T-Way Combinatorial Testing Strategy Using a Refined Evolutionary Heuristic
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Combinatorial Testing
1.2. Two-Way Combinatorial Testing Strategy
- Some tools only support generating test suites for two-way combinatorial testing strategy, potentially missing 10% to 40% or more of potential defects, which is unacceptable for critical, safety, and high-reliability scenarios.
- A small number of tools can construct combinatorial test suites within a reasonable computation time, but the results may not be optimal. More efficient algorithms are needed to improve the test suites’ quality and reduce the computation time.
- Existing tools lack interactive features and combinatorial statistical features [17]. During actual test execution, it may not be necessary to run all test cases completely, but combinatorial coverage information is crucial for fault analysis and problem localization.
1.3. Deterministic and Non-Deterministic Testing Strategy
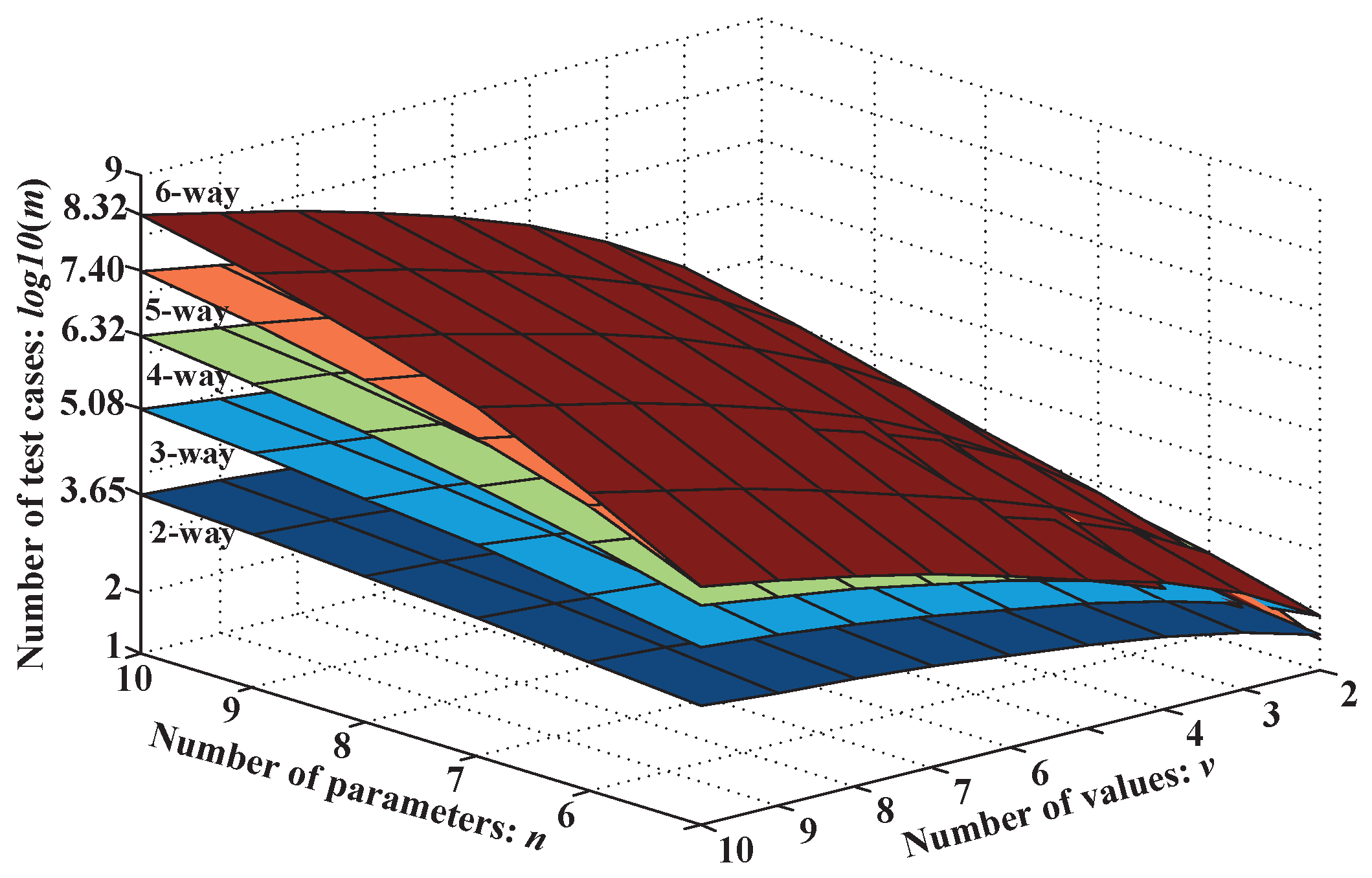
- Establishing a t-way combinatorial coverage model (t-wCCM), defining the t-way combinations coverage function and coverage criterion, and quantitatively analyzing the approximate size of the t-way combinatorial test suite.
