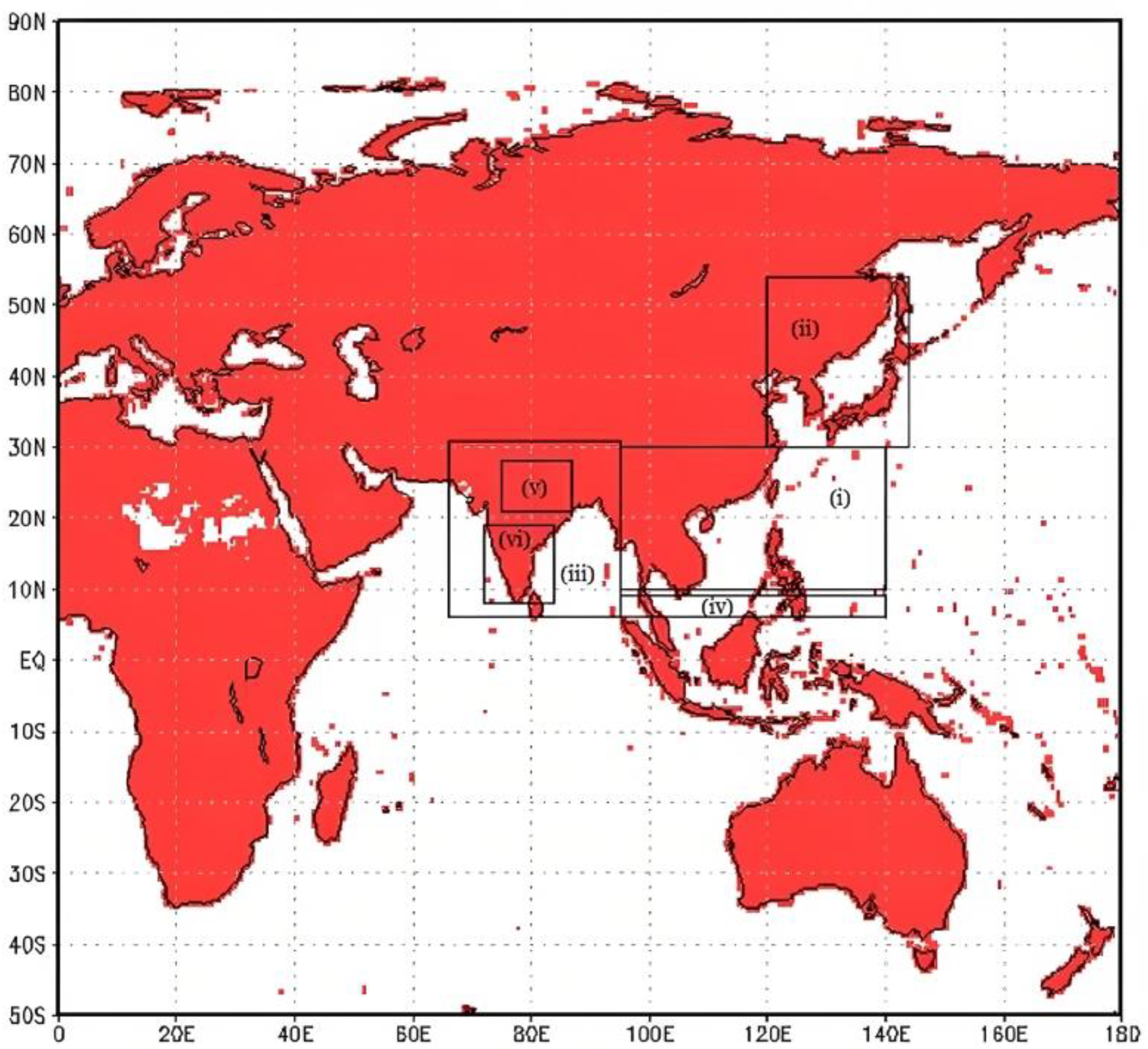
Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) is a narrow band of deep convection playing an important role in the earth’s climate. The outgoing longwave radiation (OLR) data can be used to represent the ITCZ [
1]. The shift of the ITCZ impacts water availability in the tropical regions and thus affects climate change aspects [
2]. The pole ward shift of the ITCZ increases the frequency of tropical cyclones [
3] and quantum of Indian summer monsoon rainfall [
4]. Reference [
5] discussed the behavior of regional ITCZs and regional monsoons and discussed in detail the annual variation of rainfall in the tropics and subtropics and the concept of global monsoon. Several studies have been done on the impact of climate change on rainfall pattern [
6,
7,
8] but there are very limited studies on the impact of climate change on food availability [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13]. Reference [
14] has studied the presence of strong regional circulation namely Hadley circulation zone over the Indian Ocean (HCIO) which has a deep impact on the dynamics of rainfall potential in summer monsoon. A teleconnection among the summer monsoon rainfall, ENSO (El Nino-Southern Oscillation) and IOD (Indian Ocean dipole) parameters and the rice production of certain regions has been studied recently [
15]. Asia continent shares about 90% of the rice production across the globe [
16,
17] and 50% of the global population depends on rice as staple food [
18]. There are various factors of crop production viz., crop seed variety or genetic characteristics of the crop, climate, terrain, soil properties, irrigation facility or rainfall sufficiency, nutrients availability (fertilizer and manure management), insect-pest-pathogen management etc. [
19]. Reference [
20] has studied in detail the yield gap analysis in rice crop in southwest China with multiple factors of production and reported that the rice yield gap has been found to be positively correlated with sunshine hour, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer and negatively correlated with soil available nitrogen content. Thus extensive studies and experiments have been conducted for assessing sensitivity of the rice crop to multiple factors including climatic and non-climatic factors. Reference [
21] has studied the impact of climatic factor in rice yield of Cambodia and it was reported that three climatic variables viz., maximum temperature, minimum temperature and rainfall explain approximately 63% and 56% of rice yield variability in wet and dry season, respectively and they further reported that the contributions of climatic factor and non-climatic factor in rice yield variability of Cambodia are 60% and 40%, respectively. Besides, the air temperature is the main factor among climatic factors impacting the growth of rice crop [
22] because the source of air temperature is solar radiation which also controls the sunshine hour and nutrient mobility in soil. The impact of cloud cover on satellite images of rice producing areas of China has been discussed in the context to maximize its production [
23]. In another study, rice yield variability of Asia due to climate change and ozone layer depletion has been studied [
