Responsible AI for Air Traffic Management: Application to Runway Configuration Assistance Tool
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Methodology
3.1. RCA Tool
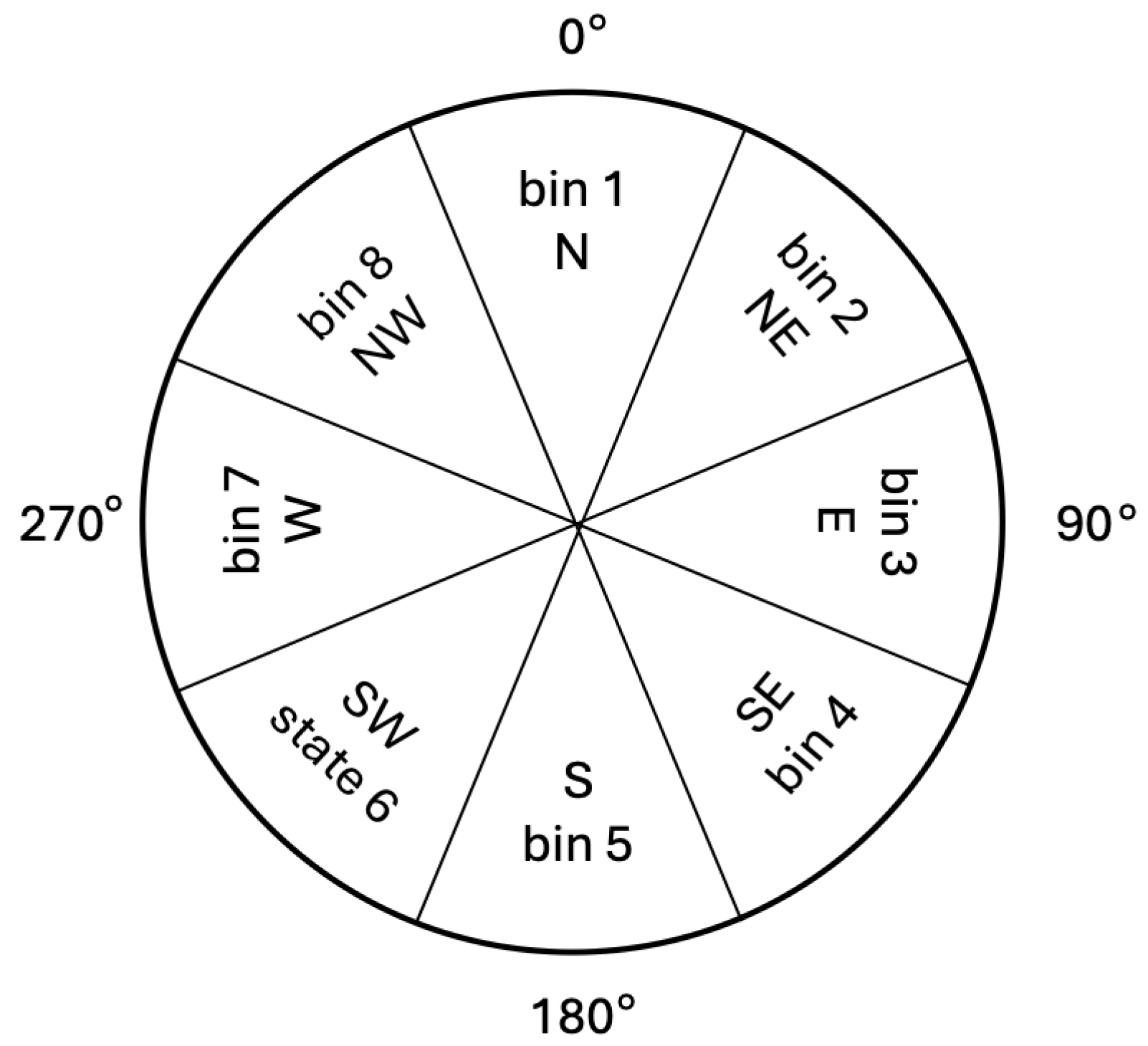
3.2. Bias Detection
| Algorithm 1 Bias detection method |
| Input: data , trained model , and labels Y Output: no/negative/positive bias
|
3.3. Bias Mitigation
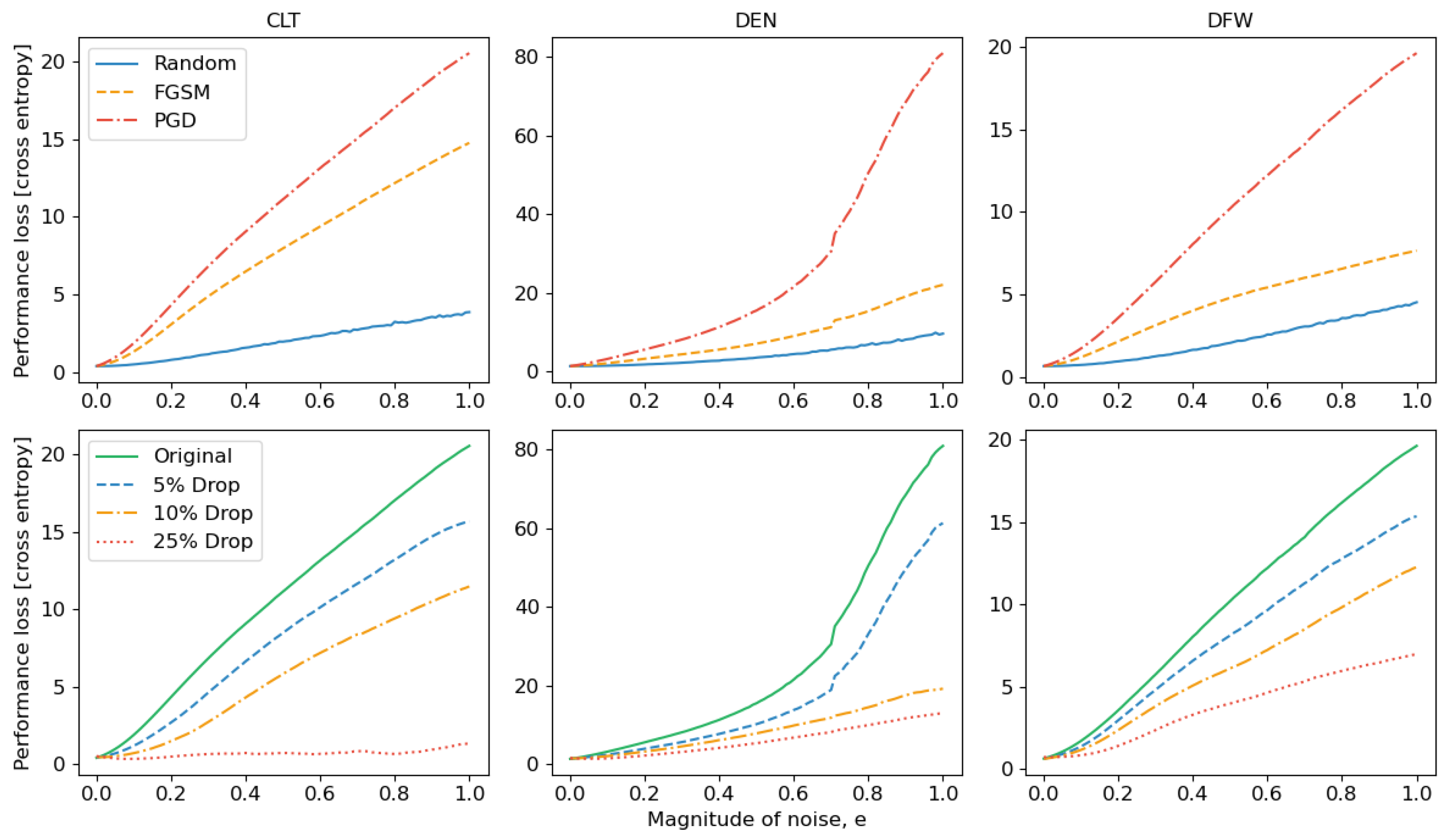
3.4. Robustness and Adversarial Training
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Data
4.2. Bias Mitigation
4.3. Adversarial Training
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roadmap for Artificial Intelligence Safety Assurance. Federal Aviation Administration. Accessed in Summer of 2024. Available online: https://www.faa.gov/media/82891 (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Stahl, B. Embedding responsibility in intelligent systems: From AI ethics to responsible AI ecosystems. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memarzadeh, M.; Puranik, T.G.; Kalyanam, K.M.; Ryan, W. Airport runway configuration management with offline model-free reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the AIAA Scitech 2023 Forum, National Harbor, MD, USA, 23–27 January 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kalyanam, K.M.; Memarzadeh, M.; Crissman, J.; Yang, R.; Tejasen, K.T.J. Applying machine learning tools for runway configuration decision support. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Research in Air Transportation (ICRAT), Singapore, 1–4 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Zhou, A.; Tucker, G.; Levine, S. Conservative Q-learning for offline reinforcement learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.04779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puranik, T.G.; Memarzadeh, M.; Kalyanam, K.M. Predicting airport runway configurations for decision-support using supervised learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/AIAA 42nd Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), Barcelona, Spain, 1–5 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 1, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hort, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.M.; Harman, M.; Sarro, F. Bias mitigation for machine learning classifiers: A comprehensive survey. ACM J. Responsible Comput. 