Distribution and Characterization of Deep Rhodolith Beds off the Campania coast (SW Italy, Mediterranean Sea)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
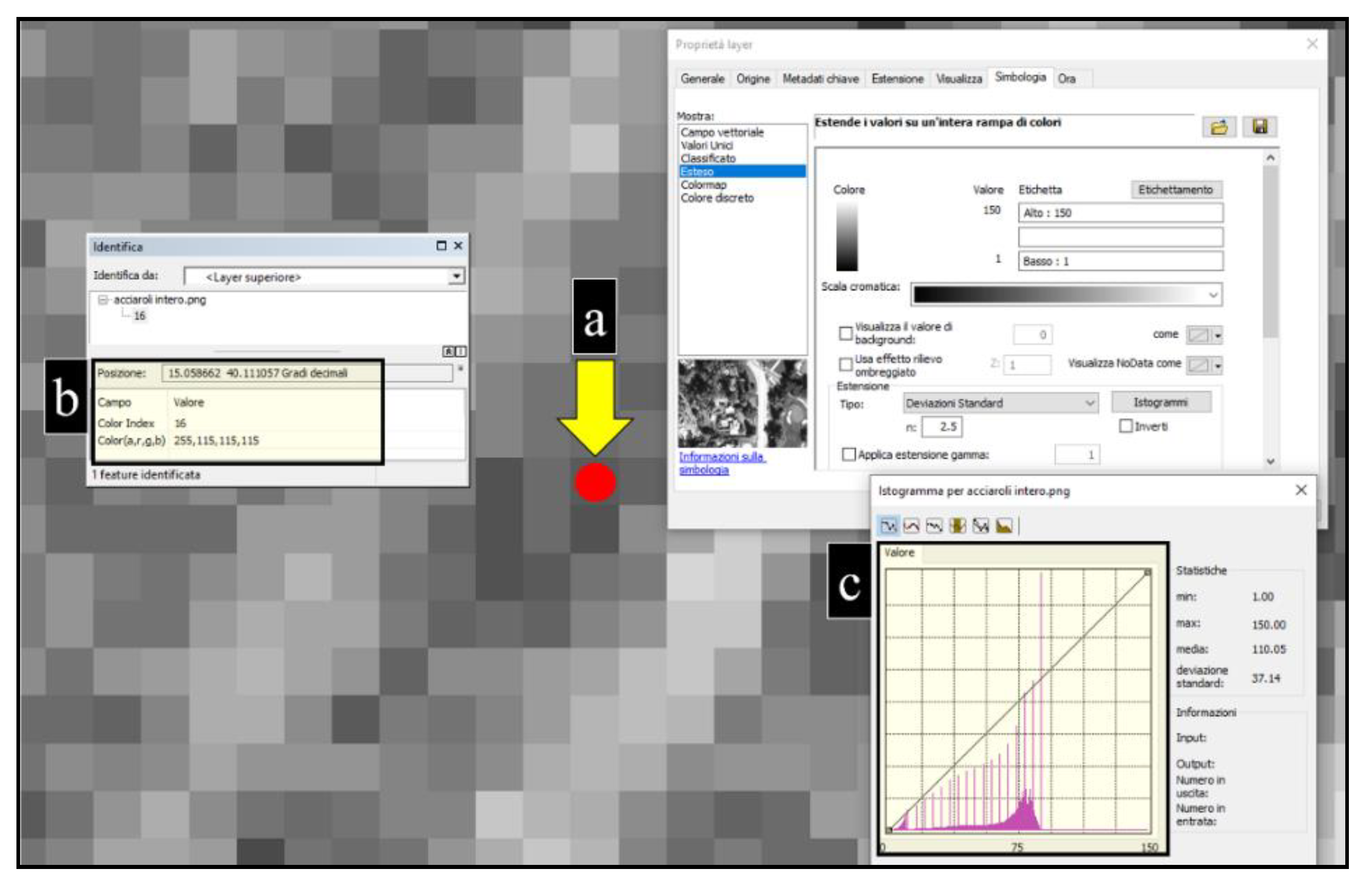
2.2. Remote Data Acquisition and Analysis
2.3. Collection and Morphological Characterization of Rhodoliths
2.4. Coralline Algal Identification
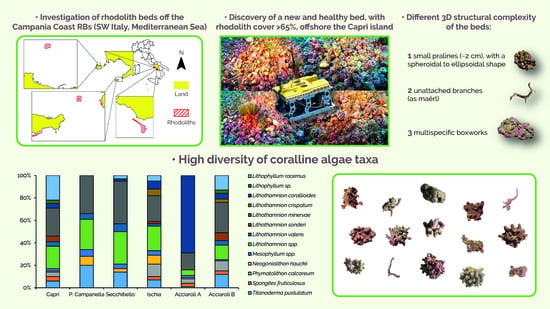
3. Results
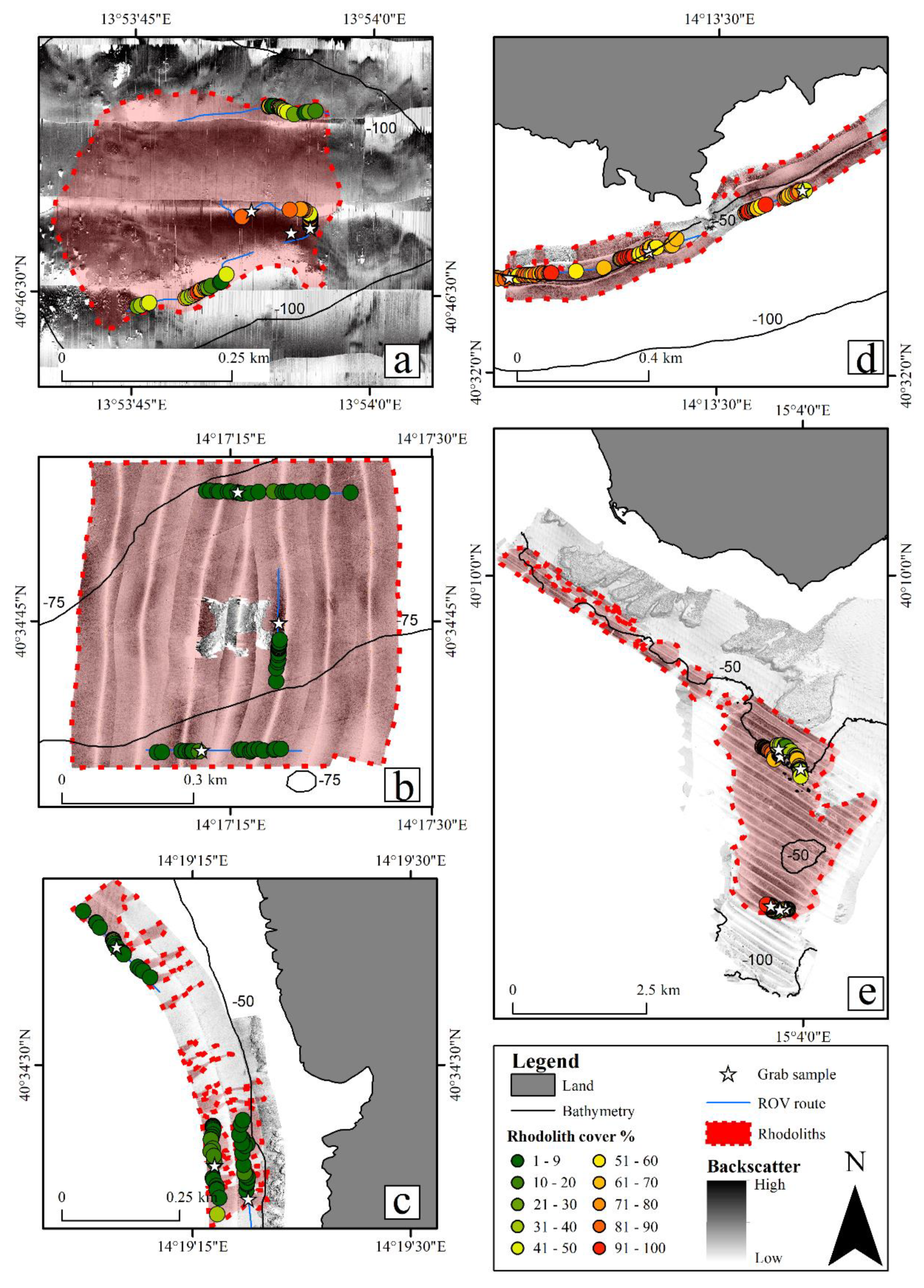
3.1. Remote Data
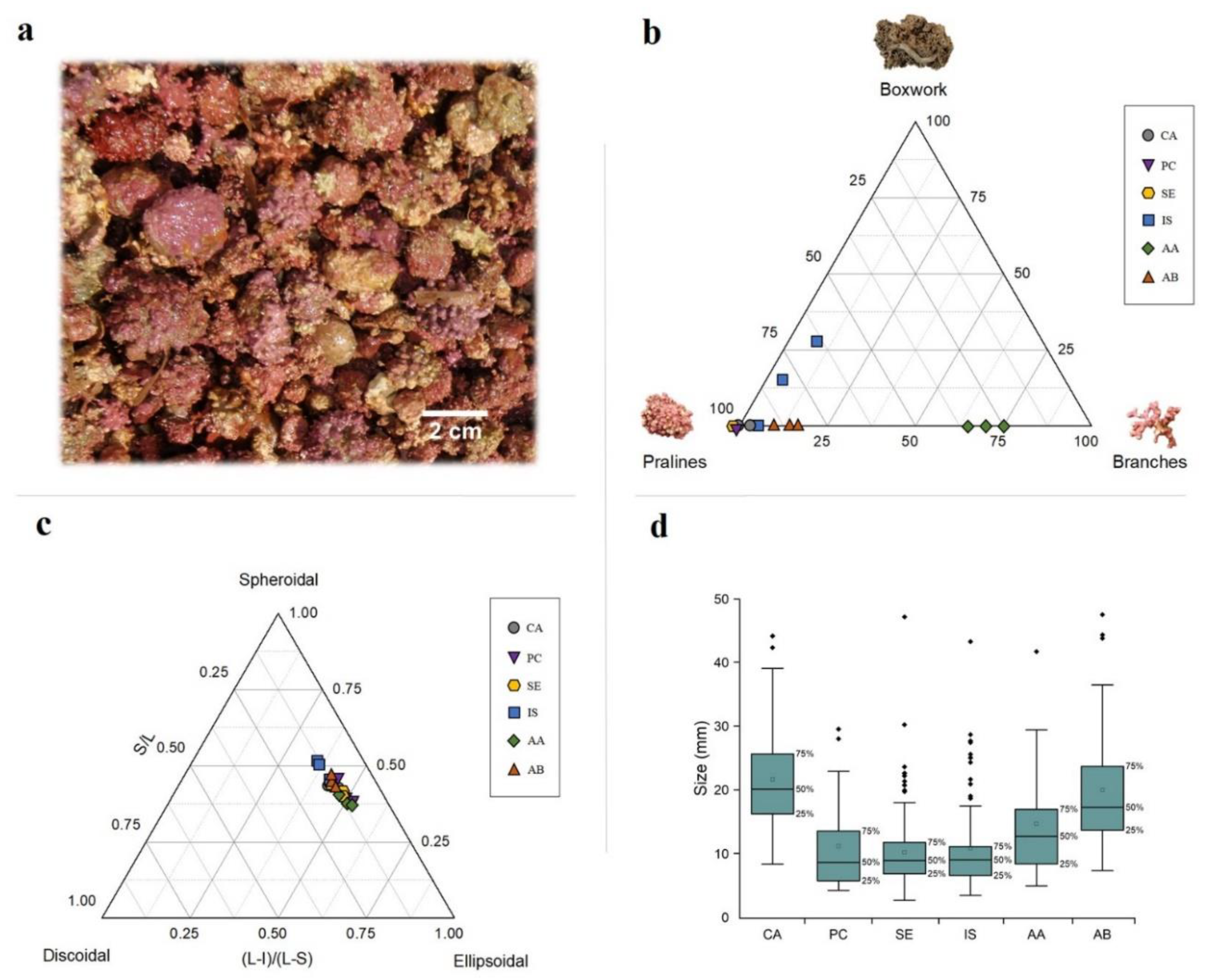
3.2. Rhodolith Morphology
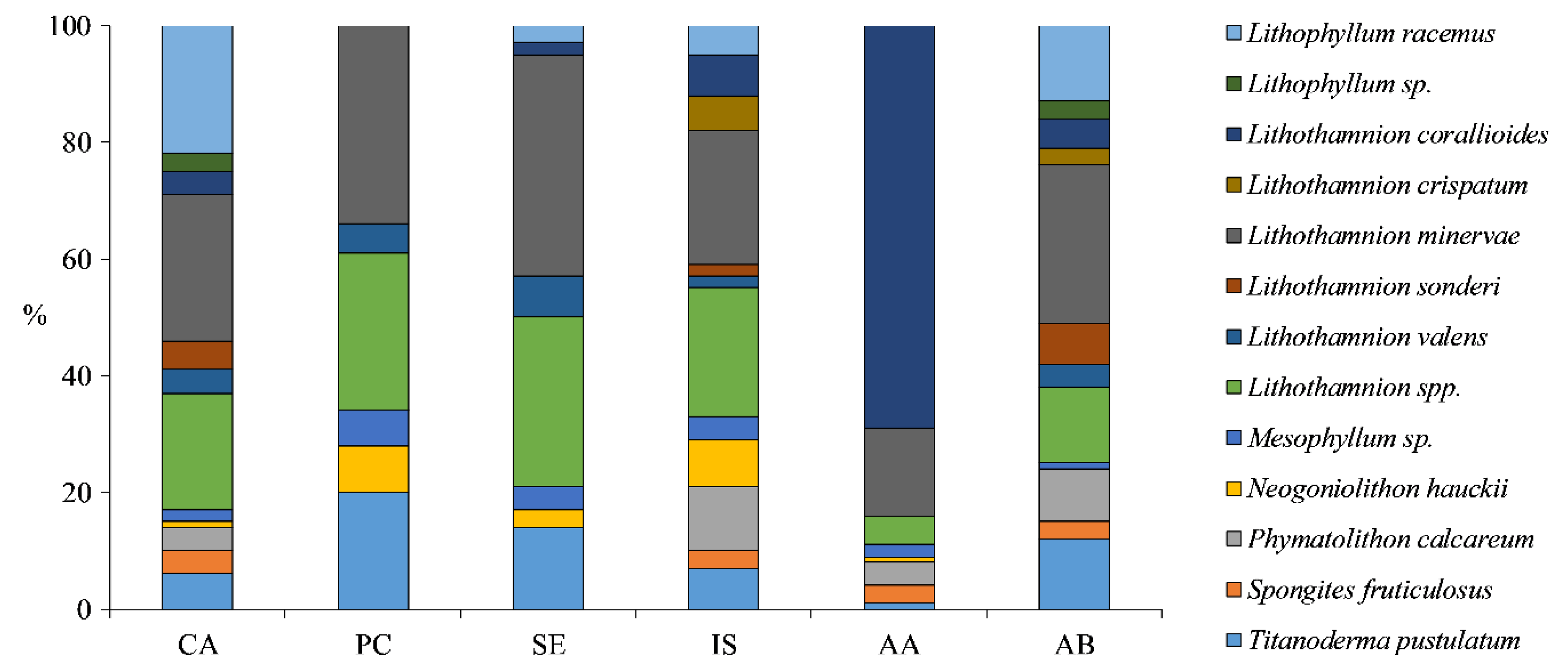
3.3. Taxonomic Composition of Coralline Algae
4. Discussion
4.1. Characterization of Rhodolith Beds
4.2. Rhodolith Morphology
4.3. Taxonomic Composition of Coralline Algae
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Basso, D.; Babbini, L.; Kaleb, S.; Bracchi, V.; Falace, A. Monitoring deep Mediterranean rhodolith beds. Aquat. Conserv. 2016, 26, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosence, D.W.J. The occurrence and ecology of recent rhodoliths (rhodoids, rhodolites). In Classification of Coated Grains; Peryt, T.M., Ed.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1983; pp. 225–242. [Google Scholar]
- Steller, D.L.; Riosmena-Rodriguez, R.; Foster, M.S.; Roberts, C.A. Rhodolith bed diversity in the Gulf of California: The importance of rhodolith structure and consequences of disturbance. Aquat. Conserv. 2003, 13, S5–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, M.S.; Filho, G.M.A.; Kamenos, K.A.; Riosmena-Rodríguez, R.; Steller, D.L. Rhodoliths and rhodolith beds. In Research and Discoveries: The Revolution of Science Through SCUBA; American Academy of Underwater Sciences: Mobile, AL, USA, 2013; pp. 143–155. [Google Scholar]
- Scoffin, T.P.; Stoddart, D.R.; Tudhope, A.W.; Woodroffe, C. Rhodoliths and coralliths of Muri Lagoon, Rarotonga, Cook Islands. Coral Reefs 1985, 4, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado-Filho, G.M.; Moura, R.L.; Bastos, A.C.; Salgado, L.T.; Sumida, P.Y.; Guth, A.Z.; Francini-Filho, R.B.; Pereira-Filho, G.H.; Abrantes, D.P.; Poliana, S.; et al. Rhodolith beds are major CaCO3 bio-factories in the tropical South West Atlantic. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosence, D.W.J. The morphology and ecology of a mound-building coralline alga (Neogoniolithon strictum) from the Florida Keys. Paleontology 1985, 28, 189–206. [Google Scholar]
- Bosence, D.W.J. Ecological studies on two unattached coralline algae from western Ireland. Palaeontology 1976, 19, 365–395. [Google Scholar]
