Abstract
The recent droughts in the American Southwest have led to increasing risks of wildfires, which pose multiple threats to the regional and national economy and security. Wildfires cause serious air quality issues during dry seasons and can increase the number of mud and landslides in any subsequent rainy seasons. However, while wildfires are often correlated with warm and dry climates, this relationship is not linear, implying that there may be other factors influencing these fires. The objective of this study was to detect and classify any nonlinear patterns in weather data by applying Topological Data Analysis (TDA) to various weather variables, such as temperature, relative humidity, and precipitation, and the five most and least intense summer fire seasons as determined by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) active fire products. In addition to TDA, persistence diagrams and frequency plots were also used to compare fire seasons and regions in the American Southwest. Active fire seasons were more likely to have a significant correlation between the weather variables and wildfires, the Fire Weather Index (FWI) alone was not an accurate predictor for wildfires in California and Nevada, and fire weather is highly dependent upon the region and season.
1. Introduction
For the last several years, wildfires have raged across the western USA and posed severe threats to society. The National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI) track weather and climate disasters in the USA, which can often total billions of dollars in damage [1]. Western USA wildfires have made the NCEI’s severity list for the past five years. Besides causing damage to homes, forests, and people, these wildfires can loosen soil, release carbon stored underground [2], and cause landslides during subsequent rainy seasons [3]. The wildfires in California were particularly disastrous in 2018 with over 8.7 million acres burned and with total costs reaching $24 billion—a USA record [4]. The recent increase in the severity of wildfires is influenced by the warm and dry weather in the area [5,6].
Previous studies have shown that wildfires occur more frequently and become more severe in hot and dry weather [7]. Thus, heat and drought indices have served as a proxy for predicting the intensity and frequency of wildfires [8,9,10]. However, accurately predicting wildfires is still difficult. For instance, one clear limitation of predictive models is the primary means of ignition; humans are responsible for 84% of the wildfires in the United States, and models have not been as successful in predicting them [11]. On the other hand, the initial spread and intensification of fires after ignition are closely tied to surrounding weather conditions, especially heat and drought, and to land conditions such as biomass load and moisture. In order to account for this, several different fire weather indices have been developed. Since this study is on a temporal and spatial scale, however, the biomass load and moisture were not taken into account.
In this study, we use Topological Data Analysis (TDA) to analyze why certain years are more prone to wildfires than others by examining the relations between wildfires and various weather and climate variables during summer fire seasons in Southwestern USA. The rest of the paper is as follows: descriptions of the data and the methods are in Section 2, Section 3 provides the main results of the topological features of weather variables and associated relationships with wildfires, and the conclusions are in Section 4.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
The California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection (CalFire) provides a continuous record of the number of acres burned by California wildfires since the 1930s. The report contains monthly breakdowns of the wildfires that CalFire responded to, including the annual total number of fires and the burned area. While the report includes wildfires responded to by other agencies in its annual total, these were not included in this study for consistency. We used the monthly burned area data for the period between 1997 and 2016 in order to identify strong and weak fire seasons (months of June, July, and August), which are called active and inactive summers, respectively. CalFire data were only used to identify active and inactive fire seasons. For the rest of our analysis, we used the fire detection data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) to analyze daily fire activities.
MODIS is an instrument on the Terra and Aqua satellites that provides the active fire product and instantaneous fire radiative power (FRP) measurements at 1-km resolution [12,13,14]. The active fire product of a region equals the number of square kilometers of land that is burning at the time that the satellite is recording the area. FRP measures the amount of radiated heat released by fires. FRP data are available from the Terra and Aqua satellites starting from February 24, 2000 and July 4, 2002, respectively, but for regularity this study used data from between 2003 and 2016. Although the MODIS land product site provides the active fire data, the files only covered one small swath of land each in hierarchical data format (HDF). For convenience, we used the tabulated data from NASA’s Fire Energetics and Emissions Research project (https://feer.gsfc.nasa.gov), which combines all of the swath files into one csv; this allowed us to use only two files a day instead of over 300.
NASA’s Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications, version 2 (MERRA-2), provided the weather variables studied in the Southwestern USA. Giovanni (https://giovanni.gsfc.nasa.gov/giovanni/), a web interface to MERRA-2, provided data for the spatially averaged daily maximum temperature (t2mmax), wind speed, and specific humidity (qv2m) at 2 meters above the surface. We chose to use the maximum temperature and specific humidity because they both have a distinctive seasonal variation, which may correlate to the seasonal characteristics of wildfires. We also used wind speed as an indicator of fire spread. In order to take into account seasonal and yearly changes in intensity, the data were normalized using the daily mean and standard deviation.
