Quaternary Correlation Prediction Compensation for Heading Commands in Virtual Autopilot
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- The signed error distance is defined to compute flight trajectory error statistics, enabling dynamic assessment of flight convergence degrees;
- (2)
- The influence of trajectory deviations is reflected in the weights of different error statistics, which are applied to construct the predictive structure and compensate for the PID control process;
- (3)
- Virtual heading commands are generated through the quaternary correlation dependence between PID control and the predictive structure, leading to more convergent flight trajectories.
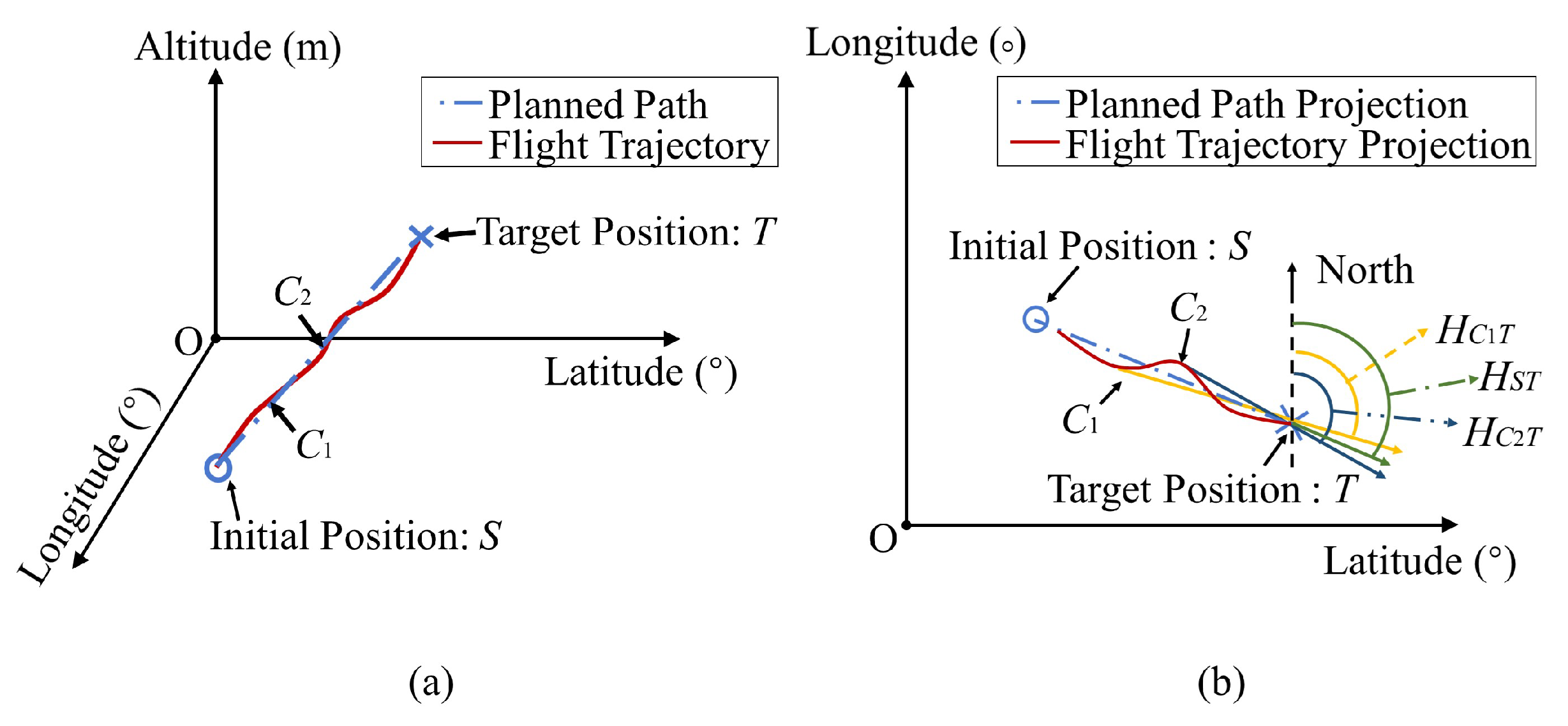
2. Preliminaries
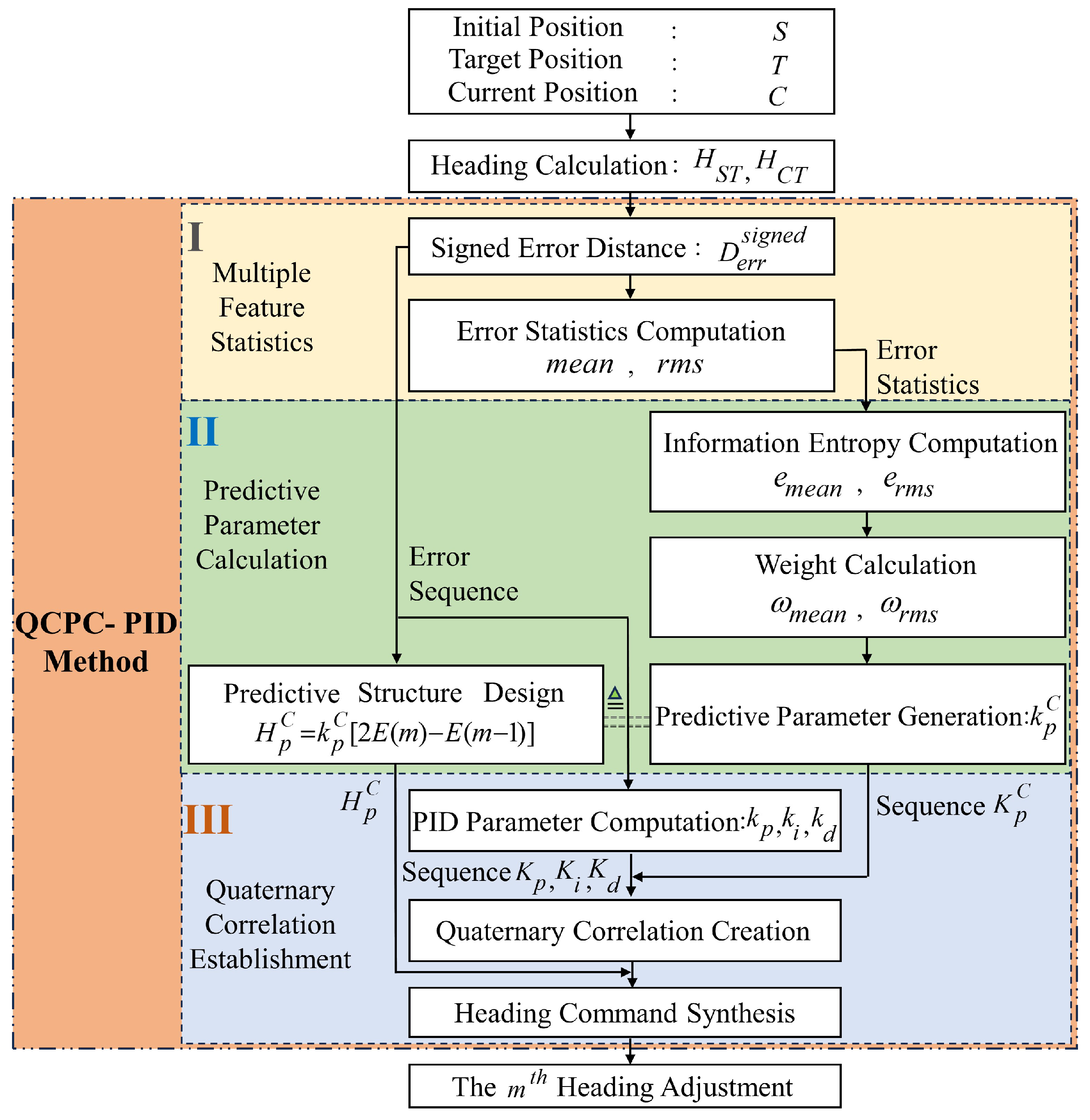
3. Methodology
3.1. Multi-Feature Statistics
3.2. Predictive Parameter Calculation
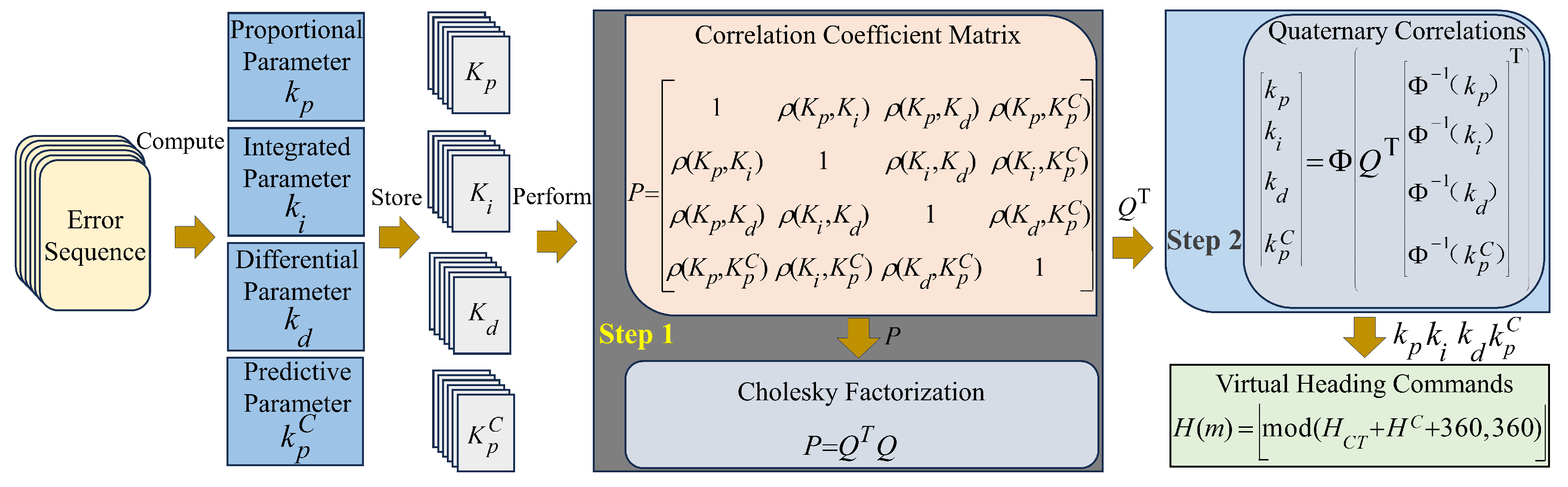
3.3. Quaternary Correlation Establishment
| Algorithm 1 Multiple-waypoint mission by QCPC-PID method |
 |
4. Experiment and Discussion
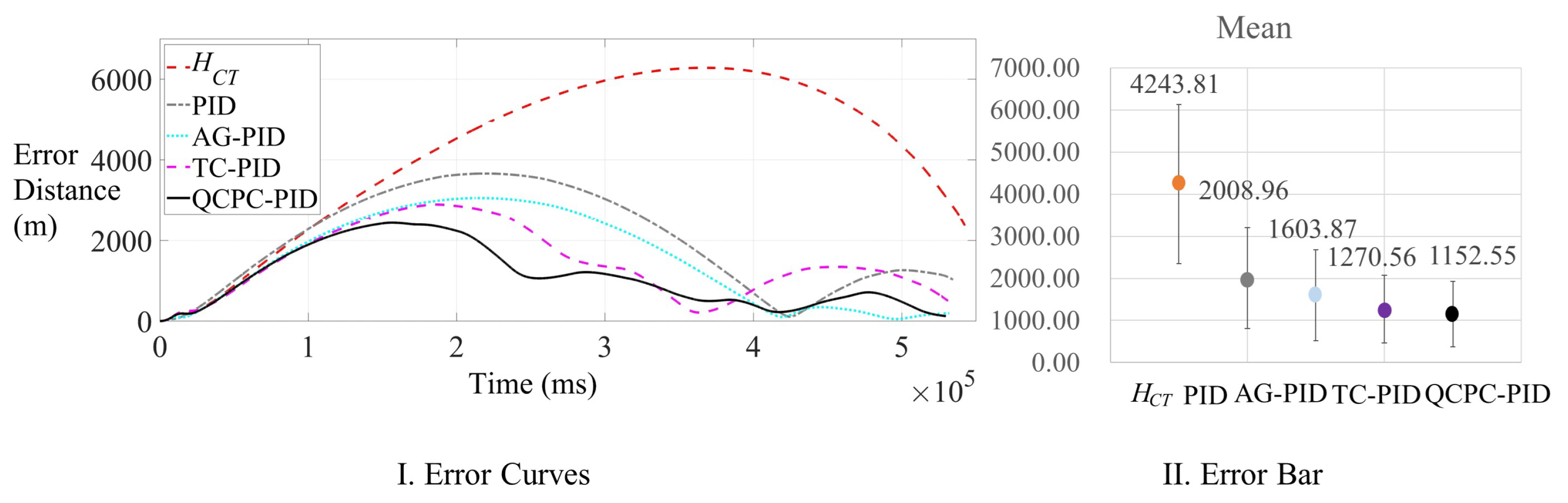
4.1. Two-Waypoint Flight Case
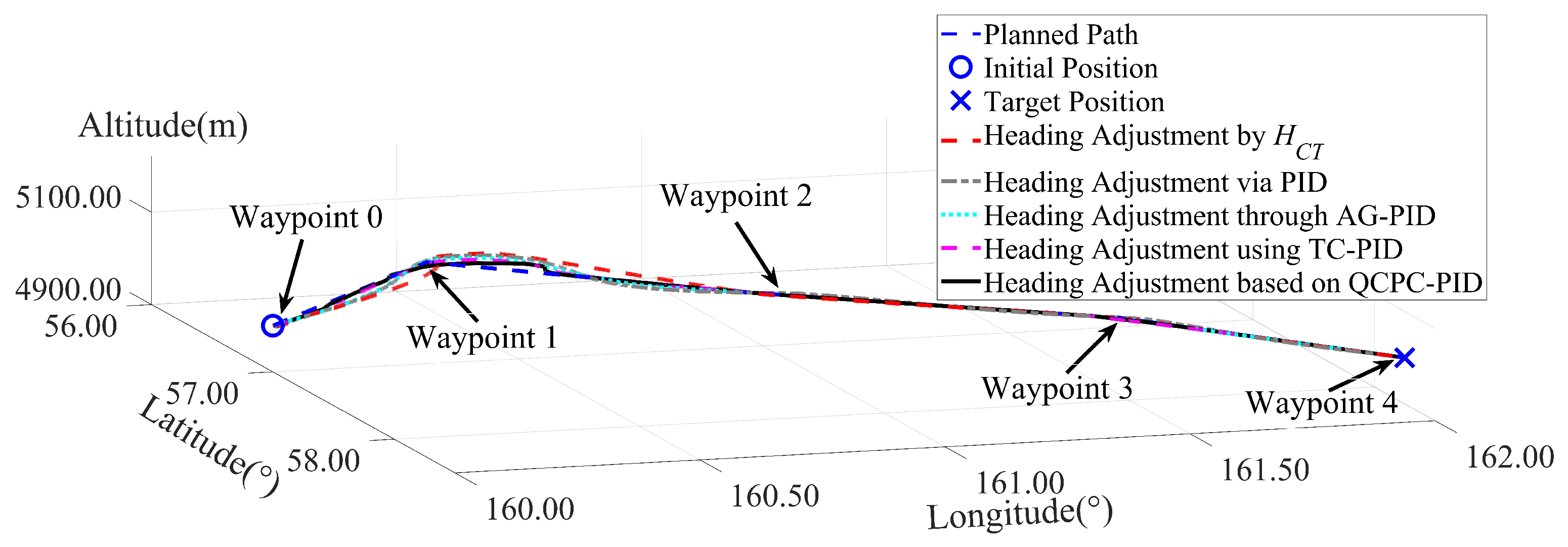
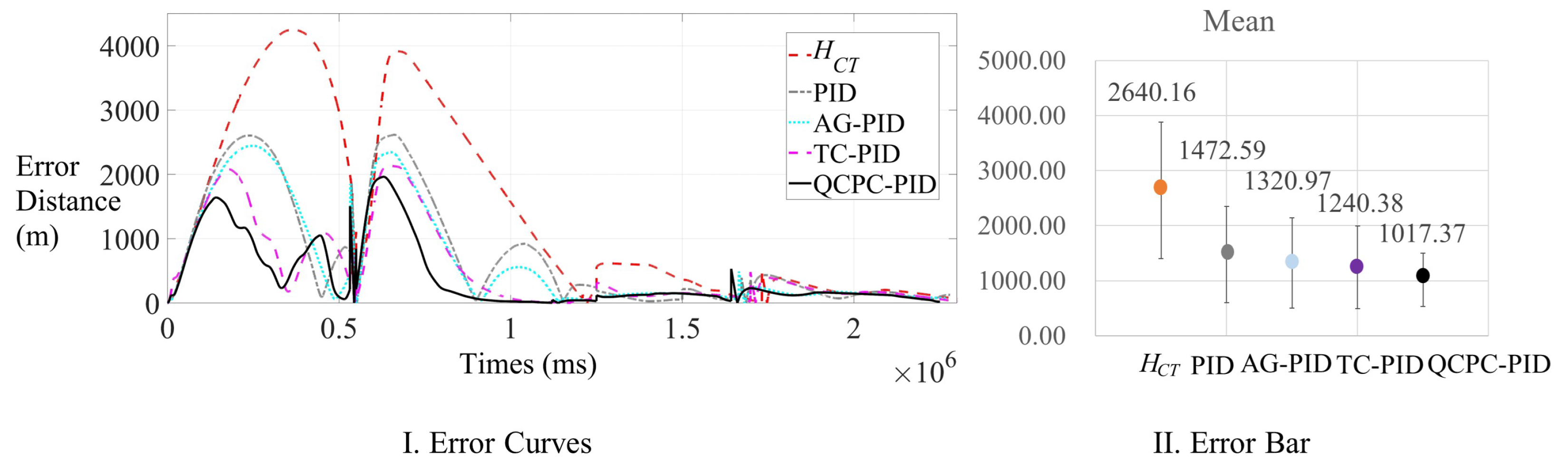
4.2. Multiple-Waypoint Flight Case
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bresó, A.; Martínez-Miranda, J.; Botella, C.; Baños, R.M.; García-Gómez, M. Usability and acceptability assessment of an empathic virtual agent to prevent major depression. Expert Syst. 2016, 33, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.J. Evolutionary game and collaboration mechanism of human-computer interaction for future intelligent aircraft cockpit based on system dynamics. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2022, 52, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.Y.; Zhou, Q.X.; Wang, X.W.; Liu, Z.Q. Simulation and Analysis of Human Neck Load and Injury During Sustaining Overload in Flight. Int. Ergon. Assoc. Congr. 2019, 822, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogeltanz, T.; Jašek, R. FlightGear application for flight simulation of a mini-UAV. AIP Conf. Proc. 2015, 1648, 550014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohani, T.A.; Dixit, A.; Agrawal, P. Adaptive PID control for autopilot design of small fixed wing UAVs. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sustainable Technologies and Advances in Automation, Aerospace and Robotics (STAAAR-2023), Sehore, India, 15–16 December 2023; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2024; Volume 393, pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revathi, V.; Rangaiah, Y.P.; Dutt, A.; Hameed, A.A.; Nagini, R.V.S.S.S.; Yadav, D.K. Design of small UAV autopilot systems using adaptive controllers, PID controllers, and AI. In Proceedings of the 2025 International Conference on Next Generation Communication & Information Processing (INCIP), Bengaluru, India, 23–24 January 2025; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, H.; Bayezit, I. Advanced autopilot design with extremum-seeking control for aircraft control. Open Eng. 2024, 14, 20240044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Geem, Z.W.; Yoon, Y. Population-based redundancy control in genetic algorithms: Enhancing max-cut optimization. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.; Sengupta, A.; Sutradhar, A. An evolutionary optimization-based design of Smith delay compensator for cascade control of MIMO time-delay industrial process. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 9339–9348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuc, T.Y.; Han, W.G. An adaptive PID learning control of robot manipulators. Automatica 2000, 36, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhou, Q.K.; Zhang, L.C.; Fan, D.P. Application in prestiction friction compensation for angular velocity loop of inertially stabilized platforms. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2014, 27, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrzej, P.; Carlos, R.; José, L.G.; Manuel, B.; Sebastián, D. Measurable disturbances compensation: Analysis and tuning of feedforward techniques for dead-time processes. Processes 2016, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Wei, J.H.; Fang, J.H.; Feng, R.L.; Wang, X.C. Position tracking control of electro-hydraulic single-rod actuator based on an extended disturbance observer. Mechatronics 2015, 27, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.Y.; Guo, Y.Q.; Zha, X.M.; Wang, Y. Real-time hybrid test control research based on improved electro-hydraulic servo displacement algorithm. Sensors 2023, 23, 4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazrat, B.; Baoqun, Y.; Muhammad, S.A.; Zeeshan, A.; Avinash, R.; Wang, Y.Z. A practical study of active disturbance rejection control for rotary flexible joint robot manipulator. Soft Comput. 