Energy-Efficient Packet Relaying in Wireless Image Sensor Networks Exploiting the Sensing Relevancies of Source Nodes and DWT Coding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Fundamental Concepts
3.1. Packet Relaying and Energy Consumption





3.2. Sensing Relevance
| Group of Relevance | SR(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Irrelevant | 0 | When the source node has no relevance for the application. Source sensors should turn off their camera’s hardware, acting only as relay nodes. |
| Low relevance | 1–4 | Source sensors are transmitting complementary visual information with low impact to the application monitoring quality. |
| Medium relevance | 5–10 | This is the initial relevance group, when source nodes are turned on. The transmitted information is relevant, but some quality loss can be accepted. |
| High relevance | 11–14 | Some sensors will have higher relevance for the application, requiring prioritized treating in packet processing, congestion control, error recovery and multipath selection algorithms. |
| Maximum relevance | 15 | This is the highest level of relevance that should be attributed to a very small group of source sensors, if any. Monitoring quality is highly dependent on visual data transmitted by these source nodes. |
| Approach | Advantages | Drawbacks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deterministic establishment of the groups of relevance. Source nodes are assigned to a GR before deployment. | No computational costs.Source nodes are statically assigned to a group of relevance. | Useful only for deterministic deployment. May not adapt to changes in the network topology and in the targets positions. | |
| Visual identification of the groups of relevance by a human operator. | Sensing relevancies of source nodes strongly reflect the application requirements. Minimal computational costs. | Requires a human operator to interpret the visual information retrieved from the monitored field.Subject to unconscious psychological factors [35]. | |
| Automatic | Computer vision algorithms are employed to identify the targets viewed by source nodes. The GR is indirectly established according to the relevance of the targets. | Automatic establishment of sensing relevancies very close to the application requirements. | High computational cost. Depends on the nature of the targets and the monitored field. |
