Mars Space Exploration and Astronautical Religion in Human Research History: Psychological Countermeasures of Long-Term Astronauts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Space Exploration and Mental Sustainability
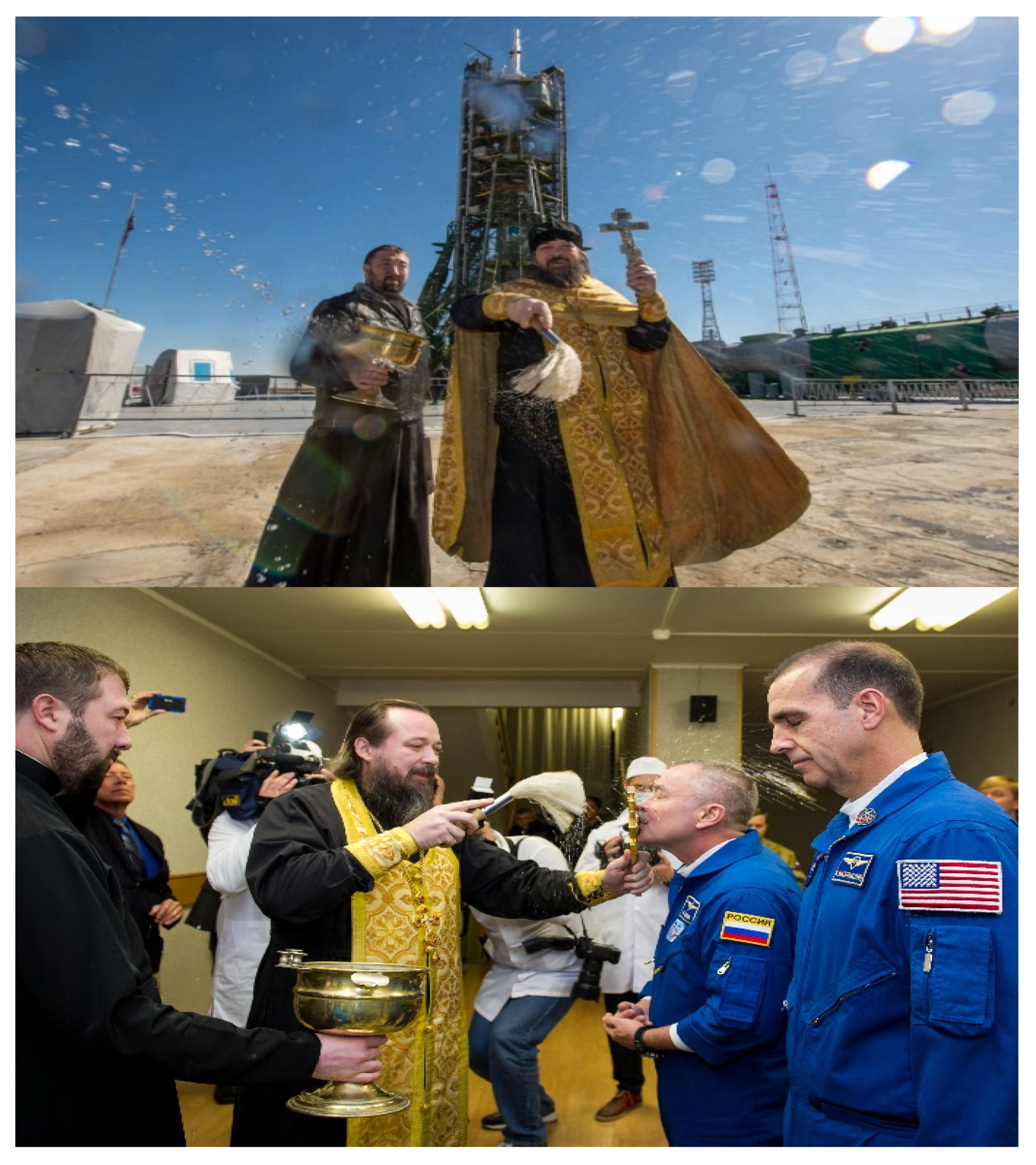
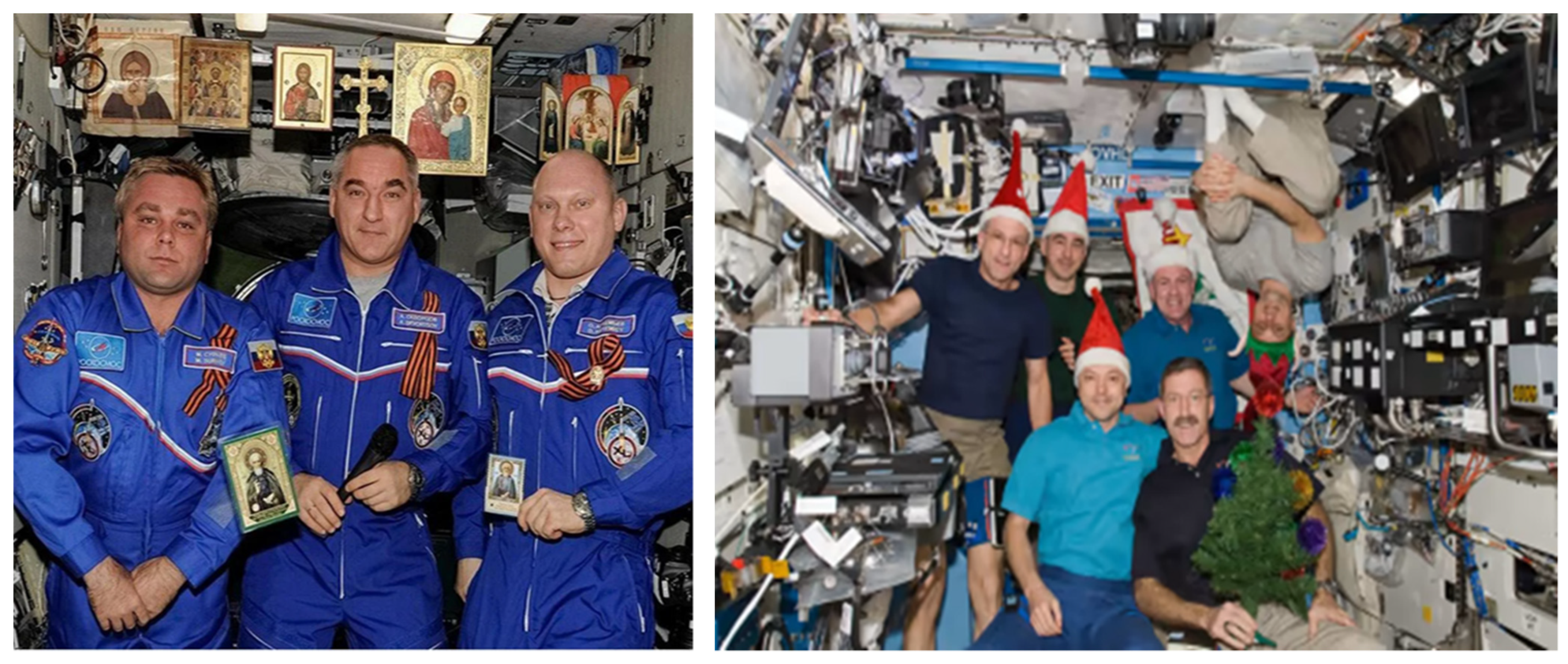
2.1. Space Experience with Religion
‘We must consider the mental and spiritual well-being of future humans in addition to providing for them physically … as we are human beings, not robots, … it is no doubt that religious stories—of course for believers—are much more efficient in providing sense and hope than science, technology, or philosophy’.
2.2. Human Factors in Space Exploration
There is not enough objective data to determine the seriousness of behavioural impairments in past spaceflight missions. Nevertheless, there are reasons to suppose that psychological problems have already occurred on spaceflights. In addition, these problems will increase in frequency and severity as missions become longer and more complex, as crews become larger and more heterogeneous, and as the dangers of spaceflight become more fully appreciated.
