Effect of Leading-Edge Slats at Low Reynolds Numbers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
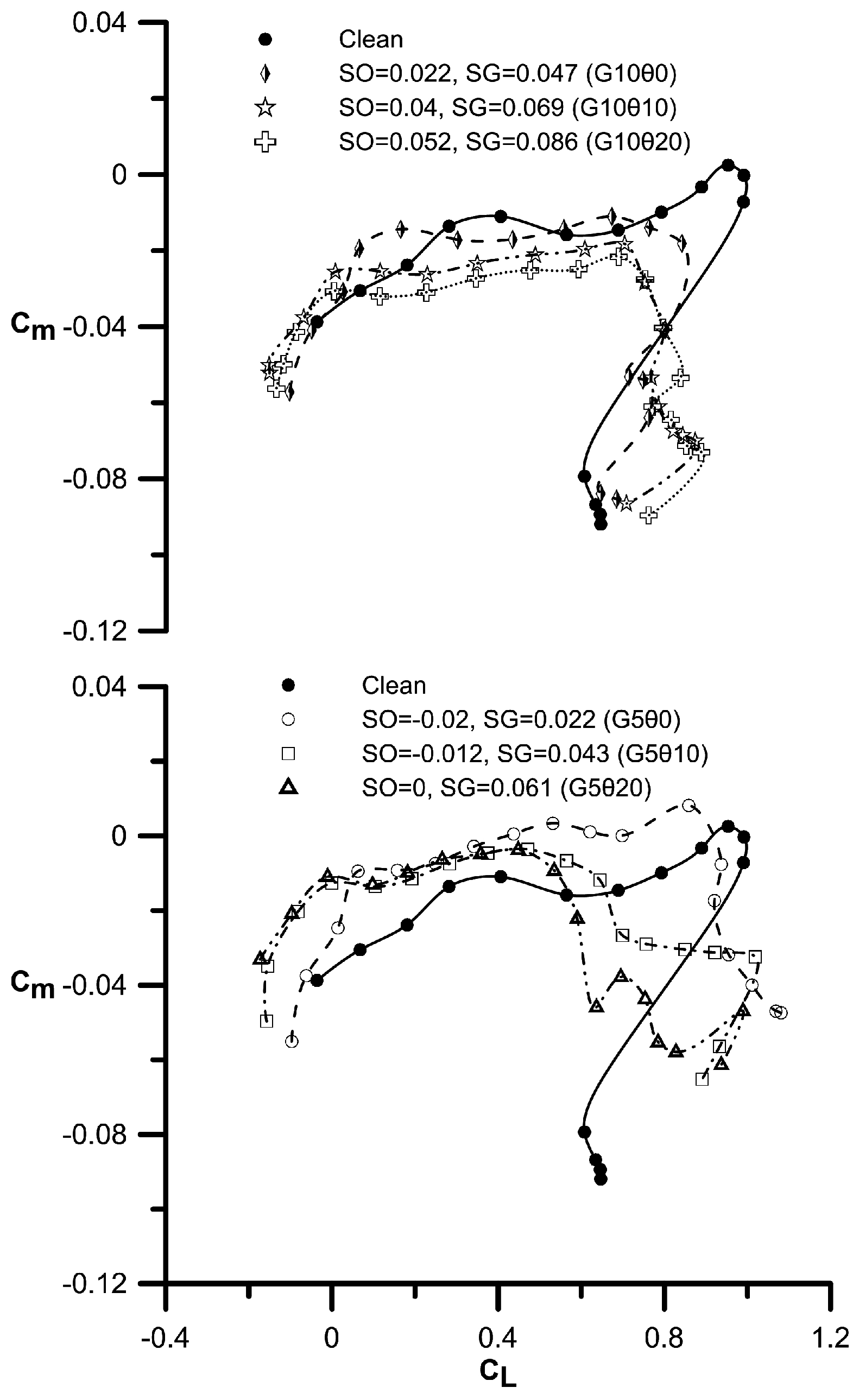
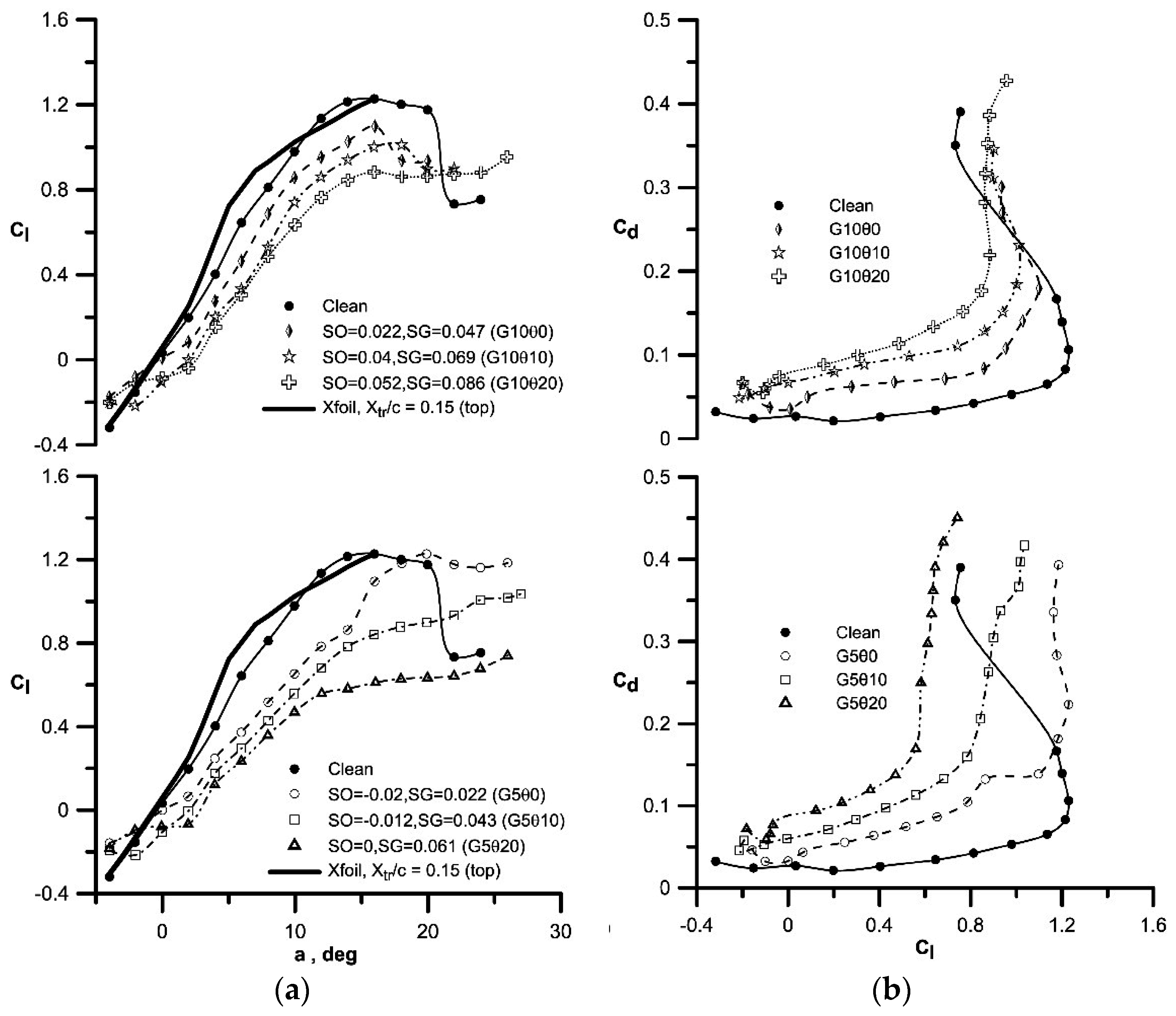
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Finite Wing Data
3.2. Airfoil Force Data
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CD | drag coefficient |
| cd | sectional drag coefficient |
| CL | lift coefficient |
| cl | sectional lift coefficient |
| CLMAX | maximum lift coefficient |
| CM | pitching moment coefficient |
| G | slat gap |
| Re | Reynolds number |
| SG | Slat gap non-dimensionalized by the airfoil chord |
| SO | Slat overhang non-dimensionalized by the airfoil chord |
| α | angle of attack |
| θ | rotation angle of slat |
References
- Kuchemann, D. The Aerodynamic Design of Aircraft; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1978; pp. 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Hoerner, S.F.; Borst, H.V. Fluid Dynamic Lift; Liselotte A. Hoerner, Hoerner Fluid Dynamics: Bricktown, NJ, USA, 1985; Chapter 6. [Google Scholar]
- Wenzinger, C.J.; Rogallo, F.M. Resume of Air-Loads on Slats and Flaps; NACA Report No. 690; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics: Washington, DC, USA, 1939.
