Plant-Produced Anti-Enterovirus 71 (EV71) Monoclonal Antibody Efficiently Protects Mice Against EV71 Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
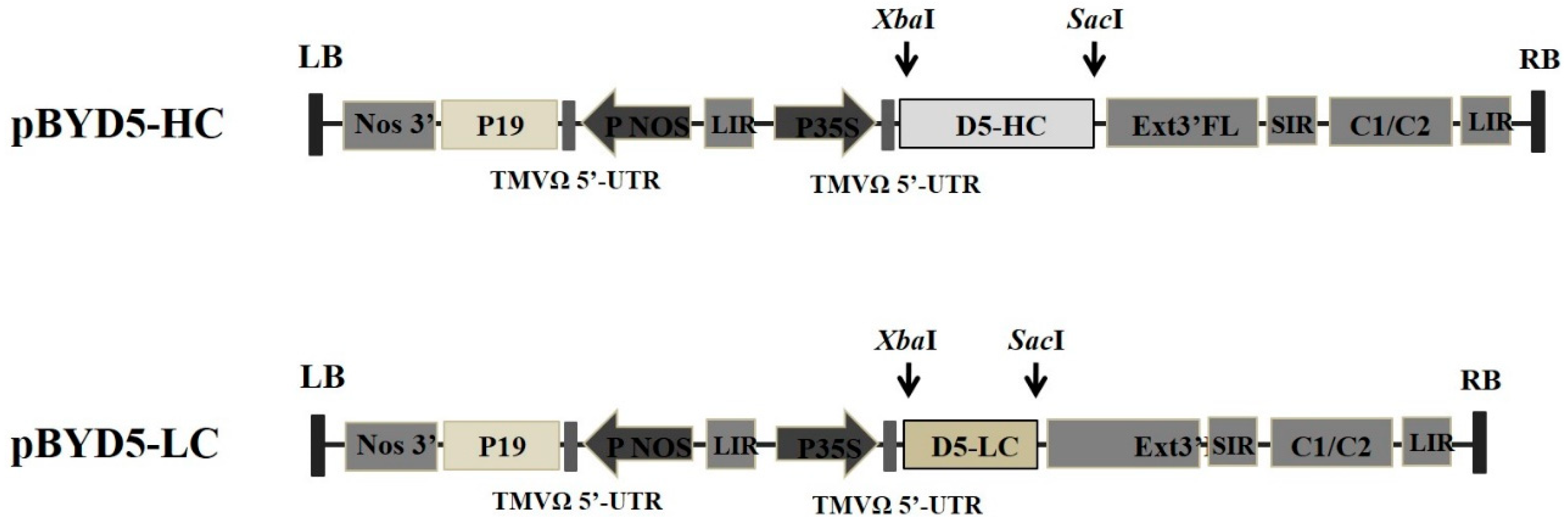
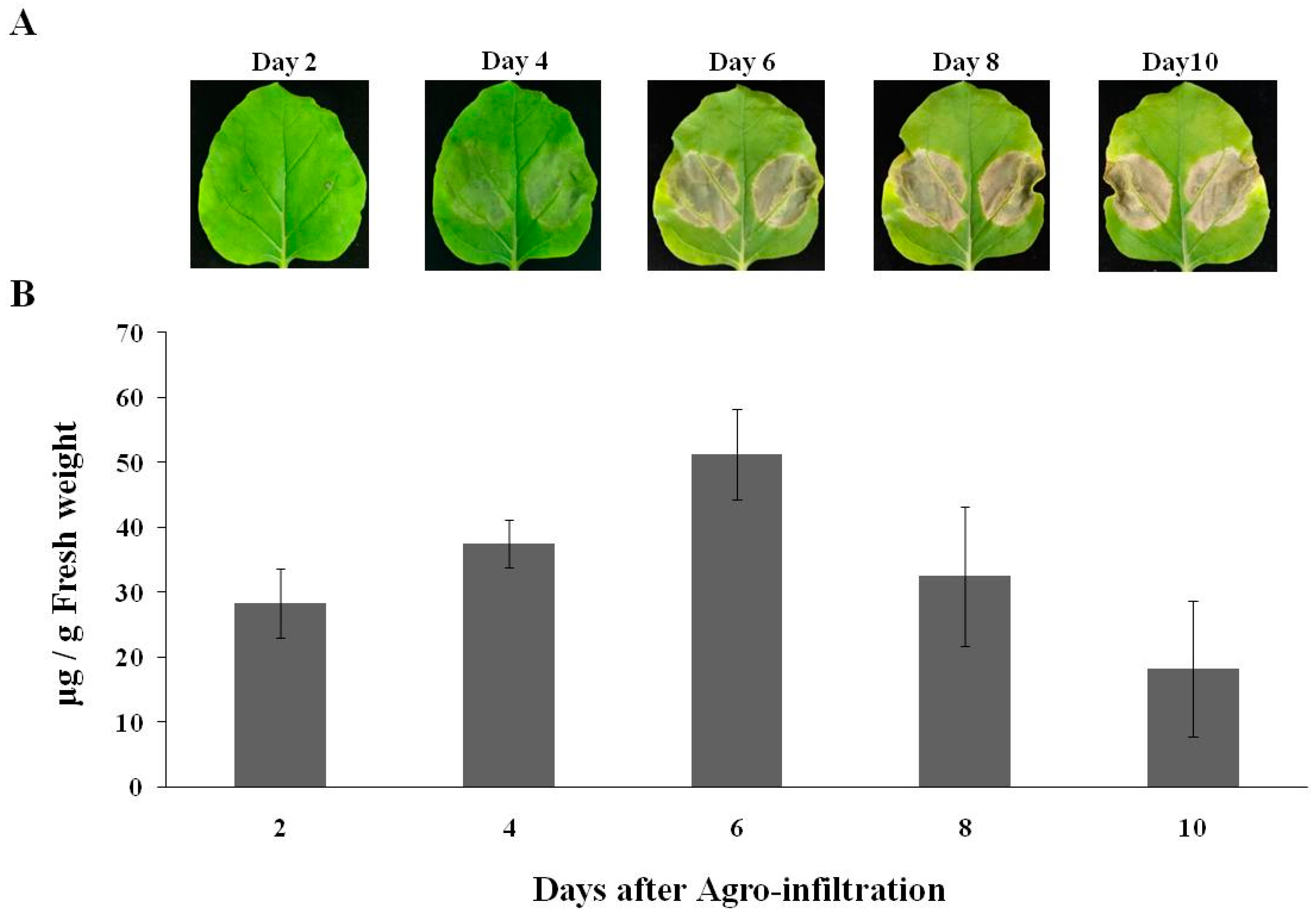
2.1. Expression of cD5 mAb in Nicotiana benthamiana
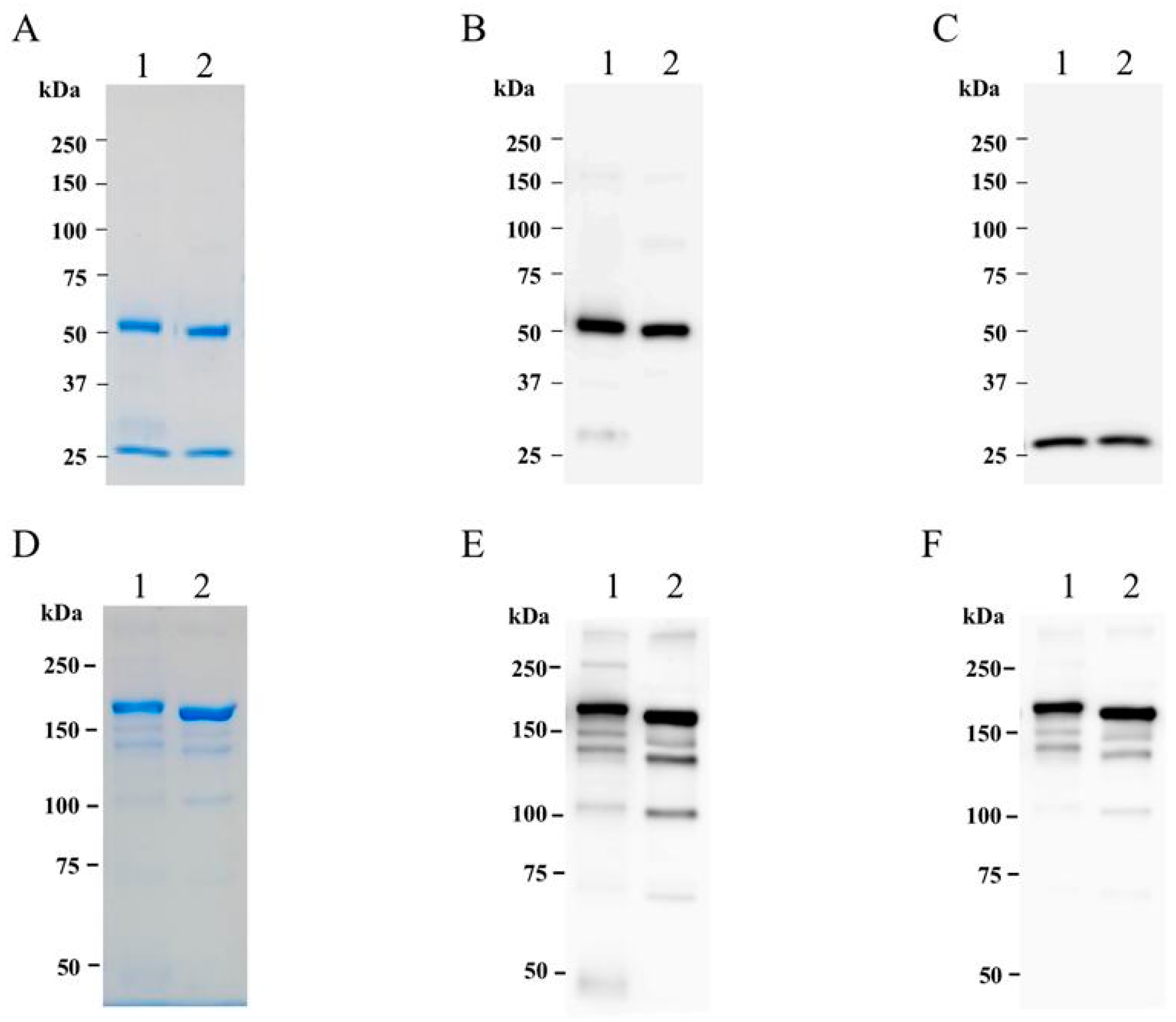
2.2. Purification of cD5 mAb from N. benthamiana Leaves
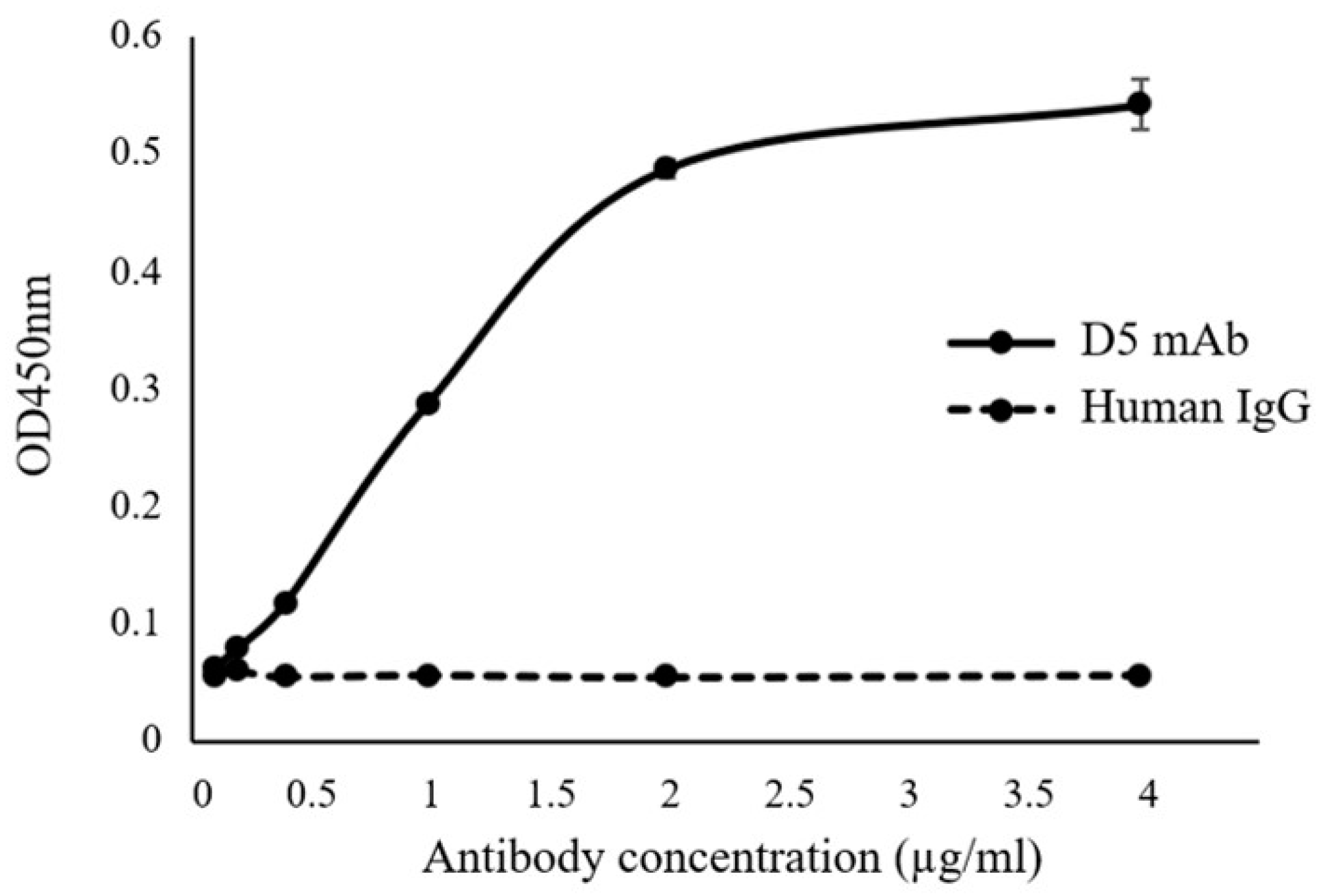
2.3. Plant-Produced cD5 mAb Retains Antigen-Binding Activity
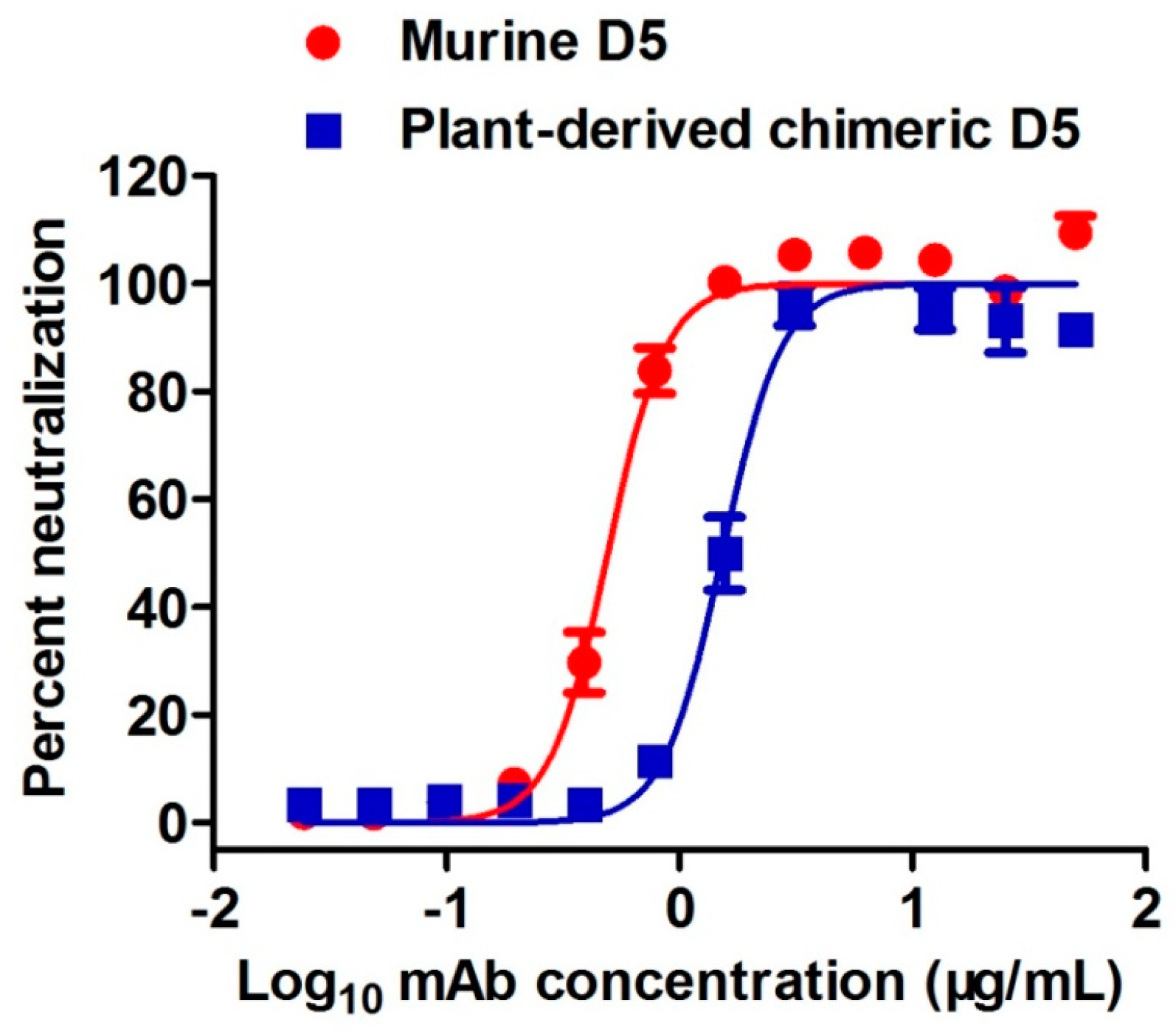
2.4. Plant-Produced cD5 mAb Efficiently Neutralized EV71
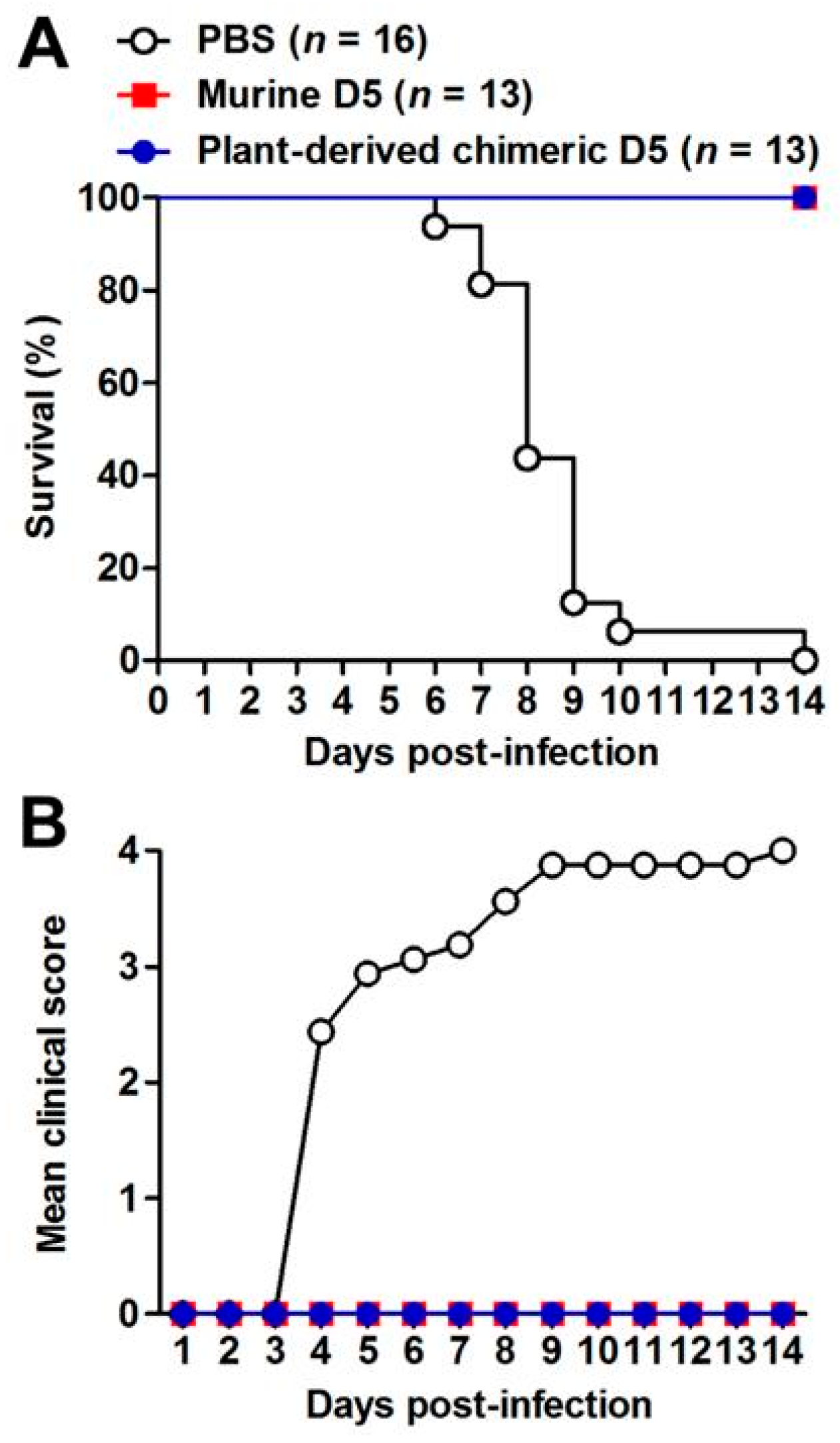
2.5. Plant-Produced cD5 mAb Protected Recipient Mice Against Lethal EV71 Infection
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Gene Construct
4.2. Protein Expression, Extraction and Quantification
4.3. Purification
4.4. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Binding Assay
4.6. Neutralization Assay
4.7. In Vivo Protection Assay
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Badaruddin, H.; Lee, V.J.; Cutter, J.; Cook, A.R. The effect of school closure on hand, foot, and mouth disease transmission in Singapore: A Modeling Approach. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, M.T.V.; Nguyen, T.A.; Tran, T.T.; Vu, T.T.H.; Le, N.T.N.; Nguyen, T.H.N.; Le, T.H.N.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Nguyen, T.H.; Le, N.T.N.; et al. Clinical and aetiological study of hand, foot and mouth disease in southern Vietnam, 2013-2015: Inpatients and outpatients. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 80, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, M.H.; Wong, S.C.; Lewthwaite, P.; Cardosa, M.J.; Solomon, T. Clinical features, diagnosis, and management of enterovirus 71. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Liu, C.C.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Wang, S.T.; Yeh, T.F. Neurologic complications in children with enterovirus 71 infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Zhao, H.; Shi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, Q. Optimized development of a candidate strain of inactivated EV71 vaccine and analysis of its immunogenicity in rhesus monkeys. Hum. Vaccin. 2010, 6, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, L.; Che, Y.; Shi, H.; Li, R.; Mo, Z.; Huang, T.; et al. Study of the integrated immune response induced by an inactivated EV71 vaccine. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Liu, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Na, R.; Liang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Q. Immunoprotection elicited by an enterovirus type 71 experimental inactivated vaccine in mice and rhesus monkeys. Vaccine 2011, 29, 6269–6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bek, E.J.; Hussain, K.M.; Phuektes, P.; Kok, C.C.; Gao, Q.; Cai, F.; Gao, Z.; McMinn, P.C. Formalin-inactivated vaccine provokes cross-protective immunity in a mouse model of human enterovirus 71 infection. Vaccine 2011, 29, 4829–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ku, Z.; Liu, Q.; Leng, Q.; Huang, Z. A combination vaccine comprising of inactivated enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 elicits balanced protective immunity against both viruses. Vaccine 2014, 32, 2406–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.H.; Chu, C.; He, C.C.; Lin, T.Y. Protection of neonatal mice from lethal enterovirus 71 infection by maternal immunization with attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium expressing VP1 of enterovirus 71. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, M.; Nagata, N.; Iwata, N.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Mizuta, K.; Iwasaki, T.; Sata, T.; Wakita, T.; Shimizu, H. An attenuated strain of enterovirus 71 belonging to genotype a showed a broad spectrum of antigenicity with attenuated neurovirulence in cynomolgus monkeys. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 9386–9395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.C.; Ho, M.S.; Wu, J.C.; Chen, W.J.; Huang, J.H.; Chou, S.T.; Hu, Y.C. Immunization with virus-like particles of enterovirus 71 elicits potent immune responses and protects mice against lethal challenge. Vaccine 2008, 26, 1855–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.N.; Lin, Y.C.; Fann, C.; Liao, N.S.; Shih, S.R.; Ho, M.S. Protection against lethal enterovirus 71 infection in newborn mice by passive immunization with subunit VP1 vaccines and inactivated virus. Vaccine 2001, 20, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Lin, S.Y.; Chung, Y.C.; Chiu, H.Y.; Chi, W.K.; Lin, Y.L.; Chiang, B.L.; Chen, W.J.; Hu, Y.C. Enterovirus 71 virus-like particle vaccine: Improved production conditions for enhanced yield. Vaccine 2010, 28, 6951–6957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ku, Z.; Dai, W.; Chen, T.; Ye, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jin, X.; Huang, Z. A bivalent virus-like particle based vaccine induces a balanced antibody response against both enterovirus 71 and norovirus in mice. Vaccine 2015, 33, 5779–5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, D.G.; Alonso, S.; Chow, V.T.; Poh, C.L. Passive protection against lethal enterovirus 71 infection in newborn mice by neutralizing antibodies elicited by a synthetic peptide. Microbes Infect. 