A Review on Liquid Pulsed Laser Propulsion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory of Interaction Between Pulsed Laser and Liquid
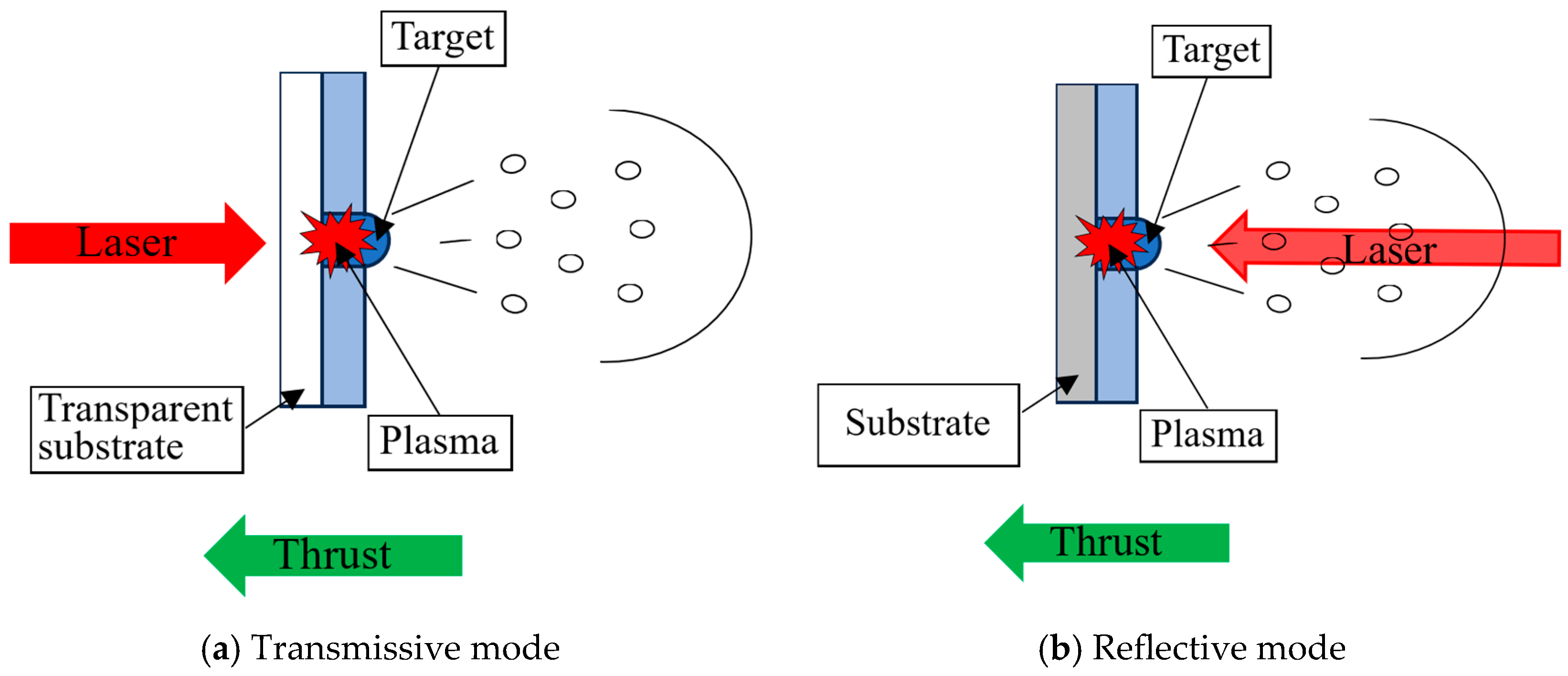
2.1. The Breakdown and Ionization Mechanisms for Liquid Propellants
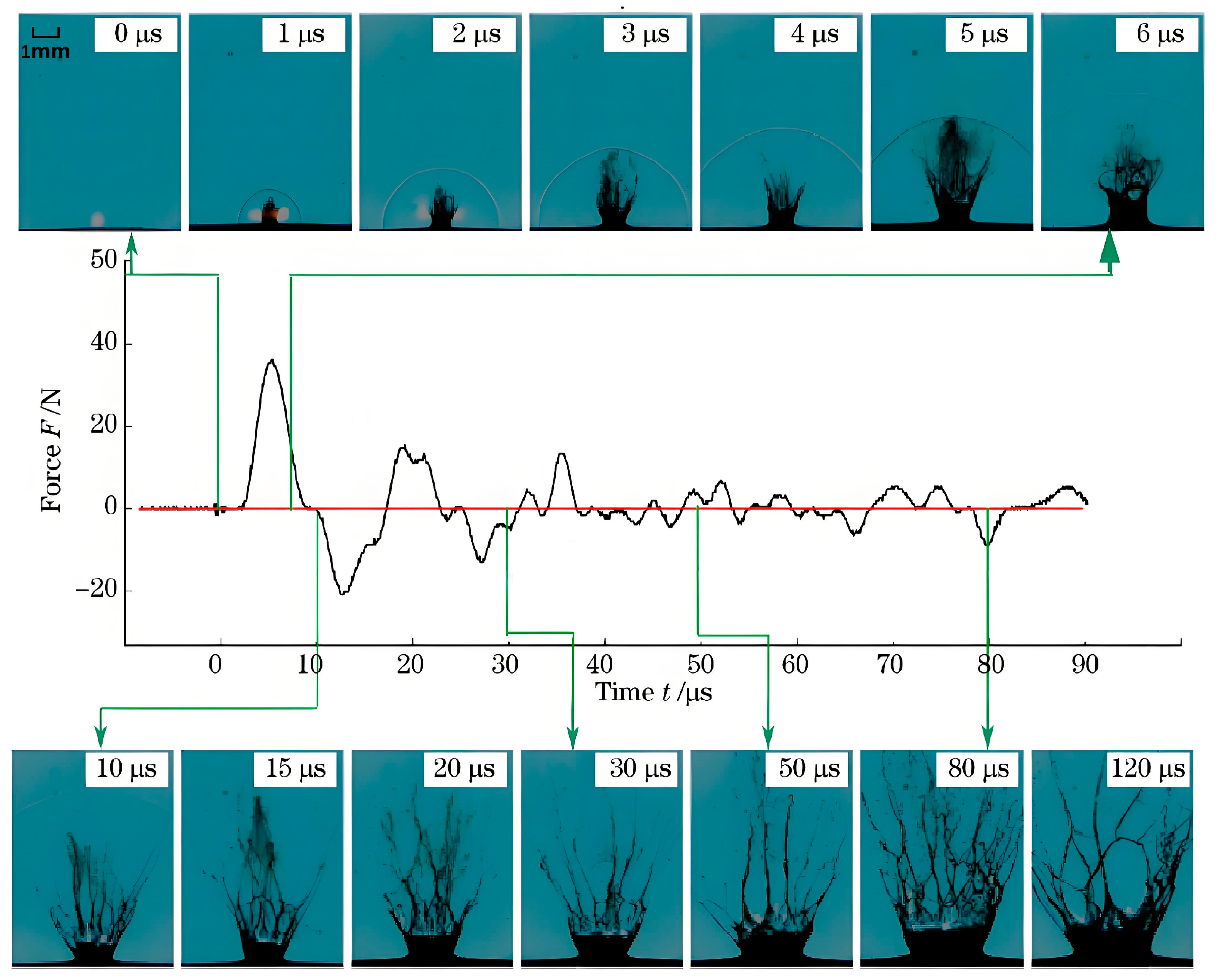
2.2. The Formation of Shock Waves from Laser Plasma
2.3. Definition and Calculation of Propulsion Parameters
3. Current Research on Pulsed Laser Propulsion Using Liquid Propellants
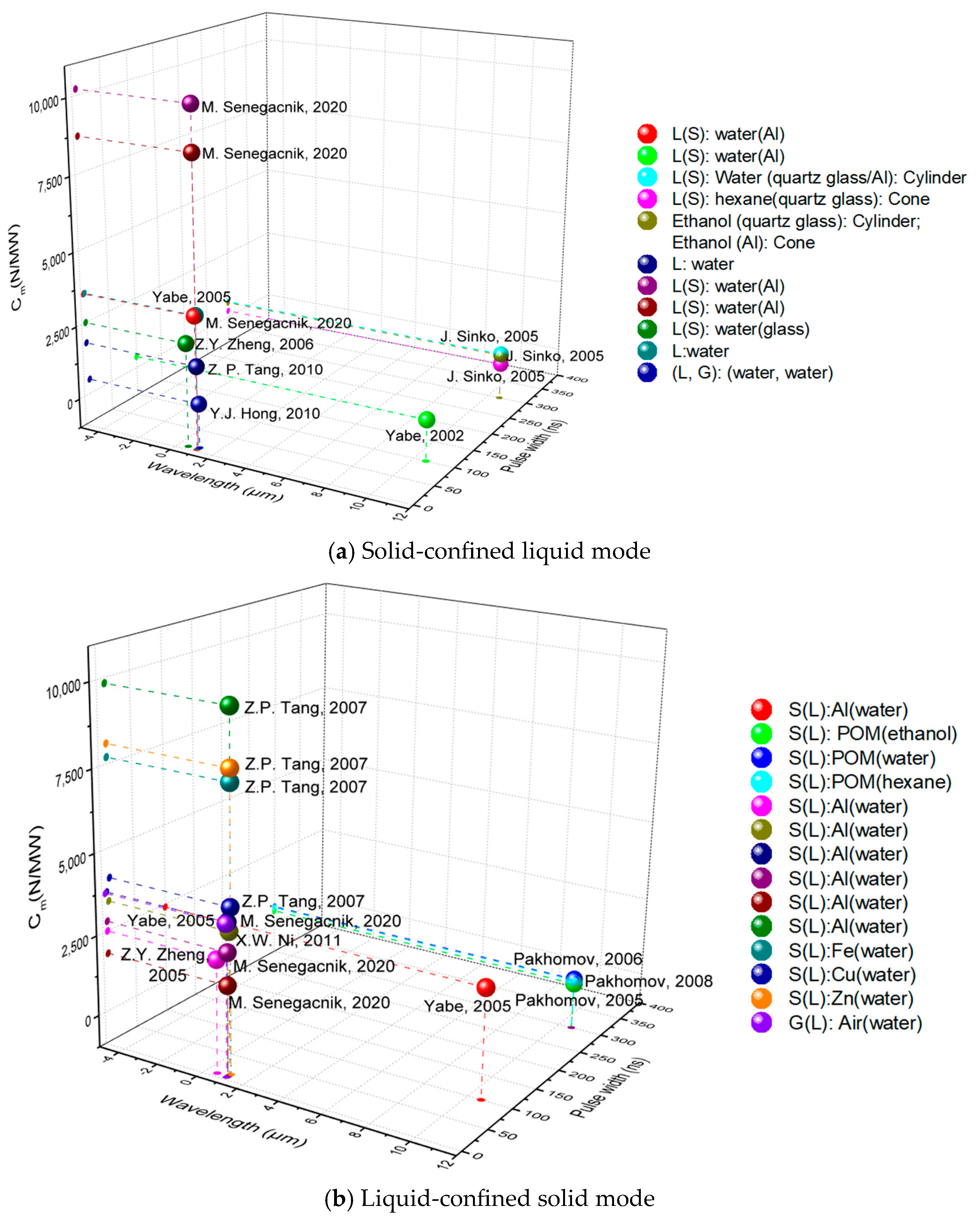
3.1. Non-Energetic Liquid Propellants
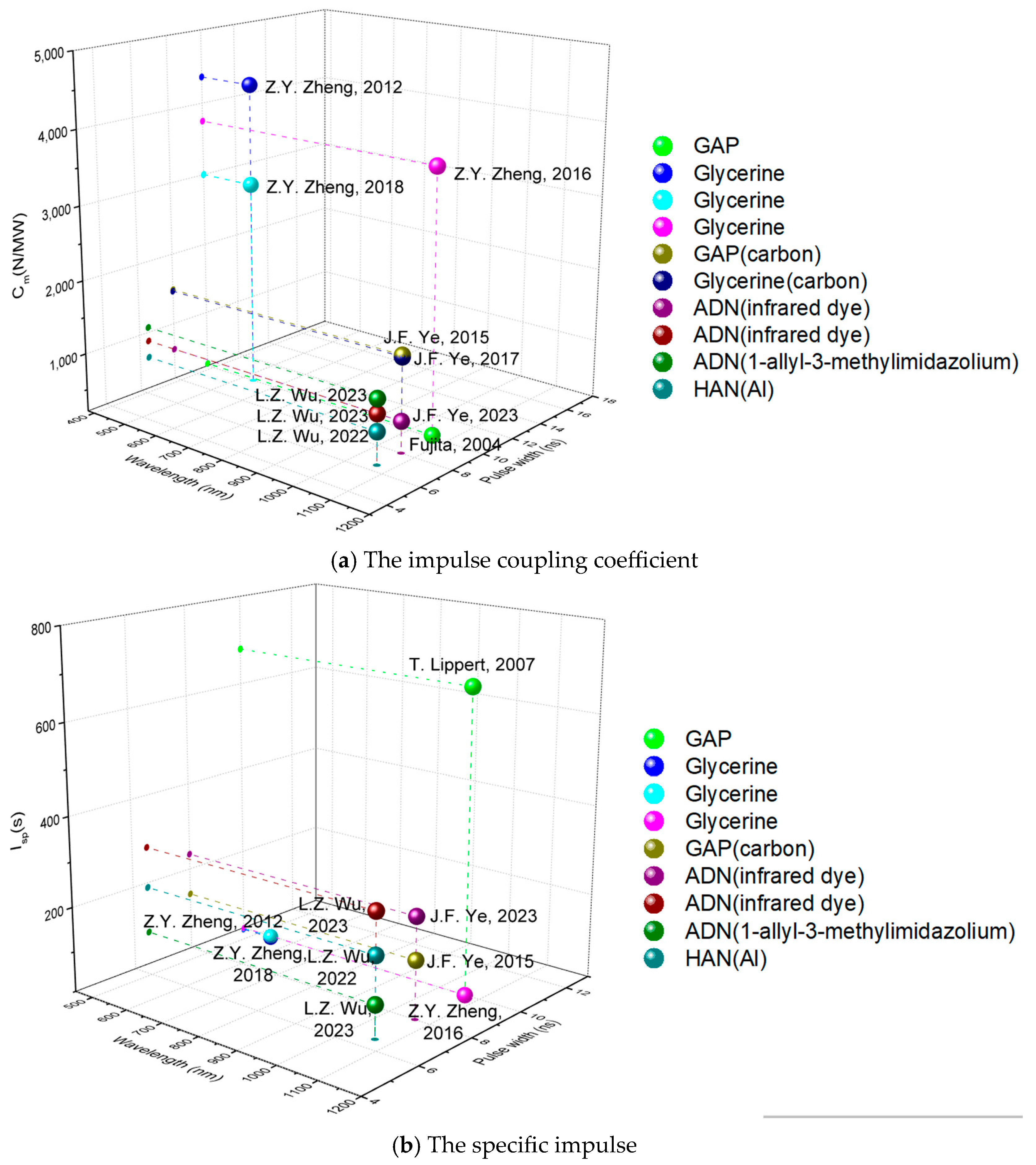
3.2. Energetic Liquid Propellants

3.3. Liquid Metal Propellants
4. Current Status of LPT Prototype Development
5. Laser Technology for Laser Propulsion
6. Conclusions and Outlook
- The impulse coupling coefficient of liquid propellants is high, but their specific impulse is low. This is because the ionization rate of propellants is low under laser ablation, and another reason is that the sputtering of propellants is relatively severe. Therefore, it is necessary to study the coupling mechanisms between laser parameters such as pulse width, energy distribution, spot size, and liquid propellants and to design a working mode that optimizes the interaction between lasers and liquid propellants over time. Especially for energetic liquid targets, reasonable laser parameters should be designed to achieve the release of chemical energy.
