Comparison of Solar Radiation Torque and Power Generation of Deployable Solar Panel Configurations on Nanosatellites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. In-Orbit External Disturbances
2.1. Solar Radiation Pressure
2.2. Other Disturbances
3. Model Parameters
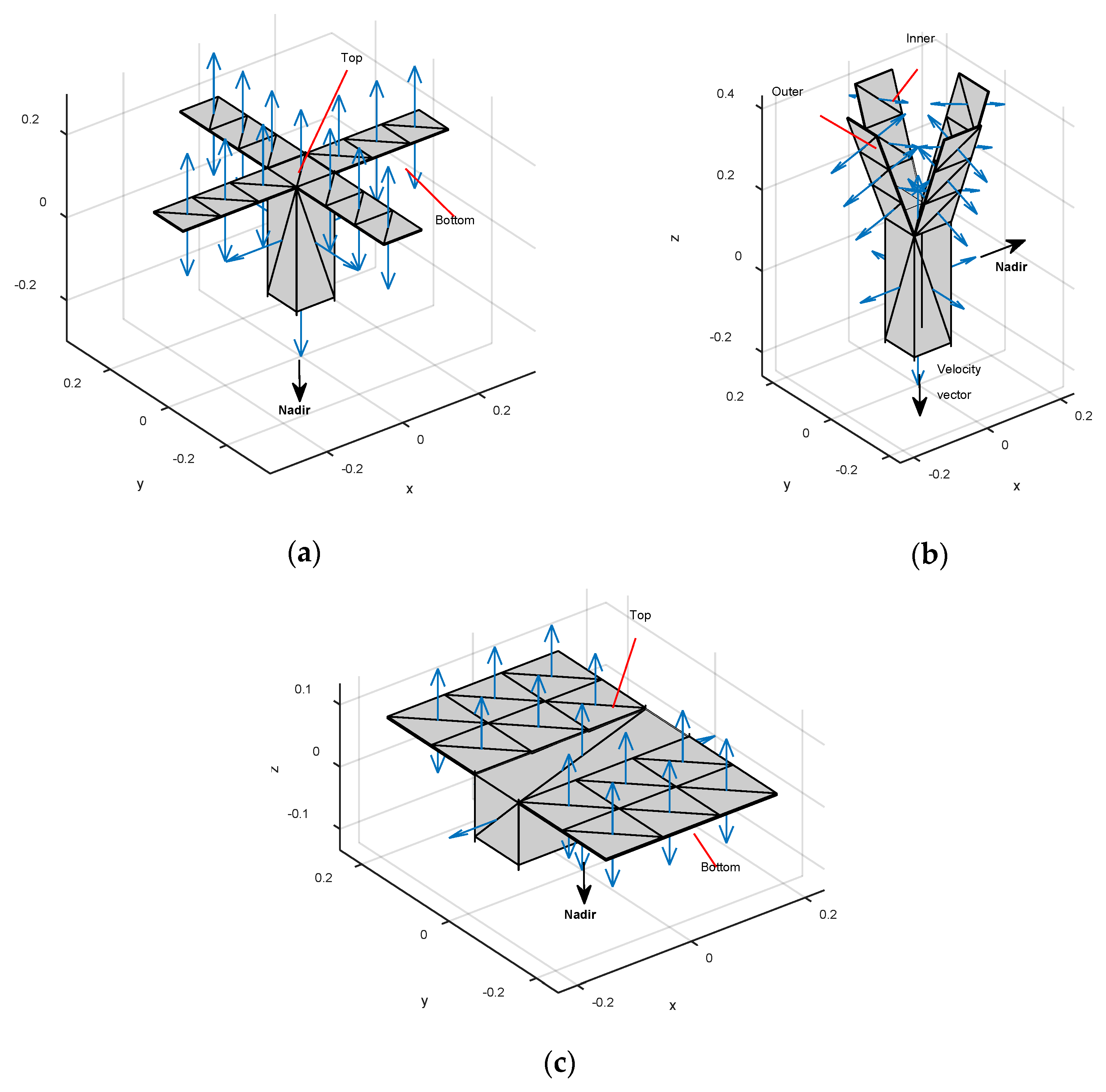
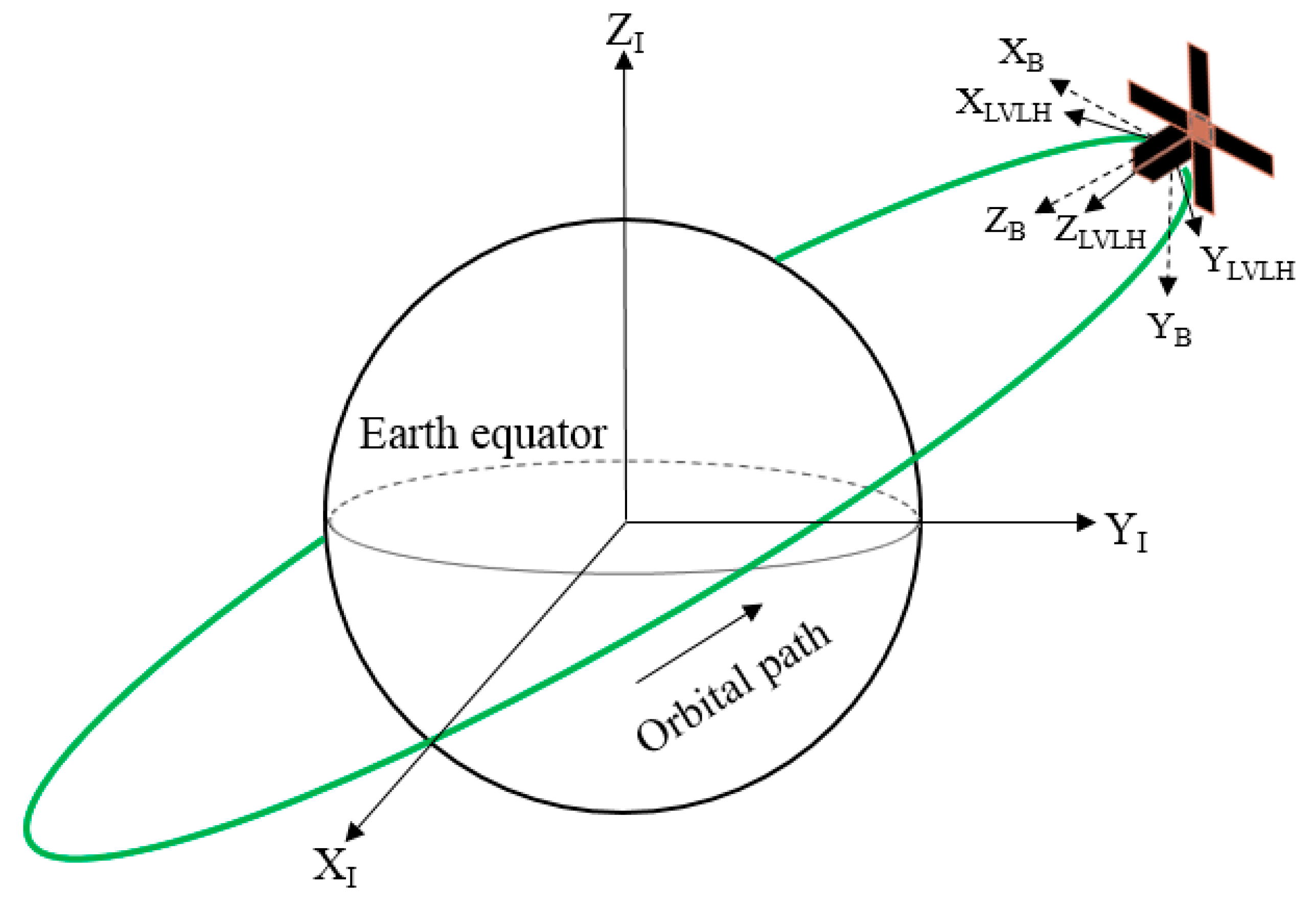
3.1. Satellite Configuration
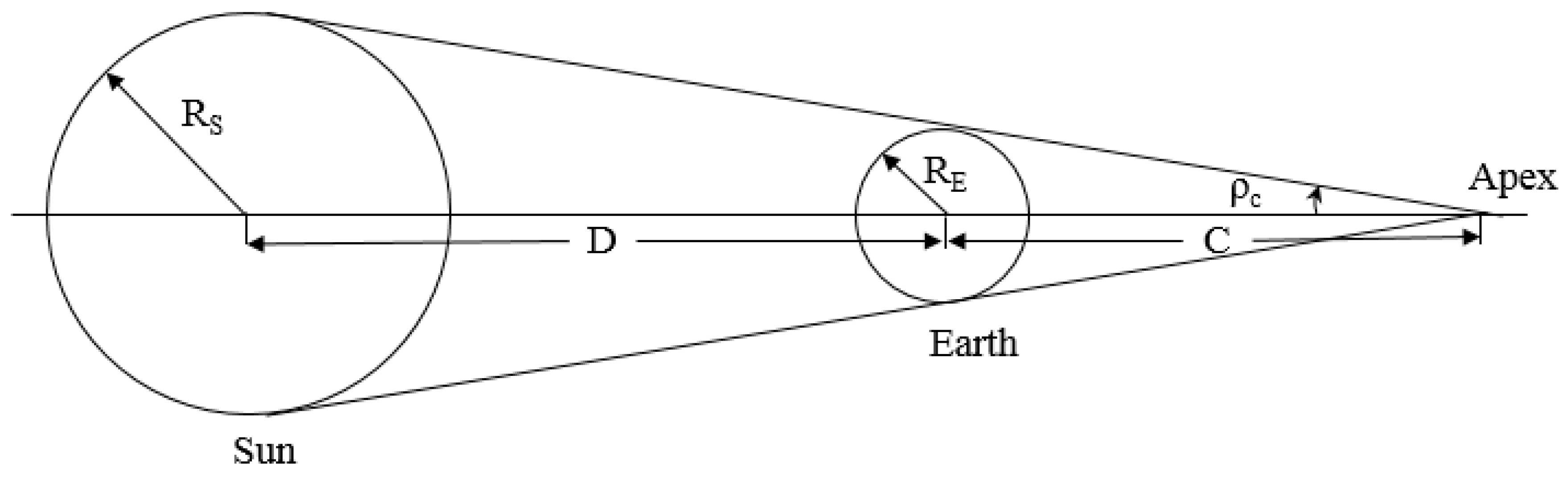
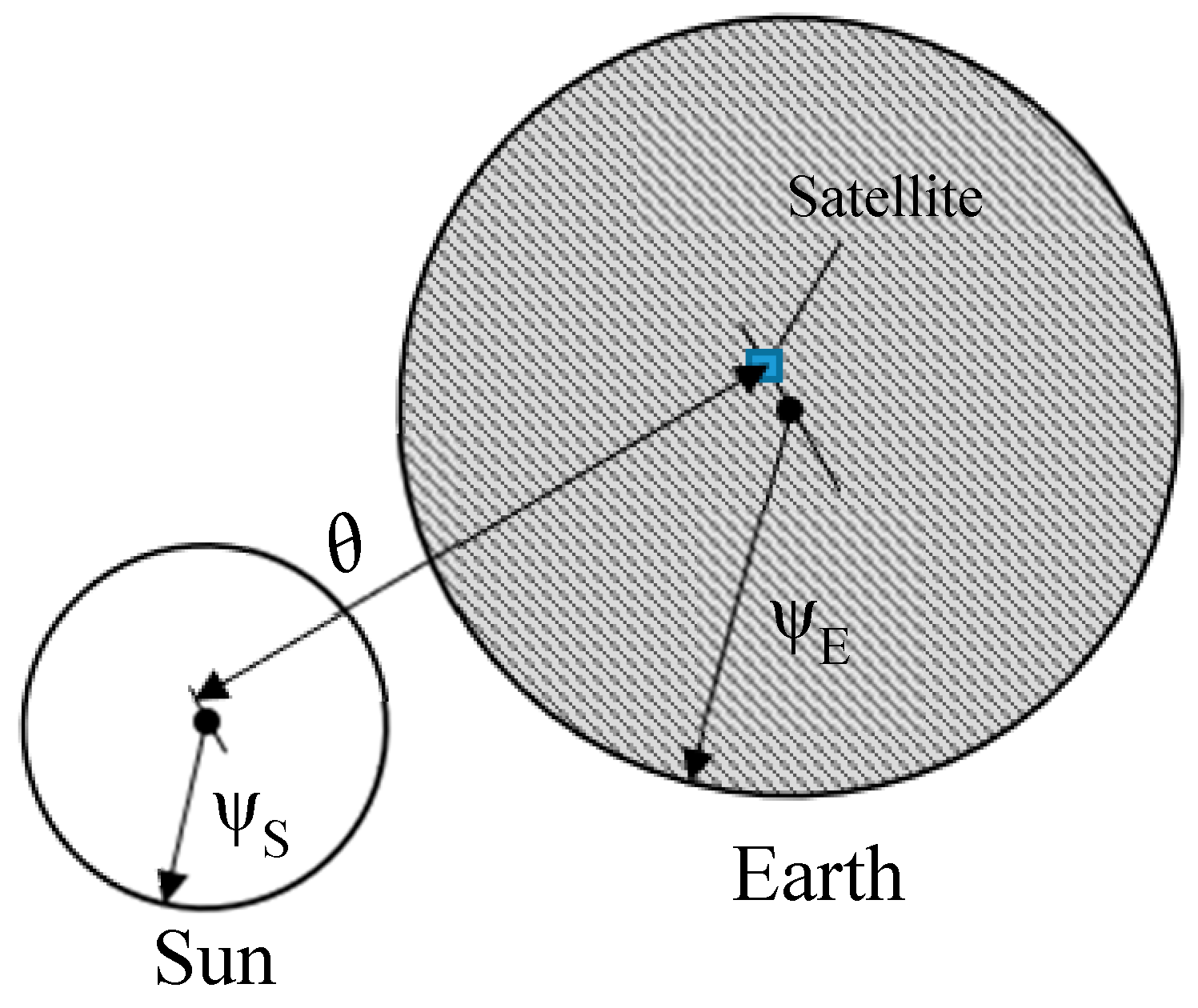
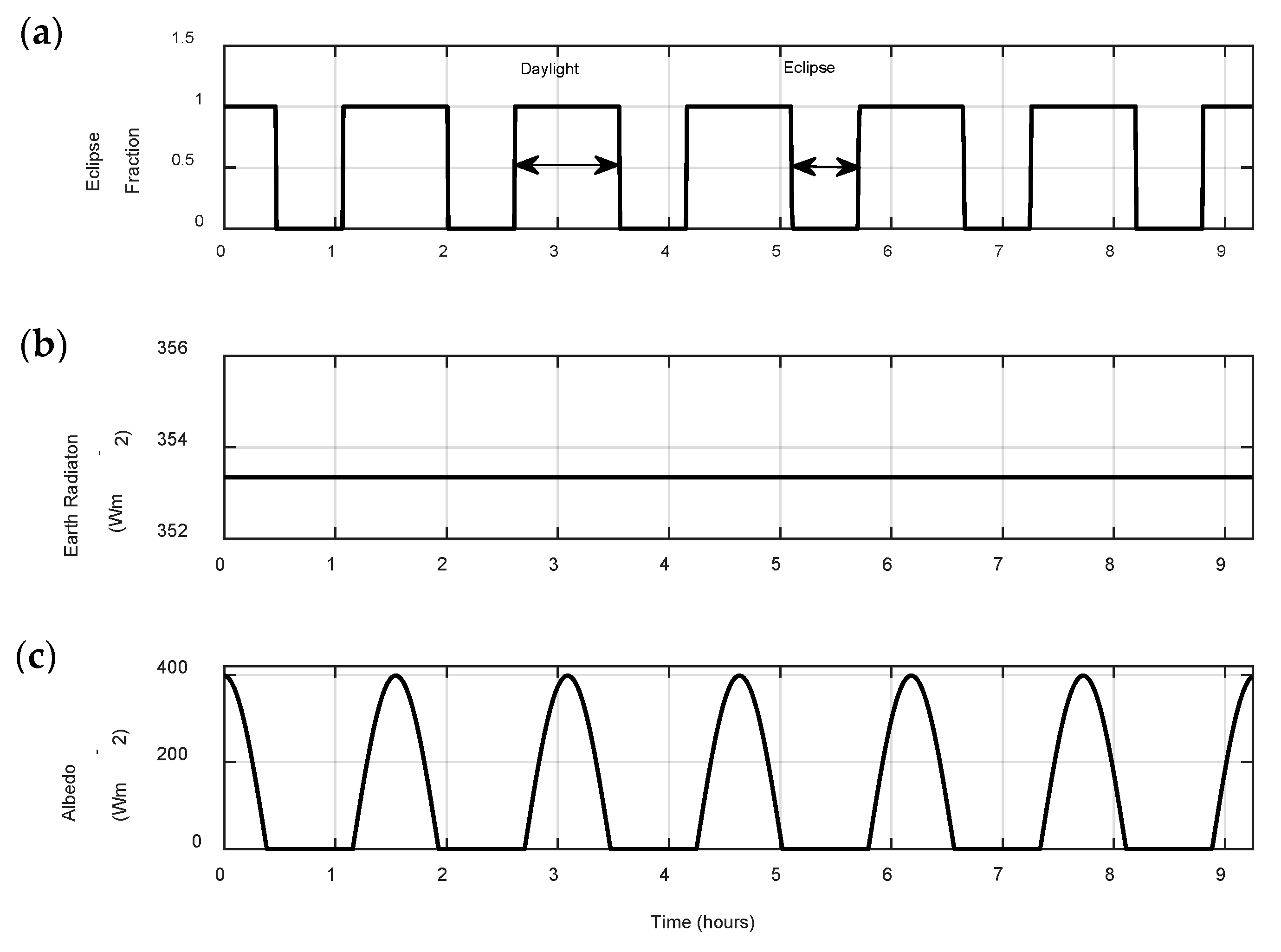
3.2. Position of the Sun and Eclipse Condition
3.3. Solar Power Calculation
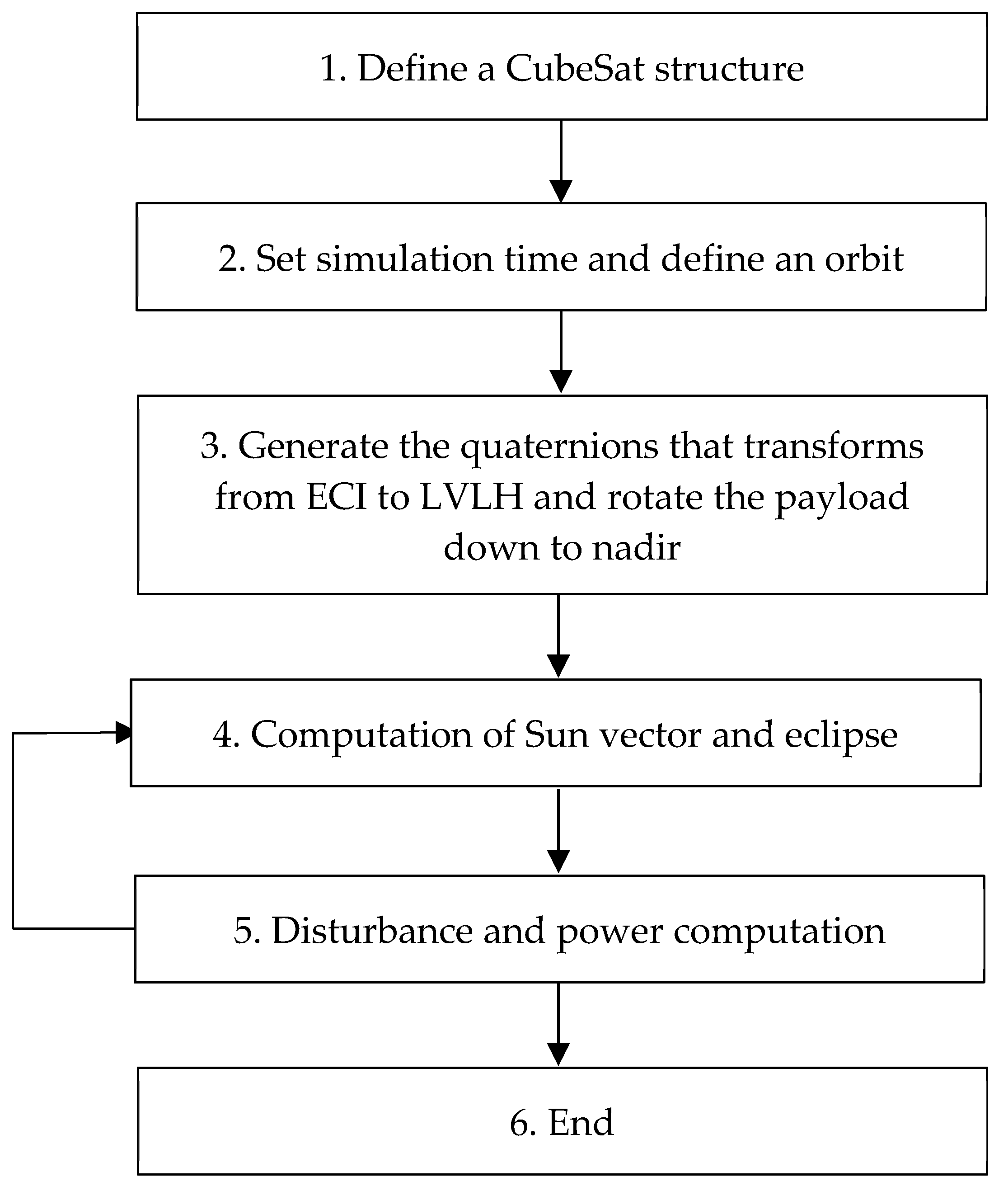
4. Simulation Program Flow
5. Disturbance and Power Evaluation
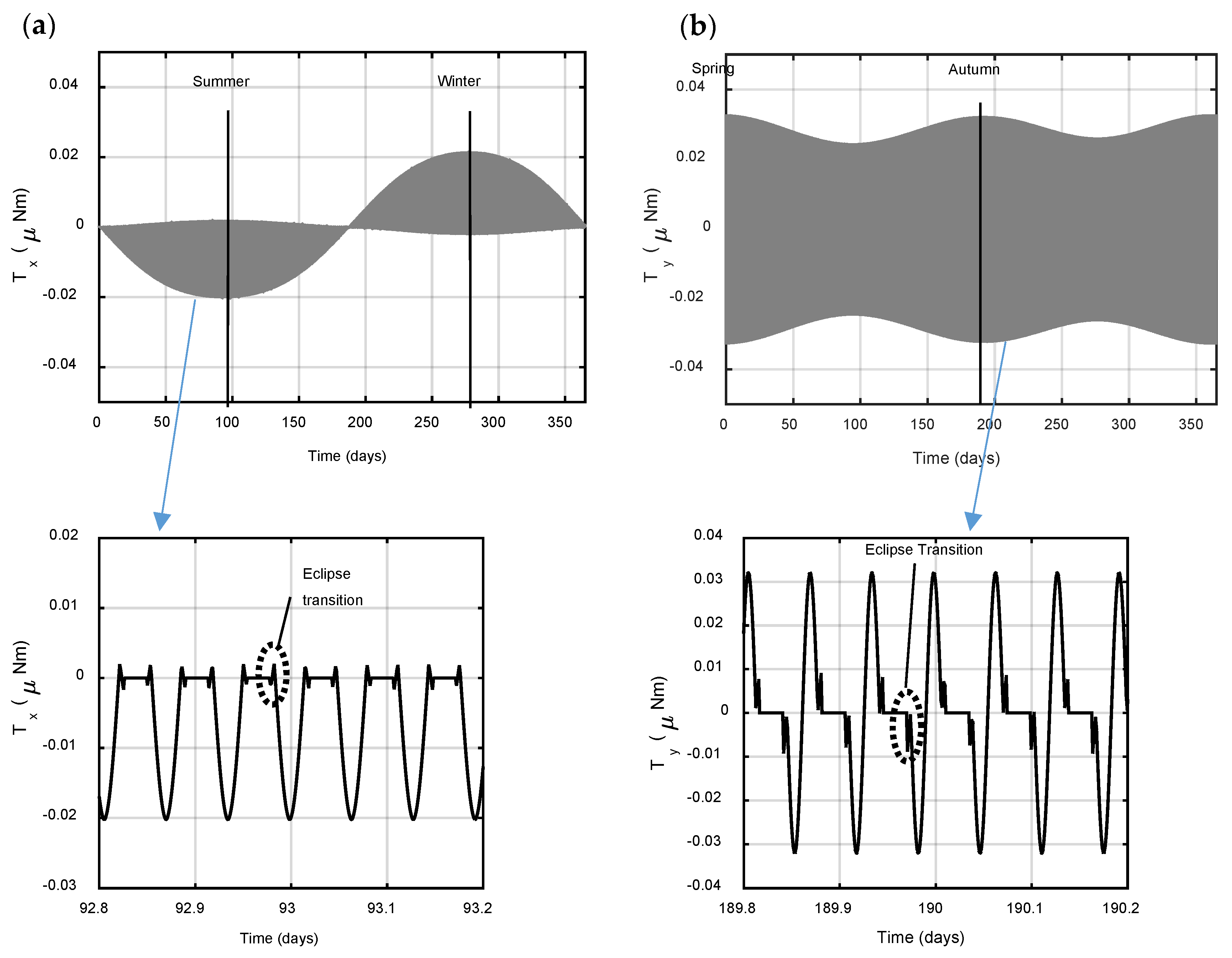
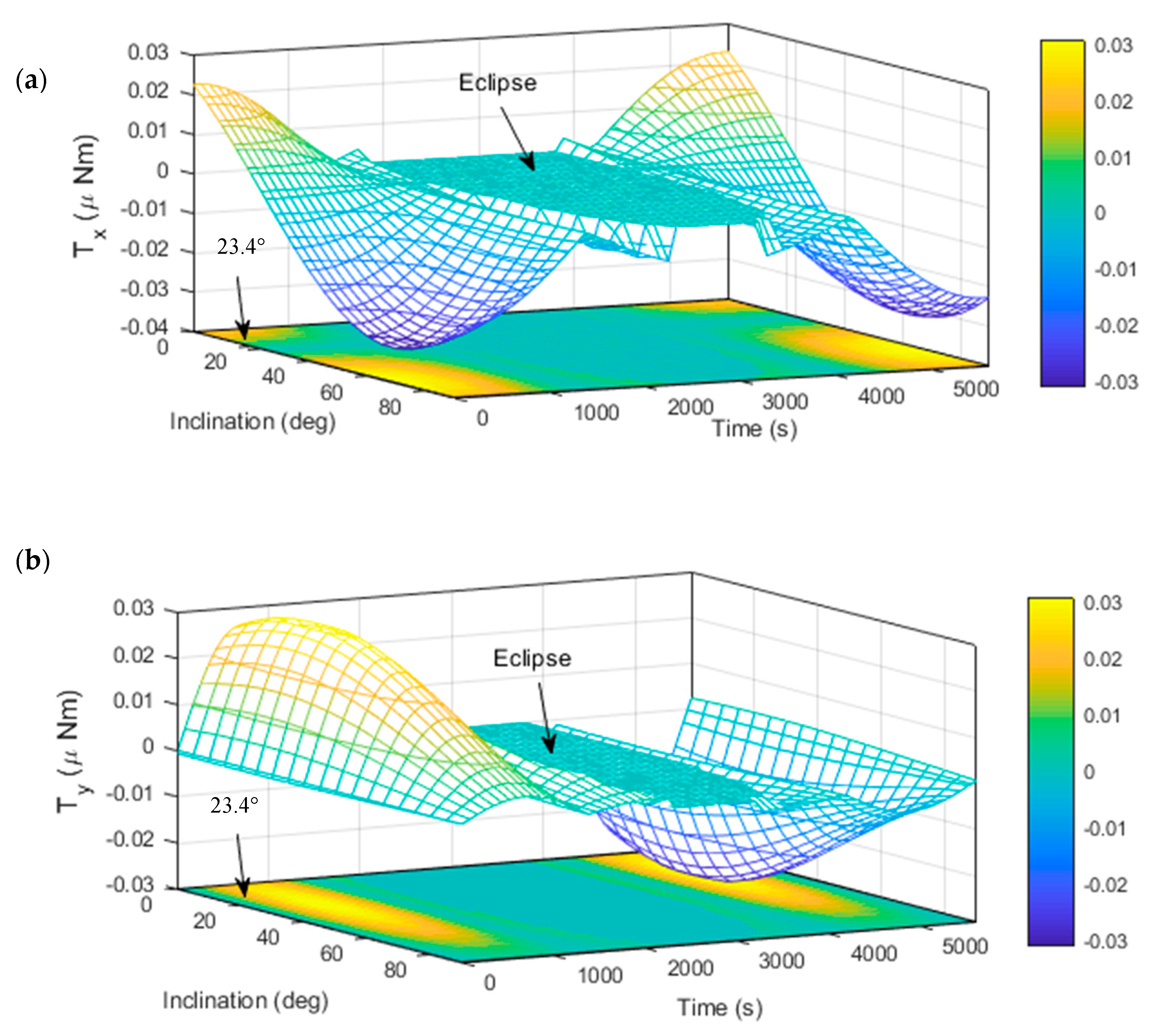
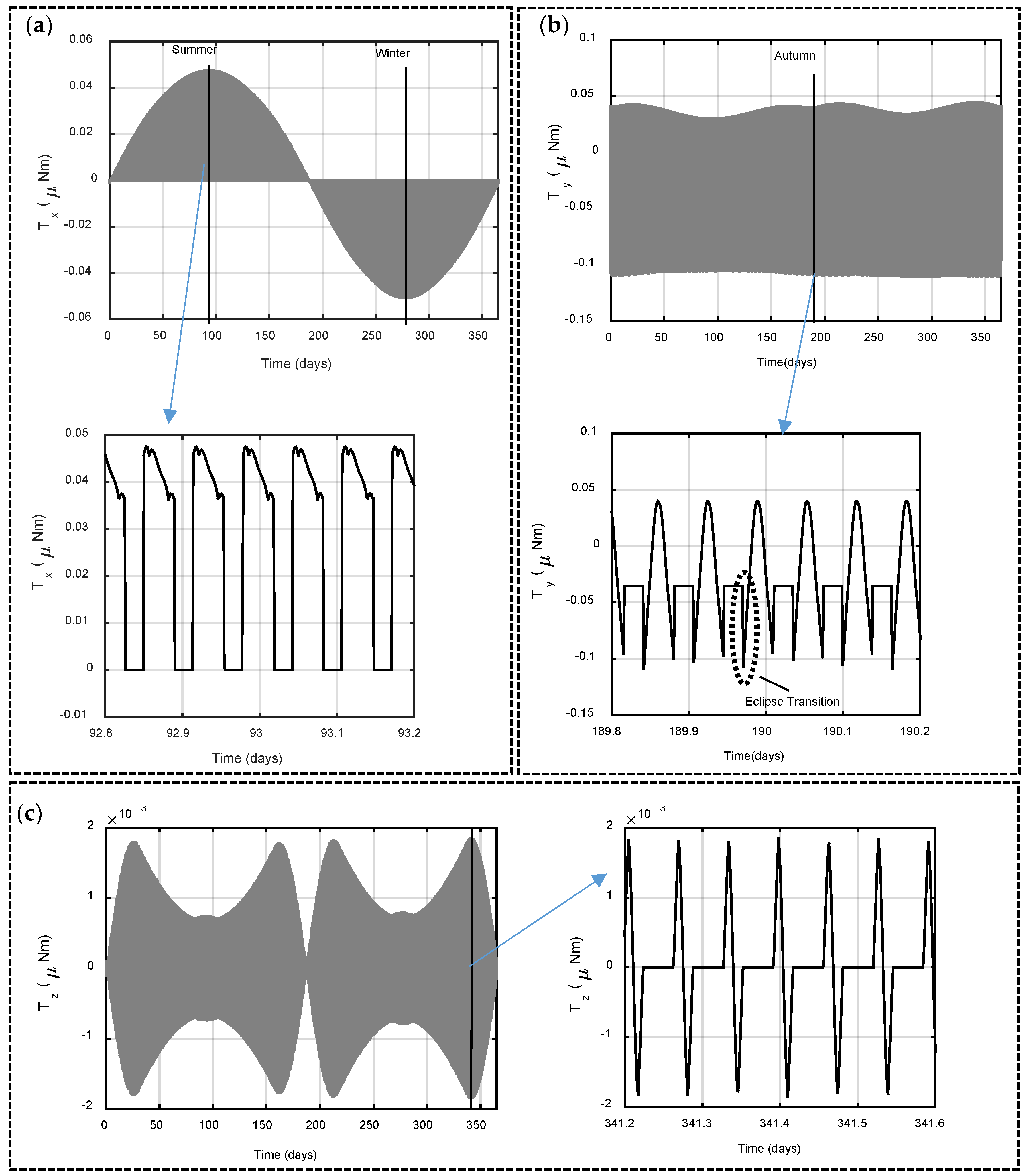
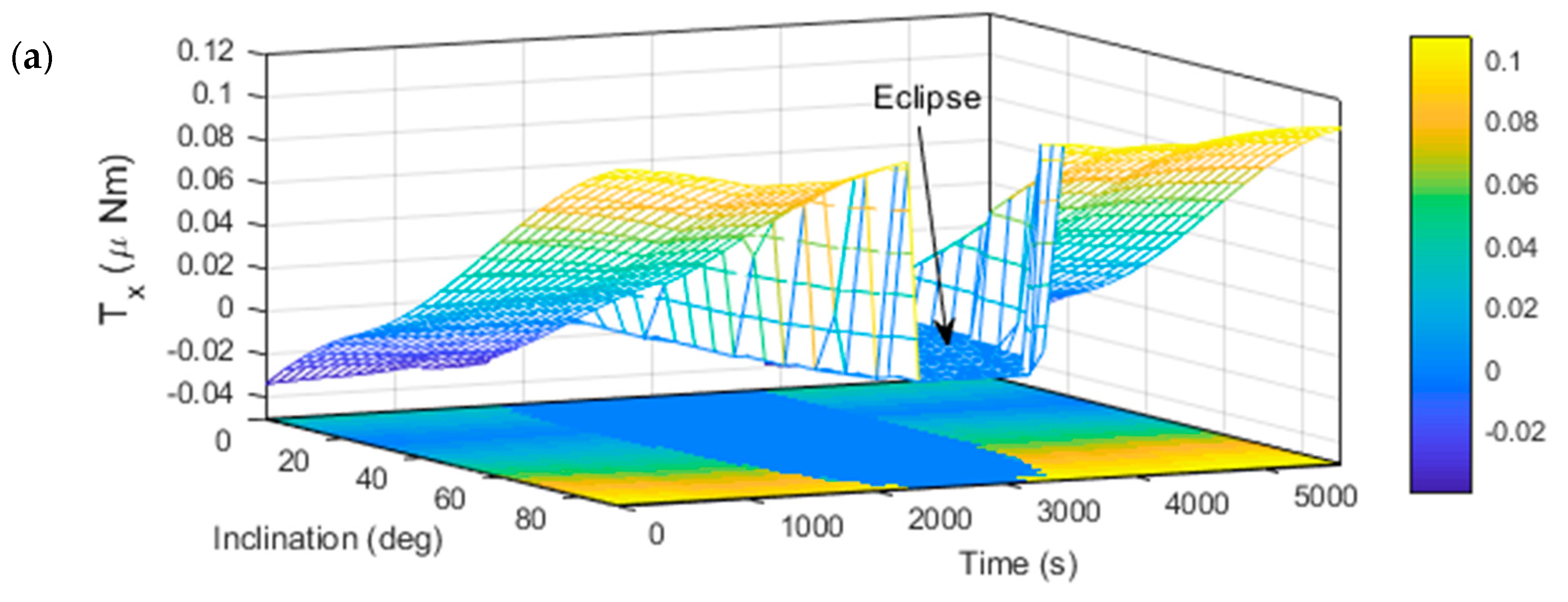
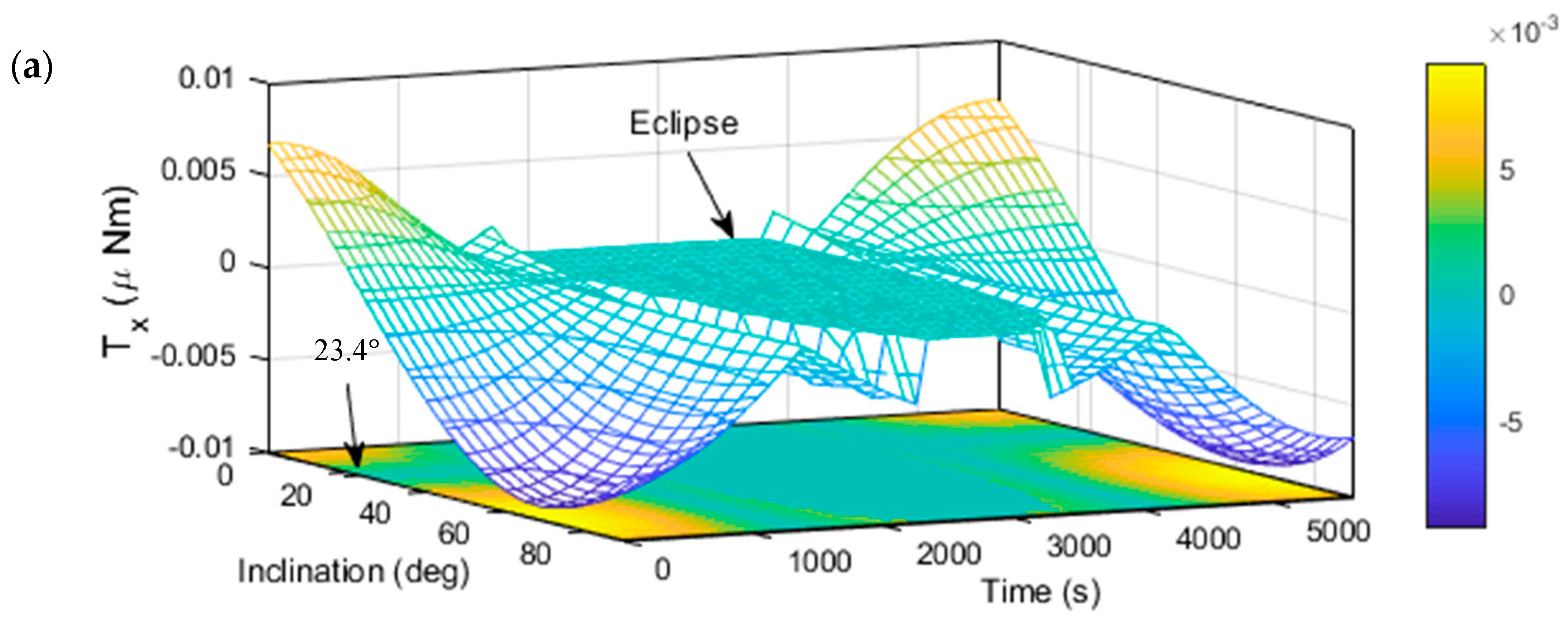
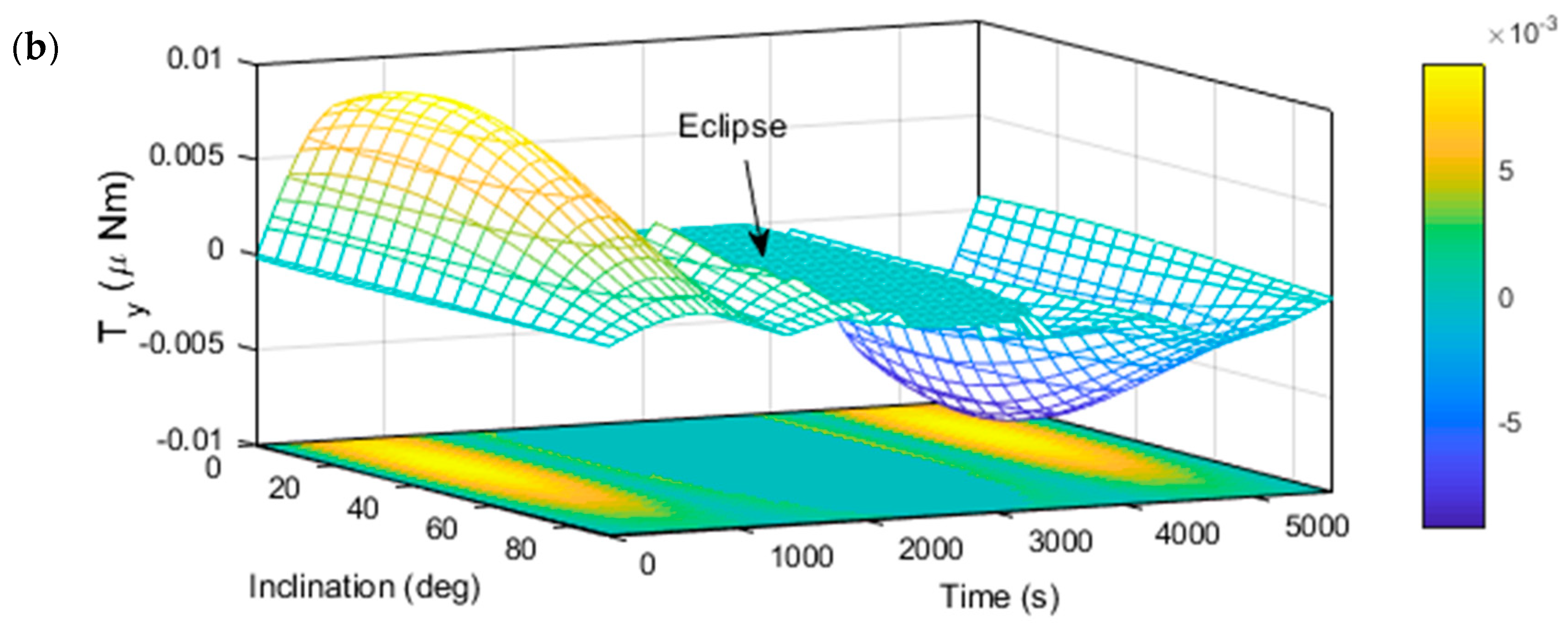
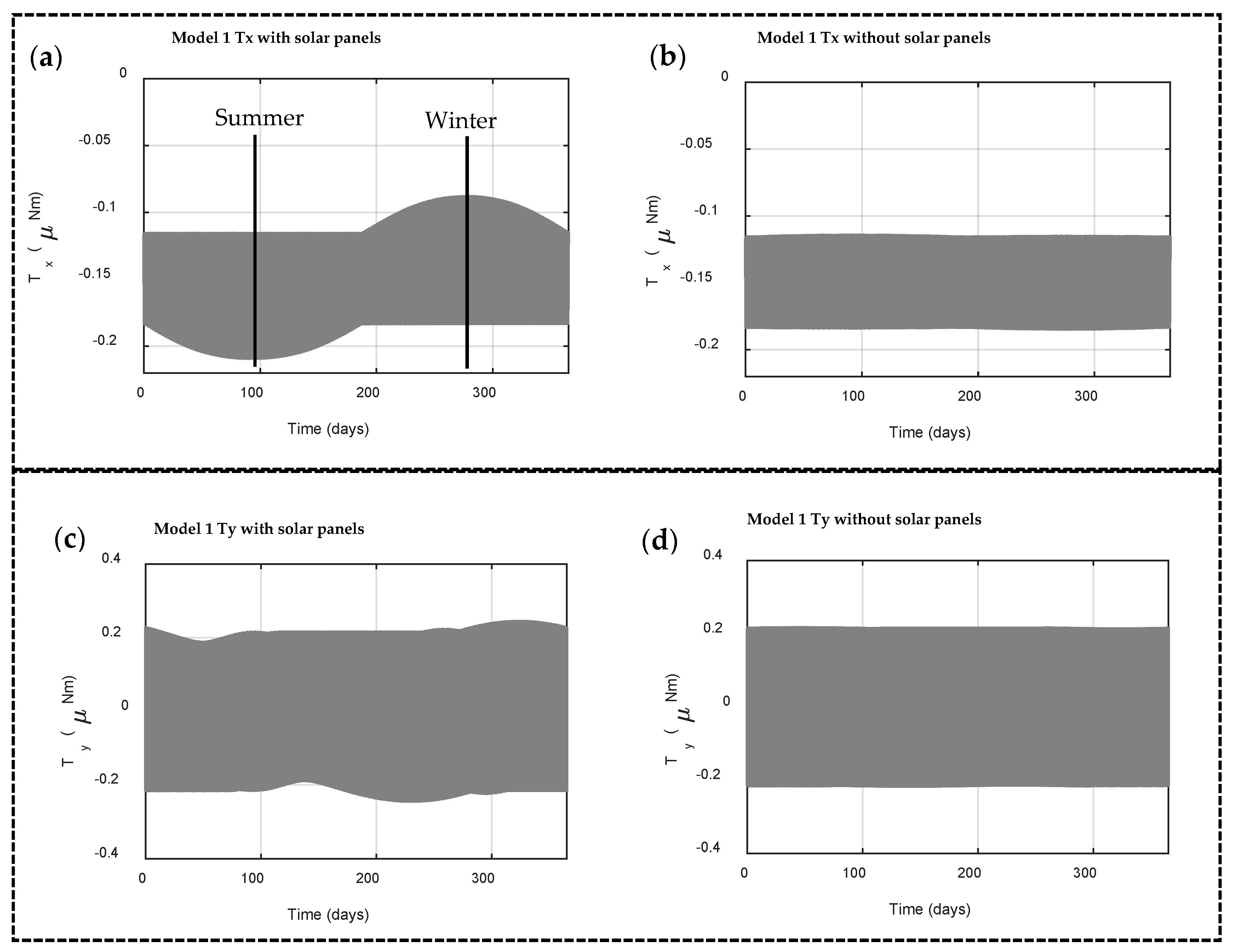
5.1. Solar Radiation Torque on Model 1
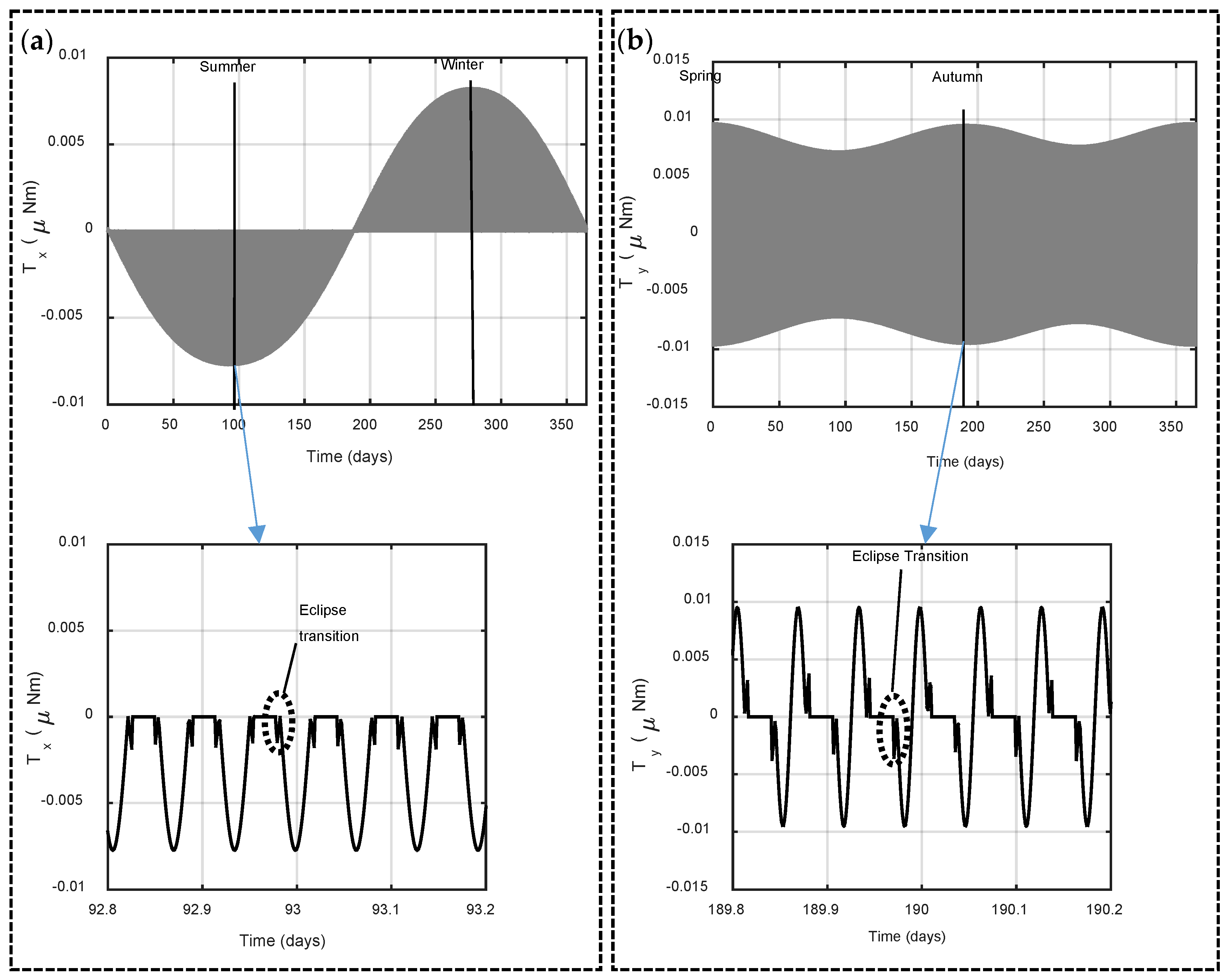
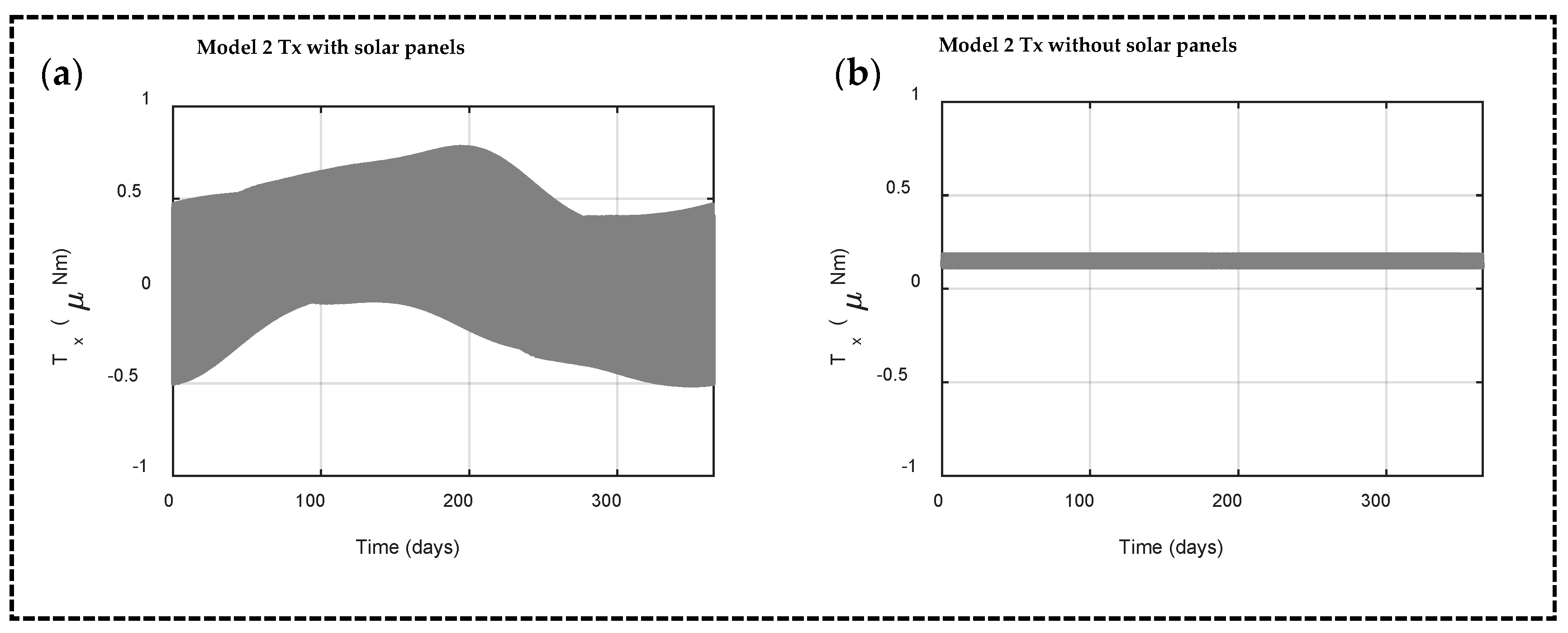
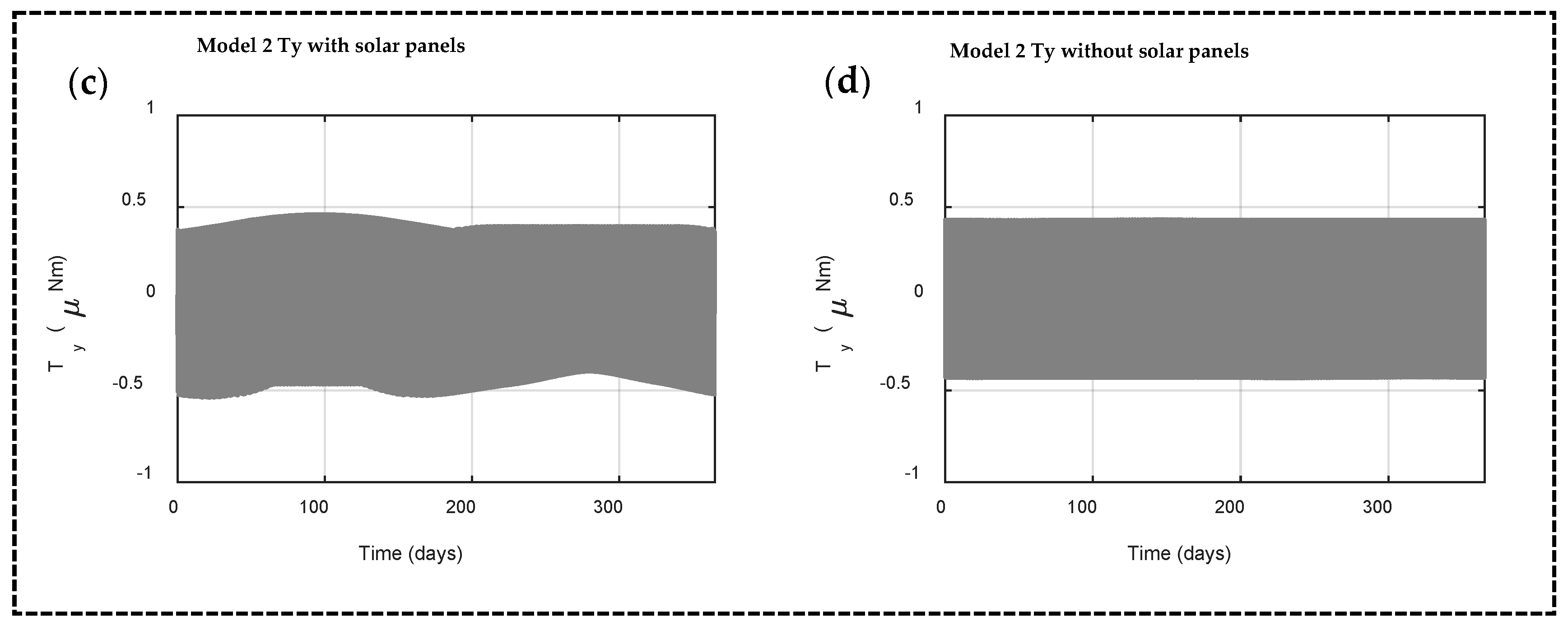
5.2. Solar Radiation Torque in Model 2
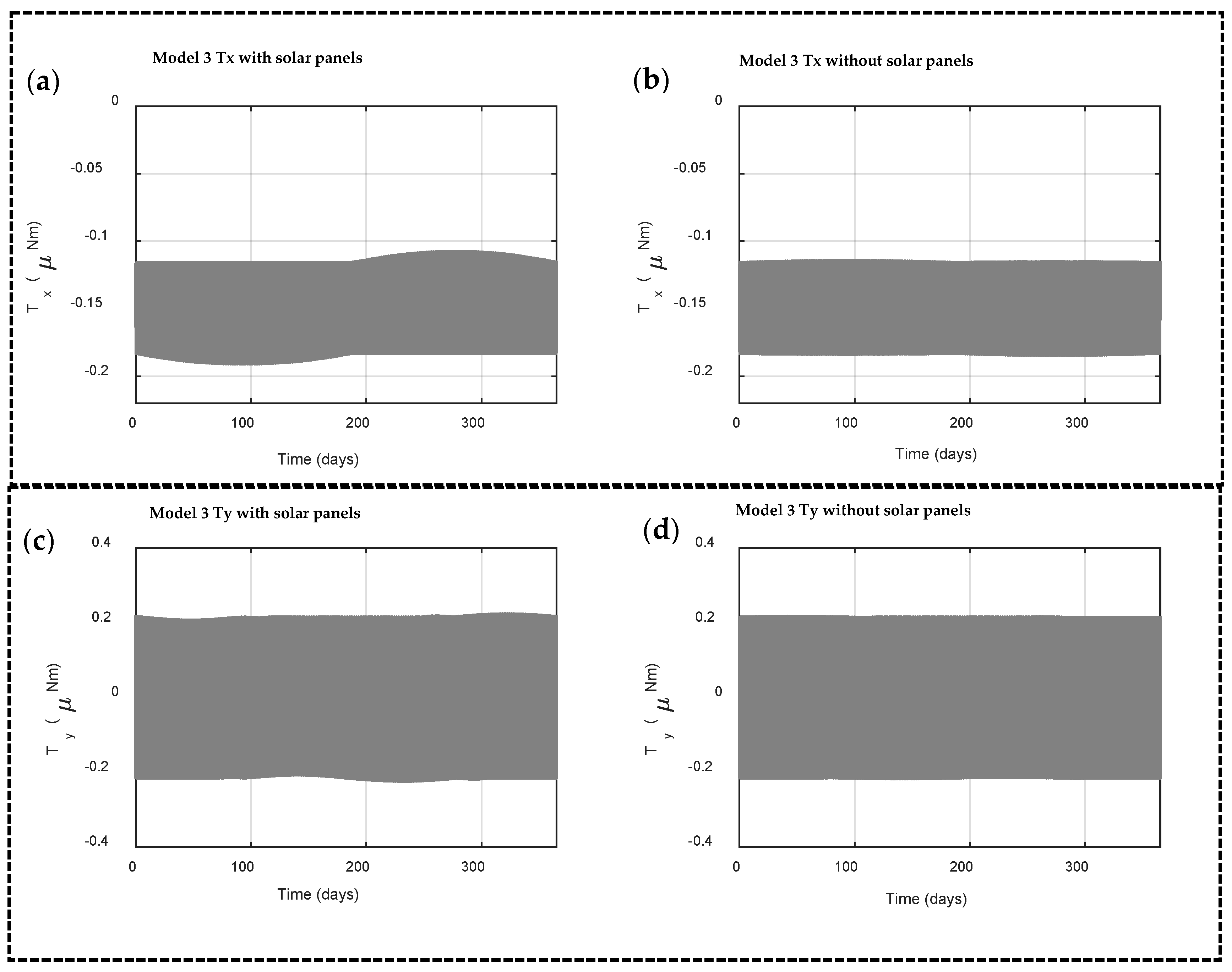
