate status, and the three-time coefficients (linear: Estimate = 0.603, SE = 0.063, p < 0.001; quadratic: Estimate = −0.272, SE = 0.063, p < 0.001; and cubic: Estimate = −0.509, SE = 0.063, p < 0.001), so follow-up analyses were run on the two cognate conditions separately. This interaction indicates that the participants’ differential proportions of fixations showed more positive results (indicating less lexical competition) in the stress-match than in the stress-mismatch condition. However, the difference between match and mismatch lines is larger in the non-cognate condition, as evidenced by the fact that only the interaction between stress and the quadratic term is significant in the cognate condition (Estimate = 0.241, SE = 0.038, p < 0.001). This difference between the two conditions can only be attributed to the presence of a cognate word with interfering stress pattern.
4. Discussion
The main purpose of this study was to determine whether suprasegmental features such as lexical stress would have an effect on the degree of bilingual activation observed in a visual world eye-tracking experiment targeting two groups of Spanish–English bilinguals. Previous studies have claimed that a perfect match between the input and the bilingual’s mental representation of the words may be required in order to find evidence of bilingual activation (Ju and Luce 2004). However, no other study has tried to further explore the role of suprasegmental features on bilingual activation.
Based on previous literature, an interaction between stress (match vs. mismatch) and cognate status (non-cognate vs. cognate) could be predicted, such that the effect of stress would be greater in the non-cognate condition than in the cognate condition, and the effect of the cognate status would be greater in the stress mismatch condition than in the stress match condition. However, we wanted to further explore how this pattern could differ depending on whether the competing language was the participants’ L1 or L2. For that reason, the first research question sought to explore whether lexical stress modulates cross-language activation in native speakers of Spanish with a mid-proficiency level in English. However, the results of the GCA analysis indicate that both cognate conditions showed a similar pattern, indicating that native speakers of Spanish do not seem to be influenced by the presence of a Spanish–English identical cognate word with a competing stress pattern.
This lack of an effect on bilingual activation could be due to several reasons. On the one hand, it could be interpreted as indicating that the strength of bilingual activation is not strong enough to be captured when the L2 tries to interfere with the processing of the L1. However, this interpretation would contradict some of the findings reported in the literature. While it is clear that language dominance is an important factor in determining the degree of bilingual activation (e.g., Marian and Spivey 2003a), there is plenty of evidence of bilingual activation attested when the L2 influences the processing of the L1 (e.g., Mishra and Singh 2016; Silverberg and Samuel 2004). Another possible interpretation, however, could be related to the specific participants tested in this study. The native speakers of Spanish lived in Spain at the time of the experimental testing and only had an intermediate level of proficiency in English; hence, these speakers were dominant in Spanish. One possibility could be that they were not proficient enough in English for this effect to be captured. Maybe by testing more advanced learners of English or by testing a group of native speakers of Spanish living in a predominantly English-speaking community, we could capture the effect we were looking for. The most likely scenario seems to be one in which target and competitor words did not show an inhibitory effect for the native speakers of Spanish due to the differential strengths of lexical activation in L1 Spanish as compared to L1 English.
The same research question was asked regarding the effect of lexical stress in the modulation of bilingual activation testing an L1-English, L2-Spanish group with an intermediate level of proficiency in their L2. In this case, however, the results of the GCA showed evidence that the difference between the match and mismatch lines was larger in the non-cognate condition. This difference between the two cognate conditions can only be attributed to the presence of a cognate word with interfering stress pattern. These results indicate that English-speaking L2 learners of Spanish activated both the Spanish and the English phonological representations of the cognate words, even in a situation in which they were expected to be in a Spanish monolingual mode.
This effect is significant, as it indicates that suprasegmental features can modulate the level of bilingual activation, in spite of the fact that segmental differences were also present in the study. Let us recall that the main manipulation in this study occurred in the second syllable. At that point in time, listeners would have heard a whole syllable in Spanish, thus, indicating to listeners that the target language was going to be Spanish and that they could inhibit the influence from English. Despite all the acoustic information indicating that only Spanish needed to be activated, the stress manipulated included in this study was still found to modulate bilingual activation. However, this effect seems to contradict some of the findings reported in the literature, which claim that the degree of cross-language competition depends, at least in part, on the precise match between the input and the bilingual’s mental representation of the words (Ju and Luce 2004). Despite the unprecise match between participants’ mental representation of the English cognate word and the Spanish target word they heard, the influence of this competition could still be captured in this study.