- Research on composite propulsion targets, such as multiple types of targets and multiphase targets. For example, hexane gun targets and high-viscosity solutions have the propulsion characteristics of both solid and liquid targets, while atomized water droplets belong to composite targets composed of liquid and gas targets. Composite target materials can combine the performance advantages of various target materials and have good propulsion performance, which is an optional development direction for liquid target laser propulsion in the future.
- The plasma emission angle and velocity of liquid-phase metals or alloys during ablation are consistent with solid metals, enabling high specific impulse and easier flow control than viscous liquids. It is a highly promising liquid propellant.
- Research on the mechanism of pulsed laser ablation of liquid propellants. The first consideration is the efficiency of laser energy deposition. An effective deposition of laser energy in the liquid can ensure that the laser effectively ablates the liquid. However, most liquid propellants have weak light absorption characteristics in the pulse width range of spaceborne lasers. Thus, the propellants require further doping, especially under high specific impulse and microscale conditions, where efficiency is crucial. In addition, the dissociation mechanism of liquid propellants by lasers is still not completely understood due to the complex chemical reactions and the variability of their states and phases. The synchronous release mechanism of laser energy and chemical energy of energetic propellants is crucial for improving the propulsion performance of liquids. The loading process of laser energy and the release process of chemical energy need to be synchronous, which helps prevent liquid from splashing out in the combustion chamber. Both energetic processes must quickly release high temperature and pressure to produce a good propulsion effect.
- Research on the design and supply technology of high-performance liquid propellants. Matching laser parameters through the design of liquid propellants is currently the most effective way to improve the performance of laser ablation liquid propulsion. Therefore, the new liquid propellants are a key research issue in LLP. In addition, the supply of liquid propellants and the coordinated operation of high-frequency lasers are also challenging technologies. The products of laser ablation are complex, and there are multiphase flows such as plasma, liquid, and gas, which can cause liquid backflow at the supply end and interfere with the supply state. Therefore, ensuring a stable supply of liquid propellant during laser ablation is a key technology for producing stable and efficient propulsion effects.
