The Solar Particle Acceleration Radiation and Kinetics (SPARK) Mission Concept
Abstract
1. Scientific Objectives
- How does impulsive energy release accelerate particles in the solar atmosphere?
- How is impulsively released energy transported and dissipated in the solar atmosphere?
- What are the physical low-corona origins of space weather events?
- How is the corona above active regions heated?
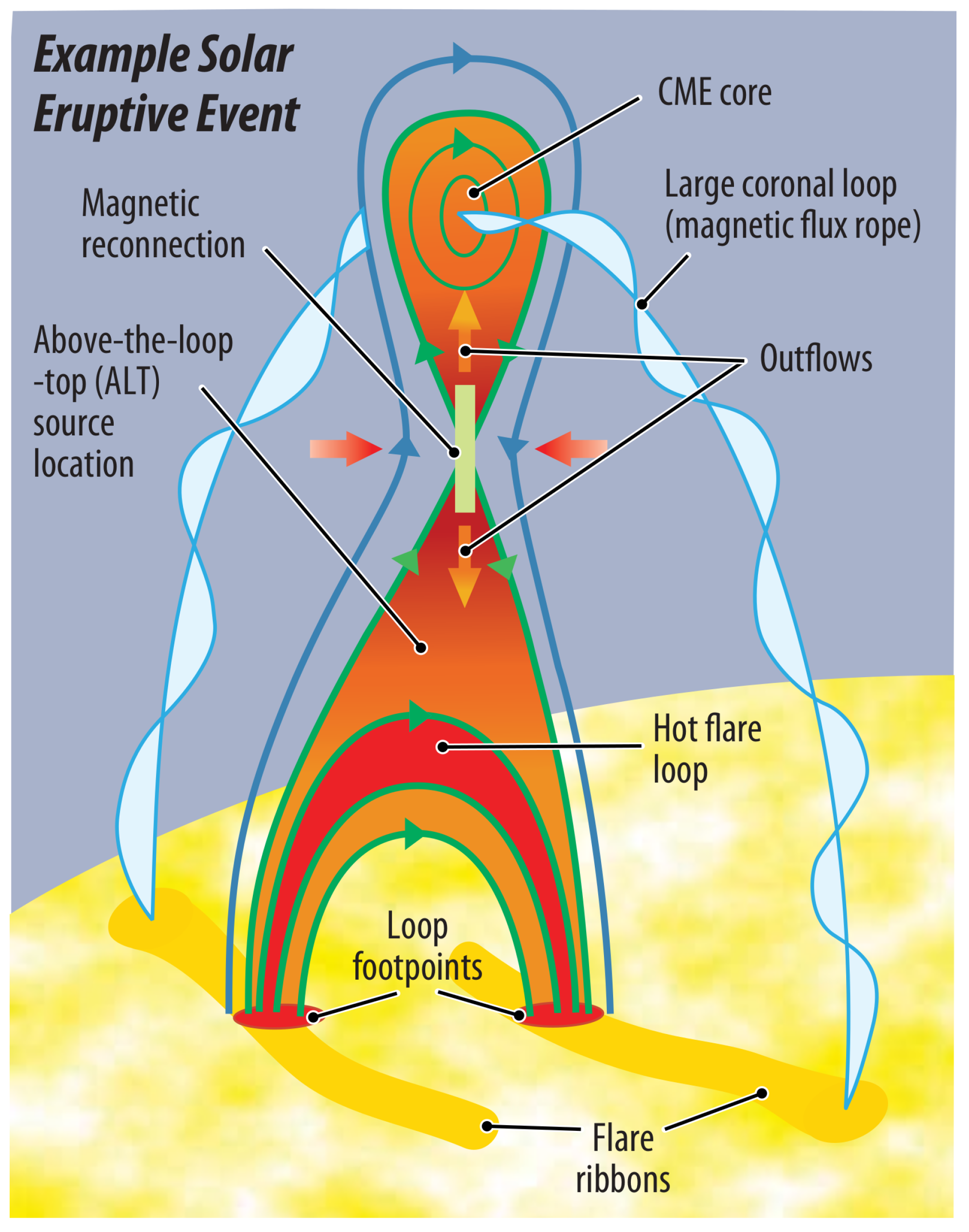
1.1. How Does Impulsive Energy Release Accelerate Particles in the Solar Atmosphere?
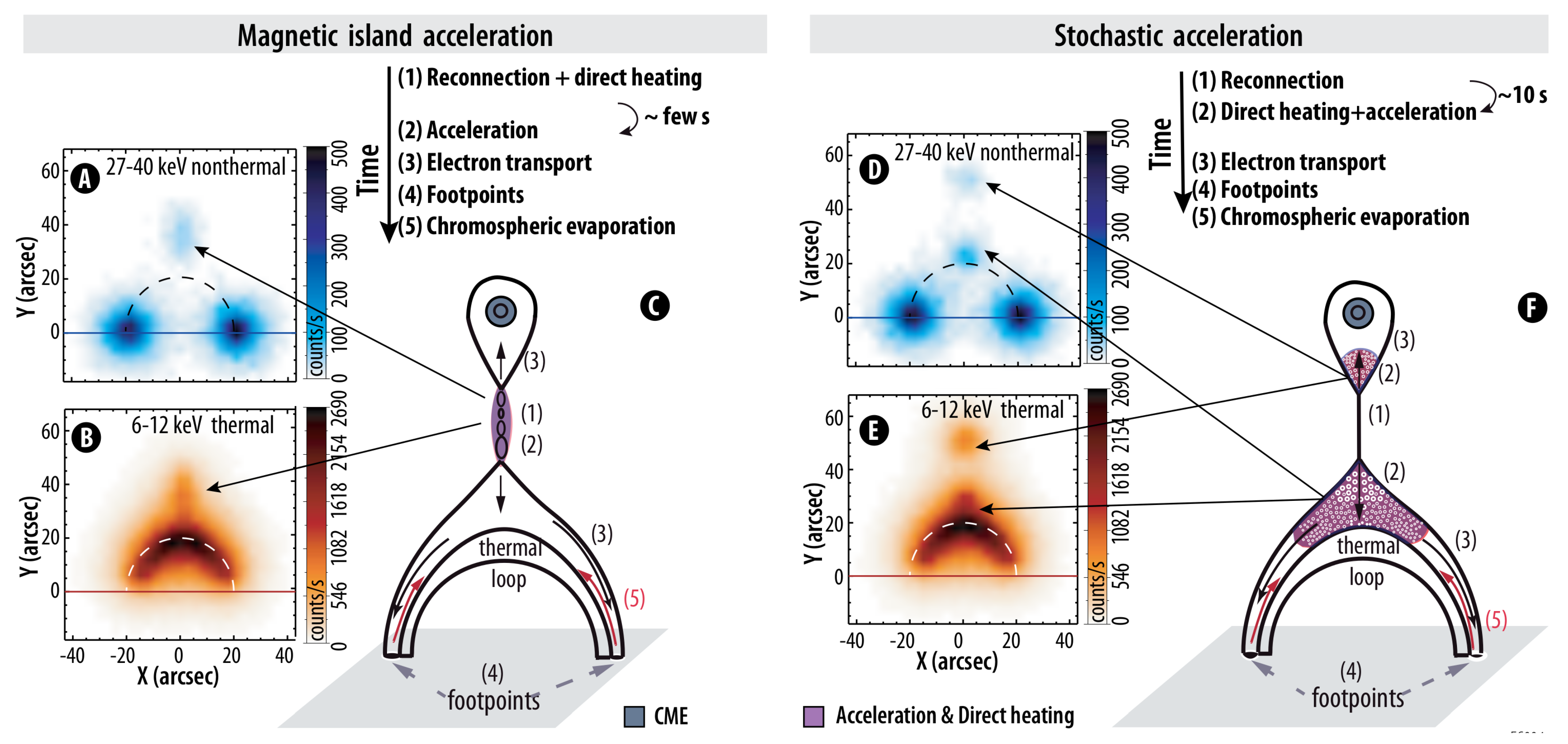
1.1.1. Where and When Do Particle Acceleration and Local Plasma Heating Occur?
1.1.2. What Are the Efficiency and Energy Content of Electron and Ion Acceleration?
1.1.3. How Do Electron and Ion Acceleration and Transport Differ in the Flaring Atmosphere?
1.1.4. Where and How Are the Most Energetic Particles Accelerated at the Sun?
1.2. How Is Impulsively Released Energy Transported and Dissipated in the Solar Atmosphere?
1.2.1. How and Where Do Accelerated Particles Lose Their Energy in the Corona and Chromosphere?
1.2.2. What Are the Origins of Modulations in Solar Flare Emission?
1.2.3. What Is the Importance of Accelerated Particles in Transporting Energy Compared with That of Other Mechanisms?
1.3. What Are the Physical Low-Corona Origins of Space Weather Events?
1.3.1. What Are the Energy Content and Spectrum of Sun-Escaping Electrons?
1.3.2. What Are the Dominant Initiation Mechanisms of Solar Eruptions?
1.4. How Is the Corona above Active Regions Heated?
1.4.1. Is Particle Acceleration Ubiquitous among Energy-Release Events at All Size Scales?
1.4.2. How Does Small-Scale Particle Acceleration Contribute to Coronal Heating?
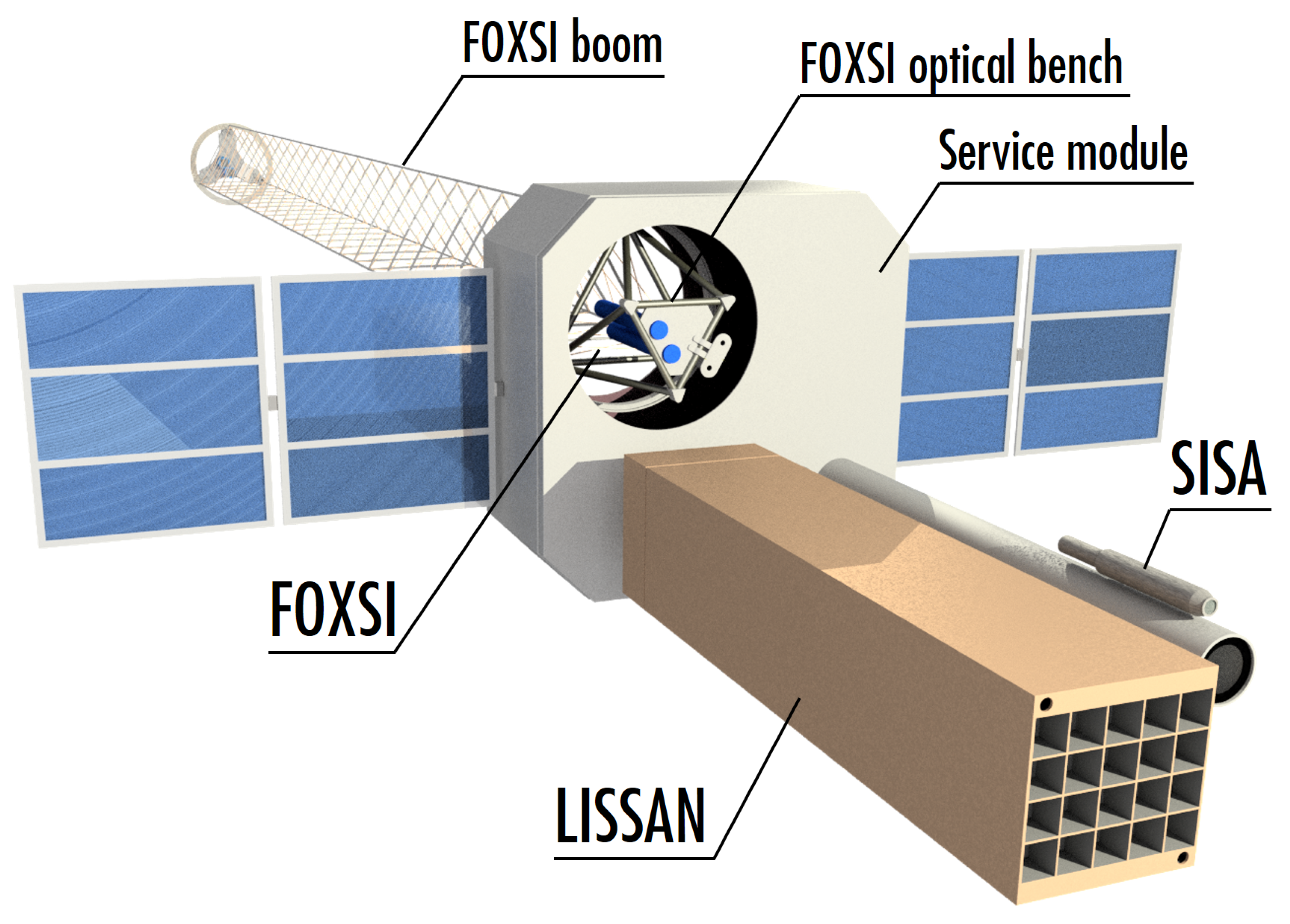
2. Payload
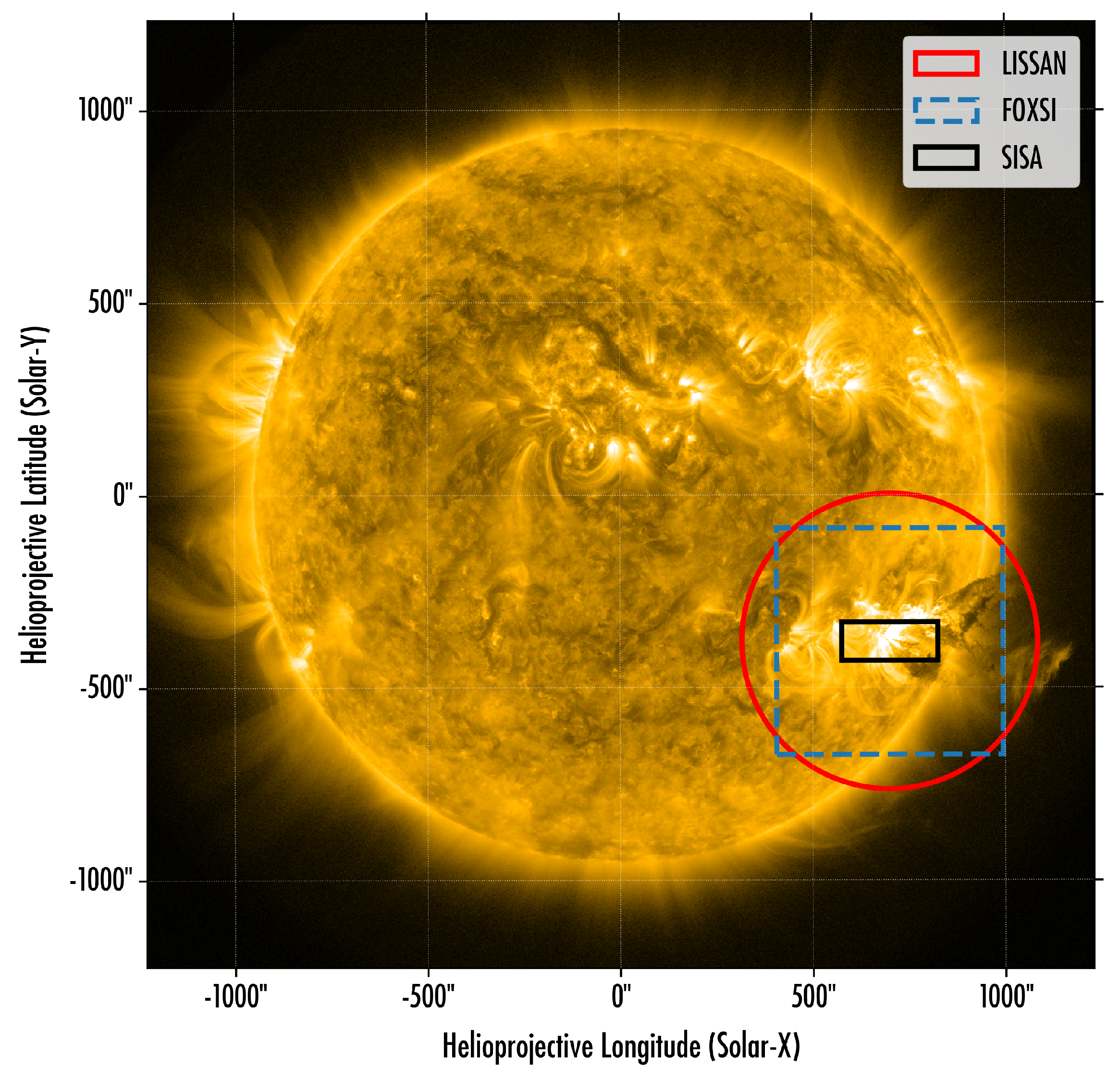
2.1. Large Imaging Spectrometer for Solar Accelerated Nuclei (LISSAN)
2.2. Focusing Optics X-ray Solar Imager (FOXSI)
2.3. Spectral Imager of the Solar Atmosphere (SISA)
2.4. Mass and Power
3. Proposed Mission Configuration and Profile
3.1. System-Level Requirements
3.2. Operations
3.3. Spacecraft Design
4. Current Status of SPARK
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIA | Atmospheric imaging assembly |
| CME | Coronal mass ejection |
| EIS | EUV Imaging Spectrometer on board Hinode |
| EUV | Extreme ultraviolet |
| EUVST | Extreme Ultraviolet High-Throughput Spectroscopic Telescope |
| EVE | EUV Variability Experiment on board SDO |
| FEE | Front-end electronics |
| FIERCE | Fundamentals of Impulsive Energy Release in the Corona Explorer |
| FPA | Focal-plane assembly |
| FOV | Field of view |
| FOXSI | Focusing Optics X-ray Solar Imager |
| FOXSI-STC | FOXSI’s Spectrometer for Temperature and Composition |
| FWHM | Full-width half maximum |
| GOES | Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite |
| HXR | Hard X-ray |
| IFS | Integral field spectrograph |
| IRIS | Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph |
| LISSAN | Large Imaging Spectrometer for Solar Accelerated Nuclei |
| MHD | Magnetohydrodynamic |
| MUSE | Multi-Slit Solar Explorer |
| NuSTAR | Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array |
| RHESSI | Reuven Ramaty High-Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager |
| SDO | Solar Dynamics Observatory |
| SEP | Solar energetic particle |
| SISA | Spectral Imager of the Solar Atmosphere |
| SPARK | Solar Particle Acceleration, Radiation, and Kinetics mission |
| STIX | Spectrometer/Telescope for Imaging X-rays |
| SXR | Soft X-ray |
References
- Shibata, K. New observational facts about solar flares from YOHKOH studies—Evidence of magnetic reconnection and a unified model of flares. Adv. Space Res. 1996, 17, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.C. The Deduction of Energy Spectra of Non-Thermal Electrons in Flares from the Observed Dynamic Spectra of Hard X-Ray Bursts. Sol. Phys. 1971, 18, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piana, M.; Massone, A.M.; Kontar, E.P.; Emslie, A.G.; Brown, J.C.; Schwartz, R.A. Regularized Electron Flux Spectra in the 2002 July 23 Solar Flare. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2003, 595, L127–L130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, G.D.; Aschwanden, M.J.; Aurass, H.; Battaglia, M.; Grigis, P.C.; Kontar, E.P.; Liu, W.; Saint-Hilaire, P.; Zharkova, V.V. Implications of X-ray Observations for Electron Acceleration and Propagation in Solar Flares. Space Sci. Rev. 2011, 159, 107–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontar, E.P.; Brown, J.C.; Emslie, A.G.; Hajdas, W.; Holman, G.D.; Hurford, G.J.; Kašparová, J.; Mallik, P.C.V.; Massone, A.M.; McConnell, M.L.; et al. Deducing Electron Properties from Hard X-ray Observations. Space Sci. Rev. 2011, 159, 301–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, A.O. Flare Observations. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2017, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chupp, E.L. High-Energy Neutral Radiations from the Sun. Annu. Rev. Astron Astrophys. 1984, 22, 359–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaty, R. Nuclear processes in solar flares. In Physics of the Sun: Volume II: The Solar Atmosphere; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1986; Volume 2, pp. 291–323. [Google Scholar]
