Abstract
To enhance the accuracy and efficiency of reliability analyses for an aero-engine vectoring exhaust nozzle (VEN), a dual-stochastic extreme response surface method based on the genetic algorithm (DSERSM-GA) is developed by integrating the genetic algorithm, the random extremum response surface method, and the dual response surface method in the paper. In the proposed method, a limited set of Monte Carlo samples is strategically utilized to construct and optimize a population-based response surface model, forming a robust mathematical framework for reliability prediction. The uncertainty sources considered include aerodynamic loads acting on the vector nozzle, material densities of the expansion plate and triangular link, as well as the elastic moduli of these components. Stress and deformation responses of both the expansion plate and triangular link are employed as the performance metrics. The proposed DSERSM-GA methodology is validated through dynamic reliability simulations applied to a vector nozzle system, yielding distributions and corresponding reliability indices of critical responses. Comparative analyses against traditional Monte Carlo Simulation (MCS) and conventional Extreme Response Surface Methods (ERSM) demonstrate that the DSERSM-GA significantly reduces computational costs while preserving high predictive accuracy.
1. Introduction
The vector nozzle of an aircraft engine represents an advanced thrust-vectoring technology designed to redirect engine exhaust flow, thereby significantly enhancing aircraft maneuverability and reducing required take-off and landing distances. As a spatially flexible mechanism possessing multiple degrees of freedom, the vector nozzle system typically comprises over 200 moving components interconnected through more than 300 kinematic pairs [1,2]. Ensuring reliable and coordinated operation of axisymmetric vector nozzles under complex operating conditions and various uncertainties—while maintaining interference-free motion among highly coupled mechanisms—remains a critical and unresolved engineering challenge. Preventing faults such as jamming, stalling, and mechanical interference is essential to achieving the designed kinematic behavior and operational reliability of the nozzle system.
Due to the intricate coupling effects arising from multiple clearances and flexible components within the vector nozzle system, the accuracy of reliability analyses based on the Single-Failure-Mode Extreme Response Surface Method (SERSM) is significantly limited. Consequently, there is a pressing need for a more robust reliability analysis approach capable of addressing dual-coupled failure modes. To enhance both the accuracy and computational efficiency of reliability analyses for complex mechanical systems, various advanced response surface models have been introduced, such as second-order polynomial response surface models, Support Vector Machine-based Response Surface Methods (SVM-RSM) [3], Artificial Neural Network-based Response Surface Methods (ANN-RSM) [4], Stochastic Response Surface Methods (SRSM) [5], and Extreme Response Surface Methods (ERSM) [6]. Furthermore, researchers have combined response surface and extreme response surface methods with additional algorithms, leading to the development of a range of sophisticated computational methods tailored specifically for reliability analysis.
Abbasi et al. [7] extended the concept of rational linear spline fuzzy numbers by introducing fuzzy arithmetic operations between two such fuzzy numbers. In their method, the reliability of each component is represented by a rational linear spline fuzzy number, providing a more flexible and intelligent framework for modeling and analyzing the reliability of fuzzy systems. Zhang et al. [8] proposed a reliability estimation method for turbine disks with hybrid fuzzy and p-box variables, based on equivalent entropy transformation and saddlepoint approximation (SPA). By leveraging entropy invariance, fuzzy variables with non-normal membership functions are transformed into normally distributed random variables. This method, combined with SPA, significantly reduces the required sample size and computational cost while improving both efficiency and accuracy. Xiao et al. [9] developed a three-layer feedforward neural network model with continuous optimization for reliability prediction. The model was trained through simulation by comparing test data errors with existing correlated reliability data. Compared to traditional BP neural networks, this model offers faster learning speed and improved nonlinear fitting capability. It was applied to the reliability analysis of CNC machine tool spindles. Eshghi et al. [10] proposed an adaptive enhanced response surface method based on traditional RSM. This method integrates the least squares approach with a novel weighting function to achieve adaptive capability and was successfully applied in saturated design and central composite design scenarios. Zhu et al. [11] combined Gaussian regression functions with response surface theory to develop a Gaussian Regression Response Surface Method, which was applied to the reliability analysis of civil engineering slopes. Nie et al. [12] represented the fuzzy characteristic parameters of structural fuzzy-random variables as the sum of their crisp values and fuzzy perturbations. By selecting equivalent perturbations, the probability density function and performance function were decomposed into a series of intervals under different α-cut levels. Taylor series expansion was then performed at the interval bounds, and a sigmoid function was introduced into the reliability function to approximate the step function via the direct integration method, yielding the fuzzy reliability index. The validity and accuracy of the proposed method were verified through simulations. Du et al. [13] established a fuzzy reliability mathematical model using a fuzzy random probability approach. An optimal membership function was selected, and to address the difficulty of evaluating multi-dimensional integrals within the model, a dual neural network-based direct integration method