Since the mean was taken across California instead of being co-located with each wildfire, the data used in this study may not represent the behavior of individual fires. Given how complex the ignition and spread of wildfires can be, there is no way to accurately predict these individual fires. Instead, the goal of this study is to investigate the correlation between weather and overall wildfire characteristics, such as its frequency and intensity, on a larger spatial and temporal scale.
The Fire Weather Index (FWI) is a measure of fire-prone weather states obtained from the Global Fire Weather Database (GFWED) at the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies (https://data.giss.nasa.gov/impacts/gfwed/). FWI, originally developed for wildfires in Canada [9], is a combination of two variables: the Initial Spread Index (ISI) and the Buildup Index (BUI). ISI combines wind speed with the moisture content of the top soil layer and represents the rate of fire spread [9]. On the other hand, BUI takes the moisture content of deeper soil layers and the Drought Code (DC) in order to measure the total fuel available to the spreading fire. When normalized, positive values for these FWI system indices indicate conditions favorable for a fire; thus, a positive ISI would indicate dry soil and strong winds and a positive BUI represents dry deep soil and a positive DC. All of the previously mentioned variables, except for the burned area data, are daily values. The burned area of fires was recorded as the mean over the summer months (June, July, and August). Further details are available from [9].
2.2. Topological Data Analysis
Topological Data Analysis (TDA) is a modern approach to characterizing the shapes and patterns of data based on its topology [15]. In order to extract the underlying shapes in point clouds, or a set of data points, TDA identifies long-lasting features by using a filtration algorithm with simplicial complexes of different sizes. This filtration algorithm takes input in the form of a point cloud and creates spheres around each data point in the cloud while increasing the size of the balls, the overlapping spheres form patterns, or features. These features, which are the simplicial complexes, are higher dimensional graphs that represent hidden patterns within the data. The existence of simplicial complexes implies that there are significant relationships between the variables that cannot be seen without TDA.
Generally, the higher the dimension of the simplicial complex and the longer lasting it is, the more significant the feature is likely to be. A single point is a 0-simplex. When two circles overlap, they form a feature called a connection or an edge that is otherwise known as a 1-complex. As more of the circles combine, 2- and 3-simplexes may form within the data as well. In this paper, 2- and 3- simplexes are loops and voids, respectively. For example, for the case of a loop of points, the first feature to appear from this loop is a connected component, which occurs when the two closest spheres overlap. The connected component is killed when the next feature is born: a loop that forms when each of the points in the circle join into one union. When the hollow cavity within the loop fills in as the spheres continue to grow, the loop dies and the void is formed.
The filtration algorithm in TDA monitors the birth and death of the topological shapes that form as the spheres overlap, such that the radius of the spheres at the time of the feature’s appearance and disappearance represent its birth and death coordinates, respectively, and these birth-death coordinates are plotted. This visualization of shapes on a two-dimensional space, called a persistence diagram, is one of the most widely used tools of TDA [15,16].
Another topological method, an extension of TDA named TDAMapper was introduced by [17] as a method to reduce high-dimensional datasets into simplicial complexes. These complexes have far fewer points and are able to capture topological and geometric information at specific resolutions [17]. This method is similar to clustering, but unlike many popular methods, TDAMapper does not require the number of clusters to be specified beforehand although it does require knowledge of the distances between points [17].
TDAMapper works by slicing the data into several overlapping intervals called bins. These bins share points with each other, and thus dictate how data divide into clusters and how the clusters are related. The TDAMapper function in R requires three parameters not related to its data input. Namely, they are: num_intervals, percent_overlap, and num_bins_when_clustering. These parameters control the number of slices, the similarity of different bins, and the number of bins per slice of data, respectively. When using TDAMapper, it is important to determine the optimal combinations of these values. For example, not having enough intervals will not be able to show how clusters are related, but too many intervals will also cause relationships to disappear. Although there is no known mathematical method for choosing parameters, the values chosen for this study were able to capture the multifaceted nature of wildfires while allowing room for interpretation.
TDA and TDAMapper have been used in a variety of areas, including fingerprint classification [18], the early detection of financial crashes [19], and breast cancer research [20,21]. However, although one recent study used TDA to detect atmospheric rivers [22], TDA has not yet been widely used in studying weather phenomena. The study revealed that TDA is an effective tool that does not require predetermined thresholds, regardless of the spatial resolution of the input data.