- Chupp, E.L. Evolution of our understanding of solar flare particle acceleration: (1942–1995). In High Energy Solar Physics; Ramaty, R., Mandzhavidze, N., Hua, X.M., Eds.; American Institute of Physics Conference Series; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 1996; Volume 374, pp. 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trottet, G.; Vilmer, N. The Production of Flare-Accelerated Particles at the Sun. In European Meeting on Solar Physics; Simnett, G.M., Alissandrakis, C.E., Vlahos, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; Volume 489, p. 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Share, G.H.; Murphy, R.J. Gamma Ray Spectroscopy in the Pre-HESSI Era. In High Energy Solar Physics Workshop—Anticipating Hess! Ramaty, R., Mandzhavidze, N., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 2000; Volume 206, p. 377. [Google Scholar]
- Vilmer, N.; MacKinnon, A.L.; Trottet, G.; Barat, C. High energy particles accelerated during the large solar flare of 1990 May 24: X/γ-ray observations. Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 412, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Share, G.H.; Murphy, R.J. Gamma Radiation From Flare-Accelerated Particles Impacting the Sun. Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 2006, 165, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilmer, N.; MacKinnon, A.L.; Hurford, G.J. Properties of Energetic Ions in the Solar Atmosphere from γ-Ray and Neutron Observations. Space Sci. Rev. 2011, 159, 167–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecker, F.W. The Cosmic γ-Ray Spectrum from Secondary Particle Production in Cosmic-Ray Interactions. Astrophys. Space Sci. 1970, 6, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.J.; Dermer, C.D.; Ramaty, R. High-Energy Processes in Solar Flares. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 1987, 63, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurford, G.J.; Schwartz, R.A.; Krucker, S.; Lin, R.P.; Smith, D.M.; Vilmer, N. First Gamma-Ray Images of a Solar Flare. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2003, 595, L77–L80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaty, R.; Mandzhavidze, N. High energy processes in solar flares. In Proceedings of the Cosmic Explosions: Tenth AstroPhysics Conference, College Park, MD, USA, 11–13 October 1999; Holt, S.S., Zhang, W.W., Eds.; American Institute of Physics Conference Series. American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 2000; Volume 522, pp. 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emslie, A.G.; Dennis, B.R.; Shih, A.Y.; Chamberlin, P.C.; Mewaldt, R.A.; Moore, C.S.; Share, G.H.; Vourlidas, A.; Welsch, B.T. Global Energetics of Thirty-eight Large Solar Eruptive Events. Astrophys. J. 2012, 759, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschwanden, M.J.; Caspi, A.; Cohen, C.M.S.; Holman, G.; Jing, J.; Kretzschmar, M.; Kontar, E.P.; McTiernan, J.M.; Mewaldt, R.A.; O’Flannagain, A.; et al. Global Energetics of Solar Flares. V. Energy Closure in Flares and Coronal Mass Ejections. Astrophys. J. 2017, 836, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.P.; Dennis, B.R.; Hurford, G.J.; Smith, D.M.; Zehnder, A.; Harvey, P.R.; Curtis, D.W.; Pankow, D.; Turin, P.; Bester, M.; et al. The Reuven Ramaty High-Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (RHESSI). Sol. Phys. 2002, 210, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krucker, S.; Hurford, G.J.; Grimm, O.; Kögl, S.; Gröbelbauer, H.P.; Etesi, L.; Casadei, D.; Csillaghy, A.; Benz, A.O.; Arnold, N.G.; et al. The Spectrometer/Telescope for Imaging X-rays (STIX). Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 642, A15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culhane, J.L.; Harra, L.K.; James, A.M.; Al-Janabi, K.; Bradley, L.J.; Chaudry, R.A.; Rees, K.; Tandy, J.A.; Thomas, P.; Whillock, M.C.R.; et al. The EUV Imaging Spectrometer for Hinode. Sol. Phys. 2007, 243, 19–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPICE Consortium; Anderson, M.; Appourchaux, T.; Auchère, F.; Aznar Cuadrado, R.; Barbay, J.; Baudin, F.; Beardsley, S.; Bocchialini, K.; Borgo, B.; et al. The Solar Orbiter SPICE instrument. An extreme UV imaging spectrometer. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 642, A14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Imada, S.; Kawate, T.; Suematsu, Y.; Hara, H.; Tsuzuki, T.; Katsukawa, Y.; Kubo, M.; Ishikawa, R.; Watanabe, T.; et al. The Solar-C (EUVST) mission: The latest status. In Space Telescopes and Instrumentation 2020: Ultraviolet to Gamma Ray; den Herder, J.W.A., Nikzad, S., Nakazawa, K., Eds.; Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020; Volume 11444, p. 114440N. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pontieu, B.; Martínez-Sykora, J.; Testa, P.; Winebarger, A.R.; Daw, A.; Hansteen, V.; Cheung, M.C.M.; Antolin, P. The Multi-slit Approach to Coronal Spectroscopy with the Multi-slit Solar Explorer (MUSE). Astrophys. J. 2020, 888, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pontieu, B.; Testa, P.; Martínez-Sykora, J.; Antolin, P.; Karampelas, K.; Hansteen, V.; Rempel, M.; Cheung, M.C.M.; Reale, F.; Danilovic, S.; et al. Probing the Physics of the Solar Atmosphere with the Multi-slit Solar Explorer (MUSE). I. Coronal Heating. Astrophys. J. 2022, 926, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, M.C.M.; Martínez-Sykora, J.; Testa, P.; De Pontieu, B.; Chintzoglou, G.; Rempel, M.; Polito, V.; Kerr, G.S.; Reeves, K.K.; Fletcher, L.; et al. Probing the Physics of the Solar Atmosphere with the Multi-slit Solar Explorer (MUSE). II. Flares and Eruptions. Astrophys. J. 2022, 926, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschwanden, M.J.; Kontar, E.P.; Jeffrey, N.L.S. Global Energetics of Solar Flares. VIII. The Low-energy Cutoff. Astrophys. J. 2019, 881, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.F.; Swisdak, M.; Che, H.; Shay, M.A. Electron acceleration from contracting magnetic islands during reconnection. Nature 2006, 443, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, H.; Drake, J.F.; Swisdak, M.; Guo, F.; Dahlin, J.T.; Chen, B.; Fleishman, G.; Glesener, L.; Kontar, E.; Phan, T.; et al. Electron Acceleration during Macroscale Magnetic Reconnection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 135101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.A.; Cargill, P.J.; Emslie, A.G.; Holman, G.D.; Dennis, B.R.; LaRosa, T.N.; Winglee, R.M.; Benka, S.G.; Tsuneta, S. Critical issues for understanding particle acceleration in impulsive solar flares. