Global Surface Pressure Pattern for a Compressible Elliptical Cavity Flow Using Pressure-Sensitive Paint
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
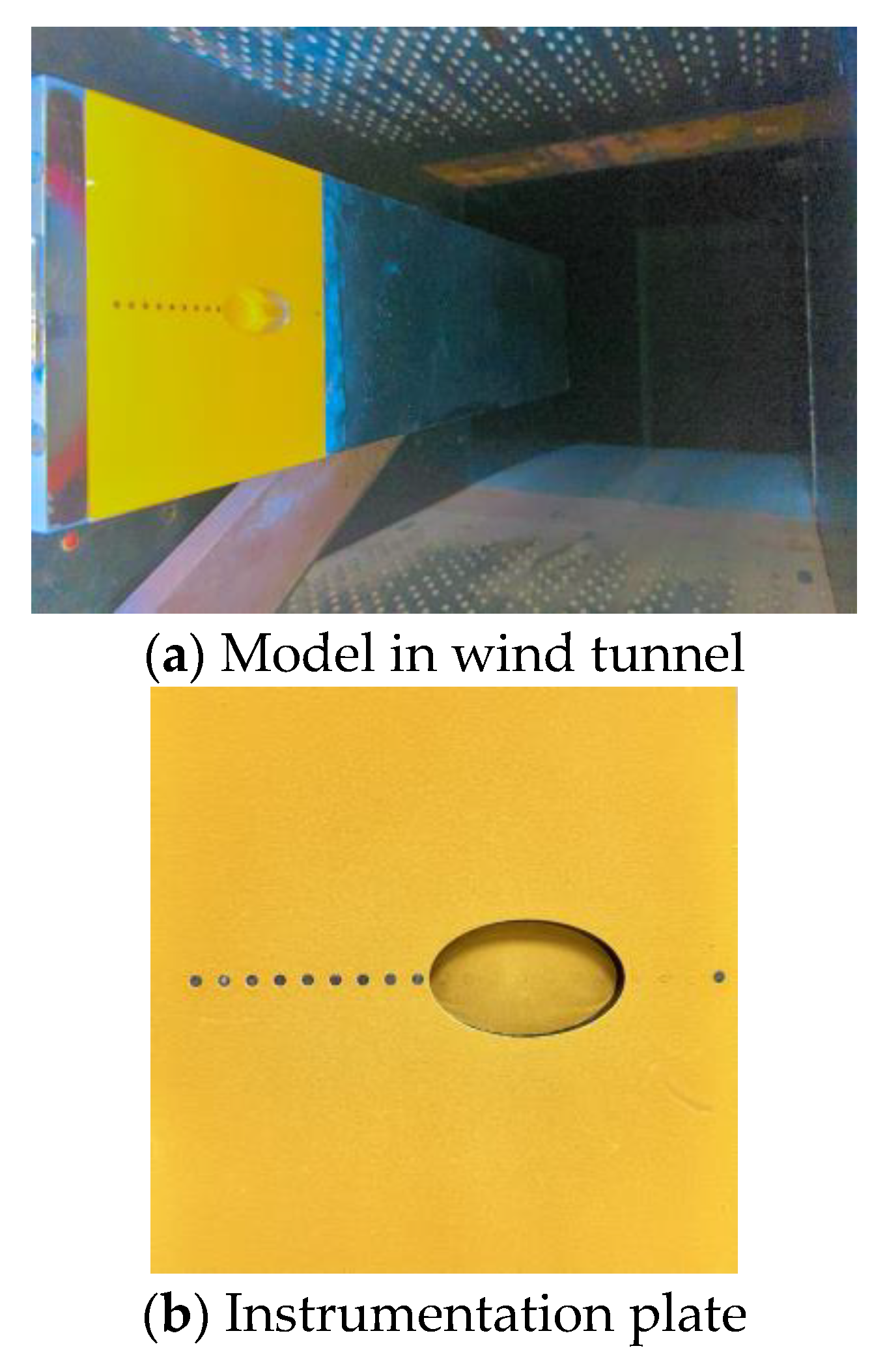
2.1. Transonic Wind Tunnel
2.2. Models and Test Conditions
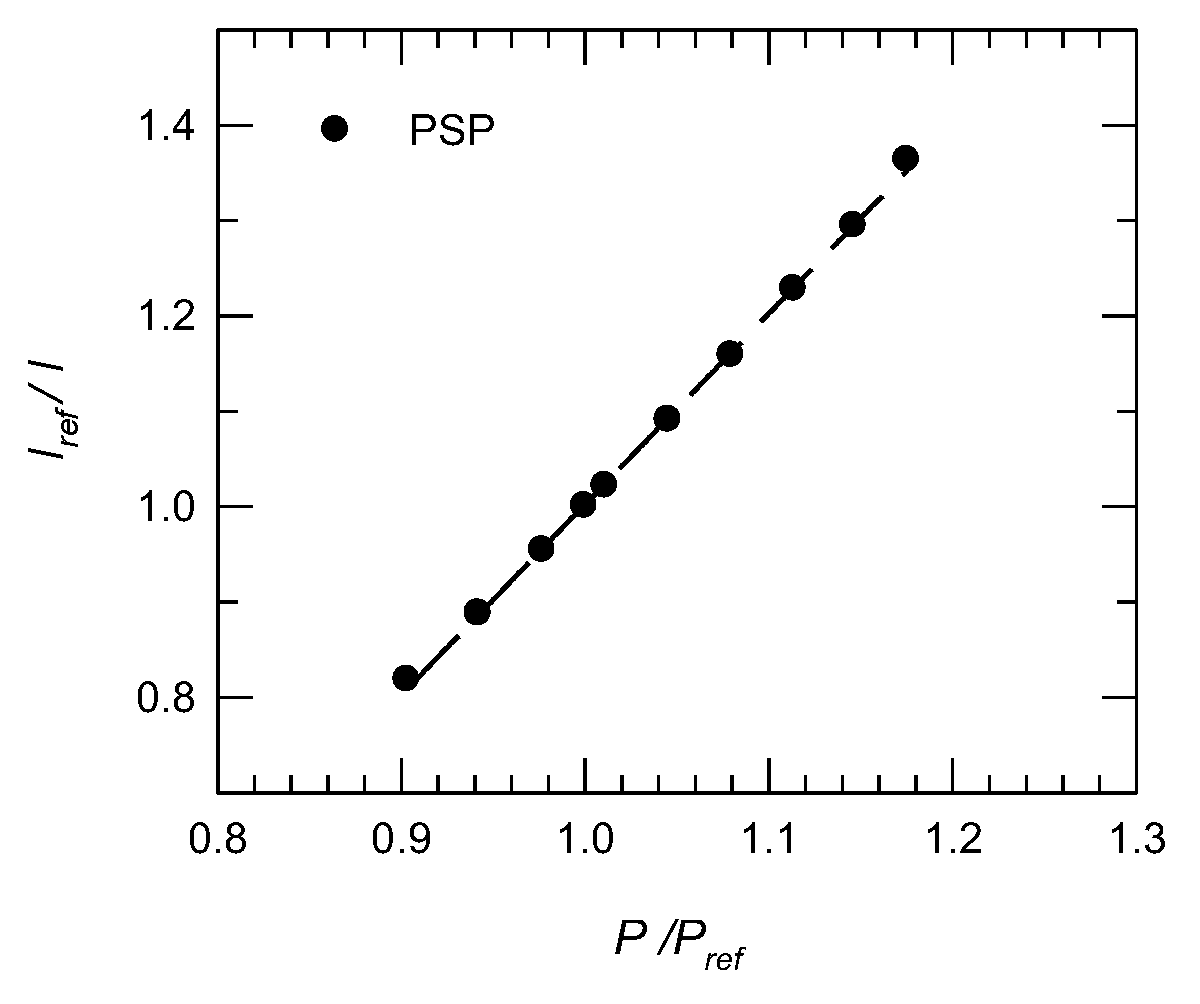
2.3. Pressure Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
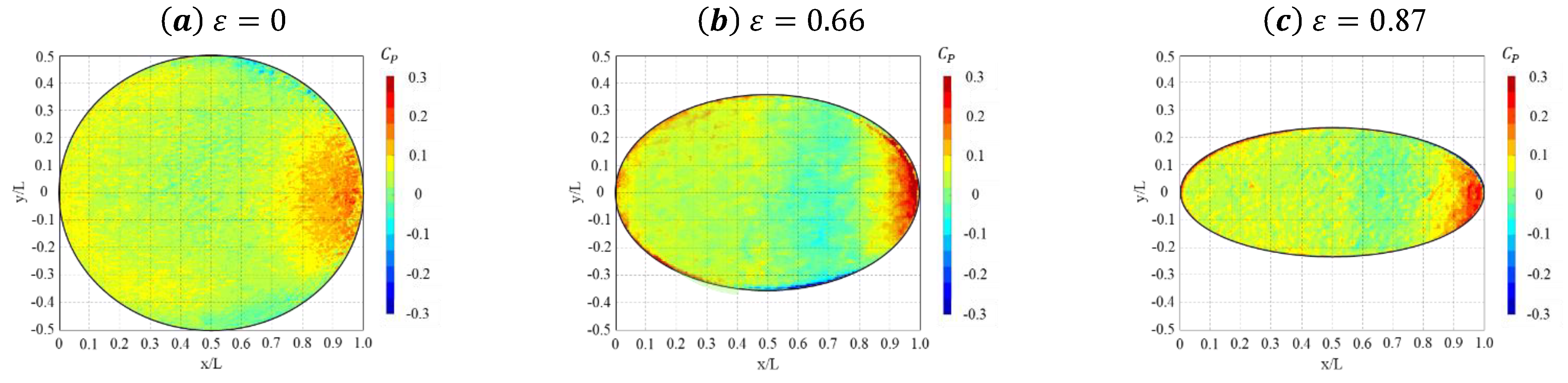
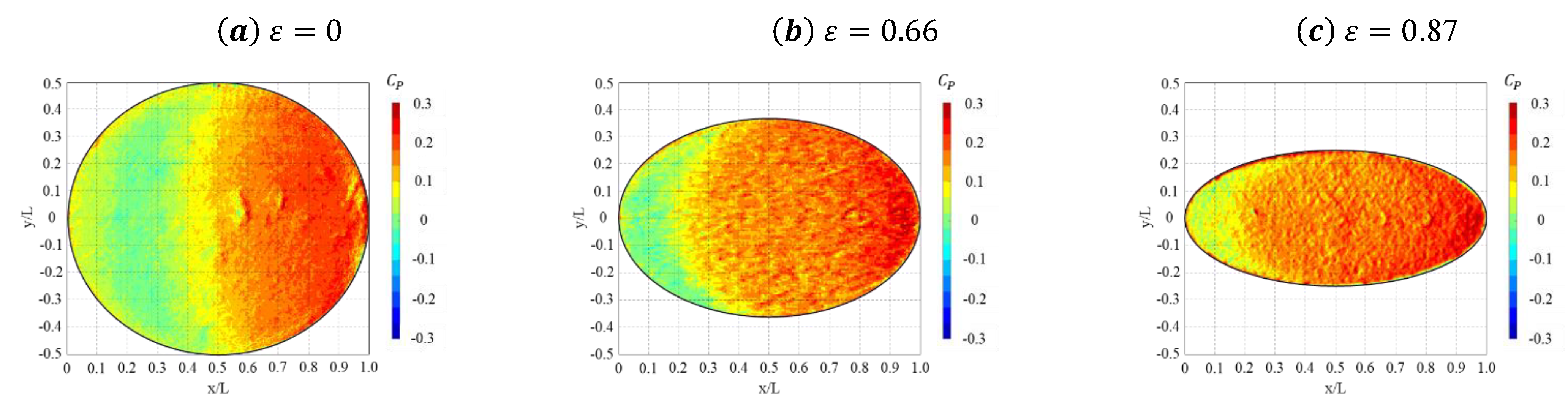
3.1. Global Pressure Pattern
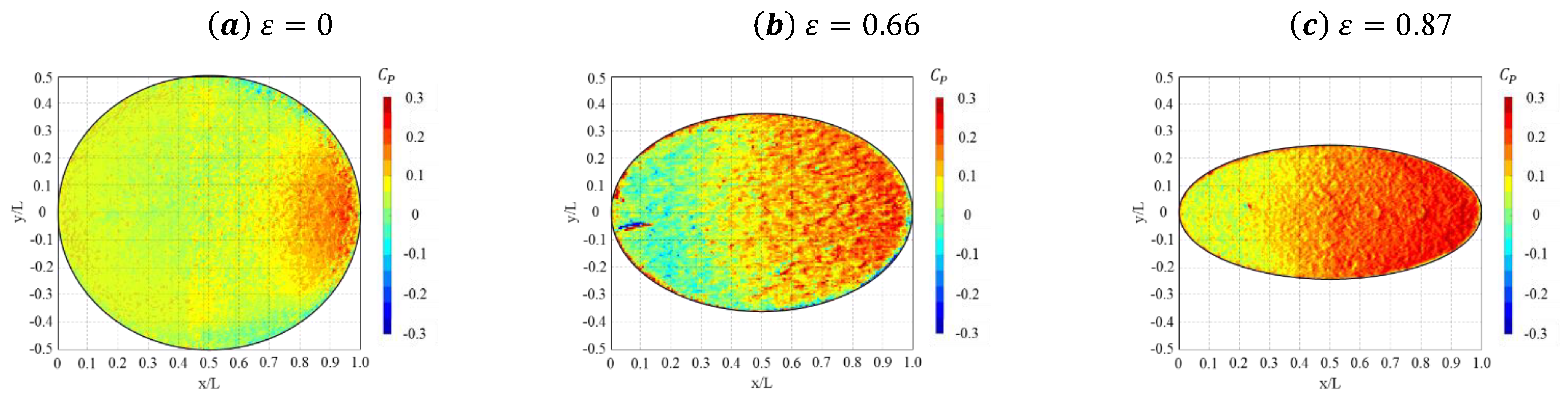
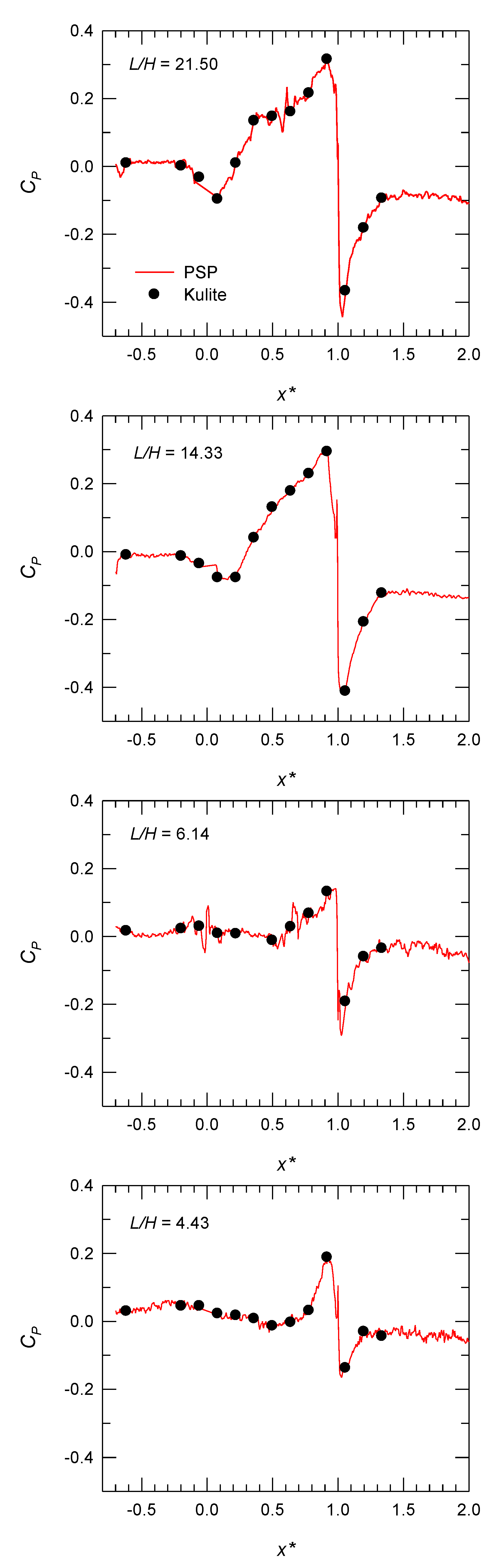
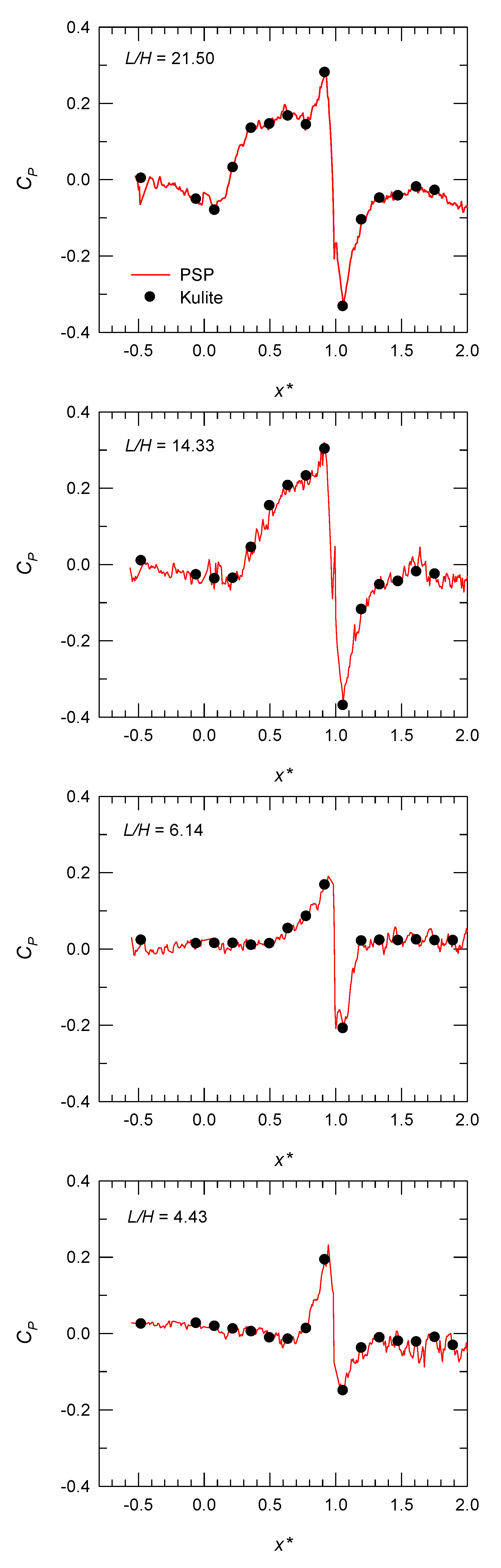
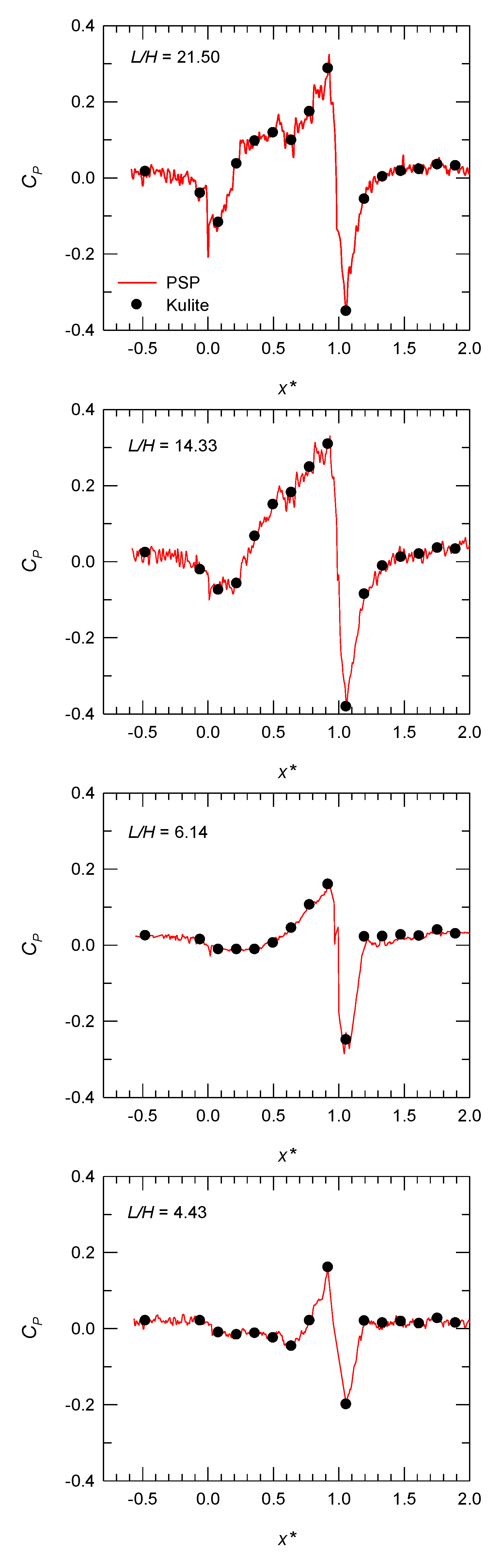
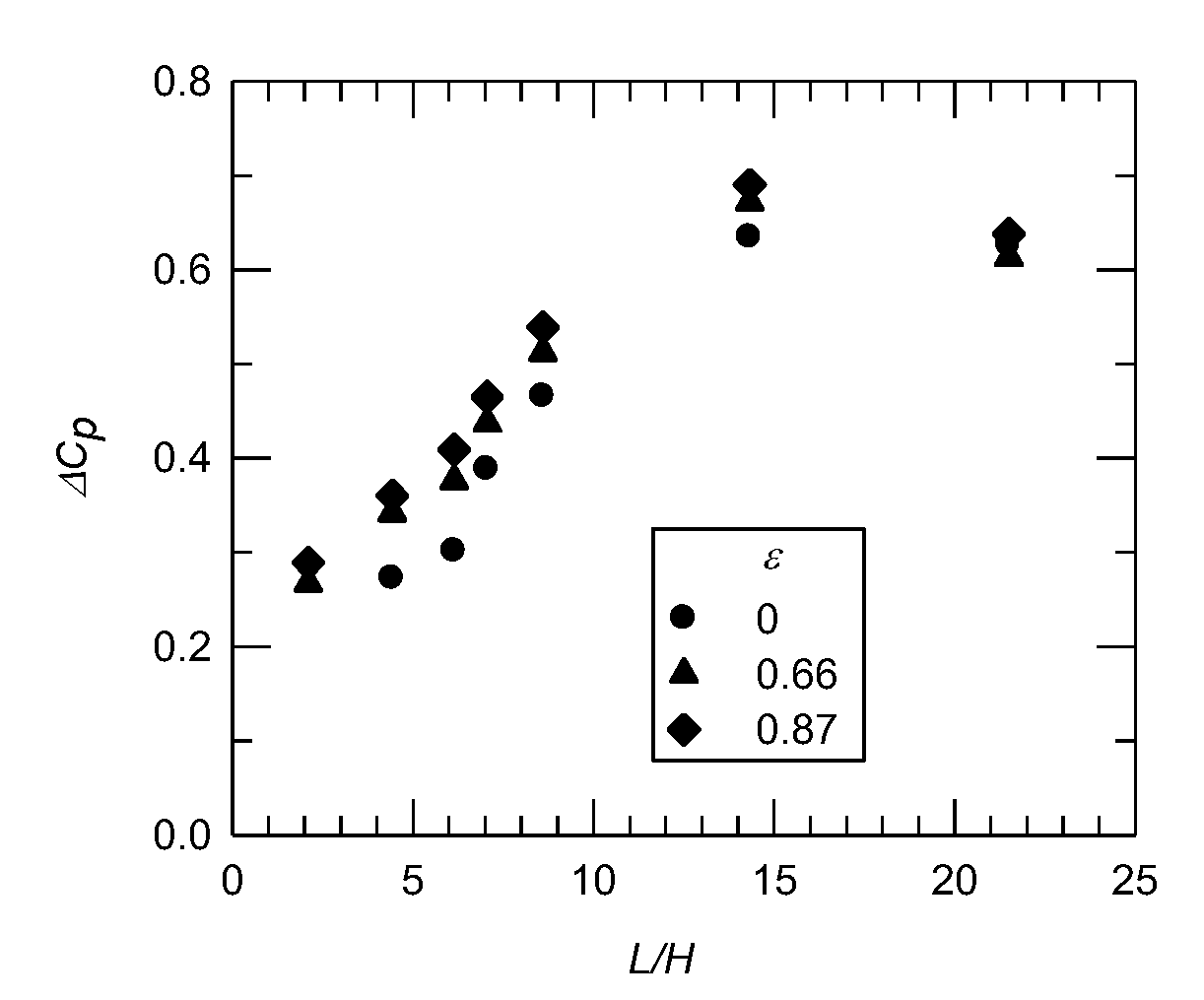
3.2. Mean Surface Distribution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | constant for PSP calibration curve |
| B | pressure sensitivity for PSP |
| Cp | pressure coefficient, (p–p∞)/q |
| Cp | pressure coefficient |
| Cp,peak | peak pressure coefficient |
| H | cavity depth |
| I | intensity of the emission |