- Bracchi, V.A.; Lorenzo, A.; Marchese, F.; Taviani, M.; Cardone, F.; Hajdas, I.; Grande, V.; Prampolini, M.; Caragnano, A.; Corselli, C.; et al. A resilient deep-water rhodolith bed off the Egadi Archipelago (Mediterranean Sea) and its actuopaleontological significance. Alp. Mediterr. Quat. 2019, 32, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Basso, D. Deep rhodolith distribution in the Pontian Islands, Italy: A model for the paleoecology of a temperate sea. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1998, 137, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciberras, M.; Rizzo, M.; Mifsud, J.R.; Camilleri, K.; Borg, J.A.; Lanfranco, E.; Schembri, P.J. Habitat structure and biological characteristics of a maerl bed off the northeastern coast of the Maltese Islands (central Mediterranean). Mar. Biodivers. 2009, 39, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiwald, A. Sedimentological and biological aspects in the formation of branched rhodoliths in northern Norway. Beiträge zur Paläontologie Osterreichs 1995, 20, 7–19. [Google Scholar]
- Teichert, S.; Woelkerling, W.; Rüggeberg, A.; Wisshak, M.; Piepenburg, D.; Meyerhöfer, M.; Form, A.; Freiwald, A. Arctic rhodolith beds and their environmental controls (Spitsbergen, Norway). Facies 2014, 60, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichert, S.; Woelkerling, W.; Rüggeberg, A.; Wisshak, M.; Piepenburg, D.; Meyerhöfer, M.; Form, A.; Büdenbender, J.; Freiwald, A. Rhodolith beds (Corallinales, Rhodophyta) and their physical and biological environment at 80°31′ N in Nordkappbukta (Nordaustlandet, Svalbard Archipelago, Norway). Phycologia 2012, 51, 371–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, R.; Pastor, X.; Torriente, A.; Garcia, S. Deep-sea coralligenous beds observed with ROV on four seamounts in the western Mediterranean. In Proceedings of the 1st Mediterranean Symposium on the Conservation of the Coralligenous and Others Calcareous Bio-Concretions, Tabarka, Tunis, 15–16 January 2009; pp. 147–149. [Google Scholar]
- Hinojosa-Arango, G.; Riosmena-Rodríguez, R. Influence of Rhodolith-forming species and growth-form on associated fauna of rhodolith beds in the central-west Gulf of California, México. Mar. Ecol. 2004, 25, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichert, S. Hollow rhodoliths increase Svalbard’s shelf biodiversity. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero-Ferrer, F.; Mannarà, E.; Cosme, M.; Falace, A.; Montiel-Nelson, J.A.; Espino, F.; Haroun, R.; Tuya, F. Early-faunal colonization patterns of discrete habitat units: A case study with rhodolith-associated vagile macrofauna. Estuar. Coast. Mar. Sci. 2019, 218, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grall, J.; Glemarec, M. Biodiversite des fonds de maërl en Bretagne: Approache fonctionnelle et impacts anthropogeniques. Vie Milieu 1997, 47, 339–349. [Google Scholar]