5.3. Solar Radiation Torque in Model 3
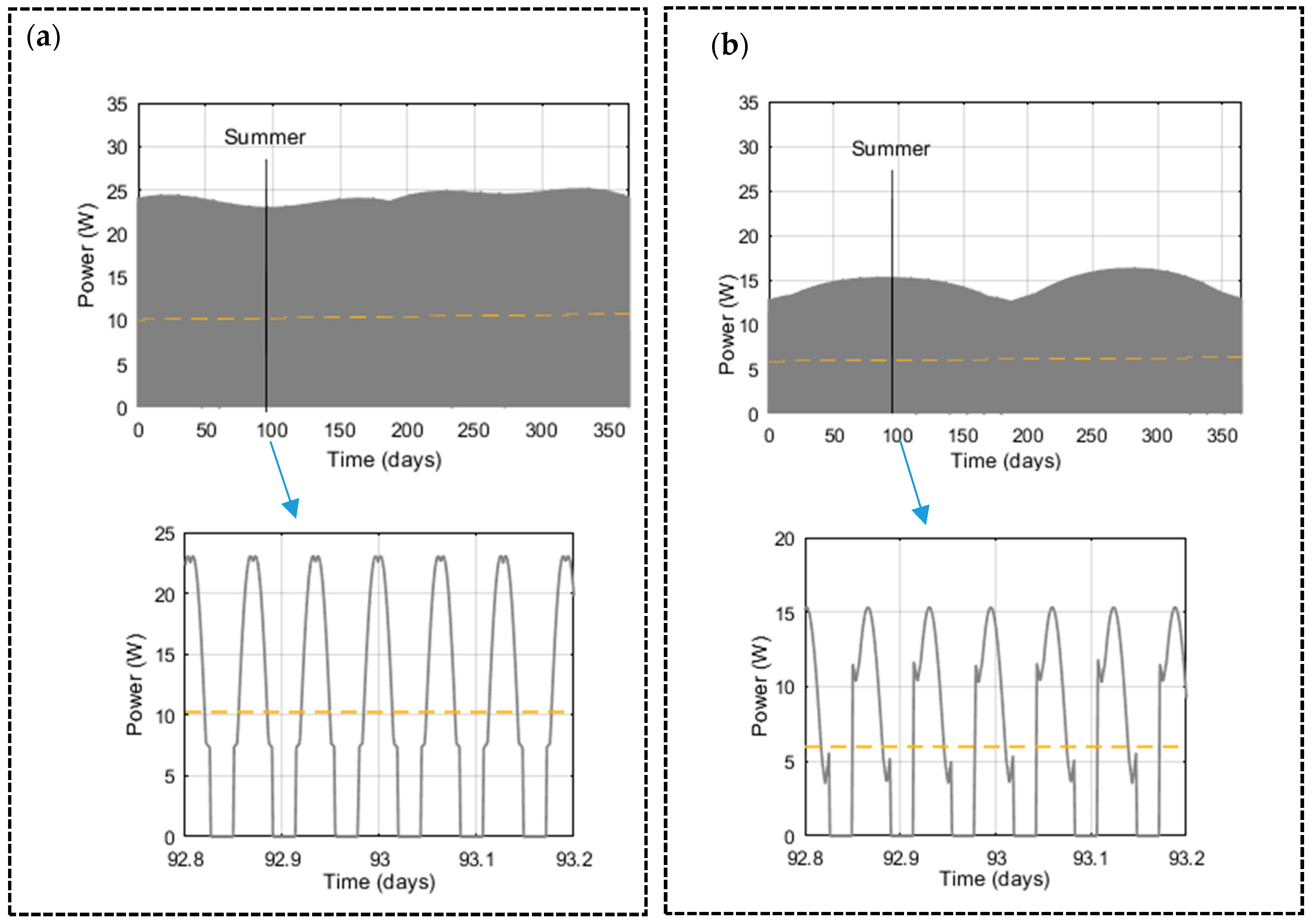
5.4. Solar Power Generation
5.5. Discussion—Effects of Adding Deployable Solar Panels on the Overall Disturbances
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meyer, R.X. Elements of Space Technology for Aerospace Engineers; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ubbels, W.J.; Bonnema, A.K. Delfi-C3: A student nanosatellite as a test-bed for thin film solar cells and wireless onboard communication. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Recent Advances in Space Technologies, Istanbul, Turkey, 9–11 June 2005; pp. 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Santoni, F.; Piergentili, F.; Donati, S.; Perelli, M.; Negri, A.; Marino, M. An innovative deployable solar panel system for Cubesats. Acta Astronaut. 2014, 95, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertat, I.; Vobornik, A. Efficient and reliable solar panels for small CubeSat picosatellites. Int. J. Photoenergy 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.; Cutler, J.W.; Mancewicz, J.; Ridley, A.J. Maximizing photovoltaic power generation of a space-dart configured satellite. Acta Astronaut. 2015, 111, 283–299. [Google Scholar]
