A Rational Design Method for the Nagoya Type-III Antenna
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Helicon Wave Modelling and Design Methods
2.1. Design Method 1
2.2. Design Method 2
2.3. Design Method 3
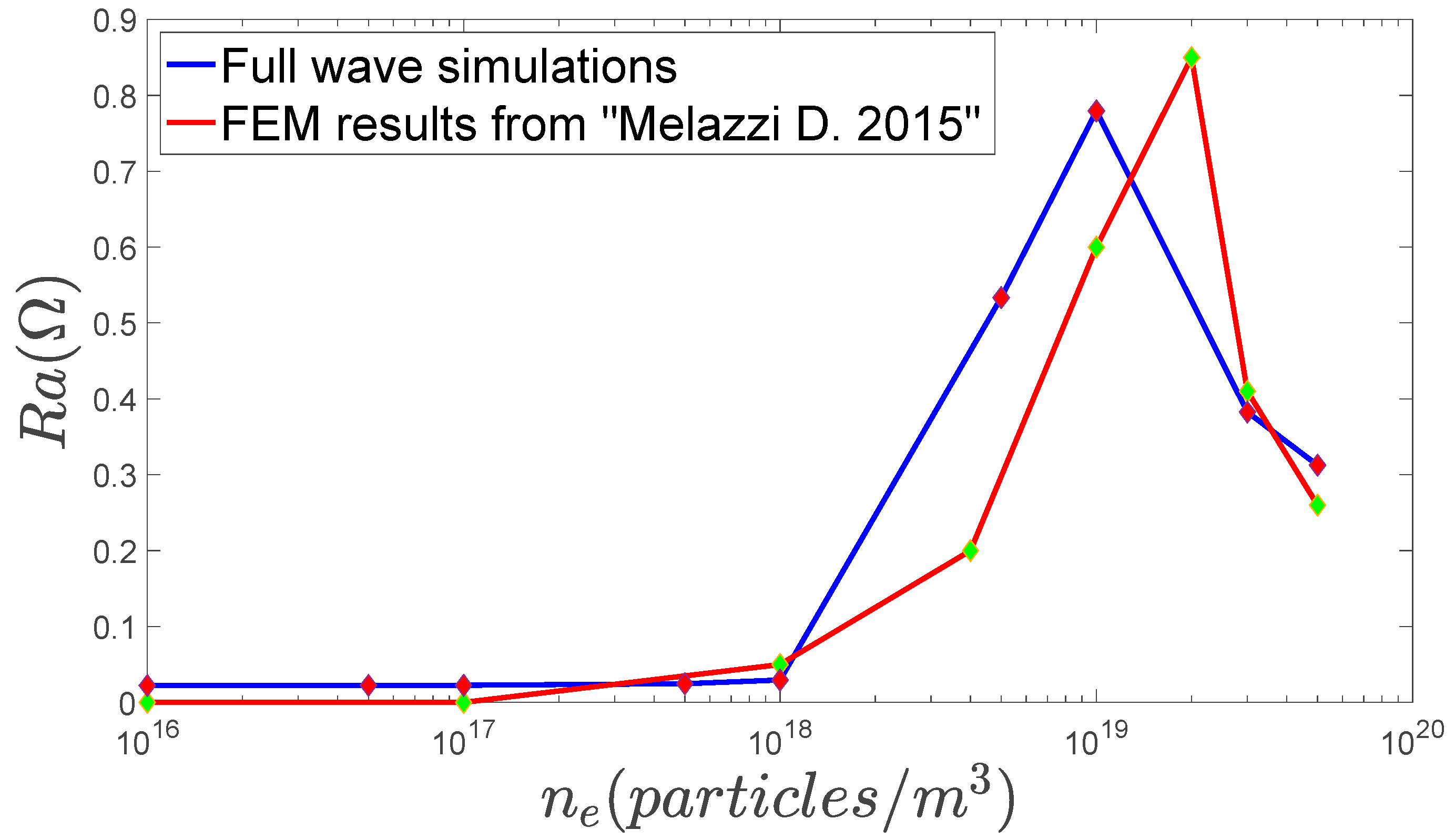
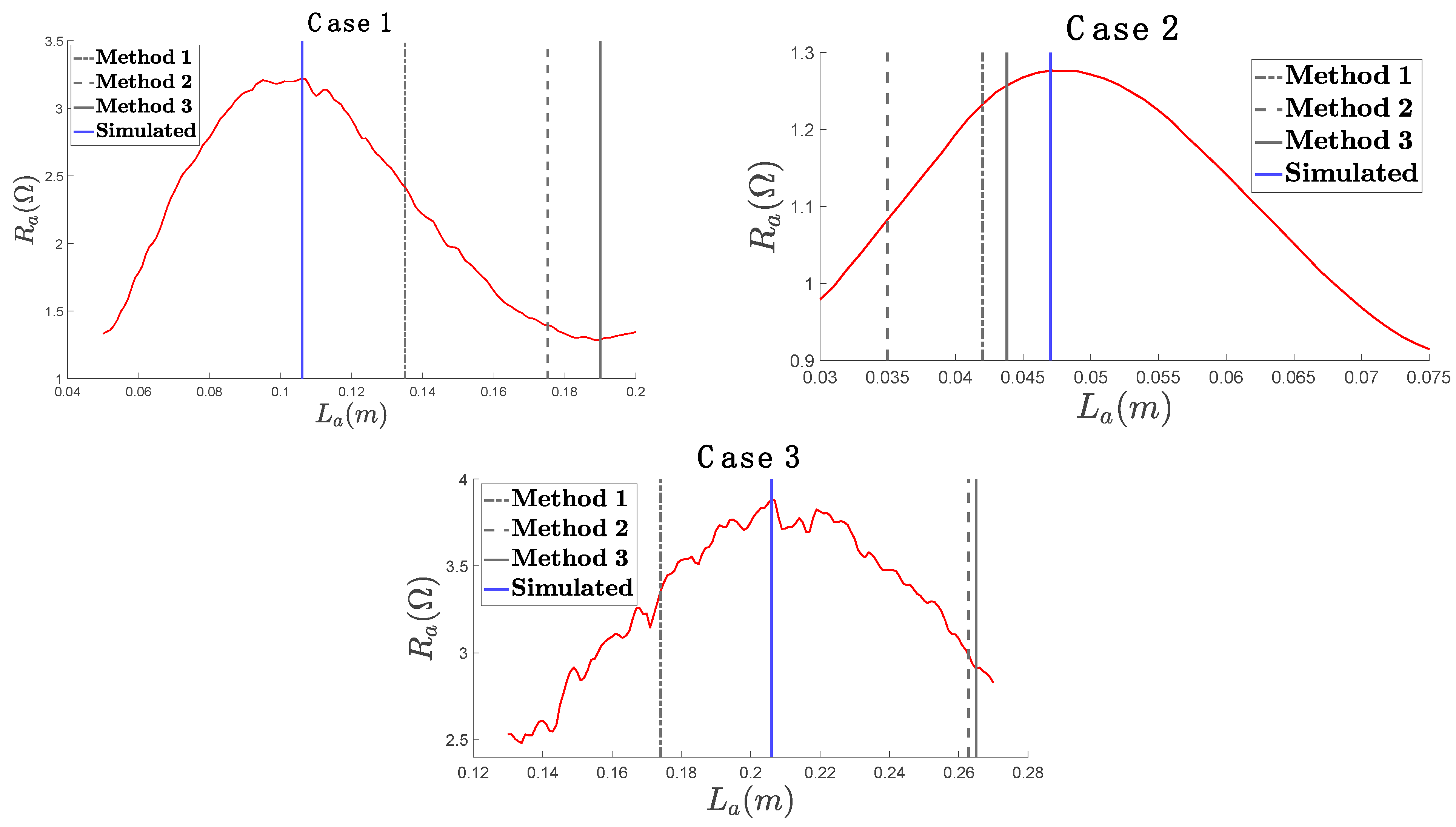
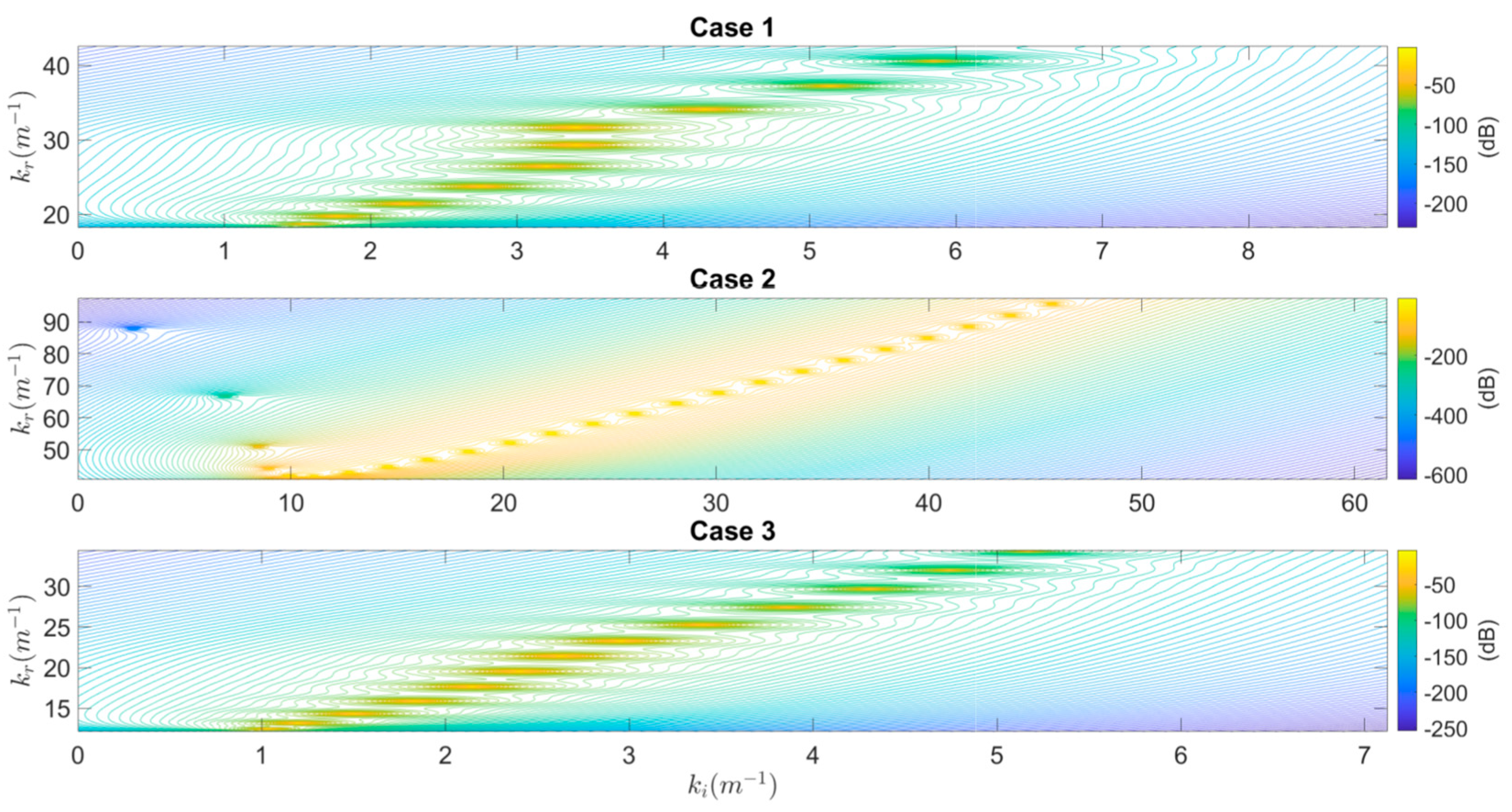
3. Simulations and Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ziemba, T.; Carscaddenl, J.; Slough, J.; Prager, J.; Winglee, R.M. High power helicon thruster. In Proceedings of the 41st AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit, Tucson, AZ, USA, 10–13 July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bathgate, S.N.; Bilek, M.M.M.; McKenzie, D.R. Electrodeless plasma thrustersfor spacecraft: A review. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2017, 19, 083001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, R.; Porteous, R.; Prytz, A.; Bouchoule, A.; Ranson, P. Some features of RF excited fully ionized low pressure argon plasma. Phys. Lett. A 1982, 91, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, R.G. Physics