- Lachmann, G. Experiments with Slotted Wings; NACA Technical Note 71; Translated from Zeitschrift fur Flugtechnik und Motorluftschiffahrt; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics: Washington, DC, USA, 1921.
- Handley Page, F. Developments in Aircraft Design by the use of Slotted Wings. Flight 1921, 13, 844–846. [Google Scholar]
- Weick, F.E.; Platt, R.C. Wind-Tunnel Tests on Model Wing with Fowler Flaps and Specially Developed Leading-Edge Slot; NACA Technical Note 459; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics: Washington, DC, USA, 1933.
- Quinn, J.H. Tests of the NACA 641A212 Airfoil Section with a Slat, a Double Slotted Flap, and Boundary Layer Control by Suction; NACA Technical Note 1293; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics: Washington, DC, USA, 1947.
- Axelson, J.A.; Stevens, G.L. Investigation of a Slat in Several Different Positions on an NACA 64A101 Airfoil for a Wide Range of Subsonic Mach Numbers; NACA Technical Note 3129; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics: Washington, DC, USA, 1954.
- Kelly, J.A.; McCullough, G.B. Aerodynamic Loads on a Leading-Edge Flap and A Leading Edge Slat on the NACA 64A101 Airfoil Section; NACA Technical Note 3220; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics: Washington, DC, USA, 1954.
- Weick, F.E.; Sanders, R. Wind Tunnel Tests of a Wing with Fixed Slots and Trailing-Edge Flap on the Lift and Drag of a Clark Y Aerofoil; NACA Report No. 472; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics: Washington, DC, USA, 1933.
- Otray, J.E.; Lissaman, P. Leading-edge slat design by a semi-inverse technique. J. Aircr. 1972, 9, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.O. High lift aerodynamics. J. Aircr. 1975, 12, 501–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.; Lin, R. Transition prediction on the slat of a high-lift system. J. Aircr. 2004, 41, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.L. A new and less complex alternative to the Handley Page slat. J. Aircr. 1986, 23, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renukumar, B.; Bramkamp, F.; Hesse, M.; Ballmann, J. Effect of flap and slat riggings on 2-D high-lift aerodynamics. J. Aircr. 2006, 43, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddah, S.R.; Bruun, H.H. An investigation of flow fields over multi-element aerofoils. ASME J. Fluid Eng. 2002, 124, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genc, M.S.; Kaynak, U.; Lock, G.D. Flow over an aerofoil without and with a leading-edge slat at a transitional Reynolds number. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2009, 223, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traub, L.W.; Freienmuth, E.O. Effect of streamwise attachment gap on aerodynamic characteristics of gurney flaps. J. Aircr. 2011, 48, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drela, M.; Youngren, H. AVL Aerodynamic Analysis. Available online: http://web.mit.edu/drela/Public/web/avl/ (accessed on 1 July 2016).
- Drela, M.; Youngren, H. XFOIL Subsonic Airfoil Development System. Available online: http://web.mit.edu/drela/Public/web/xfoil/ (accessed on 3 July 2016).