2023, 27, 4987–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jin, B.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Q. State feedback spool position control with integral compensation for servo proportional valve. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2023, 237, 4946–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.F.; Xu, C.T.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.H.M.; Zong, X. Optimization of PID controller for stepper motor speed control system based on improved sparrow search algorithm. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2024, 238, 9397–9411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.T. Ternary correlation adaptive tuning for virtual autopilot commands. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2024, 47, 1946–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Xie, P.; Liao, J.H. Cascade NMPC-PID control strategy of active heave compensation system for ship-mounted offshore crane. Ocean Eng. 2024, 302, 117648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, K.Y.; Pan, F.Y.; Yi, N.; Han, Y. Combined lateral-longitudinal vehicle trajectory tracking control based on model predictive control and fractional-order PID. In Proceedings of the IEEE 22nd International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Beijing, China, 18–20 August 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, J.; Lee, S.J. Linear PID composite controller and its tuning for flexible link robots. J. Vib. Control 2008, 14, 291–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Zhang, W.A.; Dong, H.; Yu, L. A LADRC based fuzzy PID approach to contour error control of networked motion control system with time-varying delays. Asian J. Control 2020, 22, 1973–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.J.; Zhang, W.H.; Ji, W.B.; Zhao, Y.F.; Zheng, H.W.; Mu, J.H.; Li, P.W.; Deng, R.Q. Research on constant force grinding control of aero-engine blades based on extended state observer. Ind. Robot Int. J. Robot. Res. Appl. 2022, 49, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.X.; Liang, Z.W.; Wang, T.T. Node importance measurement method based on multi-attribute fusion. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2023, 37, 2350076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roszkowska, E.; Filipowicz-Chomko, M.; Kusterka-Jefmańska, M.; Jefmański, B. The impact of the intuitionistic fuzzy entropy-based weights on the results of subjective quality of life measurement using intuitionistic fuzzy synthetic measure. Entropy 2023, 25, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.P.; Xu, Y.Y. Design and research for a multivariable neural network PID decoupling control algorithm with predictive compensation function. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Application and System Modeling (ICCASM 2010), V7-360-V7-364, Taiyuan, China, 22–24 October 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachmanto, A.D.; Iswanto, I.; Hernawati, H. Simulation and modeling of aircraft movements passing through VOR. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 830, 032021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Liu, J.M.; Peng, Y.C.; Wen, C.F. A novel method to information fusion in multi-source incomplete interval-valued data via conditional information entropy: Application to mutual information entropy based attribute reduction. Inf. Sci. 2024, 658, 120011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podviezko, A.; Podvezko, V. Influence of data transformation on multicriteria evaluation result. Procedia Eng. 2015, 122, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, P.; Furci, I.; Serra-Capizzano, S. Flipped structured matrix-sequences in image deblurring with reflective and anti-reflective boundary conditions. Numer. Algorithms 2025, 100, 277–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Gao, H.T. Accelerating calculation of Cholesky factorization of matrix with GPU. Comput. Appl. Softw. 2016, 33, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, B.; Martin, S.; Stuart, B. FlightGear Flight Simulator. Available online: http://www.flightgear.org/ (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Nguyen, D.D.; Duong, M.H.; Hoang, Q.C. Enhancing altitude control in quadrotors: A study on PID parameter selection and Euler angle influence. Int. J. Sustain. Aviat. 2025, 11, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