| Mathematical analyses and localization algorithms are used to identify areas of interest. The GR is established if source nodes view the defined area. | Groups of relevance may be established for regions.Provides a very acceptable solution, with low cost. | Depends on camera-enabled node localization algorithms.More suitable for scene/area monitoring [5]. |
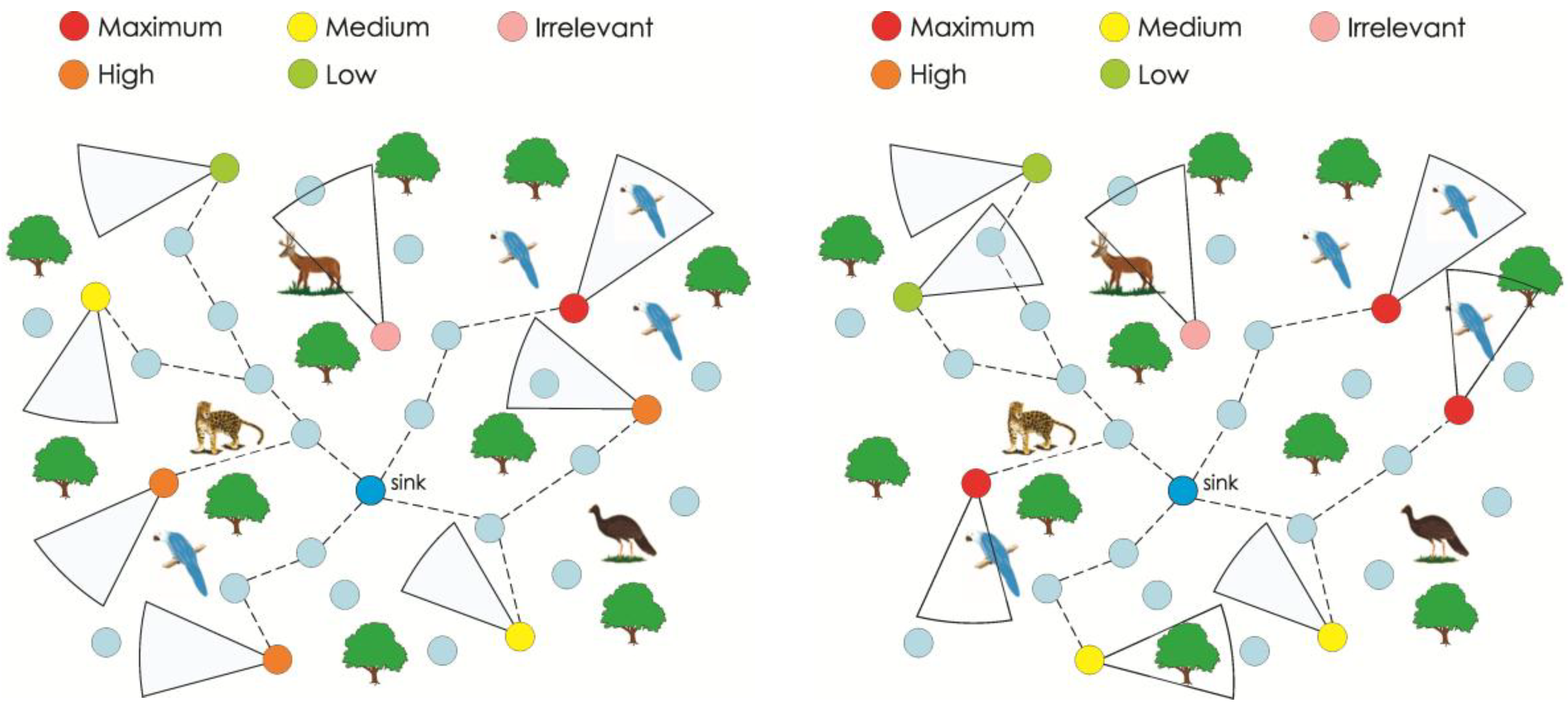
4. Proposed Energy-Efficient Relaying Mechanism
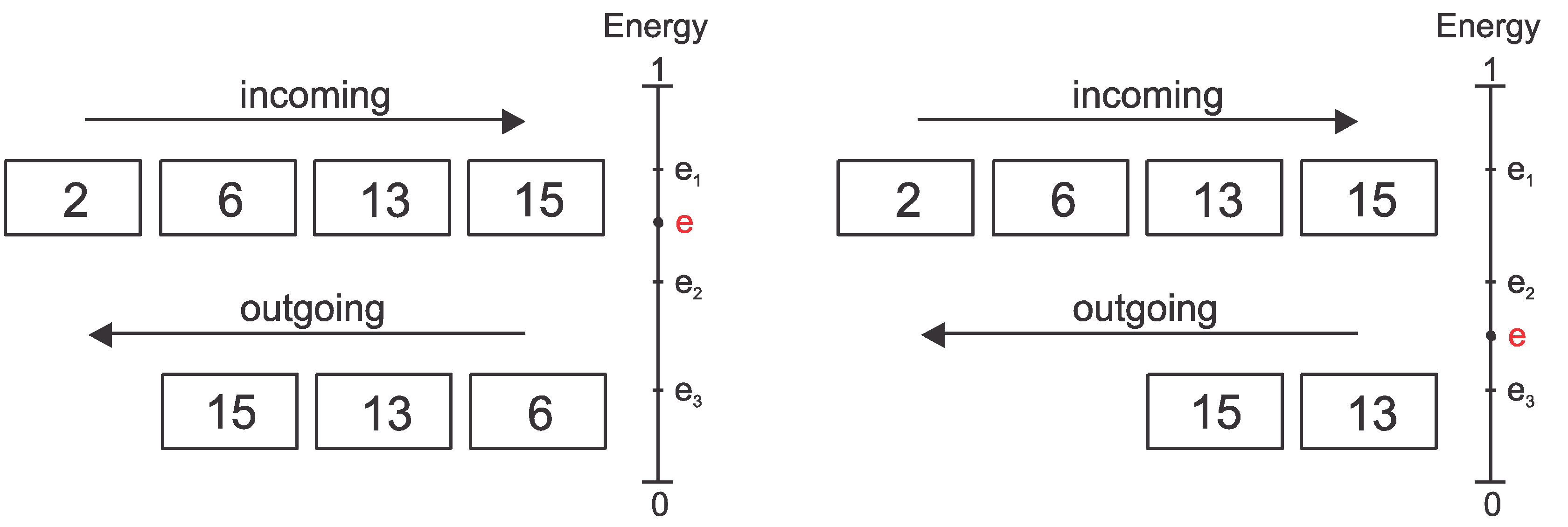
4.1. SR-Based Packet Relaying
| Energy Level | Packets that MUST be relayed to the next hop | |
|---|---|---|
| Group of Relevance | SR | |
| e ≥ e1 | All packets | 1–15 |
| e2 ≤ e < e1 | Medium, high and maximum relevance packets | 5–15 |
| e3 ≤ e < e2 | High and maximum relevance packets | 11–15 |
| e < e3 | Maximum relevance packets | 15 |
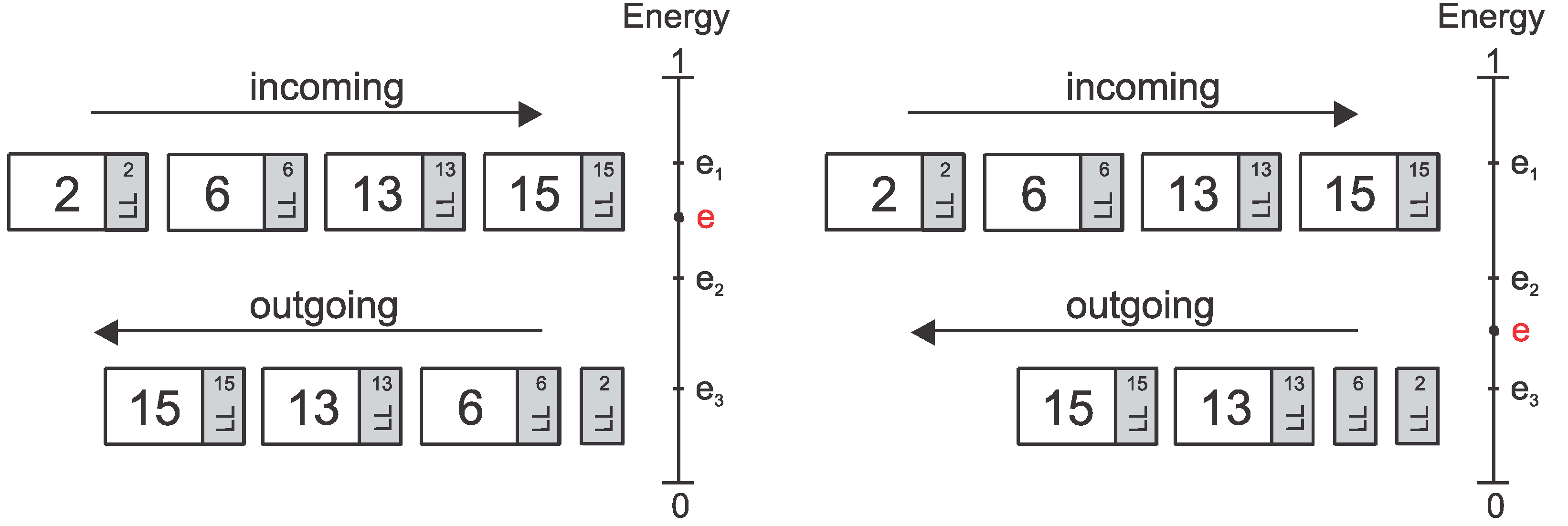
4.2. SR and DWT-Based Packet Relaying
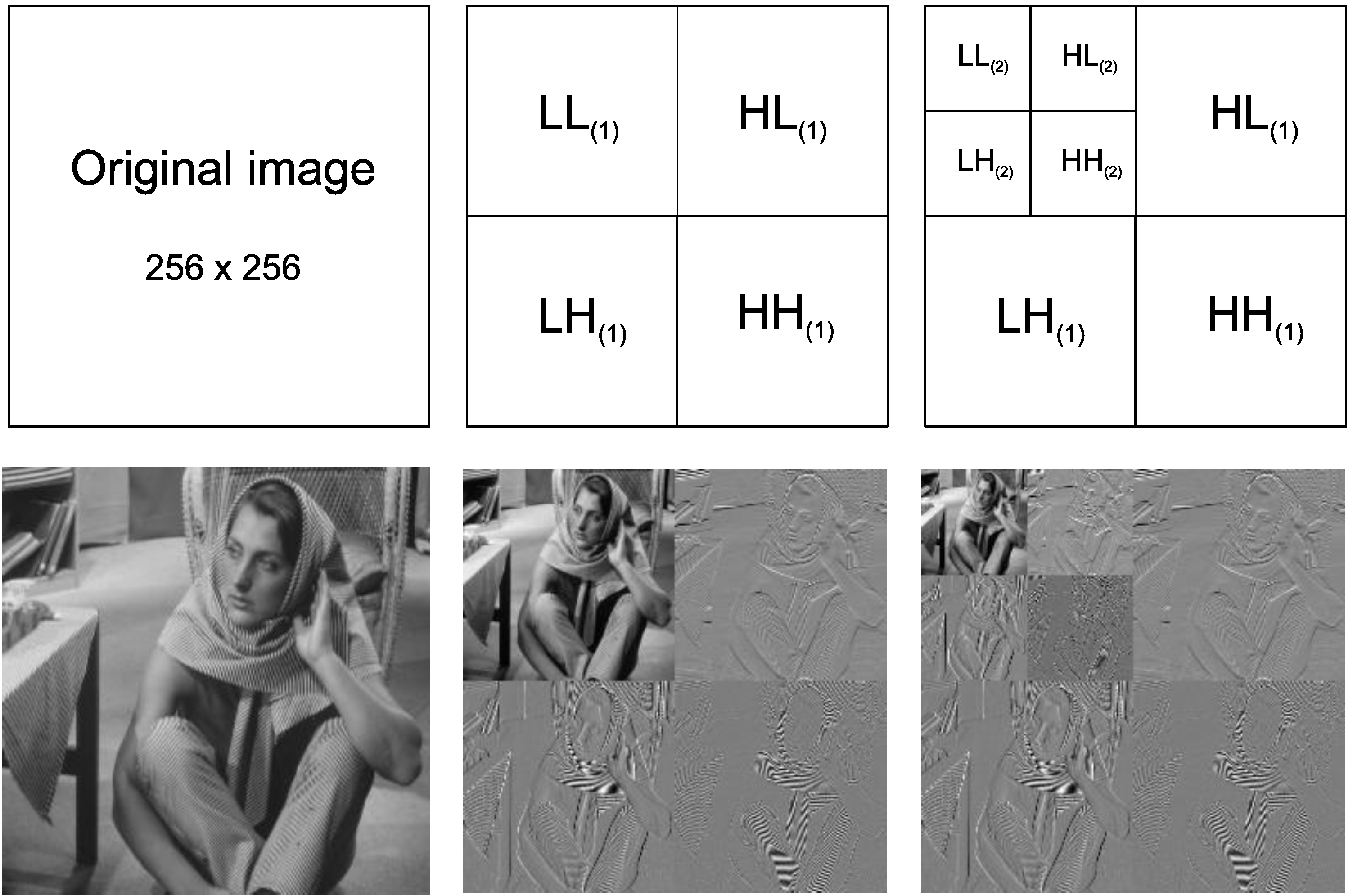
| DWT Subband | DR |
|---|---|
| HH | 0 |
| HL | 1 |
| LH | 2 |
| LL | 3 |
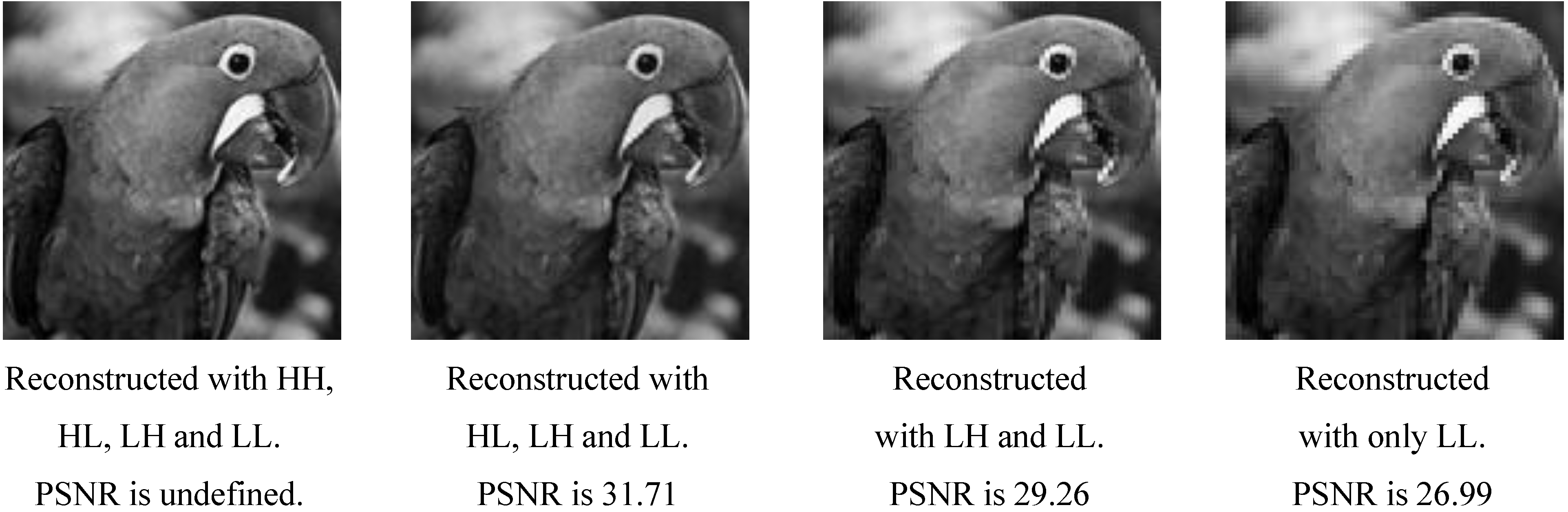

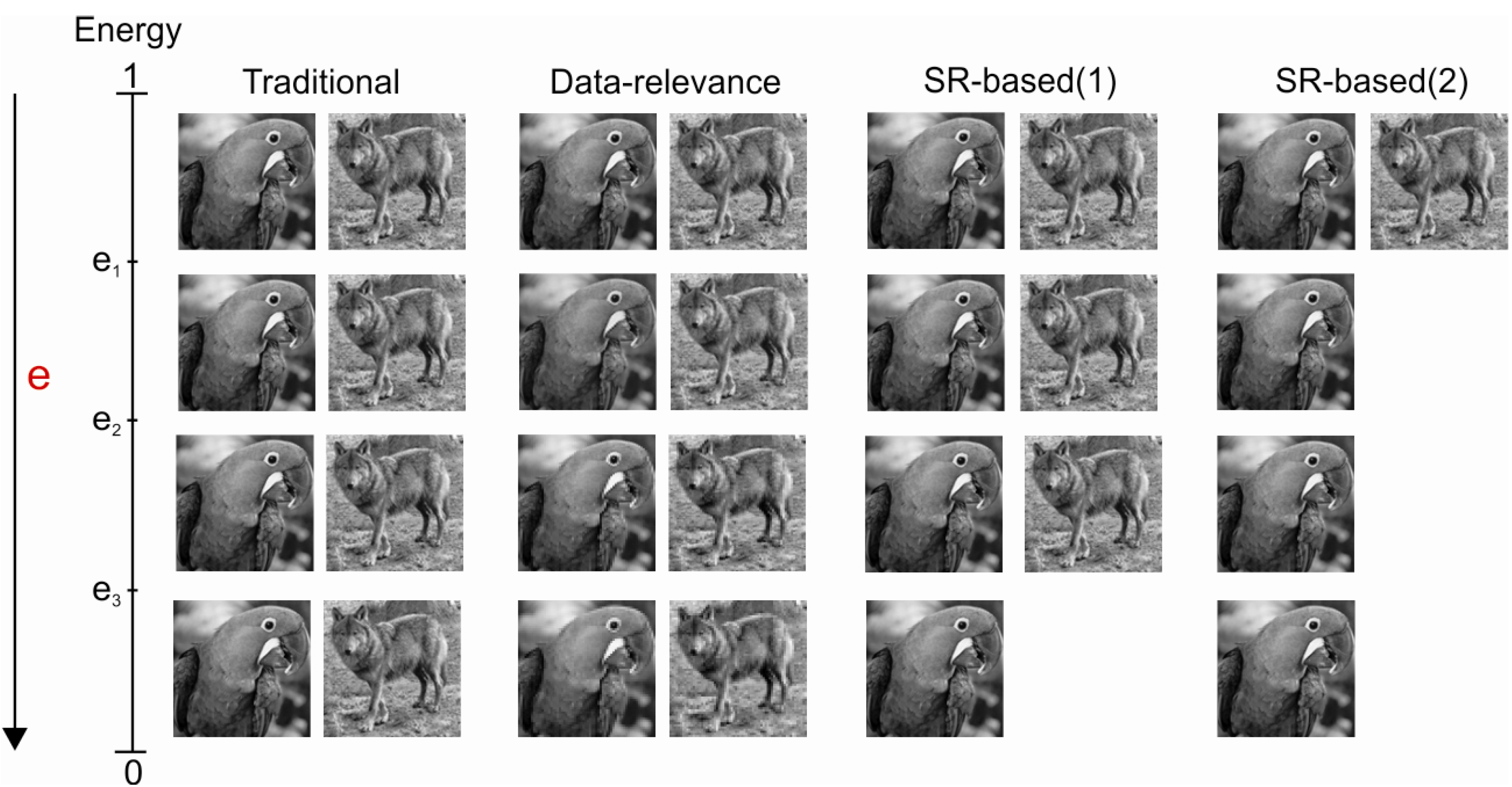
5. Simulation Results
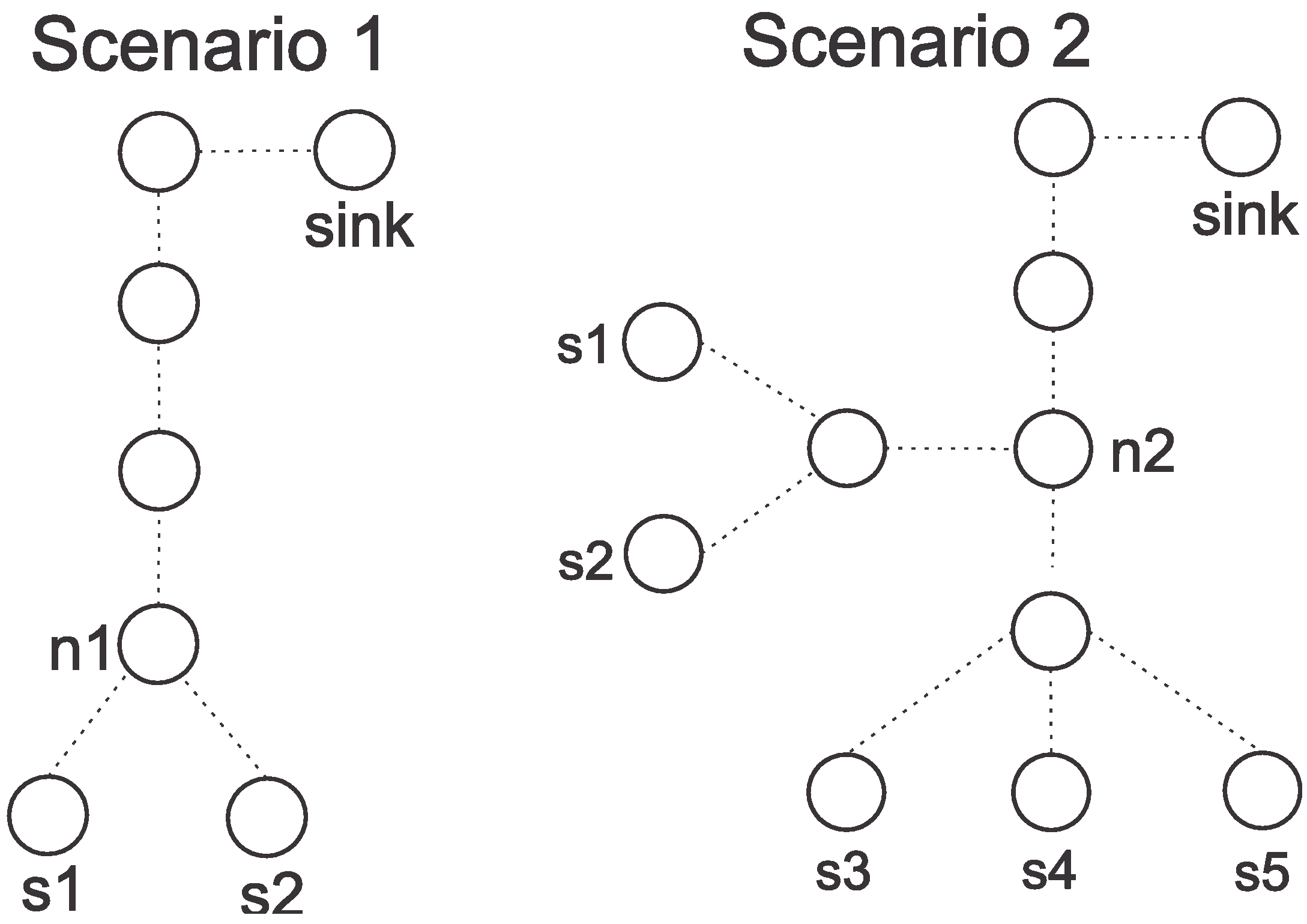
