On the Handling Qualities of Two Flying Wing Aircraft Configurations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory of Longitudinal-Lateral Coupling
2.1. Basic Coupled and Decoupled Modes
2.2. Weak Coupling and Mode Properties
2.3. Calculation of Frequency and Amplification Changes
3. Natural Stability of Flying-Wing Aircraft
3.1. Relevance of Longitudinal-Lateral Coupling
3.2. Longitudinal and Lateral Handling Qualities
3.3. Manouever Points of Two Kinds
4. Assessment of BWB 1 and BWB 2 Designs
4.1. The Dutch Roll, Spiral and Roll Modes
4.2. The Phugoid and Short-Period Modes
4.3. Implications for Control System Design
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| coefficients of polynomials (28) | |
| coefficients of polynomials (29) | |
| slope of manouever point linear approximation (45c) | |
| x-component of angular velocity (4a) | |
| y-component of angular velocity (1) | |
| z-component of angular velocity (4a) | |
| x component of linear velocity (1) | |
| position of c.g. as percentage of m.a.c. (45a) | |
| critical c.g. position for manouever point (46a–c) | |
| y-component of linear velocity (4a) | |
| z-component of linear velocity (1) | |
| vertical acceleration (38) | |
| A | characteristic polynomial of longitudinal stability sub-matrix (3b) |
| B | characteristic polynomial of lateral stability sub-matrix (4b) |
| C | characteristic polynomial of complete stability matrix (6a,b) |
| characteristic polynomial of decoupled complete stability matrix (13b) | |
| modal factor (10) | |
| modal factor for decoupled stability matrix (13a) | |
| lift coefficient slope (39b) | |
| weak coupling coefficient (14c) | |
| T | time to double amplitude (21c,d) |
| X | aircraft state variables (1, 4a) |
| Xi | coupled flight variables (5) |
| decoupled flight variables (15) | |
| Zij | stability matrix (2b) |
| ε | small quantity (8) |
| θ | Euler angle of pitch (1) |
| δab | identity matrix (3a) |
| Euler angle of bank (4a) | |
| Euler angle of sideslip (Table 5) | |
| eigenvalues (3a) for modes (18a,b; 20a–c) | |
| damping ratio (3b) | |
| decoupled damping ratio (9b) | |
| natural exact coupled frequency (3b) | |
| natural decoupled frequency (9a) | |
| oscillation frequency (19d) | |
| time constant (21b) | |
| amplification ratio () | |
| difference between the exact coupled and decoupled complete characteristic polynomial (27) | |
| difference between the exact coupled and decoupled modal factor (14a–c) | |
| difference between the exact coupled and decoupled natural frequency (9a) | |
| difference between the exact coupled and decoupled damping ratio (9b) | |
| Subscripts | |
| p or 1 | phugoid mode |
| s or 2 | short period mode |
| d or 3 | dutch roll mode |
| h or 4 | helical mode |
| r or 4- | roll mode |
| l or 4+ | spiral mode |
| Superscripts | |
| decoupled value of | |
| Abbreviations | |
| c.g. | center of gravity |
| m.a.c. | mean aerodynamic chord |
| CAP | Control Anticipation Parameter (38) |
| BWB | Blended Wing Body |
| HQs | handling qualities |
| Symbols | |
| time derivative of | |
| variation of |
References
- Von Mises, R. Theory of Flight; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1945. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, C.D.; Hage, R.E. Airplane, Performance, Stability and Control; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- George, L.; Vernet, J.F. Mécanique du Vol: Performances des Avions et Engins; Librarie Polytechique Ch. Béranger: Sablons, France, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Rabister, W. Aircraft Dynamic Stability and Response; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Lecomte, P. Mécanique du Vol: Les Qualités de Vol des Avions et Engines; Dunod: Paris, France, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Miele, A. Flight Mechanics; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1962; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Etkin, B. Dynamics of Atmospheric Fight; Wiley: Boston, MA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- McRuer, D.; Ashkenas, I.; Graham, D. Aircraft Dynamics and Automatic Control; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Etkin, B. Dynamics of Flight Stability and Control; Wiley: Boston, MA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Etkin, B.; Reid, L.D. Dynamics of Flight Stability and Control; Wiley: Boston, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Lichota, P. Multi-Axis Inputs for Identification of a Reconfigurable Fixed-Wing UAV. Aerospace 2020, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, N.; Yue, T.; Liu, H.; Zhu, J.; Jia, X. Three-axis coupled flight control law design for flying wing aircraft using eigenstructure assignment method. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2020, 33, 2510–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaletka, J. BO-105 Identification Results, LS-178 on Rotorcraft System Identification; AGARD: Neuilly sur Seine, France, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, G.E.; Harper, R.P. The Use of Pilot Rating in the Evaluation of Aircraft Handling Qualities; NASA TN D-5153: Huntsville, AL, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Heffley, R.K.; Jewell, W.F. Aircraft Handling Qualities Data; National Aeronautics and Space Administrative CR-2144: Huntsville, AL, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, R.C. Flight Stability and Automatic Control, 2nd. ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, B.L.; Lewis, F.L. Aircraft Control and Simulation; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- McCormick, B.W. Aerodynamics, Aeronautics and Flight Mechanics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Catapang, D.R.; Tischler, M.B.; Biezad, D.J. Robust crossfeed design for hovering rotorcraft. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 1994, 4, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tischler, M.B. Advances in Flight Control; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, J.B. Performance and Stability of Aircraft, 1st ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Abzug, M.J.; Larrabee, E.E. Airplane Stability and Control: A History of the Technologies That Made Aviation Possible, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Vinh, N.X. Flight Mechanics of High-Performance Aircraft; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, M.V. Flight Dynamics Principles; Arnold: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore, R.; Wakayama, S.; Roman, D. Optimization of high-subsonic blended-wing-body configurations. In Proceedings of the 9th AIAA/ISSMO Symposium on Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization AIAA 2002-5666, Atlanta, GA, USA, 4–6 September 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Liebeck, R.H. Design of the blended wing body subsonic transport. J. Aircr. 2004, 41, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.J. Longitudinal Aerodynamic Characteristics and Wing Pressure Distributions of a Blended-Wing-Body Configuration at Low and High Reynolds Number; NASA/TM-2005-213754: Huntsville, AL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, J.R. Innovation in Flight: Research of the NASA Langley Research Center on Revolutionary Advanced Concepts for Aeronautics; NASA SP-2005-4539: Huntsville, AL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nickol, C.L.; McCullers, L.A. Hybrid wing body configuration system studies. In Proceedings of the 47th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including The New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition AIAA-2009-931, Orlando, FL, USA, 5–8 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, D.; Allen, J.B.; Liebeck, R.H. Aerodynamic design challenges of the blended-wing-body subsonic transport. In Proceedings of the 18th Applied Aerodynamics Conference AIAA-2000-4335, Denver, CO, USA, 14–17 August 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pambagjo, T.E.; Nakahashi, K.; Obayashi, S.; Matsushima, K. Aerodynamic design of a medium size blended wing body airplane. In Proceedings of the 39th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit AIAA-2001-0129, Reno, NV, USA, 8–11 January 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mialon, B.; Fol, T.; Bonnaud, C. Aerodynamic optimization of subsonic flying wing configurations. In In Proceedings of the 20th AIAA-2002-2931 applied aerodynamics conference, St. Louis, MO, USA, 24–26 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, D.; Gilmore, R.; Wakayama, S. Aerodynamics of high subsonic blended-wing-body configurations. In Proceedings of the 41st Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit AIAA-2003-554, Reno, NV, USA, 6–9 January 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mialon, B.; Hepperle, M. Flying Wing Aerodynamics Studied at ONERA and DLR. 2005. Available online: https://www.yumpu.com/en/document/view/11653618/flying-wing-aerodynamics-studies-at-onera-and-dlr (accessed on 16 March 2021).