- Birkett, D.; Maggs, C.; Dring, M. Maërl, Volume V: An Overview of Dynamic and Sensitivity Characteristics for Conservation Management of Marine SACs; Scottish Association for Marine Science: Oban, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hall-Spencer, J.M.; Grall, J.; Moore, P.G.; Atkinson, R.J.A. Bivalve fishing and maerl-bed conservation in France and the UK-retrospect and prospect. Aquat. Conserv. 2003, 13, S33–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquotte, R. Etude des fonds de maerl de Méditerranée. Recueil Travaux StationMarine d’Endoume 1962, 26, 141–216. [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti, L.; Paganelli, D.; Gabellini, M. Aspetti Ambientali del Dragaggio di Sabbie Relitte a Fini di Ripascimento: Proposta di un Protocollo di Monitoraggio; ISPRA Istituto Superiore per la Protezione e la Ricerca Ambientale: Rome, Italy, 2006; Volume 5, p. 159.
- Martin, S.; Gattuso, J.P. Response of Mediterranean coralline algae to ocean acidification and elevated temperature. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 2089–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, M.S. Rhodoliths: Between rocks and soft places. J. Phycol. 2001, 37, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenos, N.A.; Moore, P.; Hall-Spencer, J. Substratum heterogeneity of dredged vs un-dredged maerl grounds. J. Mar. Biolog. Assoc. 2003, 83, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, C.; Maggs, C.A. Comparative growth rates and internal banding periodicity of maerl species (Corallinales, Rhodophyta) from northern Europe. Phycologia 2003, 42, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grave, S. The influence of sedimentary heterogeneity on within maërl bed differences in infaunal crustacean community. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1999, 49, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall-Spencer, J.M.; Moore, P.G. Scallop dredging has profound, long-term impacts on maërl habitats. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordehore, C.; Borg, J.A.; Lanfranco, E.; Ramos-Esplá, A.; Rizzo, M.; Schembri, P.J. Trawling as a major threat to Mediterranean maerl beds. In Proceedings of the Symposium on marine vegetation, Ajaccio, France, 3–4 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bordehore, C.; Ramos-Esplá, A.A.; Riosmena-Rodríguez, R. Comparative study of two maerl beds with different otter trawling history, southeast Iberian Peninsula. Aquat. Conserv. 2003, 13, S43–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall-Spencer, J.M.; White, N.; Gillespie, E.; Gillham, K.; Foggo, A. Impact of fish farms on maërl beds in strongly tidal areas. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 326, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Lázaro, C.; Belando, M.D.; Lázaro Marín-Guirao, L.; Navarrete-Mier, F.; Arnaldo, M.A. Relationship between sedimentation rates and benthic impact on Maërl beds derived from fish farming in the Mediterranean. Mar. Environ. Res. 2011, 71, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, S.J.; Ragazzola, F. Skeletal trade-offs in coralline algae in response to ocean acidification. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendina, F.; Bouchet, P.J.; Appolloni, L.; Russo, G.F.; Sandulli, R.; Kolzenburg, R.; Putra, A.; Ragazzola, F. Physiological response of the coralline alga Corallina officinalis L. to both predicted long-term increases in temperature and short-term heatwave events. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 150, 104764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rindi, F.; Braga, J.; Martin, S.; Peña, V.; Le Gall, L.; Caragnano, A.; Aguirre, J. Coralline algae in a changing Mediterranean Sea: How can we predict their future, if we do not know their present? Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberá, C.; Bordehore, C.; Borg, J.A.; Glemarec, M.; Grall, J.; Hall-Spencer, J.M.; De la Huz, C.; Lanfranco, E.; Lastra, M.; Moore, P.G.; et al. Conservation and management of northeast Atlantic and Mediterranean maërl beds. Aquat. Conserv. 2003, 13, S65–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, W. Calcified macroalgae—Critical to coastal ecosystems and vulnerable to change: A review. Mar. Freshwater Res. 2009, 60, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado-Giménez; F.; Ruiz-Fernández, J.M. Influence of an experimental fish farm on the spatio-temporal dynamic of a Mediterranean maërl algae community. Mar. Environ. Res 2012, 74, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Communities. Council directive 1992/43/EC Conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora. Off. J. Eur. Union 1992, L206, 7–50. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament. Council of the European Union Directive 2008/56/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 June 2008 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of marine environmental policy (Marine Strategy Framework Directive). Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, L164, 19. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Commission decision of 1 September 2010 on criteria and methodological standards on good environmental status of marine waters. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, L232, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Ballesteros, E. Composición y estructura de los fondos de maërl de Tossa de Mar (Girona, España). Collectanea Botanica 1989, 17, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, E. Mediterranean coralligenous assemblages: A synthesis of present knowledge. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 2006, 44, 123–195. [Google Scholar]
- Templado, J.; Calvo, M.; García-Carrascosa, A.M.; Boisset, F.; Jiménez, J. Flora y Fauna de la Reserva Marina de las Islas Columbretes; Secretaría Gral. Pesca Marítima. M° Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación: Madrid, Spain; Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales: Madrid, Spain; CSIC: Madrid, Spain, 2002; p. 263.