2.3. Astronautical Religion for Long-Term Astronauts
2.4. Psychological Countermeasures in Spirituality
3. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jorgensen, M.K.; Sharf, I. Effect of release conditions on casualty risk factor in uncontrolledre-entry of large space debris. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration. How Investing in the Moon Prepares NASA for First Human Mission to Mars. Last Modified on 4 June 2021. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/atoms/files/moon-investments-prepare-us-for-mars.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Mangold, N.; Baratoux, D.; Witasse, O.; Encrenaz, T.; Sotin, C. Mars: A small terrestrial planet. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2016, 24, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnould, A. Colonising Mars. a time frame for ethical questioning. In Human Factor in a Mission to Mars: An Interdisciplinary Approach; Szocik, K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- China’s Zhurong Rover Takes First Drive on Mars. BBC News. 22 May 2021. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-china-57211001 (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Prateek, M.; Singh, T.P.; Choudhury, T. Mars exploration 60 years: USA, China and UAE concurrently launch. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Intelligence and Data Science Applications, Dehradun, India, 4–5 September 2020; pp. 98–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, A. On a Planet Where You Cannot Breath, Is Living on Mars the Best Idea? Fla. Today. 30 December 2020. Last Modified on 11 June 2021. Available online: https://www.floridatoday.com/in-depth/tech/science/space/2020/12/29/planet-where-you-cannot-breathe-living-mars-best-idea/2579039001/ (accessed on 12 August 2022).
- Cabrol, N.A. The coevolution of life and environment of Mars: An ecosystem perspective on the robotic exploration of biosignatures. Astrobiology 2018, 18, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, G.H.; Abbey, W.; Bearman, G.H.; Mungas, G.S.; Smith, J.A.; Anderson, R.C.; Douglas, S.; Beegle, L.W. Mojave Mars simulant—Characterization of a new geologic Mars analog. Icarus 2008, 197, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum. Apollo 8 Astronaut Remembers Looking Down at Earth. Last Modified on 10 June 2021. Available online: https://airandspace.si.edu/stories/editorial/apollo-8-astronaut-remembers-looking-down-earth (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Heinicke, C.; Adeli, S.; Baque, M.; Correale, G.; Fateri, M.; Jaret, S.; Kopacz, N.; Ormo, J.; Poulet, L.; Verseux, L. Equipping an extraterrestrial laboratory: Overview of openresearch questions and recommended instrumentation for the Moon. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 2518–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozicki, J.; Kozicka, J. Human friendly architectural design for a small martian base. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 48, 1997–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palinkas, L.A. Behavioral issues. In A Strategy for Research in Space Biology and Medicine in the New Century; National Research Council, Ed.; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; pp. 194–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keh, S. Biographical Data (Scott, J. Kelly). 21 February 2016. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/atoms/files/kellysj.pdf (accessed on 21 August 2022).
- Buchanan, M. Colonizing Mars. Nat. Phys. 2017, 13, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impey, C. Mars and beyond: The feasibility of living in the solar system. In Human Factor in a Mission to Mars: An Interdisciplinary Approach; Szocik, K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 93–111. [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport, M.B.; Corbally, C. Program planning for a Mars hardship post: Social, psychological and spiritual services. In Human Factor in a Mission to Mars: An Interdisciplinary Approach; Szocik, K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Wanga, H.; Richardson, M.I. The origin, evolution, and trajectory of large dust storms on Mars during Mars years 24–30 (1999–2011). Icarus 2015, 251, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horneck, G.; Facius, R.; Reichert, M.; Rettberg, P.; Seboldt, W.; Manzey, D.; Comet, B.; Maillet, A.; Preiss, H.; Schauer, L.; et al. HUMEX, a study on the survivability and adaptation of humans to long-duration exploratory missions, part II: Missions to Mars. Adv. Space Res. 2006, 38, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Mireles, A.L.; Walker, J.N.; Caparon, M.; Hultgren, S.J. Urinary tract infections: Epidemiology, mechanisms of infection and treatment options. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloat, S. The Key to Survival on Mars Is Religion, Argues Scientist. Last Edified on 11 June 2021. Available online: https://www.inverse.com/article/38069-mars-colonies-space-religion-konrad-szocik (accessed on 29 August 2022).
