Abstract
The coupling of the longitudinal and lateral stability modes of an aeroplane is considered in two cases: (i) weak coupling, when the changes in the frequency and damping of the phugoid, short period, dutch roll, and helical modes are small, i.e., the square of the deviation is negligible compared to the square of the uncoupled value; (ii) strong coupling, when the coupled values may differ significantly from the uncoupled values. This allows a comparison of three values for the frequency and damping of each mode: (i) exact, i.e., fully coupled; (ii) with the approximation of weak coupling; (iii) with the assumption of decoupling. The comparison of these three values allows an assessment of the importance of coupling effects. The method is applied to two flying wing designs, concerning all modes in a total of eighteen flight conditions. It turns out that lateral-longitudinal coupling is small in all cases, and thus classical handling qualities criteria can be applied. The handling qualities are considered for all modes, namely the phugoid, short period, dutch roll, spiral, and roll modes. Additional focus is given to the pitch axis, considering the control anticipation parameter (CAP). The latter relates to the two kinds of manouever points, where damping vanishes, that are calculated for minimum speed, take-off, and initial and final cruise conditions. The conclusion compares two flying wings designs (the “long narrow” and “short wide” fuselage concepts) not only from the point of view of flight stability, but also from other viewpoints.
1. Introduction
The longitudinal stability of an aeroplane is specified by a 4 × 4 matrix, which determines the phugoid and short-period modes [1,2,3,4,5]. Likewise, the lateral stability is specified by a 4 × 4 matrix, which specifies the dutch roll and helical modes [6,7,8,9,10]. In the present account, the possibility of lateral-longitudinal coupling (Section 2.1) is considered leading to an 8 × 8 matrix, which includes [11,12], besides the longitudinal and lateral stability matrices, two 4 × 4 coupling matrices (Section 2.2). Relative to the case of negligible coupling, there may be weak coupling (Section 2.3) which is a small perturbation, or strong coupling (Section 2) for which significant differences occur. In the case of helicopters [13], larger stability matrices may be needed due to rotor-body coupling. The theory developed applies both to strong and weak coupling, and in the latter case specifies the error in neglecting coupling effects. The application is made to two flying wings designs (Section 3), and it is found that in all flight configurations considered the terms in the coupling matrices are quite small compared with those in the longitudinal and lateral matrices. The general theory in the weak coupling casa confirms that the small coupling terms have a negligible effect on the airplane modes (Section 3.1). This implies that it is possible to apply (Section 3.2) classical handling qualities (HQs) criteria [14,15,16,17,18] to the phugoid, short-period, dutch roll and helical modes. Focusing on pitch response the CAP (Control Anticipation Parameter) criterion is also considered. It relates to the manouever points that correspond to center of gravity positions for which mode damping vanishes and are also calculated (Section 3.3).
The stability assessment concerns two flying wing designs, a “long-narrow” and a “short-wide” fuselage concept (Section 4). The helical mode always splits into roll and spiral modes (Section 4.1), but the dutch roll mode never splits into two non-oscillatory modes. The phugoid and short-period modes do, in some flight conditions, split into two non-oscillatory modes (Section 4.2). It is found that the HQs are level 2 and level 3 for the slow modes (phugoid and dutch roll) which are easily mastered [19,20,21,22] by a fly-by-wire control system, whereas the fast (short-period, spiral and roll) modes tend to have level 1 HQs (Section 3.3). The manouever points may limit the c.g. travel, but maybe there is no need for fuel trim tanks (Section 5), as the stability matrices provide indicated generally acceptable flight characteristics [23,24]. The analysis in this paper shows that long-and-narrow BWB1 and short-and-wide BWB2 configurations can have similar stability characteristics for some modes and dissimilar for others. Each configuration difference between BWB1 and BWB2 can affect several stability derivatives. Conversely, each stability derivative can be affected by several configuration differences between BWB1 and BWB2. A detailed relation among configuration differences and changes of stability derivatives is a complex process beyond the scope of the present paper. The scope for the paper, for which the necessary and sufficient data is provided, is to consider the HQs flight modes, the CAP criterion and the manouever points comparing two BWB configurations in several low and high-speed flight conditions, including cruise, take-off, and initial and final climb.
There is considerable interest in the flying wing [25,26,27,28,29] as it is favourable from an aerodynamic [30,31,32,33,34,35,36] point-of-view of the lift-to-drag ratio, promising less drag for a given weight, and hence needing less power and implying lower fuel consumption and emissions for the same flight distance. Two alternatives of efficient aircraft configurations are the flying wing [37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47] and box wing [48,49]. A high-aspect ratio flying wing with wide-short centerbody or “fuselage” (BWB 2) would appear to be aerodynamically preferable to a low-aspect ratio flying wing with long-narrow centerbody (BWB 1) closer to a conventional tube-and-wing Cayley-type aircraft configuration [50,51,52]. However, there are counterarguments favouring BWB1 such as control [53]. The short-wide BWB2 has a smaller moment arm for pitch control and for rotation at take-off. If the flying wing has overwing engines for noise shielding, there is a strong pitch-down moment to be compensated more easily with a long moment arm by smaller deflection of pitch control surfaces with less area. The overwing engine location, while ideal for noise shielding [54,55,56,57,58,59], places the engine nacelles in an accelerated flow leading to significant wave drag at lower cruising speeds. The short-and-wide BWB2 would subject outboard passengers to larger roll motions than the long-and-narrow BWB 1. The advantages and disadvantages of the long-and-narrow (BWB 1) and short-and-wide (BWB 2) designs suggest the comparison of two notional designs as regards their stability, control, HQs, and manoeuvre points in addition to other aspects covered in the literature [60,61,62,63].
2. Theory of Longitudinal-Lateral Coupling
The link between the decoupled and strongly coupled lateral and longitudinal motions of an aeroplane (Section 2.1), is made through the case of weak coupling (Section 2.2), for which the frequency and damping changes can be calculated from the decoupled state (Section 2.3).
2.1. Basic Coupled and Decoupled Modes
We choose the usual body reference system with 0z axis vertically downwards 0x axis in the plane of symmetry, in the direction of motion, and thus 0y is orthogonal to the plane of symmetry. The decoupled motion is extensively covered in the literature [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24] and will be mentioned in passing. The decoupled longitudinal motion for a rigid aircraft is specified by the variables (1):
and denoting by dot time derivatives, they are related linearly Equation (2a) for small perturbations:
through the longitudinal stability matrix Equation (2b), whose eigenvalues Equation (3a):
specify Equation (3b) the natural frequency ω and damping ratio ζ (or amplification ratio ξ = −ζ) of the phugoid ‘p’ and short period ‘s’ modes.
Still, in the case of decoupled motion, the lateral variables (4):
are related to their time derivatives linearly Equation (2a) though the lateral stability matrix Equation (2b) with i, j = 5, 6, 7, 8. Its eigenvalues:
specify the natural frequency ω and damping ratio ζ of the dutch roll ‘d’ and helical ‘h’ modes; by helical mode is meant the combination of spiral “l” and roll “r” convergence modes; when these are separate, the complex conjugate roots for λ in (6) are replaced by distinct real roots.
In the case of arbitrary strong coupling of longitudinal Equations (1a,b) and lateral Equations (4a,b) motions, the eight variables (1) and (4) combined in (5):
are related by a complete matrix Equation (2b) of linear stability derivatives, whose eigenvalues
specify the natural frequencies ωg and damping ratios ζg of four modes g = 1,..., 4. The fundamental issue is whether these four modes can be related to the phugoid ‘1′, short period ‘2′, dutch roll ‘3′ and helical ‘4′ modes, as suggested in Table 1. This identification should be possible when the coupling is weak, that is the coupled modes with g = 1,..., 4, differ little from the decoupled modes , in the sense

