Abstract
The growth of urban areas has a significant impact on land use by replacing areas of vegetation with residential and commercial areas and their related infrastructure; this escalates the land surface temperature (LST). Rapid urban growth has occurred in Duhok City due to enhanced political and economic growth during the period of this study. The objective is to investigate the effect of land use changes on LST; this study depends on data from three Landsat images (two Landsat 5-TM and Landsat OLI_TIRS-8) from 1990, 2000 and 2016. Supervised classification was used to compute land use/cover categories, and to generate the land surface temperature (LST) maps the Mono-window algorithm was used. Images were also used to create the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), normalized difference built-up index (NDBI), normalized difference bareness index (NDBAI) and normalized difference water index (NDWI) maps. Linear regression analysis was used to generate relationships between LST with NDVI, NDBI, NDBAI and NDWI. The study outcome proves that the changes in land use/cover have a significant role in the escalation of land surface temperatures. The highest temperatures are associated with barren land and built-up areas, ranging from 47°C, 50°C, 56°C while lower temperatures are related to water bodies and forests, ranging from 25°C, 26°C, 29°C respectively, in 1990, 2000 and 2016. This study also proves that NDVI and NDWI correlate negatively with low temperatures while NDBI and NDBAI correlate positively with high temperatures.
1. Introduction
In the last decade, climate researchers’ attention was increasingly drawn to local and regional climate under anthropogenic influences to better understand the increasing change in the climate’s driving factors []. One of the main causes of global climate change is increasing industrialization and urbanization. Currently, the most crucial problem that urban areas suffer from is rising surface temperatures caused by the loss of areas of vegetation and the increase of impermeable non-transpiring, non-evaporating, hard land surfaces [,,,,]. One of the most noticeable effects of the modifications of terrestrial ecosystems by human activity is the change in land use/land cover (LULC) as it has greatly impacted the environment locally, regionally and globally [,,]. The amount of humidity in the air is greatly affected by the change of natural land surfaces to built-up areas as vegetation is a major source of humidity []. For all surface materials, certain internal properties such as inertia, conductivity and heat capacity have an immense impact on balancing the body temperature with its surroundings []. Higher thermal capability for releasing daytime heat at night and greater solar radiation absorption are usually caused in urban areas by replacing vegetative areas with paved surfaces such as buildings, parking lots, roads, etc., thus causing ‘heat islands’ (UHI) which is the contrast of temperature between the warmer urban areas and the colder surrounding rural areas often resulting from this process [,].
Environmental and urban climate studies use land surface temperature (LST) and emissivity data for numerous purposes but mainly to analyze LST patterns and how they are connected to surface characteristics, urban heat island forecasts and for the relationship of LSTs with surface energy fluxes so that landscape procedures, properties, and patterns can be characterized [,]. LST can be utilized to represent and control the biological, physical and chemical processes of earth systems; it is also a good indicator of the earth’s surface energy [,]. Awareness of LST supplies knowledge of spatial and temporal variations on the state of surface stability and therefore is essential in many applications []. A wide variety of studies employ LST as it is useful in many fields including hydrological cycles, urban climate, climate change, evapotranspiration, vegetation observations, as well as environmental observations [,,,,]. It has been recognized by, among others, the International Geosphere and Biosphere Program (IGBP) as a high-priority parameter []. Land use classification, thermal environment, urban heat island research and hydrological investigation in urban growth, or even on a larger scale, utilize the LST satellite-derived images []. Land surface temperature (LST) assisted by the thermal infrared bands of remote sensing data of space-borne sensors, which analyze the relationship between urban thermal patterns, spatial structure and urban surface characteristics, is a major application of remote sensing in urban climate studies, as it helps land use and occupation planning []. LST information on regional and global scales is obtained by thermal infrared (TIR) remote sensing; it is a unique approach as sensors in this spectral region detect the energy that is emitted directly from the land surface [].
Researchers A and Devadas, 2009 []; Abdullah, 2012 []; Fu and Weng, 2016 []; Lv and Zhou, 2011 []; Xiao et al., 2007 [] utilized remote sensing images using Landsat images to generate land use and surface temperature maps and to monitor land use changes [,,,] for commercial and business centers, government offices, residential areas and public amenities which are replacing green spaces, forest and unused lands. The Klang Valley Region in Malaysia contained the most noticeable LULC change. For sustainable development to be implemented, monitoring the changes in land use can be considered as alternative good governance for administration []. Studies noticed an increase in urban growth with a related decrease in vegetation, which resulted in an alteration of urban microclimates []. Another study determined the land surface temperature and vegetation abundance relationship. Different indices of vegetation indicate an abundance of vegetation, such as fractional vegetation cover, and the normalized vegetation index (NDVI). A negative connection between the NDVI and land surface temperature was revealed, as well as the green area’s cooling effect [,] due to soil moisture variations, land surface emissivity, albedo, and profusion of vegetation, resulting in the fall of the variable temperatures of dense vegetation []. The authors of [,] proved that political and socio-economic developments are essential factors impacting urban growth. Their results show that the urban area of their case study corresponded to sites of key economic progress. Therefore, the example of Duhok City in Iraqi Kurdistan, a fast-growing urban area, was selected to employ updated methodology to address the following:
- (1)
- To evaluate urban land use/cover changes in Duhok City and to analyze the impact of land use/cover on LST.