was proposed. This approach effectively solves structural fuzzy reliability problems involving multiple random variables, demonstrating high computational efficiency and accuracy. Chen et al. [14] proposed an adaptive learning function for the Kriging model in fuzzy uncertainty reliability analysis and validated the effectiveness and accuracy of the method through case studies. Zhai et al. [15] introduced a stochastic model updating strategy for reliability analysis, based on an improved response surface model combined with Monte Carlo simulation. This method enhances both the computational accuracy and efficiency for complex structural models. Zhang et al. [16,17,18,19] successively proposed a series of advanced intelligent reliability analysis methods, including the Improved Intelligent Response Surface Method, the Intelligent Extreme Response Surface Method, the Distributed Cooperative Generalized Regression Extreme Neural Network (DC-GRENN) Method, the Generalized Regression Extreme Neural Network (GRENN) Method, the Fuzzy Intelligent Multi-Extreme Response Surface Method for Blade Fatigue Life Reliability Analysis, and the Particle Swarm Optimization–Advanced Extreme Response Surface Method (PSO-AERSM). These methods have been applied to the reliability evaluation of turbine tip clearance, low-cycle fatigue (LCF) life and sensitivity analysis of blades under thermo-structural interactions, and the reliability analysis and optimization of flexible mechanisms. All these approaches have shown significant improvements in both computational accuracy and efficiency. Xueqin Li et al. [20] integrated the strengths of an Improved Differential Evolution (IDE) algorithm and neural network models into a decomposed cooperative framework and proposed a Multi-Agent Cooperative Modeling (MACM) method. Using a representative turbine rotor as a case study, the method was applied to fatigue reliability estimation, demonstrating enhanced accuracy and simulation efficiency in fatigue life prediction of steam turbine rotors. Song et al. [21,22] combined neural network metamodels with a distributed coordination strategy and proposed a Distributed Coordination Neural Network Metamodel and an Advanced Multi-Level Response Surface Method. These approaches were employed for probabilistic low-cycle fatigue estimation and sensitivity analysis of turbine disks, significantly improving the computational efficiency and accuracy of the fatigue reliability assessment. Yang et al. [23] proposed a reliability assessment method based on an adaptive surrogate model. This approach employs a novel learning function to adaptively select the most informative samples for model updating. Theoretically, this function can be combined with various surrogate models. The effectiveness and accuracy of the proposed method have been validated through case studies. Meng et al. [24] developed a PINN-FORM framework by integrating Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) with the First-Order Reliability Method (FORM). This method enables simultaneous prediction of partial differential equation (PDE) solutions and reliability indices within a single training process, demonstrating high computational accuracy. She et al. [25] optimized the Kriging surrogate model using an Improved Wolf Pack Algorithm (IWPA) and proposed a parallel infill strategy (IWPA-NLF) that combines IWPA with a novel learning function (NLF) to update the Kriging model. The final reliability evaluation is performed using the Subset Simulation (SS) method. The proposed approach exhibits strong function approximation capabilities and achieves accurate failure probability estimates with a limited number of function evaluations. Luo et al. [26] introduced a reliability analysis method that couples the Kriging model with the Conjugate First-Order Reliability Method (AK-CFORM). This method offers significant advantages in terms of system response efficiency and surrogate model performance, providing a stable and accurate reliability estimation framework. Song et al. [27] proposed a physical embedding multi-response regressor for the reliability assessment of time-varying systems, effectively enhancing the modeling accuracy of dynamic systems. Additionally, their team introduced a cascaded sampling-driven block mapping method [28] and a cascaded ensemble learning framework [29] for the coupled reliability analysis and multi-level reliability assessment of turbine cooling systems, significantly improving the computational efficiency and robustness of complex systems. Li et al. [30] developed a multi-variable integrated hierarchical linking strategy for the system reliability assessment of aero-engine cooling blades; in addition, they proposed a vector surrogate modeling method [31] for the probabilistic assessment of turbine rotors with multiple failure correlations, providing new ideas for reliability analysis under multiple failure modes.
The aforementioned studies on response surface methodologies have significantly improved the computational accuracy and efficiency of reliability analysis, thereby advancing the theoretical development of mechanical system reliability assessment. However, to date, no research has been reported on the application of a dual-stochastic extreme response surface method based on the genetic algorithm for the reliability analysis of vector nozzles in aircraft engines.
In this study, a dual-stochastic extreme response surface method based on the genetic algorithm (DSERSM-GA) is proposed for the reliability analysis of aircraft engine vector nozzles. Specifically, the velocities of the four actuating cylinders (P1, P2, P3 and P4), the clearances between kinematic pairs, and the random load coefficient p are treated as random input variables. A small number of samples are first drawn using the Monte Carlo method, and a trained network model is constructed to establish the mathematical formulation of the proposed method. Subsequently, large-scale joint sampling of the input random variables is performed, and the reliability index of the structure is evaluated by substituting the samples into the DSERSM-GA.