- Harrison, A.A.; Fiedler, E.R. Behavioral health. In Psychology of Space Exploration: Contemporary Research in Historical Perspective; Vakoch, D.A., Ed.; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Rodhan, N. This Is Your Brain on Mars: What Space Travel Does to Our Psychology. Prospect: Science & Technology. 27 February 2018. Available online: https://www.prospectmagazine.co.uk/science-and-technology/this-is-your-brain-on-mars-what-space-travel-does-to-our-psychology (accessed on 12 June 2022).
- Zimmerman, R. Leaving Earth: Space Stations, Rival Superpowers, and the Quest for Interplanetary Travel; Joseph Henry Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 366–373. [Google Scholar]
- Oviedo, L. Religion for a spatial colony: Raising the right questions. In Human Factor in a Mission to Mars: An Interdisciplinary Approach; Szocik, K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 217–231. [Google Scholar]
- Davenport, C.; Vitkovskaya, J. 50 Astronauts, in Their Own Words. Wash. Post. 19 June 2019. Last modified on 11 June 2021. Available online: https://www.washingtonpost.com/graphics/2019/national/50-astronauts-life-in-space/ (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Anonymous. Home from home: We cannot look to the stars to solve our planet’s problems. Nature 2016, 539, 330. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, L.D.; Axinn, W.G. The impact of family religious life on the quality of mother-child relations. Am. Sociol. Rev. 2021, 63, 810–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traphagan, J.W. Religion, science, and space exploration from a non-western perspective. Religions 2020, 11, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerman, C. One-of-a-Kind Study of Astronaut Twins Hints at Spaceflight’s Health Effects. National Geographic. 12 April 2019. Available online: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/study-of-astronaut-twins-hints-at-spaceflight-health-effects (accessed on 25 September 2022).
- Szocik, K. (Ed.) The Human Factor in a Mission to Mars: An Interdisciplinary Approach; Springer Nature: London, UK; Berlin, Germany; New York City, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S. Designing food systems for Mars explorations. Food Eng. Prog. 2004, 8, 77–90. [Google Scholar]
- Kring, J.P.; Kaminski, M.A. Gender composition and crew cohesion during long-duration space missions. In Psychology of Space Exploration: Contemporary Research in Historical Perspective; Vakoch, D.A., Ed.; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 125–141. [Google Scholar]
- Basner, M.; Dinges, D.F.; Mollicone, D.J.; Savelev, I.; Ecker, A.J.; Di Antonio, A.; Jones, C.W.; Hyder, E.C.; Kan, K.; Morukov, B.V.; et al. Psychological and behavioral changes during confinement in a 520-day simulated interplanetary mission to Mars. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, K. Mission to Mars: What psychosocial challenges would astronauts face on an epic journey to the red planet? Monit. Psychol. 2018, 49, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Haqq-Misra, J. Can deep altruism sustain space settlement? In Human Factor in a Mission to Mars: An Interdisciplinary Approach; Szocik, K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 145–155. [Google Scholar]
- Boeka, M. Exploring the Nature of Space for Human Behaviour in Ordinary Structured Environments. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Nebraska, Lincoln, NE, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rooney, B.V.; Crucian, B.E.; Pierson, D.L.; Laudenslager, M.L.; Mehta, S.K. Herpes virus reactivation in astronauts during spaceflight and its application on Earth. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaldi, K.M.; Smith, G.; Thropp, J.E. Human behavior during spaceflight-evidence from an analog environment. J. Aviat. /Aerosp. Educ. Res. 2015, 25, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ratzsch, D. Space travel and challenges to religion. Monist 1988, 71, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chancellor, J.C.; Scott, G.B.; Sutton, J.P. Space radiation: The number one risk to astronaut health beyond low Earth orbit. Life 2014, 4, 491–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.W.; Pecaut, M.; Gridley, D.S. Acute risks of space radiation. In Encyclopedia of Bioastronautics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, L.K.; Hunstad, D.A. Urinary tract infection: Pathogenesis and outlook. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 946–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, C.B.; Jpyner, C.R.; Kokan, T.S.; Levack, D.J.; Muzek, B. NTP robustness for Mars conjunction and opposition class missions. In Proceedings of the AIAA 2020–4124 Session: Nuclear Thermal Propulsion (Conference), Indianapolis, Indiana, 2 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hollingham, R. The Effects of Space Travel on the Human Body. BBC Future. 6 May 2014. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/future/article/20140506-space-trips-bad-for-your-health (accessed on 24 September 2022).