2024, 1, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, S.; Haque, M.A.; Gupta, K.D.; George, R.; Gupta, D.; Faruk, M.J.H. Survey on machine learning biases and mitigation techniques. Digital 2024, 1, 1–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, T.P.; Loureiro, R.B.; Lisboa, F.V.N.; Peixoto, R.M.; Guimaraes, G.A.S.; Cruz, G.O.R.; Araujo, M.M.; Santos, L.L.; Cruz, M.A.S.; Oliveira, E.L.S.; et al. Bias and unfairness in machine learning models: A systematic review on datasets, tools, fairness metrics, and identification and mitigation methods. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2023, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memarzadeh, M.; Kalyanam, K.M. Runway configuration assistance: An offline reinforcement learning method for air traffic management. J. Aerosp. Inf. Syst. 2025, 22, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiran, F.; Calders, T. Classifying without discriminating. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2nd International Conference on Computer, Control and Communication, Karachi, Pakistan, 17–18 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiran, F.; Calders, T. Data preprocessing techniques for classification without discrimination. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2012, 1, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, B.T.; Ruggieri, S.; Turini, F. k-NN as an implementation of situation testing for discrimination discovery and prevention. In Proceedings of the 17th ACM SIGKDD, San Diego, CA, USA, 21–24 August 2011; pp. 502–510. [Google Scholar]
- Celis, L.E.; Keswani, V.; Vishnoi, N. Data preprocessing to mitigate bias: A maximum entropy based approach. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 1349–1359. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, J.; Wang, X. Fairness with adaptive weights. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Baltimore, MD, USA, 17–23 July 2022; pp. 2853–2866. [Google Scholar]
- Du, W.; Wu, X. Fair and robust classification under sample selection bias. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Gold Coast, Australia, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 2999–3003. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, M.; Friedler, S.A.; Moeller, J.; Scheidegger, C.; Venkatasubramanian, S. Certifying and removing disparate impact. In Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD, Sydney, Australia, 10–13 August 2015; pp. 259–268. [Google Scholar]