Another conclusion could be extracted from the findings reported in this study. Findings of cross-language activation in the bilingual lexical processing literature have been reported for different language combinations (Canseco-Gonzalez et al. 2010; Cutler et al. 2006; Ju and Luce 2004; Marian and Spivey 2003a; Pivneva et al. 2014; Spivey and Marian 1999; Weber and Cutler 2004). Factors such as whether the task is conducted in the L1 or the L2 (i.e., Marian and Spivey 2003a), how proficient bilingual listeners are in the L2 (e.g., Mishra and Singh 2016; Silverberg and Samuel 2004), whether the input and bilingual listeners’ lexical representation closely match (Ju and Luce 2004), daily exposure to the language (Chen et al. 2017), and whether bilingual listeners expect to hear only one or both of their languages (Grosjean 1997; Marian and Spivey 2003a) have been reported to modulate the size of this cross-language activation. Of particular importance for this study could be the amount of exposure to the language between the two groups of bilinguals tested. The two groups resided in different countries and their exposure to the language of testing, Spanish, differed. The first group were L1 speakers of Spanish living in Spain who were found to co-activate English less than the second group who lived in the US and were L2 speakers of Spanish. It could be that the first group did not co-active English more, because they were exposed to it less in their daily lives. This is a point that should be addressed in future studies. In any case, the results of this study point to a scenario in which factors such as proficiency or daily use of the L2 may not be independent but rather interact with each other. While the language of the task (whether it is conducted in bilinguals’ L1 or L2) seems to be a critical factor, it also seems to be affected by the type of acoustic input presented to the listeners. Further studies should explore the types of interactions that may exist among the different factors influencing the degree of bilingual activation.
In conclusion, the findings of this study indicate that English-speaking L2 learners of Spanish show evidence of activating the L1 (as suggested by the cognate effect) even when nothing in the acoustic input or in the testing session made them think that they should be activating English words. Importantly, the findings of this study provide evidence on how suprasegmental information, specifically lexical stress, can modulate the degree of cross-language activation, independently of the presence of segmental cues indicating the language of the trial.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to our colleague Annie Tremblay who provided expertise that greatly assisted the research, although she may not agree with all of the interpretations provided in this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
List of experimental and distracter stimuli in the non-cognate condition. Remember that the presence of the competitors was randomized in two lists. While in List 1 a participant saw the pair asado-asados, in List 2, participants would see asado-asador.
Table A1.
List of experimental and distracter stimuli in the non-cognate condition. Remember that the presence of the competitors was randomized in two lists. While in List 1 a participant saw the pair asado-asados, in List 2, participants would see asado-asador.
| Target—Stress on the Penultimate Syllable | Competitor 1—Stress on the Penultimate Syllable | Competitor 2—Stress on the Final Syllable | Distracter 1 | Distracter 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | asado (roast) | asados (roast, pl) | asador (rotisserie) | camisón (nightshirt) | camisones (nightshirt, pl) |
| 2 | vecino (neighbor) | vecinos (neighbor, pl) | vecinal (neighboring) | orinal (potty) | orinales (potty, pl) |
| 3 | ganado (cattle/won) | ganados (cattle/won, pl) | ganador (winner) | fingidor (feigner) | fingidores (feigner, pl) |
| 4 | dinero (money) | dineros (money, pl) | dineral (fortune) | ofensor (offender) | ofensores (offender, pl) |
| 5 | jugada (play) | jugadas (play, pl) | jugador (player) | boletín (bulletin) | boletines (bulletin, pl) |
| 6 | ventana (window) | ventanas (window, pl) | ventanal (picture) | aspectual (aspectual) | aspectuales (aspectual, pl) |
| 7 | mirada (look) | miradas (look, pl) | mirador (viewpoint) | senador (senator) | senadores (senator, pl) |
| 8 | naranja (orange) | naranjas (orange, pl) | naranjal (orange grove) | unidad (unity) | unidades (unity, pl) |
| 9 | paloma (pigeon) | palomas (pigeon, pl) | palomar (dovecote) | honradez (honesty) | honradeces (honesty, pl) |
| 10 | parroquia (parish) | parroquias (parish, pl) | parroquial (parochial) | especial (special) | especiales (special, pl) |
| 11 | pesado (heavy, masc) | pesados (heavy, masc/pl) | pesadez (bore) | hormonal (hormonal) | hormonales (hormonal, pl) |
| 12 | pescado (fish) | pescados (fish, pl) | pescador (fisherman) | vaginal (vaginal) | vaginales (vaginal, pl) |
| 13 | portada (cover) | portadas (cover, pl) | portador (carrier) | mineral (mineral) | minerales (mineral, pl) |
| 14 | seguido (straight) | seguidos (straight, pl) | seguidor (fan) | coronel (colonel) | coroneles (colonel, pl) |
| 15 | sembrado (seeded plot) | sembrados (seeded plot, pl) | sembrador (sowing) | cultural (cultural) | culturales (cultural, pl) |
| 16 | pasado (past) | pasados (past, pl) | pasador (hairclip) | inquietud (inquietude) | inquietudes (inquietude, pl) |
Appendix B

Table A2.
List of experimental and distracter stimuli in the cognate condition. Remember that the presence of the competitors was randomized in two lists. While in List 1 a participant saw the pair colonia-colonias, in List 2, participants would see colonia-colonial.
