The Effect of Statistical Downscaling on the Weighting of Multi-Model Ensembles of Precipitation
Abstract
1. Introduction
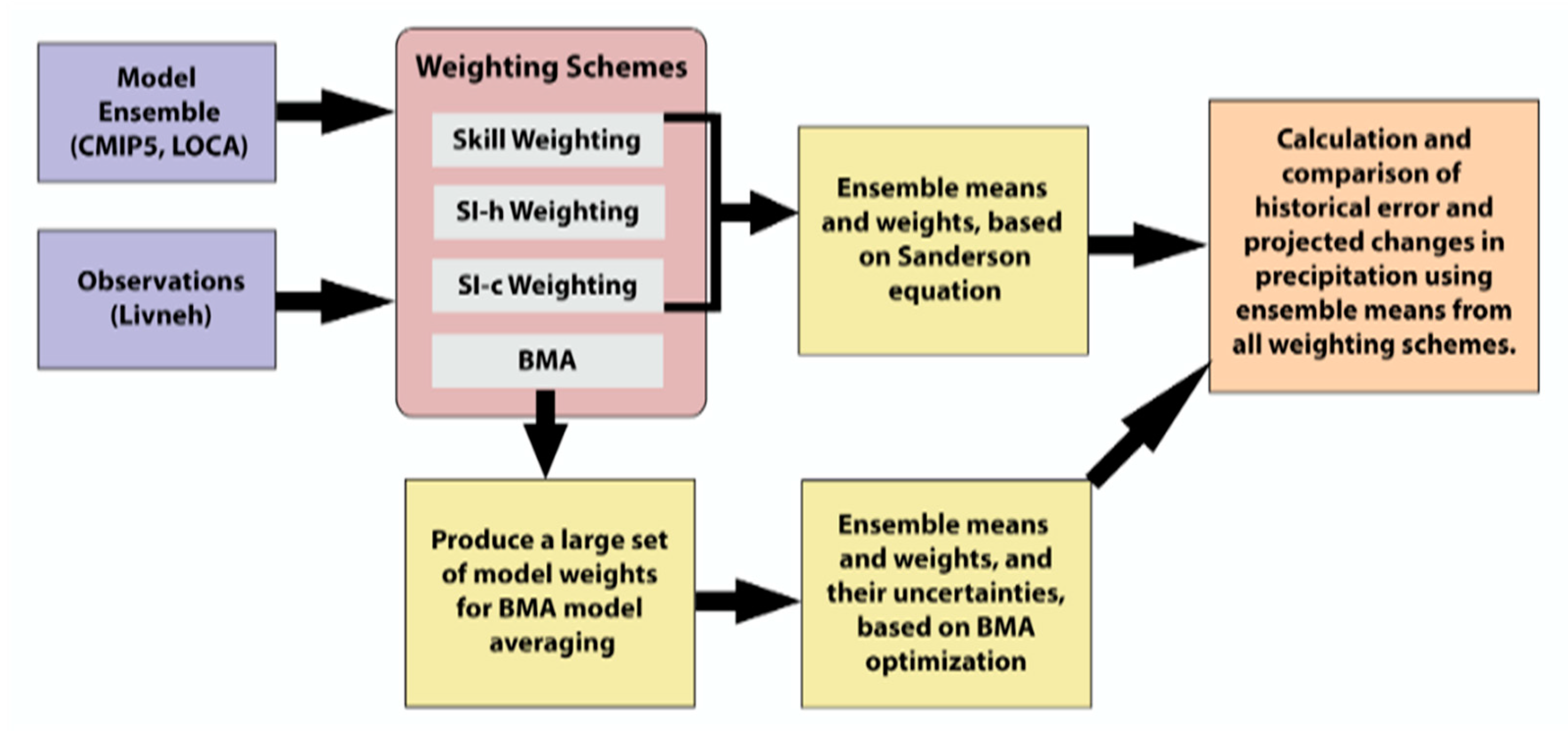
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Domain and Variables
2.2. Climate Projection Datasets
2.3. Observation Dataset
2.4. Weighting Schemes
2.4.1. Historical Skill Weighting
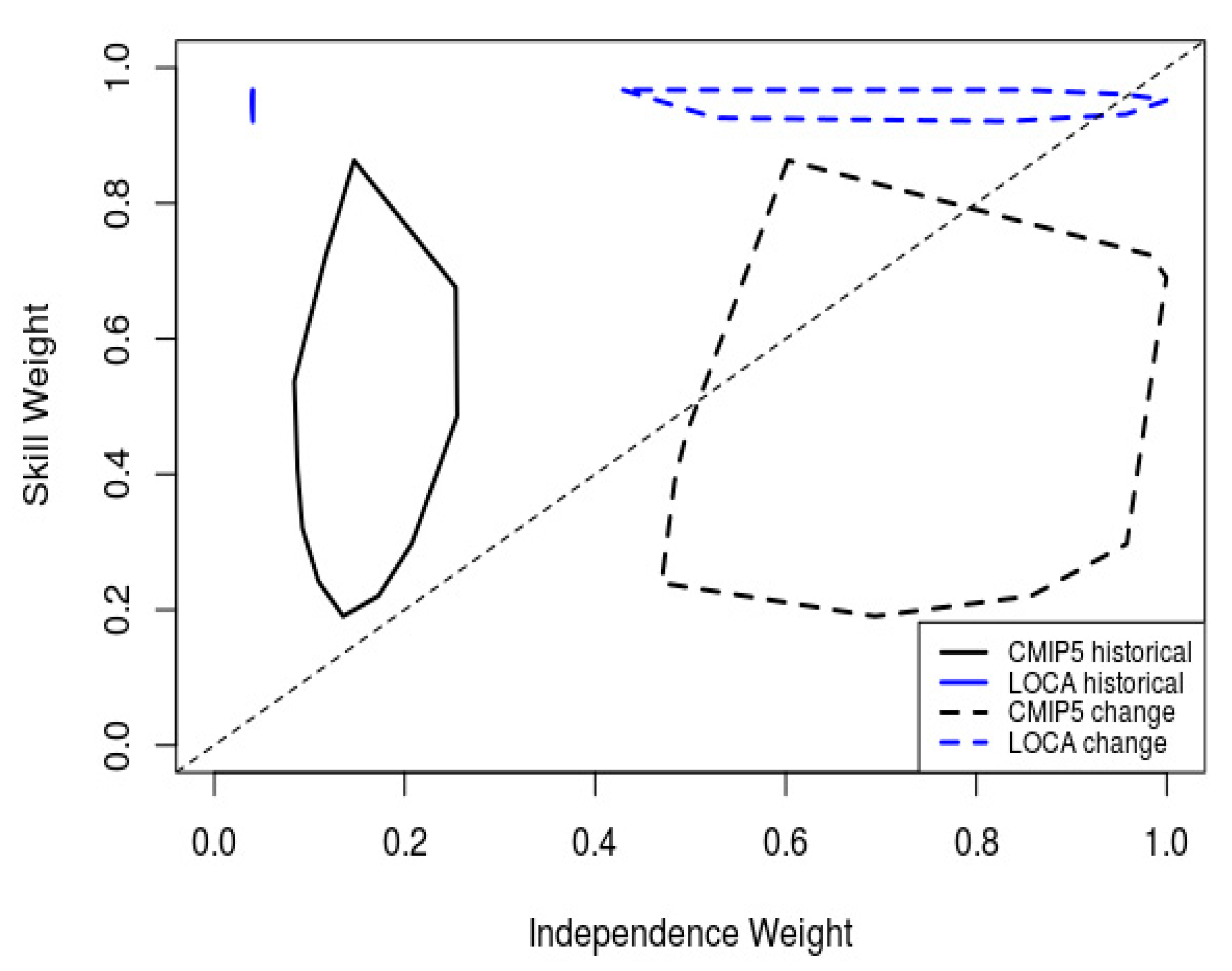
2.4.2. Historical Skill and Historical Independence Weighting (SI-h)
2.4.3. Historical Skill and Future Independence Weighting (SI-c)
2.4.4. Bayesian Model Averaging
2.4.5. Differences between SI-h and BMA
3. Results and Discussion
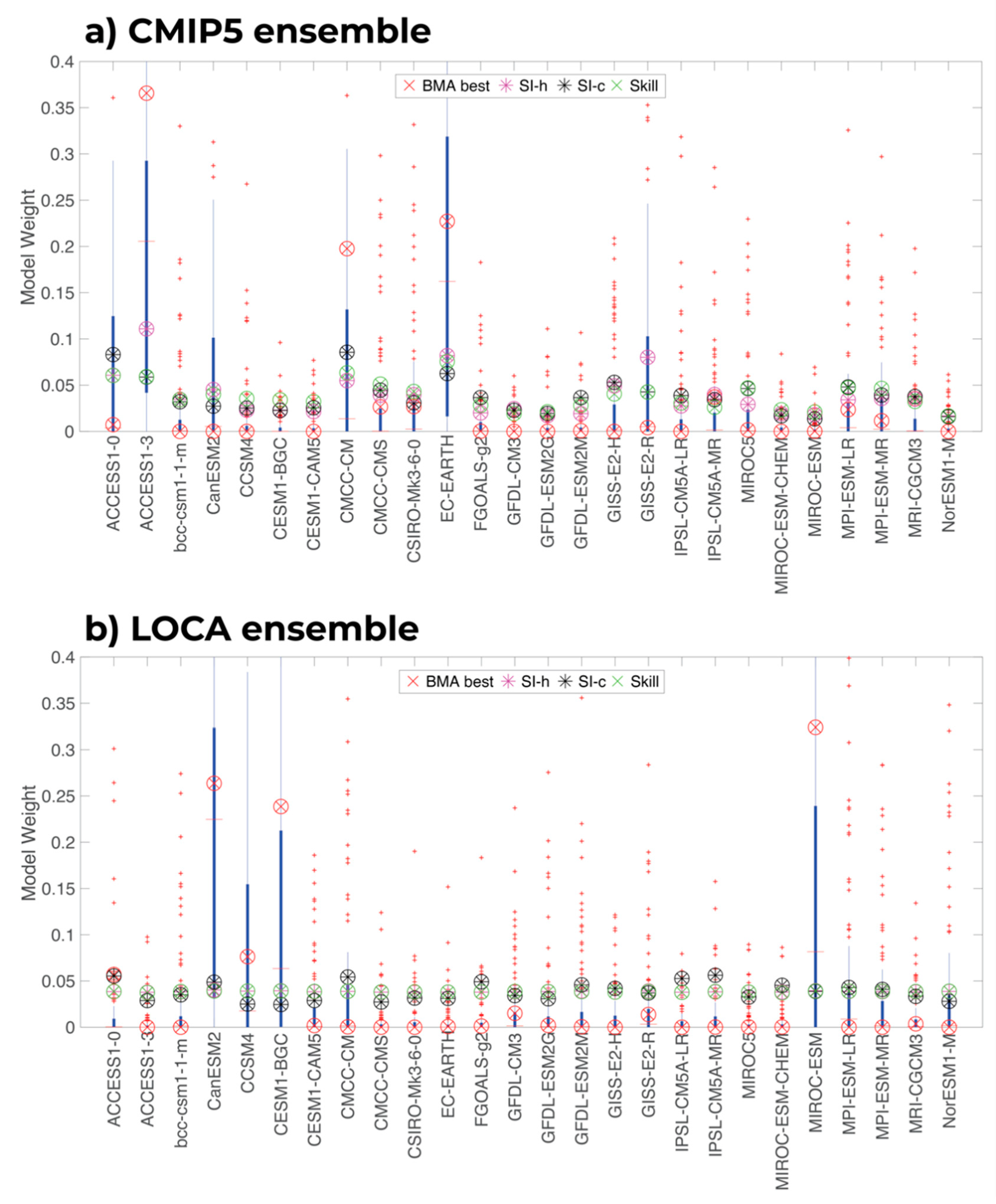
3.1. Ensemble Weights
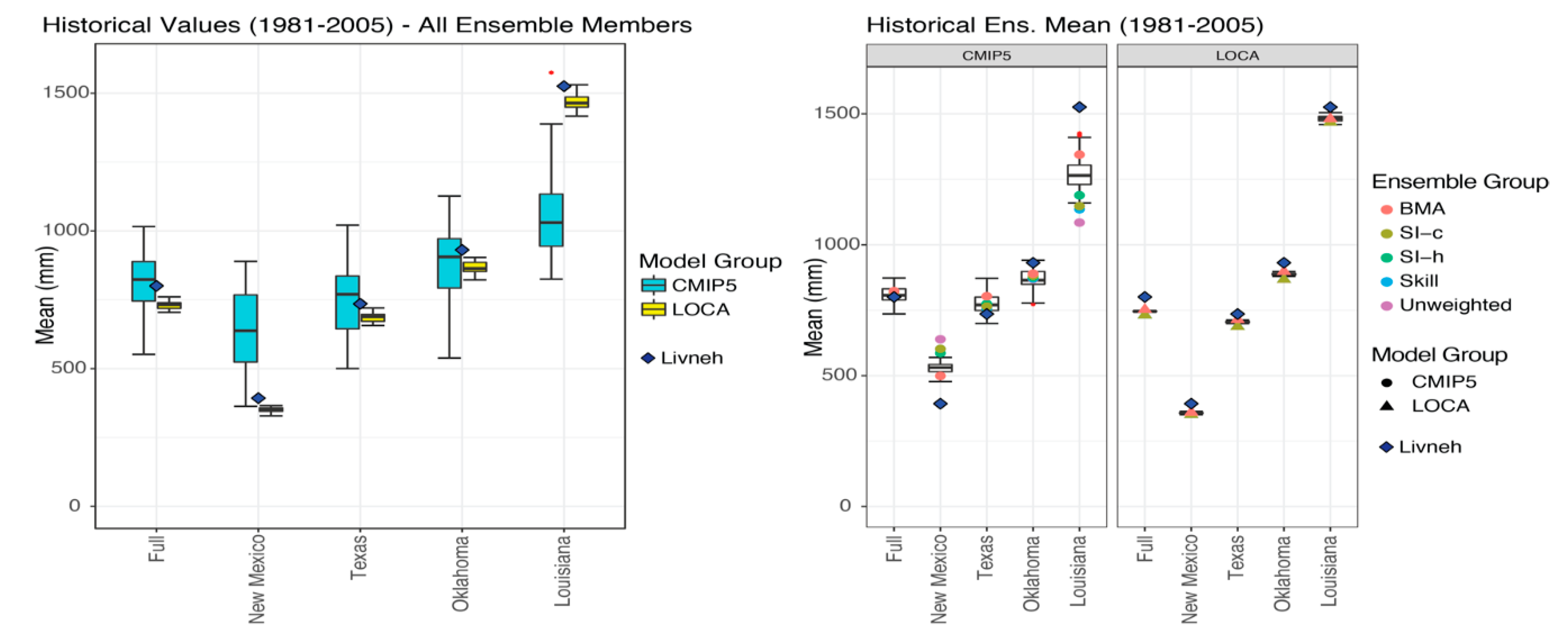
3.2. Historical Biases and RMSE
3.3. Projected Changes
3.4. Implications of Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weart, S. The development of general circulation models of climate. Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. Part B Stud. Hist. Philos. Mod. Phys. 2010, 41, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.; Stern, N. Uncertainty in science and its role in climate policy. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2011, 369, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummukainen, M. State-of-the-art with regional climate models. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2010, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummukainen, M. Added value in regional climate models. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H.; DeTroch, R.; Giot, O.; Hamdi, R.; Termonia, P.; Saeed, S.; Brisson, E.; Van Lipzig, N.; Williams, P. Local impact analysis of climate change on precipitation extremes: Are high-resolution climate models needed for realistic simulations? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 3843–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergel, D.R.; Nijssen, B.