Table 1.
Stability modes of a rigid airplane.
2.2. Weak Coupling and Mode Properties
The exact, coupled stability relation Equation (2b) with i, j = 1, …, 8, involves four 4 × 4 submatrices namely longitudinal Equation (7a), lateral Equation (7b) and upper Equation (7c) and lower Equation (7d) coupling:
and by weak longitudinal-lateral coupling it is meant (8):
that the upper Equation (7c) and lower Equation (7d) coupling matrices have terms of O(ε) smaller than O(1) for the longitudinal Equation (7a) and lateral Equation (7b) coupling matrices where ε2 is negligible.
In the general case of strong coupling, the natural frequency Δωg and damping ratio Δζg changes due to coupling:
can be introduced into the modal factors Equation (6b) of the characteristic polynomial (6a) for the coupled system:
It may be expected, in case (8) of weak coupling:
that the natural frequency and damping ratio changes be relatively small.
In the case of weak coupling Equations (11a–c), the modal factor (10) in the coupled characteristic polynomial Equation (6b) simplifies to:
where the first three terms on the r.h.s. of (12) correspond Equation (13a) to the decoupled modal factor:
for which the decoupled characteristic polynomial is Equation (13b) the product of the longitudinal (3) and lateral (4) characteristic polynomials. The deviation from decoupling in the modal factors (10) of the complete characteristic polynomial is specified (12) and Equation (13a) by Equations (14a,b):
where is introduced the weak coupling coefficient Equation (14c).
Before proceeding to calculate the changes in frequency and damping (Section 2.3), a brief review is conducted of the mode properties needed in the sequel (Section 3). The time response is specified by (15) with natural frequency and damping ratio for the decoupled modes:
and likewise, with , correspond to the coupled modes:
In both instances the eigenvalues are the roots of (17):
where ω is the natural frequency and ζ the damping ratio of any mode. Three cases I to III arise [9,24,64]. In case I of subcritical damping Equation (18a), the eigenvalues are complex conjugate Equation (18b):
and: (i) the real part is the product amplification ratio Equation (19a) or minus the damping ratio Equation (19b) by the natural frequency:
(ii) the imaginary part is the oscillation frequency Ω that equals the natural frequency Ω = ω in the absence of damping ζ = 0, it is smaller 0 < Ω < ω in the presence of subcritical damping 0 < ζ < 1 and vanishes Ω = 0 for critical damping ζ = 1.
For case II of supercritical damping Equation (20a), the oscillation frequency Equations (19c,d) would be imaginary, which means that the two eigenvalues are real Equation (20b) and involve the modulus of the oscillation frequency Equation (20c):
Thus, in case of supercritical damping Equation (20a) there are two damped modes with eigenvalues 0 > λ+ > λ− since |Ω| < ω, so that λ− has the slowest decay. In the case of amplification Equations (21a,b), the response is still oscillatory Equations (18a,b) if ζ2 < 1, but it has exponentially increasing instead of decreasing amplitude with time constant Equation (21b)
and time to double amplitude Equations (21c–d). In the case of overcritical amplification 0 > ξ > −1, the real eigenvalues Equations (20b,c) would be positive λ+ > λ− > 0 and the fastest growing mode is λ+, which could be used instead of |ζ| in the time constant Equation (20b) and time to double amplitude Equations (21c,d).
For an initial value and rate at the time t = 0, the solution of (15) or (16) specifies the response at time t that is: (i) oscillatory Equation (22a) in the case I of subcritical damping 0 < ζ <1 or amplification 0 > ξ > −1 in Equation (22b); (ii) monotonic Equation (24a) in the case II of supercritical damping ζ > 1 or amplification ξ < −1 in Equation (24b); (iii) linear in time Equation (23a) in the case III between (i) and (ii) of critical damping ζ = 1 or amplification in Equation (23b):
In all three cases, there is an exponential factor which dominates the asymptotic response because |Ω| < ω in Equation (19d), leading to decay for ζ < 0 and growth for ζ > 0 as time t increases.
2.3. Calculation of Frequency and Amplification Changes
The perturbation in natural frequency Equation (9a) and damping ratio Equation (9b) leads to a perturbation in the characteristic polynomial (6) of the coupled system Equations (25a):
relative to that Equation (25b) of the uncoupled system, which is specified by:
to first order in the perturbations by (27):
where Equations (14a,b) was used.
The perturbation of the characteristic polynomial Equation (25a) is a polynomial of degree seven in λ:
because the term of degree eight is the same λ8 in C in Equation (6b) and in the product of A in Equation (3b) by B in Equation (4b), and thus cancels by subtraction. The coefficients in (27) are the products of three modal factors of the coupled characteristic polynomial Equation (6b), and thus are polynomials of degree six in λ, with leading term λ6, viz.:
Note that the eight coefficients with a = 1, …, 8 in (28), and 4 × 6 = 24 coefficients with (g = 1, …, 4; b = 1, …, 6) in (29) are all determined from the 2 × 4 × 4 = 32 elements of the longitudinal Equation (7a) and lateral Equation (7b) stability matrices for the decoupled case. Substituting (28) and (29) in (27) leads to an identity between polynomials of degree seven in λ, viz.:
Equating the coefficients of equal powers of λ in (30) leads to a system of 8 equations, which are linear in the 4 pairs of variables with g = 1, …, 4. These variables are equivalent to , Equation (14c) in the form (31):
and thus the changes in natural frequency and damping ratio can be determined by solving the system (30).
In order to implement this solution, the system (30) is first written explicitly in the form (32),
in which the 8-vector on the l.h.s. is the sum of four terms, each consisting of an 8 × 7 matrix multiplying a 7-vector. The variables equivalent to frequency and damping changes appear linearly in the 8 × 7 matrices in (32), which can be re-written as a linear relation with the vector leading to an 8 × 8 matrix:
This system can be inverted to specify the and thus the changes (31) in damping ratios and natural frequencies . We have thus obtained three sets of results, indicated in Table 2: (i) the natural frequencies and damping ratios of the decoupled modes Equations (3a,b) and Equations (4a,b) in Table 1; (ii) the natural frequencies and damping ratios of the strongly Equations (9a,b) coupled modes Equations (6a,b); (iii) the natural frequency and damping ratio changes Equations (33, 31) for weak coupling Equations (11a–c).

Table 2.
Comparison of coupled, weakly and strongly coupled modes.
3. Natural Stability of Flying-Wing Aircraft
The flying wing configuration has attracted considerable interest for a long-time because it offers a high lift-to-drag ratio, and thus good aerodynamic efficiency. The early attempts to realize its potential, faced the stability problems inherent in the configuration. The preceding theory is applied to two flying wing aeroplane designs, considering the natural modes (Section 3.1) and resulting HQs (Section 3.2) and manouever points (Section 3.3).
3.1. Relevance of Longitudinal-Lateral Coupling
The complete 8 × 8 stability matrix Equation (2b) ≡ Equations (7a–d) with i, j = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 written explicitly (34):
where the forces and moments are divided by the mass and inertia, and steady, straight, and level flight parameters are used so that Zij has the dimensions of inverse time. There are three cases: (i) if the coupling sub-matrices vanish Equations (7c,d) then the longitudinal and transversal modes are strictly decoupled; (ii) if the coupling submatrices Equations (7c,d) have terms comparable to those of the longitudinal Equation (7a) or lateral Equation (7b) stability matrices Equations (7a,d), then there is strong coupling; (iii) if, when compared with the longitudinal Equation (7a) and lateral Equation (7b) stability matrices of O(1), the coupling submatrices Equations (7c,d) have terms O(ε) which are small but non-negligible ε2 << 1, then weak coupling results.
The application given next concerns two flying wing designs (“1” and “2”) in a total of eighteen flight conditions indicated in Table 3. Four flight conditions are broadly similar for the two configurations: (a,b) a minimum speed flying condition; (c,d) the take-off condition corresponding to a speed 14% higher; (e–h) in contrast with the preceding low-speed (a to d) flight conditions, the high-speed flight conditions (e to h) concern the final (e,f) and initial (g,h) stages of cruise, respectively, with lower and higher weight whose difference is the fuel consumption. For the first design, two further flight conditions are considered: (i) initial climb and; (j) final climb at an intermediate weight. For the four flight conditions common to the two designs, two positions of the mean aerodynamic chord are considered, leading to eight cases (“a” to “h”). The clean configuration is considered for all cases, including the extra climb cases (“i” and “j”) for the first design, the exception being the first design low-speed and take-off (cases “1a” to “1d”).