- Laser thruster’s integration and optimization. With the rapid advancement of microelectronics and micromachining technology, laser micro-thrusters are also progressing towards miniaturization and high integration. Developing laser micro-thrusters with compact size, low power consumption, reduced mass, and exceptional performance remains a significant challenge. The structural design of a micro-thruster involves the collaborative work of the laser module, power control module, and storage and supply modules. Additionally, considerations must include protecting the laser from contamination by ablation byproducts.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GAP | glycidyl azide polymer |
| HAN | hydroxylammonium nitrate |
| ADN | ammonium dinitramide |
| PLP | pulsed laser propulsion |
| LPT | laser propulsion thruster |
| LLP | liquid laser propulsion |
| CW | continuous laser |
| MFWC | metal-free water cannon |
| WC | water cannon |
| YAG | Yttrium Aluminum Garnet |
| WFC | water film cannon |
| POM | polyoxymethylene resin |
| TEA | Transversely Excited Atmospheric |
| AAD | Acetone + ADN solution + Dye solution |
References
- Kantrowitz, A. Propulsion to orbit by ground based lasers. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 1972, 10, 74–76. [Google Scholar]
- Myrabo, L.N. Brief history of the lightcraft technology demonstrator (LTD) project. AIP Conf. Proc. 2003, 664, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Phipps, C.; Luke, J.; Lippert, T.; Hauer, M.; Wokaun, A. Micropropulsion using a laser ablation jet. J. Propuls. Power 2004, 20, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, C.; Bonnal, C.; Masson, F.; Musumeci, P. Launching swarms of microsatellites using a 100 kW average power pulsed laser. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B Opt. Phys. 2018, 35, B20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurin, A.V.; Kuvaev, K.Y.; Loktionov, E.Y.; Protasov, Y.S.; Sirenko, K.N.; Zakharov, V.I. First attempt of a laser thruster space flight test: Lost at launch. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 120, 105656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, M.; Koizumi, H.; Watanabe, M.; Arakawa, Y. Laser ignition microthruster experiments on KKS-1. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Aeronaut. Space Sci. Aerosp. Technol. Jpn. 2010, 8, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrabo, L. A concept for light-powered flight. In Proceedings of the 18th Joint Propulsion Conference, Cleveland, OH, USA, 21–23 June 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Myrabo, L. World record flights of beam-riding rocket lightcraft—Demonstration of “disruptive” propulsion technology. In Proceedings of the 37th Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 8 July 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Qian, H.; Han, B.; Shen, Z.H.; Ni, X.W. Investigation of the momentum coupling coefficient for propulsion by Nd:YAG laser at 1064 nm in atmospheric and water environment. Optik 2013, 124, 1650–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wu, J.; He, Z.; Zhang, H. A novel laser ablation plasma thruster with electromagnetic acceleration. Acta Astronaut. 2016, 127, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, C.; Birkan, M.; Bohn, W.; Eckel, H.A.; Horisawa, H.; Lippert, T.; Michaelis, M.; Rezunkov, Y.; Sasoh, A.; Schall, W.; et al. Review: Laser-ablation propulsion. J. Propul. Power 2010, 26, 609–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wang, S.; Chang, H.; Hong, Y.; Li, N.; Zhou, W.; Xing, B.; Du, B.; Xie, C. Development of a laser micro-thruster and on-orbit testing. Aerospace 2023, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Sato, S.-I. Quasi-steady operation characteristics of laser-propulsion using liquid H2O fuel. In Proceedings of the AlAA 20th Fluid Dynamics, Piasma Dynamics and Lasers Conference, Buffalo, NY, USA, 12–14 June 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kurasaki, T. Laser Thrust Using Liquid Propelant. Master’s Thesis, Tokyo University, Tokyo, Japan, 1986. (In Japanese). [Google Scholar]
- Sinko, J.; Sasoh, A. Review of CO2 laser ablation propulsion with polyoxymethylene. Int. J. Aerosp. Innov. 2011, 3, 93–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhomov, A.V.; Sinko, J.E. A conceptual tree of laser propulsion. AIP Conf. Proc. 2008, 997, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, Y.; Yabe, T.; Ookubo, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Oozono, H.; Oku, T. Numerical and experimental investigation of laser propulsion. Appl. Phys. A 2004, 79, 829–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.Y.; Hong, Y.J.; Ye, J.F.; Wen, M.; Li, N.L. Effects of laser energy density on impulse coupling coefficient of laser ablation of water for propulsion. Appl. Phys. A 2011, 103, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabe, T.; Phipps, C.; Yamaguchi, M.; Nakagawa, R.; Aoki, K.; Mine, H.; Ogata, Y.; Baasandash, C.; Nakagawa, M.; Fujiwara, E.; et al. Microairplane propelled by laser driven exotic target. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 4318–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabe, T.; Nakagawa, R.; Yamaguchi, M.; Ohkubo, T.; Aoki, K.; Baasandash, C.; Oozono, H.; Oku, T.; Taniguchi, K.; Nakagawa, M.; et al. Simulation and experiments on laser propulsion by water cannon target. In Proceedings of the Beamed Energy Propulsion: First International Symposium on Beamed Energy Propulsion, Huntsville, AL, USA, 5–7 November 2003; pp. 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Sinko, J.E.; Dhote, N.B.; Pakhomov, A.V. Laser propulsion with liquid propellants part II: Thin films. In Proceedings of the Beamed Energy Propulsion: Fifth International Symposium on Beamed Energy Propulsion, Kailua-Kona, HI, USA, 12–15 November 2008; pp. 209–221. [Google Scholar]