Table A2.
List of experimental and distracter stimuli in the cognate condition. Remember that the presence of the competitors was randomized in two lists. While in List 1 a participant saw the pair colonia-colonias, in List 2, participants would see colonia-colonial.
| Target—Stress on the Penultimate Syllable | Competitor 1—Stress on the Penultimate Syllable | Competitor 2—Stress on the Final Syllable | Distracter 1 | Distracter 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | colonia (colony/cologne) | colonias (colony/cologne, pl) | colonial (colonial) | madurez (maturity) | madureces (maturity, pl) |
| 2 | evento (event) | eventos (event, pl) | eventual (eventual) | literal (literal) | literales (literal, pl) |
| 3 | creada (created, fem) | creadas (created, fem/pl) | creador (creator) | mariscal (marshal) | mariscales (marshal, pl) |
| 4 | dictado (dictation) | dictados (dictation, pl) | dictador (dictator) | ejemplar (exemplary) | ejemplares (exemplary, pl) |
| 5 | electo (elected) | electos (elected, pl) | elector (elector) | humildad (humility) | humildades (humility, pl) |
| 6 | potencia (energy) | potencias (energy, pl) | potencial (potential) | otoñal (fall, adj) | otoñales (fall, adj/pl) |
| 7 | selecto (selected) | selectos (selected, pl) | selector (selector) | inicial (initial) | iniciales (initial, pl) |
| 8 | idea (idea) | ideas (idea, pl) | ideal (ideal) | colosal (colossal) | colosales (colossal, pl) |
| 9 | industria (industry) | industrias (industry, pl) | industrial (industrial) | sepulcral (sepulchral) | sepulcrales (sepulchral, pl) |
| 10 | producto (product) | productos (product, pl) | productor (producer) | historial (record) | historiales (record, pl) |
| 11 | invento (invent) | inventos (invent, pl) | inventor (inventor) | teatral (theatrical) | teatrales (theatrical, pl) |
| 12 | notario (notary) | notarios (notary, pl) | notarial (notarial) | esencial (essential) | esenciales (essential, pl) |
| 13 | materia (subject/matter) | materias (subject/matter, pl) | material (material) | parador (tourist hotel) | paradores (tourist hotel, pl) |
| 14 | directo (direct) | directos (direct, pl) | director (director/conductor) | batallón (battalion) | batallones (battalion, pl) |
| 15 | familia (family) | familias (family, pl) | familiar (familiar) | proyectil (projectile) | proyectiles (projectile, pl) |
| 16 | tribuna (tribune) | tribunas (tribune, pl) | tribunal (tribunal) | helador (freezing) | heladores (freezing, pl) |
Appendix C

Table A3.
List of the fillers used in the experiment. These fillers appeared in both lists.
Table A3.
List of the fillers used in the experiment. These fillers appeared in both lists.
| Target | Competitor | Distracter 1 | Distracter 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | compresión (crushing) | compresa (compress) | cargadores (charger, pl) | cargados (charged, pl) |
| 2 | mejillón (mussel) | mejilla (cheek) | dotaciones (amount, pl) | dotados (gifted, pl) |
| 3 | incisión (incision) | inciso (insert) | pantalones (trouser, pl) | pantanos (swamp, pl) |
| 4 | posesión (possession) | poseso (obsessed) | objeciones (objection, pl) | objetos (object, pl) |
| 5 | infantil (childish) | infante (infant) | votadores (voter, pl) | votados (voted, pl) |
| 6 | omisión (omission) | omiso (omitted) | animales (animal, pl) | animes (anime, pl) |
| 7 | profesión (profession) | profeso (on purpose) | testadores (testador, pl) | testados (tested, pl) |
| 8 | conductor (driver) | conducto (pipe) | ilegales (illegal, pl) | ilesos (uninjured, pl) |
| 9 | natural (natural) | natura (nature) | picadores (chopper, pl) | picados (punctured, pl) |
| 10 | reducción (reduction) | reducido (reduced) | estatales (state, adj/pl) | estados (state, pl) |
| 11 | ocasión (opportunity) | ocaso (sunset) | patatales (potato field) | patatas (potato, pl) |
| 12 | oficial (official/officer) | oficio (profession) | noticiones (bombshell, pl) | noticias (news, pl) |
| 13 | medieval (medieval) | medievo (Middle Ages) | actitudes (attitude, pl) | activos (active, pl) |
| 14 | accesión (assent) | acceso (access) | salariales (salary, adj/pl) | salarios (salary, pl) |