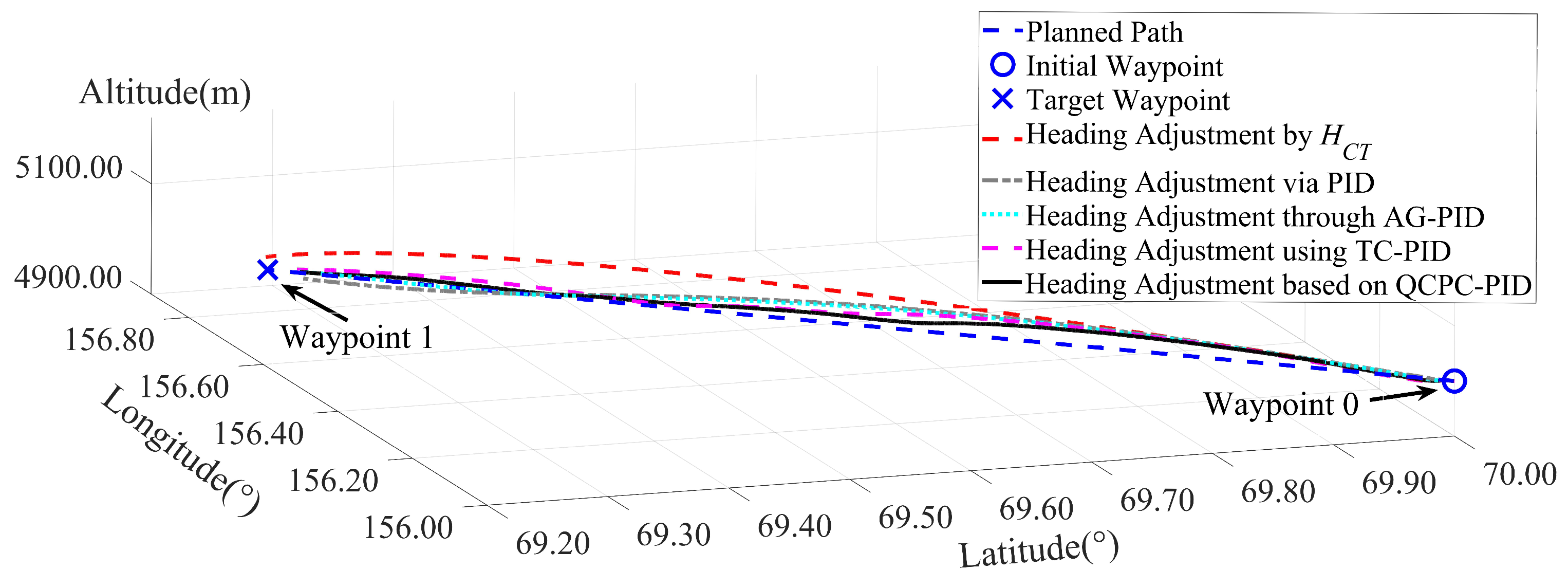
| Waypoint | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) | Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 70.00 | 156.00 | 5000.00 |
| 1 | 69.25 | 156.75 | 5000.00 |
| Method | A_FJL | A_MCT | A_HAN | A_Max | A_Mean | A_Std | S_Max | S_Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Using) | (m) | (s) | (Times) | (m) | (m) | (m) | (m) | (m) |
| 88,703.40 | 556.83 | 23 | 6308.46 | 4255.27 | 1909.42 | 78.65 | 126.73 | |
| 87,025.72 | 547.43 | 27 | 3696.37 | 2031.64 | 1198.46 | 64.02 | 57.46 | |
| AG-PID | 86,655.60 | 544.56 | 27 | 3166.06 | 1615.71 | 1084.26 | 58.02 | 56.56 |
| TC-PID | 86,776.21 | 544.98 | 27 | 2976.05 | 1298.16 | 833.15 | 58.15 | 53.97 |
| QCPC-PID | 86,699.37 | 544.23 | 27 | 2455.76 | 1176.99 | 782.29 | 50.68 | 45.02 |
| Method | A_FJL | A_MCT | A_HAN | A_Max | A_Mean | A_Std | S_Max | S_Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Using) | (m) | (s) | (Times) | (m) | (m) | (m) | (m) | (m) |
| QCPC-PID-uS | 86,841.02 | 544.40 | 22 | 2926.96 | 1436.20 | 864.20 | 115.74 | 101.07 |
| QCPC-PID-nM | 86,841.19 | 543.32 | 20 | 2930.90 | 1444.84 | 892.17 | 68.41 | 59.44 |
| QCPC-PID-nR | 86,906.98 | 545.26 | 23 | 2859.26 | 1441.52 | 852.15 | 95.53 | 107.46 |
| QCPC-PID-nQ | 86,739.99 | 544.83 | 25 | 4301.94 | 2837.15 | 1312.22 | 89.44 | 95.81 |
| Waypoint | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) | Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 57.00 | 160.00 | 5000.00 |
| 1 | 56.25 | 160.50 | 5000.00 |
| 2 | 56.90 | 161.00 | 5000.00 |