2. Basics of DSERSM-GA
2.1. DSERSM
The Dual-Extreme Response Surface Method (DERSM) involves the construction of two extreme response surface equations. For each sampled set of input random variables, two corresponding extreme output response values are calculated, as follows:
where X is the input random variable vector; Y is the output response vector, i is the number of input variables; n is the number of output responses. The extreme value of each output is used to fit the response surface using least squares, and the dual-extreme response surface model is established as shown in Equation (2).
The input random variable x in Equation (2) is transformed using Hermite polynomials to construct a double stochastic extreme response surface mathematical model, whose mathematical model is as shown in Equation (3).
where i1, i2, …, ip is assigned the value of 1, 2, …, n; denotes the polynomial coefficients, n = 1, 2; , are the constant terms; Hp(ξi1, ξ i2, …, ξip) represents the Hermite polynomial of order p, which is expressed as:
where ξ = (ξi1, ξ i2, …, ξip) is a random vector obtained by transforming the random variable x into a standard normally distributed form.
2.2. Basics of DSERSM-GA
To enhance data fitting accuracy and computational performance, the Dual-Stochastic Extreme Response Surface Method (DSERSM) is combined with the Genetic Algorithm (GA). The GA is employed to optimize the coefficients of the DSERSM, thereby achieving more accurate approximation of the data. The detailed procedure is illustrated in Figure 1.
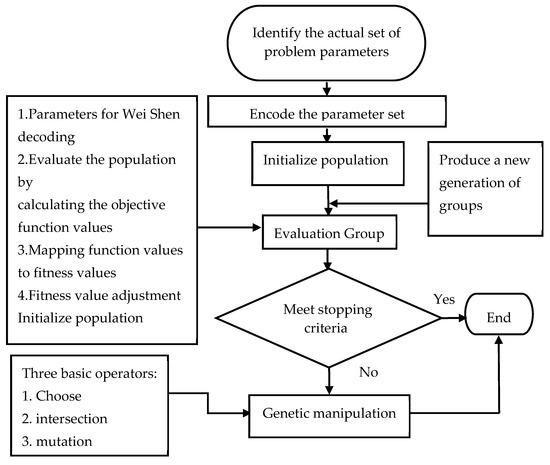
Figure 1.
Genetic Algorithm Flowchart.
(1) The constructed dual-stochastic extreme response surface equation is transformed into a minimization problem, where the set of random input variables and their corresponding output responses are treated as parameters, and the coefficients are defined as the optimization objectives. The transformed mathematical model is given in Equation (5).
(2) Real-number encoding is applied, where each chromosome is represented as a real-valued vector corresponding to a set of random variables.
(3) A total of n data sets are randomly selected from the input variables and their corresponding output responses to initialize the population.
(4) A function transformation is performed to convert the objective into a minimization problem. The reciprocal of the function value is taken as the fitness of each individual. The smaller the function value, the higher the fitness, and the better the individual. The fitness evaluation function is defined as:
(5) Individuals are selected from the current population with a certain probability to form a new population, from which the next generation is produced. The selection probability is proportional to the fitness of each individual—the higher the fitness, the greater the chance of being selected. The selection probability of individual i is given by:
(6) Two individuals are randomly selected from the population, and their superior characteristics are combined to generate a new individual. The crossover operation at the j-th position between the k-th and l-th chromosomes is defined as:
where b is a random number uniformly distributed in the interval [0, 1].
(7) One individual is randomly selected from the population, and a mutation is performed at a randomly chosen gene position to generate a potentially better individual. The mutation operation for the h-th gene of the i-th individual is defined as:
where amax denotes the upper bound of aih gene; amin is the lower bound of aih gene, r2 is a random number; g is the current iteration number, Gmax is the maximum number of generations; r is a random number uniformly distributed in the interval [0, 1].
(8) The current result obtained from the genetic algorithm is used as the initial value for local optimization. The fmincon function from the MATLAB R2023b Optimization Toolbox is employed to perform local search based on nonlinear programming. The locally optimized solution is then used to update the chromosome for further evolution.
(9) After the specified number of generations is reached, the optimal set of coefficients obtained through the optimization process is substituted into Equation (3) to construct the DSERSM-GA Model.
where , denote the optimized coefficients.
2.3. Reliability Evaluation Approach Using the DSERSM-GA
When the reliability analysis of a structural system involves two or more failure modes, the MCM (Multi-Coupled Monte Carlo) sampling technique [16] is employed to simultaneously generate samples of input random variables corresponding to each failure mode. Based on the coupled limit state function described in Equation (11), the overall structural reliability probability is then calculated.
where E denotes the failure event corresponding to each failure mode.
The MCM technique is used to perform coupled sampling of the input random variables contained in Equation (10). The sampled values are substituted into Equation (10) to compute the corresponding output responses. Each output response is then compared with its allowable limit: if the response exceeds the allowable value, it is considered a failure; otherwise, it is considered safe. By aggregating the results, the structural system reliability can be statistically estimated.