- Rawashdeh, S.A.; Lumpp, J.E. Aerodynamic stability for CubeSats at ISS orbit. J. Small Satell. 2013, 2, 85–104. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, J.; Casey, C.; Creamer, G.; Dutchover, G. Pointing control for low altitude triple CubeSat space darts. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual AIAA/USU Conference Small Satellite, Logan, UT, USA, 10–13 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ve, I.; Hrouda, J.; Hofman, J. Spectrolab Triangular Solar Cell Evaluation for Usage in PilsenCUBE Picosatellite. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Applied Electronics, Pilsen, Czech Republic, 8–9 September 2010; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Horváth, G.; Czifra, D.; Marosy, G.; Várhegyi, Z. Thermal design and characterization of solar cell arrays aimed to be used in CubeSat missions. In Proceedings of the 18th International Workshop on Thermal Investigation ICs Systems, Budapest, Hungary, 25–27 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Swartwout, M. The first one hundred CubeSats: A statistical look. J. Small Satell. 2013, 2, 213–233. [Google Scholar]
- Paluszek, M.; Bhatta, P.; Griesemer, P.; Mueller, J.; Thomas, S. Spacecraft Attitude and Orbit Control Volume 1: A Systems Approach, 3rd ed.; Princeton Satellite Systems: Plainsboro Township, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wertz, J. Spacecraft Attitude Determination and Control; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Springmann, J.; Cutler, J.; Bahcivan, H. Magnetic Sensor Calibration and Residual Dipole Characterization for Application to Nanosatellites. In Proceedings of the AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialists Conference Guidance Navigation Control, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2–5 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pumpkin Inc. CubeSat Kit—In Space. 2018. Available online: http://www.cubesatkit.com/content/space.html (accessed on 13 December 2018).
- Innovative Solutions in Space, ISIS CubeSat Solar Panels. 2018. Available online: https://www.isispace.nl/product/isis-cubesat-solar-panels/ (accessed on 20 October 2018).
- Clyde Space, Clyde Space Products. 2019. Available online: https://www.clyde.space/products (accessed on 21 January 2019).