- Pätzolda, M.; Häuslerb, B.; Tylerc, G.L.; Andertb, T.; Asmard, S.W.; Birda, M.K.; Dehante, V.; Hinsonc, D.P.; Rosenblatte, P.; Simpsonc, R.A.; et al. Mars express 10 years at Mars: Observations by the Mars express radio science experiment (MaRS). Planet. Space Sci. 2016, 127, 44–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wordsworth, R.D. The climate of early Mars. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2016, 44, 381–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, V.K.; Allen, B.D.; Caressi, C.; Kwok, S.; Chu, E.; Tran, K.K.; Chmielewski, N.N.; Giedzinski, E.; Acharya, M.M.; Britten, R.A.; et al. Cosmic radiation exposure and persistent cognitive dysfunction. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, P.L.; Lewis, S.R.; Mulholland, D.P. The physics of martian weather and climate: A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2015, 78, 125901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vbood, S. Martian environmental psychology: The choice architecture of a Mars mission and colony. In Human Factor in a Mission to Mars: An Interdisciplinary Approach; Szocik, K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosius, J.D. Separation of church and space: Religious influences on public support for U.S. space exploration policy. Space Policy 2015, 32, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vago, J.L.; Westall, F. Habitability on early Mars and the search for biosignatures with the ExoMars rover. Astrobiology 2017, 17, 471–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibel, D.L. Space Exploration as Religious Experience. Space Review. 21 August 2017. Last Modified on 17 June 2021. Available online: https://www.thespacereview.com/article/3310/1 (accessed on 26 September 2022).
- Wichman, H. Managing negative interactions in space crews: The role of simulator research. In Psychology of Space Exploration: Contemporary Research in Historical Perspective; Vakoch, D.A., Ed.; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 103–123. [Google Scholar]
- Oehler, D.Z.; Etiope, G. Methane seepage on Mars: Where to look and why. Astrobiology 2017, 17, 1233–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzek, B.J.; Horton, J.; Joyner, C.R. Mission analysis for Mars opposition missions 2033 to 2048 (preprint: AAS 20–018). Nucl. Therm. Propuls. 2020. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/James-Horton-4/publication/339213502_Mission_Analysis_for_Mars_Opposition_Missions_2033_to_2048/links/5e44691492851c7f7f340810/Mission-Analysis-for-Mars-Opposition-Missions-2033-to-2048.pdf (accessed on 7 December 2022).
- Draguns, J.G.; Harrison, A.A. Spaceflight and cross-cultural psychology. In Psychology of Space Exploration: Contemporary Research in Historical Perspective; Vakoch, D.A., Ed.; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 177–194. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, S.L. From Earth analogs to space: Getting there from here. In Psychology of Space Exploration: Contemporary Research in Historical Perspective; Vakoch, D.A., Ed.; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 47–77. [Google Scholar]
- Norenzayan, A.; Shariff, A.F.; Gervais, W.M.; Willard, A.K.; McNamara, R.A.; Slingerland, E.; Henrich, J. The cultural evolution of prosocial religions. Behav. Brain Sci. 2016, 39, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owuor, M. Religion on Mars? Will There Be a Better Alternative for Religion on Mars? Last Modified on 11 June 2021. Available online: https://medium.com/tunapanda-institute/religion-on-mars-f308d85bbe4d (accessed on 9 May 2022).