| Iref | reference intensity for emission |
| L | the length of the major axis |
| M | freestream Mach number |
| pw | mean surface pressure |
| p∞ | freestream pressure |
| q | dynamic pressure |
| W | the length of the minor axis |
| x | coordinate in the streamwsie direction |
| y | coordinate in the spanwise direction |
| x* | x/δ |
| y* | y/δ |
| δ | boundary layer thickness |
| ε | eccentricity |
References
- Chen, H.; Zhong, Q.; Wang, X.K.; Li, D.X. Reynolds number dependence of flow past a shallow open cavity. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2014, 57, 2161–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, R.F.; Xi, Z.J.; Wan, Z.H.; Sun, D.J. Effect of Mach number on the mode transition for supersonic cavity flows. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 106101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.M.; Huang, Y.X.; Lee, K.H.; Chang, K.C. Reynolds number effect on a compressible cylindrical cavity flow. Chinese J. Aero. 2020, 33, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, Y.; Ozawa, Y.; Nagata, T.; Asai, K.; Nonomura, T. Experimental investigation of the supersonic cavity by spectral-POD of high-sampling rate pressure-sensitive paint data. Exper. Fluids 2023, 64, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charwat, A.F.; Roos, J.N.; Dewey, F.C.; Hitz, J.A. An investigation of separated Flows—Part I: The pressure field. J. Aerosp. Sci. 1961, 28, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plentovich, E.; Stallings, R., Jr.; Tracy, M. Experimental cavity pressure measurements at subsonic and transonic speeds; NASA Technical Paper 3358; Langley Research Center, National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Hampton, Virginia, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, K.M. Characteristics of transonic rectangular cavity flows. J. Aircr. 