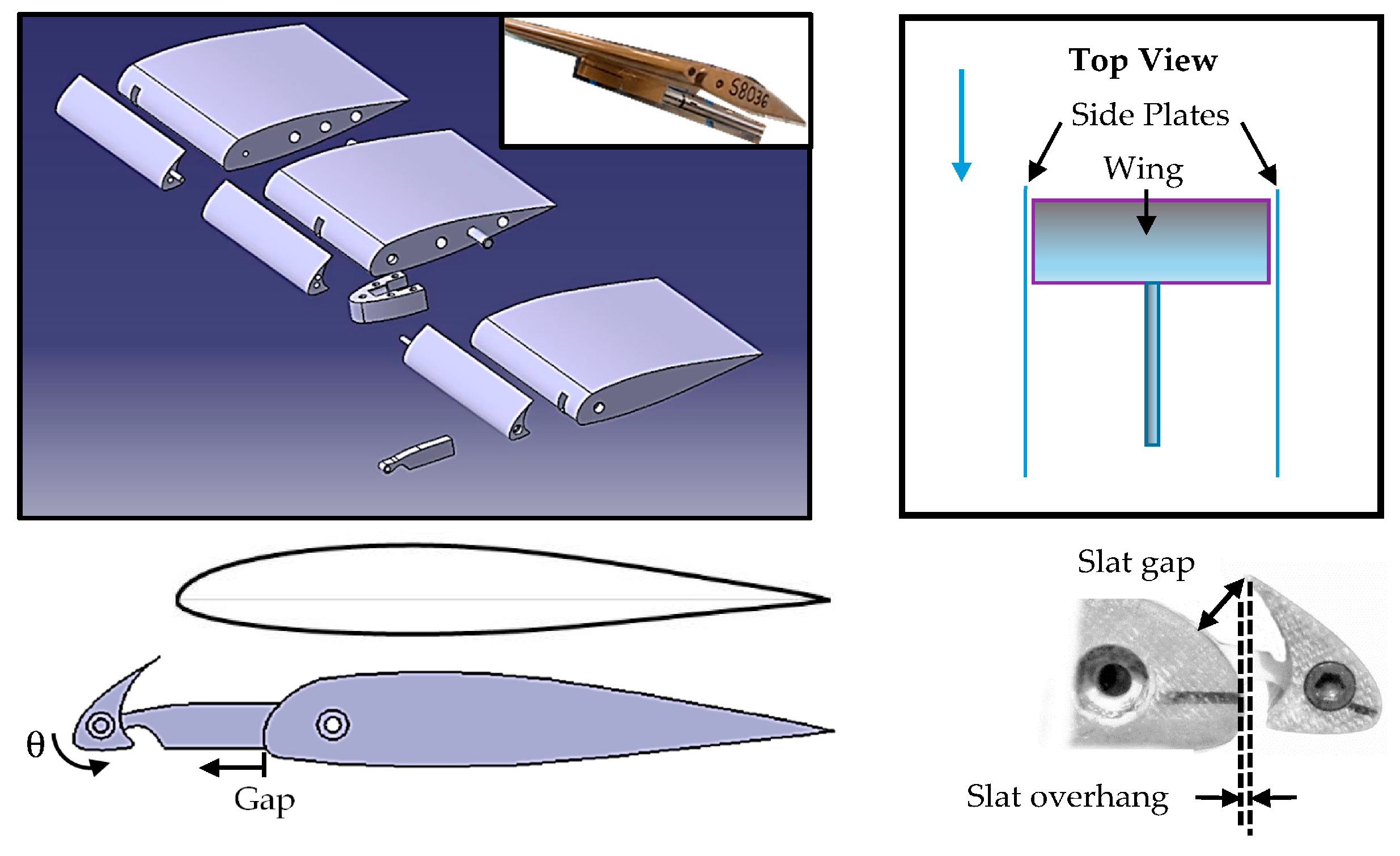
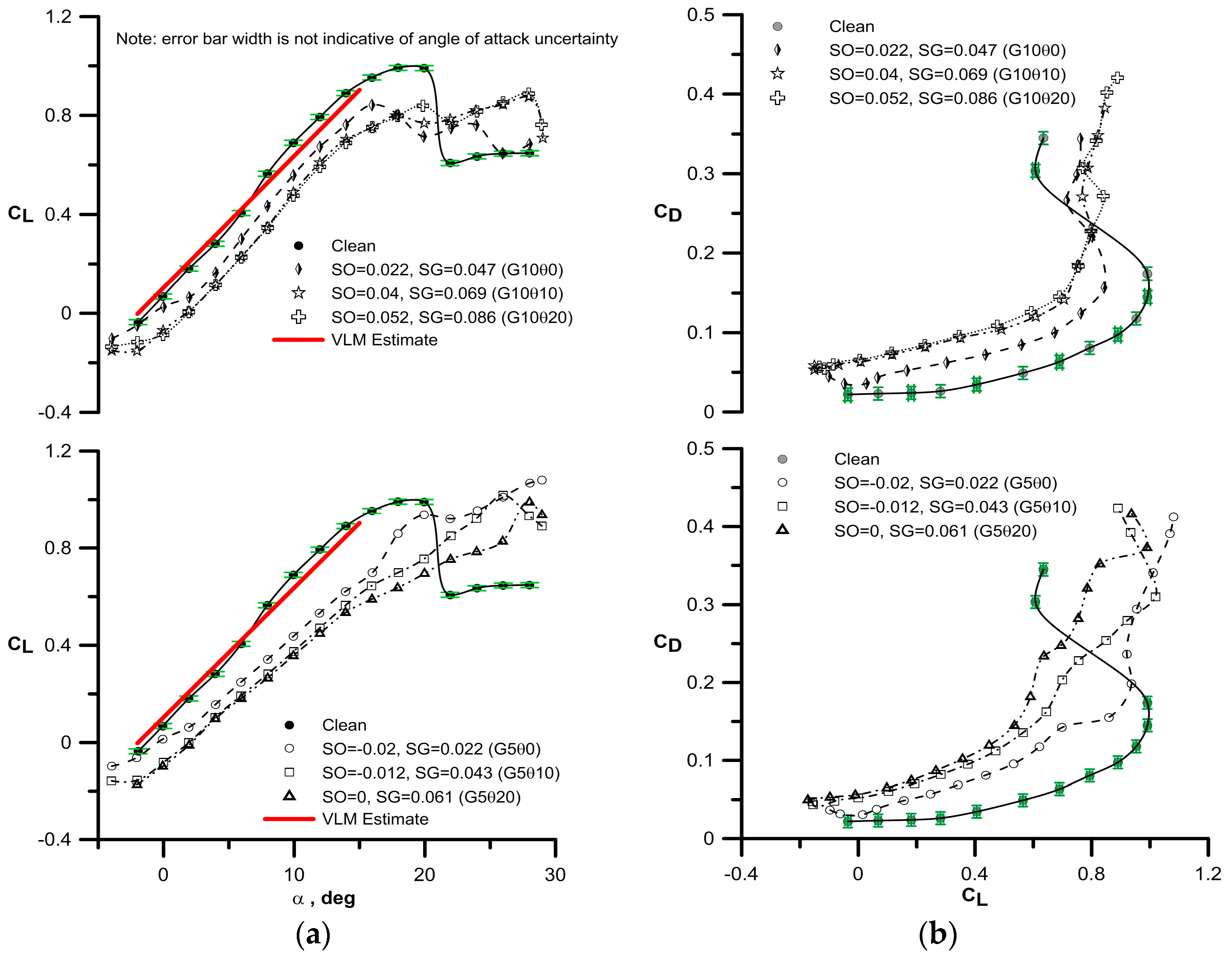
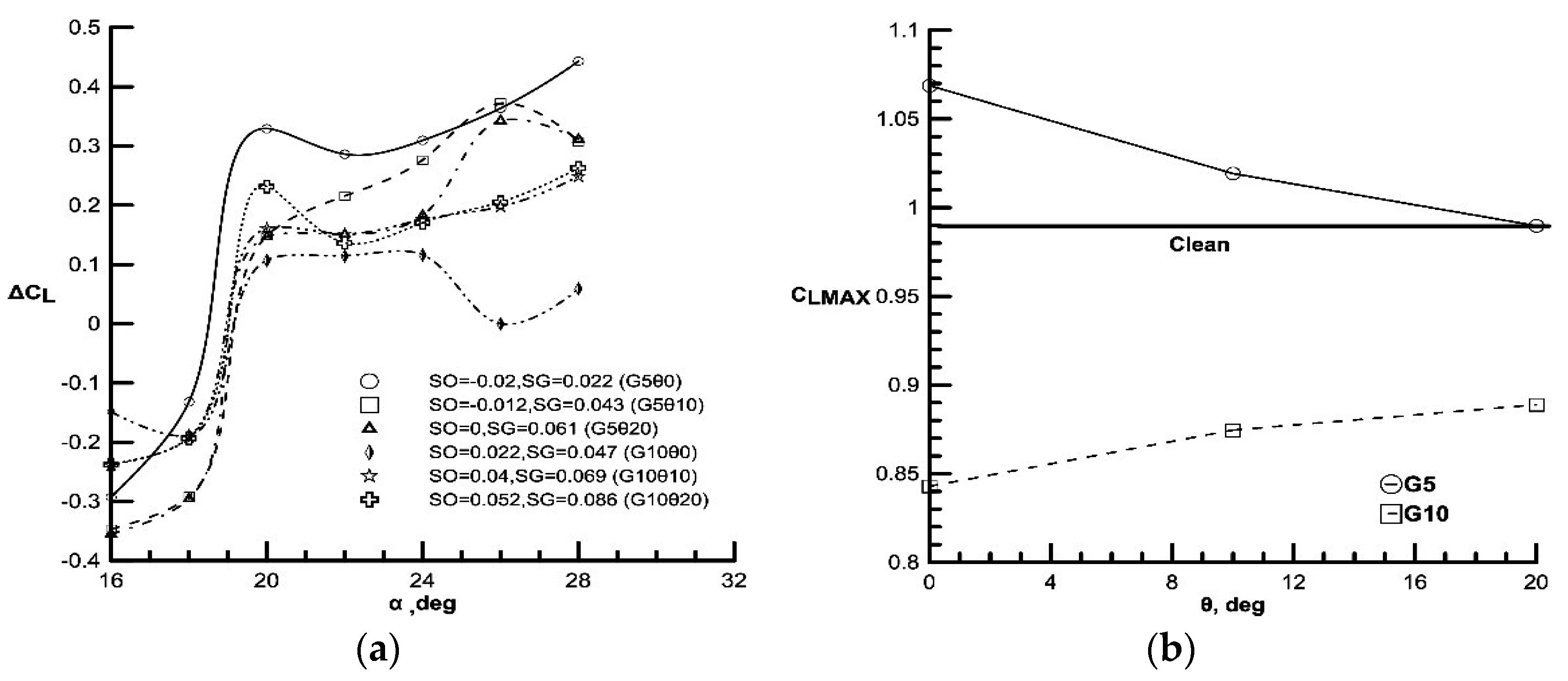
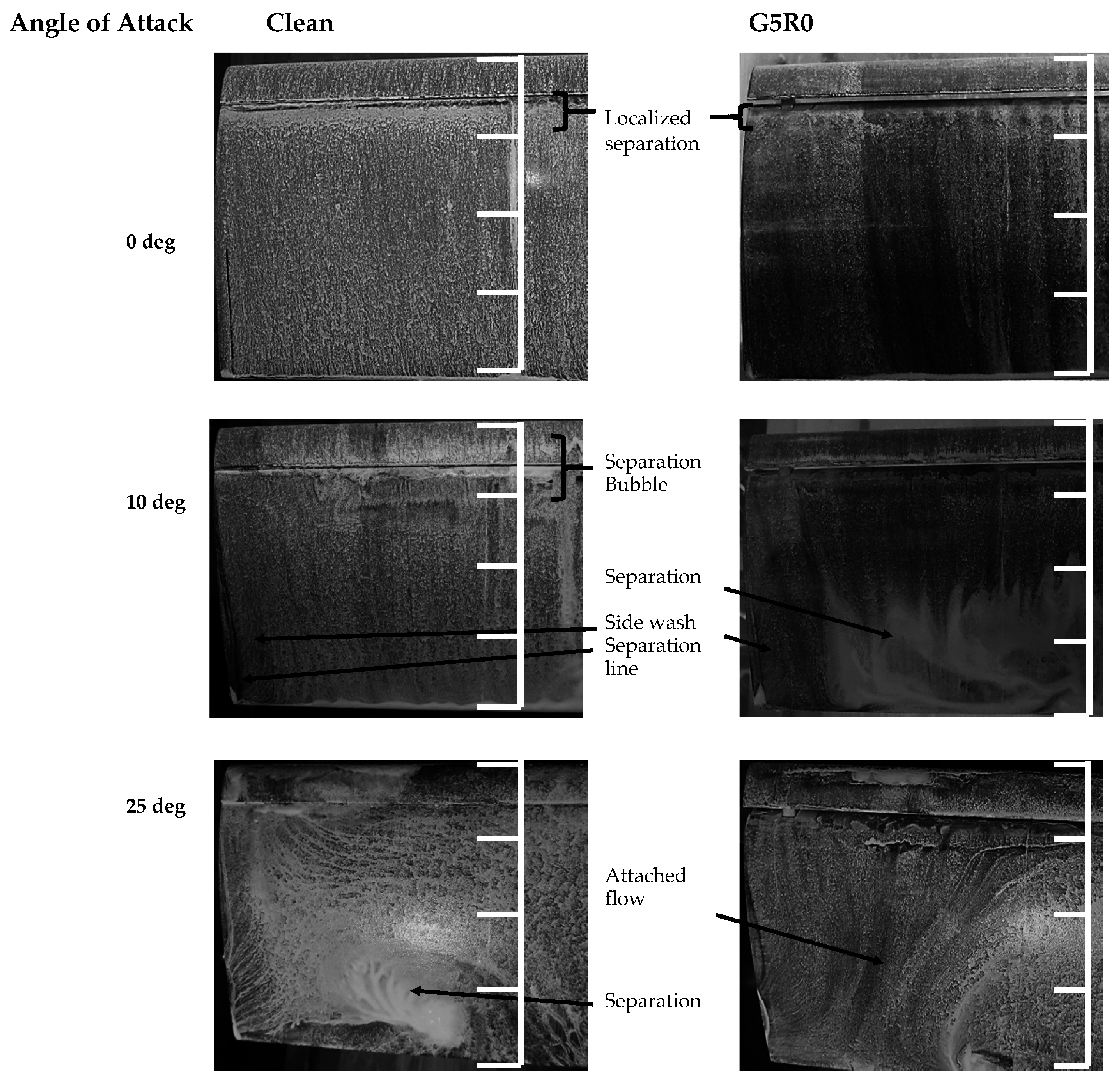

| Gap (mm) | θ (°) | SO (Slat Overhang) * | SG (Slat Gap) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0 | −0.02 | 0.022 |
| 5 | 10 | −0.012 | 0.043 |
| 5 | 20 | 0 | 0.061 |
| 10 | 0 | 0.022 | 0.047 |
| 10 | 10 | 0.04 | 0.069 |
| 10 | 20 | 0.052 | 0.086 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Traub, L.W.; Kaula, M.P. Effect of Leading-Edge Slats at Low Reynolds Numbers. Aerospace 2016, 3, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace3040039
Traub LW, Kaula MP. Effect of Leading-Edge Slats at Low Reynolds Numbers. Aerospace. 2016; 3(4):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace3040039
Chicago/Turabian StyleTraub, Lance W., and Mashaan P. Kaula. 2016. "Effect of Leading-Edge Slats at Low Reynolds Numbers" Aerospace 3, no. 4: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace3040039
APA StyleTraub, L. W., & Kaula, M. P. (2016). Effect of Leading-Edge Slats at Low Reynolds Numbers. Aerospace, 3(4), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace3040039