- Proposing a refined evolutionary heuristic (REH) algorithm that optimizes the generation of the combinatorial test suite step by step, utilizing an adaptive evolutionary mechanism to accelerate computational convergence efficiency.
2. Mathematical Modeling
2.1. t-Way Combinatorial Testing Strategy
2.2. Logical Combination Index Table
| Algorithm 1 Pseudocode for LCIT construction algorithm. |
| Require: Combination strength t, parameter set , value sets |
| Ensure: LCIT for t-way combinations |
|
2.3. Mathematical Modeling
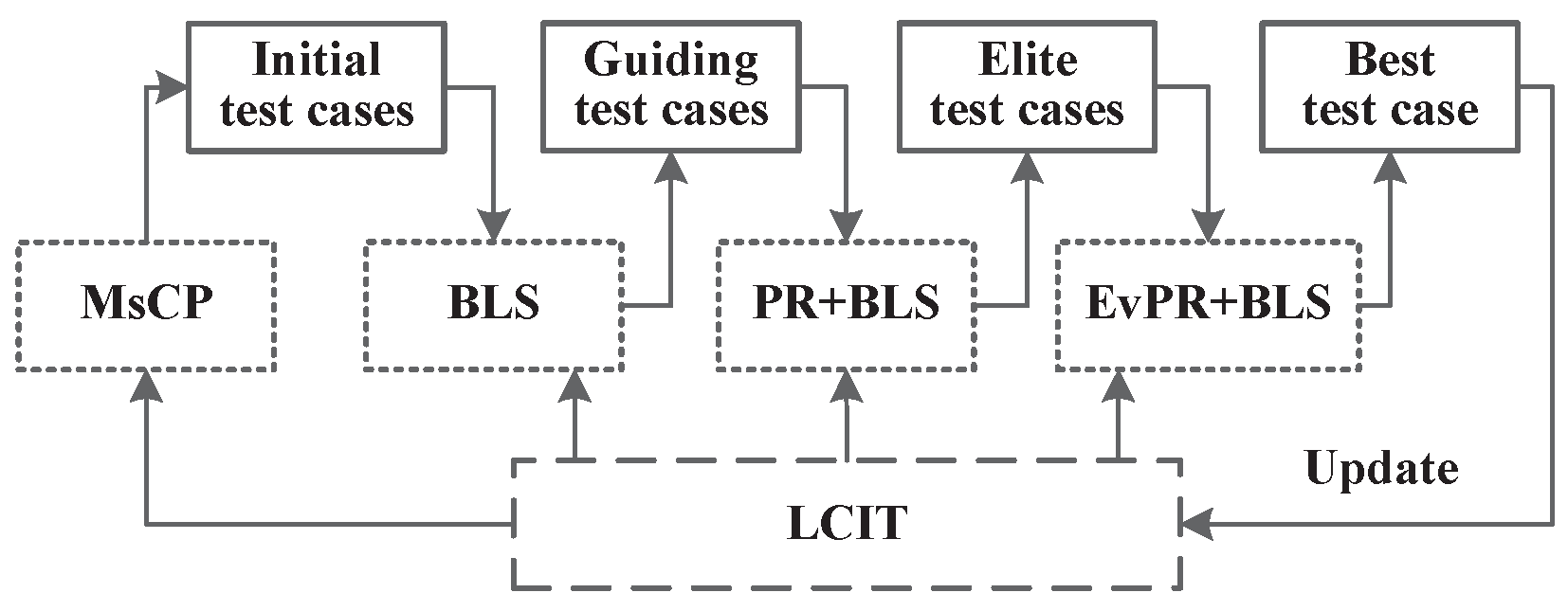
3. Refined Evolutionary Heuristic
3.1. Multi-Start Construction Procedure Algorithm
| Algorithm 2 Pseudocode for multi-start construction procedure (MsCP) algorithm. |
| Require: Parameter set , value sets , number of initial solutions m |
| Ensure: Initial solutions , t-way combinations coverage weights |
|
3.2. Balanced Local Search Algorithm
| Algorithm 3 Pseudocode for Balanced Local Search (BLS) algorithm. |
| Require: Parameter set P, value sets , number of initial solutions m, initial solution set , t-way combinations coverage weights |
| Ensure: Guiding solution set , t-way combinations coverage weights |
|
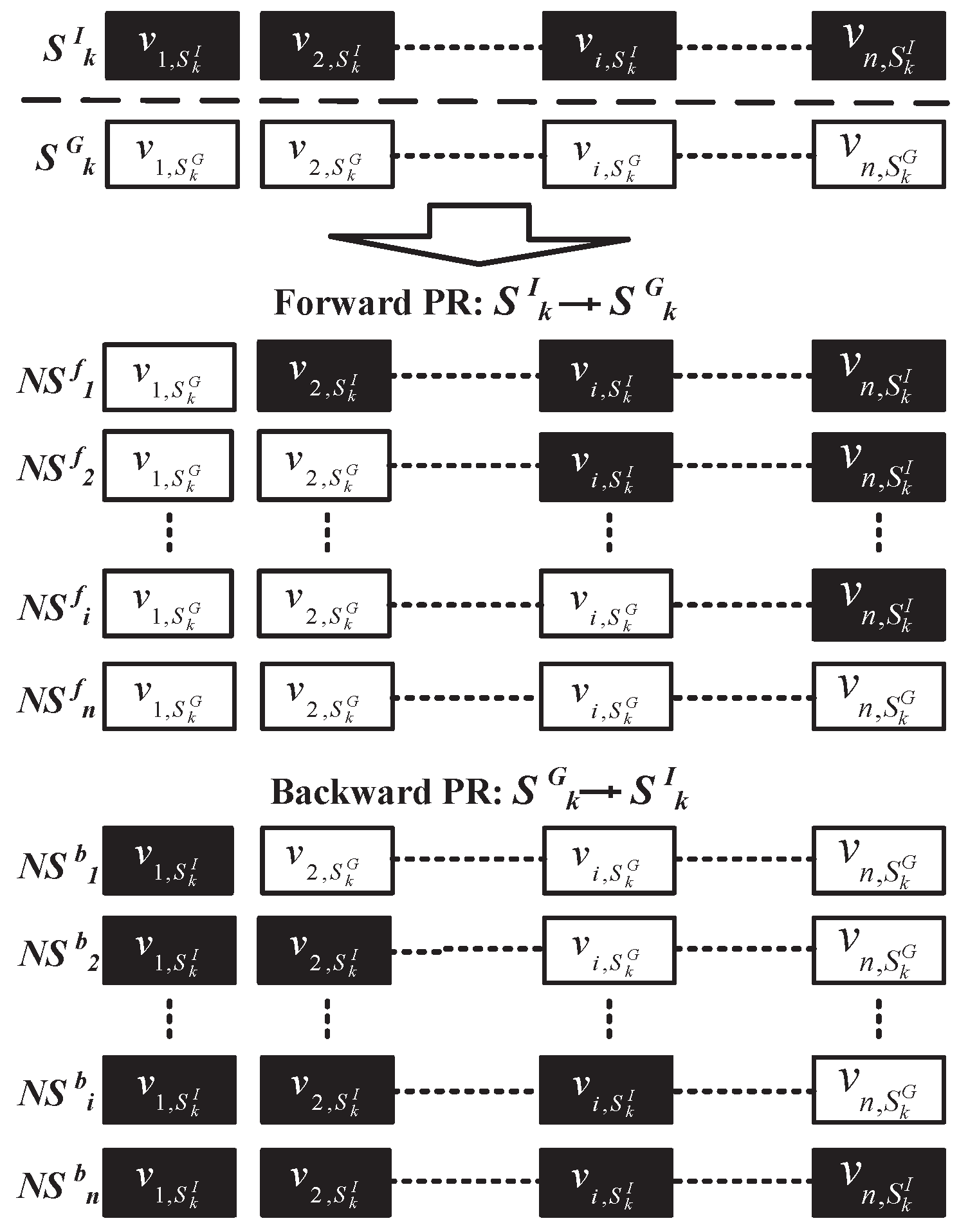
3.3. Path Relinking Algorithm
3.4. Evolutionary Path Relinking Algorithm
| Algorithm 4 Pseudocode for Evolutionary Path Relinking Algorithm (EvPR + BLS). |
| Require: Parameter set P, value sets , elite solution set , t-way combinations coverage weights , current optimal solution set , t-way combinations coverage weights |
| Ensure: New optimal solution set , t-way combinations coverage weights |
|
4. Performance Evaluation
4.1. Test Suite Size Analysis
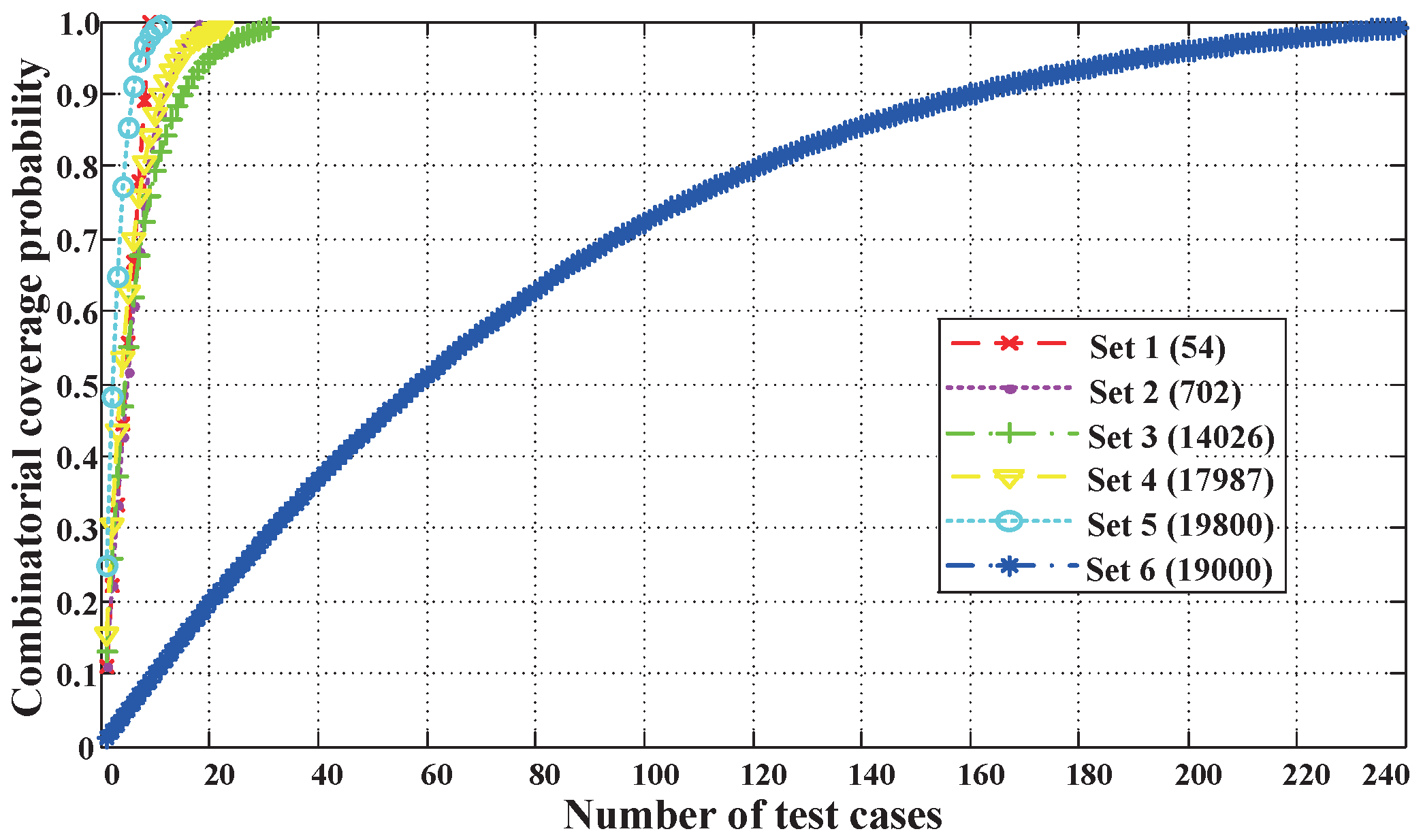
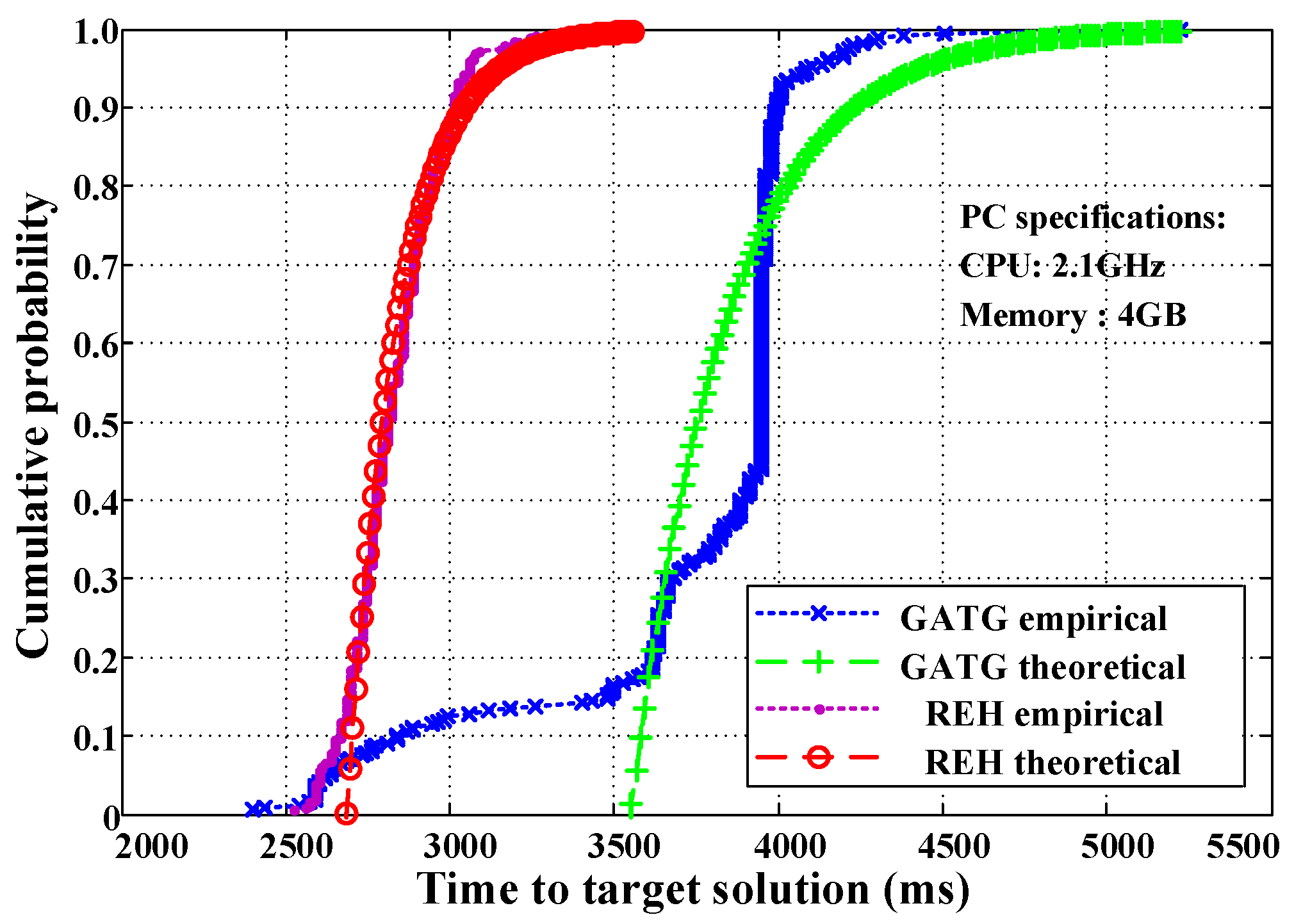
4.2. Algorithm Convergence Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuhn, D.R.; Kacker, R.N.; Lei, Y. Practical Combinatorial Testing; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA; U.S. Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. Available online: https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/legacy/sp/nistspecialpublication800-142.pdf (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Almering, V.; Von Genuchten, M.; Cloudt, G.; Sonnemans, P.J.M. Using Software Reliability Growth Models in Practice. IEEE Softw. 