3. Kinematic Reliability Analysis Theory of the Vector Nozzle
The kinematic reliability of a vector nozzle refers to the probability that the kinematic objective function values (such as nozzle exit area, yaw angle, and pitch angle) remain within the allowable deviation range during the execution of a vectoring maneuver. This analysis considers the effects of component flexibility, kinematic pair clearances, and the randomness of input variables, under the condition that the actuating cylinder velocities randomly vary around their design mean values.
Let E denote the kinematic objective function for a specific vectoring maneuver. If the required operating range is [Emin, Emax], then the kinematic reliability of this vectoring maneuver is defined as:
When multiple objective functions are used to represent the kinematic performance, the kinematic reliability of the vector nozzle is expressed as:
During the time interval of the aircraft take-off phase, the pitch angle of the vector nozzle must fall within the range ; otherwise, it will be unable to provide sufficient lift to meet the requirement for reduced runway length. The corresponding reliability calculation is given by:
4. Simulation Example
4.1. Modeling of the Vector Nozzle
Based on the geometric dimensions, assembly relationships, and kinematic pairs of the vector nozzle components, a functional virtual prototype of the vector nozzle was constructed using the multibody dynamics simulation software ADAMS, as shown in Figure 2 [32]. During operation, the nozzle performs expansion, contraction, pitch, yaw, and various combined maneuvers by controlling the motions of the four actuating cylinders.
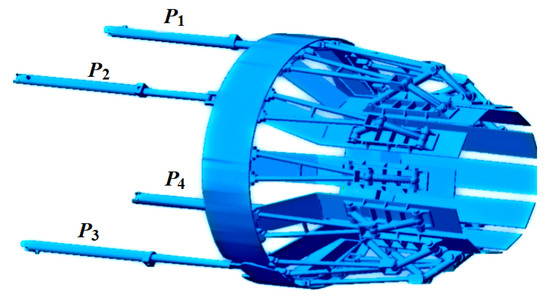
Figure 2.
Vector tail nozzle virtual mockup illustration.
To account for the flexible deformation of the triangular link and expansion adjustment plate, as well as the clearances in the kinematic pairs, finite element models of these components were developed using ANSYS 2023 R1. The flexible body models were then imported into ADAMS to establish a kinematic simulation model that incorporates the coupling effects of component flexibility and joint clearances in the vector nozzle mechanism.
4.2. Selection of Random Variables
The pitch angle of the aircraft vector nozzle is controlled by the motions of four actuating cylinders, P1, P2, P3 and P4. Its precise positioning is further influenced by the elastic deformation of the nozzle components and the clearances in the kinematic pairs. Therefore, the velocities of the four actuating cylinders (P1–P4) and the kinematic pair clearance c are selected as random input variables. The aerodynamic force acting on the expansion plate is the main load on the nozzle mechanism. Considering the continuity and correlation of the aerodynamic pressure distribution inside the expansion section, a random load coefficient with a mean value of 1 is introduced to reflect the stochastic variation in the gas pressure across the expansion section of the nozzle. The parameters of all random variables are summarized in Table 1 [32].

Table 1.
Random Variables in Dynamical Reliability Analysis of Vector Nozzle.
4.3. Deterministic Analysis of the Nozzle
According to the design requirements of the vector nozzle mechanism, the pitch angle of the nozzle must reach 20 degrees within 0.3 s after activation; otherwise, it will not provide sufficient lift to reduce the takeoff distance. The dynamic evolution curves of the pitch angle under different assumptions—rigid and flexible components—are shown in Figure 3. Curve L1 represents the pitch angle versus time when all components are assumed to be rigid. As shown, the pitch angle reaches approximately 25 degrees at 0.3 s. Curve L2 corresponds to the case where component flexibility and kinematic pair clearances are considered. It can be observed that under these conditions, the pitch angle reaches approximately 20 degrees at 0.3 s.
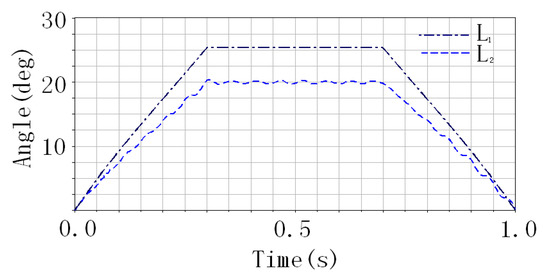
Figure 3.
Vector tail nozzle angle change illustration.
During the 0.3 s activation period, the vector actuation ring drives the expansion rotation through the triangular link. The motion of the triangular link exhibits strong nonlinearity, including a rapid initial motion to achieve the target angle followed by a slower variation caused by flexible deformation of the components. The dynamic response of the triangular link’s center of mass is shown in Figure 4.