| Configuration of the Sources | SR(1) | SR(2) | SR(3) | SR(4) | SR(5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR-based(1) | 15 | 12 | - | - | - |
| SR-based(2) | 15 | 3 | - | - | - |
| SR-DWT-based(2) | 15 | 3 | - | - | - |
| SR-based(3) | 7 | 15 | 11 | 15 | 8 |
| SR-based(4) | 2 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 15 |
| SR-DWT-based(4) | 2 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 15 |
| SR-based(5) | 6 | 9 | 15 | 8 | 7 |
| Energy Level | Packets that MUST be relayed to the next hop | |
|---|---|---|
| DR | DWT Subband | |
| e ≥ e1 | 0, 1, 2 and 3 | HH, HL, LH and LL |
| e2 ≤ e < e1 | 1, 2 and 3 | HL, LH and LL |
| e3 ≤ e < e2 | 2 and 3 | LH and LL |
| e < e3 | 3 | LL |
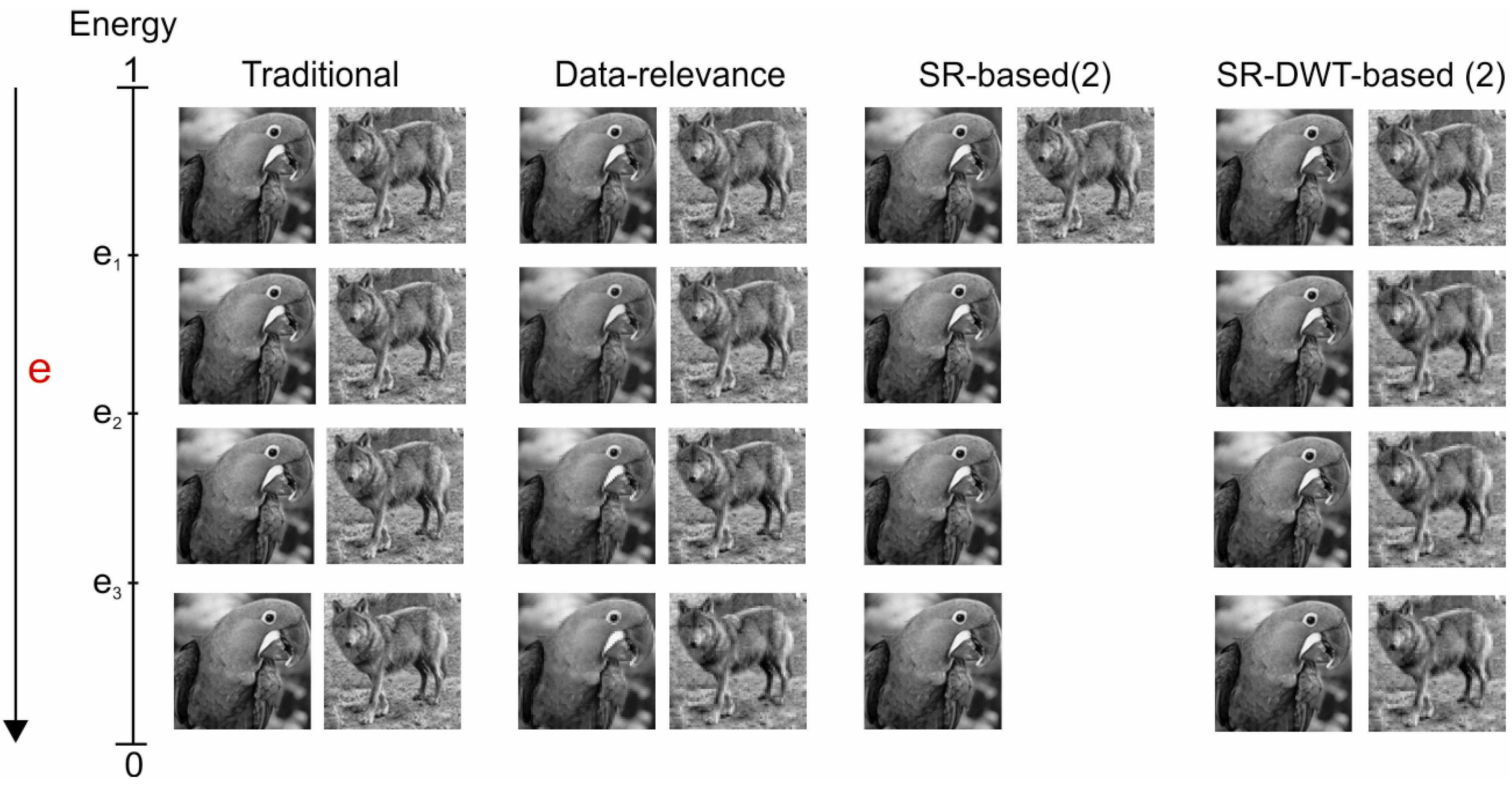


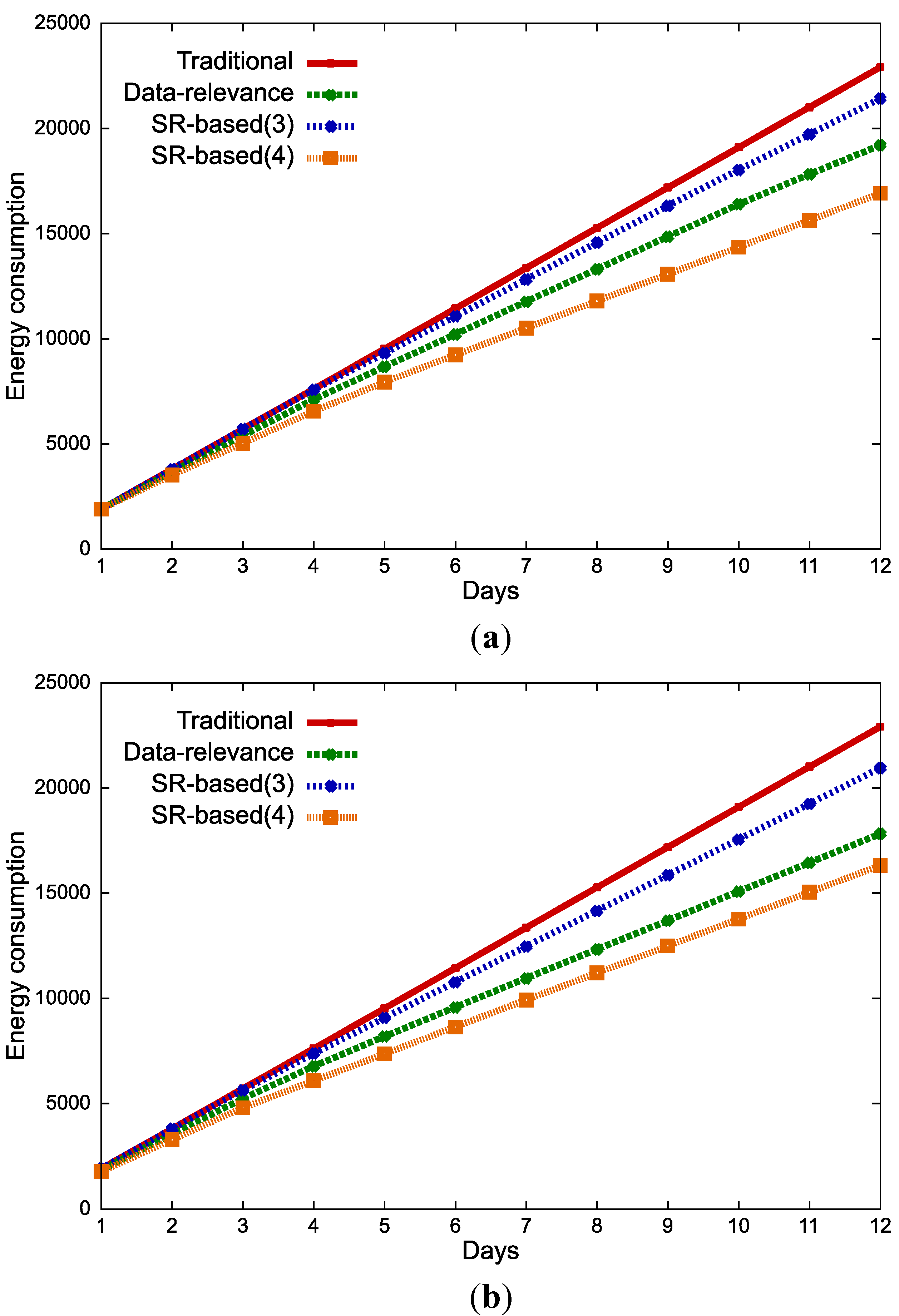

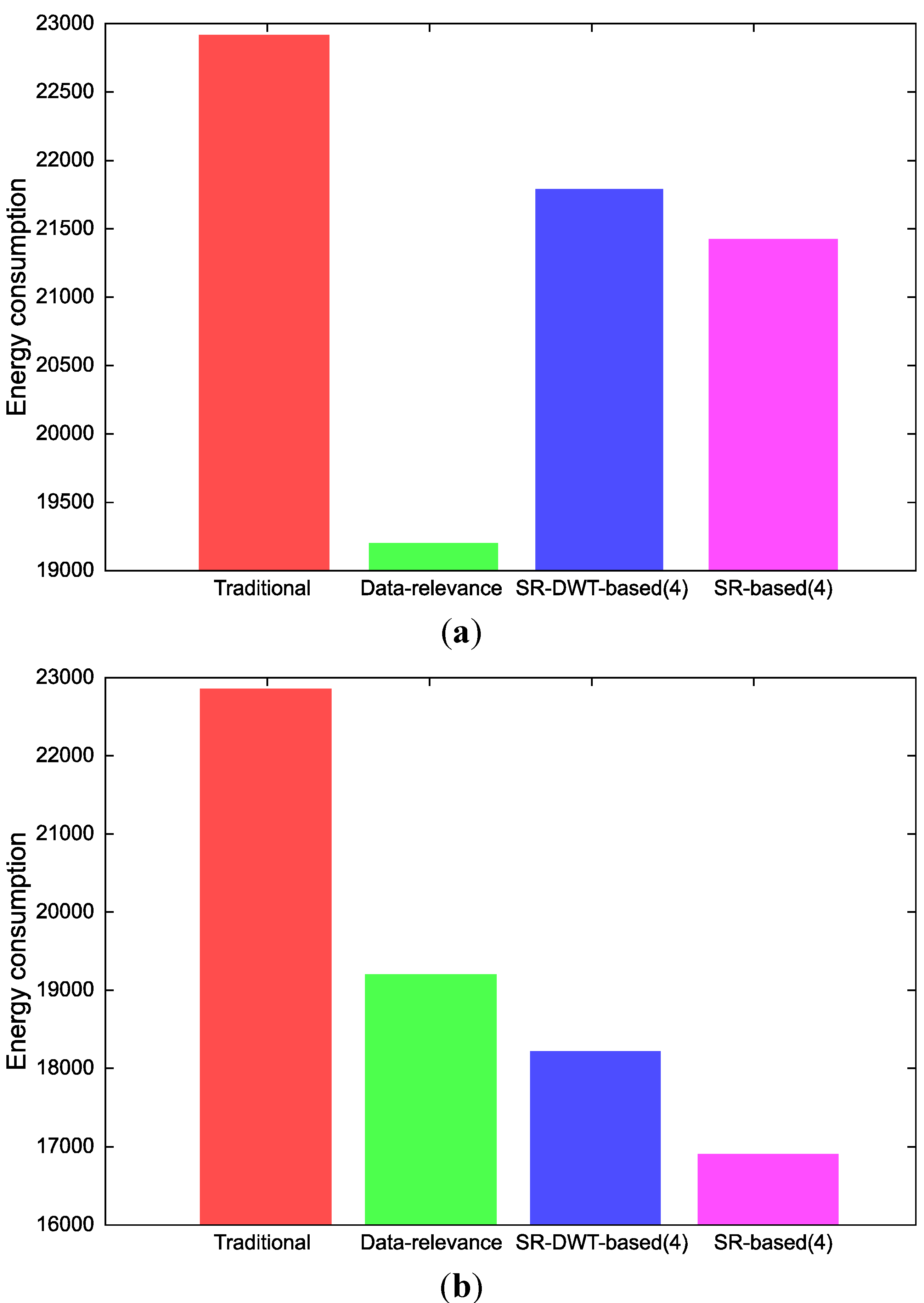

6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Akyildiz, I.; Su, W.; Sankarasubramaniam, Y.; Cayirci, E. Wireless sensor networks: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2002, 38, 393–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baronti, P.; Pillai, P.; Chook, V.; Chessa, S.; Gotta, A.; Hu, Y. Wireless sensor networks: A survey on the state of the art and the 802. 15.4 and ZigBee standards. Comput. Commun. 2006, 30, 1655–1695. [Google Scholar]