- (2)
- To examine the relationship between LST with NDVI, NDWI NDBAI and NDBI values.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study site covers the capital of Dohuk Province, Dohuk City, in the north of Iraqi Kurdistan, located between latitudes 37°00′00″ N and 37°07′30″ N and longitudes 42°27′30″ E and 42°47′30″ E [], and 585 m above mean sea-level [] Figure 1. The study area was chosen due to its strategic site on the international transport links connecting the Kurdistan Region of Iraq to Turkey as well as Syria.
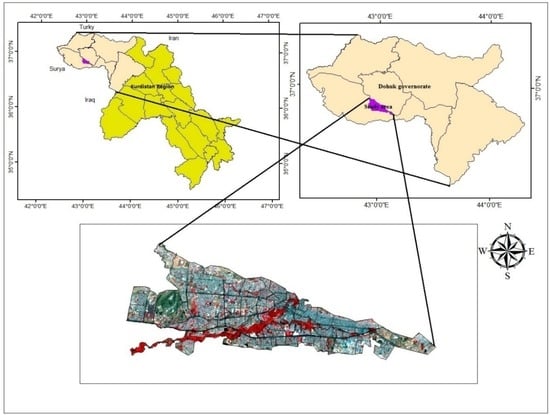
Figure 1.
Illustration of the location of the study area, Duhok City.
Duhok city is located between two opposing mountains ranges, the Bekher Mountains in the north and Zawa Mountains in the south. As the surrounding mountains are of relatively high altitudes, the climate is similar to that of the Mediterranean region [] in that the Mediterranean climate is characterized by dry summers and winters with reasonable precipitation. The summers are hot with low moisture and bright sunshine. In contrast, winters have a noticeably higher humidity and lower temperatures. In the winter season the climate is characterized by its low temperatures and snowfall on the high mountains []. Occasional drought seasons that are repeated over periods of time lead to an underground water recharge deficiency. A significant amount of rainfall as well as cold temperatures characterizes the spring seasons.
2.2. Data Used
Primary and secondary data are both adapted in the study in order to efficiently detect how land surface temperature (LST) is affected by the alteration in land use/cover. United States Geological Survey (USGS) Gloves provided the primary data of three Landsat images with the spatial resolution of 30 m, 100 m and 120 m. The first Landsat TM-5 is dated 11 October 1990, second Landsat TM-5 is dated 21 August 2000, and the third image of Landsat OLI_TIRS-8 is dated 1 August 2016. All bands were used in this study, in particular thermal bands which are popular for identifying LST (Table 1). Secondary data such as municipal boundaries, geographical wards and the master plan map were sourced from the governorate of Duhok.

Table 1.
Details of Landsat satellite images.
2.3. Methodology
Different processes for analyzing the Landsat images were used in this study: (1) Classification of the images; (2) derivation of NDVI, NDWI, NDBI and NDBAI; (3) LST for each image was retrieved; (4) All files were entered into GIS, after being converted to vector files to calculate and manipulate through attribute tables in ArcGIS, as shown in Figure 2.
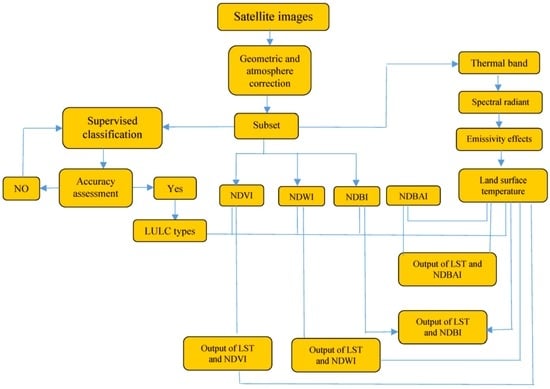
Figure 2.
Flowchart showing the methodology.
2.3.1. Image Classification and Accuracy Assessment
In order to detect the changes in land use during the period of the study, LULC classification is essential to study the effects of human actions on a regional scale. Landsat images mapped LULC changes for 1990, 2000 and 2016. Built up areas, water, barren land and vegetation lands are the four selected LULC types. The images were analyzed according to their spectral and spatial profiles so that training sites could be developed, based on ancillary information and reference data from various sources. This study designated 40 training samples of 40 pixels for each land cover class. However, Lillesand et al, 2008 [] noted the need for 20 training samples of 40 pixels for each land cover category. The statistical characteristics of the land cover categories were developed once the training sites were digitized. Landsat images were then classified by utilizing the maximum likelihood algorithm with a supervised signature extraction. The three classified maps were assessed on accuracy by stratified random sampling methods. From each LULC class, fifty samples were chosen. Apart from field checked LULC maps, a field survey was also used as reference data.