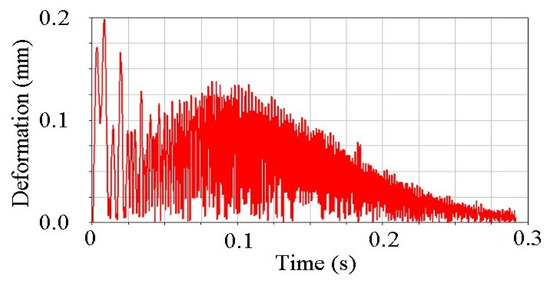
Figure 4.
Graph of change in centroid of triangular link.
4.4. DSERSM-GA Mathematical Model and Simulation
According to the method in Section 2.1, a small-batch sampling of the input random variables in Table 1 is performed using MCM. The minimum pitch angle and the maximum centroid deformation of the triangular link are extracted. Based on the sampled inputs and extreme outputs, the dual-stochastic extreme response surface model is constructed as follows:
where
Based on the DSERSM in this example (The expression is too long to write out), 10,000 coupled samples are generated using MCM. The simulation scatter plots and histograms for the pitch angle and triangular link centroid deformation are shown in Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8.
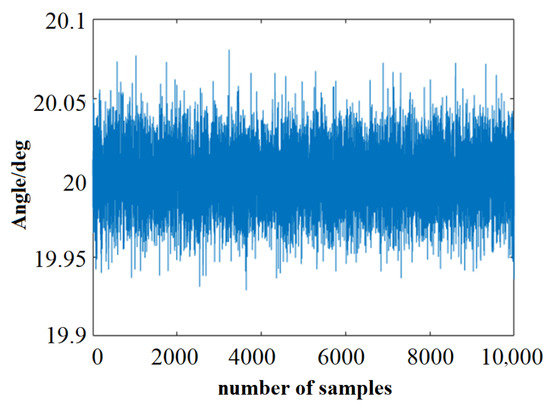
Figure 5.
Angle analog sampling map.
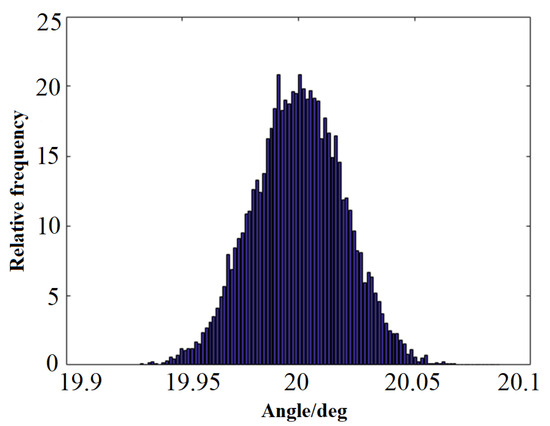
Figure 6.
Angular frequency distribution histogram.
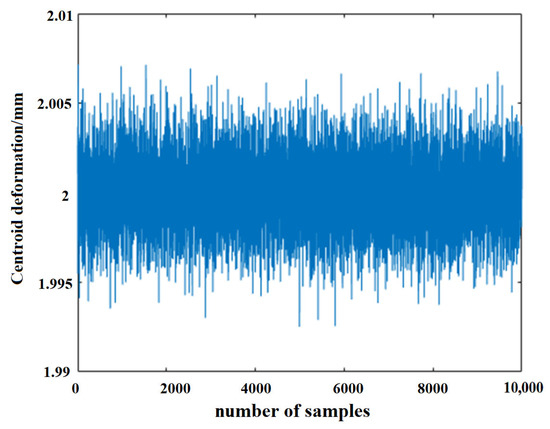
Figure 7.
Deformation simulation sampling map.
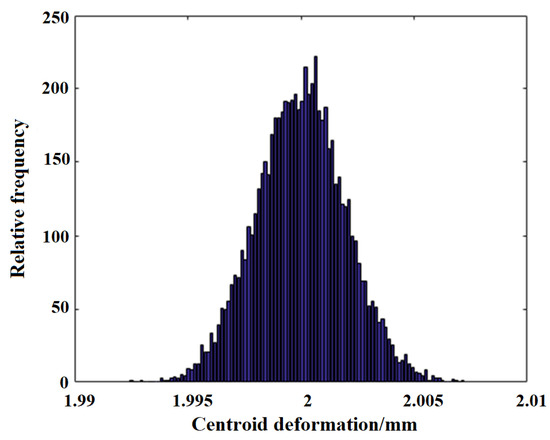
Figure 8.
Deformation distribution histogram.
The results indicate that the output responses follow a normal distribution. The mean pitch angle is 20.0 with a standard deviation of 4.0322 × 10−6, and the mean centroid deformation of the triangular link is 2 with a standard deviation of 2.6157 × 10−6. We set the allowable range of pitch angle to , the allowable range of center of gravity deformation to mm. During 10,000 simulations, 152 failures were observed, resulting in a reliability of 0.9848. The total computation time was 17.6 s.
The DSERSM Equation (15) without substituting the specific value of coefficient is substituted into Equation (5), treating the coefficients as variables, and the genetic algorithm is employed to optimize . With f(b) as the objective function, the initial population size is set to 100, the crossover probability to 0.6, the mutation rate to 0.01, and the number of generations to 500. The fmincon function is used for local optimization based on the sample points, yielding the updated coefficients . The optimization process is shown in Figure 9 and Figure 10.
