The Interactive Design Approach for Aerodynamic Shape Design Optimisation of the Aegis UAV
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
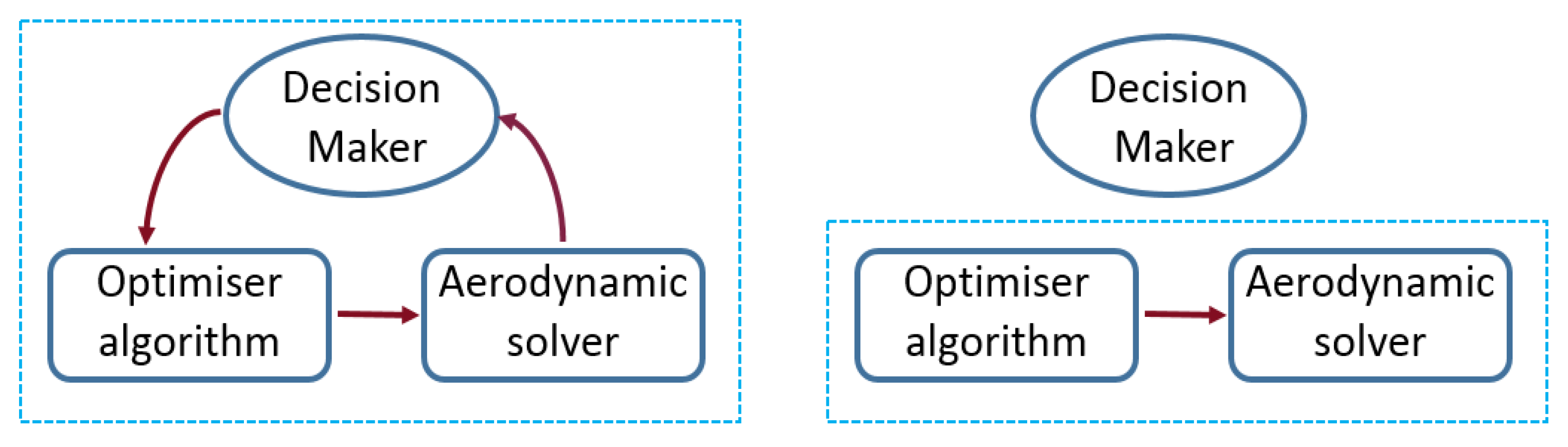
2.1. Interactive Optimisatin Framwork
2.1.1. Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimisation (MOPSO)
- When at most one point satisfying the constraints is found, a random particle is generated via a Gaussian distribution which is centred at the mid-point of the upper and lower boundaries with a standard deviation of about 10% of the separation between the upper and lower boundaries.
- When more than one point satisfying the constraints is found, but no other boundary limits have been set by the DM, a single value is chosen at random and a small turbulence value is applied to it.
- When more than one point satisfying the constraints is found and a specific boundary limit has been defined by the user, the value of the parameter is selected as determined by the convergence of the range:
- ∘
- If the selected range has less than 80% coverage by established points, a single point is randomly selected from within the largest gap.
- ∘
- If the selected range has more than 80% coverage by established points, an existing point is randomly chosen from within the range, and a small turbulence value applied to it.
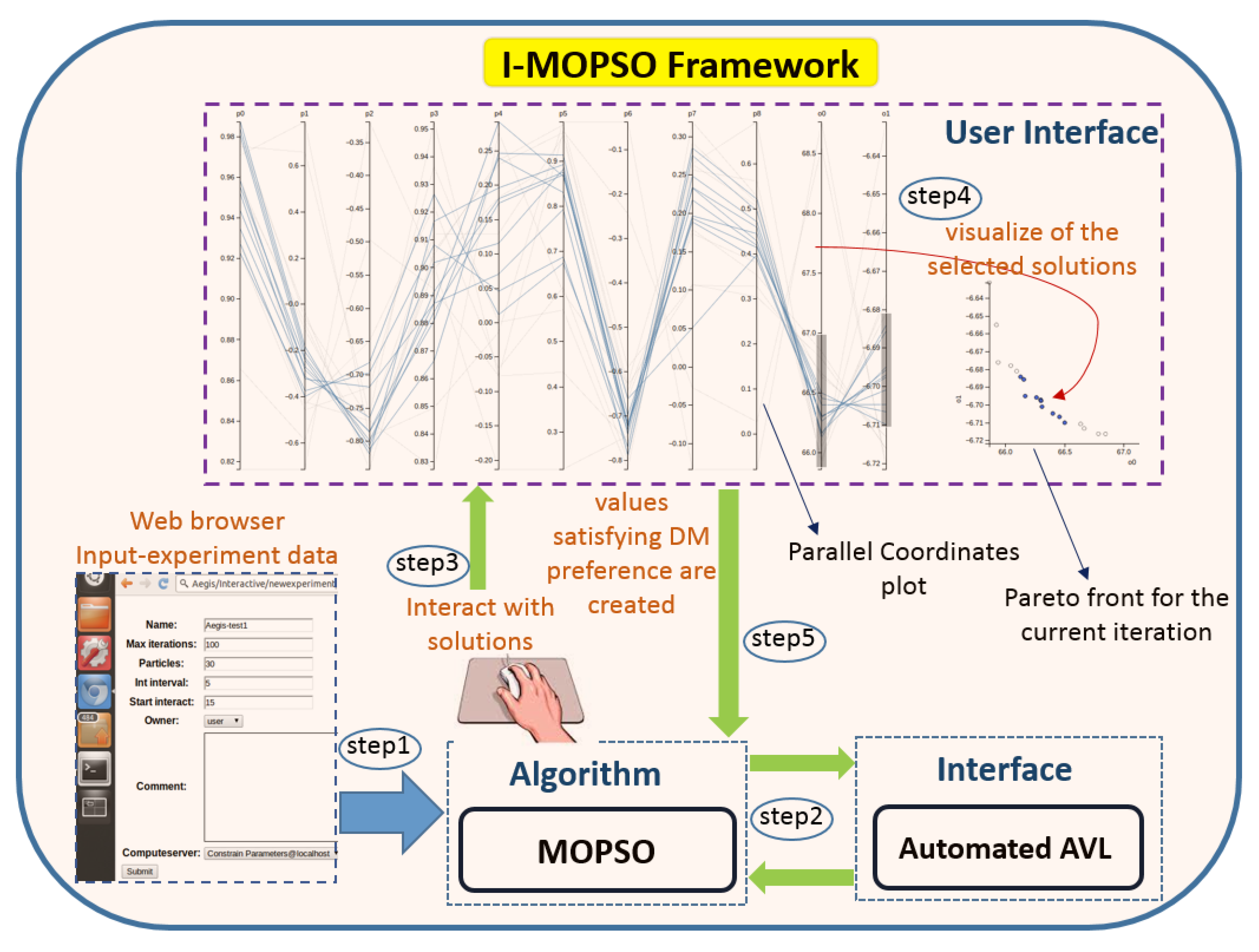
2.1.2. Particles Selection Schema on I-MOPSO Interface
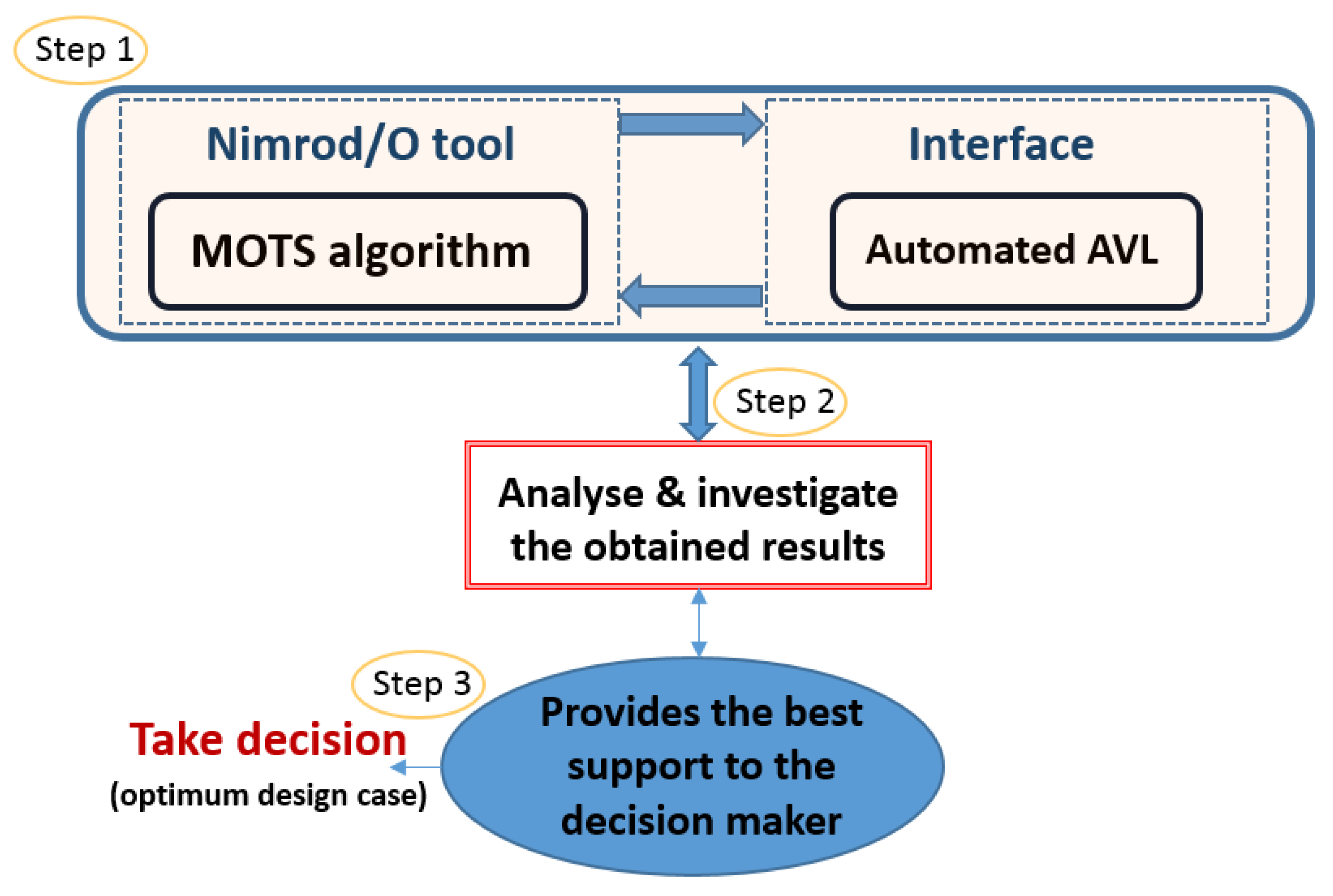