- Sondecker, I.V.G.; La Tour, P.; Abramowitz, L. SENSE: The USAF SMC/XR NanoSatellite Program for Space Environmental Monitoring Capt. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual AIAA/USU Conference Small Satellite, Logan, UT, USA, 12–15 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigo, J.; Alarcon, C.; Kim, S.; Cho, M. Aoba VELOX-IV Attitude and Orbit Control System Design for a LEO Mission Applicable to a Future Lunar Mission. In Proceedings of the 67th International Astronautical Congress, Guadalajara, Mexico, 26–30 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Selva, D.; Krejci, D. A survey and assessment of the capabilities of Cubesats for Earth observation. Acta Astronaut. 2012, 74, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, A. The Sun’s position in the sky. Eur. J. Phys. 2013, 34, 633–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickman, S.L.; Ortiz Longo, C.R. Method for the Calculation of Spacecraft Umbra and Penumbra Shadow Terminator Points Method for the Calculation of Spacecraft Umbra and Penumbra Shadow Terminator Points. 1995. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/19950023025.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2019).
- Srivastava, V.K.; Yadav, S.M.; Kumar, J.; Kushvah, B.S. Earth conical shadow modeling for LEO satellite using reference frame transformation technique: A comparative study with existing earth conical shadow models. Astron. Comput. 2015, 9, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.N.; Bakry, A.; Selim, H.H.; Shehata, M.H. Eclipse intervals for satellites in circular orbit under the effects of Earth’s oblateness and solar radiation pressure. NRIAG J. Astron. Geophys. 2015, 4, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Princeton Satellite Systems, CubeSat Toolbox. 2018. Available online: http://www.psatellite.com/products/sct/cubesat-toolbox/ (accessed on 13 December 2018).
- Sidi, M.J. Spacecraft Dynamics and Control; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, J.D.; Thornton, E.A. Thermally induced attitude dynamics of a spacecraft with a flexible appendage. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 1998, 21, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yan, S. Thermally induced vibration of composite solar array with honeycomb panels in low earth orbit. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 71, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.A.; Yamaguchi, E. Thermally induced dynamics of deployable solar panels of nanosatellite. Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JAXA, JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (J-SSOD). 2018. Available online: http://iss.jaxa.jp/en/kiboexp/jssod/ (accessed on 21 December 2018).
- Crusan, J.; Galica, C. NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative: Enabling broad access to space. Acta Astronaut. 2019, 157, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Semi major axis (a) | 408 km |
| Orbit inclination (i) | 51.64° |
| Initial right ascension of the ascending node (RAAN) | 0° |
| Argument of perigee (ω) | 0° |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0 |
| Initial mean anomaly (M) | 0° |
| Initial Julian date | 2,458,563 |
| Item | Specification | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Center of mass (x, y, z) | (0, 0, 0) | |
| All three models | Residual dipole (x, y, z) | (0, 0, 0.002 Am2) |
| Solar cell surface properties [24] | Absorbed () | 0.75 |
| Diffuse () | 0.08 | |
| Specular () | 0.17 | |
| Radiator surface properties [24] | Absorbed () | 0.15 |
| Diffuse () | 0.16 | |
| Specular () | 0.69 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Solar flux (S) | 1367 Wm−2 |
| Earth radiation | 400 Wm−2 |
| Albedo factor (aF) | 0.33 |
| Atmospheric density () | 3.725 × 10−12 |
| Drag coefficient ( | 2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, S.A.; Yamaguchi, E. Comparison of Solar Radiation Torque and Power Generation of Deployable Solar Panel Configurations on Nanosatellites. Aerospace 2019, 6, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace6050050
Ibrahim SA, Yamaguchi E. Comparison of Solar Radiation Torque and Power Generation of Deployable Solar Panel Configurations on Nanosatellites. Aerospace. 2019; 6(5):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace6050050
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Syahrim Azhan, and Eiki Yamaguchi. 2019. "Comparison of Solar Radiation Torque and Power Generation of Deployable Solar Panel Configurations on Nanosatellites" Aerospace 6, no. 5: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace6050050
APA StyleIbrahim, S. A., & Yamaguchi, E. (2019). Comparison of Solar Radiation Torque and Power Generation of Deployable Solar Panel Configurations on Nanosatellites. Aerospace, 6(5), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace6050050