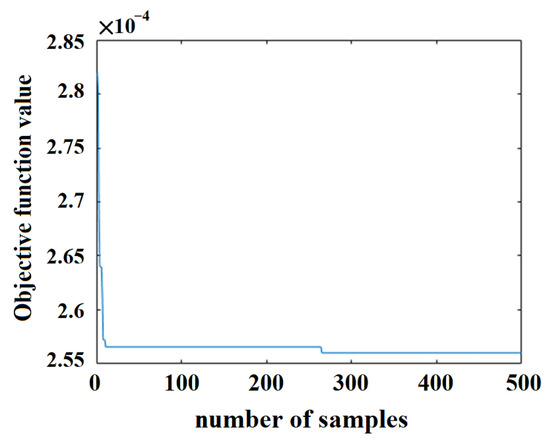
Figure 9.
Angle optimization process.
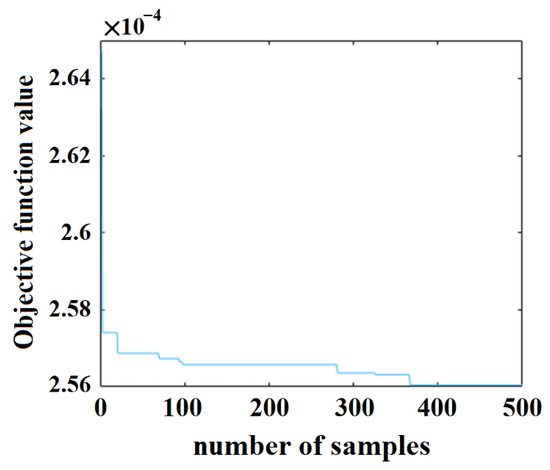
Figure 10.
Deformation optimization process.
The optimized coefficients are as follows:
Based on the DSERSM-GA model in this example (The expression is too long to write out), 10,000 coupled samples are generated using MCM. The simulation scatter plots and histograms for the pitch angle and centroid deformation are shown in Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14.
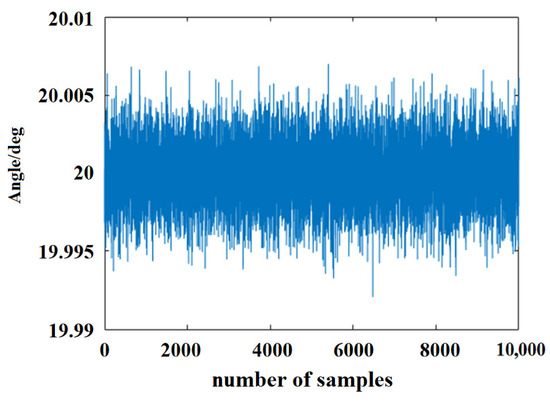
Figure 11.
Angle analog sampling map.
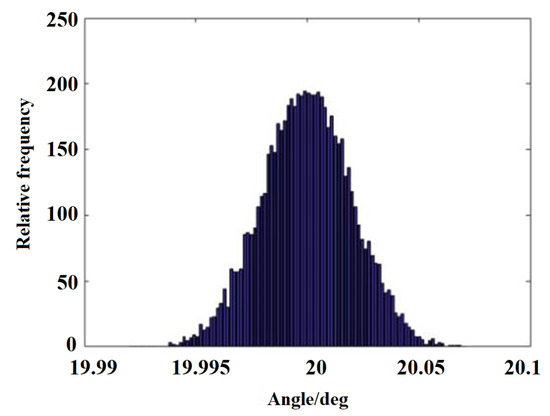
Figure 12.
Angular frequency distribution histogram.
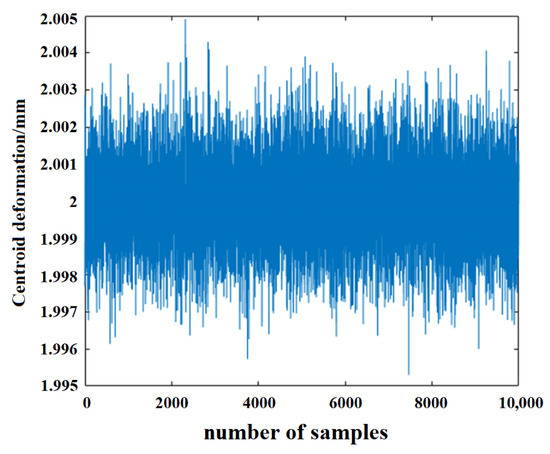
Figure 13.
Deformation simulation sampling map.