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 14631–14660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosian, A.R.; Boulesteix, J.; Comte, G.; Kunth, D.; Lecoarer, E. An interferometric study of the blue compact dwarf galaxy IZW 18. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 318, 390–404. [Google Scholar]
- Vlahos, L.; Anastasiadis, A.; Papaioannou, A.; Kouloumvakos, A.; Isliker, H. Sources of solar energetic particles. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 2019, 377, 20180095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahos, L.; Isliker, H. Particle acceleration and heating in a turbulent solar corona. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2019, 61, 014020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiener, J.; Gros, M.; Tatischeff, V.; Weidenspointner, G. Properties of the energetic particle distributions during the October 28, 2003 solar flare from INTEGRAL/SPI observations. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 445, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinenko, Y.E.; Craig, I.J.D. Flare Energy Release by Flux Pile-up Magnetic Reconnection in a Turbulent Current Sheet. Astrophys. J. 2000, 544, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, G.D.; Benka, S.G. A Hybrid Thermal/Nonthermal Model for the Energetic Emissions from Solar Flares. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1992, 400, L79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, W.M.; Tanner, W.G.; McDonald, R.A.; Schaub, G.E.; Stephenson, S.L.; McDonnell, J.A.M.; Maag, C.R. The Status of Measurement Technologies Concerning Micrometer and Submicrometer Space Articulate Matter Capture, Recovery, Velocity, and Trajectory. In Proceedings of the Particle Capture, Recovery and Velocity/Trajectory Measurement Technologies, Houston, TX, USA, 27–28 September 1993; Zolensky, M.E., Ed.; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy, P.P.; Chupp, E.L.; Bertsch, D.L.; Schneid, E.J.; Gottesman, S.R.; Kanbach, G. Gamma-Rays and Neutrons as a Probe of Flare Proton Spectra: The Solar Flare of 11 June 1991. Sol. Phys. 1999, 187, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocharov, L.G.; Lee, J.W.; Zirin, H.; Kovaltsov, G.A.; Usoskin, I.G.; Pyle, K.R.; Shea, M.A.; Smart, D.F. Neutron and electromagnetic emissions during the 1990 May 24 solar flare. Sol. Phys. 1994, 155, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocharov, L.; Debrunner, H.; Kovaltsov, G.; Lockwood, J.; McConnell, M.; Nieminen, P.; Rank, G.; Ryan, J.; Schoenfelder, V. Deduced spectrum of interacting protons accelerated after the impulsive phase of the 15 June 1991 solar flare. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 340, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Vilmer, N.; Krucker, S.; Trottet, G.; Lin, R.P. Hard X-ray and metric/decimetric spatially resolved observations of the 10 April 2002 solar flare. Adv. Space Res. 2003, 32, 2509–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbach, G.; Bertsch, D.L.; Fichtel, C.E.; Hartman, R.C.; Hunter, S.D.; Kniffen, D.A.; Kwok, P.W.; Lin, Y.C.; Mattox, J.R.; Mayer-Hasselwander, H.A. Detection of a long-duration solar gamma-ray flare on June 11, 1991 with EGRET on COMPTON-GRO. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. 1993, 97, 349–353. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, J.M.; Lockwood, J.A.; Debrunner, H. Solar Energetic Particles. Space Sci. Rev. 2000, 93, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allred, J.C.; Hawley, S.L.; Abbett, W.P.; Carlsson, M. Radiative Hydrodynamic Models of the Optical and Ultraviolet Emission from Solar Flares. Astrophys. J. 2005, 630, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allred, J.C.; Kowalski, A.F.; Carlsson, M. A Unified Computational Model for Solar and Stellar Flares. Astrophys. J. 2015, 809, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allred, J.C.; Kerr, G.S.; Gordon Emslie, A. Solar Flare Heating with Turbulent Suppression of Thermal Conduction. Astrophys. J. 2022, 931, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, A.F.; Hawley, S.L.; Carlsson, M.; Allred, J.C.; Uitenbroek, H.; Osten, R.A.; Holman, G. New Insights into White-Light Flare Emission from Radiative-Hydrodynamic Modeling of a Chromospheric Condensation. Sol. Phys. 2015, 290, 3487–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, A.F.; Allred, J.C.; Daw, A.; Cauzzi, G.; Carlsson, M. The Atmospheric Response to High Nonthermal Electron Beam Fluxes in Solar Flares. I. Modeling the Brightest NUV Footpoints in the X1 Solar Flare of 2014 March 29. Astrophys. J. 2017, 836, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio da Costa, F.; Kleint, L.; Petrosian, V.; Liu, W.; Allred, J.C. Data-driven Radiative Hydrodynamic Modeling of