- Sinko, J.E.; Pakhomov, A.V. Laser propulsion with liquid propellants part I: An overview. In Proceedings of the Beamed Energy Propulsion: Fifth International Symposium on Beamed Energy Propulsion, Kailua-Kona, HI, USA, 12–15 November 2008; pp. 195–208. [Google Scholar]
- Yabe, T. Prospect of solar-energy-pumped-laser-driven vehicles powered by water. In Proceedings of the Beamed Energy Propulsion: Third International Symposium on Beamed Energy Propulsion, Troy, NY, USA, 11–14 October 2005; pp. 567–578. [Google Scholar]
- Onda, M.; Ootani, T. Experimental study on continuous liquid propellant supply mechanisms for water cannon laser thruster. In Proceedings of the Beamed Energy Propulsion: Fourth International Symposium on Beamed Energy Propulsion, Nara, Japan, 15–18 November 2006; pp. 297–307. [Google Scholar]
- Yabe, T.; Ohzono, H.; Ohkubo, T.; Baasandash, C.; Yamaguchi, M.; Oku, T.; Taniguchi, K.; Miyazaki, S.; Akoh, R.; Ogata, Y.; et al. Proposal of liquid cannon target driven by fiber laser for micro-thruster in satellite. In Proceedings of the Beamed Energy Propulsion: Second International Symposium on Beamed Energy Propulsion, Sendai, Japan, 20–23 October 2004; pp. 503–512. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, M.; Fujita, K.; Uchida, S.; Bato, M.; Niino, M. Fundamental experiments on glycerin propellant laser thruster. In Proceedings of the Beamed Energy Propulsion: Second International Symposium on Beamed Energy Propulsion, Sendai, Japan, 20–23 October 2004; pp. 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Fardel, R.; Urech, L.; Lippert, T.; Phipps, C.; Fitz-Gerald, J.M.; Wokaun, A. Laser ablation of energetic polymer solutions: Effect of viscosity and fluence on the splashing behavior. Appl. Phys. A 2009, 94, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, S.A.; Panchenko, A.N.; Batrakov, A.V.; Ljubchenko, F.N.; Mataibaev, V.V. Experimental study of the laser ablation plasma flow from the liquid Ga–In target. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2011, 39, 1412–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, S.A.; Batrakov, A.V.; Kanonykhin, A.V.; Mataibaev, V.V. Hybrid plasma source based simultaneously on laser ablation and vacuum arc discharge for plasma propulsion. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Symposium on Discharges and Electrical Insulation in Vacuum (ISDEIV), Mumbai, India, 28 September–3 October 2014; pp. 729–732. [Google Scholar]
- Kurilovich, D.; Klein, A.L.; Torretti, F.; Lassise, A.; Hoekstra, R.; Ubachs, W.; Gelderblom, H.; Versolato, O.O. Plasma propulsion of a metallic microdroplet and its deformation upon laser impact. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2016, 6, 014018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurilovich, D.; Pinto, T.D.F.; Torretti, F.; Schupp, R.; Scheers, J.; Stodolna, A.S.; Gelderblom, H.; Eikema, K.S.E.; Witte, S.; Ubachs, W.; et al. Expansion dynamics after laser-induced cavitation in liquid tin microdroplets. Physi. Rev. Appl. 2018, 10, 054005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurilovich, D.; Basko, M.M.; Kim, D.A.; Torretti, F.; Schupp, R.; Visschers, J.C.; Scheers, J.; Hoekstra, R.; Ubachs, W.; Versolato, O.O. Power-law scaling of plasma pressure on laser-ablated tin microdroplets. Phys. Plasmas 2018, 25, 012709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ready, J.F. Effects of High-Power Laser Radiation, 1st ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Noack, J.; Vogel, A. Laser-induced plasma formation in water at nanosecond to femtosecond time scales: Calculation of thresholds, absorption coefficients, and energy density. IEEE J. Quant. Electron. 1999, 35, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, R.H.; Weller, R. Underwater explosions. Phys. Today 1948, 1, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.; Presles, H.N. Reflectivity of a 5.8 kbar shock front in water. J. Chem. Phys. 1981, 74, 6864–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhomov, A.V.; Gregory, D.A.; Thompson, M.S. Specific impulse and other characteristics of elementary propellants for ablative laser propulsion. AIAA J. 2002, 40, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabe, T.; Phipps, C.; Aoki, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Nakagawa, R.; Baasandash, C.; Ogata, Y.; Shiho, M.; Inoue, G.; Onda, M.; et al. Laser-driven vehicles—From inner-space to outer-space. Appl. Phys. A 2003, 77, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Cai, J.; Ma, H.H.; Li, G.X.; Li, L.; Shen, Z.W.; Tang, Z.P. Research on applications of rectangular beam in micro laser propulsion. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 301, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senegačnik, M.; Jezeršek, M.; Gregorčič, P. Propulsion effects after laser ablation in water, confined by different geometries. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkubo, T. Laser propulsion using metal-free water cannon target. In Proceedings of the Beamed Energy Propulsion: Third International Symposium on Beamed Energy Propulsion, Troy, NY, USA, 11–14 October 2005; pp. 394–405. [Google Scholar]
- Sinko, J.; Kodgis, L.; Porter, S.; Sterling, E.; Lin, J.; Pakhomov, A.V.; Larson, C.W.; Mead, F.B. Ablation of Liquids for Laser Propulsion with TEA CO2 Laser, Conference Presentation Slides: AFRL-PR-ED-VG-2005-395; Air Force Research Laboratory; Wright-Patterson AFB: Riverside, OH, USA, 2005; Available online: https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/tr/pdf/ADA442452.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2005).