2.2. Automated Optimisation Framework (Non-Interactive)
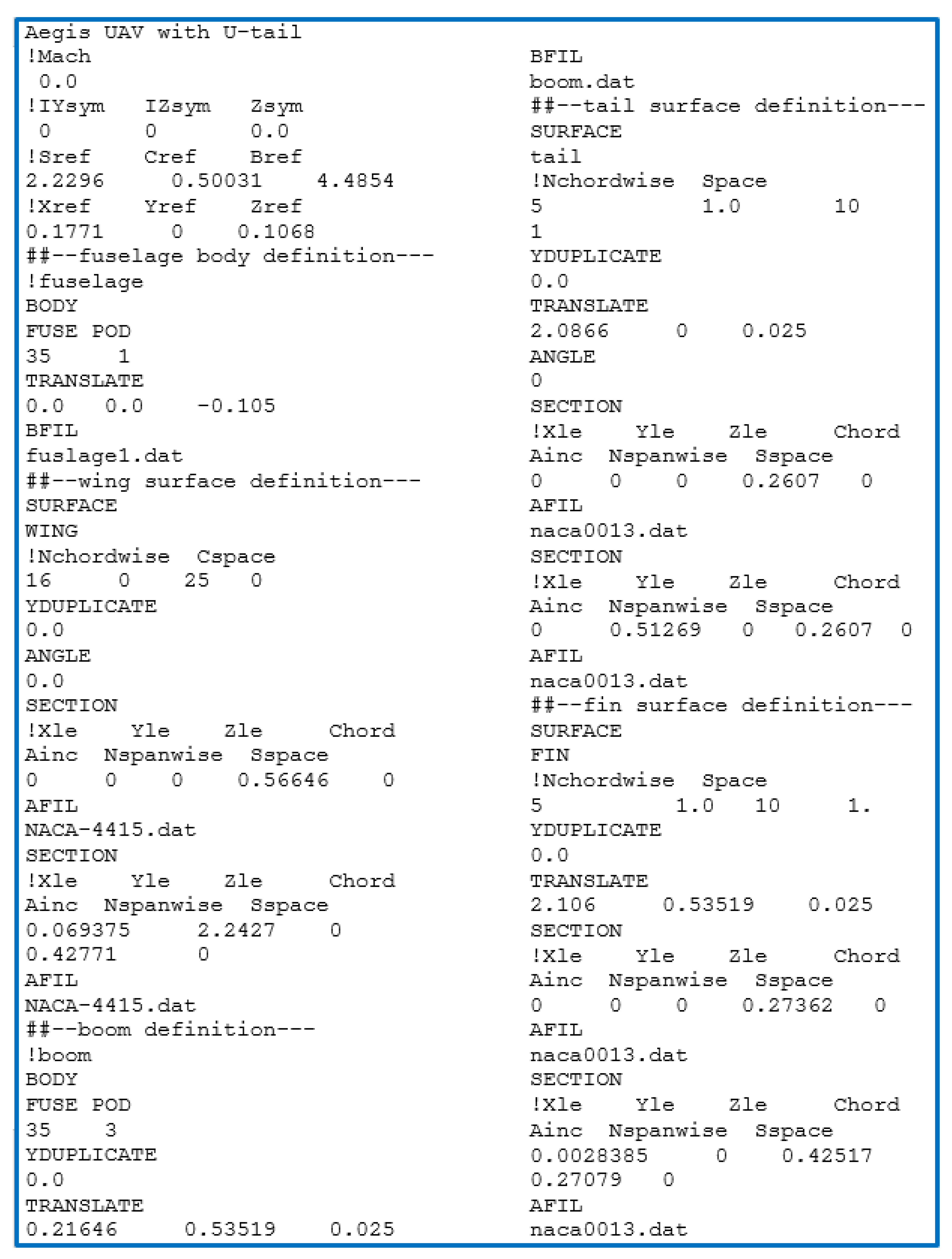
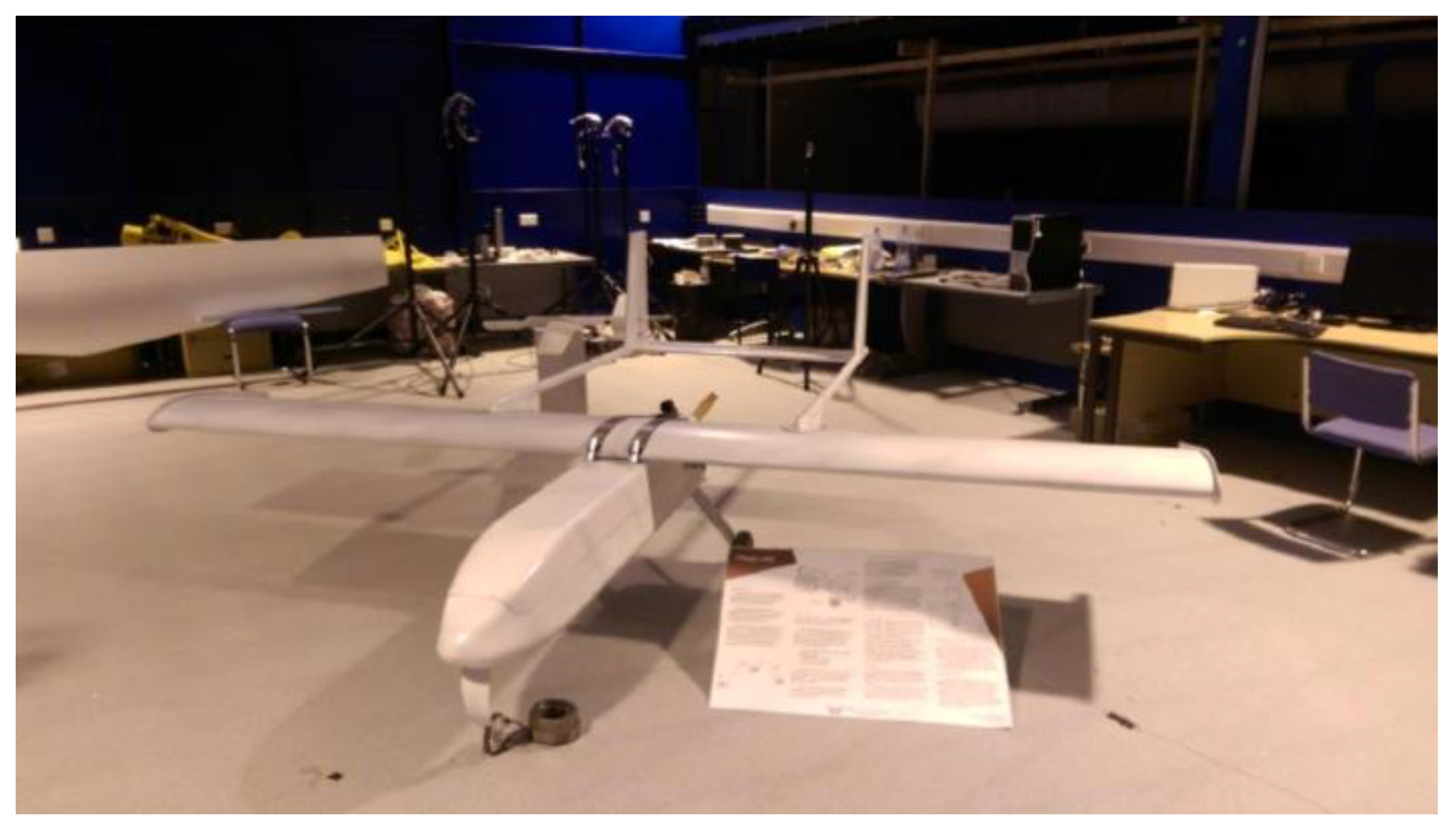
3. Description of Design Optimisation Case Study—Aegis UAV
The Architecture of the Design Problem
4. Formulation of the Non-Interactive Optimisation Problem
4.1. Using Wing Design Variables
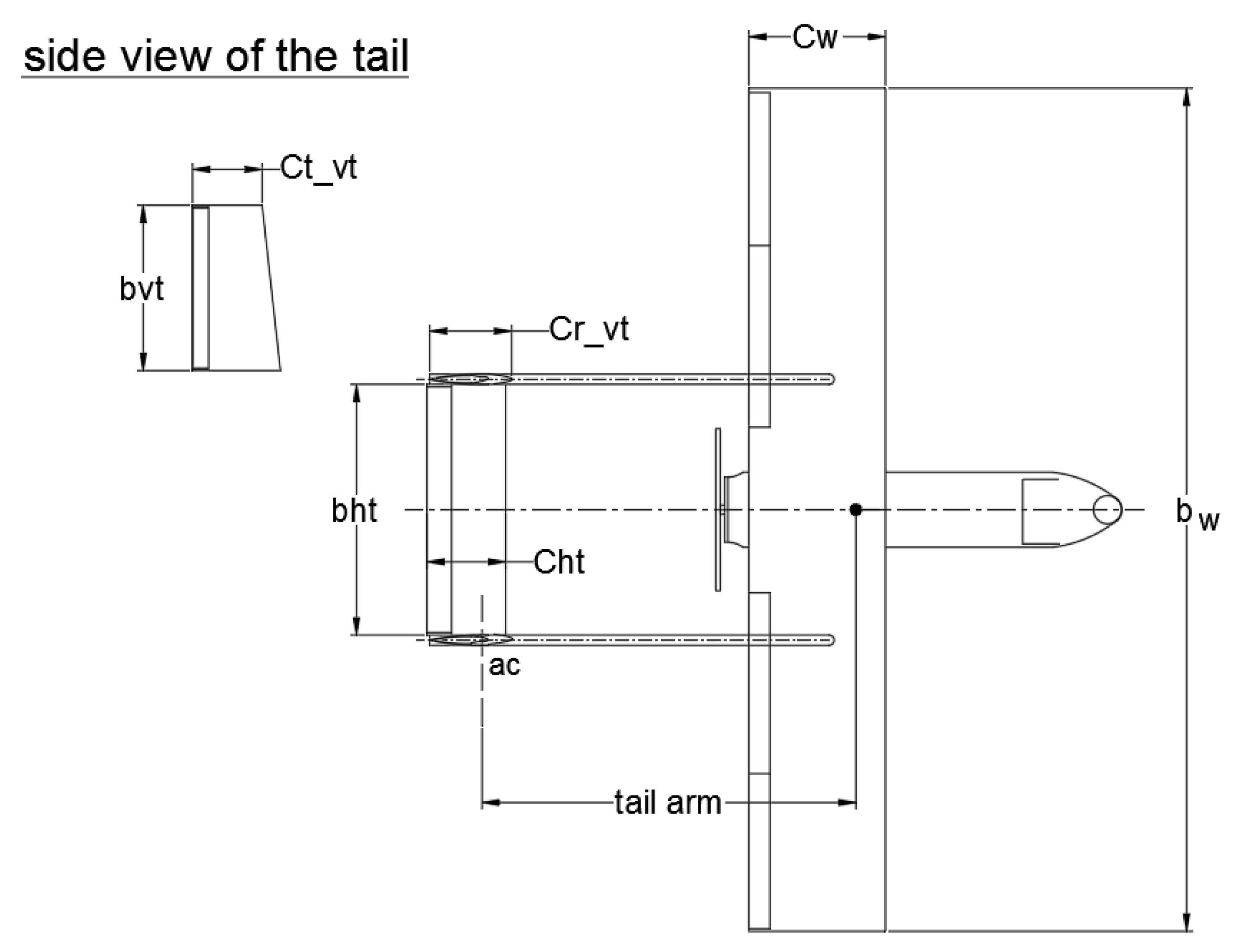
4.2. Using Wing and Tail Design Variables for Aegis UAV with U-tail Shape
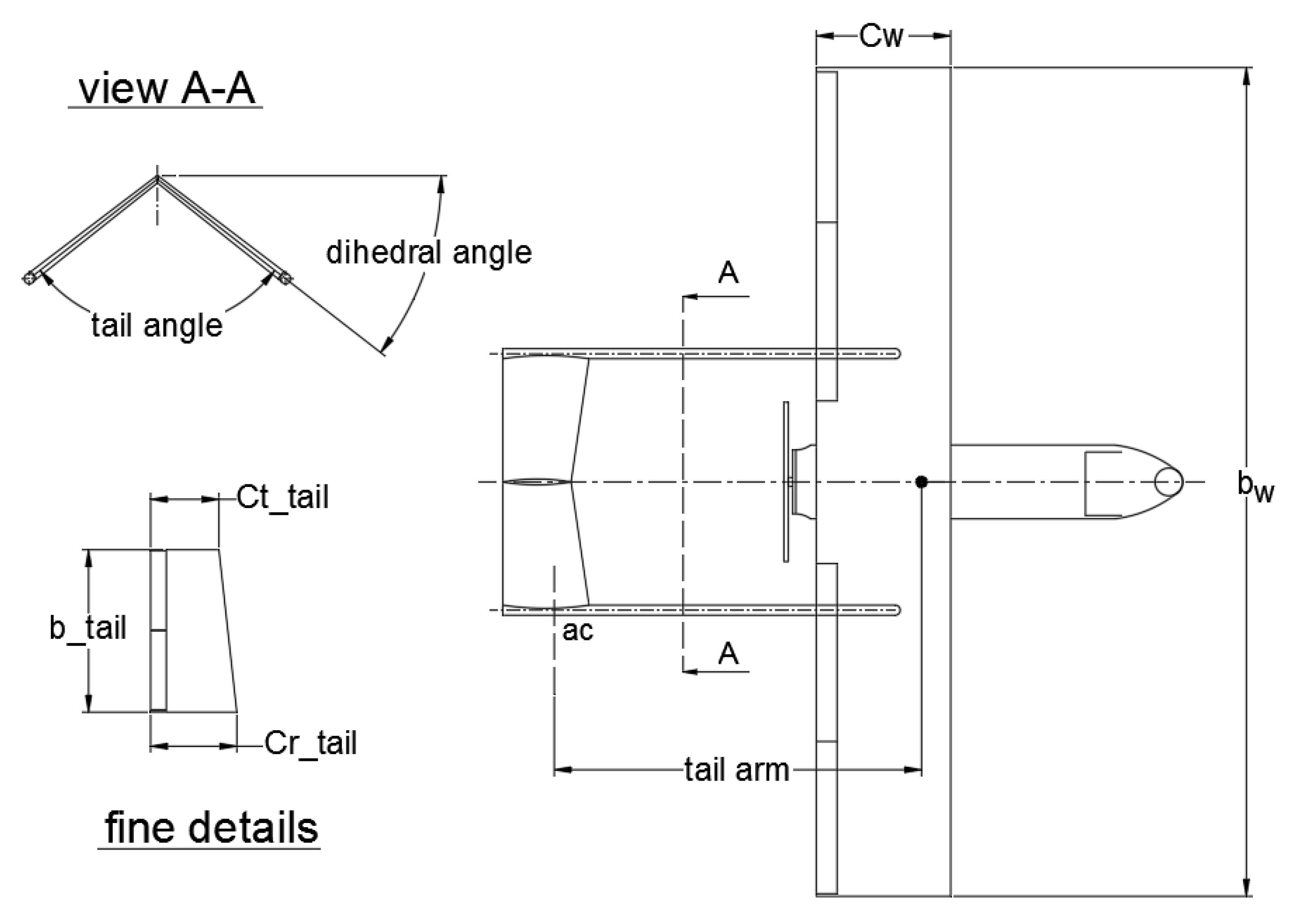
4.3. Using Wing and Tail Design Variables for Aegis UAV with Inverted V-tail Shape
5. Non-Interactive and Interactive Optimisation Process
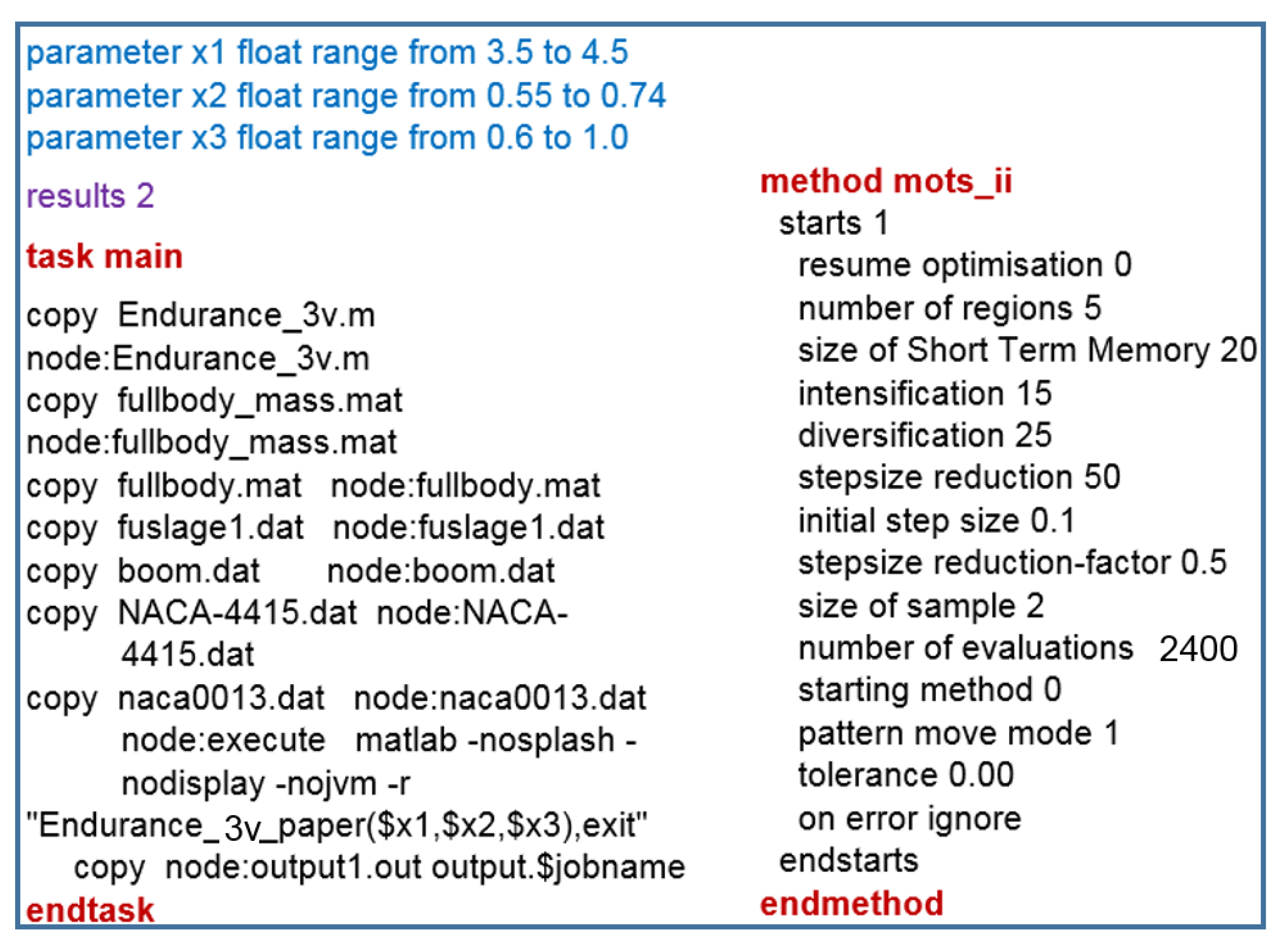
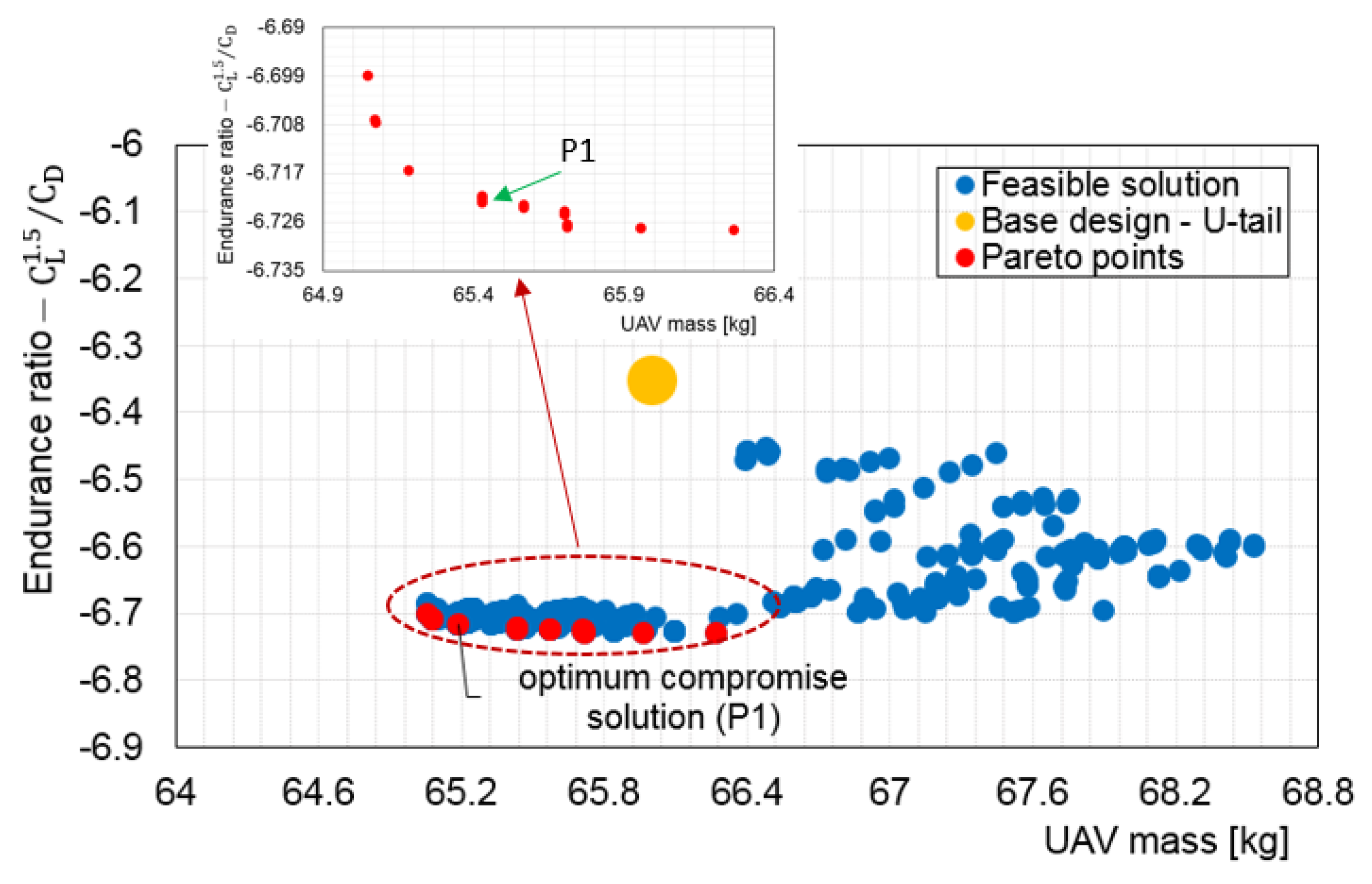
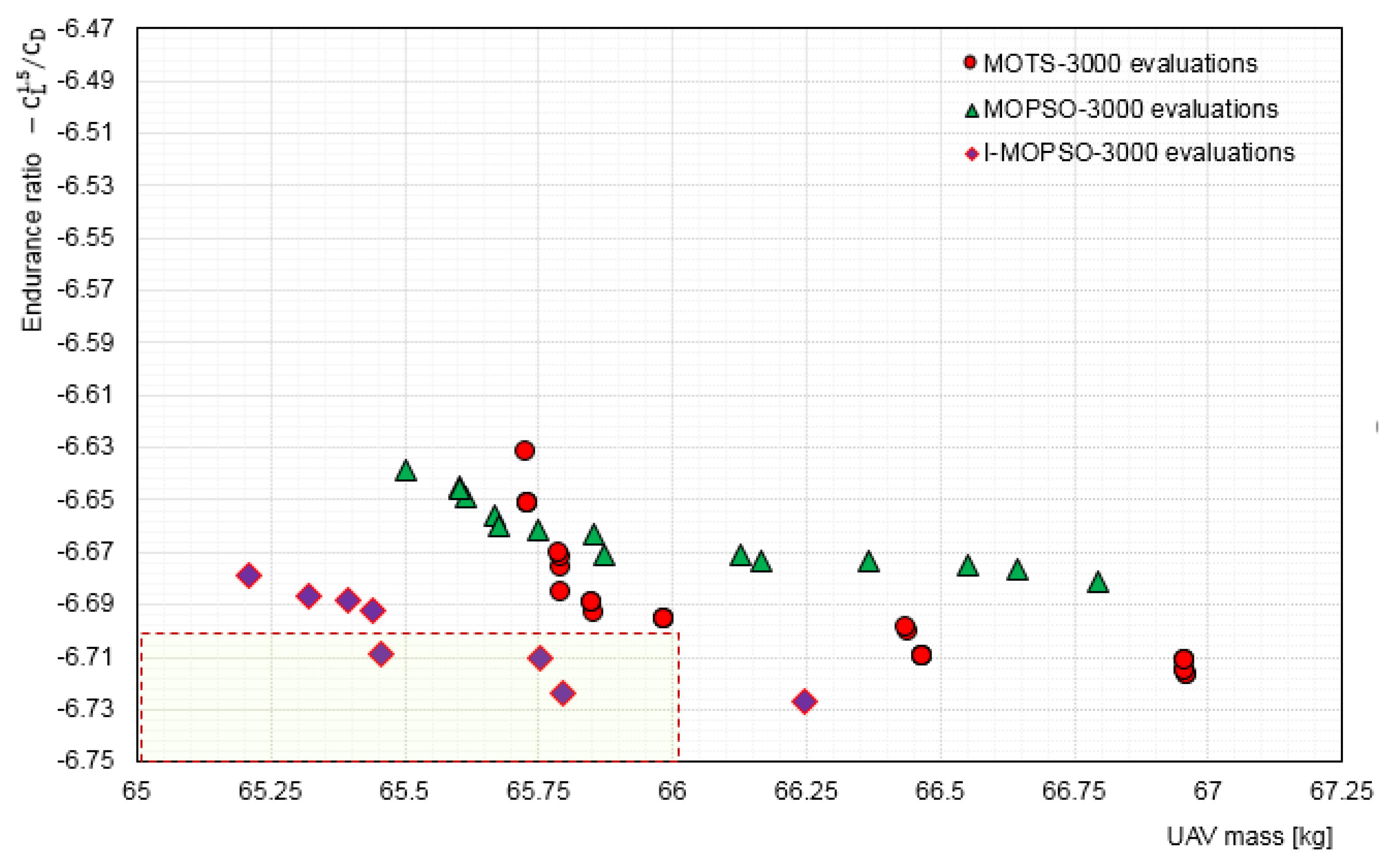
5.1. Non Interactive Optimisation (MOTS) Results and Discussion
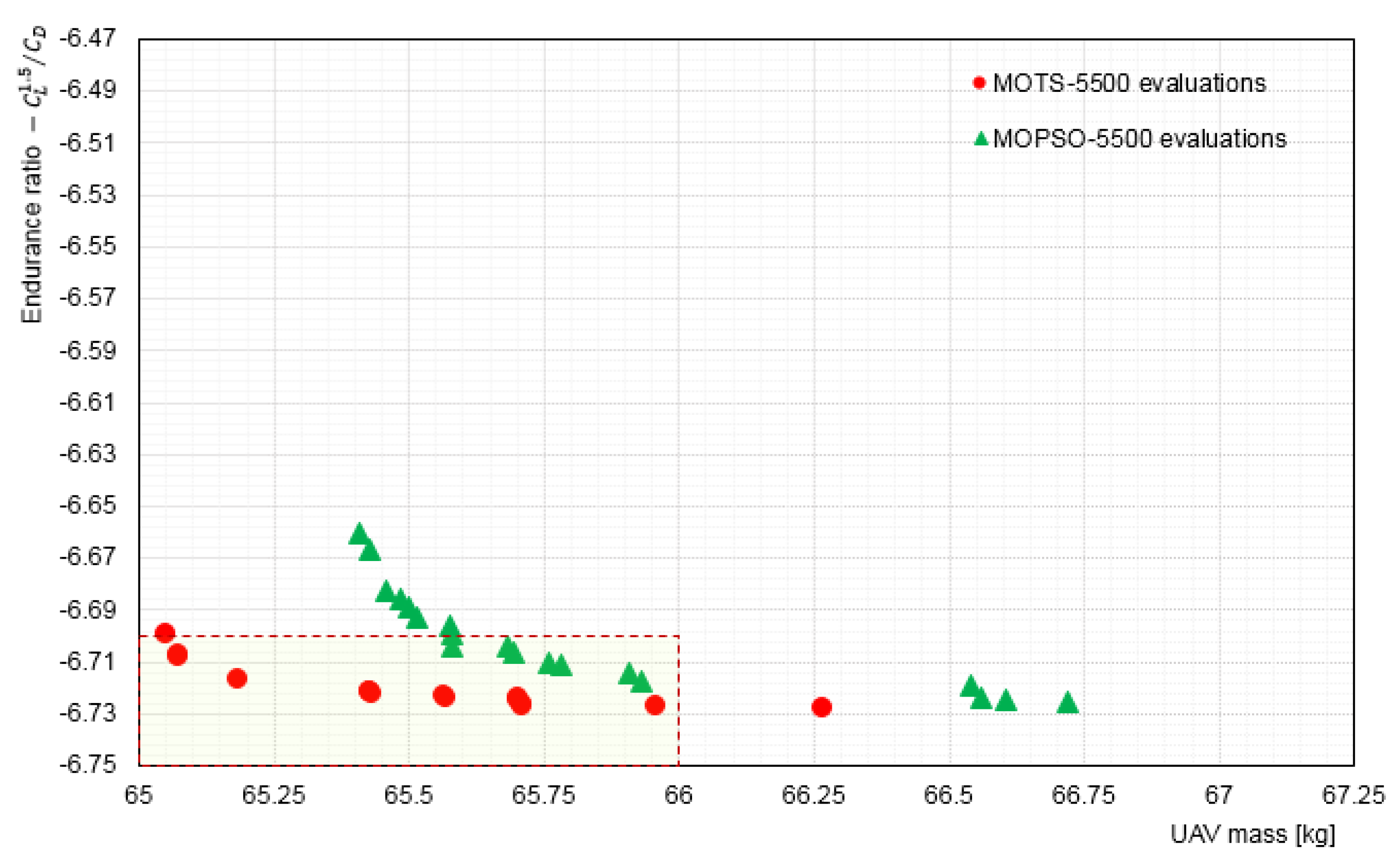
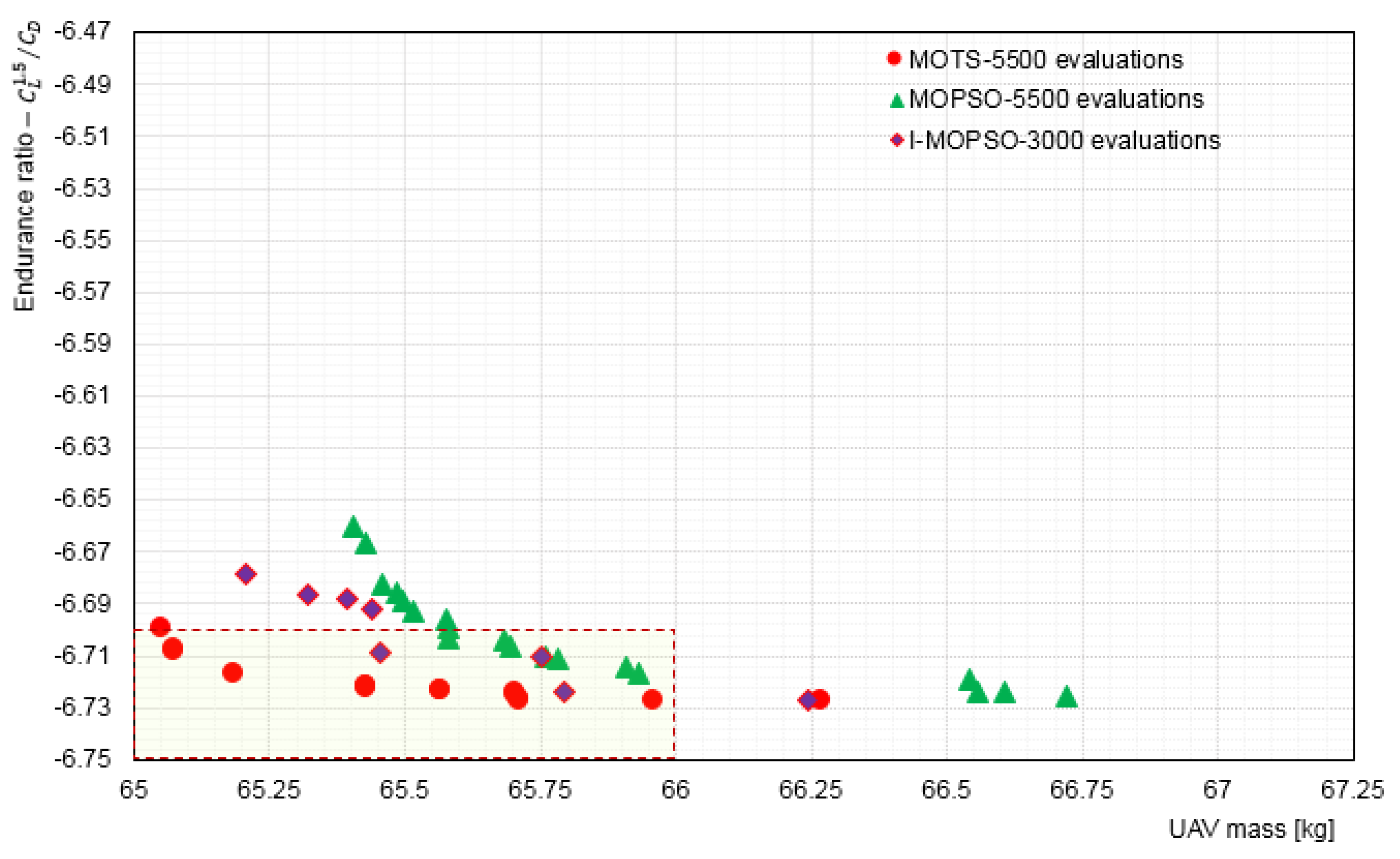
5.2. Problem Configuration of the Interactive Process
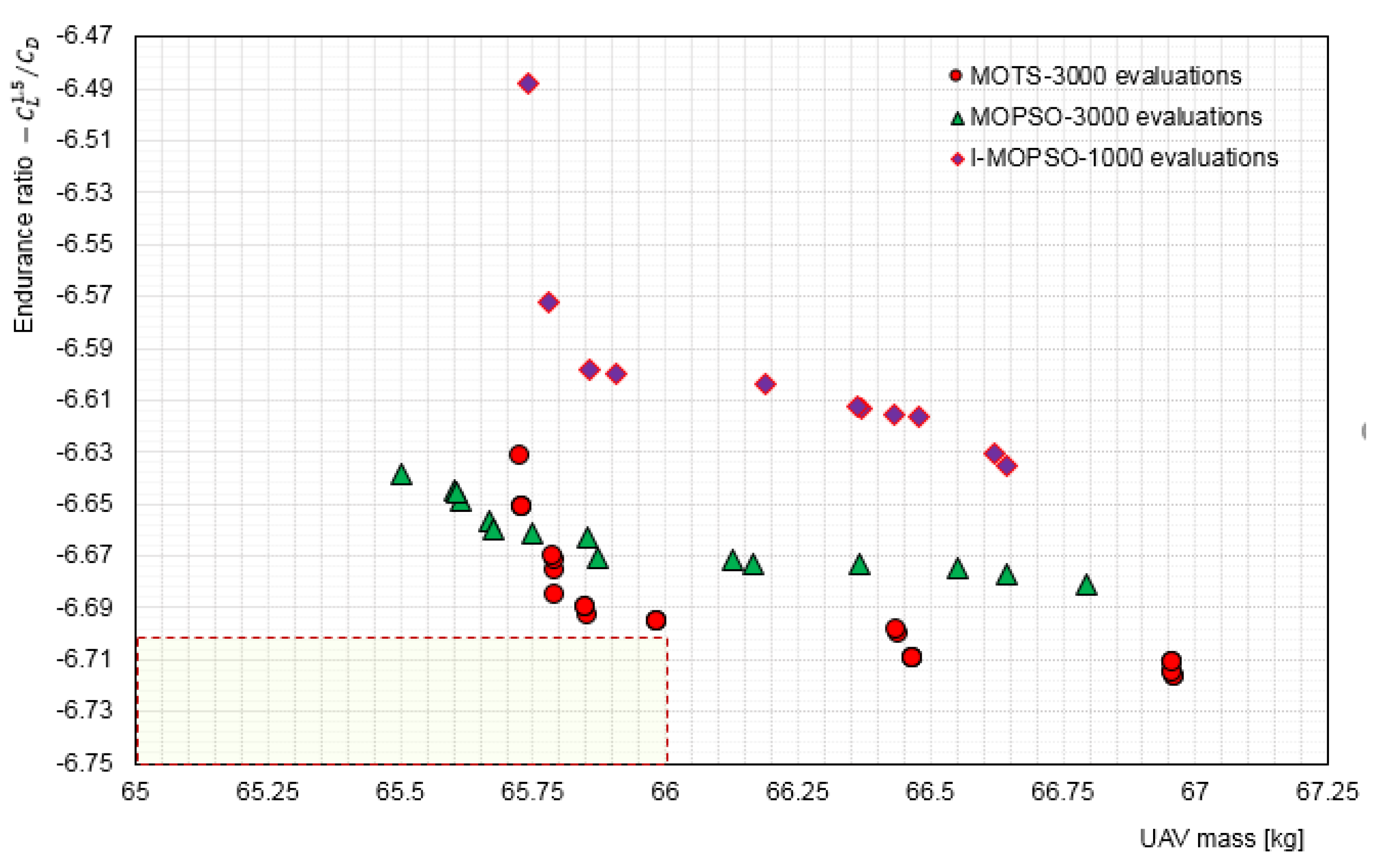
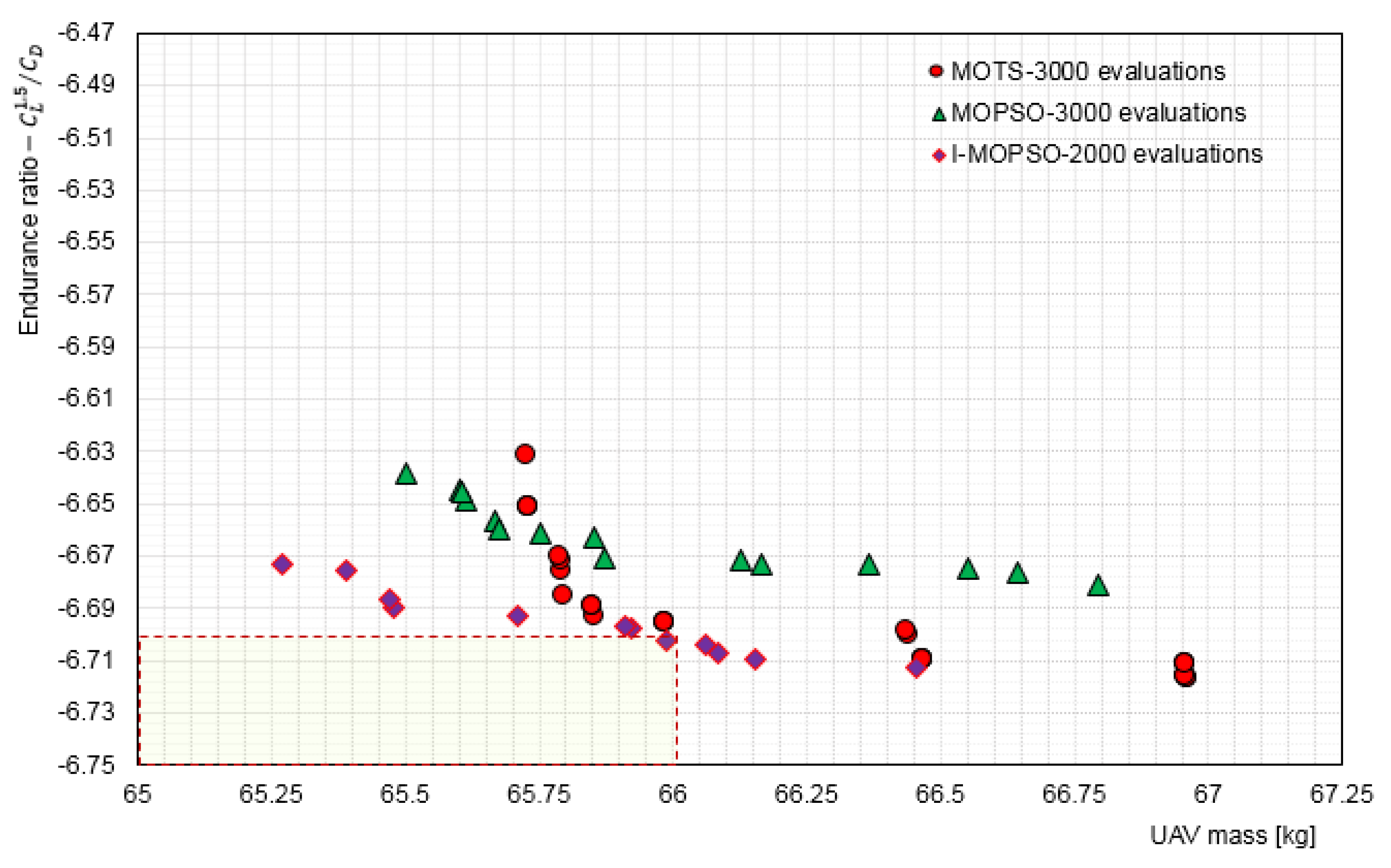
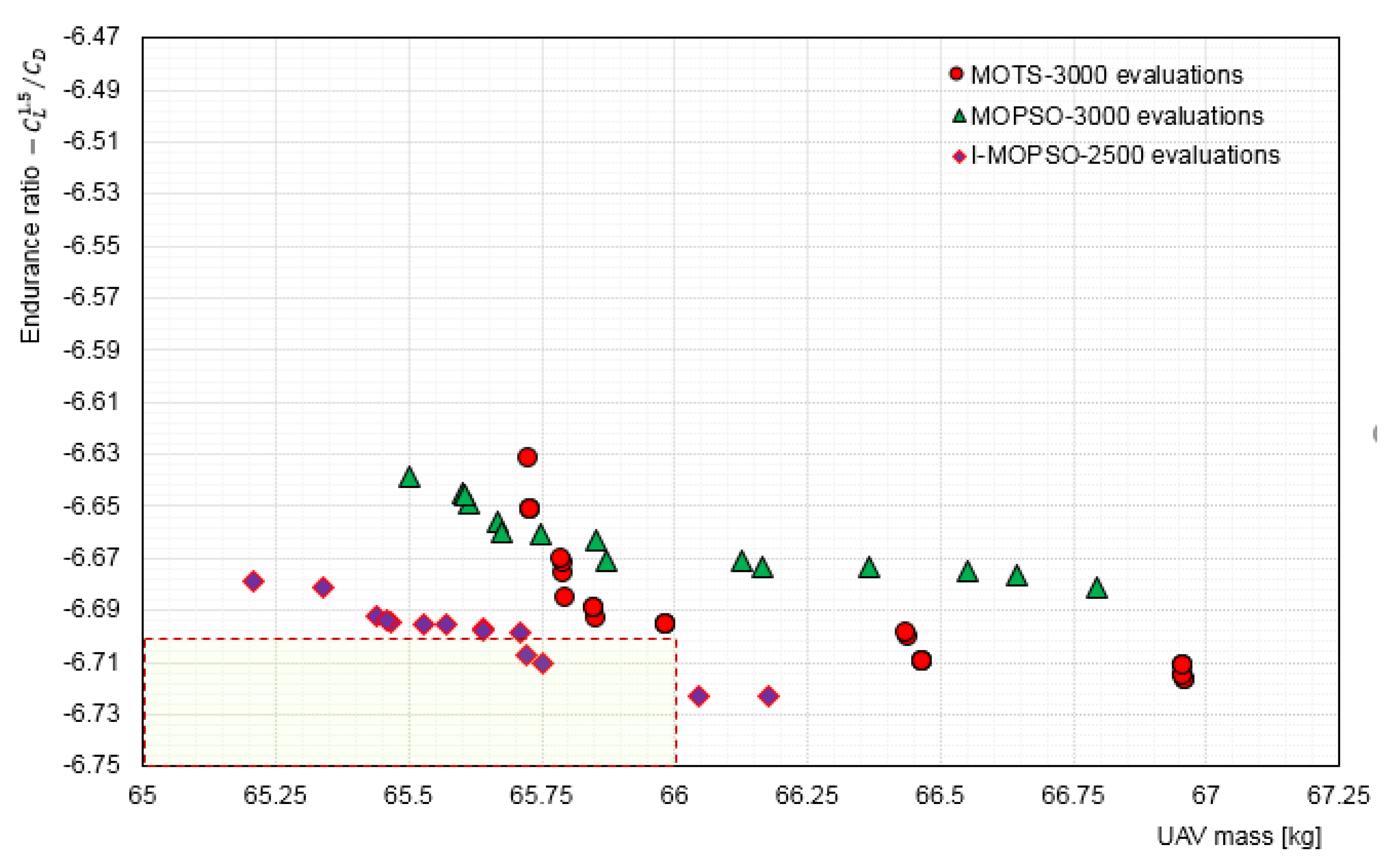
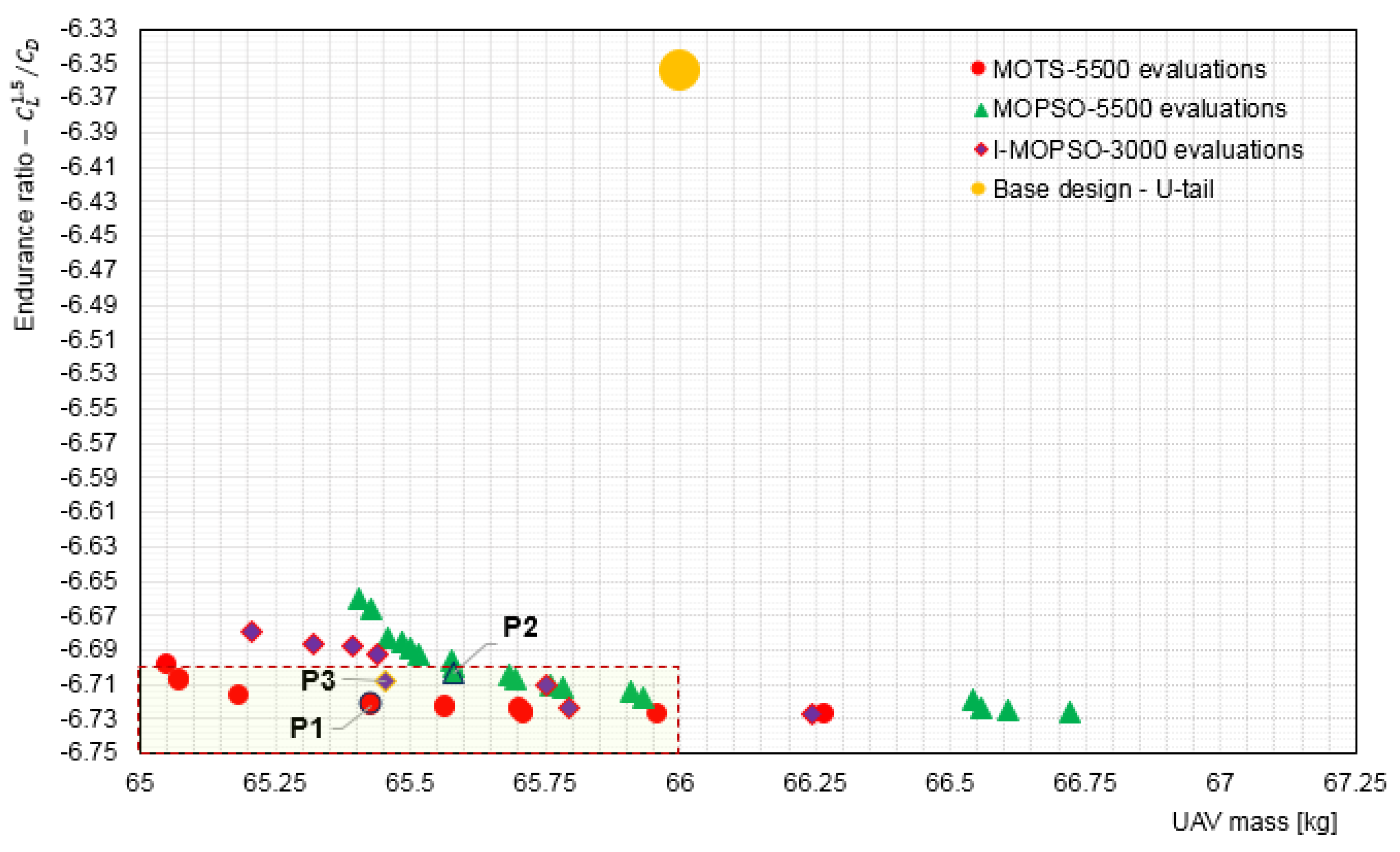
5.3. Interactive Optimisation (I-MOPSO) Results and Discussion
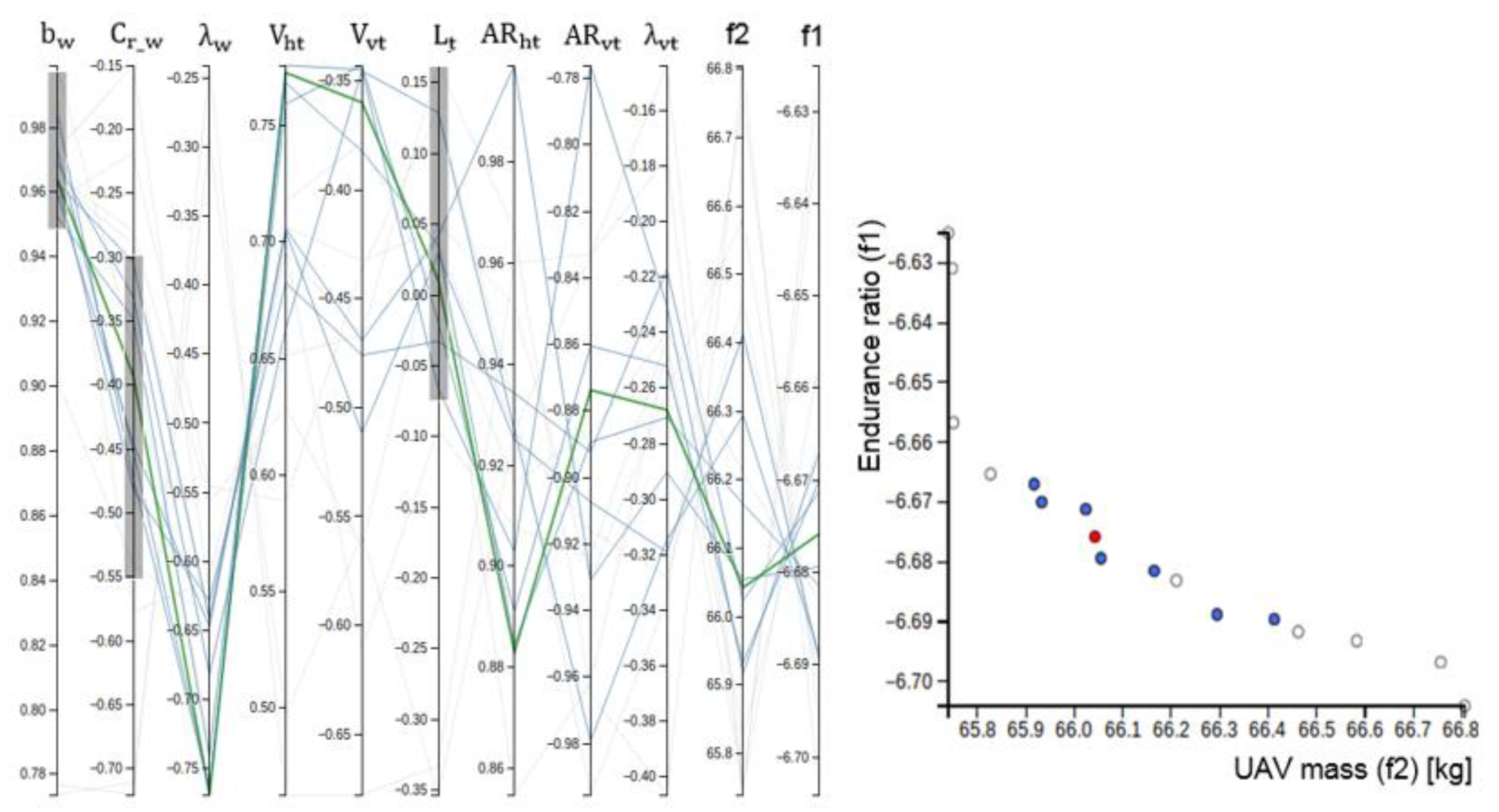
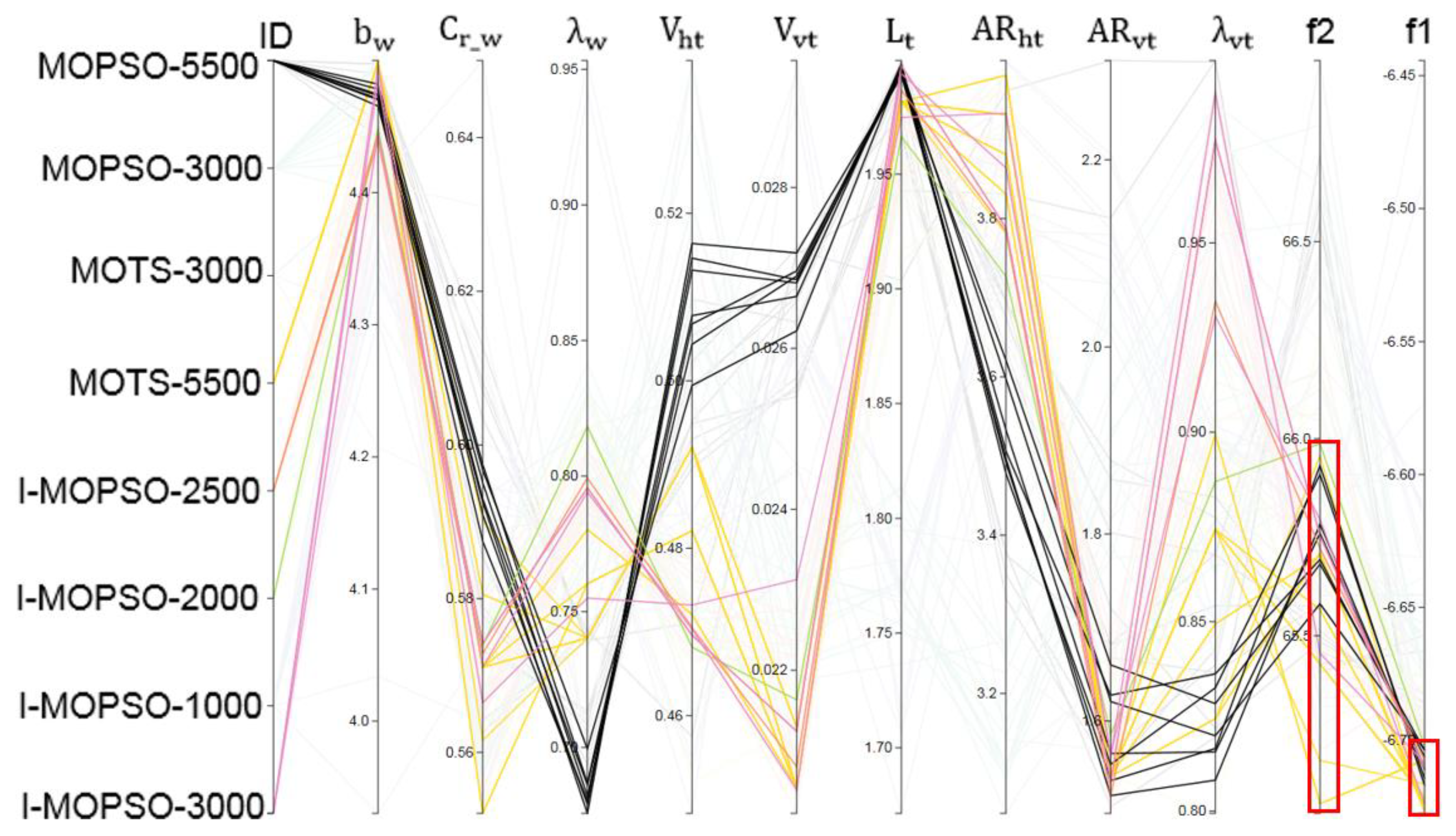
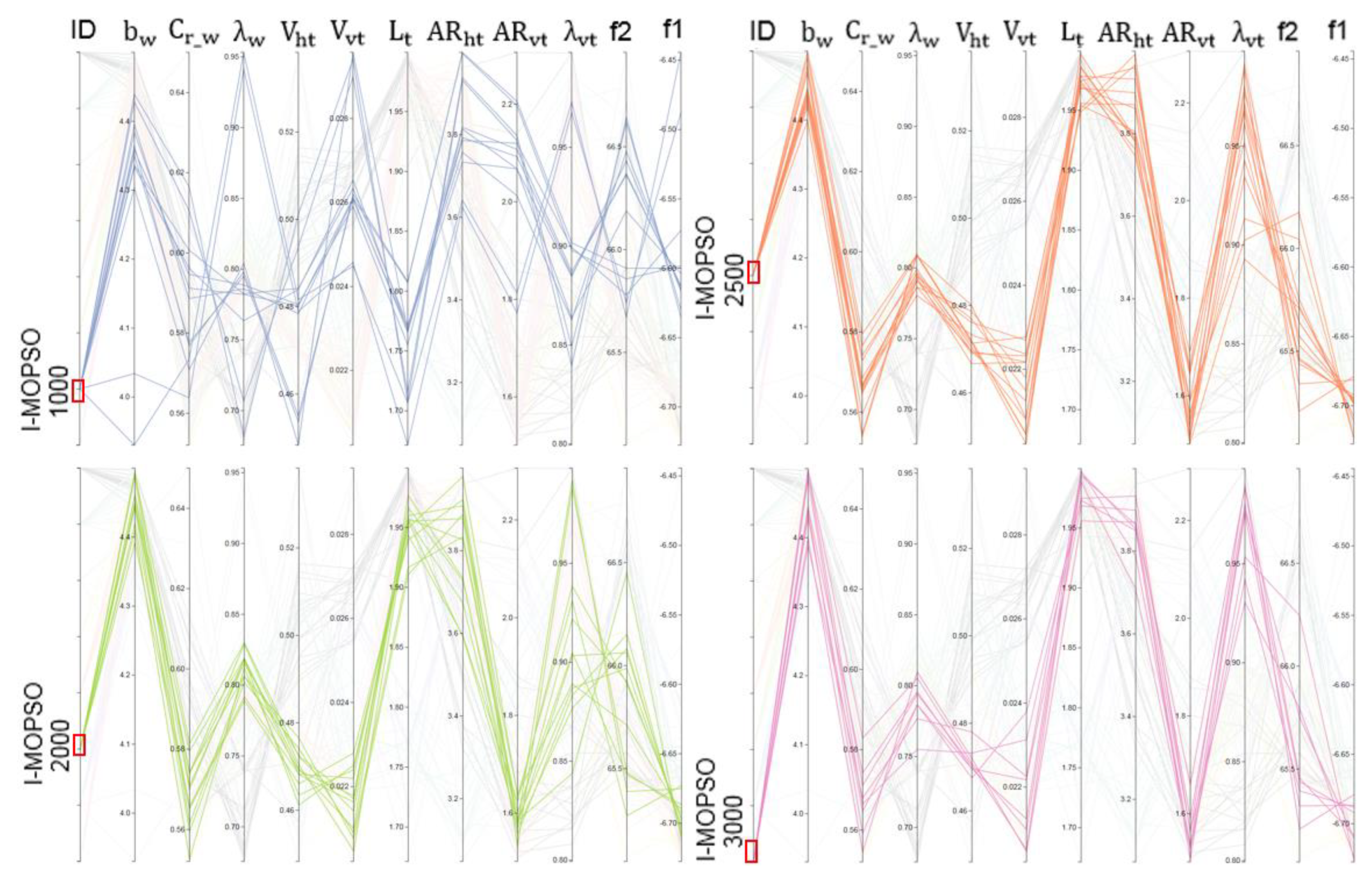
5.3.1. Visualisation of Results Using Parallel Coordinates
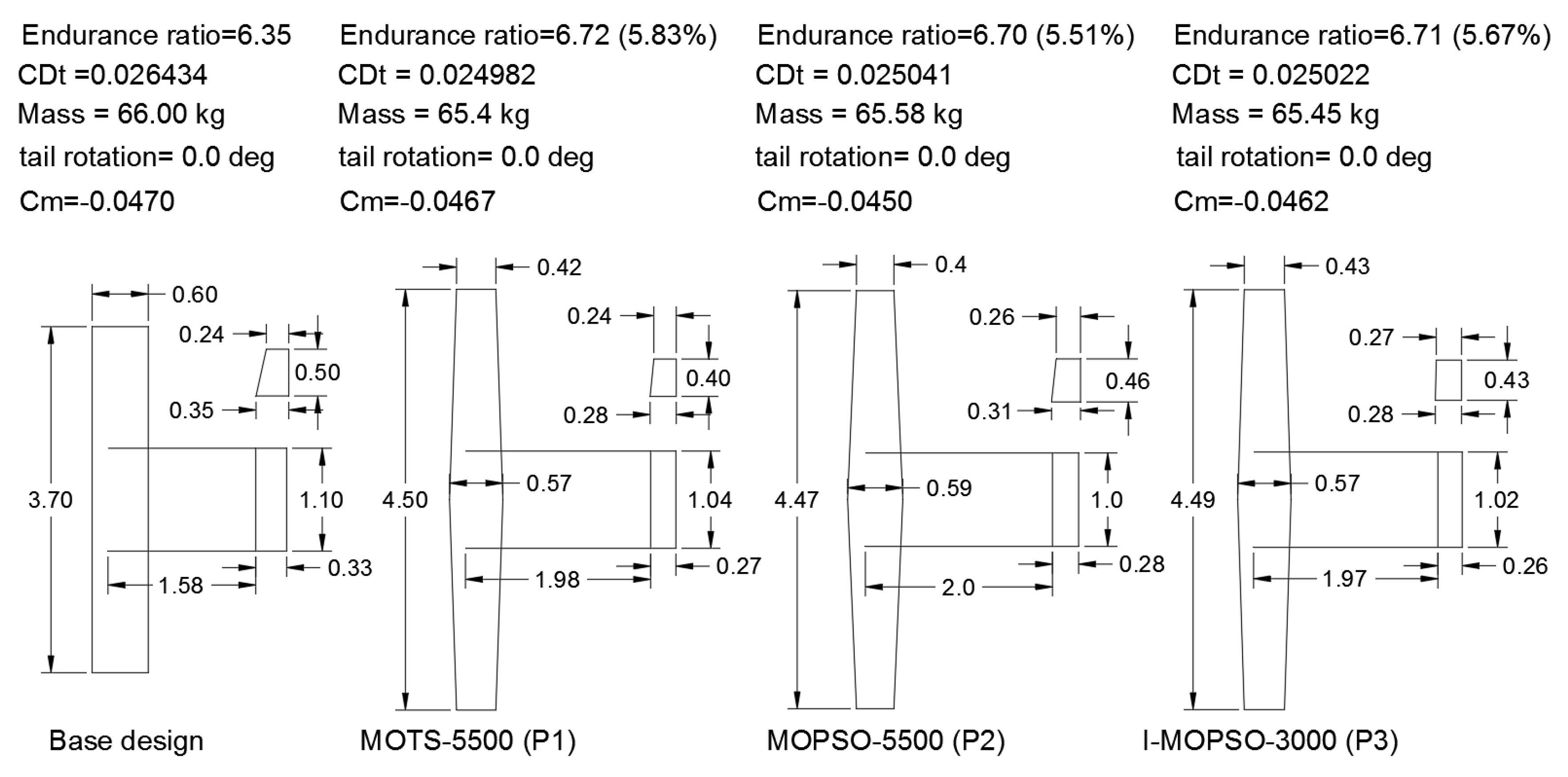
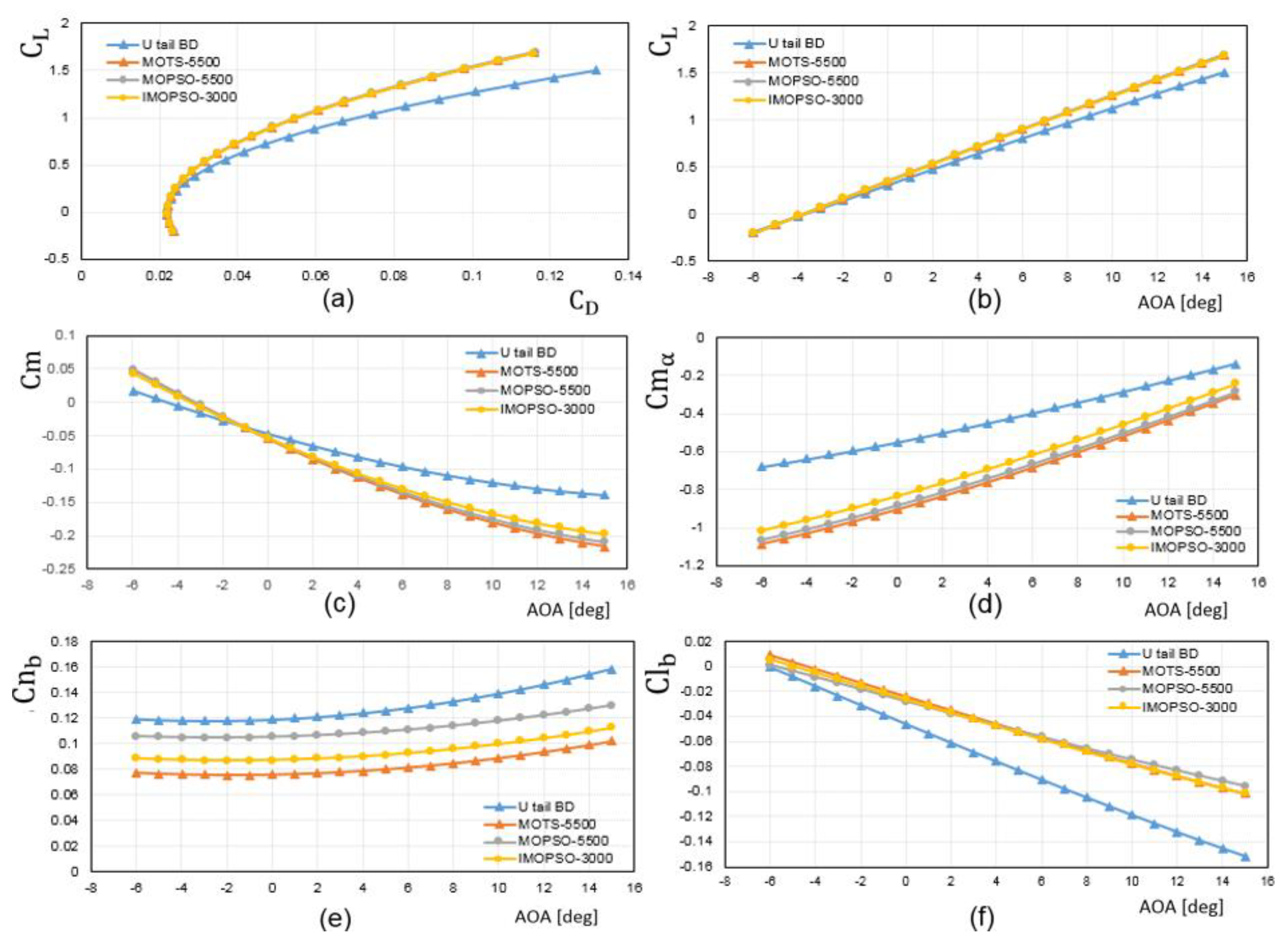