| 15 | distinción (distinction) | distancia (distance) | cantidades (quantity, pl) | cantinas (canteen, pl) |
| 16 | pelotón (squad) | pelota (ball) | compulsiones (compulsion, pl) | compuertas (floodgate, pl) |
| 17 | bananal (banana field) | bananas (banana, pl) | cardadores (hair comb, pl) | cardado (combed) |
| 18 | confusión (confusion) | confuso (confusing, pl) | voladores (flyer, pl) | volado (projecting) |
| 19 | principal (main) | principios (start, pl) | tostadores (toaster, pl) | tostado (toasted) |
| 20 | personal (personal) | personas (person, pl) | arrozales (rice field, pl) | arrobo (ectasy) |
| 21 | cerebral (cerebral) | cerebros (brain, pl) | tabacales (tobacco field, pl) | tabaco (tobacco) |
| 22 | conversión (conversion) | conversos (converse, pl) | capitales (capital, pl) | capota (car top) |
| 23 | difusión (diffusion) | difusos (diffused, pl) | concejales (city councilman, pl) | consejo (advice) |
| 24 | obsesión (obsession) | obsesos (obsessed, pl) | retracciones (retraction, pl) | retrato (portrait) |
| 25 | diversión (amusement) | diversos (diverse, pl) | pimentones (paprika, pl) | pimiento (pepper) |
| 26 | matador (matador) | matados (killed, pl) | interiores (interior, pl) | interno (intern) |
| 27 | espiral (spiral) | espiras (lap, pl) | notaciones (notation, pl) | notable (notable) |
| 28 | procesión (procession) | procesos (process, pl) | retadores (challenging, pl) | retablo (altarpiece) |
| 29 | comercial (commercial) | comercios (business, pl) | colaciones (comparison, pl) | colada (laundry) |
| 30 | saltador (jumper) | saltados (jumped, pl) | eslabones (link, pl) | eslavo (Slav) |
| 31 | catador (taster) | catados (tasted, pl) | asesores (consultant, pl) | aseo (bathroom) |
| 32 | latitud (latitude) | latidos (beat, pl) | radiadores (radiator, pl) | radiante (splendid) |
| 33 | caballos (horse, pl) | caballo (horse) | avidez (greed) | avideces (greed, pl) |
| 34 | esposos (husband, pl) | esposo (husband) | contractual (contractual) | contractuales (contractual, pl) |
| 35 | cunetas (curb, pl) | cuneta (curb) | fumador (smoker) | fumadores (smoker, pl) |
| 36 | latinos (latino, pl) | latino (latino) | temporal (storm) | temporales (storm, pl) |
| 37 | cursillos (lecture series, pl) | cursillo (lecture series) | infusión (infusion) | infusiones (infusion, pl) |
| 38 | granizos (hail, pl) | granizo (hail) | clonación (clonation) | clonaciones (clonation, pl) |
| 39 | pelusas (fluff, pl) | pelusa (fluff) | nadador (swimmer) | nadadores (swimmer, pl) |
| 40 | roperas (wardrobe, pl) | ropera (wardrobe) | ladrador (barker) | ladradores (barker, pl) |
| 41 | pasillos (corridor, pl) | pasillo (corridor) | donación (donation) | donaciones (donation, pl) |
| 42 | sopletes (blowtorch, pl) | soplete (blowtorch) | aridez (aridity) | arideces (aridity, pl) |
| 43 | espaldas (back, pl) | espalda (back) | subvención (subsidy) | subvenciones (subsidy, pl) |
| 44 | acuerdos (agreement) | acuerdo (agreement) | albañil (builder) | albañiles (builder, pl) |
| 45 | hallazgos (discovery, pl) | hallazgo (discovery) | percutor (hammer) | percutores (hammer, pl) |
| 46 | equipos (team, pl) | equipo (team) | dirección (direction) | dirección (direction) |
| 47 | bodegas (winery, pl) | bodega (winery) | celador (porter) | celador (porter) |
| 48 | bebidas (drink, pl) | bebida (drink) | contracción (contraction) | contracciones (contraction, pl) |
| 49 | barrigas (belly, pl) | barrigón (potbellied) | pedrea (minor prizes) | pedregales (rocky ground, pl) |
| 50 | borrachos (drunk, pl) | borrachín (boozer) | oriente (east) | orientales (eastern, pl) |
| 51 | cabezas (head, pl) | cabezón (stubborn) | receta (recipe) | recitales (recital, pl) |
| 52 | caseros (landlord, pl) | caserón (big ramshackle house) | litigio (contention) | litorales (coast, pl) |
| 53 | chaquetas (jacket, pl) | chaquetón (short coat) | receso (break) | recesiones (recession, pl) |
| 54 | cucharas (spoon, pl) | cucharón (ladle) | sumiso (submissive) | sumisiones (submission, pl) |
| 55 | folletos (pamphlet, pl) | folletín (melodrama) | posible (possible) | posiciones (position, pl) |