In this study, we used TDA to identify the weather characteristics associated with wildfires with a focus on topological similarities and differences between active and inactive summers. Given the nonlinearity of the relationships among climate variables, we hoped to find previously unseen structures within the data using TDA analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Climatology
The climate in the Southwestern USA exhibits distinct seasonality with wet, cold winters and dry, warm summers. Hot and dry weather provides conditions that are favorable for wildfires and more than half of the annual total of wildfires occurred during the summer months: June, July, and August. Wildfires are strongly seasonal, with 94% of fires and 98% of the area burned occurring between May and October [23]. In this study, we focused on the wildfires that occurred during the summer.
Fire seasons are further broken down into active and inactive seasons based on the total burnt area recorded by CalFire from 1997 to 2016, as shown in Table 1. On average, the total burnt area during the three summer months was 92,294 acres over the 20-year period. The average burnt area during the active and inactive summers was 214,653 acres and 22,457 acres, respectively, a ten-fold difference. This study examined the similarities and differences between the weather conditions of active and inactive fire seasons using TDA and TDAMapper.

Table 1.
The most and least active summer fire seasons in California based on the burned area of wildfires responded to by the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection (CalFire).
In order to examine the weather conditions of active and inactive wildfire seasons, we used the maximum temperature and daily mean specific humidity as proxies for daytime temperatures and the wetness of the atmosphere, respectively. Various other combinations of different variables, including the daily mean temperature and rainfall, were tested and gave similar results. Figure 1 shows a scatter diagram of the maximum temperature (t2mmax) and the specific humidity (qv2m) for five active and inactive summers. Data were averaged over the Southwestern USA and were normalized using the daily mean and standard deviation for the years between 2003 and 2017. Since air at higher temperatures can hold more moisture, temperature and moisture may be positively correlated. Figure 1 shows how the maximum temperature and specific humidity tended to be higher during the active summers when the temperature was also warmer. As a result, more of the data points are in the first quadrant in the figure. However, more data exist in the third quadrant, which has lower temperatures and less specific humidity during inactive summers. As expected, hot and humid weather is more frequent during active summers, while cold and dry conditions are more dominant during the inactive summers.
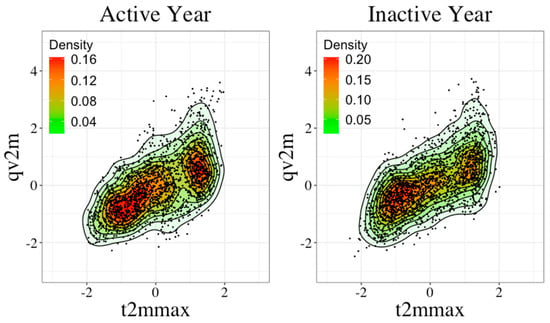
Figure 1.
Scatter plots of daily maximum temperature (t2mmax) and specific humidity (qv2m) for the active and inactive years listed in Table 1. The differences between the active and inactive summer plots were measured by applying the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test to t2mmax and qv2m. The results of this test revealed that the distribution of qv2m for active and inactive years were significantly different (p-value = 0.005), while their distributions for t2mmax were less different (p-value = 0.02). Regardless of the magnitude of their differences, there are important differences between the climate variables of active and inactive years.
The active and inactive seasons were defined based on the burnt area reports by CalFire. MODIS fire data validated the selection of active/inactive years from CalFire data in the study domain, which spans from 124° to 114° W and 32.5° to 42° N. Figure 2 shows the daily average of the MODIS fire pixel distribution as a function of the log of FRP for active and inactive summers as well as for the north and south domains of California. Northern and southern California, which were divided with respect to the 38th parallel, are represented by red and blue lines, respectively. According to Figure 2, active summers clearly have many more fires than the inactive summers do. More specifically, the active summers typically have fires more frequently in northern California, but southern California has more intense fires that cause the median FRP to be higher. The northern domain experiences more fires with smaller FRP values than the south, but as FRP increases, the two domains become comparable. On the other hand, more fires occurred in the southern domain than in the north during inactive summers.
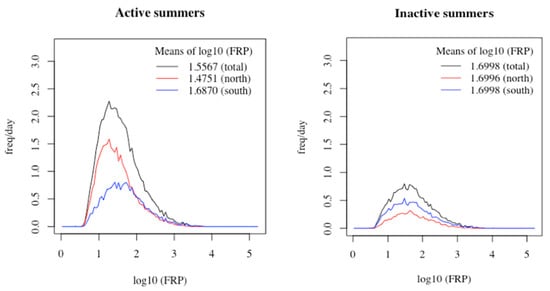
Figure 2.