Table 3.
Flying-wing flight conditions.
The stability matrices (for example in Table 4 for the case 1a in Table 3) show that the terms of the coupling matrices Equations (7c,d) are small compared with the terms of the longitudinal Equation (7a) and lateral Equation (7b) matrices and the general theory for weak coupling shows that the effect on frequency Equation (9a) and damping Equation (9b) can be neglected Equations (11a–c). The general theory with strong coupling was developed in the expectation of longitudinal-lateral coupling that may occur is some flight conditions, like high angle-of-attack close to stall. In the present cases of flight at moderate angles-of-attack far from stall, the weak coupling version of the general theory is still useful to confirm that the small terms in the coupling matrices do not affect to a significant extent the frequencies and dampings, allowing the application of the decoupled HQs criteria, for which there exists substantial literature [64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80].

Table 4.
Re-arranged 8x8 stability matrix for case 1a in Table 3.
As an example, the oscillation frequency and damping ratio of all modes is indicated in the Table 5 for the case 1g in the Table 3: (i) the phugoid and dutch roll are oscillatory modes, with oscillation frequency Ω and damping ratio ζ; (ii) the short-period and helical modes degenerate into two real modes, that may be stable ζ > 0, neutral ζ = 0 or unstable ζ < 0. The de-coupled modes, calculated from 4 × 4 longitudinal and lateral matrices, are very close to the fully coupled modes calculated from the 8 × 8 stability matrix; they coincide to three significant digits, so the weakly coupled approximations are not necessary at this level of accuracy. In most instances the decoupled and fully coupled values are not distinguishable at the sixth digit, as can be seen for two modes in the Table 5 and holds also for all modes in most cases in the Table 3.

Table 5.
Oscillation frequency and damping ratio of natural modes for case 1g in the Table 3.
3.2. Longitudinal and Lateral Handling Qualities
The stability analysis is similar for all eighteen cases. The steps are as follows: (i) the starting point is the 9 × 9 stability matrix relating linear velocities , rates and Euler angles and their rates, for example in the Table 6 for the case 1a; (ii) by omitting and re-arranging the remaining terms as in (34), the 8 × 8 stability matrix is obtained in the Table 4 again for the case 1a; (iii) the eigenvalues of the upper-left 4 × 4 matrix apply to the phugoid and short-period modes, and the eigenvalues of the lower-right 4 × 4 matrix apply to the dutch roll and the helical (spiral and roll) modes and their values are shown in the Table 7 for the case 1a and all others (whose stability matrices are omitted for brevity); (iv) since the fully coupled modes specified by the eigenvalues of the 8 × 8 matrix, are identical to the third digit in accuracy, i.e., the lateral-longitudinal coupling is negligible, the eigenvalues in the Table 7 indicate the damping or amplification ratio for all modes and oscillation frequencies of all oscillatory modes; (v) the relations between damping ζ and amplification ξ ratio Equation (19b) and natural ω and oscillation Ω frequencies Equation (19d) are recalled in Table 8; (vi) they are applied to Table 7 to specify in Table 9 the damping or amplification ratio and natural frequency for all oscillatory modes and the real eigenvalues for the non-oscillatory or monotonic modes. Table 7 and Table 9 include data for all the eighteen cases in Table 3, calculated from the original 9 × 9 and re-arranged 8 × 8 stability matrices respectively, of which only one example (case 1a) is given in Table 4 and Table 6.

Table 6.
Complete 9 × 9 stability matrix for case 1a in Table 3.

Table 7.
Eigenvalues of natural modes involving the damping ratio , natural and oscillation frequencies.

Table 8.
Eigenvalues of the stability matrix ( —natural frequency;—damping ratio; —amplification ratio).

Table 9.
Parameters of flight modes: –eigenvalues;–natural frequency; –damping ratio; CAP = control anticipant parameter.
The natural ω and oscillation Ω frequencies and damping ratio ζ are related by Equation (19d) that can be inverted leading to Equation (35a) that is used to calculate the natural frequencies in Table 9 from the values in Table 7:
the damping ratio for oscillatory modes Equations (19a–d) in Table 9 is calculated by Equation (35b) from the real part of the eigenvalues in Table 7. For example, in Table 7, there is only one case 1i with ζω > 1 for the short-period mode:
Since this is an oscillatory mode, the damping ratio must be smaller than unity ζs < 1. This is checked next noting that: (i) using Equation (35b) the natural frequency is Equation (37a):
using Equation (36a) the damping ratio Equation (35b) is Equation (37b):
which is less than unity, implying subcritical damping Equation (22b), that is consistent with oscillatory motion Equation (22a).
The data in Table 9 allows an assessment of the longitudinal and lateral HQs. The latter are considered for the standard flight phase categories A, B, C and the first three levels of the Cooper-Harper [25] rating scale. Table 10 lists the main longitudinal and lateral HQs criteria [24]. Using the data in Table 9, follows the HQs levels are listed in Table 11 for all eighteen cases illustrated in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7.

Table 10.
Longitudinal and lateral handling qualities criteria.

Table 11.
Handling Qualities for all-natural modes (− means that not even level 3 criteria are met by at that mode or a sub-mode).
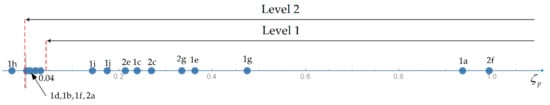
Figure 1.
Handling Qualities for the phugoid mode.
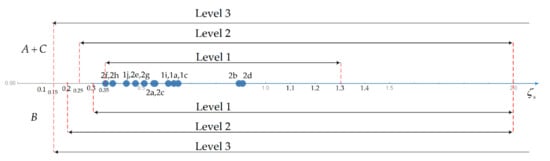
Figure 2.
Handling Qualities for the short-period mode.
Figure 3.
Damping of Short Period mode in oscillatory flight conditions.
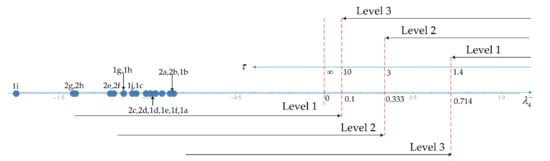
Figure 4.
Handling Qualities levels for the roll mode.
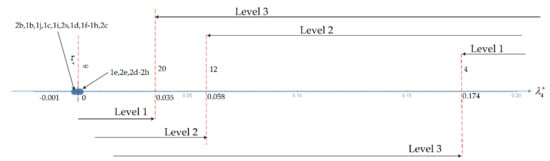
Figure 5.
Handling Qualities levels for the spiral mode.