2.3.2. Computation of NDVI, NDWI, NDBI and NDBAI
LST studies widely use the NDVI parameter because NDVI is less sensitive to the changes in atmospheric conditions than other indices; it has, therefore, become very popular to monitor vegetation statuses []. NDVI was used to present the relationship between LST and vegetation area in this study by linear regression correlation. In order to compute an NDVI image this formula was used:
NDBI is a widely-used index for evaluation built up statuses [,]. NDBI values can, depending on the spectral signature, range from medium infra-red to near infra-red band. As well as being useful for mapping human settlements [], it is also useful for some elements of surrounding constructions. NDBAI is therefore reformulated for mapping Normalized Difference Bareness Index. The water state of vegetation and the water content within vegetation is implied by the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) []. The values of NDBI, NDBAI and NDWI can vary from −1 to +1. Positive indicates water bodies and highly built up areas, whilst other land cover types are represented by negative values. The formula for calculating this index is:
2.3.3. Computation of Land Surface Temperature LST
The study employed the Mono-window algorithm developed by Qin et al., 2001 [], to generate the Land Surface Temperature (LST) maps from Landsat satellites thermal infrared with 100 m and 120 m Spatial resolution. Radiation from the surface of the earth was recorded by the thermal infrared band, with a spectral range between 10.4 and 12.5 μm [,]. Derived LST requires three steps: first, spectral radiance was gained from DN of Landsat images with this formula:
This can also be stated as
where
- = Spectral radiance w·sr−1·m−3
- LMIN = 1.238 (Spectral radiance of DN value 1)
- LMAX = 15.600 (Spectral radiance of DN value 255)
- DN = Digital Number
The next step is to transform Spectral Radiance to Temperature in Kelvin with the following formula:
where
- K1 = Calibration Constant 1 (607.76)
- K2 = Calibration Constant 2 (1260.56)
- R = Radiance values W/m2 SRμm
- TB = Surface Temperature °C
In the final step, Kelvin is converted to Celsius with the following formula:
3. Results and Discussion
Land use/land cover maps, land surface temperature distribution and the NDVI, NDWI, NDBAI and NDBI of the study area are the three main subsections in which the results of this study are presented:
3.1. Land Use/Land Cover Maps
The supervised classification maximum likelihood was applied to generate the LULC map in 1990, 2000 and 2016 with high accuracy as seen in Table 2. The total area of interest is approximately 17,007.25 hectares; in Table 3 and Figure 3, the exact area of the LULC of this study is listed. LST changes were caused by alternations of LULC, specifically in urbanized areas which have increased noticeably.

Table 2.
Accuracy assessment of land use/cover between 1990, 2000 and 2016.

Table 3.
Shows the quantity of land use change.
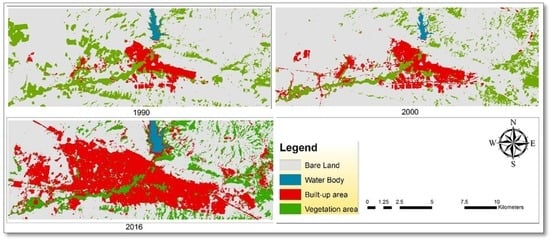
Figure 3.
Supervised classification of land use/cover map.
Table 2 shows that the built-up categories (residential, commercial and administrative buildings) increased slightly by 0.86% from 1095.77 ha to 1241.55 ha between the years 1990 and 2000, while a significant increase was recorded between the years 2000 to 2016, growing by 11.2% from 1241.55 ha to 3140.01 ha, respectively. The total area of built-up land increased from 1095.77 ha to 3140.01 ha between the years 1990 and 2016.
There are many factors contributing to the increase in urbanized areas; in old parts of the city major alternations have occurred. The study area has seen remarkable changes since 2000 (Table 3) due to political and socio-economic factors. When Saddam Hussein was forced out of power, the political and socio-economic situation improved. The outcome of the study endorses the findings of [,] who found that both political and economic factors contributed to urban growth. The government and/or private companies developed a great deal of these areas for various retail, industrial, and residential purposes; this has been a further cause of the reduction of barren land surrounding the city, as much land was developed into large buildings and skyscrapers. Impermeable materials such as steel frames and concrete were used in the construction of these buildings. On the other hand, barren land increased from 13,141.13 ha to 13,420.7 ha between the year 1990 to 2000, although this rate lowered by 12.2% from 13,420.7 ha to 11,342.2 ha between the years 2000 and 2016, while land coverage by vegetation and water decreased by 2.48% and 0.01% from 2629.78 ha to 2206.26 ha, and from 240.57 ha to 138.74 ha from 1990 to 2000. In addition, the outcomes of the study indicate that barren land and green areas dropped from 13,141.13 ha and 11,342.2 ha in 1990 to 2629.78 ha and 2381.13 ha in 2016, while water bodies increased from 140.57 ha to 143.91 ha.
3.2. Land Surface Temperature Retrieval (LST)
The outcome of the research has been to produce a map of the study area’s absolute LST. The computed LST map is illustrated in Figure 4. Respectively, in the years 1990, 2000 and 2016, LST values showed ranges between 25–47 °C, 25–50 °C and 29–56 °C. This study revealed that the maximum LST for the whole area went up by 9 °C from 1990, 2000 and 2016, which were 47 °C, 50 °C and 56 °C; during the same period of time, the minimum temperature increased by 4 °C from 25 °C, 26 °C and 29 °C, shown in Figure 4. Reasons for this increase in the range values include the different times the images were captured, meaning that different times of the year affected the results. The 1990 images were captured on 11 September 2000, the 2000 images were captured on 21 August 2000 and the 2016 images were captured on 1 August 2016. In addition, these changes could be the result of climate change. Extreme seasons have a great effect on this phenomenon. The study area experienced drought seasons particularly in 1998 and 2000; the percentage of droughts was 56% [].