- Castriota, L.; Gambi, M.C.; Zupo, V.; Sunseri, G. Structure and trophic ecology of a population of Lysidice ninetta (Polychaeta) associated to rhodoliths off the island of Ustica (Southern Tyrrhenian Sea). Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2003, 10, 517–520. [Google Scholar]
- Castriota, L.; Agamennone, F.; Sunseri, G. The mollusc community associated with maerl beds of Ustica Island (Tyrrhenian Sea). Cah. Biol. Mar. 2005, 46, 289–297. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-Esplá, A.A.; Luque, A.A. Los fondos de “maerl”. In Pradera y Bosques Marinos de Andalucía; Luque, A.A., Templado, J., Eds.; Consejería de Medio Ambiente, Junta de Andalucía: Sevilla, Spain, 2004; pp. 221–236. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-Esplá, A.A.; Luque, A.A. The Seas of Spain. Maerl Beds: A Fragile Oasis of Marine Life; Ministero del Medio Ambiente y Medio Rural y Marino: Madrid, Spain, 2008; pp. 273–290. [Google Scholar]
- Ordines, F.; Massutí, E. Relationships between macro-epibenthic communities and fish on the shelf grounds of the western Mediterranean. Aquat. Conserv. 2009, 19, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberá, C.; Moranta, J.; Ordines, F.; Ramón, M.; de Mesa, A.; Díaz-Valdés, M.; Grau, A.M.; Massutí, E. Biodiversity and habitat mapping of Menorca Channel (western Mediterranean): Implications for conservation. Biodivers. Conserv. 2012, 21, 701–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Bo, M.; Cannas, R.; Cau, A.; Follesa, C.; Meliadò, E.; Russo, G.F.; Sandulli, R.; Bavestrello, G. An overexploited Italian treasure: Past and present distribution and exploitation of the precious red coral Corallium rubrum (L., 1758) (Cnidaria: Anthozoa). Ital. J. Zool. 2016, 83, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, D.; Babbini, L.; Ramos-Esplá, A.A.; Salomidi, M. Mediterranean Rhodolith Beds. In Rhodolith/Maërl Beds: A Global Perspective; Riosmena-Rodríguez, R., Nelson, W., Aguirre, J., Eds.; Coastal Research Library; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 15. [Google Scholar]
- Donnarumma, L.; Sandulli, R.; Appolloni, L.; Di Stefano, F.; Russo, G.F. Morpho-structural and ecological features of a shallow vermetid bioconstruction in the Tyrrhenian Sea (Mediterranean Sea, Italy). J. Sea Res. 2018, 131, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrosso, G.; Cecchi, L.; Bertolino, M.; Bevilacqua, S.; Bianchi, C.N.; Bo, M.; Boscari, E.; Cardone, F.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Cau, A.; et al. Mediterranean Bioconstructions Along the Italian Coast. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2018, 79, 61–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Basso, D.; Babbini, L.; Kaleb, S.; Falace, A.; Bracchi, V. A protocol for the monitoring of Mediterranean rhodolith beds. In Proceedings of the 2nd Mediterranean Symposium on the Conservation of Coralligenous and other Calcareous Bio-Concretions, Portorož, Slovenia, 29–30 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Piazzi, L.; Gennaro, P.; Cecchi, E.; Serena, F. Improvement of the ESCA index for the evaluation of ecological quality of coralligenous habitat under the European Framework Directives. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2015, 16, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrigno, F.; Appolloni, L.; Russo, G.F.; Sandulli, R. Impact of fishing activities on different coralligenous assemblages of Gulf of Naples (Italy). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U.K. 2018, 98, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrigno, F.; Appolloni, L.; Rendina, F.; Donnarumma, L.; Russo, G.F.; Sandulli, R. Red coral (Corallium rubrum) populations and coralligenous characterization within “Regno di Nettuno MPA” (Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy). Eur. Zool. J. 2020, 87, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimienti, G.; Angeletti, L.; Rizzo, L.; Tursi, A.; Mastrototaro, F. ROV vs trawling approaches in the study of benthic communities: The case of Pennatula rubra (Cnidaria: Pennatulacea). J. Mar. Biolog. Assoc. 2018, 98, 1859–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimienti, G.; De Padova, D.; Mossa, M.; Mastrototaro, F. A mesophotic black coral forest in the Adriatic Sea. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, M.; Bava, S.; Canese, S.; Angiolillo, M.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Bavestrello, G. Fishing impact on deep Mediterranean rocky habitats as revealed by ROV investigation. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 171, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrigno, F.; Russo, G.F.; Sandulli, R. Coralligenous Bioconstructions Quality Index (CBQI): A synthetic indicator to assess the status of different types of coralligenous habitats. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 82, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendina, F.; Ferrigno, F.; Appolloni, L.; Donnarumma, L.; Sandulli, R.; Russo, G.F. Anthropic pressure due to lost fishing gears and marine litter on different rhodolith beds off the Campania coast. (Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy). Ecol. Quest. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Kantun, J.J.; Hall-Spencer, J.M.; Grall, J.; Adey, W.; Rindi, F.; Maggs, C.A.; Bárbara, I.; Peña, V. North Atlantic rhodolith beds. In Rhodolith/Maërl Beds: A Global Perspective; Riosmena-Rodríguez, R., Nelson, W., Aguirre, J., Eds.; Coastal Research Library; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 15. [Google Scholar]