the 2014 March 29 X1.0 Solar Flare. Astrophys. J. 2016, 827, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, G.S.; Fletcher, L.; Russell, A.J.B.; Allred, J.C. Simulations of the Mg II k and Ca II 8542 lines from an AlfvÉn Wave-heated Flare Chromosphere. Astrophys. J. 2016, 827, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, G.S.; Carlsson, M.; Allred, J.C.; Young, P.R.; Daw, A.N. SI IV Resonance Line Emission during Solar Flares: Non-LTE, Nonequilibrium, Radiation Transfer Simulations. Astrophys. J. 2019, 871, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, G.S.; Allred, J.C.; Polito, V. Solar Flare Arcade Modeling: Bridging the Gap from 1D to 3D Simulations of Optically Thin Radiation. Astrophys. J. 2020, 900, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.A.; Fletcher, L.; Kerr, G.S.; Labrosse, N.; Kowalski, A.F.; De La Cruz Rodríguez, J. Modeling of the Hydrogen Lyman Lines in Solar Flares. Astrophys. J. 2018, 862, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, V.; Testa, P.; Allred, J.; De Pontieu, B.; Carlsson, M.; Pereira, T.M.D.; Gošić, M.; Reale, F. Investigating the Response of Loop Plasma to Nanoflare Heating Using RADYN Simulations. Astrophys. J. 2018, 856, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, V.; Testa, P.; De Pontieu, B. Can the Superposition of Evaporative Flows Explain Broad Fe XXI Profiles during Solar Flares? Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 879, L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Kowalski, A.F.; Tian, H.; Uitenbroek, H.; Carlsson, M.; Allred, J.C. Modeling Mg II h, k and Triplet Lines at Solar Flare Ribbons. Astrophys. J. 2019, 879, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reep, J.W.; Polito, V.; Warren, H.P.; Crump, N.A. The Duration of Energy Deposition on Unresolved Flaring Loops in the Solar Corona. Astrophys. J. 2018, 856, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reep, J.W.; Russell, A.J.B. Alfvénic Wave Heating of the Upper Chromosphere in Flares. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 818, L20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reep, J.W.; Russell, A.J.B.; Tarr, L.A.; Leake, J.E. A Hydrodynamic Model of Alfvénic Wave Heating in a Coronal Loop and Its Chromospheric Footpoints. Astrophys. J. 2018, 853, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reep, J.W.; Bradshaw, S.J.; Crump, N.A.; Warren, H.P. Efficient Calculation of Non-local Thermodynamic Equilibrium Effects in Multithreaded Hydrodynamic Simulations of Solar Flares. Astrophys. J. 2019, 871, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, M.C.M.; Rempel, M.; Chintzoglou, G.; Chen, F.; Testa, P.; Martínez-Sykora, J.; Sainz Dalda, A.; DeRosa, M.L.; Malanushenko, A.; Hansteen, V.; et al. A comprehensive three-dimensional radiative magnetohydrodynamic simulation of a solar flare. Nat. Astron. 2019, 3, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurford, G.J.; Krucker, S.; Lin, R.P.; Schwartz, R.A.; Share, G.H.; Smith, D.M. Gamma-Ray Imaging of the 2003 October/November Solar Flares. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2006, 644, L93–L96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Zanna, G.; Schmieder, B.; Mason, H.; Berlicki, A.; Bradshaw, S. The Gradual Phase of the X17 Flare on October 28, 2003. Sol. Phys. 2006, 239, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, R.O.; Dennis, B.R. Velocity Characteristics of Evaporated Plasma Using Hinode/EUV Imaging Spectrometer. Astrophys. J. 2009, 699, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, R.O. Spatially Resolved Nonthermal Line Broadening during the Impulsive Phase of a Solar Flare. Astrophys. J. 2011, 740, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontar, E.P.; Perez, J.E.; Harra, L.K.; Kuznetsov, A.A.; Emslie, A.G.; Jeffrey, N.L.S.; Bian, N.H.; Dennis, B.R. Turbulent Kinetic Energy in the Energy Balance of a Solar Flare. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 118, 155101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakariakov, V.M.; Melnikov, V.F. Quasi-Periodic Pulsations in Solar Flares. Space Sci. Rev. 2009, 149, 119–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, J.A.; Nakariakov, V.M.; Dominique, M.; Jelínek, P.; Takasao, S. Modelling Quasi-Periodic Pulsations in Solar and Stellar Flares. Space Sci. Rev. 2018, 214, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimovets, I.V.; McLaughlin, J.A.; Srivastava, A.K.; Kolotkov, D.Y.; Kuznetsov, A.A.; Kupriyanova, E.G.; Cho, I.H.; Inglis, A.R.; Reale, F.; Pascoe, D.J.; et al. Quasi-Periodic Pulsations in Solar and Stellar Flares: A Review of Underpinning Physical Mechanisms and Their Predicted Observational Signatures. Space Sci. Rev. 2021, 217, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakariakov, V.M.; Kolotkov, D.Y.; Kupriyanova, E.G.; Mehta, T.; Pugh, C.E.; Lee, D.H.; Broomhall, A.M. Non-stationary quasi-periodic pulsations in solar and stellar flares. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2019, 61, 014024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, L.A.; Inglis, A.R.; Christe, S.; Dennis, B.; Gallagher, P.T. Statistical Study of GOES X-Ray Quasi-periodic Pulsations in Solar Flares. Astrophys. J. 2020, 895, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emslie, A.G.; Sturrock, P.A. Temperature minimum heating in solar flares by resistive dissipation of Alfvén waves. Sol. Phys. 1982, 80, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, L.; Hudson, H.S. Impulsive Phase Flare Energy Transport by Large-Scale Alfvén Waves and the Electron Acceleration Problem. Astrophys. J. 2008, 675, 1645–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, A.J.B.; Fletcher, L. Propagation of Alfvénic Waves from Corona to Chromosphere and Consequences for Solar Flares. Astrophys. J. 2013, 765, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laming, J.M. The FIP and Inverse-FIP Effects in Solar Flares. Astrophys. J. 2021, 909, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malandraki, O.E.; Crosby, N.B. Solar Energetic Particles and Space Weather: Science and Applications. In Solar Particle Radiation Storms Forecasting and Analysis; Malandraki, O.E., Crosby, N.B., Eds.; Astrophysics and Space Science Library; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 444, pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McComas, D.J.; Christian, E.R.; Cohen, C.M.S.; Cummings, A.C.; Davis, A.J.; Desai, M.I.; Giacalone, J.; Hill, M.E.; Joyce, C.J.; Krimigis, S.M.; et al. Probing the energetic particle environment near the Sun. Nature 2019, 576, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Herrero, R.; Pacheco, D.; Kollhoff, A.; Espinosa Lara, F.; Freiherr von Forstner, J.L.; Dresing, N.; Lario, D.; Balmaceda, L.; Krupar, V.; Malandraki, O.E.; et al. First near-relativistic solar electron events observed by EPD onboard Solar Orbiter. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 656, L3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pick, M.; Vilmer, N. Sixty-five years of solar radioastronomy: Flares, coronal mass ejections and Sun Earth connection. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2008, 16, 1–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, H.A.S.; Ratcliffe, H. A review of solar type III radio bursts. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 14, 773–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, S.; Antiochos, S.K.; DeVore, C.R. Escape of Flare-accelerated Particles in Solar Eruptive Events. Astrophys. J. 2019, 884, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, H.A.S. A review of recent type III imaging spectroscopy. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2020, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, J.L.; Aubier-Giraud, M.; Leblanc, Y.; Boischot, A. Coronal Scattering, Absorption and Refraction of Solar Radiobursts. Astron. Astrophys. 1971, 10, 362. [Google Scholar]
- Kontar, E.P.; Chen, X.; Chrysaphi, N.; Jeffrey, N.L.S.; Emslie, A.G.; Krupar, V.; Maksimovic, M.; Gordovskyy, M.; Browning, P.K. Anisotropic Radio-wave Scattering and the Interpretation of Solar Radio Emission Observations. Astrophys. J. 2019, 884, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Hilaire, P.; Krucker, S.; Christe, S.; Lin, R.P. The X-ray Detectability of Electron Beams Escaping from the Sun. Astrophys. J. 2009, 696, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longcope, D.W.; Guidoni, S.E.; Linton, M.G. Gas-dynamic Shock Heating of Post-flare Loops Due to Retraction Following Localized, Impulsive Reconnection. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2009, 690, L18–L22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, K.K.; McCauley, P.I.; Tian, H. Direct Observations of Magnetic Reconnection Outflow and CME Triggering in a Small Erupting Solar Prominence. Astrophys. J. 2015, 807, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharkova, V.V.; Arzner, K.; Benz, A.O.; Browning, P.; Dauphin, C.; Emslie, A.G.; Fletcher, L.; Kontar, E.P.; Mann, G.; Onofri, M.; et al. Recent Advances in Understanding Particle Acceleration Processes in Solar Flares. Space Sci. Rev. 2011, 159, 357–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.L.; Sterling, A.C.; Hudson, H.S.; Lemen, J.R. Onset of the Magnetic Explosion in Solar Flares and Coronal Mass Ejections. Astrophys. J. 2001, 552, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Forbes, T.G. Effects of reconnection on the coronal mass ejection process. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 2375–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antiochos, S.K.; DeVore, C.R.; Klimchuk, J.A. A Model for Solar Coronal Mass Ejections. Astrophys. J. 1999, 510, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Török, T.; Kliem, B. Confined and Ejective Eruptions of Kink-unstable Flux Ropes. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2005, 630, L97–L100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyper, P.F.; DeVore, C.R.; Antiochos, S.K. A Breakout Model for Solar Coronal Jets with Filaments. Astrophys. J. 2018, 852, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariat, E.; Dalmasse, K.; DeVore, C.R.; Antiochos, S.K.; Karpen, J.T. A model for straight and helical solar jets. II. Parametric study of the plasma beta. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 596, A36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pariat, E.; Dalmasse, K.; DeVore, C.R.; Antiochos, S.K.; Karpen, J.T. Model for straight and helical solar jets. I. Parametric studies of the magnetic field geometry. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 573, A130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyper, P.F.; DeVore, C.R.; Karpen, J.T.; Antiochos, S.K.; Yeates, A.R. A Model for Coronal Hole Bright Points and Jets Due to Moving Magnetic Elements. Astrophys. J. 2018, 864, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, C.E.; De Moortel, I. A contemporary view of coronal heating. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 2012, 370, 3217–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimchuk, J.A. On Solving the Coronal Heating Problem. Sol. Phys. 2006, 234, 41–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimchuk, J.A. Key aspects of coronal heating. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 2015, 373, 20140256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimchuk, J.A.; Luna, M. The Role of Asymmetries in Thermal Nonequilibrium. Astrophys. J. 2019, 884, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viall, N.M.; Borovsky, J.E. Nine Outstanding Questions of Solar Wind Physics. J. Geophys. Res. (Space Phys.) 2020, 125, e26005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannah, I.G.; Hudson, H.S.; Battaglia, M.; Christe, S.; Kašparová, J.; Krucker, S.; Kundu, M.R.; Veronig, A. Microflares and the Statistics of X-ray Flares. Space Sci. Rev. 2011, 159, 263–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, P.; De Pontieu, B.; Allred, J.; Carlsson, M.; Reale, F.; Daw, A.; Hansteen, V.; Martinez-Sykora, J.; Liu, W.; DeLuca, E.E.; et al. Evidence of nonthermal particles in coronal loops heated impulsively by nanoflares. Science 2014, 346, 1255724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudík, J.; Dzifčáková, E.; Meyer-Vernet, N.; Del Zanna, G.; Young, P.R.; Giunta, A.; Sylwester, B.; Sylwester, J.; Oka, M.; Mason, H.E.; et al. Nonequilibrium Processes in the Solar Corona, Transition Region, Flares, and Solar Wind (Invited Review). Sol. Phys. 2017, 292, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, A.O.; Grigis, P.C. Microflares and hot component in solar active regions. Sol. Phys. 2002, 210, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krucker, S.; Christe, S.; Lin, R.P.; Hurford, G.J.; Schwartz, R.A. Hard X-ray Microflares down to 3 keV. Sol. Phys. 2002, 210, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christe, S.; Hannah, I.G.; Krucker, S.; McTiernan, J.; Lin, R.P. RHESSI Microflare Statistics. I. Flare-Finding and Frequency Distributions. Astrophys. J. 2008, 677, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warmuth, A.; Mann, G. Constraints on energy release in solar flares from RHESSI and GOES X-ray observations. II. Energetics and energy partition. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 588, A116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, I.G.; Christe, S.; Krucker, S.; Hurford, G.J.; Hudson, H.S.; Lin, R.P. RHESSI Microflare Statistics. II. X-Ray Imaging, Spectroscopy, and Energy Distributions. Astrophys. J. 2008, 677, 704–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, A.F.; Saqri, J.; Massa, P.; Perracchione, E.; Dickson, E.C.M.; Xiao, H.; Veronig, A.M.; Warmuth, A.; Battaglia, M.; Hurford, G.J.; et al. STIX X-ray microflare observations during the Solar Orbiter commissioning phase. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 656, A4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqri, J.; Veronig, A.M.; Warmuth, A.; Dickson, E.C.M.; Battaglia, A.F.; Podladchikova, T.; Xiao, H.; Battaglia, M.; Hurford, G.J.; Krucker, S. Multi-instrument STIX microflare study. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 659, A52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glesener, L.; Krucker, S.; Duncan, J.; Hannah, I.G.; Grefenstette, B.W.; Chen, B.; Smith, D.M.; White, S.M.; Hudson, H. Accelerated Electrons Observed Down to <7 keV in a NuSTAR Solar Microflare. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 891, L34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, K.; Hannah, I.G.; Grefenstette, B.W.; Glesener, L.; Krucker, S.; Hudson, H.S.; White, S.M.; Smith, D.M.; Duncan, J. NuSTAR observations of a repeatedly microflaring active region. Mon. Not. RAS 2021, 507, 3936–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, J.; Glesener, L.; Grefenstette, B.W.; Vievering, J.; Hannah, I.G.; Smith, D.M.; Krucker, S.; White, S.M.; Hudson, H. NuSTAR Observation of Energy Release in 11 Solar Microflares. Astrophys. J. 2021, 908, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polito, V.; Peterson, M.; Glesener, L.; Testa, P.; Yu, S.; Reeves, K.K.; Sun, X.; Duncan, J. Multi-wavelength observations and modeling of a microflare: Constraining non-thermal particle acceleration. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2023, 10, 1214901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warmuth, A.; Mann, G. Thermal-nonthermal energy partition in solar flares derived from X-ray, EUV, and bolometric observations. Discussion of recent studies. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 644, A172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmelz, J.T.; Kashyap, V.L.; Saar, S.H.; Dennis, B.R.; Grigis, P.C.; Lin, L.; De Luca, E.E.; Holman, G.D.; Golub, L.; Weber, M.A. Some Like It Hot: Coronal Heating Observations from Hinode X-ray Telescope and RHESSI. Astrophys. J. 2009, 704, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosius, J.W.; Daw, A.N.; Rabin, D.M. Pervasive Faint Fe XIX Emission from a Solar Active Region Observed with EUNIS-13: Evidence for Nanoflare Heating. Astrophys. J. 2014, 790, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspi, A.; Woods, T.N.; Warren, H.P. New Observations of the Solar 0.5–5 keV Soft X-Ray Spectrum. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2015, 802, L2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Zanna, G.; Andretta, V.; Cargill, P.J.; Corso, A.J.; Daw, A.N.; Golub, L.; Klimchuk, J.A.; Mason, H.E. High resolution soft X-ray spectroscopy and the quest for the hot (5–10 MK) plasma in solar active regions. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2021, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, S.J.; Klimchuk, J.A. What Dominates the Coronal Emission Spectrum During the Cycle of Impulsive Heating and Cooling? Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2011, 194, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, L.; Hartquist, T.W.; Quillen, A.C. Comments on the Observability of Coronal Variations. Sol. Phys. 1989, 122, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, F.; Orlando, S. Nonequilibrium of Ionization and the Detection of Hot Plasma in Nanoflare-heated Coronal Loops. Astrophys. J. 2008, 684, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lörinčík, J.; Dudík, J.; del Zanna, G.; Dzifčáková, E.; Mason, H.E. Plasma Diagnostics from Active Region and Quiet-Sun Spectra Observed by Hinode/EIS: Quantifying the Departures from a Maxwellian Distribution. Astrophys. J. 2020, 893, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzifčáková, E.; Dudík, J.; Zemanová, A.; Lörinčík, J.; Karlický, M. KAPPA: A Package for the Synthesis of Optically Thin Spectra for the Non-Maxwellian κ-distributions. II. Major Update to Compatibility with CHIANTI Version 10. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2021, 257, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Zanna, G.; Polito, V.; Dudík, J.; Testa, P.; Mason, H.E.; Dzifčáková, E. Diagnostics of Non-Maxwellian Electron Distributions in Solar Active Regions from Fe XII Lines Observed by the Hinode Extreme Ultraviolet Imaging Spectrometer and Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph. Astrophys. J. 2022, 930, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, S.n.; Glesener, L.; Krucker, S.; Christe, S.; Buitrago-Casas, J.C.; Narukage, N.; Vievering, J. Detection of nanoflare-heated plasma in the solar corona by the FOXSI-2 sounding rocket. Nat. Astron. 2017, 1, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.S.; Caspi, A.; Woods, T.N.; Chamberlin, P.C.; Dennis, B.R.; Jones, A.R.; Mason, J.P.; Schwartz, R.A.; Tolbert, A.K. The Instruments and Capabilities of the Miniature X-Ray Solar Spectrometer (MinXSS) CubeSats. Sol. Phys. 2018, 293, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, A.J.; Smith, D.M.; Glesener, L.; Klimchuk, J.A.; Bradshaw, S.J.; Vievering, J.; Hannah, I.G.; Christe, S.; Ishikawa, S.n.; Krucker, S. Hard X-Ray Constraints on Small-scale Coronal Heating Events. Astrophys. J. 2018, 864, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrini, C.H.; Démoulin, P.; Klimchuk, J.A. Magnetic Field and Plasma Scaling Laws: Their Implications for Coronal Heating Models. Astrophys. J. 2000, 530, 999–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranmer, S.R.; Winebarger, A.R. The Properties of the Solar Corona and Its Connection to the Solar Wind. Annu. Rev. Astron Astrophys. 2019, 57, 157–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, D.H.; Warren, H.P.; Landi, E. Measurements of Coronal Magnetic Field Strengths in Solar Active Region Loops. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 915, L24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurford, G.J. X-ray imaging with collimators, masks and grids. Issi Sci. Rep. Ser. 2010, 9, 223–234. [Google Scholar]
- Piana, M.; Emslie, A.; Massone, A.M.; Dennis, B.R. Hard X-ray Imaging of Solar Flares; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Massa, P.; Hurford, G.J.; Volpara, A.; Kuhar, M.; Battaglia, A.F.; Xiao, H.; Casadei, D.; Perracchione, E.; Garbarino, S.; Guastavino, S.; et al. STIX imaging I—Concept. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.02485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christe, S.; Alaoui, M.; Allred, J.; Battaglia, M.; Baumgartner, W.; Buitrago-Casas, J.C.; Chen, B.; Chen, T.; Dennis, B.; Drake, J.; et al. The Focusing Optics X-ray Solar Imager (FOXSI). Bull. Am. Astron. Soc. 2023, 55, 065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krucker, S.; Christe, S.; Glesener, L.; Ishikawa, S.n.; Ramsey, B.; Takahashi, T.; Watanabe, S.; Saito, S.; Gubarev, M.; Kilaru, K.; et al. First Images from the Focusing Optics X-Ray Solar Imager. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2014, 793, L32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christe, S.; Glesener, L.; Buitrago-Casas, C.; Ishikawa, S.N.; Ramsey, B.; Gubarev, M.; Kilaru, K.; Kolodziejczak, J.J.; Watanabe, S.; Takahashi, T.; et al. FOXSI-2: Upgrades of the Focusing Optics X-ray Solar Imager for its Second Flight. J. Astron. Instrum. 2016, 5, 1640005–1640625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glesener, L.; Krucker, S.; Christe, S.; Ishikawa, S.n.; Buitrago-Casas, J.C.; Ramsey, B.; Gubarev, M.; Takahashi, T.; Watanabe, S.; Takeda, S.; et al. The FOXSI solar sounding rocket campaigns. In Space Telescopes and Instrumentation 2016: Ultraviolet to Gamma Ray; den Herder, J.W.A., Takahashi, T., Bautz, M., Eds.; Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9905, p. 99050E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musset, S.; Buitrago-Casas, J.C.; Glesener, L.; Bongiorno, S.; Courtade, S.; Athiray, P.S.; Vievering, J.; Ishikawa, S.n.; Narukage, N.; Furukawa, K.; et al. Ghost-ray reduction and early results from the third FOXSI sounding rocket flight. In UV, X-ray, and Gamma-Ray Space Instrumentation for Astronomy XXI; Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019; Volume 11118, p. 1111812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christe, S.D.; Shih, A.; Rodriguez, M.; Cramer, A.; Gregory, K.; Edgerton, M.; Gaskin, J.; Wilson-Hodge, C.; Apple, J.; Stevenson Chavis, K.; et al. The high energy replicated optics to explore the sun mission: A hard x-ray balloon-borne telescope. In Solar Physics and Space Weather Instrumentation V; Fineschi, S., Fennelly, J., Eds.; Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2013; Volume 8862, p. 886206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christe, S.; Shih, A.Y.; Rodriguez, M.; Cramer, A.; Gregory, K.; Gaskin, J.; Chavis, K.; Smith, L.; HOPE/HEROES Team. The High Energy Replicated Optics to Explore the Sun (HEROES). In Proceedings of the AAS/Solar Physics Division Abstracts #44, July 2013; AAS/Solar Physics Division Meeting. Volume 44, p. 100.76. [Google Scholar]