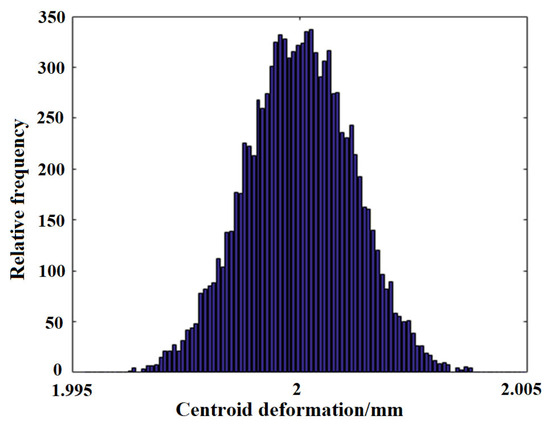
Figure 14.
Deformation distribution histogram.
The results indicate that the output responses follow a normal distribution. The mean pitch angle is 20.0 with a standard deviation of 3.9864 × 10−6, and the mean centroid deformation of the triangular link is 2 with a standard deviation of 1.4109 × 10−6. We set the allowable range of pitch angle to , the allowable range of center of gravity deformation to mm. During 10,000 simulations, 93 failures were recorded, resulting in a reliability of 0.9907. The total computation time was 9.8 s. Under the same simulation conditions, displacement error probability analyses were conducted using MCM, DSERSM, and DSERSM-GA. As the number of simulations increased, the corresponding computation times and accuracies for each method are summarized in Table 2 and Table 3.

Table 2.
Time to calculate reliability with three methods.

Table 3.
Three methods to calculate the accuracy of reliability.
As illustrated in Table 2 and Table 3, DSERSM and DSERSM-GA exhibit identical computational times for a given number of simulations, both significantly shorter than the traditional Monte Carlo Method (MCM). With an increasing number of simulations, DSERSM-GA demonstrates a clear enhancement in accuracy, surpassing DSERSM by approximately 0.5%. Furthermore, the precision advantage of DSERSM-GA becomes increasingly pronounced as the sample size expands.
5. Conclusions
The proposed DSERSM-GA method improves the accuracy of mechanical reliability analysis under the same computational efficiency. Using a small set of Monte Carlo samples, a population-trained response surface model effectively captures uncertainties related to stress and deformation in the expansion plate and triangular link. Applying DSERSM-GA to a vector nozzle system confirmed its superior computational performance compared to traditional Monte Carlo and extreme response surface methods. Through the dynamic reliability analysis of the vector nozzle, some main conclusions are summarized as follows:
- (1)
- A virtual prototype of the vector nozzle was developed, and a deterministic analysis was performed to evaluate the motion characteristics of the vector nozzle, and a deterministic analysis of the motion of the vector nozzle was conducted. The analysis showed that, considering the flexible deformation of components, its pitch angle must reach 20 degrees within 0.3 s during takeoff. At the same time, a simulation diagram of the centroid change in the triangular link within 0.3 s of startup was obtained. And the triangular link exhibited highly nonlinear motion.
- (2)
- A double random extreme response surface method (DSERSM) has been developed for dynamic reliability analysis of complex structures with multiple input variables. The simulation results of the reliability analysis of vector nozzles show that, while ensuring the calculation accuracy, the calculation efficiency of this method is greatly improved compared with the Monte Carlo method.
- (3)
- The genetic algorithm was used to optimize the function with coefficients of the DSERSM as the variable to obtain DSERSM-GA by using an initial population size of 100, a crossover probability of 0.6, a mutation rate of 0.01, and 500 generations. Reliability analysis with DSERSM-GA achieved a reliability value of 99.07%, demonstrating its effectiveness over existing methods.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.Z. and B.J.; methodology, C.Z. and L.W.; software, Z.Y. and L.W.; validation, C.Z., L.W. and B.J.; formal analysis, C.Z. and Z.Y.; investigation, C.Z. and Z.Y.; resources, C.Z.; data curation, Z.Y. and L.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.Y., L.W. and Y.X.; writing—review and editing, B.J., C.Z. and Y.X.; visualization, L.W.; supervision, C.Z. and B.J.; project administration, C.Z. and B.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This paper is co-supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 51275138), the Guangdong Province Key Construction Discipline Research Ability Enhancement Project (Grant Number: 2022ZDJS149), the Natural Science Research Project of the Guangdong University of Science and Technology (Grant Number: GKY-2022KYZDK-2), and Quality Engineering Project of the Guangdong University of Science and Technology (Grant Number GKZLGC2023177 and GKZLGC2023159). The authors would like to thank them.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Zheshan Yuan was employed by the company Shandong New Beiyang Information Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Wang, Y.X. Aircraft Engine Thrust Vectoring Nozzle; Mechanical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.B.; Luo, Z.; Wei, K.; Sun, Y.H.; Xu, C.Y. Analysis of fluid-solid-thermal coupling characteristics of axial-symmetric vectoring exhaust nozzle. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2022, 236, 9472–9484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Bai, G. Application of Least Squares Support Vector Machine for Regression to Reliability Analysis. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2009, 22, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Bai, G. New neural network response surface methods for reliability analysis. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2011, 24, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guo, Z.W.; Bai, G.C. Application of stochastic response surface method in structural stochastic response calculation. J. Aerosp. Power 2008, 23, 2021–2025. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Bai, G. Extremum response surface method of reliability analysis on two-link flexible robot manipulator. J. Cent. South Univ. 2012, 19, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, F.; Allahviranloo, T. Fuzzy Reliability Estimation Using The New Operations of Transmission Average on Rational-Linear Patchy Fuzzy Numbers. Soft Comput. 2019, 23, 3383–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, H.