- Bosellini, A.; Ginsburg, R. Form and internal structure of recent algal nodules (Rhodolites) from Bermuda. J. Geol. 1971, 79, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrack, E.C. The relationship between water motion and living rhodolith beds in the southwestern Gulf of California, Mexico. Palaios 1999, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riosmena-Rodríguez, R. Natural History of Rhodolith/ Maërl Beds: Their Role in Near-Shore Biodiversity and Management. In Rhodolith/Maërl Beds: A Global Perspective; Riosmena-Rodríguez, R., Nelson, W., Aguirre, J., Eds.; Coastal Research Library; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Babbini, L.; Bressan, G.; Massa-Gallucci, A.; Buia, M.C.; Gambi, M.C. Segnalazione di una faciesa mäerl (Rhodophyta, Corallinales) lungo le coste dell’isola d’Ischia. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2006, 13, 548–552. [Google Scholar]
- Gambi, M.C.; Buia, M.C.; Massa-Gallucci, A.; Cigliano, M.; Lattanzi, L.; Patti, F.P. The “pink mile”: Benthic assemblages of rhodolith and mäerl beds (Corallinales) off the Island of Ischia (Tyrrhenian Sea). In Proceedings of the 1st Mediterranean Symposium on the Conservation of the Coralligenous and Others Calcareous Bio-Concretions, Tabarka, Tunis, 15–16 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Toscano, F.; Vigliotti, M.; Simone, L. Variety of coralline algal deposits (rhodalgal facies) from the Bays of Naples and Pozzuoli (northern Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy). Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2006, 255, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savini, A.; Basso, D.; Bracchi, V.A.; Corselli, C.; Pennetta, M. Maerl-bed mapping and carbonate quantification on submerged terraces offshore the Cilento peninsula (Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy). Geodiversitas 2012, 34, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, S.J.; Kenny, A.J. Guidelines for the Conduct of Benthic Studies at Marine Aggregate Extraction Sites, 2nd ed.; Marine Aggregate Levy Sustainability Fund, MALSF: Lowestoft, UK, 2011; p. 80.
- Jones, D.L.; Langman, R.; Reach, I.; Gribble, J.; Griffiths, N. Using multibeam and sidescan sonar to monitor aggregate dredging. In Seafloor Mapping along Continental Shelves; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 245–259. [Google Scholar]
- Ministero Dell’ambiente e della Tutela del Territorio e del Mare. Programmi di Monitoraggio per la Strategia Marina Art. 11, D.lgs. 190/2010. Scheda Metodologica Modulo 8 Habitat Fondi a Maerl/Rodoliti; Ministero dell’Ambiente e della Tutela del Territorio e del Mare: Rome, Italy, 2016.
- Peña, V.; Barbara, I. Seasonal patterns in the mäerl community of shallow European Atlantic beds and their use as a baseline for monitoring studies. Eur. J. Phycol. 2010, 45, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlizzi, A.; Anderson, M.J.; Fraschetti, S.; Benedetti-Cecchi, L. Scales of spatial variation in Mediterranean subtidal sessile assemblages at different depths. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 332, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidetti, P.; Baiata, P.; Ballesteros, E.; Di Franco, A.; Hereu, B.; Macpherson, E.; Micheli, F.; Pais, A.; Panzalis, P.; Rosenberg, A.A.; et al. Large-scale assessment of Mediterranean marine protected areas effects on fish assemblages. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral. Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. Past: Palaeontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Bosence, D.W.J. Description and Classification of Rhodoliths (Rhodoids, Rhodolites). In Coated Grains; Peryt, T.M., Ed.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1983; pp. 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Sneed, E.D.; Folk, R.L. Pebbles in the lower Colorado River, Texas, a study of particle morphogenesis. J. Geol. 1958, 66, 114–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleb, S.; Alongi, G.; Falace, A. Coralline algae preparation for scanning electron microscopy and optical microscopy. In Protocols for Macroalgae Research; Charrier, B., Wichard, T., Reddy, C.R.K., Eds.; CRC Press, Taylor and Franciss Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 413–429. [Google Scholar]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M.; AlgaeBase. World-Wide Electronic Publication. National University of Ireland, Galway. 