Figure 6.
Level 3 Handling Qualities for the dutch roll mode.
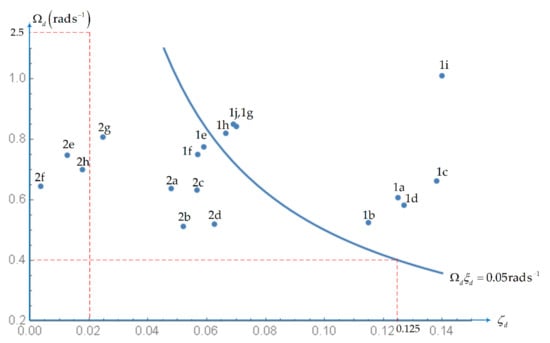
Figure 7.
Level 2 Handling Qualities for the dutch roll mode.
The HQs for the phugoid mode (Table 9) depend only on the damping (Table 10) with higher minimum values leading to better piloting characteristics in a ladder pattern in the Figure 1. The HQs are level 1 and 2 for the phugoid mode in all flight conditions in Table 11, except for 1h, 2b, 2d and 2h that are the only cases of amplification. The amplification is very small and thus level 3 is met, with 1h being oscillatory and 2b, 2d and 2h monotonic with one damped and one amplified mode, indicated in Table 11 and illustrated in Figure 1.
In the case of the short period mode (Table 10), it is necessary to distinguish (Figure 2) the high-gain flight phases (Figure 2, top half) like aggressive flight tracking (A) and precision landing (C) from low gain tasks (Figure 2, bottom half) like cruise flight (B). In both cases, the HQs depend only on damping, improve with greater damping that: (i) has the same lower bound for level 3; (ii) for levels 1 and 2 has a higher lower bound for high A + C relative to low B gain tasks. The short-period is stable (Table 9) in all oscillatory cases 1a, 1c, 1i, 1j an 2a–h with sufficiently large damping ζp > 0.04 in Table 10 to ensure level 1 HQ in Table 11. The short-period is monotonic in the remaining flight conditions 1b and 1d–1h, with one stable and one unstable mode (Table 7). Since the damping is negative, it follows (Table 10) that HQs do not even meet level 3. The oscillatory cases of short-period mode all have damping (Figure 3) in the range of level 1 HQ (Table 11) for all flight cases A, B, C as indicated in Table 11 and illustrated in Figure 2.
The roll mode is damped in all flight conditions (Table 7 and Table 9) whereas HQ levels 1, 2 and 3 allow (Table 10) progressively higher limits for the time constant (Figure 4) of instability Equation (21b). Thus, the roll mode meets level 1 HQs for all flight conditions (Table 11). The HQs levels 1, 2 and 3 for the spiral mode (Table 10) allow progressively smaller minimum time to double amplitude Equations (21c,d) as shown in Figure 5. Thus, the flight conditions with stable spiral mode 1a–1d, 1e–1j, 2a and 2c in Table 7 and Table 9 all have level 1 HQs in Table 11. The flight conditions 1e, 2b and 2d–2h with unstable spiral mode (Table 7 and Table 9) have long-time to double amplitude and thus also have level 1 HQs in Table 11. Thus, in all flight conditions the spiral mode has level 1 HQs, regardless of whether it is stable or not, as illustrated in Figure 5. The HQs depend (Table 10) on a single parameter, namely the damping of the phugoid (Figure 1) and short-period (Figure 2 and Figure 3) oscillatory modes, and the time to double amplitude of the spiral mode (Figure 4) and time constant of the roll mode (Figure 5) that are unstable.
Concerning the HQs for the dutch roll mode (Table 10) is necessary to distinguish level 3 in Figure 6 from level 2 in Figure 7 that apply to all flight conditions, from level 1 that applies differently to flight conditions A and flight conditions B+C in Figure 8. The level 3 HQs for the dutch roll (Table 10) set a minimum for the damping (Figure 6) and can be represented on a straight line as in all the preceding cases (Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5); they are met in all flight conditions except 2e, 2f and 2h when the damping is too small, so that not even level 3 HQs are met as indicated in Table 11 and illustrated in Figure 6. The level 2 and 1 HQs for the dutch roll (Table 10) depend both on damping and oscillating frequency and require representation on a plane (Figure 7 and Figure 8). In the case of level 2 HQs for the dutch roll (Table 10) there is (Figure 7) a minimum damping ξd > 0.02 and oscillation frequency Ωd > 0.40 rad.s−1 specifying an upper rectangle. Their product Ωd.ξd > 0.008 rad.s−1 may not satisfy the third condition Ωd.ξd > 0.05 rad.s−1 that specifies a hyperbola. The hyperbola Ωd.ξd = 0.05 cuts ξd = 0.02 at Ωd = 0.05/0.02 = 2.5 rad.s−1 and cuts Ωd = 0.4 rad.s−1 at ξd = 0.05/0.4 = 0.125. Thus, the region of level 2 HQs for the dutch roll lies on the right and level 3 HQs on the left of the hyperbola in Figure 7. The hyperbola on Figure 7 is one of the three hyperbolas on Figure 8, namely that which coincides with the hyperbola closest to the axis in Figure 8. The level 1 HQs for the dutch roll in flight conditions B + C impose the same condition on oscillation frequency Ωd > 0.40 but higher damping ξd > 0.08 shifting the rectangle to the right; the third condition is also more stringent Ωd.ξd > 0.15 than for level 2 shifting the second hyperbola upward and to the right in Figure 8. The level 1 HQs for flight condition A are still more stringent shifting the rectangle (Ωd > 0.40, ξd > 0.19) further the right and the third hyperbola Ωd.ξd > 0.35 further upward and to the right in Figure 8. None of the flight conditions lies within the third or second hyperbolas in Figure 7 and thus Level 1 HQs for the dutch roll are not attained. Since for the dutch roll level 1 HQs are not met in any flight condition, and not even level 3 is met for flight conditions 2e, 2f and 2h, all other flight conditions are level 2 or 3. As indicated in the Table 11 and illustrated in Figure 7. The dutch roll HQs are level 3 for flight conditions 1f, 1g, 2a–2d and 2g; the remaining flight conditions 1a–1d and 1g–1j have level 2 HQs for the dutch roll as indicated in Table 11 and illustrated in Figure 7 and Figure 8.
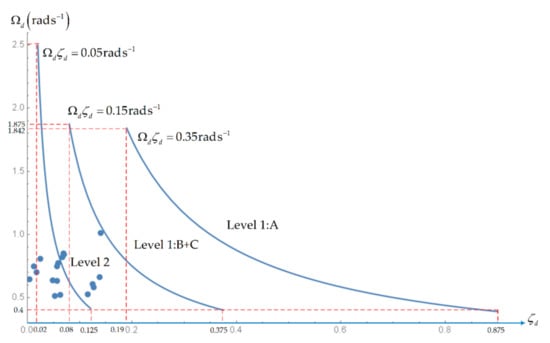
Figure 8.
Level 1 and 2 Handling Qualities for the dutch roll mode.
The HQs have been considered for all modes in the Table 7 and Table 9, Table 10, Table 11 and Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5. Figure 6, Figure 7 using only one criterion for each mode. Unsurprisingly it is the pitch axis that has received most attention in HQs criteria, including the control anticipation parameter [65], the pitch sensivity criterion [66], the bandwidth criterion [67], the Neal-Smith criterion [68], and the Gibson criteria for dropback [69], attitude pitch rate [70] and phase rate [71], plus multiple variants of several of these criteria. Most of these criteria were developed for military aircraft [72,73] for high-gain tasks like target acquisition and precision tracking. These aggressive flight manoeuvres are not relevant to civil aircraft flown as smoothly as possible so as not to upset passengers and keep far away from flight envelope boundaries that could lead to accidents. Some high gain tasks are common to military and civil aircraft like precision landing C, and some HQs criteria have been extended from military to civil applications in this context [74], for example the control anticipation parameter (CAP), briefly considered next. The CAP is defined (38) as the ratio of pitch acceleration to normal acceleration
where in the simplest approximation: (i) the pitch acceleration is related to the pitch angle by Equation (39a) the oscillation frequency of the pitch mode with fastest response, namely the short period with oscillation frequency Ωs appearing to the square; (ii) the normal acceleration relates to the lift and is thus specified Equation (39b) by the lift coefficient that is proportional to the lift slope multiplied CLθ to the pitch angle relative to the angle of zero lift assumed to be small:
Substituting Equations (39a,b) in (38) the CAP is given by Equation (40b), and using the lift slope [75,76] for the Joukowsky airfoil (40a) leads to Equation (40b):
There are more refined versions of the CAP HQs criterions [77], often used in modern literature on aircraft HQs [78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85]. The usual approaches CAP need not to be refined further here, because it is related [73,76] to the manouever margin, considered in more detailed in Section 3.3.
The CAP criterion as usually applied assumes that the short-period is oscillatory, corresponding to subcritical damping and complex conjugate eigenvalues Equations (18a,b) and (19a–d), and this is the case for flight conditions 1a, 1c, 1i, 1j and 2a–2h in Table 7. However, for flight conditions 1b and 1d–1h the short period is monotonic corresponding Equation (20a–c) to supercritical damping , with one stable and one unstable eigenvalue (41a) and it is the latter that dominates pitch response in time (41b):
Substituting (41b) and (39b) in the CAP (38) leads to (42a):
that simplifies to Equation (42b) using Equation (40a). Substituting Equation (20c) in Equation (42a) it follows that CAP is given: (i) by Equations (43a) ≡ (40b) for an oscillatory short period with subcritical damping Equation (43b); (ii) by Equation (44a) ≡ (42b, 20c) for a monotonic short period with supercritical damping or instability:
The CAP in the last column of Table 9 was calculated using Equation (43a) for the oscillatory and Equation (44a) for the monotonic short period that apply to each flight condition. The HQ criteria for the CAP assume damped response and are illustrated in the case (i) in Figure 9 in agreement with Table 11. The CAP HQs for class III in category C are level 1 for flight configurations 1i, 1j, 2a, 2c and 2e–2h, level 2 for 1a and 1c, and level 3 for 2b and 2d.
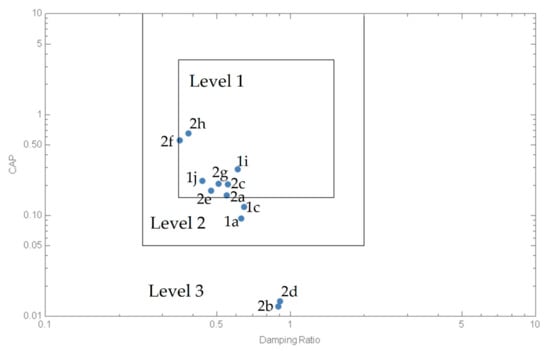
Figure 9.
CAP boundaries for class III Cat C flight phase.
3.3. Manouever Points of Two Kinds
For each of the two designs (“BWB 1” and “BWB 2”), the first eight cases (“a” to “h”) in the Table 4 correspond to the four flight conditions in the Table 12, each for a pair of positions of center-of-gravity x, specified by two values x1 and x2 of mean aerodynamic chord. The stability matrix depends on the c.g. position, and thus also the damping ratio ζ of all modes. For small c.g. excursions this dependence may be taken to the linear:
where ζ1, ζ2 are the dampings at c.g. positions respectively x1, x2 and k is the slope:

