High Light Acclimation Induces Chloroplast Precursor Phosphorylation and Reduces Import Efficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Several Chloroplast Precursors are Phosphorylated by STY8 in Vitro
2.2. High Light Treatment of Arabidopsis Enhances Phosphorylation
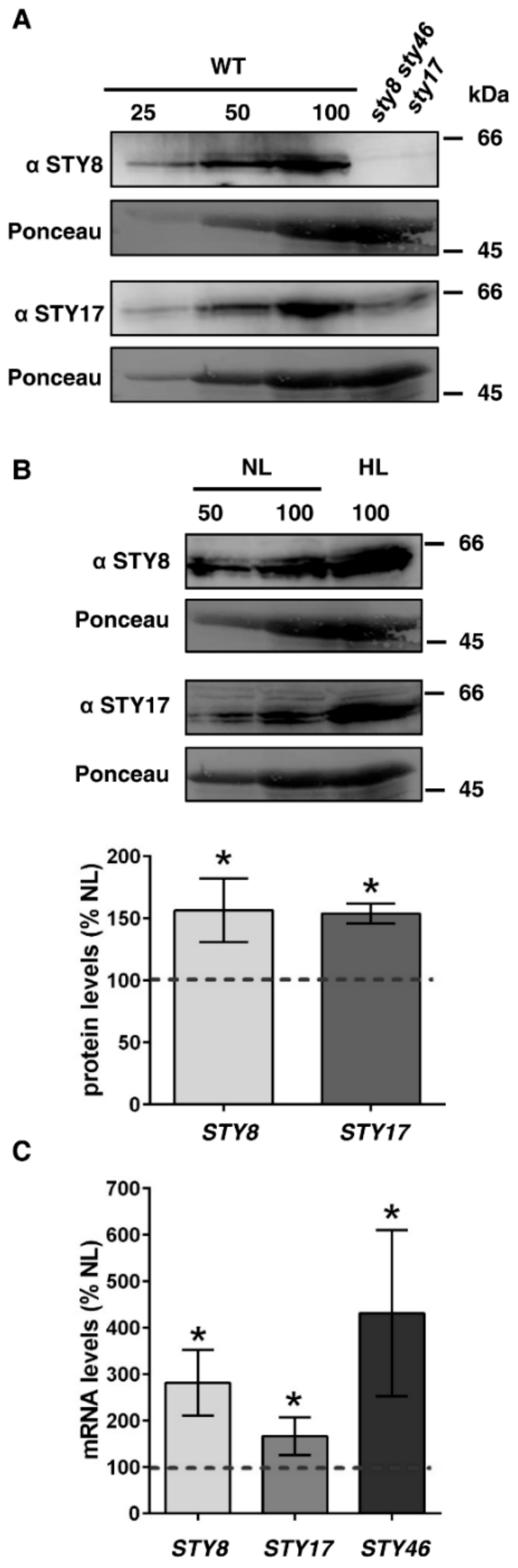
2.3. STY Kinases are Upregulated on Protein and mRNA Level under High Light
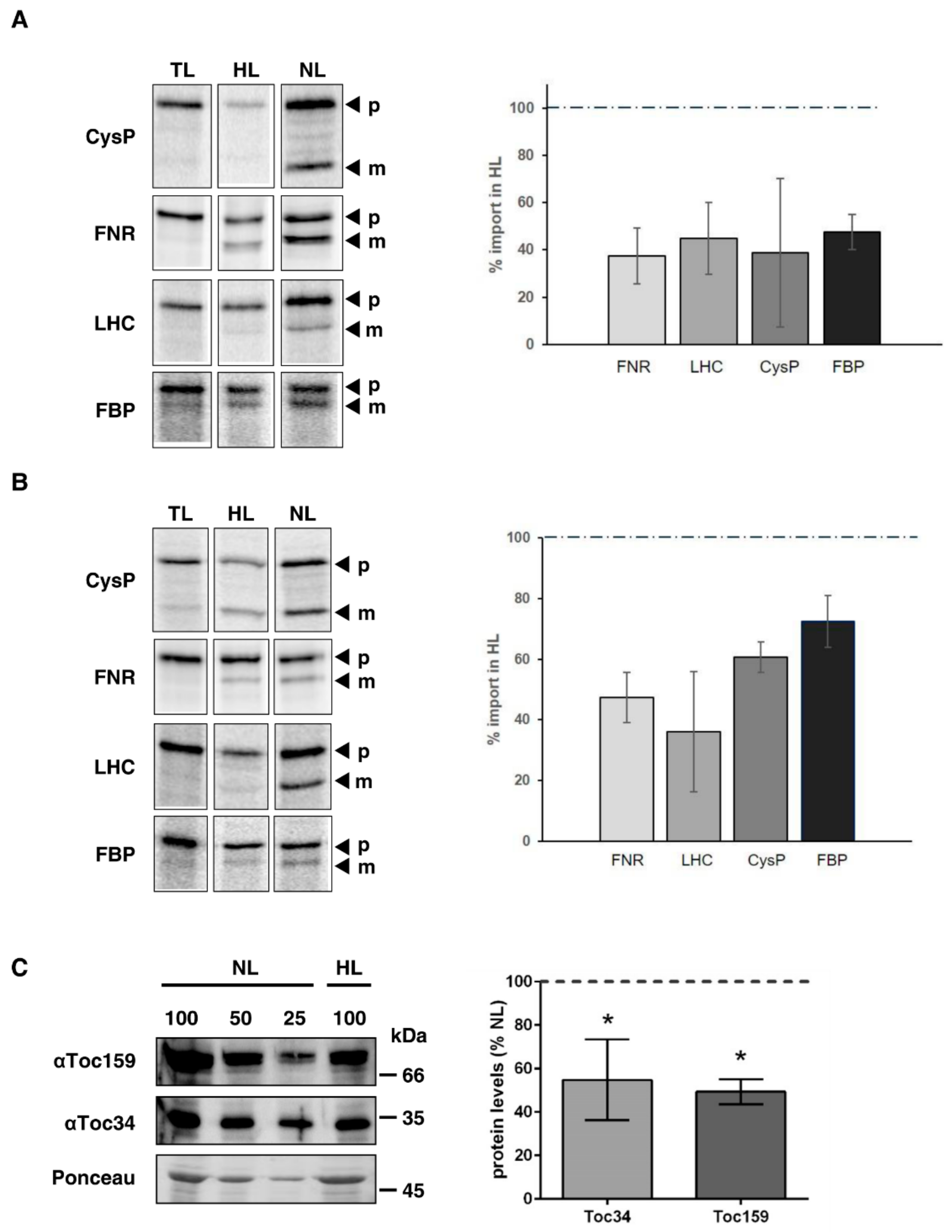
2.4. Import Efficiency into Arabidopsis and Pea Chloroplasts is Reduced in Response to High Light Treatment
2.5. High Light Treatment Leads to Reduced Accumulation of Toc159 and Toc34 in Pea
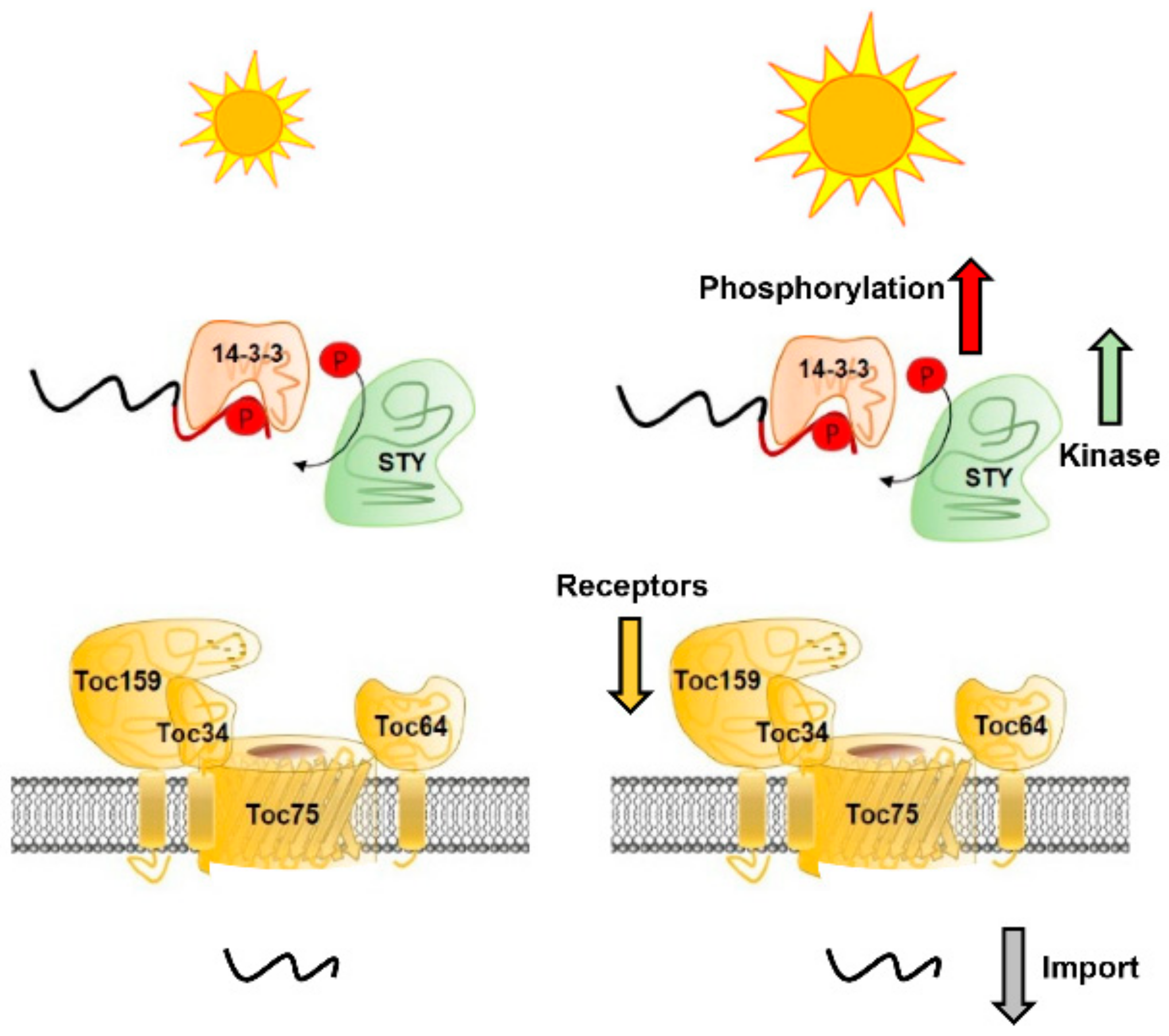
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Light Treatment
4.2. Purification of Recombinant Proteins
4.3. Phosphorylation Assays
4.4. SDS-PAGE and Immunoblotting
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.6. Transcription and Translation
4.7. Chloroplast Isolation and Protein Import
4.8. Accession Numbers
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Qi, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, T. Targeted control of chloroplast quality to improve plant acclimation: From protein import to degradation. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjuts, I.; Soll, J.; Bolter, B. Import of soluble proteins into chloroplasts and potential regulatory mechanisms. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qbadou, S.; Becker, T.; Mirus, O.; Tews, I.; Soll, J.; Schleiff, E. The molecular chaperone hsp90 delivers precursor proteins to the chloroplast import receptor toc64. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 1836–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, T.; Soll, J. 14-3-3 proteins form a guidance complex with chloroplast precursor proteins in plants. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellerer, C.; Schweiger, R.; Schongruber, K.; Soll, J.; Schwenkert, S. Cytosolic hsp90 cochaperones hop and fkbp interact with freshly synthesized chloroplast preproteins of arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.; Sharma, R.; Sippel, C.; Waegemann, K.; Soll, J.; Vothknecht, U.C. A protein kinase family in arabidopsis phosphorylates chloroplast precursor proteins. J. Biol.Chem. 2006, 281, 40216–40223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, G.; Gugel, I.L.; Meurer, J.; Soll, J.; Schwenkert, S. The cytosolic kinases sty8, sty17, and sty46 are involved in chloroplast differentiation in arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisa, A.; Bolter, B.; Schwenkert, S. The act domain in chloroplast precursor-phosphorylating sty kinases binds metabolites and allosterically regulates kinase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 17278–17288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.L.; Soll, J.; Bolter, B. The gateway to chloroplast: Re-defining the function of chloroplast receptor proteins. Biol. Chem. 2012, 393, 1263–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolter, B.; Soll, J.; Schwenkert, S. Redox meets protein trafficking. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1847, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsera, M.; Soll, J.; Buchanan, B.B. Protein import in chloroplasts: An emerging regulatory role for redox. Adv. Bot. Res. 2009, 52, 277–332. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.X.; Theg, S.M. The chloroplast protein import system: From algae to trees. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stengel, A.; Benz, J.P.; Buchanan, B.B.; Soll, J.; Bölter, B. Preprotein import into chloroplasts via the toc and tic complexes is regulated by redox signals in pisum sativum. Mol. Plant 2009, 2, 1181–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waegemann, K.; Soll, J. Phosphorylation of the transit sequence of chloroplast precursor proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 6545–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, L.G.L.; Schnell, D.J. Origins, function and regulation of the toc-tic general protein import machinery of plastids. J. Exp. Bot. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.J.; Sowden, R.G.; Jarvis, P. Abiotic stress-induced chloroplast proteome remodelling: A mechanistic overview. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 2773–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, C.; Soll, J.; Schwenkert, S. Phosphomimicking within the transit peptide of phcf136 leads to reduced photosystem ii accumulation in vivo. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkanen, L.; Rintamäki, E. Chloroplast thioredoxin systems dynamically regulate photosynthesis in plants. Biochem. J. 2019, 476, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foyer, C.H. Reactive oxygen species, oxidative signaling and the regulation of photosynthesis. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 154, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.M.; Chow, W.S.; Park, Y.-I. The grand design of photosynthesis: Acclimation of the photosynthetic apparatus to environmental cues. Photosynth. Res. 1995, 46, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballottari, M.; Dall’Osto, L.; Morosinotto, T.; Bassi, R. Contrasting behavior of higher plant photosystem i and ii antenna systems during acclimation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 8947–8958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wientjes, E.; van Amerongen, H.; Croce, R. Lhcii is an antenna of both photosystems after long-term acclimation. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics 2013, 1827, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvi, S.; Suorsa, M.; Aro, E.-M. Photosystem ii repair in plant chloroplasts—regulation, assisting proteins and shared components with photosystem ii biogenesis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics 2015, 1847, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Aro, E.-M.; Millar, A.H. Mechanisms of photodamage and protein turnover in photoinhibition. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenkert, S.; Umate, P.; Dal Bosco, C.; Volz, S.; Mlcochova, L.; Zoryan, M.; Eichacker, L.A.; Ohad, I.; Herrmann, R.G.; Meurer, J. Psbi affects the stability, function, and phosphorylation patterns of photosystem ii assemblies in tobacco. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 34227–34238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waegemann, K.; Soll, J. Characterization of the protein import apparatus in isolated outer envelopes of chloroplasts. Plant J. 1991, 1, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seedorf, M.; Waegemann, K.; Soll, J. A constituent of the chloroplast import complex represents a new type of gtp-binding protein. Plant J. 1995, 7, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firlej-Kwoka, E.; Strittmatter, P.; Soll, J.; Bolter, B. Import of preproteins into the chloroplast inner envelope membrane. Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 68, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon, D.J. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in beta vulgaris. Plant Phys. 1949, 24, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eisa, A.; Malenica, K.; Schwenkert, S.; Bölter, B. High Light Acclimation Induces Chloroplast Precursor Phosphorylation and Reduces Import Efficiency. Plants 2020, 9, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9010024
Eisa A, Malenica K, Schwenkert S, Bölter B. High Light Acclimation Induces Chloroplast Precursor Phosphorylation and Reduces Import Efficiency. Plants. 2020; 9(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleEisa, Ahmed, Katarina Malenica, Serena Schwenkert, and Bettina Bölter. 2020. "High Light Acclimation Induces Chloroplast Precursor Phosphorylation and Reduces Import Efficiency" Plants 9, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9010024
APA StyleEisa, A., Malenica, K., Schwenkert, S., & Bölter, B. (2020). High Light Acclimation Induces Chloroplast Precursor Phosphorylation and Reduces Import Efficiency. Plants, 9(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9010024