5.3.2. Investigation of Selected Configurations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| AOA | = Angle of attack |
| E | = Endurance ratio |
| UAV | = Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| = UAV total mass | |
| , , | = Inverted V-tail, horizontal tail, and vertical tail aspect ratio |
| = Aerodynamic center | |
| , | = Wing span and wing root chord |
| , | = Vertical and horizontal tail span |
| = Inverted V-tail span | |
| , | = Span for the horizontal and vertical projection area for the inverted V-tail |
| , , Cm | = Drag, lift, and pitch moment coefficient |
| = Horizontal tail chord | |
| , | = Vertical tail tip and root |
| , | = Inverted V-tail tip and root |
| = Pitching moment slope | |
| , | = Variation of rolling and yawing force coefficient with sideslip angle |
| = Variation of pitching moment coefficient with pitch rate | |
| = Variation of yawing force coefficient with yaw rate | |
| , | = Base design lift and pitching moment coefficient |
| = Inverted V-tail volume | |
| = Tail arm | |
| n/a | = Not applicable |
| , | = Horizontal tail and vertical tail volume |
| , | = Optimised UAV stall velocity and maximum velocity |
| , | = Base design stall velocity and maximum velocity |
| = Design variable | |
| , | = Lower and upper bounds of the design variables |
| ,, | = Wing, vertical tail, and inverted V-tail taper ratio |
| = Inverted V-tail angle | |
| = Dihedral angle |
Appendix A