- Peigin, S.; Epstein, B. Computational fluid dynamics driven optimization of blended wing body aircraft. AIAA J. 2006, 44, 2736–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.B.; Vicroy, D.D.; Patel, D. Blended-wing-body transonic aerodynamics: Summary of ground tests and sample results. In Proceedings of the 47th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including The New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition AIAA-2009-935, Orlando, FL, USA, 5–8 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chambon, E.; Burlion, L.; Apkarian, P. Time-response shaping using output to input saturation transformation. Int. J. Control 2017, 91, 534–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denieul, Y.; Bordeneuve, J.; Alazard, D.; Toussaint, C.; Taquin, G. Multicontrol Surface Optimization for Blended Wing–Body Under Handling Quality Constraints. J. Aircr. 2018, 55, 638–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Khalid, A. Blended Wing Body Propulsion System Design. Int. J. Aviat. Aeronaut. Aerosp. 2017, 4, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Ammar, S.; Legros, C.; Trépanier, J.-Y. Conceptual design, performance and stability analysis of a 200 passengers Blended Wing Body aircraft. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2017, 71, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotou, P.; Fotiadis-Karras, S.; Yakinthos, K. Conceptual design of a Blended Wing Body MALE UAV. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2018, 73, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakka, S.; Johnson, O. Aerodynamic Design and Exploration of a Blended Wing Body Aircraft at Subsonic Speed. Int. J. Aviat. Aeronaut. Aerosp. 2019, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Liou, M.-F. Flow simulation and drag decomposition study of N3-X hybrid wing-body configuration. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 85, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T. Design and CFD Analysis of a Blended Wing UAV (A Conceptual Design). J. Aerosp. Eng. Mech. 2019, 3, 156–160. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, M.; Tao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B. Research on analytical scaling method and scale effects for subscale flight test of blended wing body civil aircraft. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 106114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Footohi, P.; Bouskela, A.; Shkarayev, S. Aerodynamic Characteristics of the Blended-Wing-Body VTOL UAV. J. Aerosp. Eng. Mech. 2020, 4, 187–300. [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys-Jennings, C.; Lappas, I.; Sovar, D.M. Conceptual Design, Flying, and Handling Qualities Assessment of a Blended Wing Body (BWB) Aircraft by Using an Engineering Flight Simulator. Aerospace 2020, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemitola, P.; Okonkwo, P. Review of Structural Issues in the Design of a Box Wing Aircraft. J. Aerosp. Eng. Mech. 2019, 3, 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinowski, M. Aero-Structural Optimization of Joined-Wing Aircraft. Trans. Aerosp. Res. 2017, 4, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlichting, H.; Truckenbrodt, E. Aerodynamik des Flugzeuges: Erster Band; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Obert, E. Aerodynamic Design of Transport Aircraft; IOS Press: Delft, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Torenbeek, E. Advanced Aircraft Design—Conceptual Design, Analysis and Optimization of Subsonic Civil Airplanes; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Marques, J.M.G. On a Method of Lagrange Multipliers for Cruise Drag Minimization. J. Aerosp. Eng. Mech. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, L.R.; Gerhold, C.H. Inlet noise reduction by shielding for the blended-wing-body airplane. In Proceedings of the 5th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference and Exhibit AIAA-1999-1937, Bellevue, WA, USA, 10–12 May 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Diedrich, A.; Hileman, J.; Tan, D.; Willcox, K.; Spakovszky, Z. Multidisciplinary design and optimization of the silent aircraft. In Proceedings of the 44th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit AIAA-2006-1323, Reno, NV, USA, 9–12 January 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hileman, J.I.; Spakovszky, Z.S.; Drela, M.; Sargeant, M. Airframe design for “silent” aircraft. In Proceedings of the 45th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit AIAA-2007-453, Reno, NV, USA, 8–11 January 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hileman, J.I.; Spakovszky, Z.S.; Drela, M.; Sargeant, M. Aerodynamic and aeroacoustic three-dimensional design for a “silent” aircraft. In Proceedings of the 44th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit AIAA-2006-241, Reno, NV, USA, 9–12 January 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hileman, J.I.; Spakovszky, Z.S.; Drela, M.; Sargeant, M.A.; Jones, A. Airframe design for silent fuel-efficient aircraft. J. Aircr. 2010, 47, 956–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On physical aeroacoustics with some implications for low-noise aircraft design and airport operations. Aerospace 2015, 2, 17–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolsunovsky, A.L.; Buzoverya, N.P.; Gurevich, B.I.; Denisov, V.E.; Dunaevsky, A.I.; Shkadov, L.M.; Sonin, O.V.; Udzhuhu, A.J.; Zhurihin, J.P. Flying wing-problems and decisions. Aircr. Des. 2001, 4, 193–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Vavalle, A.; Le Moigne, A.; Laban, M.; Hackett, K.; Weinerfelt, P. Aerodynamic considerations of blended wing body aircraft. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2004, 40, 321–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, C.; Lin, Y. Aerodynamic design methodology for a blended wing body transport. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2012, 25, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Okonkwo, P.; Smith, H. Review of evolving trends in blended wing body aircraft design. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2016, 82, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. Linear Differential Equations and Oscillators; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bihrle, W. A Handling Qualities Theory for Precise Flight Path Control; Technical Report, AFFDL-TR-65-198; Air Force Flight Dynamics Laboratory, WPAFB: Montgomery, OH, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Sturmer, S.R. Pitch rate sensitivity criterion for category C flight phases—Class IV aircraft. In AIAA Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference; AIAA 86-2201: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hoh, R.H. Advances in Flying Qualities: Concepts and Criteria for a Mission Oriented Flying Qualities Specification; Technical Report, AGARD LS 157; AGARD: Washington, DC, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Neal, T.P.; Smith, R.E. An In-Flight Investigation to Develop Control System Design Criteria for Fighter Airplanes; Technical Report, AFFDL-TR-70-74; Wright Patterson AFB, Flight Dynamics Laboratory: Montgomery, OH, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, J.C. Piloted Handling Qualities Design Criteria for High Order Flight Control Systems; Technical Report, AGARD CP 333; AGARD: Washington, DC, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, J.C. The Definition, Design and Understanding of Aircraft Handling Qualities; Technical Report, Report LR-756; Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, J.C. Handling qualities for unstable combat aircraft. In Proceedings of the 15th Congress of the International Council of the Aeronautical Sciences, London, UK, 7–12 September 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Military Standard—Flying Qualities of Piloted Aircraft; Technical Report, MIL-STD-1797A; Department of Defense of U.S.A.: Washington, DC, USA, 1990.
- Anonymous. Defence Standard 00-970. Design and Airworthiness Requirements for Service Aircraft; Technical Report; UK Ministry of Defense: London, UK, 1983; Volume 1.