- Johndrow, J.E.; Lum, K. An algorithm for removing sensitive information: Application to race-independent recidivism prediction. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2019, 1, 189–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamishima, T.; Akaho, S.; Asoh, H.; Sakuma, J. Fairness-aware classifier with prejudice remover regularizer. In Proceedings of the Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, Bristol, UK, 24–28 September 2012; pp. 35–50. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Zemel, R.; Wu, Y.; Swersky, K.; Pitassi, T.; Dwork, C. Learning fair representations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Atlanta, GA, USA, 17–19 June 2013; pp. 325–333. [Google Scholar]
- Creager, E.; Madras, D.; Jacobsen, J.; Weis, M.; Swersky, K.; Pitassi, T.; Zemel, R. Fair and robust classification under sample selection bias. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 1436–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Roh, Y.; Lee, K.; Whang, S.; Suh, C. FR-Train: A mutual information-based approach to fair and robust training. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 8147–8157. [Google Scholar]
- Kamani, M.M.; Haddadpour, F.; Forsati, R.; Mahdavi, M. Efficient fair principal component analysis. Mach. Learn. 2022, 111, 3671–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, U.; Ferber, A.; Dilkina, B.; Steeg, G.V. Controllable guarantees for fair outcomes via contrastive information estimation. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2021, 1, 7610–7619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvi, N.; Domingos, P.; Sanghai, S.; Verma, D. Adversarial classification. In Proceedings of the tenth ACM SIGKDD, Seattle, WA, USA, 22–25 August 2004; pp. 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Lowd, D.; Meek, C. Adversarial learning. In Proceedings of the eleventh ACM SIGKDD, Chicago, IL, USA, 21–24 August 2005; pp. 641–647. [Google Scholar]
- Iosiidis, V.; Fetahu, B.; Ntoutsi, E. Fae: A fairness-aware ensemble framework. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Big Data, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 9–12 December 2019; pp. 1375–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Oneto, L.; Doninini, M.; Elders, A.; Pontil, M. Taking advantage of multitask learning for fair classification. In Proceedings of the 2019 AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27–28 January 2019; pp. 227–237. [Google Scholar]
- Calders, T.; Verwer, S. Three naive Bayes approaches for discrimination-free classification. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2010, 1, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, S.; Kumar, A.; Tucker, G.; Fu, J. Offline reinforcement learning: Tutorial, review, and perspectives on open problems. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.01643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Introduction to Reinforcement Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Shlens, J.; Szegedy, C. Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6572. [Google Scholar]