- Sterling, E.; Pakhomov, A.V.; Larson, C.W.; Mead, F.B., Jr. Absorption-enhanced liquid ablatants for propulsion with TEA CO2 Laser. In Proceedings of the Beamed Energy Propulsion: Third International Symposium on Beamed Energy Propulsion, Troy, NY, USA, 11–14 October 2005; pp. 474–481. [Google Scholar]
- Sinko, J.; Kodgis, L.; Porter, S.; Lin, J.; Pakhomov, A.V.; Larson, C.W.; Mead, J.; Franklin, B. An analysis of force generation in TEA CO2 laser ablation of liquids. In Proceedings of the High-Power Laser Ablation 2006, Taos, NM, USA, 7–12 May 2006; p. 62611W. [Google Scholar]
- Sinko, J. Time-Resolved Force and Imaging Study on the Laser Ablation of Liquids. Master’s Thesis, The University of Alabama in Huntsville, Huntsville, AL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sterling, E.; Pakhomov, A.V.; Larson, C.W.; Mead, F.B. Absorption Enhanced Liquid Ablatants for Propulsion with TEA CO2 Laser. AIP Conf. Proc. 2005, 766, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segelstein, D.J. The Complex Refractive Index of Water. Master’s Thesis, University of Missouri-Kansas City, Kansas City, MO, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Sterling, E. Absorption-Enhanced Liquid Ablatants for Laser Propulsion with Tea CO2 Laser. Master’s Thesis, The University of Alabama in Huntsville, Huntsville, Al, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.; Hao, Z.Q.; Yuan, X.H.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, X.; Wang, Z.H.; Wei, Z.Y. The characteristics of confined ablation in laser propulsion. Chin. Phys. 2006, 15, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.; Hao, Z.Q.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, M.; Lu, X.; Wang, Z.H.; Wei, Z.Y. Paper airplane propelled by laser plasma channels generated by femtosecond laser pulses in air. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 10616–10621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Zheng, Z.Y.; Liu, F.; Zhu, P.F.; Li, H.M.; Li, Y.T.; Li, Y.J.; Zhang, J. Transmitted laser propulsion in confined geometry using liquid propellant. Appl. Phys. A 2008, 91, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Chen, M.; Lu, X.; Li, Y.T. Enhancement of coupling coefficient of laser plasma propulsion by water confinement. Appl. Phys. A 2006, 85, 441–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Pan, Y.X.; Xue, Y.L.; Chen, J.; Shen, Z.H.; Lu, J.; Ni, X.W. Mechanical effects of laser-induced cavitation bubble on different geometrical confinements for laser propulsion in water. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2011, 49, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Chen, J.; Shen, Z.H.; Lu, J.; Ni, X.W. Investigation of the wedge-shaped propelled surface for laser propulsion in water environment. Opt. Laser Technol. 2011, 43, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.C.; Shen, Z.H.; Lu, J.; Ni, X.W. Influence of different interfaces on laser propulsion in water environment. Opt. Laser Technol. 2010, 42, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Shen, Z.H.; Lu, J.; Ni, X.W. Numerical study of water-confinement geometries for laser propulsion. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2010, 48, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, L.; Tang, Z.; Cai, J. Experimental investigation of liquid-propellant laser propulsion with a horizontal momentum measuring lever. In Proceedings of the Beamed Energy Propulsion: 6th International Symposium, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 1–5 November 2010; pp. 243–253. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Wang, B.; Hu, X.; Tang, Z. The experimental investigation of laser-driven water vehicle. J. Exp. Mech. 2007, 22, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinko, J. Vaporization and shock wave dynamics for impulse generation in laser propulsion. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Alabama in Huntsville, Huntsville, AL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Hong, Y.; Wen, M.; Cui, C.; He, G. Influencing factors on propulsive performances of water droplets for laser propulsion. J. Propul. Power 2010, 26, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hong, Y.; Wen, M.; Cui, C.; Chen, Z. Effects of nozzle configuration and laser focusing site on propulsive performances of atomized water droplets. High Power Part. Beams 2011, 23, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, T.; David, C.; Hauer, M.; Phipps, C.; Wokaun, A. Tailor-made polymers for laser ablation. Rev. Laser Eng. 2001, 29, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, T.; David, C.; Hauer, M.; Wokaun, A.; Robert, J.; Nuyken, O.; Phipps, C. Polymers for UV and near-IR irradiation. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2001, 145, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, T.; David, C.; Hauer, M.; Masubuchi, T.; Masuhara, H.; Nomura, K.; Nuyken, O.; Phipps, C.; Robert, J.; Tada, T.; et al. Novel applications for laser ablation of photopolymers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 186, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, T.; Hauer, M.; Phipps, C.R.; Wokaun, A. Fundamentals and applications of polymers designed for laser ablation. Appl. Phys. A 2003, 77, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Nakano, M.; Uchida, S.; Bato, M.; Niino, M. Impulse generation mechanism in glycerin propellant laser thruster. In Proceedings of the Beamed Energy Propulsion: Second International Symposium on Beamed Energy Propulsion, Sendai, Japan, 20–23 October 2004; pp. 146–151. [Google Scholar]
- Lippert, T.; Urech, L.; Fardel, R.; Nagel, M.; Phipps, C.R.; Wokaun, A. Materials for laser propulsion: “Liquid” polymers. In Proceedings of the High-Power Laser Ablation 2008, Taos, NM, USA, 20–27 April 2008; p. 700512. [Google Scholar]