- Gautrey, J.E. Flying Qualities and Flight Control System Design for a Fly-by-Wire Transport Aircraft. Ph.D. Thesis, Cranfield University, Bedford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Milne-Thomson, L.M. Theoretical Hydrodynamics; Dover: Mineola, NY, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. Complex Analysis with Applications to Flows and Fields; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gautrey, J.E.; Cook, M.V. A generic control anticipation parameter for aircraft handling qualities evaluation. Aeronaut. J. 1998, 102, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Hariyoshi, E.; Ranade, G.; Sahai, A. Control with actuation anticipation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 55th Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 12–14 December 2016; pp. 5617–5622. [Google Scholar]
- Saussié, D.; Saydy, L.; Akhrif, O. Longitudinal flight control design with handling quality requirements. Aeronaut. J. 2006, 110, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, Z.; Lixin, W.; Xiangsheng, T. Flying qualities reduction of fly-by-wire commercial aircraft with reconfiguration flight control laws. Procedia Eng. 2011, 17, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bischoff, D. The definition of short-period flying qualities characteristics via equivalent systems. J. Aircr. 1983, 20, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Min-Jea, T. Optimization for Flight Control System with Constraints supplemented Handling Qualities. In Proceedings of the 26th Congress of the International Council of the Aeronautical Sciences, London, UK, 14–19 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Weiser, C.; Ossmann, D.; Looye, G. Design and flight test of a linear parameter varying flight controller. CEAS Aeronaut. J. 2020, 11, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elarbia, E.; Ghmmam, A.; Issa, S. On Flying-Handling Qualities of B747-100 Longitudinal Flight based on Gain Scheduling Control. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Technology, Engineering and Science (IConTES), Antalya, Turkey, 29 October–1 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Marques, J.M.G. On the comparison of ten pitch trim strategies for cruise drag minimization. J. Aerosp. Eng. Mech. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]

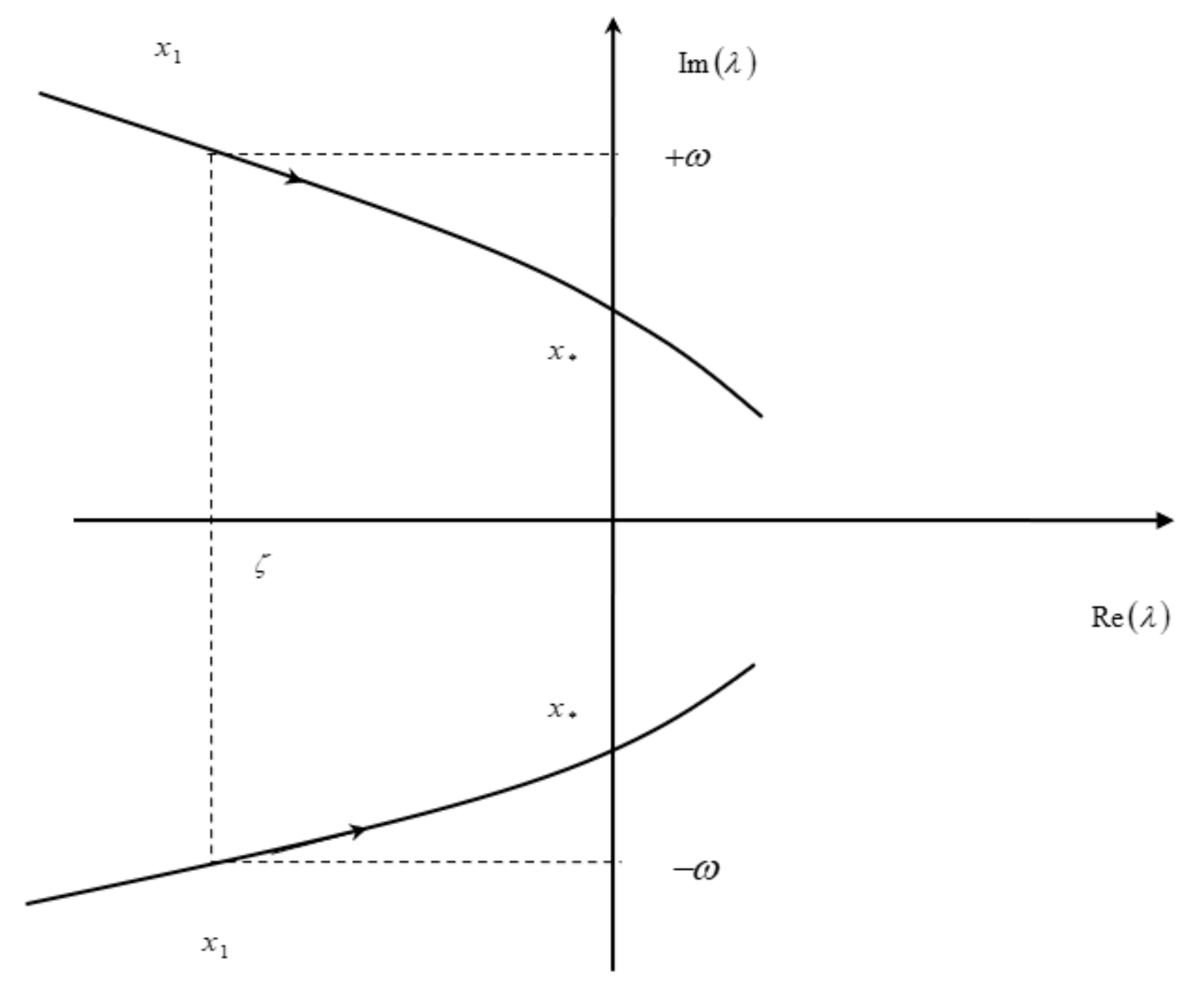