2007, 24, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balera, J.; Santiago, V., Jr. An algorithm for combinatorial interaction testing: Definitions and rigorous evaluations. J. Softw. Eng. Res. Dev. 2017, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, D.; Kacker, R.; Lei, Y. Advanced Combinatorial Test Methods for System Reliability. In Reliability Society 2010 Annual Technical Report; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, D.; Kacker, R.; Lei, Y. Combinatorial Coverage Measurement. NIST Interagency/Internal Report. Available online: https://www.nist.gov/publications/combinatorial-coverage-measurement (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Hagar, J.; Kuhn, R.; Kacker, R.; Wissink, T. Introducing Combinatorial Testing in a Large Organization: Pilot Project Experience Report. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Software Testing Verification and Validation, Cleveland, OH, USA, 31 March–4 April 2014; p. 153. [Google Scholar]
- Muazu, A.A.; Hashim, A.S.; Sarlan, A. Review of Nature Inspired Metaheuristic Algorithm Selection for Combinatorial t-Way Testing. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 27404–27431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, S.; Schmidt, T.J.; Krieter, S.; Pett, T.; Thum, T.; Lochau, M. Coverage Metrics for T-Wise Feature Interactions. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE Conference on Software Testing, Verification and Validation (ICST), Napoli, Italy, 31 March–4 April 2025; pp. 198–209. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, G.; Zheng, J.; Tsuchiya, T. Meta-Heuristic Algorithm for Constructing Higher-Index Covering Arrays for Combinatorial Interaction Testing. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Software Testing, Verification and Validation Workshops, Dublin, Ireland, 16–20 April 2023; pp. 190–196. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Song, X.; Zhou, J.T.; Wang, F.; Tang, K. An Effective Approach to High Strength Covering Array Generation in Combinatorial Testing. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 2023, 49, 4566–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojanasoonthon, S.; Bard, J. A GRASP for Parallel Machine Scheduling with Time Windows. INFORMS J. Comput. 2005, 17, 32–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garey, M.; Johnson, D. Computers and Intractability: A Guide to the Theory of NP-Completeness; W.H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Htay, K.M.; Othman, R.R.; Amir, A.; Zakaria, H.L.; Ramli, N. A Pairwise t-Way Test Suite Generation Strategy Using Gravitational Search Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Science Technology (ICAICST), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 29–30 June 2021; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc150619.aspx (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Available online: https://www.pairwise.org/tools.html (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Lin, J.; Cai, S.; He, B.; Fu, Y.; Luo, C.; Lin, Q. FastCA: An Effective and Efficient Tool for Combinatorial Covering Array Generation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/ACM 43rd International Conference on Software Engineering: Companion Proceedings (ICSE-Companion), Madrid, Spain, 25–28 May 2021; pp. 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P.; Bao, X.; Shu, Z. Test case generation based on adaptive genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on. Quality, Reliability, Risk, Maintenance, and Safety Engineering (ICQR2MSE), Chengdu, China, 15–18 June 2012; pp. 863–866. [Google Scholar]
- Grindal, M.; Offutt, J.; Andler, S.F. Combination testing strategies: A survey. Softw. Test. Verif. Reliab. 2005, 15, 167–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, M.; Zamli, K.; Isa, N. IRPS Can efficient test data generation strategy for pairwise testing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge-Based and Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems, Zagreb, Croatia, 3–5 September 2008; pp. 493–500. [Google Scholar]