- Fardel, R.; Feurer, P.; Lippert, T.; Nagel, M.; Nüesch, F.A.; Wokaun, A. Laser ablation of aryltriazene photopolymer films: Effects of polymer structure on ablation properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 254, 1332–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Y.; He, R.; Dong, A.G.; Fan, Z.J. Effect of viscosity of liquid glycerol on laser plasma propulsion. Phys. Exp. 2012, 32, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Ye, J.; Zhou, W. Effects of dopant on impulse coupling of laser ablated glycerin. J. Propul. Technol. 2015, 36, 1595–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Dou, Z.; Ye, J.; Li, N.; Zhang, G.; Wan, Y. Experimental study on influence of splashing behavior on mechanical effects. High Power Laser Part. Beams 2014, 26, 101020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Hong, Y.; Li, N. Experimental study on thrust performance of carbon doped liquid working substance processed by laser ablation. Chin. J. Lasers 2017, 44, 0202001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Hong, Y.; Li, N. Impulse coupling performance of liquid propellant with ns laser micro ablation. Infrar. Laser Eng. 2015, 44, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Hong, Y.; Li, N. Splash generation and evolvement in the laser ablation with liquid working substance. In Proceedings of the Selected Proceedings of the Photoelectronic Technology Committee Conferences, Suzhou, China, 21 February 2014; p. 914218. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Zhang, S.; Liang, T.; Xiao, K.; Tang, W.; Zheng, Z. Ablation characteristics of carbon-doped glycerol irradiated by a 1064 nm nanosecond pulse laser. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2018, 20, 035508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Y.; Liang, T.; Zhang, S.Q.; Gao, L.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Z.L. Ablation of carbon-doped liquid propellant in laser plasma propulsion. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Y.; Zhang, S.Q.; Liang, T.; Gao, L.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Z.L. Characteristics of droplets ejected from liquid glycerol doped with carbon in laser ablation propulsion. Chin. Phys. B 2016, 25, 045204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Y.; Zhang, S.Q.; Liang, T.; Tang, W.C.; Xiao, K.; Liang, W.F.; Gao, L.; Gao, H.; Xing, J.; Wu, X.W.; et al. Characterization of laser ablation of carbon-doped glycerol at different laser wavelengths. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P. An overview on properties, thermal decomposition, and combustion behavior of ADN and ADN based solid propellants. Def. Technol. 2018, 14, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Xue, B.; Chen, J.G.; He, Z.H.; Ji, Y.; Wang, B.; Lu, J.; Liu, Z.W.; Liu, Z.T. A combined experimental and theoretical study of the thermal decomposition mechanism and kinetics of ammonium dinitramide (ADN). New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 6833–6844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenmann, D.; Ciezki, H.K. ADN and HAN-based monopropellants—A minireview on compatibility and chemical stability in aqueous media. Propell. Explos. Pyrot. 2019, 44, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Cao, J.; Zheng, Y.; Du, B.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Ye, Y.; Shen, R. Effects of pulse laser energy on propulsion characteristics of ADN-based propellant. J. Propul. Technol. 2023, 44, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Cui, H.; Zheng, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Zhou, B.; Ye, Y.; Shen, R. Effect of absorption depth on chemical energy release from laser ablation of ADN-based liquid propellants. Acta Astronaut. 2023, 204, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Du, B.; Wu, L.; Zhang, W.; Pan, Y.; Ye, Y.; Shen, R.; Zhou, B. The influence of aluminum nanoparticles on the laser ablation characteristics of hydroxylamine nitrate-based liquid propellants. Acta Astronaut. 2022, 197, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Zheng, Y.; Mao, C.; Cui, H.; Han, J.; Jiang, L.; Ye, J.; Hong, Y. Transmissive mode laser micro-ablation performance of ammonium dinitramide-based liquid propellant for laser micro-thruster. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.L.; Zhao, F.Q.; Kuo, K.K.; Zhang, X.H.; Zeman, S.; DeLuca, L.T. Catalytic effects of nano additives on decomposition and combustion of RDX-, HMX-, and AP-based energetic compositions. Prog. Energy Combus. Sci. 2016, 57, 75–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.; Srivastava, P.K.; Varma, M. Recent advances in catalytic combustion of AP-based composite solid propellants. Def. Technol. 2021, 17, 1013–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Jiang, L.; Du, B.; Zheng, Y.; Cui, H.; Wang, D.; Ye, J.; Han, J.; Hong, Y. Theoretical investigation of laser ablation propulsion using micro-scale fluid in atmosphere. Aerospace 2024, 11, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Mao, C.; Han, J.; Cui, H.; Du, B.; Zheng, Y.; Ye, J.; Hong, Y. Effects of different initial conditions on combustion process of ammonium dinitramide-based energetic propellant in straight nozzle. Aerospace 2024, 11, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhomov, A.V.; Thompson, M.S.; Swift, W.; Gregory, D.A. Ablative laser propulsion: Specific impulse and thrust derived from force measurements. AIAA J. 2002, 40, 2305–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, C.R.; Luke, J.R. Laser plasma thruster. US6530212B1, 11 March 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Götz, T.; Stuke, M. Short-pulse UV laser ablation of solid and liquid metals: Indium. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 1997, 64, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zergioti, I.; Stuke, M. Short pulse UV laser ablation of solid and liquid gallium. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 1998, 67, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.N.; Schou, J.; Lunney, J.G. Langmuir probe study of plasma expansion in pulsed laser ablation. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 1999, 69, S601–S604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi, L.; Andò, L.; Ciavola, G.; Gammino, S.; Barnà, A. Angular distribution of ejected atoms from Nd:YAG laser irradiating metals. Rev. Sci. Instr. 2001, 72, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, D.; Butt, M.Z.; Khaleeq-ur-Rahman, M. Ablation yield and angular distribution of ablated particles from laser-irradiated metals: The most fundamental determining factor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2854–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bykovskii, Y.A.; Degtyarenko, N.N.; Elesin, V.F.; Kozyrev, Y.P.; Sil’nov, S.M. Mass spectrometer investigation of a laser plasma. Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 1971, 60, 1306–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urech, L.; Lippert, T.; Phipps, C.R.; Wokaun, A. Polymer ablation: From fundamentals of polymer design to laser plasma thruster. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 6409–6415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumakov, A.N.; Bosak, N.A.; Petrenko, A.M.; Bogdanovich, M.V.; Yenzhyieuski, A.I.; Pozhidaev, A.V.; Shemelev, M.A.; Ryabtsev, A.G.; Ryabtsev, G.I.; Stankevich, Y.A. Pulsed plasma thruster based on solid-state lasers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Lasers, Applications, and Technologies ‘07, Minsk, Belarus, 28 May–15 June 2007; p. 673510. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales, D.A.; Baker, R.P. Micropropulsion using a Nd:YAG microchip laser. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on High-Power Laser Ablation 2002, Taos, NM, USA, 21–26 April 2002; p. 752. [Google Scholar]
- Chumakov, A.N.; Grabtchikov, A.S.; Orlovich, V.A.; Shpak, P.V.; Bosak, N.A.; Petrenko, A.M.; Chekan, P.V.; Malevich, P.N. Study of microchip laser use possibility in laser-plasma thrusters for space application. In Proceedings of the 7th Belarussian-Russian Workshop: Semiconductor Lasers and System, Minsk, Belarus, 1–5 June 2009; pp. 124–128. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, S.A.; Dubrovskaya, E.L.; Batrakov, A.V. The concept of a hybrid pulsed plasma thruster for small-size space satellites. Russ. Phys. J. 2019, 61, 2079–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schein, J.; Qi, N.; Binder, R.; Krishnan, M.; Ziemer, J.K.; Polk, J.E.; Anders, A. Inductive energy storage driven vacuum arc thruster. Rev. Sci. Instr. 2002, 73, 925–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, B.; Ye, J.; Li, N. Laser ablation characteristics of liquid energetic polymers with micro flow feed system. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Laser Interaction with Matter, Changsha, China, 11–14 November 2019; p. 64. [Google Scholar]
- O’Briant, S.A.; Gupta, S.; Vasu, S. Review: Laser ignition for aerospace propulsion. Propuls. Power Res. 2016, 5, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroupa, G.; Tabakaev, D.; Börner, M.; Rackemann, N.; Soller, S. Overview and recent applications of the miniaturized HiPoLas ignition system. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 42289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Country | Leader | Laser Parameters | Target | Constrained State | Cm (N/MW) | Isp (s) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | Yabe | 1.064 μm 5 ns | Water (Al) | L(S) | 3536 | - | [19,41] |
| 10.6 μm 100 ns | Water (Al) | L(S) | 400 | - | |||
| America | Pakhomov | 10.6 μm 300 ns | Water (quartz glass/Al): Cylinder | L(S) | 600 | - | [44,45] |
| Hexane (quartz glass/Al): Cone | L(S) | 240 | - | ||||
| Ethanol (quartz glass): Cylinder | L(S) | 560 | - | ||||
| Ethanol (Al): Cone | |||||||
| Water (Al) | L(S) | 450 | [46] | ||||
| China | Z.Y. Zheng | 0.532 μm 7 ns | Water | L(S) | 2500 | 8.9 | [52] |
| Slovenia | Matej Senegačnik | 1.064 μm 7 ns | Water: F | L | 1800 | - | [40] |
| Water (Al): D2 | L(S) | 10,200 | - | ||||
| Water (Al): D3 | L(S) | 8700 | - | ||||
| China | Z.P. Tang | 1.064 μm 12 ns | Water | L(S) | 1790 | 19 | [57] |
| China | Y.J. Hong | 1.064 μm 10 ns | Water droplet | (L, G) | 500 | 100 | [60] |
| Japan | Yabe | 10.6 μm 100 ns | MFWC | S(L) | 2400 | - | [19,41] |
| America | Pakhomov | 10.6 μm 300 ns | POM (Water) | S(L) | 600 | - | [42,44] |
| POM (NaBF4) | S(L) | 450 | 3 | [43] | |||
| POM (hexane) | S(L) | 570 | - | [59] | |||
| China | Z.Y. Zheng | 0.532 μm 7 ns | Water model car | S(L) | 3990 | - | [49,50] |
| China | X.W. Ni | 1.064 μm 10 ns | Al (Water) | S(L) | 3400 | - | [53] |
| Slovenia | Matej Senegačnik | 1.064 μm 7 ns | Al (Water): F | S(L) | 6900 | - | [40] |
| Al (Water): D2 | S(L) | 10,200 | - | ||||
| Al (Water): D3 | S(L) | 5800 | - | ||||
| China | Z.P. Tang | 1.064 μm 12 ns | Al (Water) | S(L) | 9839 | - | [58] |
| Fe (Water) | S(L) | 7700 | - | ||||
| Cu (Water) | S(L) | 4100 | - | ||||
| Zn (Water) | S(L) | 8100 | - | ||||
| Japan | Yabe | 1.064 μm 5 ns | WFC | G(L) | 3680 | - | [19,41] |
| Country | Leader | Laser Parameters | Target | Dopant | Cm (N/MW) | Isp (s) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | Fujita | 1.064 μm 10 ns | GAP | - | 232 | - | [66] |
| Switzerland | T. Lippert | 1.064 μm 6 ns | GAP | infrared dye | - | 680 | [67,68] |
| China | Zhiyuan Zheng | 0.532 nm 10 ns | Glycerine | - | 4360 | 6 | [69] |
| 0.532 nm 10 ns | Glycerine | - | 3000 | 8 | [75,76,77,78] | ||
| 1.064 nm 10 ns | Glycerine | - | 3750 | 9.5 | |||
| China | Jifei Ye | 1.064 nm 8 ns | GAP | carbon | 1493 | 140 | [73] |
| Glycerine | carbon | 1470 | - | [72] | |||
| ADN | infrared dye | 624.3 | 234.9 | [85] | |||
| China | Lizhi Wu | 1.064 nm 6.5 ns | ADN | infrared dye | 875.7 | 281.6 | [82] |
| ADN | 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium dicyandiamide | 1070 | 84.14 | [83] | |||
| HAN | aluminum nanoparticles | 640 | 189 | [84] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Du, B.; Cui, Q.; Ye, J.; Cui, H.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Han, J. A Review on Liquid Pulsed Laser Propulsion. Aerospace 2025, 12, 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12070604
Li S, Du B, Cui Q, Ye J, Cui H, Gao H, Wang Y, Zheng Y, Han J. A Review on Liquid Pulsed Laser Propulsion. Aerospace. 2025; 12(7):604. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12070604
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Sai, Baosheng Du, Qianqian Cui, Jifei Ye, Haichao Cui, Heyan Gao, Ying Wang, Yongzan Zheng, and Jianhui Han. 2025. "A Review on Liquid Pulsed Laser Propulsion" Aerospace 12, no. 7: 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12070604
APA StyleLi, S., Du, B., Cui, Q., Ye, J., Cui, H., Gao, H., Wang, Y., Zheng, Y., & Han, J. (2025). A Review on Liquid Pulsed Laser Propulsion. Aerospace, 12(7), 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12070604