References
- Crombecq, K.; Laermans, E.; Dhaene, T. Efficient space-filling and non-collapsing sequential design strategies for simulation-based modeling. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2011, 214, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goertz, S.; Ilic, C.; Jepsen, J.; Leitner, M.; Schulze, M.; Schuster, A.; Scherer, J.; Becker, R.; Zur, S.; Petsch, M. Multi-Level MDO of a Long-Range Transport Aircraft Using a Distributed Analysis Framework. In Proceedings of the 18th AIAA/ISSMO Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 5–9 June 2017; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leifsson, L.; Koziel, S.; Bekasiewicz, A. Fast low-fidelity wing aerodynamics model for surrogate-based shape optimization. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 29, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, A. Re-Engineering the Design Process through Computation. J. Aircr. 1999, 36, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.; Rai, D.; Balic, J. A multi-objective algorithm for optimization of modern machining processes. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2017, 61, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettenhausen, J.; Lewis, A.; Randall, M.; Kipouros, T. Interactive Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimisation using Decision Space Interaction. In Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Cancun, Mexico, 20–23 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Branke, J.; Greco, S.; Słowiński, R.; Zielniewicz, P. Interactive evolutionary multiobjective optimization driven by robust ordinal regression. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2010, 58, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Sinha, A.; Korhonen, P.J.; Wallenius, J. An interactive evolutionary multiobjective optimization method based on progressively approximated value functions. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2010, 14, 723–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebro, A.J.; Ruiz, A.B.; Barba-González, C.; García-Nieto, J.M.; Luque, M.; Aldana-Montes, J.F. InDM2: Interactive Dynamic Multi-Objective Decision Making using evolutionary algorithms. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2018, 40, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özmen, M.; Karakaya, G.; Köksalan, M. Interactive evolutionary approaches to multiobjective feature selection. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2018, 25, 1027–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, P.J.; Purshouse, R.C. Many-objective optimization: An engineering design perspective. In International conference on evolutionary multi-criterion optimization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 14–32. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Chen, R.; Savic, D.; Yao, X. Interactive Decomposition Multi-Objective Optimization via Progressively Learned Value Functions. Neural Evol. Comput. 2018, arXiv:1801.00609. [Google Scholar]
- Hettenhausen, J.; Lewis, A.; Mostaghim, S. Interactive multi-objective particle swarm optimization with heatmap-visualization-based user interface. Eng. Optim. 2010, 42, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninian, D.; Dakka, S. Design, Development and Testing of Shape Shifting Wing Model. Aerospace 2017, 4, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.; Kenway, G.K.W.; Martins, J.R.R.A. Aerodynamic Shape Optimization Investigations of the Common Research Model Wing Benchmark. AIAA J. 2015, 53, 968–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leifsson, L.; Koziel, S. Simulation-Driven Aerodynamic Design Using Variable-Fidelity Models; World Scientific: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Quagliarella, D.; Della Cioppa, A. Della Genetic algorithms applied to the aerodynamic design of transonic airfoils. J. Aircr. 1995, 32, 889–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.; Martins, J.R.R.A. Aerodynamic Design Optimization Studies of a Blended-Wing-Body Aircraft. J. Aircr. 2014, 51, 1604–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, R.M.; Murman, E.M.; Vanderplaats, G.N. An Assessment of Airfoil Design by Numerical Optimization; National Aeronautics and Space Administration; NASA Ames Research Center: Moffett Field, CA, USA, 1974.
