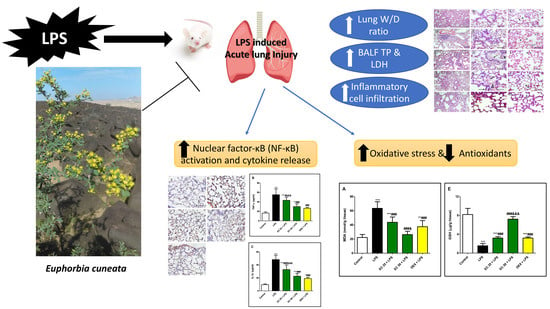
Euphorbia cuneata Represses LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice via Its Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Plant Material
2.3. Extraction Procedures for Pharmacological Study
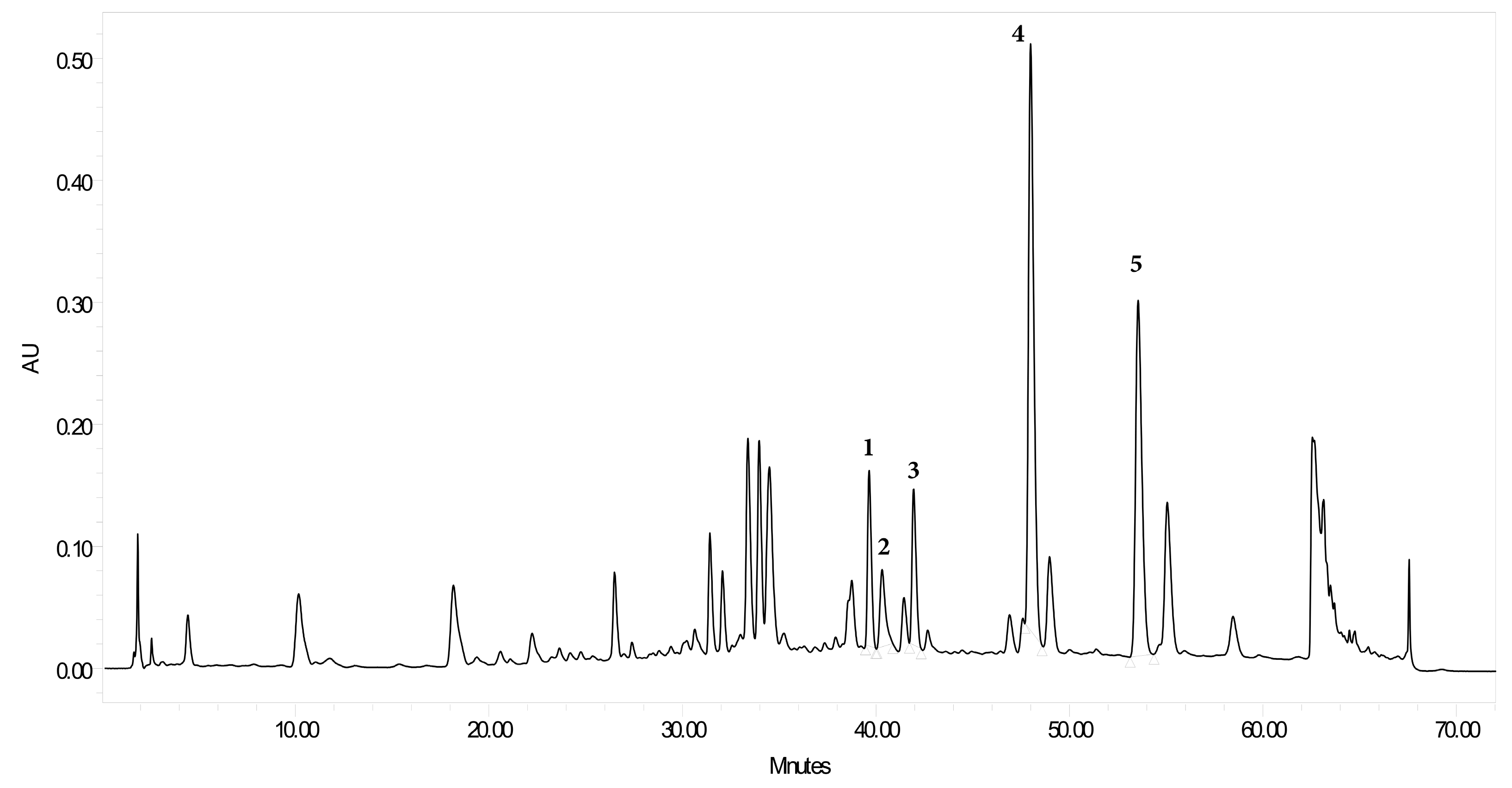
2.4. Extraction Procedures of Plant Material for High Performance Liquid Chromatography Diode-Array Detection
2.5. HPLC Photodiode Array Determination of Flavonoid Content in TEC
2.6. Calibration Curve of the Isolated Compounds
2.7. Biological Study
2.7.1. Animals and Experimental Model
2.7.2. Lung Wet/Dry Weight (W/D) Ratio
2.7.3. Protein Content
2.7.4. LDH Activity
2.7.5. Total and Differential Cell Counts
2.7.6. Lung Histology
2.7.7. Immunohistopathology
2.7.8. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants
2.7.9. NF-κB and Inflammatory Cytokines
2.7.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
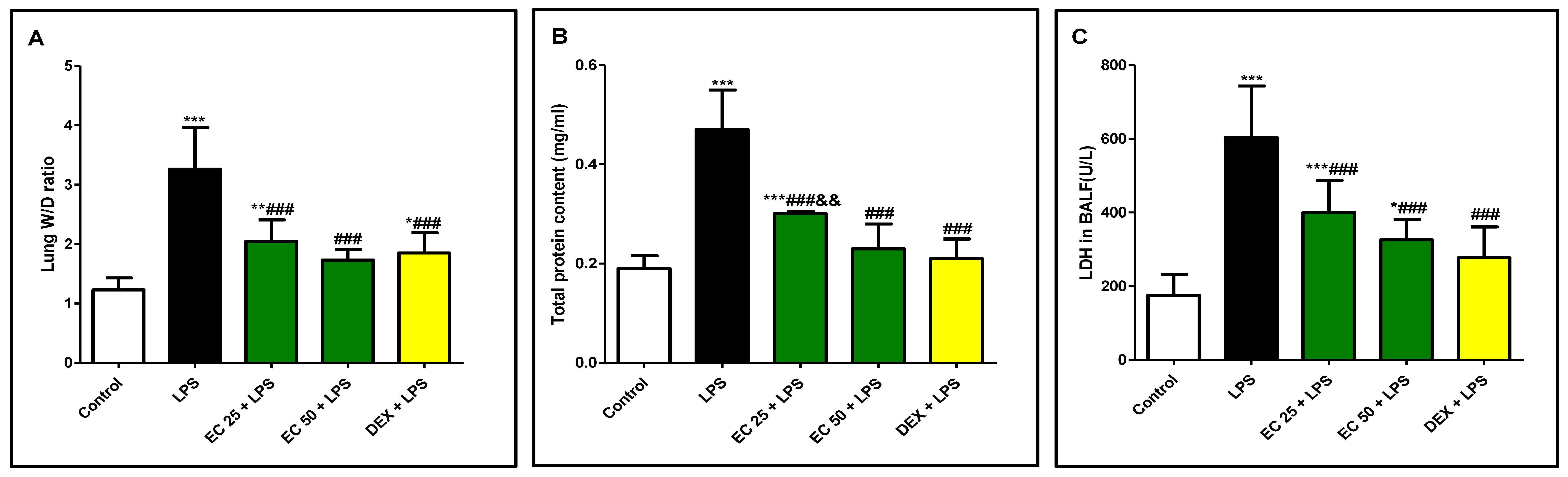
3.1. Effect of EC on LPS-Induced Lung Edema
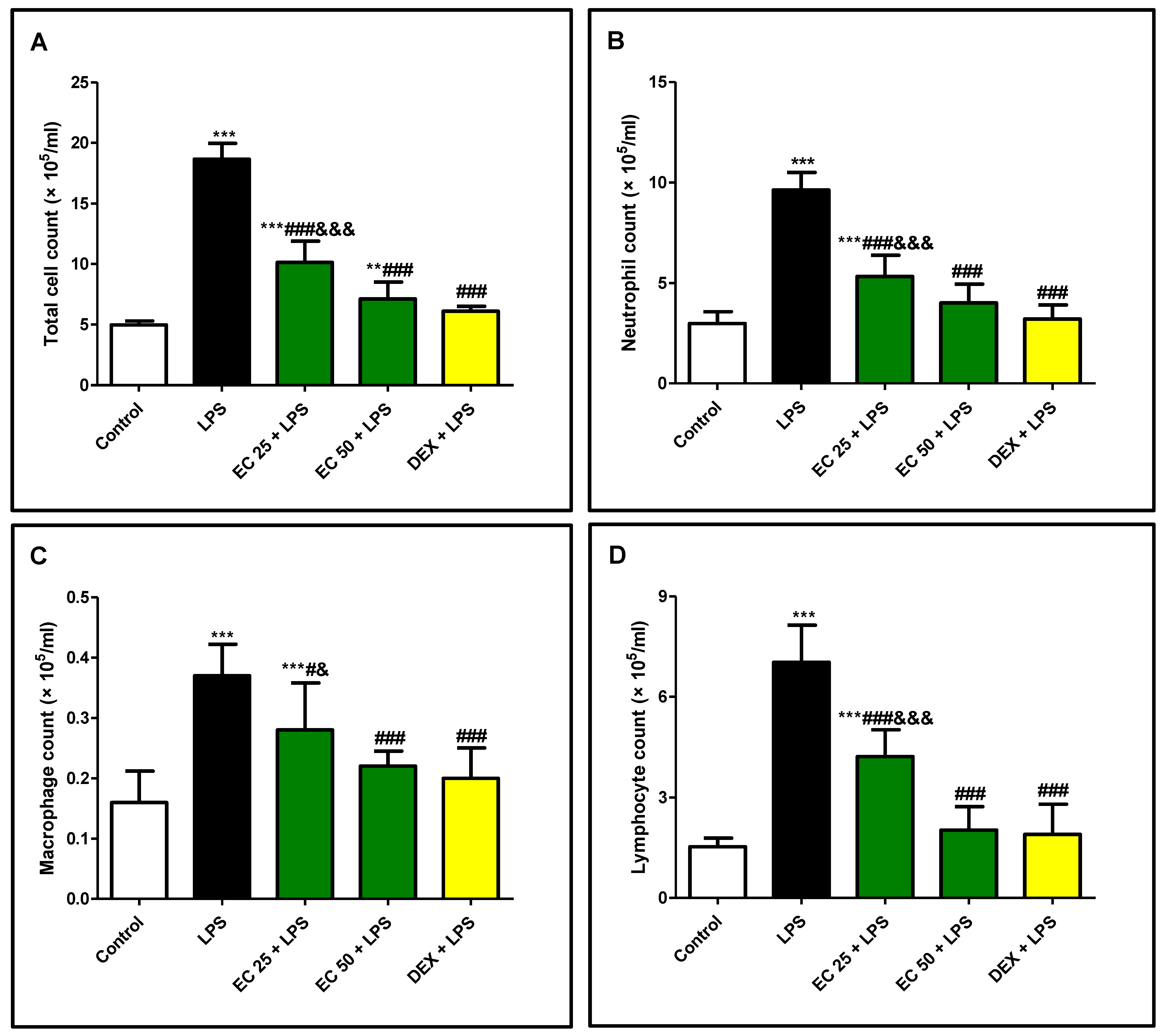
3.2. Effect of EC on LPS-Induced Increase in the Total and Differential Inflammatory Cell Counts in BALF
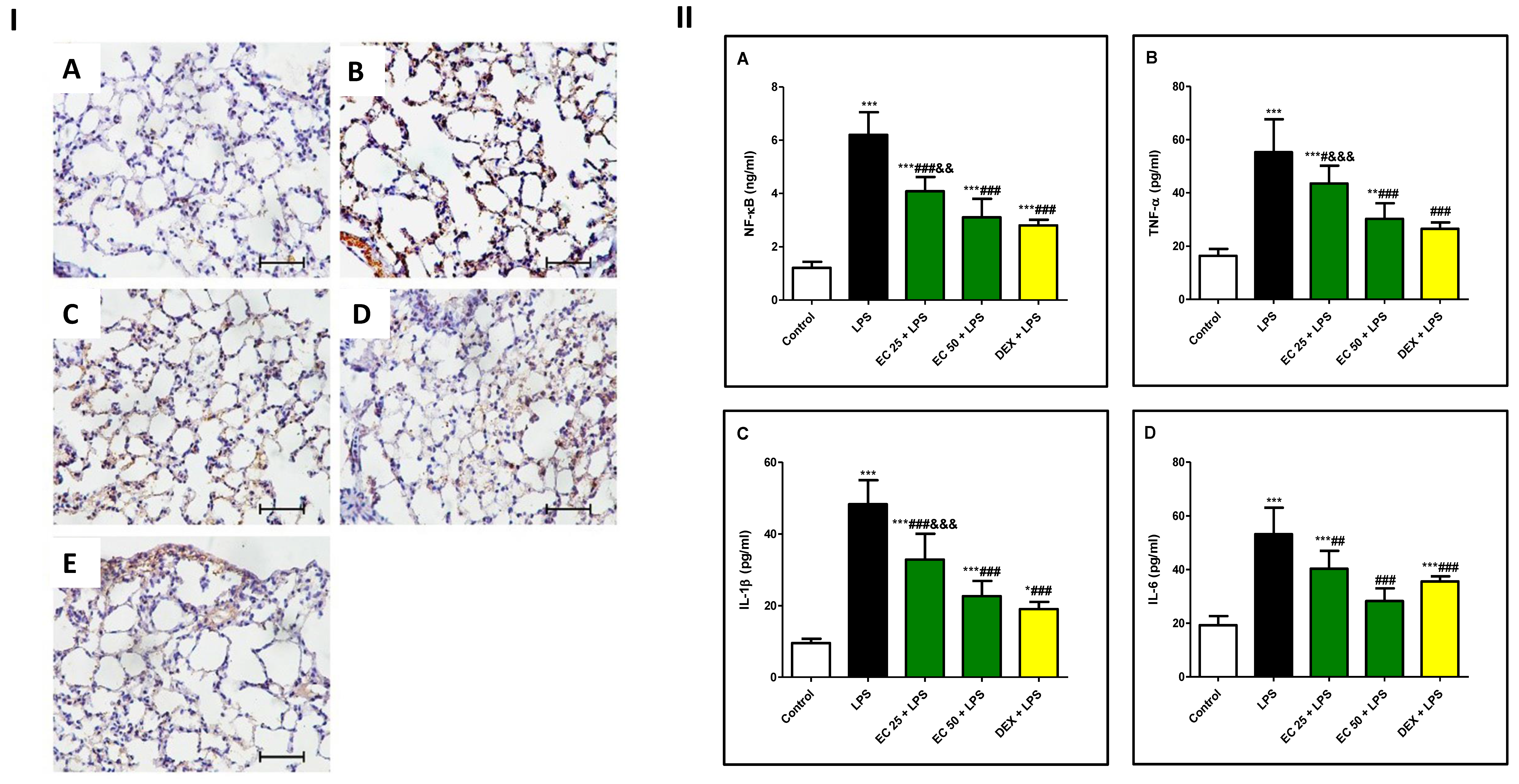
3.3. Effect of EC on LPS-Induced Lung Damage
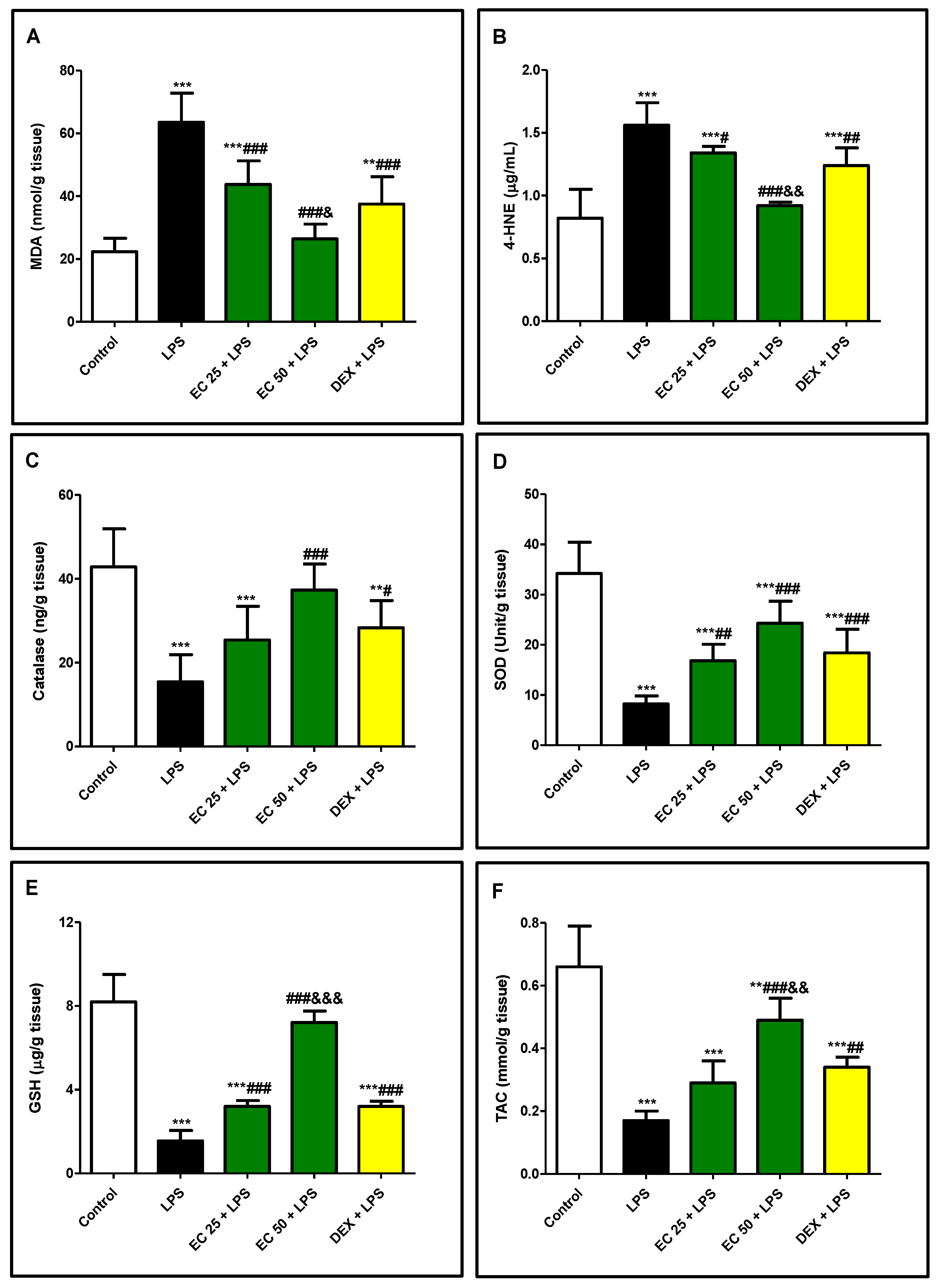
3.4. Effect of EC on LPS-Induced Lipid Peroxidation and Antioxidants in Lung
3.5. Effect of EC on LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response in Lung
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Agamy, D.S.; Mohamed, G.A.; Ahmed, N.; Elkablawy, M.A.; Elfaky, M.A.; Elsaed, W.M.; Mohamed, S.G.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.M. Protective anti-inflammatory activity of tovophyllin A against acute lung injury and its potential cytotoxicity to epithelial lung and breast carcinomas. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 28, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Ahmed, N.; Almalki, S.; Alharbi, N.; El-Agamy, D.S.; Alahmadi, L.A.; Saubr, M.K.; Elkablawy, M.A.; Elshafie, R.M.; Mohamed, G.A.; et al. Vitex agnus-castus safeguards the lung against lipopolysaccharide-induced toxicity in mice. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 43, e12750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, T.-L.; Chen, M.-F.; Tsai, M.-J.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-P.; Lee, T.J.F. Oroxylin-A rescues LPS-induced acute lung injury via regulation of NF-κB signaling pathway in rodents. PLOS ONE 2012, 7, e47403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaaban, A.A.; El-Kashef, D.H.; Hamed, M.F.; El-Agamy, D.S. Protective effect of pristimerin against LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 59, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Agamy, D.S. Nilotinib ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 253, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Jiang, K.; Wu, H.; Yang, C.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhao, G.; Deng, G. Magnoflorine ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via suppressing NF-κB and MAPK activation. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Wang, D.-X.; Zhang, W.; Liao, X.-Q.; Guan, X.; Bo, H.; Sun, J.-Y.; Huang, N.-W.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.-K.; et al. Andrographolide protects against LPS-induced acute lung injury by inactivation of NF-κB. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e56407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Wu, Y.; Guo, H.; Huang, X. Salidroside protects lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Dose-Response 2016, 14, 1559325816678492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Aljuhani, N.; Salamah, S.; Surrati, H.; El-Agamy, D.S.; Elkablawy, M.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Mohamed, G.A. Pulicaria petiolaris effectively attenuates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury in mice. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2018, 70, 699–706. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Yang, Y.; Guo, S.; Yang, J.; Jiang, K.; Zhao, G.; Qiu, C.; Deng, G. Nuciferine ameliorates inflammatory responses by inhibiting the TLR4-mediated pathway in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Zeng, M.; Lin, D.; Wang, Y.; Wen, X.; Xu, C.; Yang, L.; Fan, X.; Gong, Y.; et al. Apelin-13 administration protects against LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting NF-κB pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 1918–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, G.A.; Al-Abd, A.M.; El-Halawany, A.M.; Abdallah, H.M.; Ibrahim, S.R.M. New xanthones and cytotoxic constituents from Garcinia mangostana fruit hulls against human hepatocellular, breast, and colorectal cancer cell lines. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 198, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasas, A.; Hohmann, J. Euphorbia diterpenes: Isolation, structure, biological activity, and synthesis (2008–2012). Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 8579–8612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.; Akter, M. Taxonomy and medicinal uses of Euphorbiaceae (Spurge) family of Rajshahi, Bangladesh. Res. Plant Sci. 2013, 1, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Awaad, A.S.; Al-Jaber, N.A.; Moses, J.E.; El-Meligy, R.M.; E Zain, M. Antiulcerogenic activities of the extracts and isolated flavonoids of Euphorbia cuneata Vahl. Phytother. Res. 2012, 27, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awaad, S.A.; Alothman, M.R.; Zain, Y.M.; Alqasoumi, S.I.; Alothman, E.A. Quantitative and qualitative analysis for standardization of Euphorbia cuneata Vahl. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 1175–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Alam, S.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Das, B.K. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity of Euphorbia antiquorum Linn. Am. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 10, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fatimi, M. Ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants in central Abyan governorate, Yemen. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 241, 111973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zain, M.E.; Awaad, A.S.; Al-Outhman, M.R.; El-Meligy, R.M. Antimicrobial activities of Saudi Arabian desert plants. Phytopharmacology 2012, 2, 106–113. [Google Scholar]
- Elghamdi, A.A.; Abdallah, H.M.; Shehata, I.A.; Mohamed, G.A.; Shati, A.A.; Alfaifi, M.Y.; Elbehairi, S.E.I.; Koshak, A.E.; Ibrahim, S.R.M. Cyclocuneatol and cuneatannin, new cycloartane triterpenoid and ellagitannin glycoside from Euphorbia cuneata. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 12375–12379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazanfar, S.A. Handbook of Arabian Medicinal Plants; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Collenette, S. Wildflowers of Saudi Arabia; National Commission for Wildlife Conservation and Development; NCWCD: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 1999; p. 167. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Harbi, N.O.; Imam, F.; Al-Harbi, M.M.; Ansari, M.A.; Zoheir, K.M.A.; Korashy, H.M.; Sayed-Ahmed, M.M.; Attia, S.M.; Shabanah, O.A.; Ahmad, A.M. Dexamethasone attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury through inhibition of NF-κB, COX-2, and pro-inflammatory mediators. Immunol. Investig. 2016, 45, 349–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Du, J. Anti-inflammatory and protective effects of D-carvone on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury in mice. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2020, 32, 1592–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kholy, A.A.; Elkablawy, M.A.; El-Agamy, D.S. Lutein mitigates cyclophosphamide induced lung and liver injury via NF-κB/MAPK dependent mechanism. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Xiu, Y.; Zhou, P.; Qiu, Y.; Li, Y.-H. A New Use for an Old Drug: Carmofur attenuates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury via inhibition of FAAH and NAAA activities. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yu, X.; Yu, S.; Kou, J. Molecular mechanisms in lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary endothelial barrier dysfunction. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 29, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Ci, X.; Wen, Z.; Peng, L. Diosmetin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through activating the Nrf2 pathway and inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome. Biomol. Ther. 2018, 26, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Du, F.; Zhou, X.; Song, Q.; Zhao, J.; Fang, R. Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via MerTK-dependent activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xu, D.; Liu, J.; Gu, L. Protective effect of sophocarpine on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 70, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Huo, P.; Li, X.-O.; Kong, D.; Mu, W.; Fang, W.; Li, L.; Liu, N.; Fang, L.; et al. Protective effect of Jolkinolide B on LPS-induced mouse acute lung injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 26, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uto, T.; Qin, G.-W.; Morinaga, O.; Shoyama, Y. 17-Hydroxy-jolkinolide B, a diterpenoid from Euphorbia fischeriana, inhibits inflammatory mediators but activates heme oxygenase-1 expression in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated murine macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 12, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, S.; Cheng, X.; Lu, C.; Tao, W.; Zhang, Y.; William, B.C.; Cao, X.; Yi, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Euphorbia factor L2 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury and inflammation in mice through the suppression of NF-κB activation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 155, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yao, J.; Han, C.; Yang, J.; Chaudhry, M.T.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y. Quercetin, inflammation and immunity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen-Ngo, C.; Willcox, J.C.; Lappas, M. Anti-Diabetic, anti-Inflammatory, and anti-Oxidant effects of naringenin in an in vitro human model and an in vivo murine model of gestational diabetes mellitus. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1900224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon-Montano, J.M.; Burgos-Moron, E.; Perez-Guerrero, C.; Lopez-Lazaro, M. A Review on the dietary flavonoid kaempferol. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 298–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdallah, H.M.; El-Agamy, D.S.; Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Mohamed, G.A.; Elsaed, W.M.; Elghamdi, A.A.; Safo, M.K.; Malebari, A.M. Euphorbia cuneata Represses LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice via Its Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Plants 2020, 9, 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111620
Abdallah HM, El-Agamy DS, Ibrahim SRM, Mohamed GA, Elsaed WM, Elghamdi AA, Safo MK, Malebari AM. Euphorbia cuneata Represses LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice via Its Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Plants. 2020; 9(11):1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111620
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdallah, Hossam M., Dina S. El-Agamy, Sabrin R. M. Ibrahim, Gamal A. Mohamed, Wael M. Elsaed, Amjad A. Elghamdi, Martin K. Safo, and Azizah M. Malebari. 2020. "Euphorbia cuneata Represses LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice via Its Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Activities" Plants 9, no. 11: 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111620
APA StyleAbdallah, H. M., El-Agamy, D. S., Ibrahim, S. R. M., Mohamed, G. A., Elsaed, W. M., Elghamdi, A. A., Safo, M. K., & Malebari, A. M. (2020). Euphorbia cuneata Represses LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice via Its Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Plants, 9(11), 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111620