- Greenstein, L. The Mental Health Benefits of Religion & Spirituality. National Alliance on Mental Illness. 21 December 2016. Last Modified on 21 June 2021. Available online: https://www.nami.org/Blogs/NAMI-Blog/December-2016/The-Mental-Health-Benefits-of-Religion-Spiritual (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Fagan, P. Why Religion Matters even more: The Impact of Religious Practice on Social Stability. Report Civil Society. 2006. Last modified on 21 June 2021. Available online: https://www.heritage.org/civil-society/report/why-religion-matters-the-impact-religious-practice-social-stability (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Fagan, P. 95 Social science reasons for religious worship and practice. Relig. Soc. 2012. Available online: https://downloads.frc.org/EF/EF12J37.pdf (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Capova, K.A. Human extremophiles: Mars as a camera obscura of the extraterrestrial scientific culture. In Human Factor in a Mission to Mars: An Interdisciplinary Approach; Szocik, K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Hordern, J. Religion, culture and conscience: Healthcare ethics and communication. Medicine 2020, 48, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.C. Religious faith and charitable giving. Policy Rev. 2003, 121, 20–45, Last modified on 21 June 2021. Available online: https://www.hoover.org/research/religious-faith-and-charitable-giving (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Brooks, A.C. Compassion, religion, and politics. Public Interest 2004, 157, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, H.W.; Cross, D.R.; Purvis, K.B.; Young, M.J. A study of the benefit of social and religious support on church members during times of crisis. Pastor. Psychol. 2003, 51, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A. The comparative endurance and efficiency of religion: A public choice perspective. Public Choice 2020, 189, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lino, C. The Psychology of Willpower: Training the Brain for Better Decisions. Positive Psychology. 2021. Last Modified on 21 June. Available online: https://positivepsychology.com/psychology-of-willpower/ (accessed on 30 July 2022).
- Wilcox, W.B. Soft Patriarchs, New Men: How Christianity Shapes Fathers and Husbands; University of Chicago: Chicago, IL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, G.E. Prayers: Overcoming fear and anxiety. In Developing Christian Servant Leadership; Palgrave MacMillian: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 211–213. [Google Scholar]
- Monchon, D.; Norton, M.I.; Ariely, D. Who benefits from religion? Soc. Indic. Res. 2011, 101, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.B.; Larson, D.B.; De Li, S.; Jang, S.J. Escaping from the crime of inner cities: Church attendance and religious salience among disadvantaged youth. Justice Q. 2006, 17, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattyn, N.; Buckle, S.; Bessone, L.; Shepanek, M. Human behavior and performance training: Lessons from analogue environments and space research. In Proceedings of the 19th IAA Humans in Space Symposium, Cologne, Germany, 7–12 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sandal, G.M.; Leon, G.R. From the past to the future. In Psychology of Space Exploration: Contemporary Research in Historical Perspective; Vakoch, D.A., Ed.; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Suedfeld, P.; Wilk, K.E.; Cassel, L. Flying with strangers: Postmission reflections of multinational space crews. In Psychology of Space Exploration: Contemporary Research in Historical Perspective; Vakoch, D.A., Ed.; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 143–175. [Google Scholar]
- Ives, C.D.; Kidwell, J. Religion and social values for sustainability. Sustain. Sci. 2018, 14, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelhamer, M. Enabling and enhancing human health and performance for Mars colonies: Smart spacecrafts and smart habitats. In Human Factor in a Mission to Mars: An Interdisciplinary Approach; Szocik, K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Hering, D.; Carvalho, L.; Argillier, C.; Beklioglu, M.; Borja, A.; Cardoso, A.C.; Duel, H.; Ferreira, T.; Globevnik, L.; Hanganu, J.; et al. Managing aquatic ecosystems and water resources under multiple stress—An introduction to the MARS project. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 503, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losch, A. Interplanetary sustainability: Mars as a means of a long-term sustainable development of humankind in the solar system? In Human Factor in a Mission to Mars: An Interdisciplinary Approach; Szocik, K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 157–167. [Google Scholar]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.W. Mars Space Exploration and Astronautical Religion in Human Research History: Psychological Countermeasures of Long-Term Astronauts. Aerospace 2022, 9, 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9120814
Kim DW. Mars Space Exploration and Astronautical Religion in Human Research History: Psychological Countermeasures of Long-Term Astronauts. Aerospace. 2022; 9(12):814. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9120814
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, David W. 2022. "Mars Space Exploration and Astronautical Religion in Human Research History: Psychological Countermeasures of Long-Term Astronauts" Aerospace 9, no. 12: 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9120814
APA StyleKim, D. W. (2022). Mars Space Exploration and Astronautical Religion in Human Research History: Psychological Countermeasures of Long-Term Astronauts. Aerospace, 9(12), 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9120814