Table 12.
Longitudinal and lateral maneuver points.
The maneuver point where the damping would vanish thus corresponds to the critical c.g. position:
and can thus be calculated by linear interpolation of data at two c.g. positions. The manoeuver points of the first kind for oscillatory modes are calculated by Equation (46c) from the damping ratio ζ. In the case of the manouever points of the second kind for monotonic modes the larger eigenvalue λ+ is used in (47):
The process of linear interpolation is: (i) more accurate for small c.g. deviations, that is, for c.g. position between the positions for which the data is supplied, viz. ; (ii) potentially less accurate for large c.g. deviations out-of-range, e.g., with . The estimate of the manouever point by linear interpolation can be checked by considering a third stability matrix at the estimated manouever point; this will be more relevant in the case (ii) of extrapolation out-of-the-range of starting values. The manouever point can be calculated for each mode, and two kinds exist, as explained next.
The stability matrix (34) and hence the characteristic polynomial Equations (6a,b), its eigenvalues λ, the frequencies and dampings of the natural modes depend on the c.g. position. Since the stability matrix is real, the characteristic polynomial is also real, and its roots or eigenvalues can be: (i) real or (ii) complex conjugate pairs. A complex conjugate pair represents an oscillatory mode, and if it is damped the roots lie on the l.h.s. λ-plane in Figure 10. As the c.g. position moves aft, usually the damping reduces, and where it vanishes, a manouever point of first kind results. As shown in the Figure 10, at a manouever point of first kind the mode is oscillatory with zero damping, and the roots are conjugate imaginary. It may happen that as the c.g. moves the complex conjugate roots coalesce to a real double root, and then evolve to two distinct roots, as shown in Figure 11; it may happen instead that the mode consists of two real negative roots at the c.g. position , meaning that it is damped. As the c.g. moves the first root which ceases to be negative, specifies a manouever point of the second kind. Thus, at a manouever point of the second kind one eigenvalue is zero and the other zero or negative. The comparison of manouever points of the first and the second kind is made in the Table 12. The manouever points in Table 13 were calculated using Equation (46c) from the damping in the Table 9 and are discussed next, as part of the stability assessment of BWB 1 and BWB 2 designs.
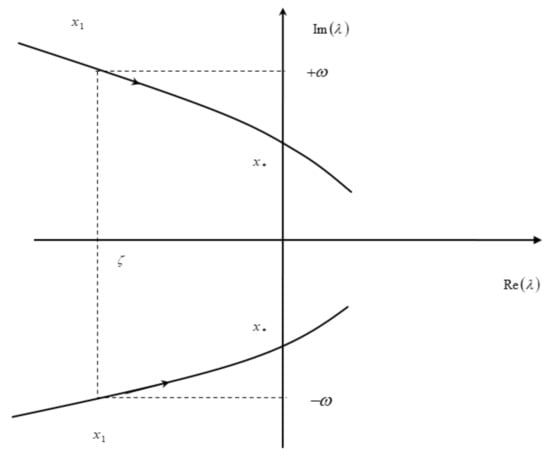
Figure 10.
Manouever points of first kind for oscillatory modes at zero damping.
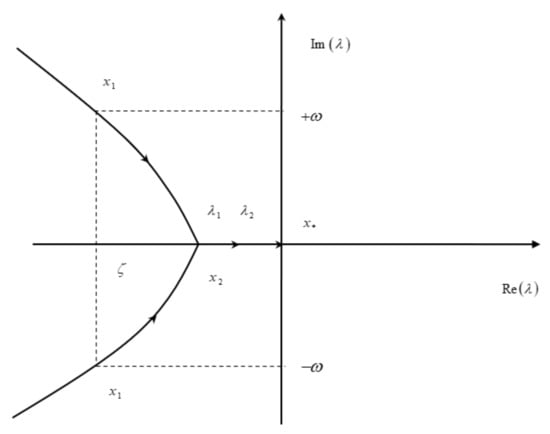
Figure 11.
Manouever points of the second kind for oscillatory modes becoming monotonic modes (convergent or divergent) before zero damping.