- Klaib, M.; Muthuraman, S.; Noraziah, A. A Parallel Tree Based Strategy for t-Way Combinatorial Interaction Testing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Software Engineering and Computer Systems, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–22 May 2011; pp. 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Shiba, T.; Tsuchiya, T.; Kikuno, T. Using artificial life techniques to generate test cases for combinatorial testing. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual International Computer Software and Applications Conference, Hong Kong, China, 28–30 September 2004; pp. 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Mandl, R. Orthogonal Latin Squares: An application of experiment design to compiler testing. Commun. ACM 1985, 28, 1054–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.; Dalal, S.; Fredman, M.; Patton, G. The AETG system: An approach to testing based on combinatorial design. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 1997, 7, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M. Designing Test Suites for Software Interactions Testing. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, P.; Cheon, Y. Pwisegen: Generating test cases for pairwise testing using genetic algorithms. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Science and Automation Engineering, Shanghai, China, 10–12 June 2011; pp. 747–752. [Google Scholar]
- Avila, H.; Torres, J.; Hernández, V.; Gonzalez, L. Simulated annealing for constructing mixed covering arrays. Distrib. Comput. Artif. Intell. 2012, 15, 657–664. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Cai, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C.; Huang, C. A Test Case Generation Method of Combinatorial Testing based on t-Way Testing with Adaptive Random Testing. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering Workshops, Wuhan, China, 25–28 October 2021; pp. 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, L.; Rangel, N.; Torres, J. Construction of Mixed Covering Arrays of Variable Strength Using a Tabu Search Approach. In Combinatorial Optimization and Applications (COCOA 2010); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Muazu, A.A.; Hashim, A.S.; Audi, U.I.; Maiwada, U.D. Refining a One-Parameter-at-a-Time Approach Using Harmony Search for Optimizing Test Suite Size in Combinatorial t-Way Testing. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 137373–137398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Shu, W. Generation of Pairwise Test Sets using Novel DPSO algorithm. Green Commun. Netw. 2012, 11, 479–487. [Google Scholar]