2007, 9, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.N.; Wang, W.; Duo, J.Y.; Hao, Y.; Ma, C.M.; Li, W.B.; Lin, S.Z.; Gao, X.Z.; Liu, X.L.; Xu, Y.F.; et al. Combined peptides of human enterovirus 71 protect against virus infection in mice. Vaccine 2010, 28, 7444–7451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Han, J.; Qin, E.; Qin, C. [Mechanism of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for severe hand-foot-mouth disease: A review]. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao 2011, 27, 712–716. [Google Scholar]
- Elgundi, Z.; Reslan, M.; Cruz, E.; Sifniotis, V.; Kayser, V. The state-of-play and future of antibody therapeutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 122, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, X.F.; Jia, Q.; Khong, W.X.; Yan, B.; Premanand, B.; Alonso, S.; Chow, V.T.; Kwang, J. Characterization of an isotype-dependent monoclonal antibody against linear neutralizing epitope effective for prophylaxis of enterovirus 71 infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiener, T.K.; Jia, Q.; Meng, T.; Chow, V.T.; Kwang, J. A novel universal neutralizing monoclonal antibody against enterovirus 71 that targets the highly conserved “knob” region of VP3 protein. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, G.H.; Luo, Y.J.; Wu, X.Y.; Si, B.Y.; Lin, L.; Zhu, Q.Y. Monoclonal antibody induced with inactived EV71-Hn2 virus protects mice against lethal EV71-Hn2 virus infection. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.C.; Chou, A.H.; Lien, S.P.; Lin, H.Y.; Liu, S.J.; Chang, J.Y.; Guo, M.S.; Chow, Y.H.; Yang, W.S.; Chang, K.H.; et al. Identification and characterization of a cross-neutralization epitope of Enterovirus 71. Vaccine 2011, 29, 4362–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.Q.; Ma, J.; Xu, L.J.; Li, Y.X.; Zhao, H.; Han, J.F.; Tao, J.; Li, X.F.; Zhu, S.Y.; Qin, E.D.; et al. Generation and characterization of a protective mouse monoclonal antibody against human enterovirus 71. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 7663–7671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Xianyu, L.; Lyu, S. Monoclonal neutralizing antibodies against EV71 screened from mice immunized with yeast-produced virus-like particles. Virol. Sin. 2015, 30, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, Z.; Ye, X.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Z. Single Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting the VP1 GH Loop of Enterovirus 71 Inhibit both Virus Attachment and Internalization during Viral Entry. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 12084–12095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Fan, C.; Ku, Z.; Zuo, T.; Kong, L.; Zhang, C.; Shi, J.; Liu, Q.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Structural Basis for Recognition of Human Enterovirus 71 by a Bivalent Broadly Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Davis, K.R. The potential of plants as a system for the development and production of human biologics. F1000Reserch 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Engle, M.; Fuchs, A.; Keller, T.; Johnson, S.; Gorlatov, S.; Diamond, M.S.; Chen, Q. Monoclonal antibody produced in plants efficiently treats West Nile virus infection in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2419–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Phoolcharoen, W.; Lai, H.; Piensook, K.; Cardineau, G.; Zeitlin, L.; Whaley, K.J.; Arntzen, C.J.; Mason, H.S.; Chen, Q. High-level rapid production of full-size monoclonal antibodies in plants by a single-vector DNA replicon system. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2010, 106, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Both, L.; van Dolleweerd, C.; Wright, E.; Banyard, A.C.; Bulmer-Thomas, B.; Selden, D.; Altmann, F.; Fooks, A.R.; Ma, J.K. Production, characterization, and antigen specificity of recombinant 62-71-3, a candidate monoclonal antibody for rabies prophylaxis in humans. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 2055–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Q.Y.; Wang, Y.; Bian, L.; Xu, M.; Liang, Z. EV71 vaccine, a new tool to control outbreaks of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD). Expert Rev. Vaccines 2016, 15, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Templar, A.; Marsh, D.; Nesbeth, D.N. A synthetic biology standard for Chinese Hamster Ovary cell genome monitoring and contaminant detection by polymerase chain reaction. Springerplus 2016, 5, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q. Plant-made vaccines against West Nile virus are potent, safe, and economically feasible. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 10, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S.; Kwong, A.T.; Holtz, B.R.; Erwin, R.L.; Marcel, S.; McDonald, K.A. Techno-economic analysis of a transient plant-based platform for monoclonal antibody production. MAbs 2016, 8, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lai, H.; Hurtado, J.; Stahnke, J.; Leuzinger, K.; Dent, M. Agroinfiltration as an Effective and Scalable Strategy of Gene Delivery for Production of Pharmaceutical Proteins. Adv. Tech. Biol. Med. 