2020. Available online: http://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Hedley, J. VidAna 1.0 Software for Cover Analysis from Video Footage or Still Images; Marine Spatial Ecology Lab, School of Biological & Chemical Sciences, University of Exeter: Exeter, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ingrassia, M.; Martorelli, E.; Sañé, E.; Falese, F.G.; Bosman, A.; Bonifazi, A.; Argenti, L.; Chiocci, F.L. Coralline algae on hard and soft substrata of a temperate mixed siliciclastic-carbonatic platform: Sensitive assemblages in the Zannone area (western Pontine Archipelago; Tyrrhenian Sea). Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 147, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adey, W.H.; MacIntyre, I.G. Crustose coralline algae: A re-evaluation in the geological sciences. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1973, 84, 883–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado-Filho, G.M.; Maneveldt, G.; Manson, R.C.C.; Marina Rosa, B.V.; Pacheco, M.R.; Guimarães, S.M.P.D. Structure of rhodolith beds from 4 to 55 meters deep along the southern coast of Espírito Santo state, Brazil. Cienc. Mar. 2007, 33, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, P.; Matheson, K.; Stapleton, M. Variation in rhodolith morphology and biogenic potential of newly discovered rhodolith bed in Newfoundland and Labrador (Canada). Bot. Mar. 2012, 55, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracchi, V.A.; Basso, D. The contribution of calcareous algae to the biogenic carbonates of the continental shelf: Pontian Islands, Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy. Geodiversitas 2012, 34, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steneck, R.S. The ecology of coralline algal crusts: Convergent patterns and adaptive strategies. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1986, 17, 273–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sañé, E.; Chiocci, F.L.; Basso, D.; Martorelli, E. Environmental factors controlling the distribution of rhodoliths: An integrated study based on seafloor sampling, ROV and side scan sonar data, offshore the W-Pontine Archipelago. Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 129, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérès, J.M.; Picard, J. Nouveau manuel de bionomie benthique de la Mer Méditerranée. Rec. Trav. St. Mar. Endoume 1964, 31, 5–137. [Google Scholar]
- Menna, M.; Mercatini, A.; Uttieri, M.; Buonocore, B.; Zambianchi, E. Wintertime transport processes in the Gulf of Naples investigated by HF radar measurements of surface currents. Il Nuovo Cimento C 2007, 30, 605–622. [Google Scholar]
- Uttieri, M.; Cianelli, D.; Nardelli, B.B.; Buonocore, B.; Falco, P.; Colella, S.; Zambianchi, E. Multiplatform observation of the surface circulation in the Gulf of Naples (Southern Tyrrhenian Sea). Ocean Dyn. 2011, 61, 779–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianelli, D.; Falco, P.; Iermano, I.; Mozzillo, P.; Uttieri, M.; Buonocore, B.; Zambardino, G.; Zambianchi, E. Inshore/offshore water exchange in the Gulf of Naples. J. Mar. Syst. 2015, 145, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulicino, G.; Cotroneo, Y.; Lacava, T.; Sileo, G.; Fusco, G.; Carlon, R.; Budillon, G. Results of the first Wave Glider experiment in the southern Tyrrhenian Sea. Adv. Oceanogr. Limnol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, P.; Buonocore, B.; Cianelli, D.; De Luca, L.; Giordano, A.; Iermano, I.; Kalampokis, A.; Saviano, S.; Uttieri, M.; Zambardino, G.; et al. Dynamics and sea state in the Gulf of Naples: Potential use of high-frequency radar data in an operational oceanographic context. J. Oper. Oceanogr. 2016, 9, s33–s45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagno, P.; de Ruggiero, P.; Pierini, S.; Zambianchi, E.; De Alteris, A.; De Stefano, M.; Budillon, G. Hydrographic and dynamical characterisation of the Bagnoli-Coroglio Bay (Gulf of Naples, Tyrrhenian Sea). Chem. Ecol. 2020, 36, 598–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruggiero, P.; Napolitano, E.; Iacono, R.; Pierini, S. A high-resolution modelling study of the circulation along the Campania coastal system, with a special focus on the Gulf of Naples. Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 122, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruggiero, P.; Napolitano, E.; Iacono, R.; Pierini, S.; Spezie, G. A baroclinic coastal trapped wave event in the Gulf of Naples (Tyrrhenian Sea). Ocean Dyn. 2018, 68, 1683–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruggiero, P.; Esposito, G.; Napolitano, E.; Iacono, R.; Pierini, S.; Zambianchi, E. Modelling the marine circulation of the Campania coastal system (Tyrrhenian Sea) for the year 2016: Analysis of the dynamics. J. Mar. Syst. 2020, 210, 103388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caragnano, A.; Basso, D.; Rodondi, G. Growth rates and ecology of coralline rhodoliths from the Ras Ghamila back reef lagoon, Red Sea. Mar. Ecol. 2016, 37, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfranco, E.; Rizzo, M.; Hall-Spencer, J.; Borg, J.A.; Schembri, P.J. Maerl-forming coralline algae and associated phytobenthos from the Maltese Islands. Central Mediterr. Nat. 1999, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Basso, D. Study of living calcareous algae by a paleontological approach: The non-geniculate Corallinaceae (Rhodophyta) of the soft bottoms of the Tyrrhenian Sea (Western Mediterranean). The genera Phymatolithon Foslie and Mesophyllum Lemoine. Riv. It. Paleont. Strat. 1994, 100, 575–596. [Google Scholar]
- Basso, D. Living calcareous algae by a paleontological approach: The genus Lithothamnion Heydrich nom. cons. from the soft bottoms of the Tyrrhenian Sea (Mediterranean). Riv. It. Paleont. Strat. 1995, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, D.; Rodondi, G. A Mediterranean population of Spongites fruticulosus (Rhodophyta, Corallinales), the type species of Spongites, and the taxonomic status of S. stalactitica and S. racemosa. Phycologia 2006, 45, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, D.; Fravega, P.; Vannucci, G. Fossil and living corallinaceans related to the mediterranean endemic species Lithophyllum racemus (Lamarck) Foslie. Facies 1996, 35, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressan, G.; Babbini, L. Biodiversità marina delle coste italiane: Corallinales del Mar Mediterraneo. Guida alla determinazione. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2003, 10, 1–237. [Google Scholar]
- Falace, A.; Kaleb, S.; Agnesi, S.; Annunziatellis, A.; Salvati, E.; Tunesi, L. Macroalgal composition of rhodolith beds in a pilot area of the Tuscan archipelago (Tyrrhenian Sea): Primary elements to evaluate the degree of conservation of this habitat. In Second Mediterranean Symposium on the conservation of Coralligenous and other Calcareous Bio-Concretions; Bouafif, C., Langar, H., Ouerghi, A., Eds.; RAC/SPA: Tunis, Tunisia, 2014; pp. 213–214. [Google Scholar]
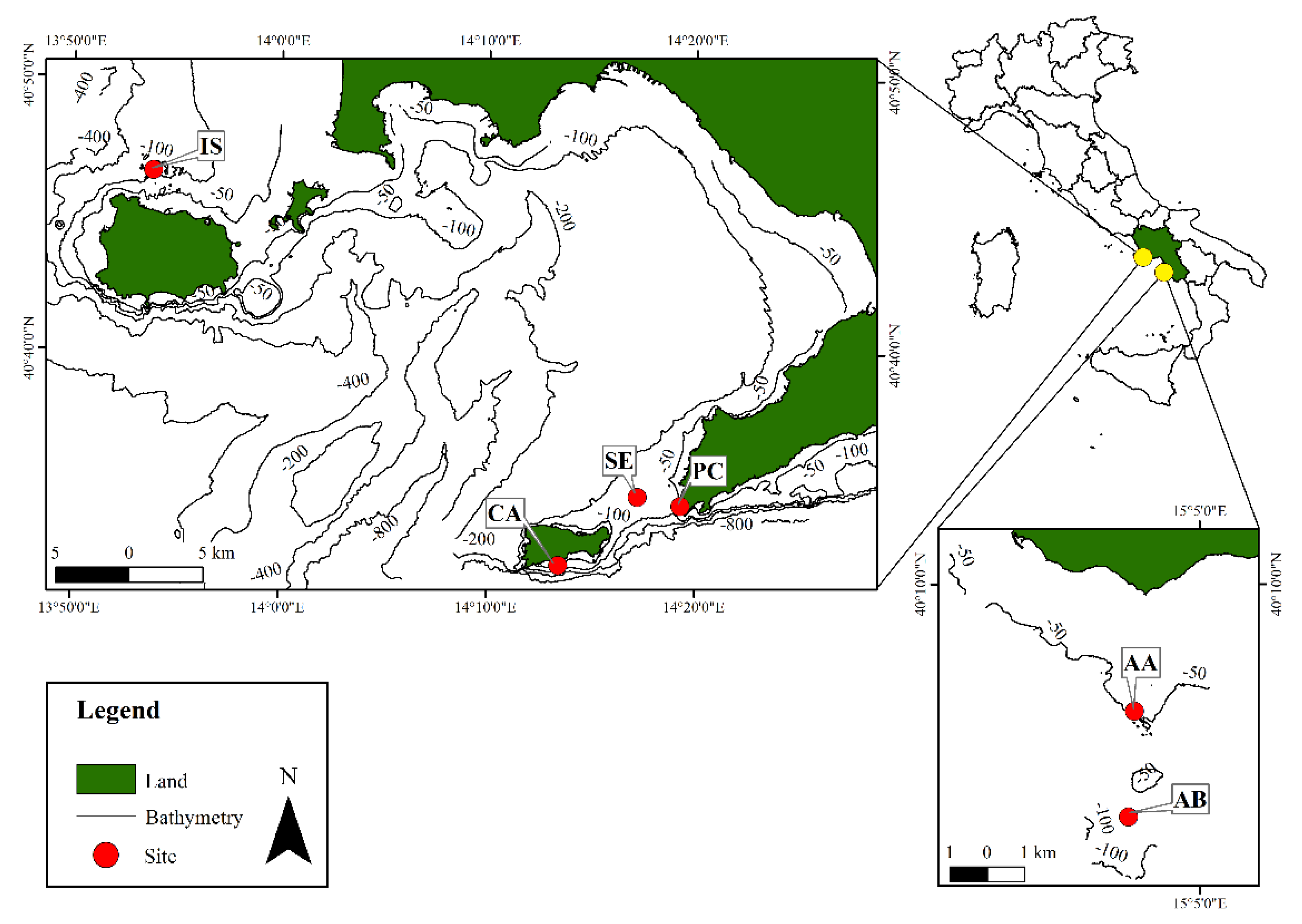



| Site | Latitude | Longitude | Time Period | ROV Routes’ Depth | Grab Samples’ Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capri (CA) | 40°32’20.545’’ N | 14°13’17.653’’ E | Jul-18 | 42–64 m | 55–59 m |
| Punta Campanella (PC) | 40°34’26.08’’ N | 14°19’19.049’’ E | Jul-18 | 53–62 m | 52–62 m |
| Secchitiello (SE) | 40°34’45.538’’ N | 14°17’15.261’’ E | Aug-18 | 70–78 m | 68–72 m |
| Ischia (IS) | 40°46’34.774’’ N | 13°53’49.401’’ E | Apr-17 | 58–73 m | 62–72 m |
| Acciaroli A (AA) | 40°8’9.582’’ N | 15°3’46.011’’ E | Jul-17 | 49–52 m | 48–49 m |
| Acciaroli B (AB) | 40°6’37.685’’ N | 15°3’39.149’’ E | Jul-17 | 65–73 m | 62–65 m |
| Site | Depth Interval | Substrate Type |
|---|---|---|
| Capri (CA) | Shallow | Coarse |
| Punta Campanella (PC) | Shallow | Coarse |
| Secchitiello (SE) | Deep | Fine |
| Ischia (IS) | Deep | Fine |
| Acciaroli A (AA) | Shallow | Coarse |
| Acciaroli B (AB) | Deep | Fine |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rendina, F.; Kaleb, S.; Caragnano, A.; Ferrigno, F.; Appolloni, L.; Donnarumma, L.; Russo, G.F.; Sandulli, R.; Roviello, V.; Falace, A. Distribution and Characterization of Deep Rhodolith Beds off the Campania coast (SW Italy, Mediterranean Sea). Plants 2020, 9, 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9080985
Rendina F, Kaleb S, Caragnano A, Ferrigno F, Appolloni L, Donnarumma L, Russo GF, Sandulli R, Roviello V, Falace A. Distribution and Characterization of Deep Rhodolith Beds off the Campania coast (SW Italy, Mediterranean Sea). Plants. 2020; 9(8):985. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9080985
Chicago/Turabian StyleRendina, Francesco, Sara Kaleb, Annalisa Caragnano, Federica Ferrigno, Luca Appolloni, Luigia Donnarumma, Giovanni Fulvio Russo, Roberto Sandulli, Valentina Roviello, and Annalisa Falace. 2020. "Distribution and Characterization of Deep Rhodolith Beds off the Campania coast (SW Italy, Mediterranean Sea)" Plants 9, no. 8: 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9080985
APA StyleRendina, F., Kaleb, S., Caragnano, A., Ferrigno, F., Appolloni, L., Donnarumma, L., Russo, G. F., Sandulli, R., Roviello, V., & Falace, A. (2020). Distribution and Characterization of Deep Rhodolith Beds off the Campania coast (SW Italy, Mediterranean Sea). Plants, 9(8), 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9080985