- Allington-Smith, J. Basic principles of integral field spectroscopy. New Astron. Rev. 2006, 50, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Zanna, G.; Mason, H.E. Solar UV and X-ray spectral diagnostics. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2018, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, E.; Hutton, R.; Brage, T.; Li, W. Hinode/EIS Measurements of Active-region Magnetic Fields. Astrophys. J. 2020, 904, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudík, J.; Del Zanna, G.; Mason, H.E.; Dzifčáková, E. Signatures of the non-Maxwellian κ-distributions in optically thin line spectra. I. Theory and synthetic Fe IX-XIII spectra. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 570, A124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dudík, J.; Mackovjak, Š.; Dzifčáková, E.; Del Zanna, G.; Williams, D.R.; Karlický, M.; Mason, H.E.; Lörinčík, J.; Kotrč, P.; Fárník, F.; et al. Imaging and Spectroscopic Observations of a Transient Coronal Loop: Evidence for the Non-Maxwellian K Distributions. Astrophys. J. 2015, 807, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S.A.; Reid, H.A.S.; Baker, D.; Bloomfield, D.S.; Browning, P.K.; Calcines, A.; Del Zanna, G.; Erdelyi, R.; Fletcher, L.; Hannah, I.G.; et al. The high-energy Sun—probing the origins of particle acceleration on our nearest star. Exp. Astron. 2022, 54, 335–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
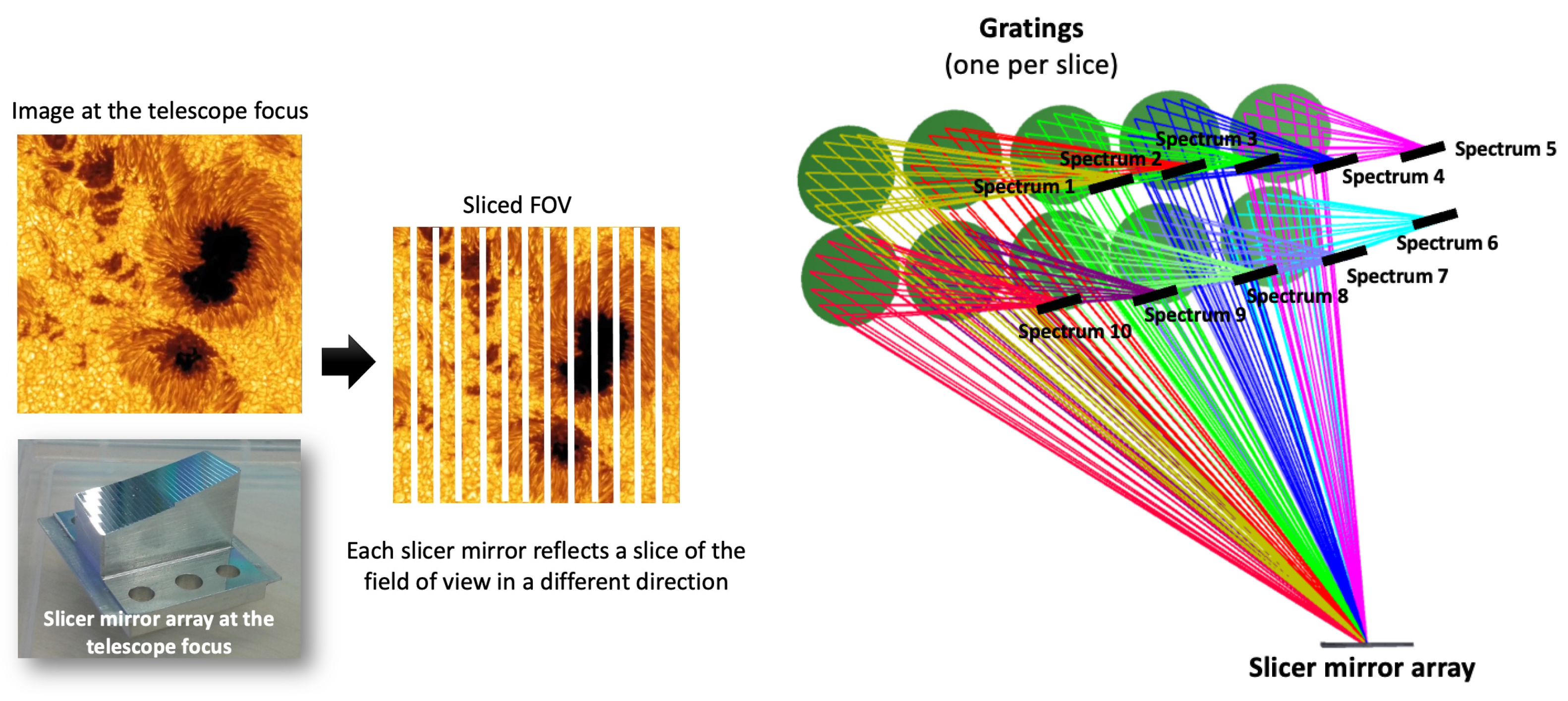
| LISSAN Parameter | Expected Performance |
|---|---|
| Energy Range—Low | 40 keV |
| Energy Range—High | 100 MeV |
| Imaging Effective Area (2.2 MeV) | 100 cm2 |
| Spectro Effective Area (2.2 MeV) | 440 cm2 |
| Sensitivity (2.2 MeV) | 50 photons/cm2 |
| Sensitivity (6.1 MeV) | 5 photons/cm2 |
| Imaging Time Resolution | 1 s |
| Angular Resolution | 8 |
| Field of View | 12.8 diameter |
| Energy Resolution (6.1 MeV) | 1.5% dE/E |
| Largest Observable Flare | >X5 |
| FOXSI Parameter | Expected Performance |
|---|---|
| Energy Range—Low | 3 keV |
| Energy Range—High | 55 keV |
| Imaging Dynamic Range 1 | 20:1 beyond 20 separation |
| Imaging Dynamic Range 2 | 1000:1 beyond 45 separation |
| Effective Area (at 20 keV) | 40 cm2 |
| Sensitivity | 0.2 photons/cm2 |
| Imaging Time Resolution | 0.1 s |
| Angular Resolution | 6.3 FWHM |
| Field of View | 9.8 × 9.8 |
| Energy Resolution | 0.8 keV FWHM |
| Largest Observable Flare | >X10 |
| FOXSI-STC Parameter | Expected Performance |
|---|---|
| Energy Range—Low | 0.8 keV |
| Energy Range—High | 15 keV |
| Effective Area | 0.01 cm2 |
| Energy Resolution | 0.2 keV FWHM below 1.5 keV |
| Field of View | 9.8 × 9.8 |
| Time Resolution | 0.5 s |
| Largest Observable Flare | >X10 |
| SISA Parameter | Expected Performance |
|---|---|
| Spectral Window 1 | 178–184 Å |
| Spectral Window 2 | 221–264 Å |
| Spectral Resolution | 0.05 Å FWHM |
| Spectral Resolving Power (R) | 3560–5160 |
| Field of View | 100 × 250 |
| Spatial Resolution | 1 in 2 pixels |
| Temporal Resolution (high signal) | 1 s |
| Temporal Resolution (low signal) | 10 s |
| Resource | LISSAN | FOXSI | SISA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass | 370 kg | 120 kg | 78 kg |
| Volume | 1.96 m3 | (105 cm)3 (stowed) | 0.5 m3 |
| Power | 125 W (peak) | 170 W (average) | 130 W (average) |
| Data Rate | 25 Mbits/s (peak) | 1 Mbits/s (peak) | 50 Mbits/s (average) |
| Operating Temp. | 0 °C (FEE) | −20–0 °C (FPA) | <−40 °C (FPA) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reid, H.A.S.; Musset, S.; Ryan, D.F.; Andretta, V.; Auchère, F.; Baker, D.; Benvenuto, F.; Browning, P.; Buchlin, É.; Calcines Rosario, A.; et al. The Solar Particle Acceleration Radiation and Kinetics (SPARK) Mission Concept. Aerospace 2023, 10, 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10121034
Reid HAS, Musset S, Ryan DF, Andretta V, Auchère F, Baker D, Benvenuto F, Browning P, Buchlin É, Calcines Rosario A, et al. The Solar Particle Acceleration Radiation and Kinetics (SPARK) Mission Concept. Aerospace. 2023; 10(12):1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10121034
Chicago/Turabian StyleReid, Hamish A. S., Sophie Musset, Daniel F. Ryan, Vincenzo Andretta, Frédéric Auchère, Deborah Baker, Federico Benvenuto, Philippa Browning, Éric Buchlin, Ariadna Calcines Rosario, and et al. 2023. "The Solar Particle Acceleration Radiation and Kinetics (SPARK) Mission Concept" Aerospace 10, no. 12: 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10121034
APA StyleReid, H. A. S., Musset, S., Ryan, D. F., Andretta, V., Auchère, F., Baker, D., Benvenuto, F., Browning, P., Buchlin, É., Calcines Rosario, A., Christe, S. D., Corso, A. J., Dahlin, J., Dalla, S., Del Zanna, G., Denker, C., Dudík, J., Erdélyi, R., Ermolli, I., ... Warmuth, A. (2023). The Solar Particle Acceleration Radiation and Kinetics (SPARK) Mission Concept. Aerospace, 10(12), 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10121034