| 56 | juguetes (toy, pl) | juguetón (playful) | devoto (devoted) | devociones (devotion, pl) |
| 57 | maletas (suitcase, pl) | maletín (briefcase) | edicto (edict) | editores (editor, pl) |
| 58 | orejas (ear, pl) | orejón (dried peach/apricot) | locura (insanity) | locutores (announcer, pl) |
| 59 | pelucas (wig, pl) | peluquín (toupee) | abrigo (coat) | abridores (opener, pl) |
| 60 | solteras (single, fem/pl) | solterón (bacherlo) | morada (home/purple) | moradores (inhabitant, pl) |
| 61 | medallas (medal, pl) | medallón (medallion) | perenne (evergreen) | perejiles (parsley, pl) |
| 62 | abusos (abuse, pl) | abusón (bully) | agreste (wild) | agresores (attacker, pl) |
| 63 | intrusos (intruder, pl) | intrusión (intrusion) | ascenso (promotion) | ascensores (elevator, pl) |
| 64 | sucesos (event, pl) | sucesión (succession) | represa (dam) | represores (repressive, pl) |
| 65 | abejones (drone, pl) | abeja (bee) | ligeros (light, pl) | ligerez (lightness) |
| 66 | abismales (huge, pl) | abismo (abyss) | sobacos (armpit, pl) | sobacal (underarm) |
| 67 | semanales (weekly, pl) | semana (week) | obispos (bishop, pl) | obispal (related to bishops) |
| 68 | coladores (strainer, pl) | colado (in love) | carcomas (woodworm, pl) | carcamal (decrepit) |
| 69 | bordadores (Needleman, pl) | bordado (embroidery) | neuronas (neuron, pl) | neuronal (neuronal) |
| 70 | borradores (rubber, pl) | borrado (condition) | lucibles (glowing, pl) | lucidez (lucidity) |
| 71 | domadores (tamer, pl) | domado (tamed) | vendidos (sold, pl) | vendedor (seller) |
| 72 | labradores (farmer, pl) | labrado (cultivated) | comicios (election, pl) | comisión (commission) |
| 73 | dispersiones (dispersion, pl) | disperso (unfocused) | galantes (gallant, pl) | galardón (award) |
| 74 | chuletones (steak, pl) | chuleta (chop) | maracas (maraca, pl) | maratón (marathon) |
| 75 | cantorales (group of singers, pl) | cantora (singer) | canallas (despicable, pl) | canalón (gutter) |
| 76 | narradores (narrator, pl) | narrados (narrated, pl) | hospital (hospital) | hospicio (hostel) |
| 77 | pecadores (sinner, pl) | pecados (sin, pl) | carnaval (carnival) | carnaza (ground bait) |
| 78 | protectores (protector, pl) | protestas (complaint, pl) | delantal (apron) | delante (in front) |
| 79 | pastorales (pastorals, pl) | pastoras (shepherd, pl) | comunión (communion) | comuna (commune) |
| 80 | canelones (cannellone, pl) | canelas (cinnamon, pl) | palmeral (palm tree field) | palmera (palm tree) |
| 81 | redondeles (circle, pl) | redondos (round, pl) | alcacil (artichoke) | alcalde (major) |
| 82 | vencedores (winner, pl) | vencidos (defeated, pl) | espadón (broadsword) | espada (sword) |
| 83 | cazadores (hunter, pl) | cazados (hunted, pl) | caridad (charity) | caricia (caress) |
| 84 | callejones (alley, pl) | callejas (narrow street, pl) | secesión (secession) | seseo (seseo) |
| 85 | calderones (cauldron, pl) | calderas (boiler, pl) | paladar (palate) | palada (shovelful) |
| 86 | salvadores (rescuer, pl) | salvados (saved, pl) | chupetón (slurp) | chupete (pacifier) |
| 87 | fundadores (founder, pl) | fundador (founder) | abajo (downhill) | abanos (type of cigar, pl) |
| 88 | comprensiones (understanding, pl) | comprensión (understanding) | marino (marine) | maridos (husband, pl) |
| 89 | pulsadores (push button, pl) | pulsador (push button) | escala (scale) | escamas (scale ‘fish’, pl) |
| 90 | dimensiones (dimension, pl) | dimensión (dimension) | entrada (entry) | entrañas (guts, pl) |
| 91 | revolcones (tumble, pl) | revolcón (tumble) | revuelo (disturbance) | revueltos (scrambled eggs, pl) |
| 92 | condiciones (condition, pl) | condición (condition) | pirata (pirate) | pirañas (piranha, pl) |
| 93 | colisiones (collision, pl) | colisión (collision) | espiga (ear ‘wheat’) | espinas (hawthorn, pl) |
| 94 | amistades (friendship, pl) | amistad (friendship) | balido (bleating) | batidos (milkshake, pl) |
| 95 | colofones (colophon, pl) | colofón (colophon) | cosita (little thing) | colitis (little tale, pl) |
| 96 | socavones (subsidence, pl) | socavón (subsidence) | acera (sidewalk) | aceros (iron, pl) |
Appendix D

Table A4.