Table 13.
Two kinds of manouever points.
4. Assessment of BWB 1 and BWB 2 Designs
The stability assessment of the BWB 1 and BWB 2 designs concerns lateral (Section 4.1) and longitudinal (Section 4.2) handling qualities and manouever points and have implications for (Section 4.3) control system design.
4.1. The Dutch Roll, Spiral and Roll Modes
It can be seen from the Table 7 that the “helical mode” always has two real roots, and thus splits into “spiral” and “roll” modes. As seen in the Table 9 the roll mode has positive damping, that is stable in all cases; the Table 10 shows that level 1 HQs would allow moderate instability with rise time not exceeding 1.4s. Thus, the roll mode has level 1 HQs in all cases as shown in the Table 11 and Figure 4. The same Table 11 and Figure 4 show that the spiral mode also has level 1 HQs in all cases in Figure 4 because: (i) it is stable in all cases, except 1e, 2b and 2d to 2h, as seen in the Table 9; (ii) in these seven unstable cases the rise time is above the 20s in the Table 10 for level 1 HQs.
The other lateral mode in the Table 7, the dutch roll is oscillatory in all cases, and corresponds to complex conjugate roots. The dutch roll damping is always low, meeting level 2 HQs in the Table 11 (cases 1a–1d and 1g–1j), and other cases (1f, 1g, 2a–2d and 2g) having level 3 HQs; the exception is BWB 2 in cruise conditions (cases 2e, 2f and 2h), for which the damping is so low it fails to meet even level 3 dutch roll handling characteristics. These conclusions from Table 11 are illustrated in Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7. Since the dutch roll is always oscillatory, it can only have a manouever point of first kind (Figure 10). The stability matrices were supplied for two c.g. positions, for BWB 1 and BWB 2, each at four flight conditions. Since the dutch roll mode is damped in all cases, the manouever point lies outside the c.g. range. For the BWB 1, the damping decreases as the c.g. moves aft all flight conditions, and thus the manouever point is aft of the two c.g. values considered. The same applies to BWB 2 in low-speed flight conditions. For BWB 2 in cruise conditions, the damping increases as the c.g. moves forward, and the manouever point is forward of both c.g. positions.
4.2. The Phugoid and Short-Period Modes
From the Table 7 it follows that the phugoid is an oscillatory mode for BWB 1 flight conditions 1a–1j and BWB2 flight conditions 2b, 2d and 2h. The damping is large enough for level 1 HQs in cases 1a, 1c, 1e, 1g, 1i, 1j, 2c, and 2e–2g, with level 2 HQs for cases 1b, 1d, 1f and 2a, as illustrated in Figure 1. The level 3 HQs correspond (Table 11) to an unstable oscillatory mode in flight condition 1h, and to flight conditions 2b, 2d, and 2h with monotonic modes one of which is instable.
The short period mode is oscillatory for BWB 1 only in cases 1a, 1c, 1i and 1j, i.e., low-speed flight conditions at forward c.g. as seen in the Table 7. The short-period mode degenerates to two real roots for: (i) low-speed flight at the aft c.g. position; (ii) cruise at any (forward or aft) c.g. position. It follows that the manouever point lies between the two c.g. positions at low-speed and forward of the forward c.g. position in cruise, as seen in the Table 13. The short period mode is well damped in all modes, except 1b and 1d-h which have an unstable mode. Thus, HQs are level 1 for the short-period mode, except for those six cases in which it does not even meet level 3 as shown in Figure 2.
The longitudinal manouever points for BWB 1 are of the second kind (Figure 11), because they arise from two real roots in the short-period mode. For BWB 2 the short period mode is always oscillatory (Table 7), and well-damped (Table 9) leading to HQs (Table 10) which are level 1 in all cases (Table 11). In the case of BWB 2 it is the phugoid which ceases to be oscillatory, and degenerates to two real roots, in cases 2b, 2d and 2h. The phugoid damping implies that the HQs are level 1 or 2 in all cases (Table 11), except the unstable case 2d, when the rise time is long, so that HQs meet the level 3 criterion. For BWB 2 the longitudinal manouever points at low-speed are due to the phugoid and are due to the short-period in cruise and lie beyond the aft c.g. position except in the case 2c, d, when it lies on the aft c.g. position.
4.3. Implications for Control System Design
It is seen in Table 11 that the HQs are worst for the slow modes, viz. level 2 or 3 for the phugoid and level 2 or 3 or worse (unstable) for the dutch roll, due to poor damping or weak instability. This is of little concern, since a fly-by-wire control system is quite effective at damping these modes. The fast modes, viz. the roll and spiral modes always have level 1 HQs, and the same is true for the short-period mode, except for BWB 1 in cruise when it is unstable. The latter situation may require attention in control system design.
The lateral manouever point is aft of the rear c.g. position in all cases, except BWB 2 in cruise, when it is forward of the forward c.g. position. The longitudinal manouever point for BWB 1 is forward of the forward c.g. position in cruise, and between the c.g. positions at low speed. For BWB 2 the longitudinal manouever point lies aft of the aft c.g. position, except on take-off. Thus, the cost and complexity of a trim fuel tank could be avoided by small modifications.
5. Discussion
The two flying wing designs represent different approaches (Table 14) in the sense that: (a) the long, narrow fuselage of BWB 1 is closer to a conventional design; (b) the wide, short fuselage of BWB 2 is a more radical departure from conventional design. The main qualitative differences are: (i) for the same fineness ratio and surface area, that is equal drag, BWB 1 has a thicker fuselage with higher volume; (ii) BWB 1 also has a longer tail moment arm, allowing longitudinal trim with smaller elevator area, assuming the same elevator deflection and c.g. range; (iii) pitching motion is more noticeable to the passengers at the ends of the longer BWB 1 fuselage but it is the rolling motion which may affect most passengers at the sides of the wide BWB 2 fuselage; (iv) the longer BWB 1 fuselage has greater side area for speedy passenger evacuation. In conclusion, the conservative BWB 1 design appears qualitatively to be less risky.