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, J.A.; Hilton, J.F.; White, J.M.; Hoover, C.I.; Wycoff, K.L.; Yu, L.; Larrick, J.W.; Featherstone, J.D. Clinical trial of a plant-derived antibody on recolonization of mutans streptococci. Caries Res. 2005, 39, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.K.; Drossard, J.; Lewis, D.; Altmann, F.; Boyle, J.; Christou, P.; Cole, T.; Dale, P.; van Dolleweerd, C.J.; Isitt, V.; et al. Regulatory approval and a first-in-human phase I clinical trial of a monoclonal antibody produced in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 1106–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuse, D.; Ku, N.; Bendandi, M.; Becerra, C.; Collins, R., Jr.; Langford, N.; Sancho, S.I.; Lopez-Diaz de Cerio, A.; Pastor, F.; Kandzia, R.; et al. Clinical Safety and Immunogenicity of Tumor-Targeted, Plant-Made Id-KLH Conjugate Vaccines for Follicular Lymphoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 648143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, J.; Qi, X.; Yan, H. Monoclonal antibody against EV71 3D(pol) inhibits the polymerase activity of RdRp and virus replication. BMC Immunol. 2019, 20, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanongsaksrikul, J.; Srimanote, P.; Tongtawe, P.; Glab-Ampai, K.; Malik, A.A.; Supasorn, O.; Chiawwit, P.; Poovorawan, Y.; Chaicumpa, W. Identification and production of mouse scFv to specific epitope of enterovirus-71 virion protein-2 (VP2). Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Ng, Q.; Chin, W.; Meng, T.; Chow, V.T.K.; Wang, C.I.; Kwang, J.; He, F. Effective in vivo therapeutic IgG antibody against VP3 of enterovirus 71 with receptor-competing activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, Z.; Shi, J.