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Stumbaugh, M.R. Effect of climate change on snowpack and fire potential in the western USA. Clim. Chang. 2017, 141, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allstadt, A.J.; Vavrus, S.J.; Heglund, P.J.; Pidgeon, A.M.; Thogmartin, W.E.; Radeloff, V.C. Spring plant phenology and false springs in the conterminous US during the 21st century. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 104008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, B.; Hyndman, D.W.; Kendall, A.D.; Grace, P.R.; Roberston, G.P. Can impacts of climate change agricultural adaptation strategies be accurately quantified if crop models are annually re-initialized? PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatichi, S.; Ivanov, V.Y.; Caporali, E. Simulation of future climate scenarios with a weather generator. Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 448–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Babovic, V. Multi-site multivariate downscaling of global climate model outputs: An integrated framework combining quantile mapping, stochastic weather generator and Empirical Copula approaches. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 5775–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGCRP. Climate Science Special Report: Fourth National Climate Assessment Volume I; U.S. Global Change Research Program: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; 470p. [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Bony, S.; Meehl, G.A.; Senior, C.A.; Stevens, B.; Souffer, R.J.; Taylor, K.E. Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1937–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Goodman, A.; McGibbney, L.; Waliser, D.E.; Kim, J.; Loikith, P.C.; Gibson, P.B.; Massoud, E.C. Regional Climate Model Evaluation System powered by Apache Open Climate Workbench v1.3.0: An enabling tool for facilitating regional climate studies. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, P.B.; Waliser, D.E.; Lee, H.; Tian, B.; Massoud, E. Climate model evaluation in the presence of observational uncertainty: Precipitation indices over the contiguous United States. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 20, 1339–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoud, E.C.; Espinoza, V.; Guan, B.; Waliser, D.E. Global Climate Model Ensemble Approaches for Future Projections of Atmospheric Rivers. Earth’s Future 2019, 7, 1136–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoud, E.C.; Lee, H.; Gibson, P.B.; Loikith, P.; Waliser, D.E. Bayesian Model Averaging of Climate Model Projections Constrained by Precipitation Observations over the Contiguous United States. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 2401–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parding, K.M.; Dobler, A.; McSweeney, C.; Landgren, O.A.; Benestad, R.; Erlandsen, H.B.; Mezghani, A.; Gregow, H.; Raty, O.; Viktor, E. GCMeval—An interactive tool for evaluation and selection of climate model ensembles. Clim. Serv. 2020, 18, 100167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaconescu, E.; Gachon, P.; Laprise, R.; Scinocca, J. Evaluation of Precipitation Indices over North America from Various Configurations of Regional Climate Models. Atmosphere-Ocean 2016, 54, 418–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, B.M.; Knutti, R.; Caldwell, P. Addressing interdependency in a multimodel ensemble by interpolation of model properties. J. Clim. 2015, 13, 5150–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, B.M.; Wehner, M.; Knutti, R. Skill and independence weighting for multi-model assessments. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 2379–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutti, R. The end of model democracy? Clim. Chang. 2010, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutti, R.; Sedlacek, J.; Sanderson, B.M.; Lorenz, R.; Fischer, E.M.; Eyring, V. A climate model weighting scheme accounting for performance and independence. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.; Herger, N.; Sedlacek, J.; Eyring, V.; Fischer, E.M.; Knutti, R. Prospects and Caveats of Weighting Climate Models for Summer Maximum Temperature Projections Over North America. J. Geophys. Res. Lett. Atmos. 2018, 123, 4509–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Lee, Y.; Park, J. A weighting scheme in a multi-model ensemble for bias-corrected climate simulation. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, B.M.; Wehner, M.F. Model Weighting Strategy. In Climate Science Special Report: Fourth National Climate Assessment Volume I; Wuebbles, D.J., Fahey, D.W., Hibbard, K.A., Dokken, D.J., Stewart, B.C., Maycock, T.K., Eds.; U.S. Global Change Research Program: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; pp. 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutti, R.; Masson, D.; Gettelman, A. Climate model genealogy: Generation CMIP5 and how we got there. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnke, R.; Vavrus, S.; Allstadt, A.; Thogmartin, W.; Radelhoff, V.C. Evaluation of downscaled gridded climate data for the conterminous United States. Ecol. Appl. 2016, 26, 1338–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootten, A.M.; Dixon, K.W.; Adams-Smith, D.J.; McPherson, R.A. Statistically downscaled precipitation sensitivity to gridded observation data and downscaling technique. Int. J. Climatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Cox, P.M.; Flato, G.M.; Glecker, P.J.; Abramowitz, G.; Caldwell, P.; Collins, W.D. Taking climate model evaluation to the next level. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotamarthi, R.; Mearns, L.; Hayhoe, K.; Castro, C.L.; Wuebbles, D. Use of Climate Model Information for Decision-Making and Impacts Research: State of Our Understanding; Department of Defense, Strategic Environemental Research and Development Program: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; 55p.