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.Z. A Novel Reliability Analysis Method for Turbine Discs with the Mixture of Fuzzy and Probability-Box Variables. Int. J. Turbo Jet-Engines 2022, 39, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, P.; Lang, H. Reliability Prediction of CNC Machine Tool Spindle Based on Optimized Cascade Feedforward Neural Network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 60682–60688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshghi, A.T.; Lee, S. Adaptive improved response surface method for reliability-based design optimization. Eng. Optim. 2019, 51, 2011–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Pei, H.; Yang, Q. An intelligent response surface method for analyzing slope reliability based on Gaussian process regression. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2019, 43, 2431–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Li, H. Fuzzy Reliability Analysis with Fuzzy Random Variables Based on Perturbation Principle. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 78898–78908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Li, H. Direct integration method based on dual neural networks to solve the structural reliability of fuzzy failure criteria. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2019, 233, 7183–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lu, Z.; Feng, K. A novel learning function of adaptively updating Kriging model for reliability analysis under fuzzy uncertainty. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2023, 66, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Fei, C.W.; Wang, J.J. A stochastic model updating strategy-based improved response surface model and advanced Monte Carlo simulation. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 82, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Song, L.K.; Lu, C. Advanced multiple response surface method of sensitivity analysis for turbine blisk reliability with multi-physics coupling. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2016, 29, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wei, J.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Z.S.; Fei, C.W.; Lu, C. Creep-Based Reliability Evaluation of Turbine Blade-Tip Clearance with Novel Neural Network Regression. Materials 2019, 12, 3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wei, J.; Jing, H.; Fei, C.; Tang, W. Reliability-Based Low Fatigue Life Analysis of Turbine Blisk with Generalized Regression Extreme Neural Network Method. Materials 2019, 12, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y. Advanced Extremum Response Surface Method for Dynamic Reliability Analysis on Flexible Mechanism. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 53, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bai, G.; Song, L.; Wen, J. Fatigue Reliability Estimation Framework for Turbine Rotor Using Multi-Agent Collaborative Modeling. Structures 2021, 29, 1967–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.K.; Bai, G.C.; Fei, C.W. Multi-failure probabilistic design for turbine bladed disks using neural network regression with distributed collaborative strategy. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 464–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Ba, G.; Li, X. A Novel Metamodeling Approach for Probabilistic LCF Estimation of Turbine Disk. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 120, 105074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Meng, D.B.; Wang, H.T.; Yang, C. A novel learning function for adaptive surrogate-model-based reliability evaluation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2024, 382, 20220395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Qian, Q.C.; Xu, M.Q.; Yu, B.; Yıldız, A.R.; Mirjalili, S. PINN-FORM: A new physics-informed neural network for reliability analysis with partial differential equation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2023, 414, 116172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Q.; Wang, L.J.; Peng, Y.L.; Li, J. Structural reliability analysis based on improved wolf pack algorithm AK-SS. In Structures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; Volume 57. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, C.Q.; Zhu, S.P.; Keshtegar, B.; Macek, W.; Branco, R.; Meng, D. Active Kriging-based conjugate first-order reliability method for highly efficient structural reliability analysis using resample strategy. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2024, 423, 116863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.K.; Tao, F.; Li, X.Q.; Yang, L.C.; Wei, Y.P.; Beer, M. Physics-embedding multi-response regressor for time-variant system reliability assessment. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2025, 263, 111262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.K.; Tao, F.; Choy, Y.; Yang, L.C.; Wei, Y.F. Cascade sampling-driven block mapping for coupled reliability evaluation of turbine cooling systems. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2025, 236, 113008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.K.; Li, X.Q.; Zhu, S.P.; Choy, Y.S. Cascade ensemble learning for multi-level reliability evaluation. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2024, 148, 109101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Song, L.K.; Choy, Y.S.; Bai, G.C. Multivariate ensembles-based hierarchical linkage strategy for system reliability evaluation of aeroengine cooling blades. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2023, 138, 108325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Song, L.K.; Bai, G.C. Vectorial surrogate modeling approach for multi-failure correlated probabilistic evaluation of turbine rotor. Eng. Comput. 2023, 39, 1885–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Bai, G.; Yu, L. Simulation and Reliability Analysis of Axisymmetric Vectoring Exhaust Nozzle Flexible Mechanism. J. Syst. Simul. 2006, 18 (Suppl. S2), 175–178. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).