24]. Thus few studies have been conducted on the impact of climatic and non-climatic factors on rice yield on regional scale. In the context of climate change scenario, there are many standardized management practices to cope with other non-climate factors of production of rice and those standardized management practices are well within the ambit of research & development of modern agricultural sciences. Comparatively, climatic factors are exerting unprecedented challenges in climate change scenario where neo normal of the climatic variables has been challenging the long term mean or pattern of those variables. In reality, many rice growing regions are found with suitable or favourable (or non- suitable/unfavourable) climatic factors but with non-suitable or unfavourable (or suitable/favourable) non-climatic factors and vice versa. In practice, it is easy to ameliorate the unfavourable non-climatic factors vis-à-vis a favourable climatic factors applying various scientific and technical innovative approaches like fertilizer and manure management, irrigation management, integrated nutrient and pest management (INPM) techniques, bio-control, precision farming, improved or genetically engineered planting materials or seed etc. But in case of unfavourable climatic factors it is not so easy to ameliorate the negative impact of climatic factors even in presence of favourable non-climatic factors. This inequality of impact of factors of production is also present in rice crop. Even though, various novel techniques for irrigation facility like drip irrigation, sprinkler irrigation, flood or splash irrigation techniques, zero tillage techniques etc may ameliorate the impact of less rainfall but mitigating the impact of air temperature is not convincing one in rice crop. The unfavourable climatic factors trigger a gradual change in genetic makeup of the rice crop as part of its climate adaptation tendency. This complexity of impact of unfavourable climate on rice production thus poses a serious concern for natural adaptation in rice crop biology in the near future. Thus the rice cultivars of various zones of the world under climate change scenario are being exposed to various degree of climatic adaptation. Therefore, there is a requirement of assessing the trend of climatic suitability only of rice crop production in major rice producing zones irrespective of its present rice crop production in a varied interplay of climatic and non-climatic factors. Thus the present study has been limited its scope with assessment of the role of climatic factors on rice and the agro-climatic suitability of rice has been assessed based on climatic parameters only. No study has been done yet on the major rice producing zones of Asia to investigate the pattern and trend of deep convective activity in ITCZ and its relation with major climatic variables in rice. The present study explores the relationship between the OLR parameter representing the ITCZ and the various climatic variables like temperatures (maximum, minimum, mean), precipitation, cloud cover for major rice growing regions. Broad physiological suitability criteria of agro-climate of rice growth has been assessed in this study.