- Soro, S.; Heinzelman, W. A survey of visual sensor networks. Adv. Multimed 2009, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charfi, Y.; Canada, B.; Wakamiya, N.; Murata, M. challenging issues in visual sensor networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2009, 16, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.; Guedes, L. The coverage problem in video-based wireless sensor networks: A survey. Sensors 2010, 10, 8215–8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalkawi, I.; Zapata, M.; Al-Karaki, J.; Morillo-Pozo, J. Wireless multimedia sensor networks: Current trends and future directions. Sensors 2010, 10, 6662–6717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.; Guedes, L.; Vasques, F.; Portugal, P. Effect of Frame Size on Energy Consumption in Wireless Image Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Conference on Imaging Systems and Techniques (IST), Manchester, UK, 16–17 July 2012; pp. 239–244.
- Qaisar, S.; Radha, H. Multipath Multi-stream Distributed Reliable Video Delivery in Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of 43rd Annual Conference on Proceeding of the Information Sciences and Systems, CISS 2009, Baltimore, MD, USA, 18–20 March 2009; pp. 207–212.
- Lecuire, V.; Duran-Faundez, C.; Krommenacker, N. Energy-efficient transmission of wavelet-based images in wireless sensor networks. EURASIP J. Image Video Process 2007, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghmaee, M.; Adjeroh, D. A New Priority Based Congestion Control Protocol for Wireless Multimedia Sensor Networks. In Proceeding of the WoWMoM 2008. 2008 International Symposium on a World of WirelessMobile and Multimedia Networks, Newport Beach, CA, USA, 23–26 June 2008; pp. 1–8.
- Lee, J.-H.; Jun, I.-B. Adaptive-compression based congestion control technique for wireless sensor networks. Sensors 2010, 10, 2919–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Jamieson, K.; Balakrishnan, H.; Morris, R. SPAN: An energy efficient coordination algorithm for topology maintenance in ad hoc wireless networks. Wirel Netw. 2002, 8, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.; Guedes, L. Exploiting the sensing relevancies of source nodes for optimizations in visual sensor networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2013, 64, 549–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, K.-Y.; Lui, K.-S.; Lam, E. Achieving 3600 Angle Coverage with Minimum Transmission Cost in Visual Sensor Networks. In Proceedings IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Cancun, Mexico, 28–31 March 2011; pp. 4112–4116.
- Ai, J.; Abouzeid, A. Coverage by directional sensors in randomly deployed wireless sensors networks. J. Comb. Optim. 2006, 11, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politis, I.; Tsagkaropoulos, M.; Dagiuklas, T.; Kotsopoulos, S. Power efficient video multipath transmission over wireless multimedia sensor networks. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2008, 13, 274–284. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, D.; Guedes, L. A survey on multimedia-based cross-layer optimization in visual sensor networks. Sensors 2011, 11, 5439–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.; Guedes, L.; Vasques, F.; Portugal, P. Energy-Efficient Visual Monitoring Based on the Sensing Relevancies of Source Nodes for Wireless Image Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium, Brescia, Italy, 7–9 February 2012; pp. 1–6.