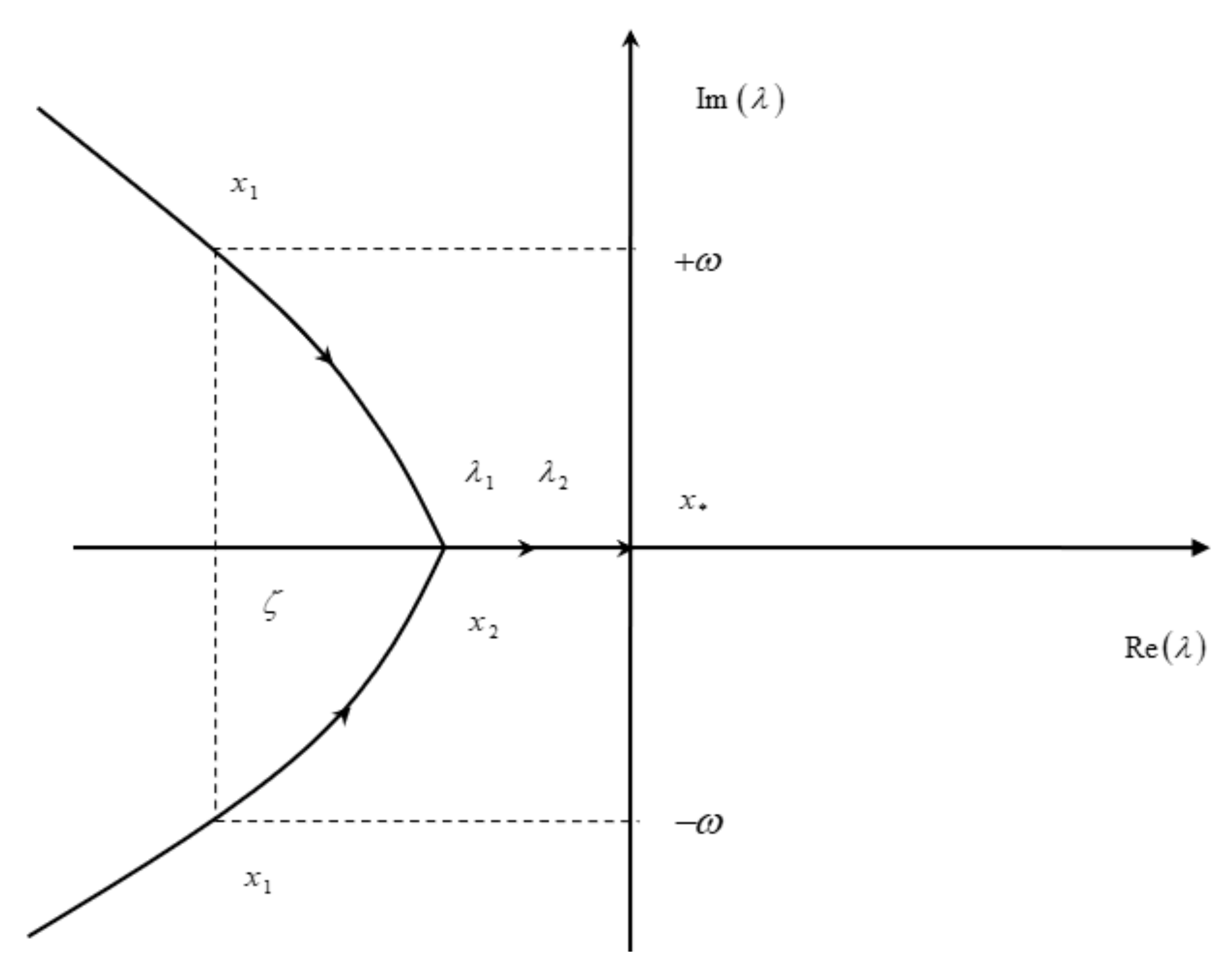
| Type | Mode | Frequency | Damping |
|---|---|---|---|
| Longitudinal | Phugoid | ||
| Short period | |||
| Lateral | Dutch roll | ||
| Helical |
| Mode | Natural Frequency | Damping Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Decoupled | ||
| Weakly coupled | ||
| Condition | ||
| Strongly coupled | ||
| Condition |
| Design | Flight Condition | Mass | Speed | Altitude | Flaps | c.g. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BWB | Case | ×103 kg | kts | ×103 ft | degrees | % mac |
| 1 | 1a | 550 | 176 | 0 | 15/25 | 25 |
| 1b | 550 | 176 | 0 | 15/25 | 35 | |
| 1c | 550 | 200 | 0 | 15/25 | 25 | |
| 1d | 550 | 200 | 0 | 15/25 | 35 | |
| 1e | 670 | M = 0.85 | 39 | clean | 35 | |
| 1f | 670 | M = 0.85 | 39 | clean | 39 | |
| 1g | 760 | M = 0.85 | 35 | clean | 35 | |
| 1h | 760 | M = 0.85 | 35 | clean | 39 | |
| 1i | 700 | 300 | 0 | clean | 35 | |
| 1j | 700 | M = 0.70 | 30 | clean | 39 | |
| 2 | 2a | 550 | 176 | 0 | clean | 35 |
| 2b | 550 | 176 | 0 | clean | 39 | |
| 2c | 550 | 200 | 0 | clean | 35 | |
| 2d | 550 | 200 | 0 | clean | 39 | |
| 2e | 670 | M = 0.85 | 39 | clean | 35 | |
| 2f | 670 | M = 0.85 | 39 | clean | 39 | |
| 2g | 760 | M = 0.85 | 35 | clean | 35 | |
| 2h | 760 | M = 0.85 | 35 | clean | 39 |
| [m/s] | [m/s] | [rad/s] | [rad] | [m/s] | [rad/s] | [rad/s] | [rad] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [m/s2] | −2.10 × 10−4 | 1.51 × 10−1 | −8.91 | −9.94 × 10−1 | 1.13 × 10−7 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| [m/s2] | −1.54 × 10−1 | −6.55 × 10−1 | 8.05 × 101 | 1.10 × 10−1 | −1.24 × 10−6 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| [rad/s2] | 5.98 × 10−4 | −7.16 × 10−3 | −6.13 × 10−1 | 0 | −1.07 × 10−9 | −4.93 × 10−5 | 4.93 × 10−5 | 0 |
| [rad/s] | 0 | 0 | 1.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| [m/s2] | 4.66 × 10−17 | 4.66 × 10−17 | 0 | 0 | −5.27 × 10−2 | 1.11 × 101 | −8.81 × 101 | 9.94 × 10−1 |
| [rad/s2] | −1.34 × 10−16 | −1.19 × 10−17 | 0 | 0 | −6.68 × 10−3 | −9.07 × 10−1 | 2.30 × 10−1 | 0 |
| [rad/s2] | −5.06 × 10−15 | −2.03 × 10−19 | 0 | 0 | 2.68 × 10−3 | −1.85 × 10−1 | −1.12 × 10−1 | 0 |
| [rad/s] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.00 | 1.11 × 10−1 | 0 |
| Type | Mode | Frequency Damping | De-Coupled | Weakly Coupled Approximation | Fully Coupled |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Longitudinal | Phugoid | 0.201769 0.114 | 0.202 0.114 | 0.201968 0.113596 | |