- Zabidi, N.S.; Ibrahim, N.; Rejab, M.M.; Mamat, M.; Nazir, S.; Tuselim, N.H.M. Optimizing Variable-Strength Combinatorial Test Suite Generation via Fuzzy Adaptive Sine Cosine Algorithm (FASCA). In Proceedings of the 2024 1st International Conference on Cyber Security and Computing, Melaka, Malaysia, 6–7 November 2024; pp. 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Muazu, A.A.; Hashim, A.S.; Sarlan, A.; Maiwada, U.D. Proposed Method of Seeding and Constraint in One-Parameter-At-a-Time Approach for t-Way Testing. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Digital Transformation and Intelligence (ICDI), Kuching, Malaysia, 1–2 December 2022; pp. 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, M.L.; Sastry, J.K.R.; Mallikarjuna, B.; Sitaramulu, V.; Srinivasulu, C.; Naib, B.B. Development of a Programmed Generation of t-Way Test cases Using an Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Strategy. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd International Conference on Advance Computing and Innovative Technologies in Engineering (ICACITE), Greater Noida, India, 28–29 April 2022; pp. 1394–1399. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.; Shi, C.; Tsuchiya, T. Summary of Constrained Detecting Arrays: Mathematical Structures for Fault Identification in Combinatorial Interaction Testing. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Software Testing, Verification and Validation Workshops, Toronto, ON, Canada, 27–31 May 2024; pp. 215–216. [Google Scholar]
- Resende, M. Greedy randomized adaptive search procedures Greedy Randomized Adaptive Search Procedures: GPASP Greedy randomized adaptive search procedures GPASP. In Encyclopedia of Optimization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1460–1469. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.; Tsuchiya, T. A Two-Step Heuristic Algorithm for Generating Constrained Detecting Arrays for Combinatorial Interaction Testing. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 29th International Conference on Enabling Technologies: Infrastructure for Collaborative Enterprises, Bayonne, France, 10–13 September 2020; pp. 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Resende, M.; Ribeiro, C. Greedy randomized adaptive search procedures: Advances, hybridizations, and applications. In Handbook of Metaheuristics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 283–319. [Google Scholar]