- Costa, D.; Guedes, L.; Vasques, F.; Portugal, P. A Semi-Reliable Energy-Efficient Retransmission Mechanism Based on the Sensing Relevancies of Source Nodes for Wireless Image Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems, Paris, France, 28–31 August 2012; pp. 506–510.
- Maimour, M.; Pham, C.; Amelot, J. Load Repartition for Congestion Control in Multimedia Wireless Sensor Networks with Multipath Routing. In Proceedings of International Symposium on Wireless Pervasive Computing, Santorini, Greece, 7–9 May 2008; pp. 11–15.
- Yu, W.; Sahinoglu, Z.; Vetro, A. Energy Efficient JPEG 2000 Image Transmission over Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of Globecom, Dallas, TX, USA, 29 November–3 December 2004; pp. 2738–2743.
- Akyildiz, I.; Melodia, T.; Chowdhury, K. A survey on wireless multimedia sensor networks. Comput. Netw. 2007, 51, 921–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hauswirth, M.; Shu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Reynolds, V.; Han, G. Multi-Priority Multi-Path Selection for Video Streaming in Wireless Multimedia Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of International Conference on Ubiquitous Intelligence and Computing, Oslo, Norway, 23–25 June 2008; pp. 439–452.
- Costa, D.; Guedes, L. A discrete wavelet transform (DWT)-based energy-efficient selective retransmission mechanism for wireless image sensor networks. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2012, 1, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, T.; Langendoe, K. An Adaptive Energy-Efficient MAC Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 5–7 November 2003; pp. 171–180.
- Heinzelman, W.; Chandrakasan, A.; Balakrishnan, H. An application-specific protocol architecture for wireless microsensor networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2002, 1, 660–670. [Google Scholar]
- Bajaber, F.; Awan, I. Adaptive decentralized re-clustering protocol for wireless sensor networks. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 2011, 77, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, J.; Wang, Y. Effect of Packet Size on Loss Rate and Delay in Wireless Links. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 13–17 March 2005; pp. 1608–1613.
- Pekhteryev, G.; Sahinoglu, Z.; Orlik, P.; Bhatti, G. Image Transmission over IEEE 802.15.4 and ZigBee Networks. In Proceeding of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Kobe, Japan, 23–26 May 2005; pp. 539–3542.
- Wu, H.; Abouzeid, A. Error resilient image transport in wireless sensor networks. Comput. Netw. 2006, 50, 2873–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecuire, V.; Duran-Faundez, C.; Krommenacker, N. Energy-efficient image transmission in sensor networks. Int. J. Sens. Netw. 2008, 4, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Latré, B.; Mil, P.; Moerman, I.; Dhoedt, B.; Demeester, P. Throughput and delay analysis of unslotted IEEE 802.15.4. J. Netw. 2006, 1, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Peng, W. Minimizing energy consumptions in wireless sensor networks via two-modal transmission. ACM SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 2010, 40, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Lee, S. Efficient Packet Error Rate Estimation in Wireless Networks. In Proceedings of Conference on Testbeds and Research Infrastructure for the Development of Networks and Communities, Orlando, FL, USA, 21–23 May 2007; pp. 1–9.
- Brooks, P.; Hestnes, B. User measures of quality of experience: Why being objective and quantitative is important. IEEE Netw. 2010, 24, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, D.; Govindan, R.; Shenker, S.; Estrin, D. Highly-resilient, energy-efficient multipath routing in wireless sensor networks. Mob. Comput. Commun. Rev. 2001, 4, 10–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tselishchev, Y.; Boulis, A.; Libman, L. Experiences and Lessons from Implementing a Wireless Sensor Network MAC Protocol in the Castalia Simulator. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Sydney, Australia, 18–21 April 2010; pp. 1–6.
- Costa, D.; Guedes, L.; Vasques, F.; Portugal, P. QoV: Assessing the Monitoring Quality in Visual Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the2012 IEEE 8th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile ComputingNetworking and Communications (WiMob), Barcelona, Spain, 8–10 October 2012; pp. 667–674.
- Tavli, B.; Bicakci, K.; Zilan, R.; Barcelo-Ordinas, J. A survey of visual sensor network platforms. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2012, 60, 689–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seema, A.; Reisslein, M. Towards efficient wireless video sensor networks: A survey of existing node architectures and proposal for A Flexi-WVSNP design. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tut. 2011, 13, 462–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, S.; Reisslein, M. Low-memory wavelet transforms for wireless sensor networks: A tutorial. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tut. 2011, 13, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, D.G.; Guedes, L.A.; Vasques, F.; Portugal, P. Energy-Efficient Packet Relaying in Wireless Image Sensor Networks Exploiting the Sensing Relevancies of Source Nodes and DWT Coding. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2013, 2, 424-448. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan2030424
Costa DG, Guedes LA, Vasques F, Portugal P. Energy-Efficient Packet Relaying in Wireless Image Sensor Networks Exploiting the Sensing Relevancies of Source Nodes and DWT Coding. Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks. 2013; 2(3):424-448. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan2030424
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Daniel G., Luiz Affonso Guedes, Francisco Vasques, and Paulo Portugal. 2013. "Energy-Efficient Packet Relaying in Wireless Image Sensor Networks Exploiting the Sensing Relevancies of Source Nodes and DWT Coding" Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks 2, no. 3: 424-448. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan2030424
APA StyleCosta, D. G., Guedes, L. A., Vasques, F., & Portugal, P. (2013). Energy-Efficient Packet Relaying in Wireless Image Sensor Networks Exploiting the Sensing Relevancies of Source Nodes and DWT Coding. Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks, 2(3), 424-448. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan2030424