| Short period | /0.124521 /1.7013 | /0.124 /−1.700 | /0.124266 /−1.70135 | ||
| Lateral | Dutch roll | 0.845291 0.0595375 | 0.845291 0.0595 | 0.845291 0.0595375 | |
| Helical | /−4.28162 × 10−6 /−1.13662 | /−4.28 × 10−6 /−1.137 | /−4.28162 × 10−6 /−1.13662 |
| [m/s] | [m/s] | [m/s] | [rad/s] | [rad/s] | [rad/s] | [rad] | [rad] | [rad] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [m/s2] | −2.10 × 10−4 | 1.13 × 10−7 | 1.51 × 10−1 | 0 | −8.91 | 0 | 0 | −9.94 × 10−1 | 0 |
| [m/s2] | 4.66 × 10−17 | −5.27 × 10−2 | 4.66 × 10−17 | 1.11 × 101 | 0 | −8.81 × 101 | 9.94 × 10−1 | 0 | 0 |
| [m/s2] | −1.54 × 10−1 | −1.24 × 10−6 | −6.55 × 10−1 | 0 | 8.05 × 101 | 0 | 0 | 1.10 × 10−1 | 0 |
| [rad/s2] | −1.34 × 10−16 | −6.68 × 10−3 | −1.19 × 10−17 | −9.07 × 10−1 | 0 | 2.30 × 10−1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| [rad/s2] | 5.98 × 10−4 | −1.07 × 10−9 | −7.16 × 10−3 | −4.93 × 10−5 | −6.13 × 10−1 | 4.93 × 10−5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| [rad/s2] | −5.06 × 10−15 | 2.68 × 10−3 | −2.03 × 10−19 | −1.85 × 10−1 | 0 | −1.12 × 10−1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| [rad/s] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.00 | 0 | 1.11 × 10−1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| [rad/s] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| [rad/s] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Stability Mode | Longitudinal | Lateral | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phugoid | Short-Period | Dutch Roll | Roll | Spiral | |
| or | or | or | |||
| 1a | −0.102 ± i0.0374 | −0.624 ± i0.768 | −0.0759 ± i0.602 | −0.920 | −0.000397 |
| 1b | −0.000684 ± i0.0719 | −1.031 / 0.268 | −0.0605 ± i0.522 | −0.853 | −0.000382 |
| 1c | −0.00816 ± i0.0332 | −0.720 ± i0.877 | −0.0916 ± i0.657 | −1.065 | −0.000205 |
| 1d | −0.000146 ± i0.0641 | −1.495 / 0.308 | −0.0738 ± i0.576 | −0.985 | −0.000112 |
| 1e | −0.0727 ± i0.186 | −1.503 / 0.138 | −0.0458 ± i0.774 | −0.958 | −0.0000104 |
| 1f | −0.00150 ± i0.0695 | −2.172 / 0.804 | −0.0426 ± i0.748 | −0.956 | −0.0000110 |
| 1g | −0.114 ± i0.202 | −1.701 / 0.124 | −0.0595 ± i0.845 | −1.136 | −0.00000428 |
| 1h | 0.00227 ± i0.0771 | −2.429 / 0.798 | −0.0545 ± i0.819 | −1.136 | −0.0000258 |
| 1i | −0.00479 ± i0.0332 | −1.031 ± i1.346 | −0.141 ± i1.000 | −1.743 | −0.000181 |