Information regarding the experimental trials in this experiment. Non-cognate condition. The log frequency of the target and competitor words was obtained using the subtitle token corpus in EsPal (Duchon et al. 2013), provided by the Basque Center on Cognition, Brain, and Language.
Table A4.
Information regarding the experimental trials in this experiment. Non-cognate condition. The log frequency of the target and competitor words was obtained using the subtitle token corpus in EsPal (Duchon et al. 2013), provided by the Basque Center on Cognition, Brain, and Language.
| Target—Penultimate | Competitor 1—Final | Competitor 2—Penultimate | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log Freq | Length (# of Letters) | Log Freq | Length (# of Letters) | Log Freq | Length (# of Letters) | ||||
| 1 | asado (roast) | 0.88 | 6 | asador (rotisserie) | 0.22 | 6 | asados | 0.27 | 6 |
| 2 | vecino (neighbor) | 1.34 | 7 | vecinal (neighboring) | 0.13 | 7 | vecinos | 1.49 | 7 |
| 3 | ganado (cattle/won) | 1.78 | 7 | ganador (winner) | 1.39 | 7 | ganados | 0.19 | 7 |
| 4 | dinero (money) | 2.86 | 7 | dineral (fortune) | 0.36 | 7 | dineros | 0.06 | 7 |
| 5 | jugada (play) | 1.18 | 7 | jugador (player) | 1.40 | 7 | jugadas | 0.58 | 7 |
| 6 | ventana (window) | 1.91 | 8 | ventanal (picture window) | 0.09 | 8 | ventanas | 1.40 | 8 |
| 7 | mirada (look) | 1.65 | 7 | mirador (viewpoint) | 0.28 | 7 | miradas | 0.78 | 7 |
| 8 | naranja (orange) | 1.25 | 8 | naranjal (orange grove) | 1.25 | 8 | naranjas | 0.72 | 8 |
| 9 | paloma (pidgeon) | 0.91 | 7 | palomar (dovecote) | 0.24 | 7 | palomas | 0.79 | 7 |
| 10 | parroquia (parrish) | 0.66 | 10 | parroquial (parochial) | 0.13 | 10 | parroquias | 0.06 | 10 |
| 11 | pesado (heavy) | 1.38 | 7 | pesadez (bore) | 0.14 | 7 | pesados | 0.85 | 7 |
| 12 | pescado (fish) | 1.51 | 8 | pescador (fisherman) | 0.82 | 8 | pescados | 0.51 | 8 |
| 13 | portada (cover) | 1.02 | 8 | portador (carrier) | 0.71 | 8 | portadas | 0.34 | 8 |
| 14 | seguido (straight) | 1.47 | 8 | seguidor (fan) | 0.41 | 8 | seguidos | 0.79 | 8 |
| 15 | sembrado (seeded plot) | 0.30 | 9 | sembrador (sowing) | 0.04 | 9 | sembrados | 0.06 | 9 |
| 16 | pasado (past) | 2.59 | 7 | pasador (hairclip) | 0.23 | 7 | pasados | 0.80 | 7 |
| Average | 1.42 | 7.56 | 0.49 | 7.56 | 0.61 | 7.56 | |||
| SD | 0.66 | 0.96 | 0.47 | 0.96 | 0.44 | 0.96 | |||
Appendix E

Table A5.
Information regarding the experimental trials in this experiment. Cognate condition. The log frequency of the target and competitor words was obtained using the subtitle token corpus in EsPal (Duchon et al. 2013), provided by the Basque Center on Cognition, Brain, and Language.
Table A5.
Information regarding the experimental trials in this experiment. Cognate condition. The log frequency of the target and competitor words was obtained using the subtitle token corpus in EsPal (Duchon et al. 2013), provided by the Basque Center on Cognition, Brain, and Language.