Number of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) fire pixels per day in the study domain as a function of the fire radiative power (FRP) for active and inactive summers. The red and blue lines indicate the number of fire pixels from the northern and southern domains, respectively, while the black lines represent all of California. The means for log10 (FRP) were calculated for each domain and are listed in the legend of both plots.
3.2. Topological Data Analysis
As Figure 1 shows, the relationship between the maximum temperature and specific humidity is positive and roughly linear, and there are two preferable states: the cold and dry conditions and the warm and wet conditions. In this study, we applied TDA to the data in order to identify hidden structures of the data in two dimensions. Similar to Chazal et al. [15] and other previous studies, persistence maps were created to show the birth and death of topological shapes.
Figure 3 is a persistence diagram using the maximum temperature and specific humidity from active and inactive summers. In the diagrams, black dots represent connected components, red triangles indicate loops, and the blue squares are voids. The pink band, calculated by bootstrapping the points, represents the confidence of the diagram and the statistical significance of each topological shape represented. Given how the diagrams are created, features plotted within this pink band died soon after their birth, and are thus considered to be noise. The farther away a point lays from the diagonal line, the longer-lasting the feature is, and the more significant it is. The confidence of the diagram is thus a measure of how many features lie within the pink band.
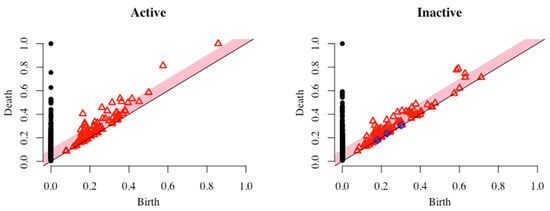
Figure 3.
Persistence diagrams based on the daily maximum temperatures and specific humidity shown in Figure 1 for active and inactive summers. The black dots, red triangles, and blue squares indicate connected components, loops, and voids, respectively. The pink bands represent the confidence interval.
In these persistence diagrams, active summers tended to have more components further away from the band, suggesting that these seasons have more significant features. At this point in the study, it is not yet clear what the meaning of these features are, nor how it can help distinguish fire weather in active and inactive summers.
3.3. TDAMapper
To better understand the underlying meaning of the topological features identified by TDA, TDAMapper was applied to the same data in order to split the data into groups based on the distances between the data points. The main goal of the mapper algorithm is to obtain a low-dimensional image by allowing parts of each cluster to overlap [17]. The intervals and amount of overlap control the resolution of the mapper output. Further details of the Mapper are available from [17].
Figure 4 shows the mapper output for five active and five inactive summers based on the point clouds of the daily maximum temperature and specific humidity (Figure 1). The mapper algorithm was computed using five intervals, or bins, with a 60% overlap. Each circle represents one of the nodes, or clusters, formed by the algorithm, and the size denotes the total number of fire pixels from each of the days in the cluster. As predicted, the clusters are larger in the active summer plot, which indicates more fires, while the inactive summers have only a few nodes with a significant amount of fire activity.
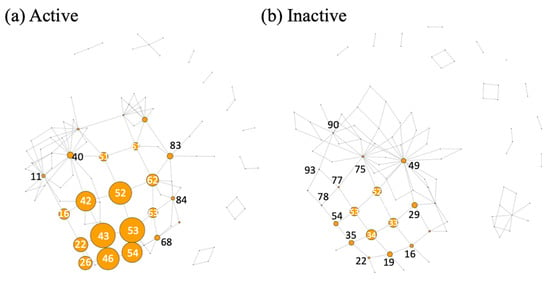
Figure 4.
Mapper graphs for (a) active and (b) inactive summers. The sizes of circles at each node are proportional to the total number of MODIS fire pixels from the days included in each node. The numbers on each node are a sequence of numbers generated by mapper. The same numbers are depicted in the subsequent maps (Figure 5, Figure 6, Figures 8 and 9) as a reference.
In order to examine the weather conditions at each node, the average daily maximum temperature, wind speed, and specific humidity were calculated at each node. This was done by collecting the maximum temperatures from each of the days that belong to a certain node and then averaging these values. Figure 5 and Figure 6 take the plots from Figure 4 and map the same nodes that have been resized and recolored to depict these averages and labelled with their node number as identified by the mapper algorithm. The size of the nodes is proportional to the magnitude of the average of each weather variable and the colors show the sign of the average, where red and blue indicate positive and negative values, respectively. Separating the weather variables into different plots in this way shows how the different weather variables correlate to the count of fire pixels in each cluster.