- Dilling, L.; Berrgren, J. What do stakeholders need to manage for climate change and variability? A document-based analysis from three mountain states in the Western USA. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2014, 15, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeting, J.A.; Madigan, D.; Raftery, A.E.; Volinsky, C.T. Bayesian model averaging: A tutorial. Stat. Sci. 1999, 14, 382–401. [Google Scholar]
- Cesana, G.; Suselj, K.; Brient, F. On the Dependence of Cloud Feedback on Physical Parameterizations in WRF Aquaplanet Simulations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 10762–10771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiador, F.J.; Roca, R.; Genio, A.D.; Dewitte, B.; Petersen, W.; Zhang, F. Is Precipitation a good metric for model performance? Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paschalis, A.; Molnar, P.; Fatichi, S.; Burlando, P. A stochastic model for high-resolution space-time precipitation simulation. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 8400–8417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Meshgi, A.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Tay, S.H.X.; Pijcke, G.; Manocha, N.; Ong, M.; Nguyen, M.T.; Babovic, V. Three resampling approaches based on method of fragments for daily-to-subdaily precipitation disaggregation. Int. J. Clim. 2018, 38, e1119–e1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livneh, B.; Rosenberg, E.A.; Lin, C.; Nijissen, B.; Mishra, V.; Andreadis, K.M.; Maurer, E.P.; Lettenmaier, D.P. A long-term hydrologically based dataset of land surface fluxes and states for the conterminous United States: Updates and extensions. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 9384–9392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amante, C.; Eakins, B.W. ETOPO1 1 Arc-Minute Global Relief Model: Procedures, Data Sources and Analysis; NOAA Technical Memorandum NESDIS NGDC-24; National Geophysical Data Center, NOAA: Boulder, CO, USA, 2009.
- GRDC. Major River Basins of the World/Global Runoff Data Centre, GRDC, 2nd ed.; Federal Institute of Hydrology (BfG): Koblenz, Germany, 2020.