| 1j | −0.0037 ± i0.0208 | −0.576 ± i1.181 | −0.0587 ± i0.848 | −1.087 | −0.000296 |
| 2a | −0.0130 ± i0.0386 | −0.652 ± i0.995 | −0.0305 ± i0.636 | −0.873 | −0.00226 |
| 2b | −0.0286 /−0.00306 | −0.555 ± i0.281 | −0.0267 ± i0.511 | −0.874 | 0.00160 |
| 2c | −0.00982 ± i0.0352 | −0.751 ± i1.131 | −0.0359 ± i0.632 | −1.010 | −0.00160 |
| 2d | −0.0241 /0.000679 | −0.642 ± i0.299 | −0.0325 ± i0.519 | −1.009 | 0.00112 |
| 2e | −0.00344 ± i0.00246 | −0.567 ± i1.051 | −0.00800 ± i0.644 | −1.193 | 0.000336 |
| 2f | −0.00419 ± i0.0155 | −0.706 ± i1.867 | −0.00271 ± i0.746 | −1.211 | 0.000471 |
| 2g | −0.00566 ± i0.00194 | −0.677 ± i1.142 | −0.0173 ± i0.700 | −1.407 | 0.000316 |
| 2h | −0.00194 /0.00459 | −0.841 ± i2.028 | −0.0144 ± i0.808 | −1.421 | 0.000442 |
| Eigenvalue | Quantity | Symbol = Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complex | Oscillation frequency | ||
| Real part | Positive | Damping ratio | |
| Negative | Time constant | ||
| Time to double amplitude | |||
| Stability | Longitudinal | Lateral | CAP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | Phugoid | Short-Period | Dutch Roll | Roll | Spiral | ||||
| Parameter | |||||||||
| Units | s−1 | −/s−1 | s−1 | −/s−1 | s−1 | -/s−1 | s−1 | s−1 | s−2 |
| 1a | 0.109 | 0.936 | 0.990 | 0.630 | 0.607 | 0.125 | 0.920 | 0.000397 | 0.0939 |
| 1b | 0.0719 | 0.00651 | /1.301 | /0.208 | 0.525 | 0.115 | 0.853 | 0.000382 | 0.0114 |
| 1c | 0.0342 | 0.239 | 1.135 | 0.647 | 0.663 | 0.138 | 1.065 | 0.000205 | 0.122 |
| 1d | 0.0641 | 0.00228 | /1.495 | /0.308 | 0.581 | 0.127 | 0.985 | 0.000112 | 0.0151 |
| 1e | 0.200 | 0.363 | /1.503 | /0.138 | 0.775 | 0.0591 | 0.958 | −0.0000104 | 0.00303 |
| 1f | 0.0695 | 0.0216 | /2.172 | /0.804 | 0.749 | 0.0569 | 0.956 | 0.0000110 | 0.103 |
| 1g | 0.240 | 0.475 | /1.701 | /0.124 | 0.847 | 0.0702 | 1.136 | 0.00000428 | 0.00245 |
| 1h | 0.0771 | −0.0295 | /2.429 | /0.798 | 0.820 | 0.0605 | 1.136 | 0.0000258 | 0.101 |
| 1i | 0.0335 | 0.143 | 1.695 | 0.608 | 1.010 | 0.140 | 1.743 | 0.000181 | 0.288 |
| 1j | 0.0211 | 0.175 | 1.314 | 0.438 | 0.850 | 0.0691 | 1.087 | 0.000296 | 0.222 |
| 2a | 0.411 | 0.0316 | 1.189 | 0.548 | 0.637 | 0.0479 | 0.873 | 0.000226 | 0.158 |
| 2b | /0.0286 | /0.00300 | 0.622 | 0.892 | 0.512 | 0.0521 | 0.874 | −0.00160 | 0.0126 |
| 2c | 0.0364 | 0.270 | 1.356 | 0.554 | 0.633 | 0.0567 | 1.01 | 0.00160 | 0.204 |
| 2d | /0.024 | /−0.000679 | 0.708 | 0.907 | 0.520 | 0.0625 | 1.009 | −0.00112 | 0.0142 |