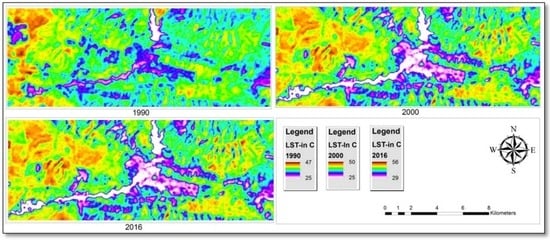
Figure 4.
Land surface temperature map extract in thermal band.
Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7 display the spatial distribution of LST; higher temperatures are detected outside the city rather than at the outskirts. The LST in Duhok ranged from 25 °C to 47 °C, from 26 °C to 50 °C and from 29 °C to 56 °C in 1990, 2000 and 2016, respectively. The city has a number of LULC categories including vegetation cover, water bodies, barren land, as well as high-density, high-rise buildings in the city, interspersed with large areas covered with high-density housing. The highest temperatures around and in the city were 47 °C, 50 °C and 56 °C, and were shown in large areas of barren land and built-up areas with concrete surfaces. Most of the study site possesses densely built-up areas which cause high temperatures in contrast to the water and vegetation areas. The highest temperature of 47 °C from 1990 was recorded in Lower Malta, Meda, Shakhka, Shandokha, and Razato in the west of the study area, as well as in a part of Mazi and Pishazazi. The highest temperature of 50 °C in 2000 was noted in Zanko, Upper Malta, Lower Malta, Media, Shandokha and Raza, in the west of the city. The highest temperature of 56 °C in 2016 was recorded in Zanko, Masike and a part of Etite. In 1990 the LST of 37 °C to 43 °C was recorded in the north, south, east and west of the study area including Upper Malta, Zanko, Sarbasti, Mahabad and Mazi. In 2000 the LST of 37 °C to 44 °C was recorded in the center, north and east of the city including Shorsh, Gre Base, Shahidan, Gall, Shele, Khabat and Sarhaldan, whereas in 2016 a moderate temperature was recorded in the whole study area, apart from Zanko and Etite in the west and east of the study area, respectively, shown in Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7. The Duhok dam and the area of vegetation had mainly a lower LST between 25 °C and 29 °C and are surrounded by water bodies and greener areas. The zones previously mentioned present a moderate range of temperatures as they are along built-up areas.
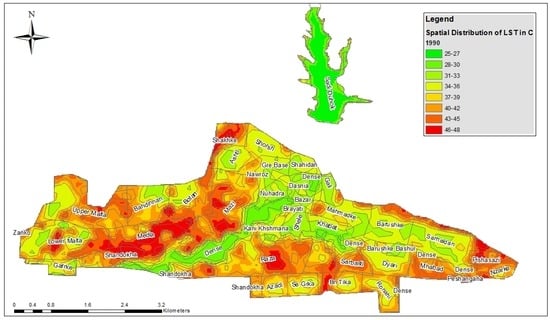
Figure 5.
Spatial distribution of land surface temperature (LST) for 1990.
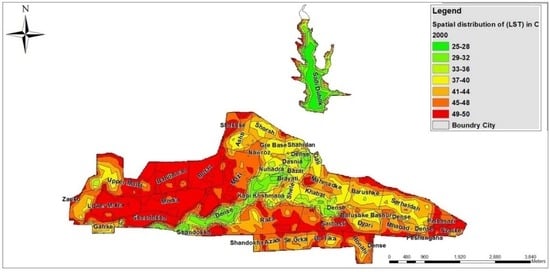
Figure 6.
Spatial distribution of land surface temperature (LST) for 2000.
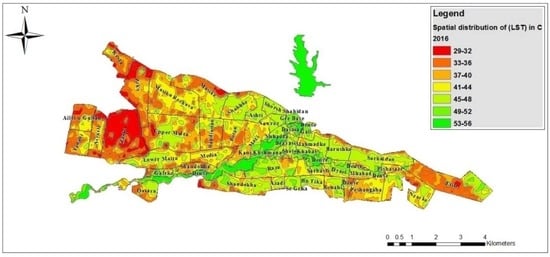
Figure 7.
Spatial distribution of land surface temperature (LST) for 2016.
3.3. Relationship between Land Surface Temperature and Different Land Covers
The investigation of the thermal signature of each LULC type is essential to understand the relationship between LST and land cover []. Therefore, a comparison of LULC and LST was carried out; sampling points for each LULC category in the study area were selected to compare the LST values. The mean temperature of each land use/cover category was calculated by averaging all consistent pixels of a given LULC category. The results indicated the highest LST in the rock outcrops while the lowest was recorded for water bodies. Cold anchor pixels were observed in vegetated areas and water bodies, while the warmest were rock, built-up areas or bare soils. The surface temperature pixels ranged from 25 °C to 56 °C (Figure 7).