of Electric Propulsion; Dover Books: Mineola, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Boswell, R.W. Plasma Production Using a Standing Helicon Wave. Phys. Rev. Lett. A 1970, 33, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, R.W. Very efficient plasma generation by whistler waves near the lowerhybrid frequency. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 1984, 26, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.F. Plasma ionization by helicon waves. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 1991, 33, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.F.; Blackwell, D.D. Upper limit to Landau damping inhelicon discharges. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.F.; Arnush, D. Generalized theory of helicon waves I. Normal modes. Phys. Plasmas 1997, 4, 3411–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnush, D.; Chen, F.F. Generalized theory of helicon waves II. Excitation and absorption. Phys. Plasmas 1998, 5, 1239–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isayama, S.; Shinohara, S.; Hada, T. Review of Helicon High-Density Plasma: Production Mechanism and Plasma/Wave Characteristics. Plasma Fusion Res. 2018, 13, 1101014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.F. Helicon discharges and sources: A review. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2015, 24, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivelpiece, A.W.; Gould, R.W. Space charge waves in cylindrical plasma columns. J. Appl. Phys. 1959, 30, 1784–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamrai, K.P. Stable modes and abrupt density jumps in a helicon plasma source. Plasma Sources Sci. 1998, 7, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, D.D.; Madziwa, T.G.; Arnush, D.; Chen, F.F. Evidence for Trivelpiece-Gould modes in a helicon discharge. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 145002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinohara, S.; Yonekura, K. Discharge modes and wave structures using loop antennae in a helicon plasma source. Plasma Phys. Control Fusion 2000, 42, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisoa, M.N.; Sakawa, Y.S.; Shoji, T.S. Plasma Production by m=0 Standing Helicon Waves. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 39, L429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, M.; Chen, F.F. Helicon wave excitation with helical antennas. Phys. Plasmas 1995, 2, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guittienne, P.; Jacquier, R.; Duteil, B.P.; Howling, A.A. Helicon wave plasma generated by a resonant birdcage antenna: Magnetic field measurements and analysis in the RAID linear device. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2021, 30, 075023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, F.; Chan, Y.A.; Herdrich, G.; Traub, C.; Fasoulas, S.; Roberts, P.; Crisp, N.; Holmes, B.; Edmondson, S.; Haigh, S.; et al. Design, set-up, and first ignition of the RF Helicon-based Plasma Thruster. In Proceedings of the Space Propulsion Conference 2021, Online, 17–19 March 2021; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/350124196_Design_Set-Up_and_First_Ignition_of_the_RF_Helicon-based_Plasma_Thruster (accessed on 5 November 2024).