| 2e | 0.0161 | 0.214 | 1.194 | 0.475 | 0.746 | 0.0125 | 1.211 | −0.000471 | 0.176 |
| 2f | 0.00422 | 0.993 | 1.996 | 0.354 | 0.644 | 0.00363 | 1.193 | −0.000336 | 0.555 |
| 2g | 0.0169 | 0.335 | 1.328 | 0.510 | 0.700 | 0.0247 | 1.421 | −0.000442 | 0.208 |
| 2h | /0.0194 | /0.00459 | 2.195 | 0.383 | 0.808 | 0.0178 | 1.407 | −0.000316 | 0.655 |
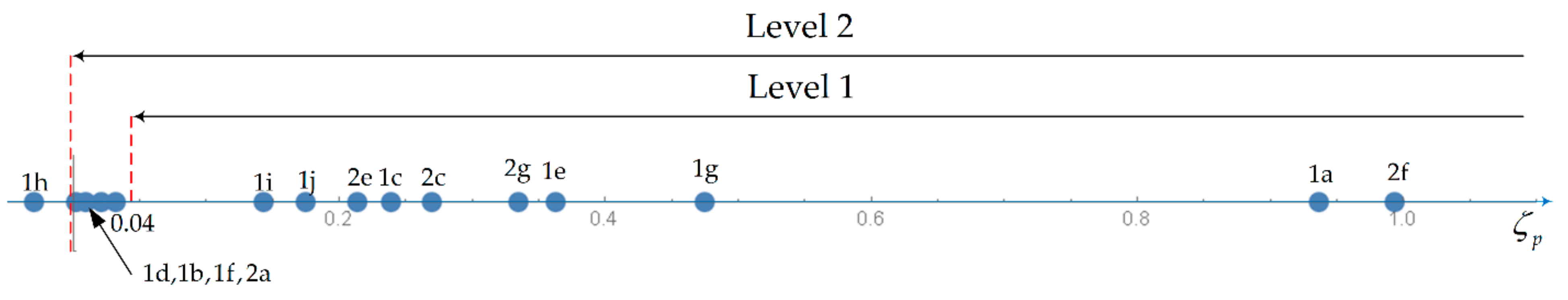
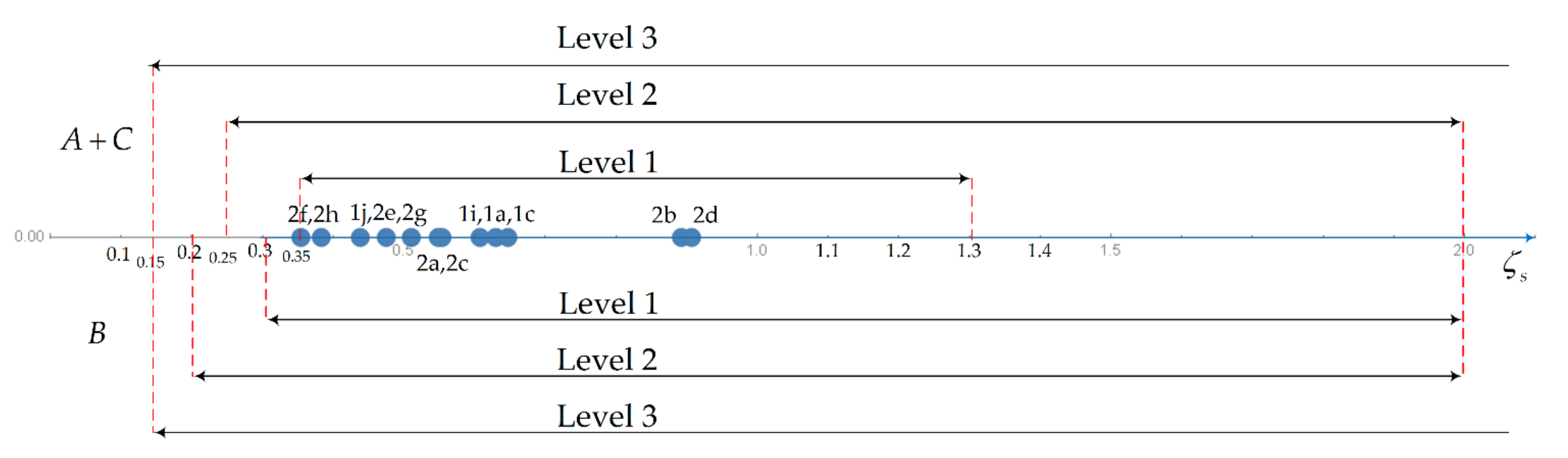
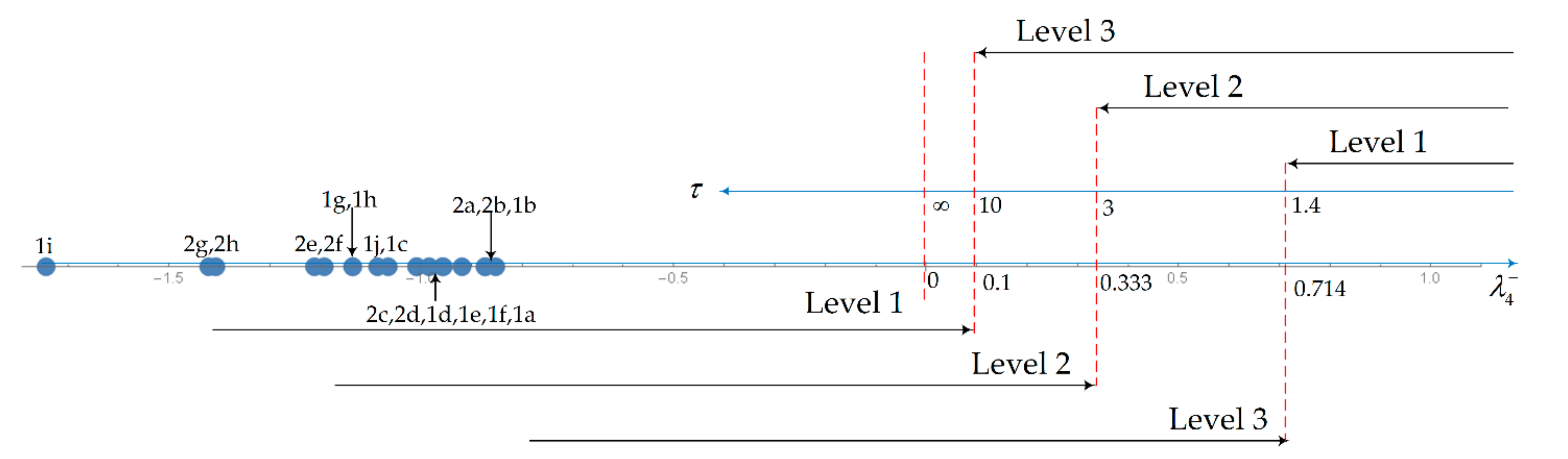
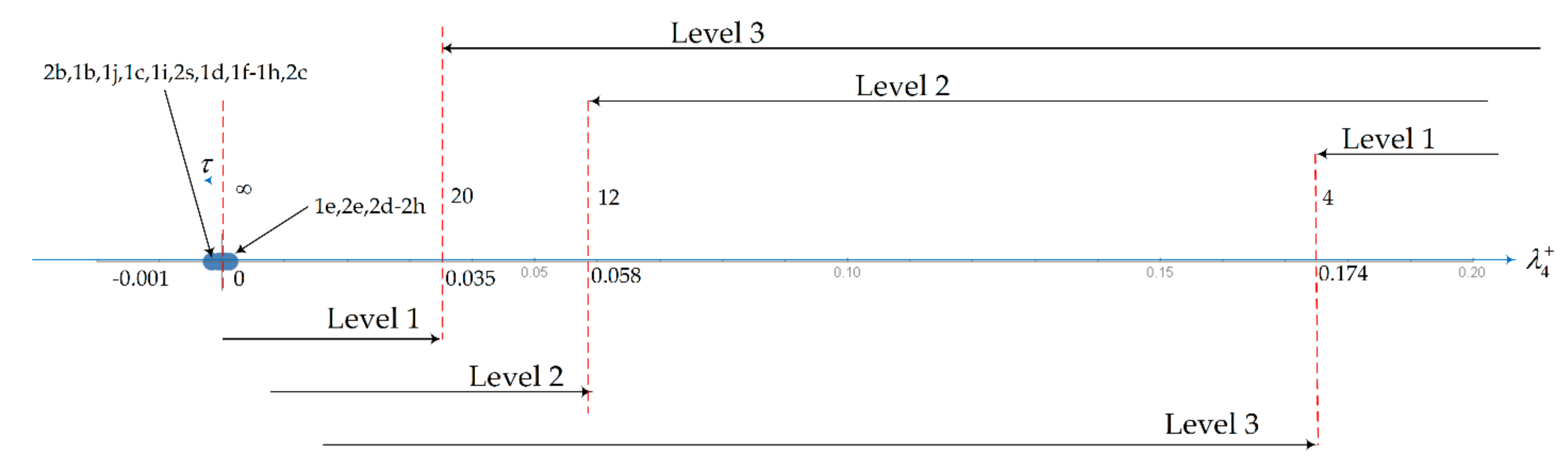
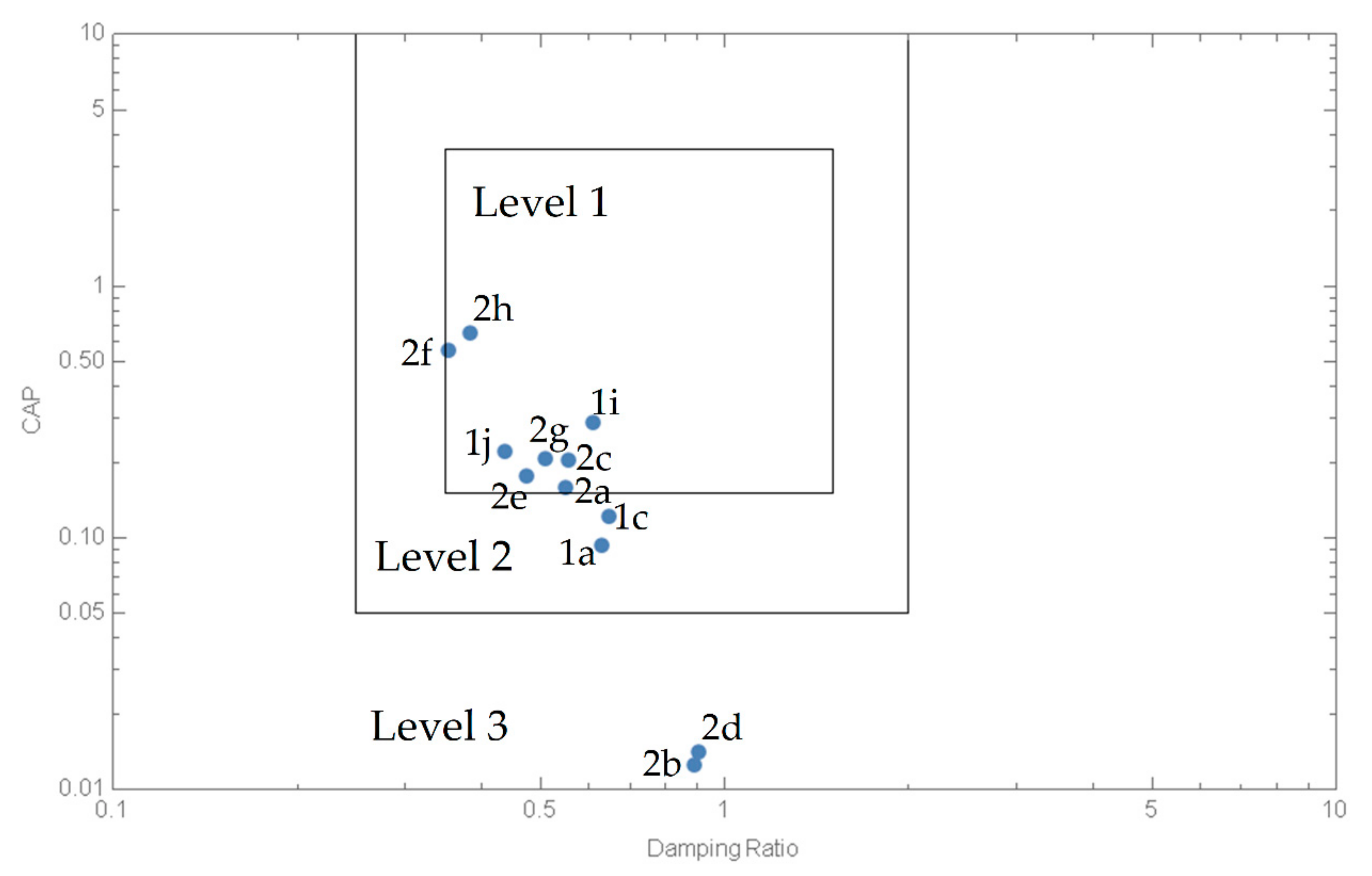
| Mode | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phugoid | ζp > 0.04 | ζp > 0 | Tp > 55 s | |
| Short period | A + C | 0.35 < ζs < 1.30 | 0.25 < ζs < 2.30 | ζs > 0.15 |
| B | 0.30 < ζs < 2.00 | 0.20 < ζs < 2.00 | ζs > 0.15 | |
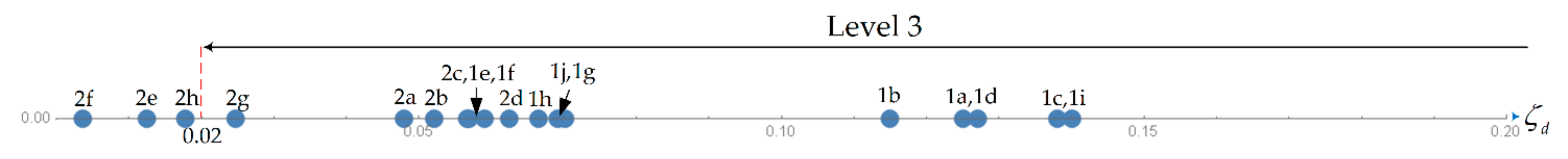
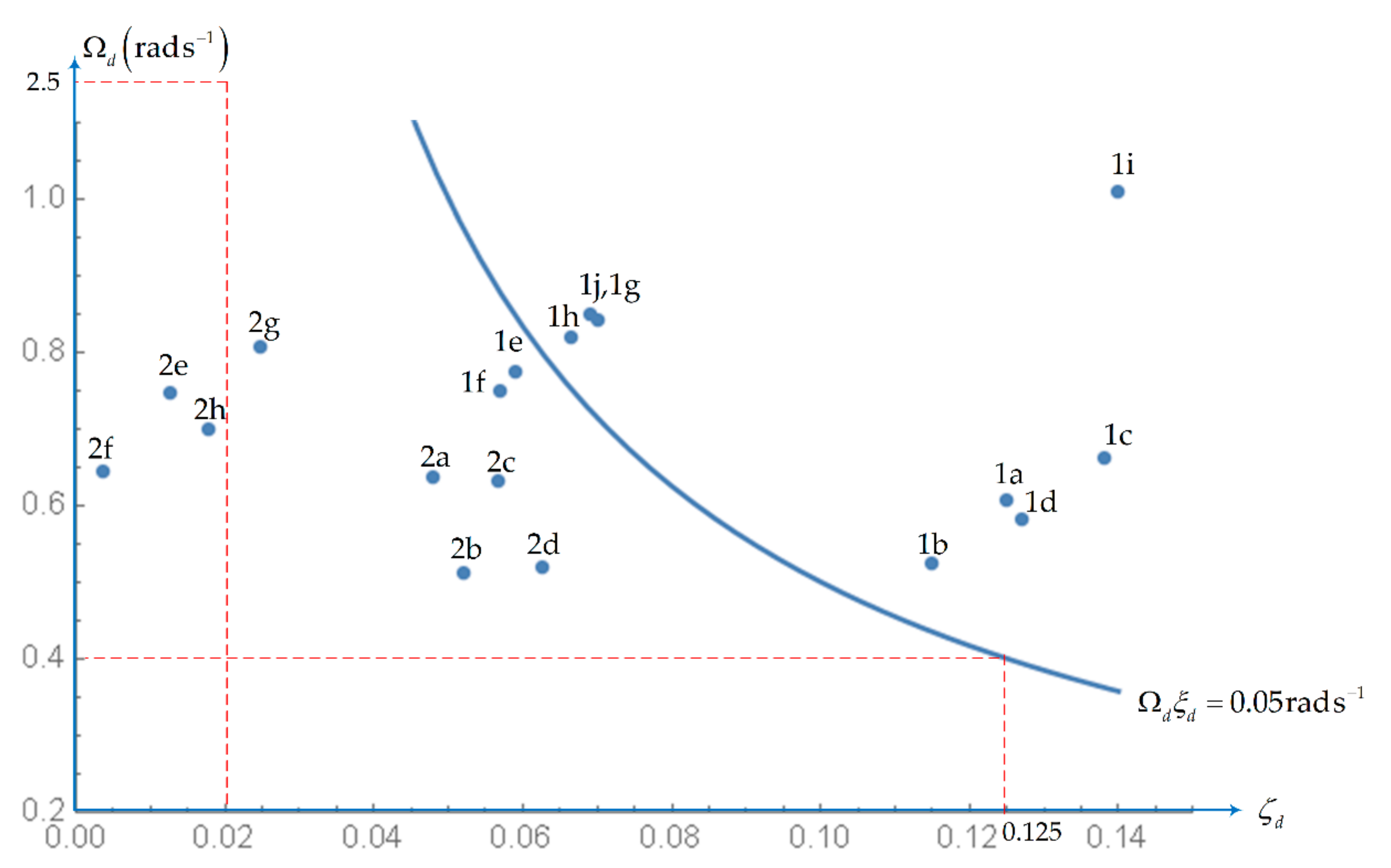
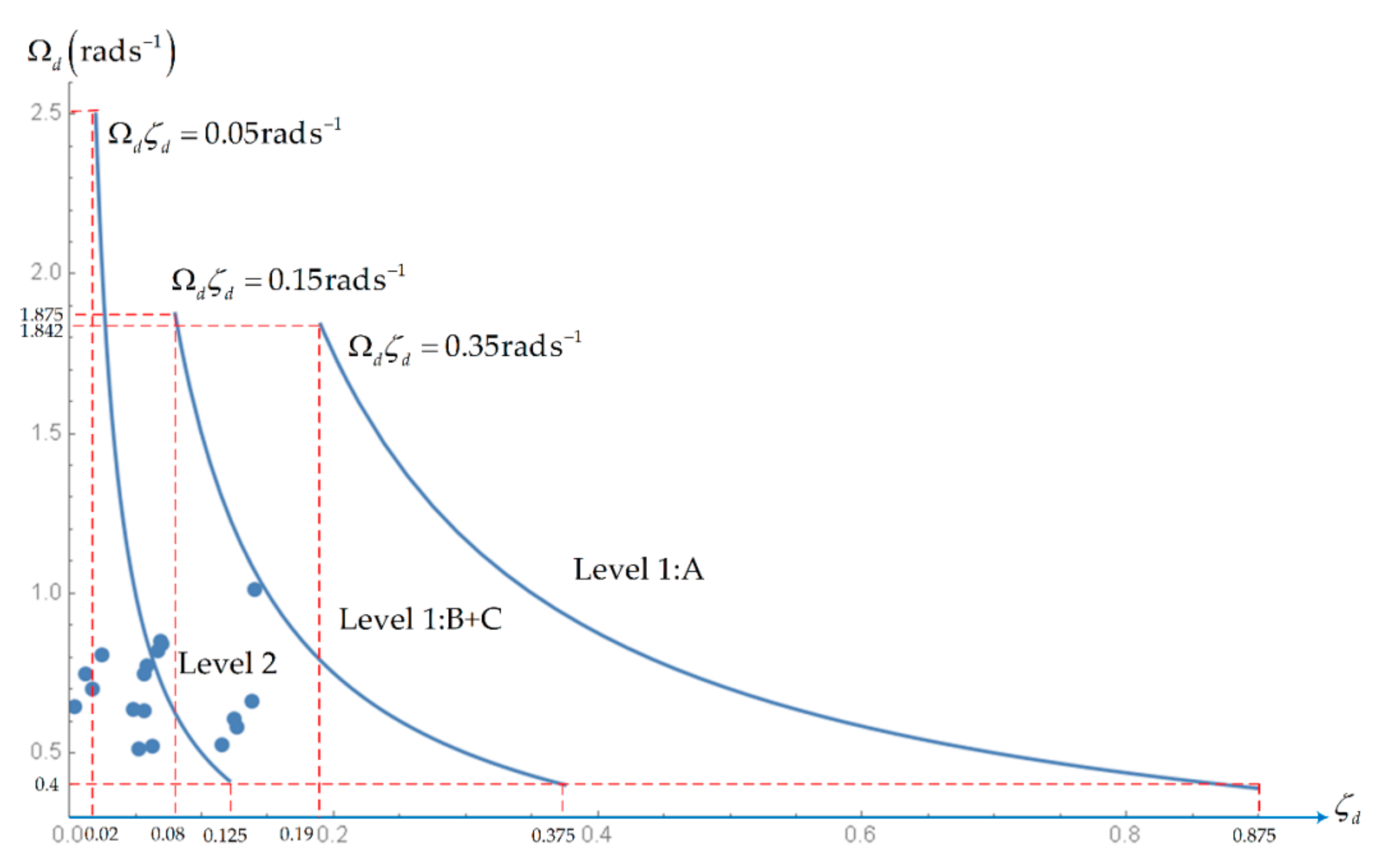
| Dutch Roll | A: ζd > 0.19 B+C: ζd > 0.08 | ζd > 0.02 | ζs > 0.02 | |
| A: Ωdζd > 0.35 rad/s B+C: Ωdζd > 0.15 rad/s | Ωdζd > 0.05 rad/s | - | ||
| Ωd > 0.40 rad/s | Ωd > 0.40 rad/s | Ωd > 0.40 rad/s | ||
| Spiral Mode | Ts > 20 s | Ts > 12 s | Ts > 4 s | |
| Roll Mode | τr < 1.4 s | τr < 3.0 s | τr < 10 s | |
| Mode | Phugoid | Short-Period | Dutch Roll | Roll | Spiral | CAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 1b | 2 | − | 2 | 1 | 1 | - |
| 1c | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 1d | 2 | − | 2 | 1 | 1 | - |
| 1e | 1 | − | 3 | 1 | 1 | - |
| 1f | 2 | − | 3 | 1 | 1 | - |
| 1g | 1 | − | 2 | 1 | 1 | - |
| 1h | 3 | − | 2 | 1 | 1 | - |
| 1i | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1j | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2a | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2b | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 2c | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2d | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 2e | 1 | 1 | − | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2f | 1 | 1 | − | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2g | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2h | 3 | 1 | − | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Design | Case | Flight Condition | Manouver Point | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speed/ Mach | Altitude | Weight | Longitudinal | Lateral | |||||