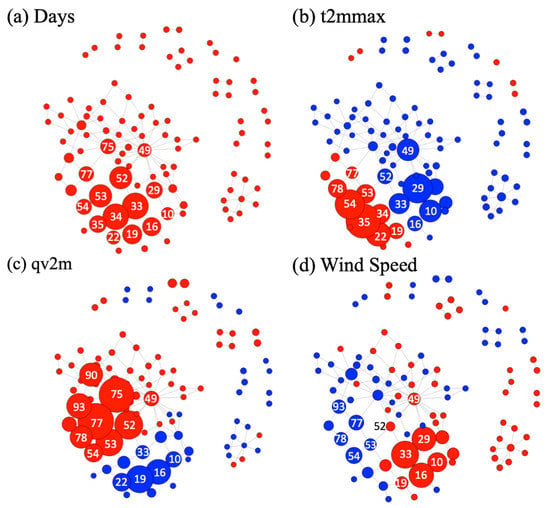
Figure 5.
Mapper graphs for active summers. The sizes of the nodes are proportional to (a) the number of days at each node, the averages of (b) daily maximum temperature (tmax), (c) (2 meters) specific humidity (qv2m), and (d) surface wind speed. Red indicates that the averages are higher than the mean, while blue means that they are lower.
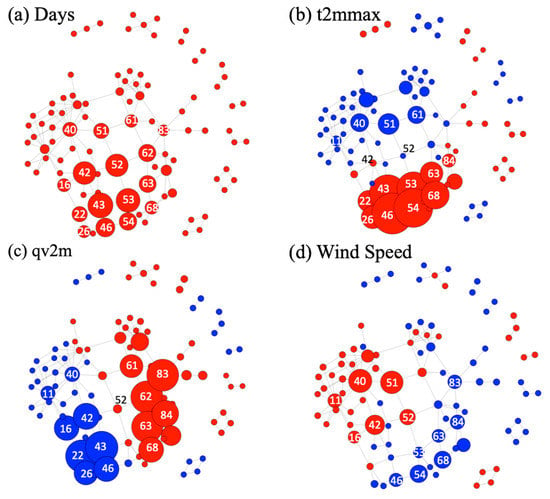
Figure 6.
Same as Figure 5, but for inactive summers.
As shown in Figure 4, nodes 52, 53, 54, 42, 43, and 46 have the most wildfires. Nodes 53, 54, 43, and 46 had warmer than average temperatures and, as expected, had a higher fire count. However, as shown in Figure 5b, nodes 52 and 42 had closer to average temperatures, but they still had a significant fire count. Figure 5c suggests more wildfires occurred when the specific humidity is lower than average, though clusters such as nodes 52, 53, and 54 had closer to normal humidity conditions. To summarize, the occurrence of wildfires was not confined to only hot and dry weather.
Wind is an important influence on the initiation and spread of wildfires; it enables embers to cross longer distances and provides fuel for a fire to ignite. However, in the mapper algorithm, wind speed shows less organized patterns when compared to temperature and humidity, possibly because the regional averages of wind speed are not appropriately correlated with the local winds associated with intensifying wildfires.
Figure 6 shows the same averaged weather variables for inactive summers as Figure 5 did for active summers. Nodes 52, 53, 54, and 33 had the most wildfires, although their total fire count was less than half of those represented in active summers (Figure 2). All four of these nodes show slightly different weather patterns: node 53 was warm and moist, node 33 was cold and dry and had stronger winds, node 52 was cold and moist, and node 54 was warm and dry. Overall, fire activity was weaker during the inactive seasons. Since inactive summers had dramatically fewer wildfires than active summers did, using active summers may be preferable in order to accurately analyze fire conditions.
A careful investigation of the nodes in Figure 5 revealed three types of patterns, as represented by the panels in Figure 7. Figure 7 shows the distribution of the MODIS fire pixel data as a function of FRP for selected active summer nodes. The black line plots the total fire pixel count by day from the study domain while the blue and red lines represent the fire distribution from the southern and northern domain, respectively. In all of the panels, northern California shows a higher frequency of weak fire pixels, though the relationship between north and south varies across the nodes. In node 62, for example, there were more fires in the north, while the numbers of fires were almost even between domains in node 43. Node 42 has a similar pixel distribution as node 43, but the intensity of fires in the north and south are more evenly matched.