- Vanderplaats, G.N.; Springs, C. Design Optimisation a Powerful Tool for the Competitive Edge. In Proceedings of the 1st AIAA Aircraft, Technol. Integr. Oper., Los Angeles, CA, USA, 16–18 October 2001; Volume 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coello Coello, C.A.; Lamont, G.B.; Veldhuizen, D. Evolutionary Algorithms for Solving Multi-Objective Problems; Springer Science + Business Media, LLC All: New York, NY, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-387-33254-3. [Google Scholar]
- Deb, K. Multi-Objective Optimization Using Evolutionary Algorithms; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 047187339X. [Google Scholar]
- Van Herwijnen, M. Multiple−Attribute Value Theory (MAVT). Available online: http://www.ivm.vu.nl/en/images/MCA1_tcm234-161527.pdf (accessed on 23 February 2018).
- Agrawal, S.; Dashora, Y.; Tiwari, M.; Son, Y.J. Interactive particle swarm: A Pareto-adaptive metaheuristic to multiobjective optimization. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 2008, 38, 258–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Kumar, A. Interactive evolutionary multi-objective optimization and decision-making using reference direction method. In Proceedings of the 9th Annu. Conf. Genet. Evol. Comput.—GECCO ’07, London, UK, 7–11 July 2007; Volume 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps, S.; Koksalan, M. An Interactive Evolutionary Metaheuristic for Multiobjective Combinatorial Optimization. Manag. Sci. 2003, 49, 1726–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, J.W.; Gel, E.S.; Köksalan, M.M.; Korhonen, P.; Marquis, J.L.; Wallenius, J. Interactive evolutionary multi-objective optimization for quasi-concave preference functions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 206, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapotecas Martinez, S.; Arias Montano, A.; Coello Coello, C.A. Constrained Multi-objective Aerodynamic Shape Optimization via Swarm Intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conf. Genet. Evol. Comput., Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12–16 July 2014; pp. 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coello Coello, C.A.; Reyes-Sierra, M. Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimizers: A Survey of the State-of-the-Art. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Res. 2006, 2, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettenhausen, J.; Lewis, A.; Kipouros, T. A web-based system for visualisation-driven interactive multi-objective optimisation. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 29, 1915–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipouros, T.; Peachey, T.; Abramson, D.; Savill, A.M. Enhancing and Developing the Practical Optimization Capabilities and Intelligence of Automatic Design Software. In Proceedings of the 53rd AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Struct. Struct. Dyn. Mater. Conf., Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–26 April 2012; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drela, M.; Youngren, H. AVL 3.26 User Primer. Available online: http://web.mit.edu/drela/Public/web/avl/ (accessed on 25 November 2015).
- Kipouros, T.; Jaeggi, D.M.; Dawes, W.N.; Parks, G.T.; Savill, A.M.; Clarkson, P.J. Insight into high-quality aerodynamic design spaces through multi-objective optimization. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2008, 37, 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Pirim, H.; Bayraktar, E.; Eksioglu, B. Tabu Search: A Comparative Study; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2008; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Jaeggi, D.M.; Parks, G.T.; Kipouros, T.; Clarkson, P.J. The development of a multi-objective Tabu Search algorithm for continuous optimisation problems. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 185, 1192–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, A.; Clarkson, J.P.; Shaphar, S.; Leonard, P. Engineering design optimisation using Tabu search. In Proceedings of the Des. Excell. Eng. Des. Conf. (EDC 2000), Uxbridge, London, UK; 2000; pp. 371–378. [Google Scholar]
- Ghisu, T.; Parks, G.T.; Jaeggi, D.M.; Jarrett, J.P.; Clarkson, P.J. The benefits of adaptive parametrization in multi-objective Tabu Search optimization. Eng. Optim. 2010, 42, 959–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusignani, G. Available online: https://www.cranfield.ac.uk/press/news-2017/0816-supercomputer powers up at cranfield university (accessed on 27 September 2018).
- Riley, M.J.W.; Peachey, T.; Abramson, D.; Jenkins, K.W. Multi-objective engineering shape optimization using differential evolution interfaced to the Nimrod/O tool. In Proceedings of the IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng., Sydney, Australia, 19–23 July 2010; Volume 10, p. 012189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, D.; Lewis, A.; Peachey, T.; Fletcher, C. An Automatic Design Optimization Tool and its Application to Computational Fluid Dynamics Searching for Optimal Designs. In Proceedings of the 2001 ACM/IEEE Conf. Supercomput., Denver, CO, USA, 10–16 November 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Abramson, D.; Peachey, T.; Lewis, A. Model Optimization and Parameter Estimation with Nimrod/O. In Proceedings of the 6th Int. Conf. Comput. Sci., Reading, UK, 28–31 May 2006; Volume 1, pp. 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azabi, Y.; Savvaris, A.; Kipouros, T. Initial Investigation of Aerodynamic Shape Design Optimisation for the Aegis UAV. Transp. Res. Procedia 2018, 29, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coello Coello, C.A.; Lechuga, M.S. MOPSO: A proposal for multiple objective particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the 2002 Congr. Evol. Comput., CEC 2002, Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–17 May 2002; Volume 2, pp. 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiev, J.; Panayotov, H. Comparative Investigation of VLM Codes for Joined-Wing Analysis. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2013, 2, 478–482. [Google Scholar]
- Sadraey, M. Aircraft Performance Analysis; VDM Verlag Dr. Muller: Mannheim, Germany, 2009; ISBN 3639200136. [Google Scholar]
- Beaverstock, C.; Woods, B.; Fincham, J.; Friswell, M. Performance Comparison between Optimised Camber and Span for a Morphing Wing. Aerospace 2015, 2, 524–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilocca, G. Interactive Optimisation for Aircraft Application. Msc Thesis, Cranfield University, Cranfield, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Inselberg, A. Parallel Coordinates: Visilization Multidimensional Geometry and Its Applications; Shneiderman, B., Ed.; Spring Science: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-387-21507-5. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich, J.; Weiskopf, D. Parallel Coordinates for Multidimensional Data Visualization: IEEE CS AIP 2015, 1521–9615. Available online: http://joules.de/files/heinrich_parallel_2015.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2016).