| Target—Penultimate | Competitor 1—Final | Competitor 2—Penultimate | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spanish | Log Freq | Length (Number of Letters) | Spanish | Log Freq | Length (Number of Letters) | Spanish | Log Freq | Length (Number of Letters) | |
| 1 | colonia (colony) | 1.16 | 7 | colonial | 0.58 | 8 | colonias | 0.81 | 8 |
| 2 | evento (event) | 1.26 | 6 | eventual | 0.19 | 8 | eventos | 1.11 | 7 |
| 3 | creada (created) | 0.65 | 6 | creador | 0.94 | 7 | creadas | 0.33 | 7 |
| 4 | dictado (dictation) | 0.37 | 7 | dictador | 0.61 | 8 | dictados | 0.13 | 8 |
| 5 | electo (elected) | 0.48 | 6 | elector | 0.11 | 7 | electos | 0.14 | 7 |
| 6 | potencia (energy) | 1.26 | 8 | potencial | 0.59 | 9 | potencias | 0.26 | 9 |
| 7 | selecto (selected) | 0.29 | 7 | selector | 0.03 | 8 | selectos | 0.17 | 8 |
| 8 | idea | 2.65 | 4 | ideal | 1.27 | 5 | ideas | 1.71 | 5 |
| 9 | industria (industry) | 1.26 | 9 | industrial | 0.89 | 10 | industrias | 0.83 | 10 |
| 10 | producto (product) | 1.29 | 8 | productor | 1.12 | 9 | productos | 1.19 | 9 |
| 11 | invento (invent) | 0.93 | 7 | inventor | 0.59 | 8 | inventos | 0.46 | 8 |
| 12 | notario (notary) | 0.48 | 7 | notarial | 0.13 | 8 | notarios | 0.03 | 8 |
| 13 | materia (materia) | 1.17 | 7 | material | 1.53 | 8 | materias | 0.43 | 8 |
| 14 | directo (direct) | 1.67 | 7 | director | 1.92 | 8 | directos | 0.60 | 8 |
| 15 | familia (family) | 2.59 | 7 | familiar | 1.66 | 8 | familias | 1.53 | 8 |
| 16 | tribuna (tribune) | 0.38 | 7 | tribunal | 1.57 | 8 | tribunas | 0.10 | 8 |
| Average | 1.12 | 6.88 | 0.86 | 7.94 | 0.61 | 7.88 | |||
| SD | 0.72 | 1.09 | 0.60 | 1.06 | 0.53 | 1.09 | |||
References
- Allopenna, Paul D., James S. Magnuson, and Michael K. Tanenhaus. 1998. Tracking the Time Course of Spoken Word Recognition Using Eye Movements: Evidence for Continuous Mapping Models. Journal of Memory and Language 38: 419–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, Douglas, Martin Mächler, Ben Bolker, and Steve Walker. 2015. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software 67: 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenfeld, Henrike K., and Viorica Marian. 2011. Bilingualism influences inhibitory control in auditory comprehension. Cognition 118: 245–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfieni, Michela, Holly P. Branigan, Martin J. Pickering, and Antonella Sorace. 2019. Cognitive control in bilinguals: Effects of language experience and individual variability. Bilingualism Language and Cognition, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, James Dean. 1980. Relative merits of four methods for scoring cloze tests. Modern Language Journal 64: 311–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canseco-Gonzalez, Enriqueta, Laurel Brehm, Cameron A. Brick, Sarah Brown-Schmidt, Kara Fischer, and Katie Wagner. 2010. Carpet or Cárcel: The effect of age of acquisition and language mode on bilingual lexical access. Language and Cognitive Processes 25: 669–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Peiyao, Susan C. Bobb, Noriko Hoshino, and Viorica Marian V. 2017. Neural signatures of language co-activation and control in bilingual spoken word comprehension. Brain Research 1665: 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colomé, Àngels. 2001. Lexical activation in bilinguals’ speech production: Language-specific or language-independent? Journal of Memory and Language 45: 721–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, Nicole, Anne Cutler, and Roger Wales. 2002. Constraints of lexical stress on lexical access in English: Evidence from native and non-native listeners. Language and Speech 45: 207–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, Anne, and Dennis Pasveer. 2006. Explaining cross-linguistic differences in effects of lexical stress on spoken-word recognition. In Speech Prosody. Edited by Rüdiger Hoffman and Hansjörg Mixdorff. Dresden: TUD Press. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, Anne, Andrea Weber, and Takashi Otake. 2006. Asymmetric mapping from phonetic to lexical representations in second-language listening. Journal of Phonetics 34: 269–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, Anne, Roger Wales, Nicole Cooper, and Joris Janssen. 2007. Dutch listeners’ use of suprasegmental cues to English stress. Saarbrücken 60: 1913–16. [Google Scholar]
- Desmet, Timothy, and Wouter Duyck. 2007. Bilingual language processing. Language and Linguistics Compass 1: 168–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, Ton. 2005. Bilingual visual word recognition and lexical access. In Handbook of Bilingualism: Psycholinguistic Approaches. New York: Oxford University Press, pp. 179–201. [Google Scholar]
- Duchon, Andrew, Manuel Perea, Nuria Sebastián-Gallés, Antonia Martí, and Manuel Carreiras. 2013. EsPal: one-stop shopping for Spanish word properties. Behavior Research Methods 45: 1246–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flege, James Emil. 1984. The detection of French accent by American listeners. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 76: 692–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flege, James Emil. 1991. Age of learning affects the authenticity of voice-onset time (VOT) in stop consonants produced in a second language. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 89: 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flege, James Emil, and Robert M. Hammond. 1982. Mimicry of Non-distinctive Phonetic Differences Between Language Varieties. Studies in Second Language Acquisition 5: 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Grosjean, François. 1997. The Bilingual Individual. Interpreting 2: 163–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosjean, François. 2010. Bilingual: Life and Reality. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Taomei, and Danling Peng. 2006. Event-related potential evidence for parallel activation of two languages in bilingual speech production. Neuroreport 17: 1757–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huettig, Falk, and James M. McQueen. 2007. The tug of war between phonological, semantic, and shape information in language-mediated visual search. Journal of Memory and Language 54: 460–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Min, and Paul A. Luce. 2004. Falling on Sensitive Ears: Constraints on Bilingual Lexical Activation. Psychological Science 15: 314–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemhöfer, Kristin, and Mirjam Broersma. 2012. Introducing LexTALE: A quick and valid Lexical Test for Advanced Learners of English. Behavior Research Methods 44: 325–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luce, Paul A. 1986. A computational analysis of uniqueness points in auditory word recognition. Perception & Psychophysics 39: 155–58. [Google Scholar]