- Madry, A.; Makelov, A.; Schmidt, L.; Tsipras, D.; Vladu, A. Towards deep learning models resistant to adversarial attacks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.06083. [Google Scholar]


| Configuration [Arr/Dep] | Usage [%] |
|---|---|
| CLT | |
| N/N | 60.8 |
| S/S | 39.2 |
| DEN | |
| SE/SE | 18.8 |
| S/S | 15 |
| N/NEW | 14.5 |
| S/SEW | 12.6 |
| N/N | 12.3 |
| NE/NE | 11.7 |
| NW/NW | 8.6 |
| SW/SW | 3.4 |
| E/E | 1.6 |
| NS/EW | 1.2 |
| W/W | 0.3 |
| DFW | |
| SSE/S | 61.5 |
| NNW/NNW | 21.3 |
| S/S | 7.6 |
| N/NNW | 5.1 |
| NNW/N | 3 |
| N/N | 1.1 |
| SSE/NNW | 0.2 |
| NNW/S | 0.1 |
| NW/NW | 0.1 |
| Feature | Class Blc | Feat. Blc | Reg. | Relab. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hour | +18% | −23% | −11% | −14% |
| Wind | −17% | −17% | −36% | −43% |
| Cloud | −11% | −23% | −26% | −30% |
| Visibility | +20% | −22% | −55% | −53% |
| Arrival | +20% | +25% | −29% | −39% |
| Departure | −13% | −14% | −6% | −12% |
| Average | +3% | −12% | −27% | −32% |
| Method | 5% Drop | 10% Drop | 25% Drop |
|---|---|---|---|
| Random | 0.14 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| FGSM | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.09 |
| PGD | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Memarzadeh, M.; Wang, Z.; Masrour Shalmani, F.; Razzaghi, P.; Kalyanam, K.M. Responsible AI for Air Traffic Management: Application to Runway Configuration Assistance Tool. Aerospace 2025, 12, 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12100872
Memarzadeh M, Wang Z, Masrour Shalmani F, Razzaghi P, Kalyanam KM. Responsible AI for Air Traffic Management: Application to Runway Configuration Assistance Tool. Aerospace. 2025; 12(10):872. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12100872
Chicago/Turabian StyleMemarzadeh, Milad, Zili Wang, Farzan Masrour Shalmani, Pouria Razzaghi, and Krishna M. Kalyanam. 2025. "Responsible AI for Air Traffic Management: Application to Runway Configuration Assistance Tool" Aerospace 12, no. 10: 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12100872
APA StyleMemarzadeh, M., Wang, Z., Masrour Shalmani, F., Razzaghi, P., & Kalyanam, K. M. (2025). Responsible AI for Air Traffic Management: Application to Runway Configuration Assistance Tool. Aerospace, 12(10), 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12100872