Table 14.
Comparison of flying wing designs.
The purpose of the present paper is to assess quantitatively the stability of the two designs. The assessment concerns the basic flight conditions of minimum speed, take-off, initial and final cruise; the extreme conditions, like the low-speed, high-altitude or high-speed, low-altitude would be a next step. The stability assessments made before have in all cases been limited to steady, straight flight; stability during flight manouevers would be another aspect. It has been found that the damping of the slow modes (phugoid and dutch roll) is small, but this is of no concern for a fly-by-wire control system. The fast lateral modes (roll and spiral) always have level 1 HQs. The fast longitudinal mode also has level 1 HQs, except for BWB 1 on approach to land and in cruise when it degenerates into two real modes, one of which is unstable. This requires attention, because it could lead to a PIO (pilot induced oscillation or “probably inevitable oscillation”).
The availability, for each of the four flight conditions of BWB 1 and 2, of the stability matrix at a forward and an aft c.g. position, allows a rough estimate of manouever points. The method of linear extrapolation applies best for small c.g. changes, and the conclusions could be checked by reconsidering the stability matrix at the estimated manouever point. The lateral manouever point, due to the vanishing of dutch roll damping, is always out of the c.g. range, viz. rearwards (except for BWB 2 in cruise where is forward). The longitudinal manouever point for BWB 1 is due to the vanishing of damping of the short-period for BWB 1 and lies forward of the c.g. range in cruise and within the c.g. range at low-speed. For BWB 2 the longitudinal manouever point is aft of the c.g. range and is due to the short-period in cruise and phugoid at low-speed. It may be possible to avoid the cost and complexity of fuel trim tanks by small design adaptations.
The CAP appears in the Table 9 both for: (i) the oscillatory case with sub-critical damping (43a,b); (ii) the monotonic case when one mode is damped and the other is amplified, with the latter appearing in (44a,b). Since the HQs for the CAP assume positive damping (Figure 9), only the oscillatory short-period modes are considered and for: (i) the BWB 1 configuration leads to level 1 HQs in flight conditions 1i and 1j, and level 2 in flight conditions 1a and 1c; (ii) the BWB 2 configuration leads to level 1 HQs for flight conditions 2a, 2c, and 2d–2h, and level 3 HQs, for flight condition 2b and 2d. The short period is oscillatory for all flight conditions of BWB 2 and for flight conditions 1a, 1c, 1i, and 1j for BWB 1 which CAP HQs are always better than level 3. For BWB 1, the flight conditions 1b and 1d–1h have an unstable monotonic mode and the negative damping may be understood as not meeting even level 3 HQs for CAP.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.M.B.C.C.; Methodology, L.M.B.C.C.; Formal Analysis, L.M.B.C.C. and J.M.G.M.; Resources, L.M.B.C.C. and J.M.G.M.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, L.M.B.C.C. and J.M.G.M.; Writing—Review & Editing, L.M.B.C.C. and J.M.G.M.; Visualization, L.M.B.C.C. and J.M.G.M.; Project Administration, L.M.B.C.C. and J.M.G.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by FCT, through IDMEC, under LAETA, project UIDB/50022/2020.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This work was started under the VELA project of the European Union and benefited from comments of other partners in this activity.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Nomenclature
| coefficients of polynomials (28) | |
| coefficients of polynomials (29) | |
| slope of manouever point linear approximation (45c) | |
| x-component of angular velocity (4a) | |
| y-component of angular velocity (1) | |
| z-component of angular velocity (4a) | |
| x component of linear velocity (1) | |
| position of c.g. as percentage of m.a.c. (45a) | |
| critical c.g. position for manouever point (46a–c) | |
| y-component of linear velocity (4a) | |
| z-component of linear velocity (1) | |
| vertical acceleration (38) | |
| A | characteristic polynomial of longitudinal stability sub-matrix (3b) |
| B | characteristic polynomial of lateral stability sub-matrix (4b) |
| C | characteristic polynomial of complete stability matrix (6a,b) |
| characteristic polynomial of decoupled complete stability matrix (13b) | |
| modal factor (10) | |
| modal factor for decoupled stability matrix (13a) | |
| lift coefficient slope (39b) | |
| weak coupling coefficient (14c) | |
| T | time to double amplitude (21c,d) |
| X | aircraft state variables (1, 4a) |
| Xi | coupled flight variables (5) |
| decoupled flight variables (15) | |
| Zij | stability matrix (2b) |
| ε | small quantity (8) |
| θ | Euler angle of pitch (1) |
| δab | identity matrix (3a) |
| Euler angle of bank (4a) | |
| Euler angle of sideslip (Table 5) | |
| eigenvalues (3a) for modes (18a,b; 20a–c) | |
| damping ratio (3b) | |
| decoupled damping ratio (9b) | |
| natural exact coupled frequency (3b) | |
| natural decoupled frequency (9a) | |
| oscillation frequency (19d) | |
| time constant (21b) | |
| amplification ratio () | |
| difference between the exact coupled and decoupled complete characteristic polynomial (27) | |
| difference between the exact coupled and decoupled modal factor (14a–c) | |
| difference between the exact coupled and decoupled natural frequency (9a) | |
| difference between the exact coupled and decoupled damping ratio (9b) | |
| Subscripts | |
| p or 1 | phugoid mode |
| s or 2 | short period mode |
| d or 3 | dutch roll mode |
| h or 4 | helical mode |
| r or 4- | roll mode |
| l or 4+ | spiral mode |
| Superscripts | |
| decoupled value of | |
| Abbreviations | |
| c.g. | center of gravity |
| m.a.c. | mean aerodynamic chord |
| CAP | Control Anticipation Parameter (38) |
| BWB | Blended Wing Body |
| HQs | handling qualities |
| Symbols | |
| time derivative of | |
| variation of |
References
- Von Mises, R. Theory of Flight; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1945. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, C.D.; Hage, R.E. Airplane, Performance, Stability and Control; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- George, L.; Vernet, J.F. Mécanique du Vol: Performances des Avions et Engins; Librarie Polytechique Ch. Béranger: Sablons, France, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Rabister, W. Aircraft Dynamic Stability and Response; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Lecomte, P. Mécanique du Vol: Les Qualités de Vol des Avions et Engines; Dunod: Paris, France, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Miele, A. Flight Mechanics; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1962; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Etkin, B. Dynamics of Atmospheric Fight; Wiley: Boston, MA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- McRuer, D.; Ashkenas, I.; Graham, D. Aircraft Dynamics and Automatic Control; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Etkin, B. Dynamics of Flight Stability and Control; Wiley: Boston, MA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Etkin, B.; Reid, L.D. Dynamics of Flight Stability and Control; Wiley: Boston, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Lichota, P. Multi-Axis Inputs for Identification of a Reconfigurable Fixed-Wing UAV. Aerospace 2020, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, N.; Yue, T.; Liu, H.; Zhu, J.; Jia, X. Three-axis coupled flight control law design for flying wing aircraft using eigenstructure assignment method. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2020, 33, 2510–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaletka, J. BO-105 Identification Results, LS-178 on Rotorcraft System Identification; AGARD: Neuilly sur Seine, France, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, G.E.; Harper, R.P. The Use of Pilot Rating in the Evaluation of Aircraft Handling Qualities; NASA TN D-5153: Huntsville, AL, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Heffley, R.K.; Jewell, W.F. Aircraft Handling Qualities Data; National Aeronautics and Space Administrative CR-2144: Huntsville, AL, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, R.C. Flight Stability and Automatic Control, 2nd. ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, B.L.; Lewis, F.L. Aircraft Control and Simulation; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- McCormick, B.W. Aerodynamics, Aeronautics and Flight Mechanics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Catapang, D.R.; Tischler, M.B.; Biezad, D.J. Robust crossfeed design for hovering rotorcraft. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 1994, 4, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tischler, M.B. Advances in Flight Control; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, J.B. Performance and Stability of Aircraft, 1st ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Abzug, M.J.; Larrabee, E.E. Airplane Stability and Control: A History of the Technologies That Made Aviation Possible, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Vinh, N.X. Flight Mechanics of High-Performance Aircraft; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, M.V. Flight Dynamics Principles; Arnold: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore, R.; Wakayama, S.; Roman, D. Optimization of high-subsonic blended-wing-body configurations. In Proceedings of the 9th AIAA/ISSMO Symposium on Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization AIAA 2002-5666, Atlanta, GA, USA, 4–6 September 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Liebeck, R.H. Design of the blended wing body subsonic transport. J. Aircr. 2004, 41, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.J. Longitudinal Aerodynamic Characteristics and Wing Pressure Distributions of a Blended-Wing-Body Configuration at Low and High Reynolds Number; NASA/TM-2005-213754: Huntsville, AL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, J.R. Innovation in Flight: Research of the NASA Langley Research Center on Revolutionary Advanced Concepts for Aeronautics; NASA SP-2005-4539: Huntsville, AL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nickol, C.L.; McCullers, L.A. Hybrid wing body configuration system studies. In Proceedings of the 47th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including The New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition AIAA-2009-931, Orlando, FL, USA, 5–8 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, D.; Allen, J.B.; Liebeck, R.H. Aerodynamic design challenges of the blended-wing-body subsonic transport. In Proceedings of the 18th Applied Aerodynamics Conference AIAA-2000-4335, Denver, CO, USA, 14–17 August 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pambagjo, T.E.; Nakahashi, K.; Obayashi, S.; Matsushima, K. Aerodynamic design of a medium size blended wing body airplane. In Proceedings of the 39th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit AIAA-2001-0129, Reno, NV, USA, 8–11 January 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mialon, B.; Fol, T.; Bonnaud, C. Aerodynamic optimization of subsonic flying wing configurations. In In Proceedings of the 20th AIAA-2002-2931 applied aerodynamics conference, St. Louis, MO, USA, 24–26 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, D.; Gilmore, R.; Wakayama, S. Aerodynamics of high subsonic blended-wing-body configurations. In Proceedings of the 41st Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit AIAA-2003-554, Reno, NV, USA, 6–9 January 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mialon, B.; Hepperle, M. Flying Wing Aerodynamics Studied at ONERA and DLR. 2005. Available online: https://www.yumpu.com/en/document/view/11653618/flying-wing-aerodynamics-studies-at-onera-and-dlr (accessed on 16 March 2021).