This study detected higher temperatures in the outskirts and the non-built up areas of the city rather than inside the city. Therefore, the LST outcomes of this study may disagree with previous studies [,,] which show higher LST values in urban areas than in the areas surrounding and outside cities. In the period studied, Duhok City showed a lower LST in urban areas than in the suburbs (Figure 8); this is due to the sun’s heat in surrounding areas being absorbed directly into the ground, causing it to heat up faster than in other land cover categories. In contrast, roads, pavements, buildings, concrete and other features that make up urban surfaces tend to release the absorbed heat slowly. In other words, built-up land has a tendency to retain the heat longer than other land cover classes such as barren land on the outskirts that does not retain heat for as long. The results of this study prove that the surrounding areas/barren lands have higher temperatures than urban areas; this outcome could be a result of the timing of the Landsat images captured. At approximately 7 a.m. the sun is just beginning to heat up the ground. Urban surfaces take in temperature more slowly, so the features in built-up areas warm up and cool down slower than other land cover categories such as barren land, which is why lower LST values were recorded in built-up areas compared to barren areas. Despite that, the changing of the LST is also caused by the land changes, since each type of land has its own qualities in terms of energy radiation and absorption. Built-up lands possesses lower albedo and higher absorption than barren lands due to the surrounding areas/ barren lands having higher temperatures than urban areas. These outcomes conform to the findings of [], who noticed that areas with bare soil and built-up areas show a higher LST while other categories, such as water bodies, agriculture and vegetation, have lower LST values during daytime. In contrast, during the night built-up and barren lands have lower LST values, while water bodies and vegetation are found to have higher LST values.
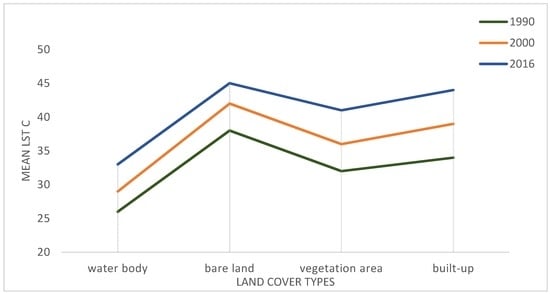
Figure 8.
The differences of mean LST over variations of land cover types in 1990, 2000 and 2016.
The LST of each LULC class therefore depends on its particular characteristic. Weng (2001) [] showed that studying the relationship between land cover types and thermal signatures is the most efficient approach in understanding the way LST is affected by LULC changes. To investigate the connection of LST to NDVI, NDWI and NDBI derived from the Landsat TM-5 1990, 2000 and Landsat OLI_TIRS-8 2016, respectively, a sample point method using 50 randomly selected points was applied. The four transect lines in Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12 and Figure 13 clearly demonstrate the degree of correlation and the relationships of the LST, NDVI, NDWI, NDBI and NDBAI. These relationships were investigated in the performance of the Pearson’s correlation coefficient analysis and correlation analysis. The result shows that lower NDVI and NDWI values were detected in areas characterized by higher temperature and higher NDBI and NDBAI. However, a positive relationship between NDBI and LST existed, with a correlation coefficient of R2 = 0.8714, R2 = 0.848 and R2 = 0.9397 indicated in all images, between NDBI-derived built-up fractions and the surface temperature (LST), as shown in Figure 9. The results of the linear relationship detected a positive correlation between NDBAI-derived bare land fractions and LST with correlation coefficients of R2 = 0.8137, R2 = 0.8027 and R2 = 0.841, as shown in Figure 10.
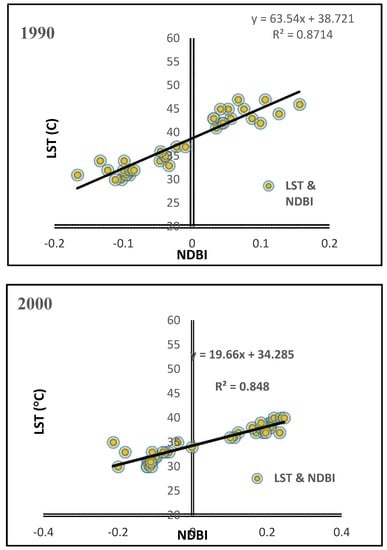
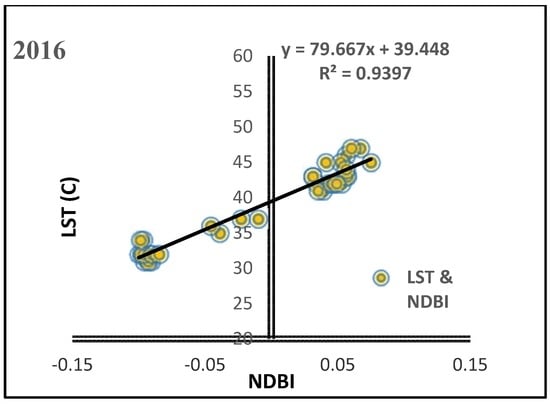
Figure 9.
Correlation between NDBI and LST in the period of the study (1990, 2000 and 2016).
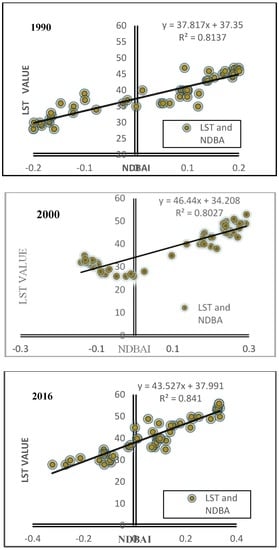
Figure 10.
Correlation between NDBAI and LST in the period of the study (1990, 2000 and 2016).
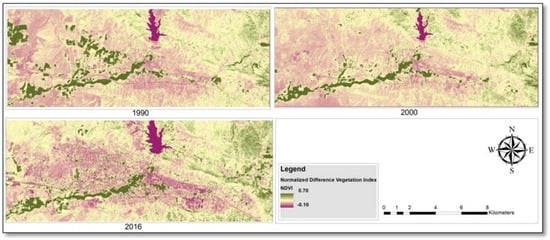
Figure 11.
Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) in 1990, 2000 and 2016.
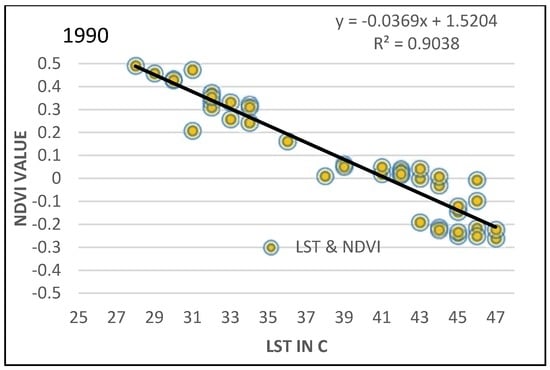
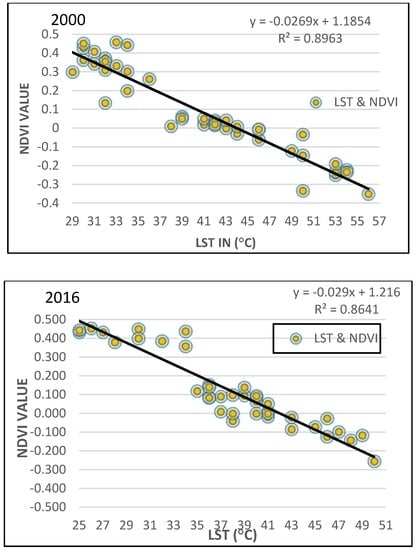
Figure 12.
Correlation between NDVI and LST in the period of the study (1990, 2000 to 2016).
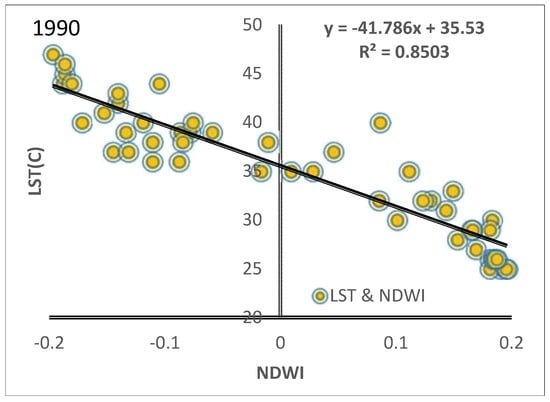
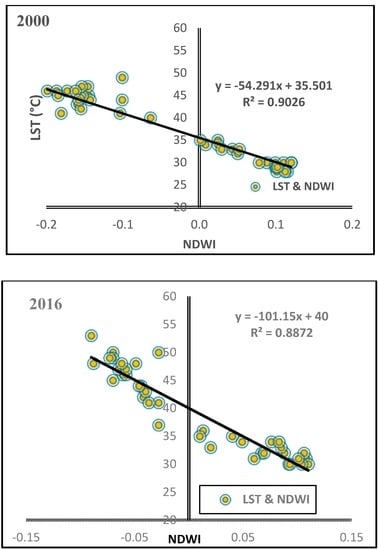
Figure 13.
Correlation between NDWI and LST in the period of the study (1990, 2000 and 2016).
In addition to a negative correlation between NDVI and LST, a negative relationship between LST and NDVI-derived vegetation fractions was shown in the results (Figure 11) of the linear relationship, with the correlation coefficients of R2 = 0.9038, R2 = 0.8641 and R2 = 0.8963 (Figure 12). The linear relationship results detected a negative correlation between NDWI-derived water fractions and LST, with correlation coefficients of R2 = 0.8503, R2 = 0.9026 and R2 = 0.887, as shown in Figure 13. This is a negative correlation with regard to physical changes, ground surfaces, increased soil moisture in the irrigated areas, land surface emissivity, albedo, profusion of vegetation, etc., that has a great effect on the heating of the ground surface []. This study’s results matched the discoveries of [], which leaned towards weak evaporation feedback of bare soils, open shrub lands and a highly possible relation to soil moisture levels. Likewise, [,] regarded lower temperatures in vegetation area due to processes such as transpiration and evapotranspiration.