- Jin, J.M. Electromagentic Analysis and Design in Magnetic Resonance Imaging; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Romano, F.; Chan, Y.-A.; Herdrich, G.; Traub, C.; Fasoulas, S.; Roberts, P.; Smith, K.; Edmondson, S.; Haigh, S.; Crisp, N.; et al. RF helicon-based inductive plasma thruster (IPT) design for an atmosphere-breathing electric propulsion system (ABEP). Acta Astronaut. 2020, 176, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guittienne, P.; Chevalier, E.; Hollenstein, C. Towards an optimal antenna for helicon waves excitation. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 083304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furno, I.; Agnello, R.; Fantz, U.; Howling, A.; Jacquier, R.; Marini, C.; Plyushchev, G.; Guittienne, P.; Simonin, A. Helicon wave-generated plasmas for negative ion beams for fusion. EPJ Web Conf. 2017, 157, 03014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Agnello, R.; Barbisan, M.; Furno, I.; Guittienne, P.; Howling, A.A.; Jacquier, R.; Pasqualotto, R.; Plyushchev, G.; Andrebe, Y.; Béchu, S.; et al. Cavity ring-down spectroscopy to measure negative ion density in a helicon plasma source for fusion neutral beams. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 103504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watari, T.; Hatori, T.; Kumazawa, R.; Hidekuma, S.; Aoki, T.; Kawamoto, T.; Inutake, M.; Hiroe, S.; Nishizawa, A.; Adati, K.; et al. Radio-frequency plugging of a high density plasma. Phys. Fluids 1978, 21, 2076–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melazzi, D.; Lancellotti, V. A comparative study of radiofrequency antennas for Helicon plasma sources. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2015, 24, 025024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.S. NRL Plasma Formulary; Pulsed Power Physics Branch, Plasma Physics Division, Naval Research Laboratory: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Soltani, B.; Habibi, M. Development of a Helicon Plasma Source for Neutral Beam Injection System of the Alborz Tokamak. J. Fusion Energy 2017, 36, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partial Differential Equation Toolbox™; MATLAB R2023b; MathWorks: Portola Valley, CA, USA, 2023.
- Iannarelli, D.; Ingenito, A.; Napoli, F.; Cichocki, F.; Castaldo, C.; De Ninno, A.; Mannori, S.; Cardinali, A.; Taccogna, F. Full Helicon thruster modeling. In Proceedings of the 38th International Electric Propulsion Conference, Toulouse, France, 23–28 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Stix, T.H. Waves in Plasmas; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Cardinali, A.; Melazzi, D.; Manente, M.; Pavarin, D. Ray-tracing WKB analysis of Whistler waves in non-uniform magnetic fields applied to space thrusters. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2014, 23, 015013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Argon | Argon | Argon |
| f | 13.56 MHz | 13.56 MHz | 13.56 MHz |
| B0 | 10 mT | 10 mT | 15 mT |
| 1.0 × | 5.00 × | 1.00 × | |
| 3 eV | 3 eV | 3 eV | |
| 2 Pa | 2 Pa | 2 Pa | |
| b | 4.5 cm (antenna, Figure 1) | 4.5 cm (antenna, Figure 1) | 4.5 cm (antenna, Figure 1) |
| a | 4.0 cm (quartz tube, Figure 1) | 4.0 cm (quartz tube, Figure 1) | 4.0 cm (quartz tube, Figure 1) |
| - | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Average Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method 1 | 13.50 cm (27.36%) | 4.20 cm (−12.5%) | 17.40 cm (−15.53%) | 18.46% |
| Method 2 | 17.52 cm (65.28%) | 3.50 cm (−27.08%) | 26.28 cm (27.57%) | 39.98% |
| Method 3 | 19.00 cm (79.25%) | 4.38 cm (−8.75%) | 26.50 cm (28.60%) | 38.87% |
| Simulated | 10.60 cm | 4.80 cm | 20.60 cm | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iannarelli, D.; Napoli, F.; Ingenito, A.; Cardinali, A.; De Ninno, A.; Mannori, S. A Rational Design Method for the Nagoya Type-III Antenna. Aerospace 2024, 11, 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11121056
Iannarelli D, Napoli F, Ingenito A, Cardinali A, De Ninno A, Mannori S. A Rational Design Method for the Nagoya Type-III Antenna. Aerospace. 2024; 11(12):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11121056
Chicago/Turabian StyleIannarelli, Daniele, Francesco Napoli, Antonella Ingenito, Alessandro Cardinali, Antonella De Ninno, and Simone Mannori. 2024. "A Rational Design Method for the Nagoya Type-III Antenna" Aerospace 11, no. 12: 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11121056
APA StyleIannarelli, D., Napoli, F., Ingenito, A., Cardinali, A., De Ninno, A., & Mannori, S. (2024). A Rational Design Method for the Nagoya Type-III Antenna. Aerospace, 11(12), 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11121056