2000, 37, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossiter, J. Wind tunnel experiments on the flow over rectangular cavities at subsonic and transonic speeds; Technical Report 64037; Royal Aircraft Establishment: Farnborough, UK, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, H.; Bliss, D. Aerodynamically induced pressure oscillations in cavities physical mechanisms and suppression concepts; Technological Report AFFDL-TR-74-133; Air Force Flight Dynamics Laboratory: Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, OH, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, K.M. Three-dimensional effect on transonic rectangular cavity flows. Exper. Fluids 2001, 30, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozalp, C.; Pinarbasi, A.H.M.E.T.; Sahin, B. Experimental measurement of flow past cavities of different shapes. Exper. Thermal Fluid Sci. 2010, 34, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdugo, F.R.; Guitton, A.; Camussi, R. Experimental investigation of a cylindrical cavity in a low Mach number flow. J Fluids Structures 2012, 28, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, P.W.; Ekmekci, A. Flow features of shallow cylindrical cavities subject to grazing flow. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 027115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.M.; Lee, K.H.; Chang, K.C. Characteristics of cylindrical cavities in a compressible turbulent flow. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2017, 66, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadivi, T.; Savory, E. Experimental and numerical study of flow structures associated with low aspect ratio elliptical cavities. J. Fluids Eng. 2013, 135, 041104-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, T.; Savory, E. Flow regimes and drag characteristics of yawed elliptical cavities with varying depth. J. Fluids Eng. 2007, 129, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadivi, T.; Savory, E. Effect of yaw angle on the flow structure of low aspect ratio elliptical cavities. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2017, 30, 04017002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Qin, L.; Wu, J. On aerodynamic characteristics of rarefied hypersonic flows over variable eccentricity elliptical cavities. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2023, 134, 108160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, P.H.; Huang, Y.X.; Chung, K.M.; Huang, C.Y.; Isaev, S.A. Effective distance for vortex generators in high subsonic flows. Aerosp. 2023, 10, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Campbell, B.T.; Burns, S.P.; Sullivan, J.P. Temperature-and pressure-sensitive luminescent paints in aerodynamics. Appl. Mech. Rev. 1997, 50, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Guille, M.; Sullivan, J.P. Accuracy of pressure-sensitive paint. AIAA J. 2001, 39, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare-Behtash, H.; Yang, L.; Gongora-Orozco, N.; Kontis, K.; Jones, A. Anodized aluminium pressure sensitive paint: Effect of paint application technique. Meas. 2012, 45, 1902–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, M.; Suzuki, A.; Egami, Y.; Nonomura, T.; Asai, K. A platinum-based fast-response pressure-sensitive paint containing hydrophobic titanium dioxide. Sensors Actr. A-Phys. 2023, 350, 114140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.H.; Schairer, E.T.; Hand, L.A.; Mehta, R.D. Surface pressure measurements using luminescent coatings. Annul. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2001, 33, 155–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| M | po, Pa | Reδ | To |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.83 | 1.72 × 105 | 1.69 × 105 | 28–32 °C |
| L/H | L, mm | W, mm | ε |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.43 | 43 | ||
| 6.14 | 43 | 43.0, 32.3, 21.5 | 0, 0.66, 0.87 |
| 14.33 | 43 | ||
| 21.50 | 43 |
| Luminophore | Polymer | Solvent | Particle | Spray Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ru(dpp) | RTV-118 | Toluene | SiO2 | 37.5 cm2 |
| 2.5 mg | 250 mg | 5 ml | 125 mg |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.-X.; Chung, K.-M. Global Surface Pressure Pattern for a Compressible Elliptical Cavity Flow Using Pressure-Sensitive Paint. Aerospace 2024, 11, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11020159
Huang Y-X, Chung K-M. Global Surface Pressure Pattern for a Compressible Elliptical Cavity Flow Using Pressure-Sensitive Paint. Aerospace. 2024; 11(2):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11020159
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yi-Xuan, and Kung-Ming Chung. 2024. "Global Surface Pressure Pattern for a Compressible Elliptical Cavity Flow Using Pressure-Sensitive Paint" Aerospace 11, no. 2: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11020159
APA StyleHuang, Y.-X., & Chung, K.-M. (2024). Global Surface Pressure Pattern for a Compressible Elliptical Cavity Flow Using Pressure-Sensitive Paint. Aerospace, 11(2), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11020159