4. Conclusions
This paper applied, and depends on, multi-temporal remote sensing data to monitor changes in land use/cover and how it impacts the LST in Dohuk City. The applied approaches utilized in this study were very efficient in achieving the aims of this project. The study attempted to identify the changes in land use classes and their effects on LST. The study area was classified into four categories: urban areas, barren land, areas of vegetation and water bodies. The outcome of the land cover classification showed that the built-up areas and water bodies increased by 12.02% and 0.1%, respectively, while the barren land and vegetation decreased by 1.63% and 1.46%, respectively, during the study period, due to political and socio-economic factors. LST and LULC have a strongly connected relationship. The research proved that the LST value varied over the different categories, for example barren land and urban areas had increased radiant temperature. Higher temperatures on the borders and non-built-up areas of the city, rather than inside the city, may disagree with previous studies that reported higher LST values in urban areas than in the areas surrounding and outside of urban areas. This is due to the city’s high temperatures, particularly in the summer. The environment of the city, being semi-arid, is the main reason that urban expansion had the opposite impact on the LST, with alternations in natural and physical characteristics of land cover, including the replacement of vegetation in built-up areas. In addition, the study found that the vegetation area (NDVI) and water bodies (NDWI) have a negative relationship with the land surface temperature. The LST was highly influenced by the LULC, and very sensitive to vegetation and soil moisture; specifically, the amount of vegetation was discovered to be the main factor on which this relationship is built. Higher LST is seen in areas with less vegetated LULC, and vice versa, although it showed a positive relationship between NDBI, NDBAI and LST.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Adegoke, J.O.; Pielke, R.A., Sr.; Eastman, J.; Mahmood, R.; Hubbard, K.G. Impact of irrigation on midsummer surface fluxes and temperature under dry synoptic conditions: A regional atmospheric model study of the US High Plains. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, Y.; Bharath, B.D.; Mallick, J.; Atzberger, C.; Kerle, N. Satellite-based analysis of the role of land use/land cover and vegetation density on surface temperature regime of Delhi, India. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2009, 37, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Bhalla, P.; Palria, S. Remote sensing based analysis of the role of land use/land cover on surface temperature and temporal changes in temperature; A case study of Ajmer District, Rajasthan. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, 8, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, S.; Niyogi, D.; Gluhovsky, A.; Pielke, R.A.; Kalnay, E.; Rochon, G. Impacts of land use land cover on temperature trends over the continental United States: Assessment using the North American Regional Reanalysis. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 1980–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.S.; Bhaskar, P.U.; Padmakumari, K. Estimation of land surface temperature to study urban heat island effect using Landsat ETM+ image. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2012, 4, 771–778. [Google Scholar]
- Buyadi, S.N.A.; Mohd, W.M.N.W.; Misni, A. Impact of land use changes on the surface temperature distribution of area surrounding the National Botanic Garden, Shah Alam. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 101, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. A remote sensing? GIS evaluation of urban expansion and its impact on surface temperature in the Zhujiang Delta, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 1999–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Weng, Q. The impact of land use and land cover changes on land surface temperature in a karst area of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, S.D.; Cheng, M.M.; Shu, Y. Procedia Environmental sciences assess the effect of different degrees of urbanization on land surface temperature using remote sensing images. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, H.J. The Use of Landsat-5 TM Imagery to Detect Urban Expansion and Its Impact on Land Surface Temperatures in The City of Erbil. Iraqi Kurdistan. Master’s Thesis, Leicester University, Leicester, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.B. Introduction to Remote Sensing, 3rd ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Quattrochi, D.A.; Luvall, J.C. Thermal Infrared Remote sensing for analysis of landscape ecological processes: methods and applications. Landsc. Ecol. 1999, 14, 577–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Lu, D.; Schubring, J. Estimation of Land Surface Temperature—Vegetation abundance relationship for urban heat island studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Thermal infrared remote sensing for urban climate and environmental studies: Methods, applications, and trends. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2009, 64, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorovencii, I.; Oprea, L.; Ienciu, I.; Popescu, C. Evaluation of land surface temperature for different land cover using Landsat TM Thermal Infrared band. Ann. West Univ. Timis. Ser. Chem. 2013, 22, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Feizizadeh, B.; Blaschke, T.; Nazmfar, H.; Akbari, E.; Kohbanani, H.R. Monitoring land surface temperature relationship to land use/land cover from satellite imagery in Maraqeh County, Iran. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2013, 56, 1290–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Lagouarde, J.P.; Nerry, F.; Ottlé, C. Land surface temperature retrieval techniques and applications. In Thermal Remote Sensing in Land Surface Processes; Quattrochi, D.A., Luvall, J.C., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 33–109. [Google Scholar]
- Bendib, A.; Dridi, H.; Kalla, M.I. Contribution of Landsat 8 data for the estimation of Land Surface Temperature in Batna city, Eastern Algeria. Geocarto Int. 2016, 6049, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, F.N. Operational space technology for global vegetation assessment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 82, 1949–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Tang, B.H.; Wu, H.; Ren, H.; Yan, G.; Wan, Z.; Trigo, I.F.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite-derived Land Surface Temperature: Current status and perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenstein, O.; Qin, Z.; Derimian, Y.; Karnieli, A. Derivation of Land Surface Temperature for Landsat-8 TIRS using a split window algorithm. Sensors 2014, 14, 5768–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randrianjatovo, R.N.; Rakotondraompiana, S.; Rakotoniaina, S. Estimation of Land Surface Temperature over Reunion Island using the thermal infrared channels of Landsat-8. In Proceeding of the 2014 IEEE Canada International Humanitarian Technology Conference-(IHTC), Montréal, QC, Canada, 1–4 June 2014.
- Shi, T.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Shi, C.E.; Yang, Y.J. Influence of urbanization on the thermal environment of meteorological station: Satellite-observed evidence. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2015, 6, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Zhao, H.M.; Li, P.X.; Yin, Z.Y. Remote sensing image-based analysis of the relationship between urban heat island and land use/cover changes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 104, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Guo, X.; Wu, Z. Land surface temperature retrieval from LANDSAT 8 TIRS-comparison between radiative transfer equation-based method, split window algorithm and single channel method. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9829–9852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, L.; Devadas, M.D. Analysis Of Land Surface Temperature And Land Use/Land Cover Types Using Remote Sensing Imagery—A Case In Chennai city, India. In Proceeding of the Seventh International Conference on Urban Climate, Yokohama, Japan, 29 June–3 July 2009; pp. 1998–2001.