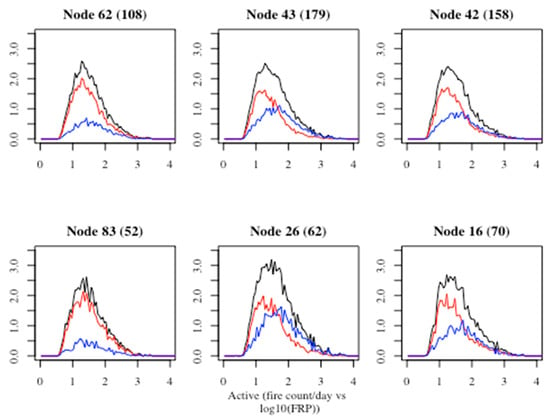
Figure 7.
Number of MODIS fire pixels per day in the study domain as a function of the FRP for selected nodes from active summers. The node number and the number of days in each node are at the top of each plot. The red and blue lines indicate the number of fire pixels from northern and southern domains, respectively.
Since the Mapper algorithm allows clusters to overlap, some nodes may be highly correlated with their neighbors. The lower three panels in Figure 7 show some examples of nodes that show a high level of similarity with the corresponding panel above it. Node 83, for example, contained 52 days, 44 of which were also included in node 62. As a result, the distributions are similar, however, although node 62 contains a larger number of days, it has more fire pixels in the northern domain. Thus, node 83 is an extreme subset of node 62 with an overlap of 84%. The overlap between nodes 26 and 43 is even larger, with 91% of the 62 days in node 26 also belonging to node 43. Node 26 is therefore also an extreme subset of node 43 with overall stronger and more frequent fires in southern California. Node 16, however, is a complete subset of node 42, meaning that all of the 70 days in node 16 are also contained in node 42. As a result, the distribution of node 16 is very similar to that of node 42.
In this study, we also explored the relationships between fire types (Figure 7) and the FWI system. Figure 8 shows the Mapper graphs for active summers using the average values for FWI, ISI, BUI, and DC such that the size and color of each cluster depends on the number of nodes and the sign of the resulting average, respectively. Nodes with a large number of fires (e.g., nodes 42, 43, 46, 52, 53, and 54) have a positive average FWI value, which indicates more fire-prone weather states. However, this relationship was not constant. For example, the value of FWI at nodes 52 and 53 were significantly smaller when compared to FWI at nodes 42 and 43 even though the total number of fires in each of the nodes were similar (Figure 4). Thus, at nodes 52 and 53, DC is a better representation of the number of fire pixels. Although the number of fires in node 62 is large, none of the variables in the FWI system returned a positive value; the node is blue in each graph. Similarly, node 83 was also associated with large negative values. This is because FWI is not always successful in predicting fire seasons. For example, it may return a negative value when wildfires are actually prone to occur. These discrepancies may be because FWI was developed for Canadian forests, thus it is not the best for California weather and should be analyzed in a future study.
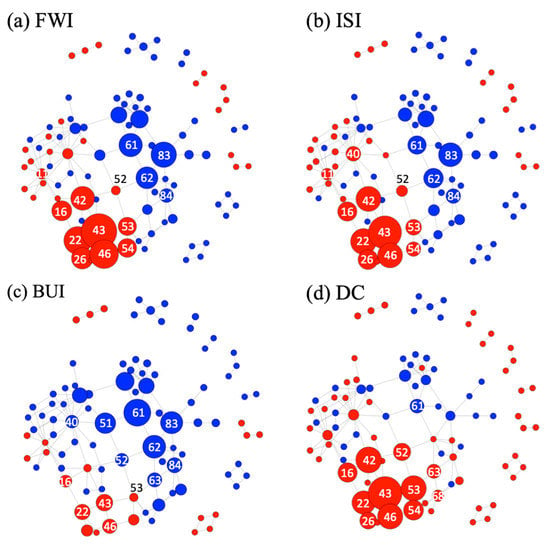
Figure 8.
Mapper graphs for active summers. The size of nodes is proportional to (a) the Fire Weather Index (FWI), (b) the Initial Spread Index (ISI), (c) the Buildup Index (BUI), and (d) the Drought Code (DC). Red nodes indicate a positive average and blue nodes indicate a negative average.
As shown in Figure 7, most of the fires detected at nodes 62 and 83 were from northern California. Since nodes 62 and 83 correlated with more negative values of FWI, ISI, BUI, and DC, these results suggest that the FWI system works better for wildfires in southern California. In Figure 8, the color and size distribution of clusters in FWI correlated highly with those of ISI and BUI, and DC tended to resemble FWI more than BUI. This was surprising because DC is a subcomponent of BUI.