| kt | ×103 ft | ×103 kg | Range of Values | Estimated Value | Range of Values | Estimated Value | |||
| BWB 1 | 1a/b | Minimum speed | 176 | 0 | 550 | 0.25 < xs < 0.35 | xs = 0.320 | xr > 0.35 | xr = 0.743 |
| 1c/d | approach | 200 | 0 | 550 | 0.25 < xs < 0.35 | xs = 0.320 | xr > 0.35 | xr = 0.779 | |
| 1e/f | Initial cruise | M = 0.85 | 39 | 670 | xs < 0.35 | xs = 0.345 | xr > 0.39 | xr = 0.992 | |
| 1g/h | Final cruise | M = 0.85 | 35 | 760 | xs < 0.35 | xs = 0.342 | xr > 0.39 | xr = 0.826 | |
| BWB 2 | 2a/b | Minimum speed | 176 | 0 | 550 | xs > 0.39 | xs = 0.402 | xr > 0.39 | xr = 0.671 |
| 2c/d | approach | 200 | 0 | 550 | 0.35 < xs < 0.39 | xs = 0.390 | xr > 0.39 | xr = 0.772 | |
| 2e/f | Initial cruise | M = 0.85 | 39 | 670 | xs > 0.39 | xs = 0.553 | xr < 0.35 | xr = 0.330 | |
| 2g/h | Final cruise | M = 0.85 | 35 | 760 | xs > 0.39 | xs = 0.419 | xr < 0.35 | xr = 0.151 | |
| Manoeuver point | First kind | Second kind |
|---|---|---|
| Illustration | Figure 10 | Figure 11 |
| Eigenvalue | ||
| At manouever point | ||
| Condition | ||
| Mode | oscillatory | non-oscillatory |
| Example | BWB 1 | BWB 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fuselage | Length Width | Long Narrow | Short Wide |
| Equal Fineless | Thickness Volume | Thick High | Thin Low |
| Tail | Moment arm Elevator area | Long Small | Short Large |
| Passenger motion | Pitch Roll | Large Small | Small Large |
| Evacuation | Easy | Difficult | |
| Conclusion | Conservative | Radical | |
| Risk | Lower | Higher | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campos, L.M.B.C.; Marques, J.M.G. On the Handling Qualities of Two Flying Wing Aircraft Configurations. Aerospace 2021, 8, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace8030077
Campos LMBC, Marques JMG. On the Handling Qualities of Two Flying Wing Aircraft Configurations. Aerospace. 2021; 8(3):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace8030077
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampos, Luís M. B. C., and Joaquim M. G. Marques. 2021. "On the Handling Qualities of Two Flying Wing Aircraft Configurations" Aerospace 8, no. 3: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace8030077
APA StyleCampos, L. M. B. C., & Marques, J. M. G. (2021). On the Handling Qualities of Two Flying Wing Aircraft Configurations. Aerospace, 8(3), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace8030077