- Taylor, A.; Gregory, J.M.; Webb, M.J.; Taylor, K.E. Forcing, feedbacks and climate sensitivity in CMIP5 couple atmosphere-ocean climate models. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, D.W.; Cayan, D.R.; Thrasher, B.L. Statistical downscaling using Localized Constructed Analogs (LOCA). J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 2558–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vuuren, D.P.; Edmonds, J.; Kainuma, M.; Riahi, K.; Thomson, A.; Hibbard, K.; Hurtt, G.C.; Kram, T.; Krey, V.; Lamarque, J.-F.; et al. The representative concentration pathways: An overview. Clim. Chang. 2011, 5, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, K.; Grubler, A.; Nakicenovic, N. Scenarios of long-term socio-economic and environmental development under climate stabilization. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2007, 74, 887–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, V.; Waliser, D.E.; Guan, B.; Lavers, D.A.; Ralph, F.M. Global Analysis of Climate Change Projection Effects on Atmospheric Rivers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 4299–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavers, D.A.; Ralph, F.M.; Waliser, D.; Gershunov, A.; Dettinger, M.D. Climate change intensification of horizontal water vapor transport in CMIP5. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 5617–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.R.; Williams, C.N.; Young, P.J.; Wendland, W.M. A model to estimate the time of observation bias associated with monthly mean maximum, minimum, and mean temperatures for the United States. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1986, 25, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatzoglou, J. Development of gridded surface meteorological data for ecological applications and modeling. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoof, J.T. Statistical downscaling in climatology. Geogr. Compass 2013, 7, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raftery, A.E.; Gneiting, T.; Balabdaoui, F.; Polakowski, M. Using Bayesian model averaging to calibrate forecast ensembles. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 1155–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gneiting, T.; Raftery, A.E. Weather forecasting with ensemble methods. Science 2005, 310, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Q.; Newsha, K.A.; Gao, X.; Sorooshian, S. Multi-model ensemble hydrologic prediction using Bayesian model averaging. Adv. Water Resour. 2007, 30, 1371–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrugt, J.A.; Robinson, B.A. Treatment of uncertainty using ensemble methods: Comparison of sequential data assimilation and Bayesian model averaging. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrugt, J.A.; Cajo, T.F.; Clark, M.P.; Hyman, J.M.; Robinson, B.A. Treatment of input uncertainty in hydrologic modeling: Doing hydrology backward with Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.H.; Shanley, K.T. Bayesian model averaging’s problematic treatment of extreme weather and a paradigm shift that fixes it. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 4641–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, R.; Fan, Y.; Evans, J.P. A simple method for Bayesian model averaging of regional climate model projections: Application to southeast Australian temperatures. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 7661–7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, R.; An, S.; Fan, Y.; Evans, J.P. Accounting for skill in trend, variability, and autocorrelation facilitates better multi-model projections: Application to the AMOC and temperature time series. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Olson, R.; Evans, J.P. A Bayesian posterior predictive frameworks for weighting ensemble regional climate models. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 2321–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrugt, J.A.; Massoud, E.C. Uncertainty quantification of complex system models: Bayesian analysis. In Handbook of Hydrometeorological Ensemble Forecasting; Duan, Q., Pappenberger, F., Thielen, J., Wood, A., Cloke, H.L., Schaake, J.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gelman, A.; Rubin, D.B. Inference from iterative simulation using multiple sequences. Stat. Sci. 1992, 7, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, L.; Zou, X.; Song, X. Comparison of Three Statistical Downscaling Methods and Ensemble Downscaling Method Based on Bayesian Model Averaging in Upper Hanjiang River Basin, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempreviva, A.M.; Schiano, M.E.; Pensieri, S.; Semedo, A.; Tomé, R.; Bozzano, R.; Borghini, M.; Grasso, F.; Soerensen, L.L.; Teixeira, J.; et al. Observed development of the vertical structure of the marine boundary layer during the LASIE experiment in the Ligurian Sea. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 28, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

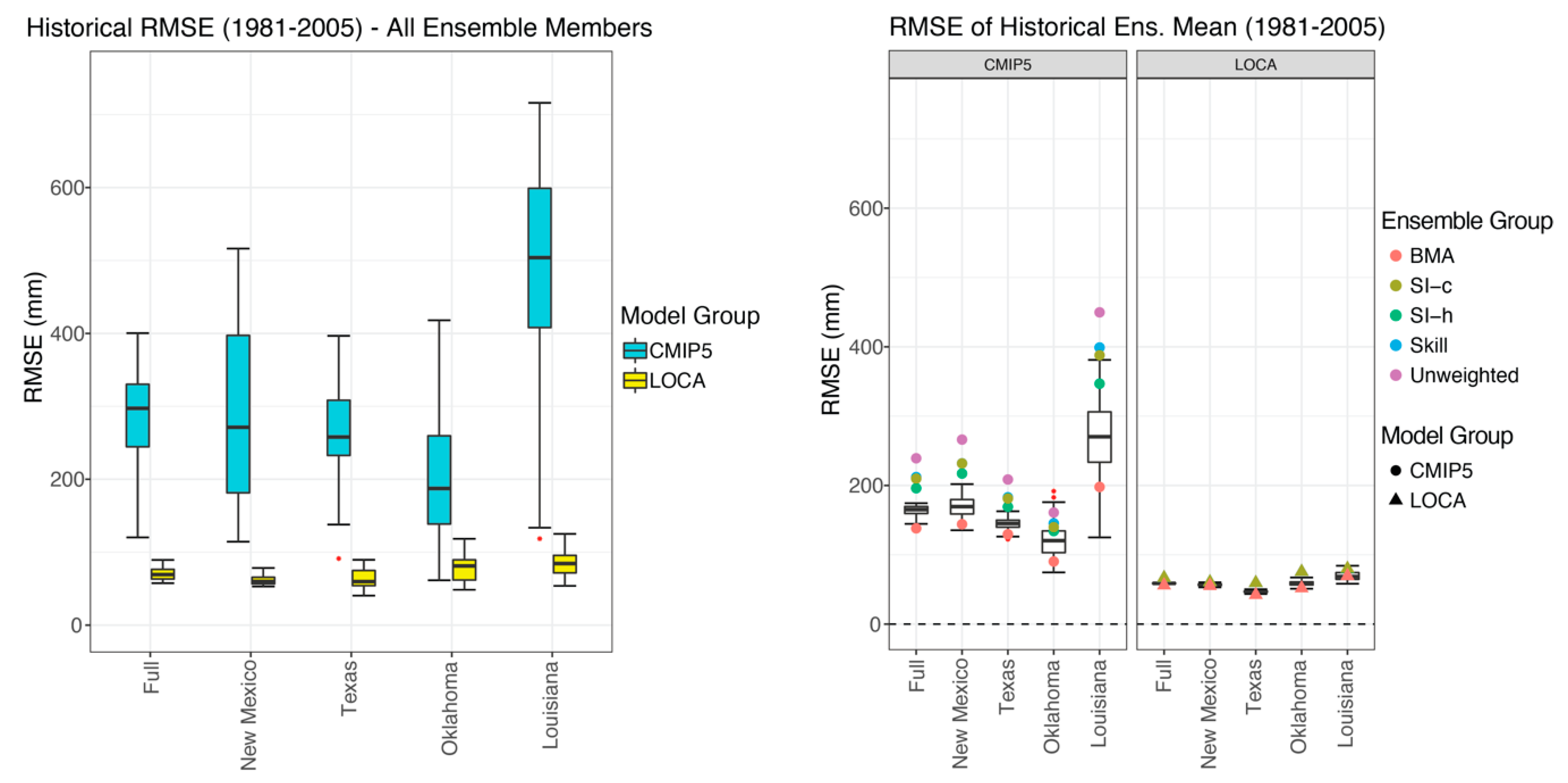
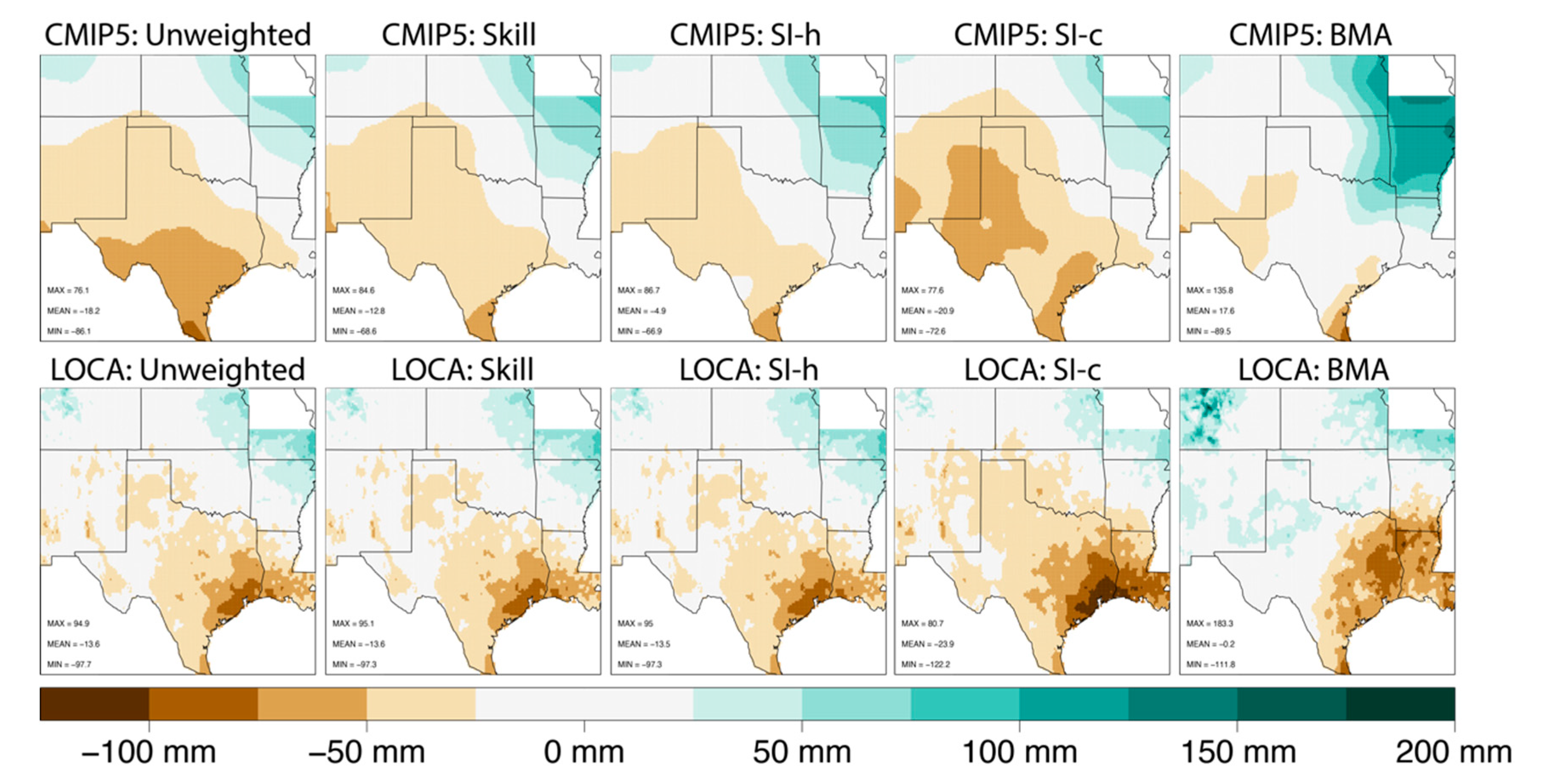
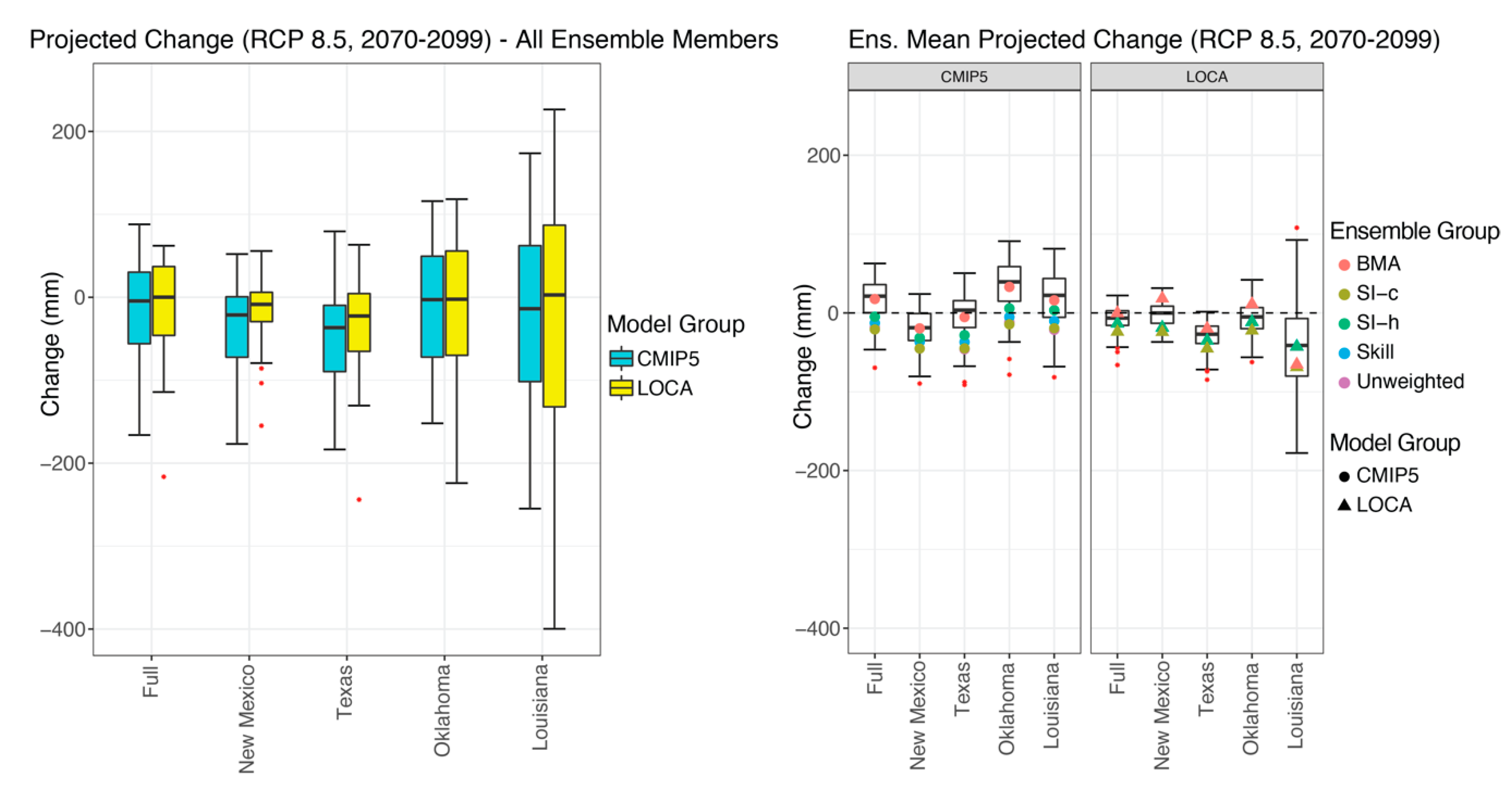