- Kipouros, T.; Inselberg, A.; Parks, G.; Savill, A.M. Parallel Coordinates in Computational Engineering Design. In Proceedings of the AIAA Multidiscip. Des. Optim. Spec., Boston, MA, USA, 8–11 April 2013; Volume 1750, pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, R.; Kennedy, J.; Blackwell, T. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Int. Conf. Neural Netw., Perth, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Coello, C.A.C.; Pulido, G.T.; Lechuga, M.S. Handling multiple objectives with particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2004, 8, 256–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobergte, D.R.; Curtis, S. A Multi-objective Tabu Search Algorithm for Constrained Optmisation Problems. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, W.H.; Knill, D.L.; Giunta, A.A.; Grossman, B.; Watson, L.T.; Mason, W.H.; Knill, D.L.; Giunta, A.A.; Grossman, B.; Watson, L.T. Getting the Full Benefits of CFD in Conceptual Design. In Proceedings of the 16th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 15–18 June 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Chau, T.; Zingg, D.W. Aerodynamic shape optimization of a box-wing regional aircraft based on the reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes equations. In Proceedings of the 35th AIAA Appl. Aerodyn. Conf., Denver, CO, USA, 5–9 June 2017; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iemma, U.; Diez, M. Optimal Conceptual Design of Aircraft Including Community Noise Prediction. In Proceedings of the 12th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conf. (27th AIAA Aeroacoustics Conf.), Cambridge, MA, USA, 8–10 May 2006; pp. 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, R.A.; Iden, S.; Snyder, R.D.; Allison, D.L. An Overview of the Optimized Integrated Multidisciplinary Systems Program. In Proceedings of the 57th AIAA/ASCE/AHS/ASC Struct. Struct. Dyn. Mater. Conf., San Diego, CA, USA, 4–8 January 2016; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolai, L.M.; Carichner, G.E. Fundamentals of Aircraft and Airship Design: Volume 1; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-60086-751-4. [Google Scholar]
- Piperni, P.; DeBlois, A.; Henderson, R. Development of a Multilevel Multidisciplinary-Optimization Capability for an Industrial Environment. AIAA J. 2013, 51, 2335–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Jungo, A.; Gastaldi, A.; Melin, T. Aircraft Geometry and Meshing with Common Language Schema CPACS for Variable-Fidelity MDO Applications. Aerospace 2018, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, D.; Bethwaite, B.; Enticott, C.; Garic, S.; Peachey, T. Parameter space exploration using scientific workflows. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Science, Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 25–27 May 2009; pp. 104–113. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, P.; Singh, D.; Pant, M. Problem Solving and Uncertainty Modeling through Optimization and Soft Computing Application; Information Science Reference: Harrisburg, PA, USA, 2016; ISBN 9781466698864. [Google Scholar]
- Peachey, T.; Abramson, D.; Lewis, A.; Kurniawan, D.; Jones, R. Optimization using Nimrod/O and its Application to Robust Mechanical Design. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Parallel Processing and Applied Mathematics, Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 7–10 September 2003; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Keast, S. Modeling, Simulation, and Sil Testing of the Aegis UAV. MSc Thesis, Cranfield University, Cranfield, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Turquand, C. Aerodynamic Analysis and Optimisation of the Aegis TUAV. MSc Thesis, Cranfield University, Cranfield, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gudmundsson, S. General Aviation Aircraft Design: Applied Methods and Procedures; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-0-12-397308-5. [Google Scholar]
- Gundlach, J. Designing Unmanned Aircraft Systems: A Comprehensive Approach; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-1-60086-843-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J. General Aviation Aircraft Design. AIAA J. 2015, 54, 793–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadraey, M.H. Aircraft Design: A Systems Engineering Approach; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, West Sussex, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-1-118-35280-9. [Google Scholar]
- Mader, C.A.; Martins, J.R.R.A. Computing Stability Derivatives and Their Gradients for Aerodynamic Shape Optimization. AIAA J. 2014, 52, 2533–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, N.; Rademacher, M.; Goodman, E.; Averill, R.; Sidhu, R. A Benchmark Study of Multi-Objective Optimization Methods; Multi-objective Optimization Problem; red cedar Technol.: East Lansing, MI, USA, 2009; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Gendreau, M. An Introduction to Tabu Search. Handb. Metaheuristics 2003, 57, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Yen, G.G. An improved visualization approach in many-objective optimization. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Congr. Evol. Comput., CEC 2016, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 1618–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotn, M. Outlier-preserving Focus + Context Visualization in Parallel Coordinates. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2006, 12, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, C.; Keane, A. Visualization Methodologies in Aircraft Design. In Proceedings of the 10th AIAA/ISSMO Multidiscip. Anal. Optim. Conf., Albany, NY, USA, 30 August–1 September 2004; Volume 3, pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

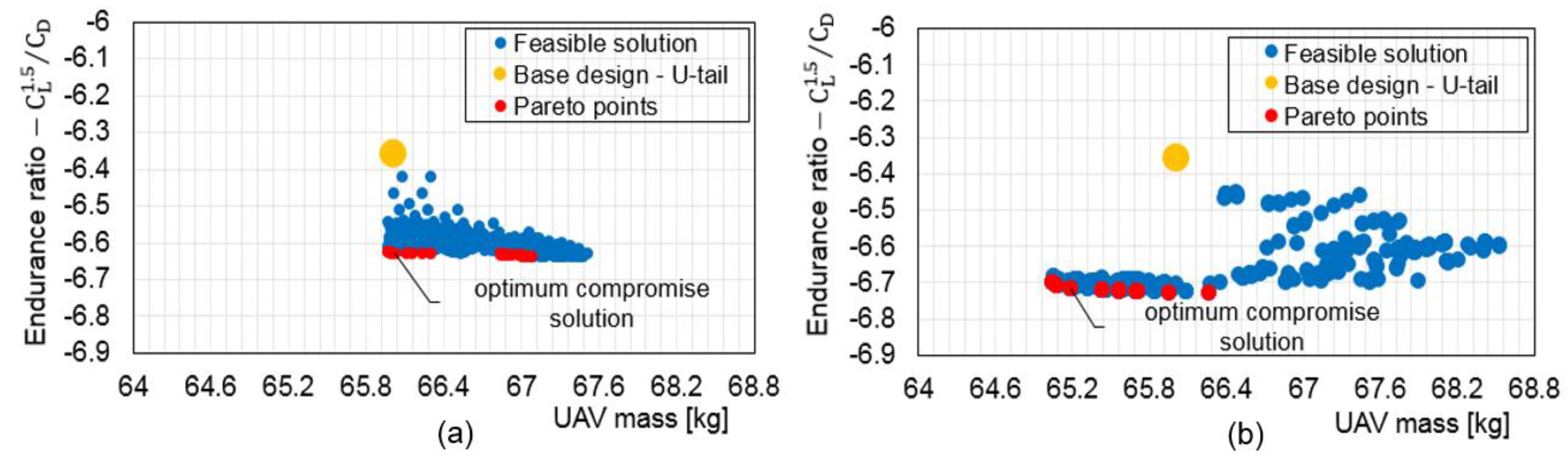
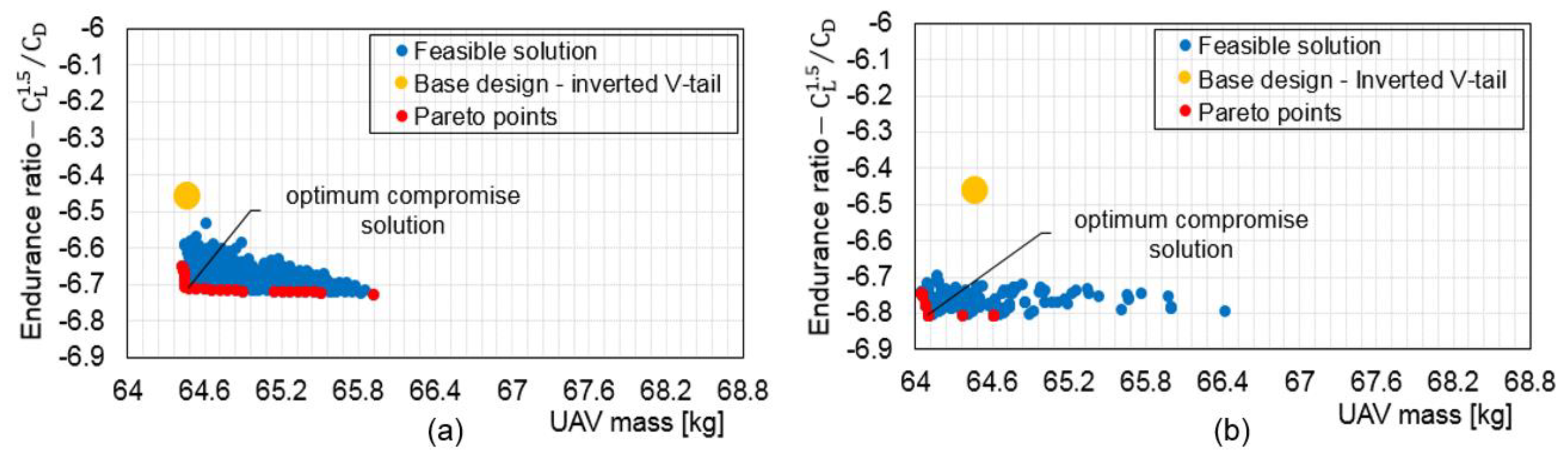
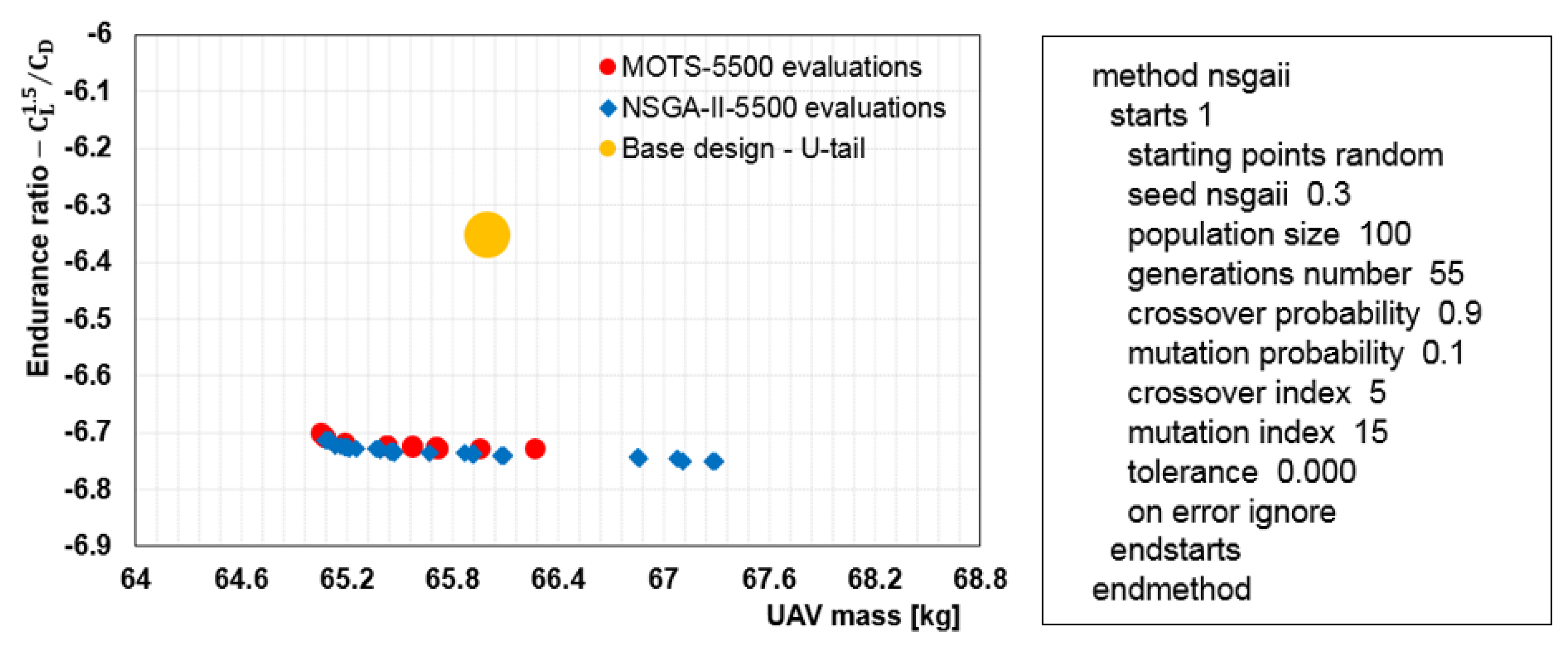
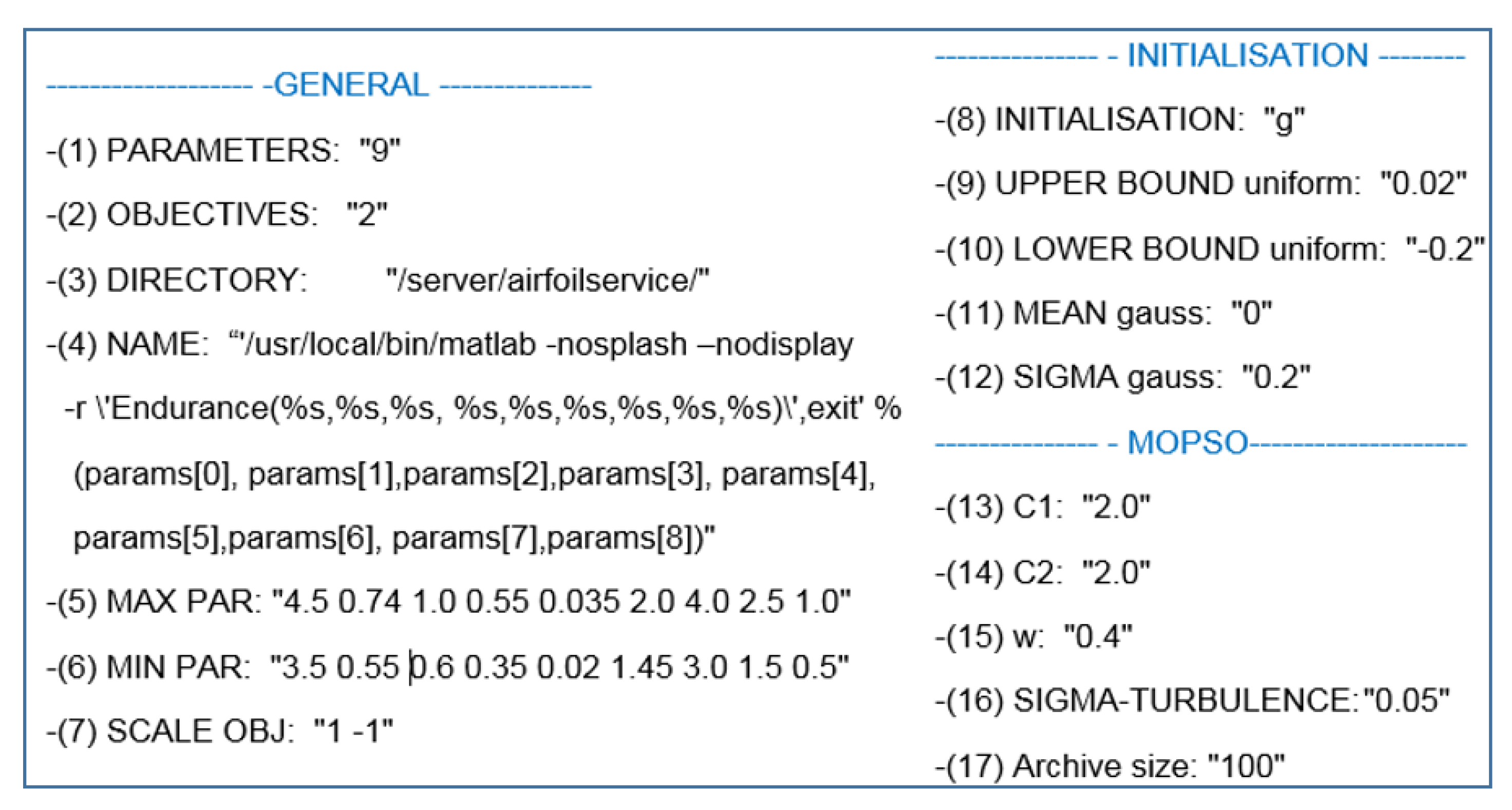

| Parameters | Lower bounds | Base design | Upper bounds | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-tail | Inverted V-tail | U-tail | Inverted V-tail | U-tail | Inverted V-tail | ||
| [m] | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 4.5 | 4.5 | |
| [m] | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.74 | 0.74 | |
| [ - ] | 0.6 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| [ - ] | 0.35 | n/a | 0.43 | n/a | 0.55 | n/a | |
| [ - ] | 0.02 | n/a | 0.029 | n/a | 0.035 | n/a | |
| [m] | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.58 | 1.58 | 2.00 | 2.00 | |
| [ - ] | 3.00 | n/a | 3.33 | n/a | 4.00 | n/a | |
| [ - ] | 1.50 | n/a | 1.69 | n/a | 2.50 | n/a | |
| [ - ] | 0.50 | n/a | 0.68 | n/a | 1.00 | n/a | |
| [ - ] | n/a | 0.13 | n/a | 0.19 | n/a | 0.25 | |
| [ - ] | n/a | 1.5 | n/a | 2.1 | n/a | 2.5 | |
| [ - ] | n/a | 0.65 | n/a | 0.79 | n/a | 1.00 | |
| [deg] | n/a | 95.0 | n/a | 104.0 | n/a | 120.0 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azabi, Y.; Savvaris, A.; Kipouros, T. The Interactive Design Approach for Aerodynamic Shape Design Optimisation of the Aegis UAV. Aerospace 2019, 6, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace6040042
Azabi Y, Savvaris A, Kipouros T. The Interactive Design Approach for Aerodynamic Shape Design Optimisation of the Aegis UAV. Aerospace. 2019; 6(4):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace6040042
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzabi, Yousef, Al Savvaris, and Timoleon Kipouros. 2019. "The Interactive Design Approach for Aerodynamic Shape Design Optimisation of the Aegis UAV" Aerospace 6, no. 4: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace6040042
APA StyleAzabi, Y., Savvaris, A., & Kipouros, T. (2019). The Interactive Design Approach for Aerodynamic Shape Design Optimisation of the Aegis UAV. Aerospace, 6(4), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace6040042