Figure 9 shows the Mapper diagrams for inactive summers using the FWI system variables. The mean values and DC and BUI clearly indicate that inactive summers are, on average, wetter than active seasons. Similar to the active summers in Figure 8, the FWI Mapper diagram resembles that of ISI. Unlike the active summers, however, the DC diagram is more closely consistent with BUI.
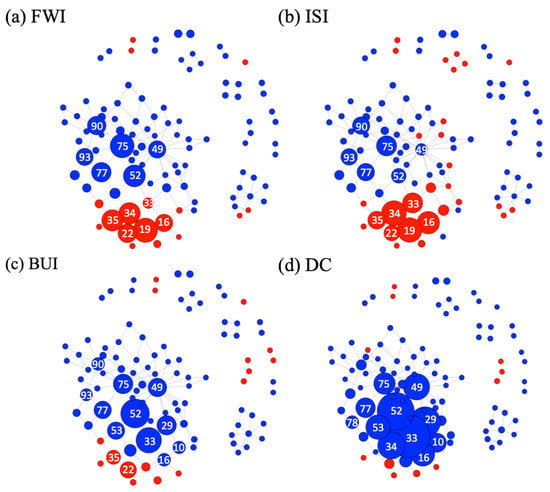
Figure 9.
Same as Figure 8, but for inactive summers.
During the inactive summers, only four of the nodes (53, 54, 33, and 34) have sizable fires. Among those, nodes 33 and 34 have positive values for FWI and ISI, but a negative DC and BUI. Although the summers were wetter in general, as represented by a negative DC and BUI, the fires detected at nodes 33 and 34 may correlate with short-term drought conditions and strong Santa Ana winds. These short droughts may be represented by a positive value of ISI; since ISI takes the moisture of the top layer of soil into account, more moisture (when ISI is negative) would indicate recent rainfall. On the other hand, clusters such as nodes 52 and 53 had fires that occurred when all the FWI variables had a negative mean, likely resulting in shorter and weaker fires.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we demonstrated the potential of using TDA and TDA Mapper on the diagnostics of fire-prone weather in the Southwestern USA in order to analyze the influence of various climate variables (daily maximum temperature, specific humidity, and wind speed) on wildfires in California. Since fires in the past have been more frequent during the summer, these wildfires—occurring during the months of June, July, and August—were the focus of this study. Using the burned area of wildfires during these months, the five most severe and five least severe years were identified.
The active and inactive seasons were further analyzed using TDA, and when compared it was found that active summers consisted of more significant and long-lasting features within the data, implying less noise and more variables that have a heavy impact upon wildfires. In contrast, weather variables did not have a substantial influence on wildfires during the inactive seasons. TDAMapper was applied in order to analyze these relationships.
TDAMapper allowed for an examination of the weather conditions in each cluster. Warm temperatures were the most distinctive feature of active summers, while inactive summers were more likely to have a negative drought index. While this was an overarching theme for each summer, as active seasons were mostly hot and inactive seasons were more likely to be wet, it was rarely consistent, and TDA also showed that wildfires were also likely to start during colder and wetter seasons. In addition, because the weather variables had all been averaged, wind speed was not as significant as a factor as previously believed. However, since wind is a crucial factor in the initial spread and duration of wildfires, this result should be taken with caution. A future study may address this by studying the duration of wildfires, which may show more impact from wind than this study has.
It was predicted that the results of TDAMapper would have been greatly impacted by averaging variables over the entirety of California, so the study was narrowed to the northern and southern domains individually. When analyzing north and south California with frequency graphs, southern California had more frequent fire outbreaks than the north on average. On the other hand, when northern California had fires, they were more intense than those in the south. Since the goal was to identify the influence of climate and weather variables on wildfires on a climatic scale, these discrepancies did not impact our results. However, they are still important to keep in mind.