| 3 | 57.50 | 161.60 | 5000.00 |
| 4 | 58.25 | 162.00 | 5000.00 |
| Method | A_FJL | A_MCT | A_HAN | A_Max | A_Mean | A_Std | S_Max | S_Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Using) | (m) | (s) | (Times) | (m) | (m) | (m) | (m) | (m) |
| 347,639.24 | 2344.74 | 33 | 4245.32 | 2715.54 | 1362.55 | 443.75 | 349.66 | |
| 344,823.10 | 2328.43 | 55 | 2573.50 | 1417.78 | 852.42 | 380.58 | 284.99 | |
| AG-PID | 341,608.60 | 2305.43 | 55 | 2431.05 | 1283.83 | 842.69 | 289.92 | 231.84 |
| TC-PID | 345,158.03 | 2327.76 | 58 | 2331.09 | 1178.30 | 713.19 | 264.99 | 269.02 |
| QCPC-PID | 343,842.00 | 2317.87 | 69 | 1945.98 | 1062.89 | 559.29 | 253.52 | 145.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Fu, S. Quaternary Correlation Prediction Compensation for Heading Commands in Virtual Autopilot. Aerospace 2025, 12, 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12100936
Zhou Y, Fu S. Quaternary Correlation Prediction Compensation for Heading Commands in Virtual Autopilot. Aerospace. 2025; 12(10):936. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12100936
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yutong, and Shan Fu. 2025. "Quaternary Correlation Prediction Compensation for Heading Commands in Virtual Autopilot" Aerospace 12, no. 10: 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12100936
APA StyleZhou, Y., & Fu, S. (2025). Quaternary Correlation Prediction Compensation for Heading Commands in Virtual Autopilot. Aerospace, 12(10), 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12100936