- Glover, F.; Laguna, M.; Martí, R. Fundamentals of scatter search and path relinking. Control Cybern. 2010, 29, 653–684. [Google Scholar]
- Resendel, M.; Ribeiro, C. GRASP with path-relinking: Recent advances and applications. In Metaheuristics: Progress as Real Problem Solvers; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 29–63. [Google Scholar]
- Villegas, J.; Prins, C.; Prodhon, C. A GRASP with evolutionary path relinking for the truck and trailer routing problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2011, 38, 1319–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Kuang, L.; Chen, X.; Yan, J.; Lu, J.; Wang, X. Adaptive subsequence adjustment with evolutionary asymmetric path-relinking for TDRSS scheduling. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2014, 25, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiex, M.; Resende, M.; Ribeiro, C. Probability distribution of solution time in GRASP: An experimental investigation. J. Heuristics 2002, 8, 343–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiex, R.; Resende, M.; Ribeiro, C. TTT plots: A perl program to create time-to-target plots. Optim. Lett. 2007, 1, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Sets of Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | |
| I (Duplex Mode) | TDD | ||
| II (Carrier Bandwidth) | 100 MHz | 200 MHz | |
| III (Coding Scheme) | LDPC | Polar | |
| IV (Modulation Order) | BPSK | QPSK | 16QAM |
| Row No. | Index (Value Set) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | |
| 1 | −1(TDD) | +1(100 MHz) | +1(LDPC) | +1(BPSK) |
| 2 | −1(TDD) | +2(200 MHz) | +2(Polar) | +2(QPSK) |
| 3 | −1(TDD) | +3(16QAM) | ||
| 4 | −2() | +1(100 MHz) | +1(LDPC) | +1(BPSK) |
| 5 | −2() | +2(200 MHz) | +2(Polar) | +2(QPSK) |
| 6 | −2() | +3(16QAM) | ||
| 7 | −3() | +1(100 MHz) | +1(LDPC) | +1(BPSK) |
| 8 | −3() | +2(200 MHz) | +2(Polar) | +2(QPSK) |
| 9 | −3() | +3(16QAM) | ||
| 10 | −1(100 MHz) | +1(LDPC) | +1(BPSK) | |
| 11 | −1(100 MHz) | +2(Polar) | +2(QPSK) | |