Most importantly, the FWI did not turn out to be an accurate indicator of wildfires. FWI has been successful in predicting fires in Canadian forests in the past. According to the results of this study, however, it was only capable of correctly labeling some clusters as fire seasons for California. FWI and its component variables – ISI and BUI – were not able to identify fire seasons in other clusters. We speculate that FWI may be a better index for wildfires associated with hot and dry conditions, but not in California. A new approach is needed to include other aspects of fire weather conditions, especially those traditionally considered as unfavorable for wildfires. Those fires may be caused by human activities rather than natural ignition. Results from this study may shed light on new models that include the impact of humans on wildfires and can develop a new indicator.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.K. and C.V.; Methodology, H.K. and C.V.; Software, H.K.; Formal Analysis, H.K.; Investigation, H.K. and C.V.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, H.K.; Writing—Review and Editing, C.V.; Visualization, H.K.; Supervision, C.V.; and Funding Acquisition, no funding.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the ASPIRE Program at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory. This research was incubated and conducted through the ASPIRE program between June 2018 and September 2019.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Smith, A.B.; Katz, R.W. US billion-dollar weather and climate disasters: Data sources, trends, accuracy and biases. Nat. Hazards 2013, 67, 387–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmsheimer, R.W.; Bowyer, J.L.; Fried, J.S.; Gee, E.; Izlar, R.L.; Miner, R.A.; Munn, I.A.; Oneil, E.; Stewart, W.C. Managing Forests Because Carbon Matters: Integrating Energy, Products, and Land Management. Policy. J. For. 2011, 109, S5–S48. [Google Scholar]
- Verdin, K.L.; Dupree, J.A.; Elliott, J.G. Probability and Volume of Potential Postwildfire Debris Flows in the 2012 High Park Burn Area near Fort Collins, Colorado. In Open-File Report; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI) U.S. Billion-Dollar Weather and Climate Disasters. 2019. Available online: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/billions/ (accessed on 15 November 2016).
- Cayan, D.R.; Das, T.; Pierce, D.W.; Barnett, T.P.; Tyree, M.; Gershunov, A. Future dryness in the southwest US and the hydrology of the early 21st century drought. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21271–21276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerling, A.L.; Hidalgo, H.G.; Cayan, D.R.; Swetnam, T.W. Warming and Earlier Spring Increase Western U.S. Forest Wildfire Activity. Science 2006, 313, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crockett, J.L.; Westerling, A.L. Greater temperature and precipitation extremes intensify western US droughts, wildfire severity, and Sierra Nevada tree mortality. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, D.A. A lower atmospheric severity index for wildland fire. Natl. Weather. Dig. 1988, 13, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wagner, C.E. Development and Structure of the Canadian Forest Fire Weather Index System; Canadian Forestry Service Ottawa: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- McEvoy, D.J.; Hobbins, M.; Brown, T.J.; VanderMolen, K.; Wall, T.; Huntington, J.L.; Svoboda, M. Establishing relationships between drought indices and wildfire danger outputs: A test case for the California-Nevada drought early warning system. Climate 2019, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balch, J.K.; Bradley, B.A.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Nagy, R.C.; Fusco, E.J.; Mahood, A.L. Human-started wildfires expand the fire niche across the United States. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2946–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justice, C.O.; Giglio, L.; Korontzi, S.; Owens, J.; Morisette, J.; Roy, D.; Descloitres, J.; Alleaume, S.; Petitcolin, F.; Kaufman, Y.J. The MODIS fire products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 244–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichoku, C.; Kaufman, Y.J. A method to derive smoke emission rates from MODIS fire radiative energy measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2636–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Schroeder, W.; Hall, J.V.; Justice, C.O. MODIS Collection 6 Active Fire Product User’s Guide. Revision B; University of Maryland: College Park, MD, USA, 2018; p. 64. [Google Scholar]
- Charzal, F.; de Solva, V.; Oudot, S. Persistence stability for geometric complexes. Geom. Dedicata. 2014, 173, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubenik, P. Statistical topological data analysis using persistence landscapes. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2015, 16, 77–102. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, G.; Memoli, F.; Carlsson, G. Topological methods for the analysis of high dimensional data sets and 3D object recognition. Eurogr. Symp. Point-Based Graph. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giansiracusa, N.; Giansiracusa, R.; Moon, C. Persistent homology machine learning for fingerprint classification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.09158v1. [Google Scholar]
- Gidea, M.; Katz, Y. Topological data analysis of financial time series: Landscapes of crashes. Physica A 2018, 491, 820–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau, M.; Levine, A.J.; Carlsson, G. Topology based data analysis identifies a subgroup of breast cancers with a unique mutational profile and excellent survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7265–7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lum, P.Y.; Singh, G.; Lehman, A.; Ishkanov, T.; Vejdemo-Johansson, M.; Alagappan, M.; Carlsson, J.; Carlsson, G. Extracting insights from the shape of complex data using topology. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszynski, G.; Kashinath, K.; Kurlin, V.; Wehner, M.; Prabhat. Topological data analysis and machine learning for recognizing atmospheric river patterns in large climate datasets. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerling, A.L.; Gershunov, A.; Brown, T.J.; Cayan, D.R.; Dettinger, M.D. Climate and wildfire in the western United States. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).