- Fu, P.; Weng, Q. A time series analysis of urbanization induced Land Use and Land Cover change and its impact on Land Surface Temperature with Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Zhou, Q. Utility of Landsat image in the study of Land Cover and Land Surface Temperature change. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.B.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Zheng, H.; Li, W.F.; Schienke, E.W.; Wang, X.K. Spatial pattern of impervious surfaces and their impacts on Land Surface Temperature in Beijing, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Using remote sensing and GIS to detect and monitor Land Use and Land Cover change in Dhaka Metropolitan of Bangladesh during 1960–2005. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 150, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belal, A.A. Detecting urban growth using remote sensing and GIS techniques in Al Gharbiya governorate, Egypt. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2011, 14, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Kumar, S.; Fazal, S. Assessment of Land use/Land Cover Change in the North-West District of Delhi Using remote sensing and gis techniques. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2012, 40, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, W.; Hashim, N.; Thet, K.M. Application of remote sensing and GIS for monitoring urban heat island in Kuala Lumpur Metropolitan area. In Proceedings of the Map Asia 2010 and the International Symposium and Exhibition on Geo-information, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 26–28 July 2010.
- Zurina, M.; Hukil, S. Appraising Good Governance in Malaysia Based on Sustainable Development Values. J. Asian Behav. Stud. Sustain. Sci. Manag. 2012, 7, 247–253. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Tian, G. Analysis of the impact of Land use/Land cover change on Land Surface Temperature with remote sensing. Proc. Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Arthur, S.T. The impact of land Use Land Cover changes due to urbanization on surface microclimate and hydrology: A satellite perspective. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2000, 25, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, R.; Li, F.; Yang, W.; Zhou, C.; Jin, J.; Shi, Y. Simulation of thermal effects due to different amounts of urban vegetation within the built-up area of Beijing, China. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2009, 16, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zeng, S.; Xle, C. Remote Sensing and GIS for urban growth analysis in China. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 593–598. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulla, H.H. Rock Slop Analysis in Duhok Governorate/Bekhair anticline by using GIS technique. J. Al-Nahrain Univ. 2013, 16, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, H.D.; Ali, M.A. Monitoring and prediction of urban growth using GIS techniques: A Case study of Dohuk City Kurdistan Region of Iraq. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2014, 5, 1480–1488. [Google Scholar]
- Koeppe, C.E.; De Long, G.C. Weather and Climate; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, J. Land use and cover change assessment using Remote Sensing and GIS: Dohuk City, Kurdistan, Iraq (1998–2011). Int. J. Geomat. Geosci. 2013, 3, 552–569. [Google Scholar]
- Lillesand, T.; Kiefer, R.W.; Chipman, J. Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Raynolds, M.K.; Comiso, J.C.; Walker, D.A.; Verbyla, D. Relationship between satellite-derived Land Surface Temperatures, arctic vegetation types, and NDVI. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1884–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, A. Monitoring Spatial patterns of Land Surface Temperature and urban heat island for sustainable megacity: A case study of Mumbai, India, using Landsat TM data. Environ. Urban Asia 2016, 7, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, S.Y. The effect of land use on land surface temperature in The Netherlands. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Sensors & Models in Remote Sensing & Photogrammetry, Kish Island, Iran, 23–25 November 2015.
- He, C.; Shi, P.; Xie, D.; Zhao, Y. Improving the normalized difference built-up index to map urban built-up areas using a semiautomatic segmentation approach. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 1, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Zhu, X.; Rahman, M.S.; Choi, K. Simulating land cover changes and their impacts on Land Surface Temperature in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 5969–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Karnieli, A.; Berliner, P. A mono-window algorithm for retrieving land surface temperature from Landsat TM data and its application to the Israel-Egypt border region. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 3719–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Y. Urban heat island analysis using the Landsat TM data and ASTER data: A case study in Hong Kong. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 1535–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-galiano, V.; Pardo-Iguzquiza, E.; Sanchez-Castillo, M.; Chica-Olmo, M.; Chica-Rivas, M. Downscaling Landsat 7 ETM + thermal imagery using Land Surface Temperature and NDVI images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2012, 18, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abas, K.A. Analysis of Climate and Drought Conditions in the Fedral Region of Kurdistan; College of Basic Education, Salahaddin University: Erbil, Iraq, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rogan, J.; Ziemer, M.; Martin, D.; Ratick, S.; Cuba, N.; DeLauer, V. The impact of tree cover loss on Land Surface Temperature: A case study of central Massachusetts using Landsat Thematic Mapper thermal data. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 45, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, W.; Verbeiren, B.; van der Kwast, J.; Van de Voorde, T.; Batelaan, O. Evaluation of the DisTrad thermal sharpening methodology for urban areas. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2012, 19, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, J.O.; Carleton, A.M. Relations between soil moisture and satellite vegetation indices in the US Corn Belt. J. Hydrometeorol. 2002, 3, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanamean, J.R., Jr.; Pielke, R.A., Sr.; Castro, C.L.; Ojima, D.S.; Reed, B.C.; Gao, Z. Vegetation greenness impacts on maximum and minimum temperatures in northeast Colorado. Meteorol. Appl. 2003, 10, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).