- Peigin, S.; Epstein, B. Computational fluid dynamics driven optimization of blended wing body aircraft. AIAA J. 2006, 44, 2736–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.B.; Vicroy, D.D.; Patel, D. Blended-wing-body transonic aerodynamics: Summary of ground tests and sample results. In Proceedings of the 47th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including The New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition AIAA-2009-935, Orlando, FL, USA, 5–8 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chambon, E.; Burlion, L.; Apkarian, P. Time-response shaping using output to input saturation transformation. Int. J. Control 2017, 91, 534–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denieul, Y.; Bordeneuve, J.; Alazard, D.; Toussaint, C.; Taquin, G. Multicontrol Surface Optimization for Blended Wing–Body Under Handling Quality Constraints. J. Aircr. 2018, 55, 638–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Khalid, A. Blended Wing Body Propulsion System Design. Int. J. Aviat. Aeronaut. Aerosp. 2017, 4, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Ammar, S.; Legros, C.; Trépanier, J.-Y. Conceptual design, performance and stability analysis of a 200 passengers Blended Wing Body aircraft. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2017, 71, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotou, P.; Fotiadis-Karras, S.; Yakinthos, K. Conceptual design of a Blended Wing Body MALE UAV. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2018, 73, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakka, S.; Johnson, O. Aerodynamic Design and Exploration of a Blended Wing Body Aircraft at Subsonic Speed. Int. J. Aviat. Aeronaut. Aerosp. 2019, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Liou, M.-F. Flow simulation and drag decomposition study of N3-X hybrid wing-body configuration. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 85, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T. Design and CFD Analysis of a Blended Wing UAV (A Conceptual Design). J. Aerosp. Eng. Mech. 2019, 3, 156–160. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, M.; Tao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B. Research on analytical scaling method and scale effects for subscale flight test of blended wing body civil aircraft. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 106114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Footohi, P.; Bouskela, A.; Shkarayev, S. Aerodynamic Characteristics of the Blended-Wing-Body VTOL UAV. J. Aerosp. Eng. Mech. 2020, 4, 187–300. [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys-Jennings, C.; Lappas, I.; Sovar, D.M. Conceptual Design, Flying, and Handling Qualities Assessment of a Blended Wing Body (BWB) Aircraft by Using an Engineering Flight Simulator. Aerospace 2020, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemitola, P.; Okonkwo, P. Review of Structural Issues in the Design of a Box Wing Aircraft. J. Aerosp. Eng. Mech. 2019, 3, 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinowski, M. Aero-Structural Optimization of Joined-Wing Aircraft. Trans. Aerosp. Res. 2017, 4, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlichting, H.; Truckenbrodt, E. Aerodynamik des Flugzeuges: Erster Band; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Obert, E. Aerodynamic Design of Transport Aircraft; IOS Press: Delft, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Torenbeek, E. Advanced Aircraft Design—Conceptual Design, Analysis and Optimization of Subsonic Civil Airplanes; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Marques, J.M.G. On a Method of Lagrange Multipliers for Cruise Drag Minimization. J. Aerosp. Eng. Mech. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, L.R.; Gerhold, C.H. Inlet noise reduction by shielding for the blended-wing-body airplane. In Proceedings of the 5th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference and Exhibit AIAA-1999-1937, Bellevue, WA, USA, 10–12 May 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Diedrich, A.; Hileman, J.; Tan, D.; Willcox, K.; Spakovszky, Z. Multidisciplinary design and optimization of the silent aircraft. In Proceedings of the 44th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit AIAA-2006-1323, Reno, NV, USA, 9–12 January 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hileman, J.I.; Spakovszky, Z.S.; Drela, M.; Sargeant, M. Airframe design for “silent” aircraft. In Proceedings of the 45th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit AIAA-2007-453, Reno, NV, USA, 8–11 January 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hileman, J.I.; Spakovszky, Z.S.; Drela, M.; Sargeant, M. Aerodynamic and aeroacoustic three-dimensional design for a “silent” aircraft. In Proceedings of the 44th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit AIAA-2006-241, Reno, NV, USA, 9–12 January 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hileman, J.I.; Spakovszky, Z.S.; Drela, M.; Sargeant, M.A.; Jones, A. Airframe design for silent fuel-efficient aircraft. J. Aircr. 2010, 47, 956–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. On physical aeroacoustics with some implications for low-noise aircraft design and airport operations. Aerospace 2015, 2, 17–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolsunovsky, A.L.; Buzoverya, N.P.; Gurevich, B.I.; Denisov, V.E.; Dunaevsky, A.I.; Shkadov, L.M.; Sonin, O.V.; Udzhuhu, A.J.; Zhurihin, J.P. Flying wing-problems and decisions. Aircr. Des. 2001, 4, 193–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Vavalle, A.; Le Moigne, A.; Laban, M.; Hackett, K.; Weinerfelt, P. Aerodynamic considerations of blended wing body aircraft. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2004, 40, 321–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, C.; Lin, Y. Aerodynamic design methodology for a blended wing body transport. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2012, 25, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Okonkwo, P.; Smith, H. Review of evolving trends in blended wing body aircraft design. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2016, 82, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. Linear Differential Equations and Oscillators; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bihrle, W. A Handling Qualities Theory for Precise Flight Path Control; Technical Report, AFFDL-TR-65-198; Air Force Flight Dynamics Laboratory, WPAFB: Montgomery, OH, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Sturmer, S.R. Pitch rate sensitivity criterion for category C flight phases—Class IV aircraft. In AIAA Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference; AIAA 86-2201: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hoh, R.H. Advances in Flying Qualities: Concepts and Criteria for a Mission Oriented Flying Qualities Specification; Technical Report, AGARD LS 157; AGARD: Washington, DC, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Neal, T.P.; Smith, R.E. An In-Flight Investigation to Develop Control System Design Criteria for Fighter Airplanes; Technical Report, AFFDL-TR-70-74; Wright Patterson AFB, Flight Dynamics Laboratory: Montgomery, OH, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, J.C. Piloted Handling Qualities Design Criteria for High Order Flight Control Systems; Technical Report, AGARD CP 333; AGARD: Washington, DC, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, J.C. The Definition, Design and Understanding of Aircraft Handling Qualities; Technical Report, Report LR-756; Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, J.C. Handling qualities for unstable combat aircraft. In Proceedings of the 15th Congress of the International Council of the Aeronautical Sciences, London, UK, 7–12 September 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Military Standard—Flying Qualities of Piloted Aircraft; Technical Report, MIL-STD-1797A; Department of Defense of U.S.A.: Washington, DC, USA, 1990.
- Anonymous. Defence Standard 00-970. Design and Airworthiness Requirements for Service Aircraft; Technical Report; UK Ministry of Defense: London, UK, 1983; Volume 1.
- Gautrey, J.E. Flying Qualities and Flight Control System Design for a Fly-by-Wire Transport Aircraft. Ph.D. Thesis, Cranfield University, Bedford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Milne-Thomson, L.M. Theoretical Hydrodynamics; Dover: Mineola, NY, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C. Complex Analysis with Applications to Flows and Fields; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gautrey, J.E.; Cook, M.V. A generic control anticipation parameter for aircraft handling qualities evaluation. Aeronaut. J. 1998, 102, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Hariyoshi, E.; Ranade, G.; Sahai, A. Control with actuation anticipation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 55th Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 12–14 December 2016; pp. 5617–5622. [Google Scholar]
- Saussié, D.; Saydy, L.; Akhrif, O. Longitudinal flight control design with handling quality requirements. Aeronaut. J. 2006, 110, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, Z.; Lixin, W.; Xiangsheng, T. Flying qualities reduction of fly-by-wire commercial aircraft with reconfiguration flight control laws. Procedia Eng. 2011, 17, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bischoff, D. The definition of short-period flying qualities characteristics via equivalent systems. J. Aircr. 1983, 20, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Min-Jea, T. Optimization for Flight Control System with Constraints supplemented Handling Qualities. In Proceedings of the 26th Congress of the International Council of the Aeronautical Sciences, London, UK, 14–19 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Weiser, C.; Ossmann, D.; Looye, G. Design and flight test of a linear parameter varying flight controller. CEAS Aeronaut. J. 2020, 11, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elarbia, E.; Ghmmam, A.; Issa, S. On Flying-Handling Qualities of B747-100 Longitudinal Flight based on Gain Scheduling Control. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Technology, Engineering and Science (IConTES), Antalya, Turkey, 29 October–1 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.M.B.C.; Marques, J.M.G. On the comparison of ten pitch trim strategies for cruise drag minimization. J. Aerosp. Eng. Mech. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).