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Z. Development of murine monoclonal antibodies with potent neutralization effects on enterovirus 71. J. Virol. Methods 2012, 186, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, Z.; Ye, X.; Huang, X.; Cai, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Su, Z.; Huang, Z. Neutralizing antibodies induced by recombinant virus-like particles of enterovirus 71 genotype C4 inhibit infection at pre- and post-attachment steps. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ku, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, T.; Ye, X.; Li, D.; Jin, X.; Huang, Z. High-yield production of recombinant virus-like particles of enterovirus 71 in Pichia pastoris and their protective efficacy against oral viral challenge in mice. Vaccine 2015, 33, 2335–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rattanapisit, K.; Chao, Z.; Siriwattananon, K.; Huang, Z.; Phoolcharoen, W. Plant-Produced Anti-Enterovirus 71 (EV71) Monoclonal Antibody Efficiently Protects Mice Against EV71 Infection. Plants 2019, 8, 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8120560
Rattanapisit K, Chao Z, Siriwattananon K, Huang Z, Phoolcharoen W. Plant-Produced Anti-Enterovirus 71 (EV71) Monoclonal Antibody Efficiently Protects Mice Against EV71 Infection. Plants. 2019; 8(12):560. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8120560
Chicago/Turabian StyleRattanapisit, Kaewta, Zhang Chao, Konlavat Siriwattananon, Zhong Huang, and Waranyoo Phoolcharoen. 2019. "Plant-Produced Anti-Enterovirus 71 (EV71) Monoclonal Antibody Efficiently Protects Mice Against EV71 Infection" Plants 8, no. 12: 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8120560
APA StyleRattanapisit, K., Chao, Z., Siriwattananon, K., Huang, Z., & Phoolcharoen, W. (2019). Plant-Produced Anti-Enterovirus 71 (EV71) Monoclonal Antibody Efficiently Protects Mice Against EV71 Infection. Plants, 8(12), 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8120560