- Luce, Paul. A., and David B. Pisoni. 1998. Recognizing spoken words: The neighborhood activation model. Ear and hearing 19: 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marian, Viorica, and Michael Spivey. 2003a. Bilingual and monolingual processing of competing lexical items. Applied Psycholinguistics 24: 173–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, Viorica, and Michael Spivey. 2003b. Competing activation in bilingual language processing: Within- and between-language competition. Bilingualism Language and Cognition 6: 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, Viorica, Henrike K. Blumenfeld, and Olga V. Boukrina. 2008. Sensitivity to phonological similarity within and across languages. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research 37: 141–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marslen-Wilson, William, and Paul Warren. 1994. Levels of perceptual representation and process in lexical access: Words, phonemes, and features. Psychological Review 101: 653–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirman, Daniel, James A. Dixon, and James S. Magnusom. 2008. Statistical and computational models of the visual world paradigm: Growth curves and individual differences. Journal of Memory and Language 59: 475–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, Ramesh Kumar, and Niharika Singh. 2016. The influence of second language proficiency on bilingual parallel language activation in Hindi–English bilinguals. Journal of Cognitive Psychology 5911: 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivneva, Irina, Julie Mercier, and Debra Titone. 2014. Executive control modulates cross-language lexical activation during L2 reading: evidence from eye movements. Journal of Experimental Psychology Learning Memory and Cognition 40: 787–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulpen, Béryl, Ton Dijkstra, Herbert J. Schriefers, and Mark Hasper. 2003. Recognition of interlingual homophones in bilingual auditory word recognition. Journal of Experimental Psychology Human Perception and Performance 29: 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverberg, Stu, and Arthur G. Samuel. 2004. The effect of age of second language acquisition on the representation and processing of second language words. Journal of Memory and Language 51: 381–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, Carlos, and François Grosjean. 1984. Bilinguals in a monolingual and a bilingual speech mode: The effect on lexical access. Memory & Cognition 12: 380–86. [Google Scholar]
- Soto-Faraco, Salvador, Núria Sebastián-Gallés, and Anne Cutler. 2001. Segmental and suprasegmental mismatch in lexical access. Journal of Memory and Language 45: 412–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spivey, Michael J., and Viorica Marian. 1999. Cross Talk Between Native and Second Languages: Partial Activation of an Irrelevant Lexicon. Psychological Science 10: 281–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, Annie. 2008. Is second language lexical access prosodically constrained? Processing of word stress by French Canadian second language learners of English. Applied Psycholinguistics 29: 553–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Anne, Katherine, Maria Teresa Martínez-García, Rachel Brown, and Annie Tremblay. 2014. English and Spanish listeners’ use of ‘positive’ stress in Spanish word recognition. Paper Presented at the 33rd Annual Second Language Research Forum (SLRF), Columbia, SC, USA, October 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, Andrea, and Anne Cutler. 2004. Lexical competition in non-native spoken-word recognition. Journal of Memory and Language 50: 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, Andrea, Alissa Melinger, and Lourdes Lara Tapia. 2007. The mapping of phonetic information to lexical representation in Spanish: Evidence from eye movements. In Proceedings of the 16th International Congress of Phonetic Sciences (ICPhS 2007). Edited by Jürgen Trouvain and William J. Barry. Dudweiler: Pirrot, pp. 1941–44. [Google Scholar]
| 1 | Other variables, such as neighborhood density or phonological neighborhood density should have also been taken into account. However, it was impossible to match words (between conditions) in all these variables. While Spanish–English have a decent amount of cognate words, there are not so many that do meet all the requirements to be used in this experiment (mismatching stress pattern, same/similar length, or similar frequency). We matched stimuli as closely as possible, yet we acknowledge that the matching may not have been completely perfect. |
| 2 | The main point of using the GCA is to make sure the analysis is not limited to a specific time window. This statistical method gives a comparison on how two shapes change over time (in this case, the eye-fixations of both conditions), but it does not provide any information regarding what happens at specific points in time. Thus, it is not possible to establish at which time window any potential competitor stress effects occurred. |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).