| Group—Weighting | Full | New Mexico | Texas | Oklahoma | Louisiana |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMIP5—Unweighted | 119.96 | 149.24 | 133.61 | 140.29 | 216.42 |
| CMIP5—Skill | 111.37 | 139.51 | 124.86 | 127.60 | 226.01 |
| CMIP5—SI-h | 122.63 | 139.91 | 138.72 | 137.11 | 255.65 |
| CMIP5—SI-c | 112.91 | 134.55 | 125.47 | 132.19 | 225.47 |
| CMIP5—BMA | 30.62 | 20.96 | 38.51 | 38.38 | 62.52 |
| LOCA—Unweighted | 13.96 | 9.60 | 18.19 | 22.39 | 29.18 |
| LOCA—Skill | 13.94 | 9.59 | 18.16 | 22.36 | 29.15 |
| LOCA—SI-h | 14.00 | 9.62 | 18.23 | 22.42 | 29.28 |
| LOCA—SI-c | 14.14 | 9.99 | 18.36 | 21.90 | 29.74 |
| LOCA—BMA | 1.85 | 2.42 | 3.14 | 3.92 | 11.07 |
| Group—Weighting | Full | New Mexico | Texas | Oklahoma | Louisiana |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMIP5—Unweighted | 62.82 | 60.59 | 69.28 | 77.19 | 116.53 |
| CMIP5—Skill | 64.19 | 59.03 | 73.16 | 81.50 | 111.35 |
| CMIP5—SI-h | 68.19 | 63.40 | 76.26 | 83.84 | 116.78 |
| CMIP5—SI-c | 67.40 | 61.51 | 77.11 | 84.36 | 118.63 |
| CMIP5—BMA | 26.62 | 24.68 | 28.62 | 34.51 | 36.73 |
| LOCA—Unweighted | 65.06 | 46.59 | 69.85 | 82.75 | 178.51 |
| LOCA—Skill | 64.99 | 46.57 | 69.79 | 82.61 | 178.31 |
| LOCA—SI-h | 64.88 | 46.60 | 69.69 | 82.53 | 178.26 |
| LOCA—SI-c | 70.87 | 52.31 | 75.72 | 87.78 | 188.64 |
| LOCA—BMA | 16.32 | 14.87 | 19.05 | 21.55 | 59.39 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wootten, A.M.; Massoud, E.C.; Sengupta, A.; Waliser, D.E.; Lee, H. The Effect of Statistical Downscaling on the Weighting of Multi-Model Ensembles of Precipitation. Climate 2020, 8, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8120138
Wootten AM, Massoud EC, Sengupta A, Waliser DE, Lee H. The Effect of Statistical Downscaling on the Weighting of Multi-Model Ensembles of Precipitation. Climate. 2020; 8(12):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8120138
Chicago/Turabian StyleWootten, Adrienne M., Elias C. Massoud, Agniv Sengupta, Duane E. Waliser, and Huikyo Lee. 2020. "The Effect of Statistical Downscaling on the Weighting of Multi-Model Ensembles of Precipitation" Climate 8, no. 12: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8120138
APA StyleWootten, A. M., Massoud, E. C., Sengupta, A., Waliser, D. E., & Lee, H. (2020). The Effect of Statistical Downscaling on the Weighting of Multi-Model Ensembles of Precipitation. Climate, 8(12), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8120138