| 12 | −1(100 MHz) | +3(16QAM) | ||
| 13 | −2(200 MHz) | +1(LDPC) | +1(BPSK) | |
| 14 | −2(200 MHz) | +2(Polar) | +2(QPSK) | |
| 15 | −2(200 MHz) | +3(16QAM) | ||
| 16 | −3() | +1(LDPC) | +1(BPSK) | |
| 17 | −3() | +2(Polar) | +2(QPSK) | |
| 18 | −3() | +3(16QAM) | ||
| 19 | −1(LDPC) | +1(BPSK) | ||
| 20 | −1(LDPC) | +2(QPSK) | ||
| 21 | −1(LDPC) | +3(16QAM) | ||
| 22 | −2(Polar) | +1(BPSK) | ||
| 23 | −2(Polar) | +2(QPSK) | ||
| 24 | −2(Polar) | +3(16QAM) | ||
| 25 | −3() | +1(BPSK) | ||
| 26 | −3() | +2(QPSK) | ||
| 27 | −3() | +3(16QAM) | ||
| Row No. | Index | |
|---|---|---|
| ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ |
| ID | Instance | AETG | IPO | TConfig | CTS | Jenny | ecfeed | AllPairs | PICT | IPO-s | GATG | Mean | REH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9.3 | 9 | |
| 2 | 15 | 17 | 15 | 15 | 18 | 19 | 17 | 18 | 17 | 19 | 17.0 | 18 | |
| 3 | 41 | 34 | 40 | 39 | 38 | 37 | 34 | 37 | 32 | 38 | 37.0 | 31 | |
| 4 | 28 | 26 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 28 | 26 | 27 | 23 | 31 | 27.6 | 22 | |
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 14 | 10 | 16 | 16 | 14 | 15 | 10 | 14 | 13.4 | 11 | |
| 6 | 180 | 212 | 231 | 210 | 193 | 203 | 197 | 210 | 220 | 245 | 210.1 | 239 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, P.; She, J.; Chen, X. T-Way Combinatorial Testing Strategy Using a Refined Evolutionary Heuristic. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14050095
Lin P, She J, Chen X. T-Way Combinatorial Testing Strategy Using a Refined Evolutionary Heuristic. Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks. 2025; 14(5):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14050095
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Peng, Jinzhao She, and Xiang Chen. 2025. "T-Way Combinatorial Testing Strategy Using a Refined Evolutionary Heuristic" Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks 14, no. 5: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14050095
APA StyleLin, P., She, J., & Chen, X. (2025). T-Way Combinatorial Testing Strategy Using a Refined Evolutionary Heuristic. Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks, 14(5), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14050095






