CaGβ Promotes CaWRKY40 to Activate Immunity Against Ralstonia solanacearum but Disables It from Activating Thermotolerance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
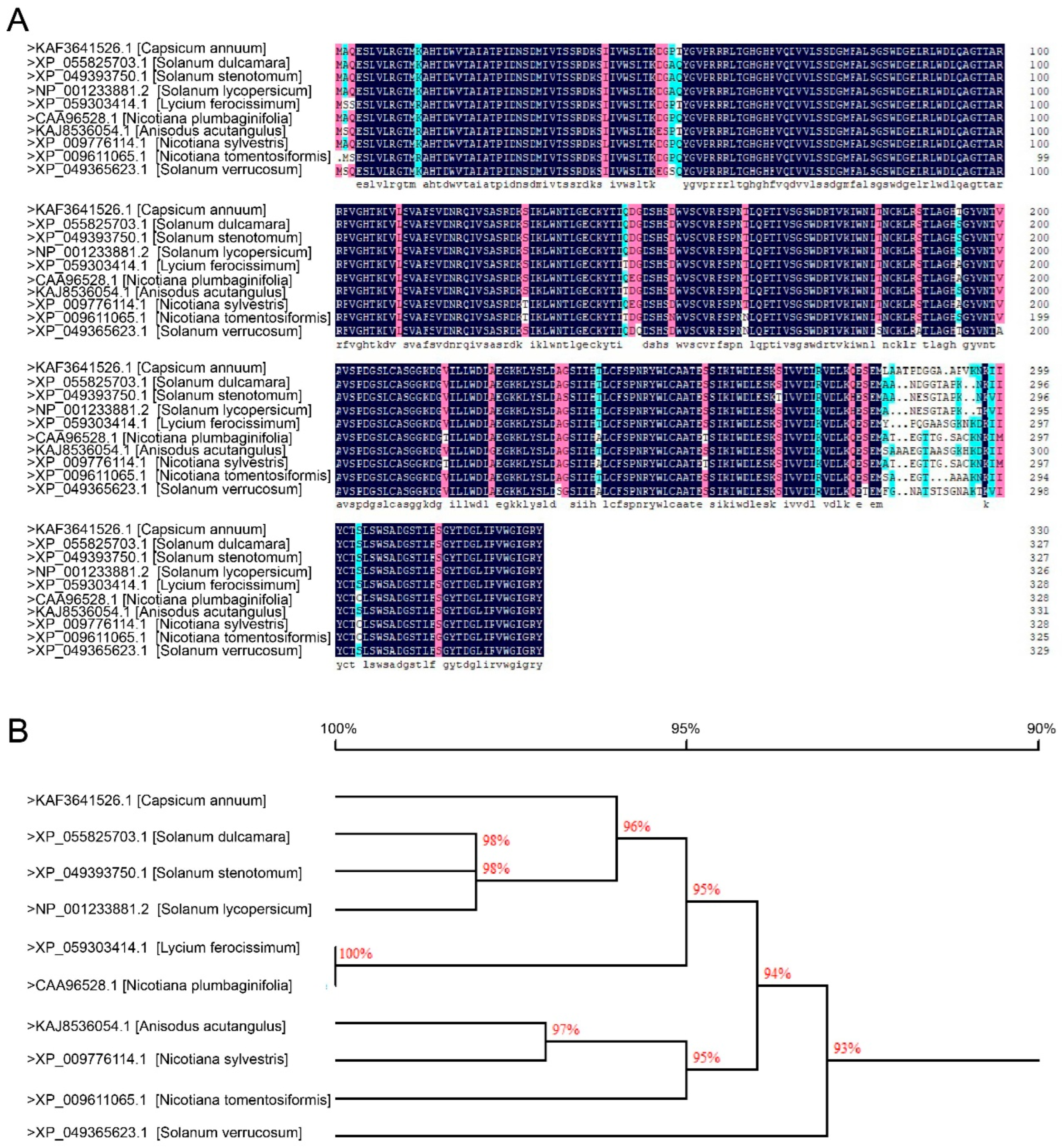
2.1. CaGβ Exhibit High Sequence Similarity to Its Orthologs in Solanaceas
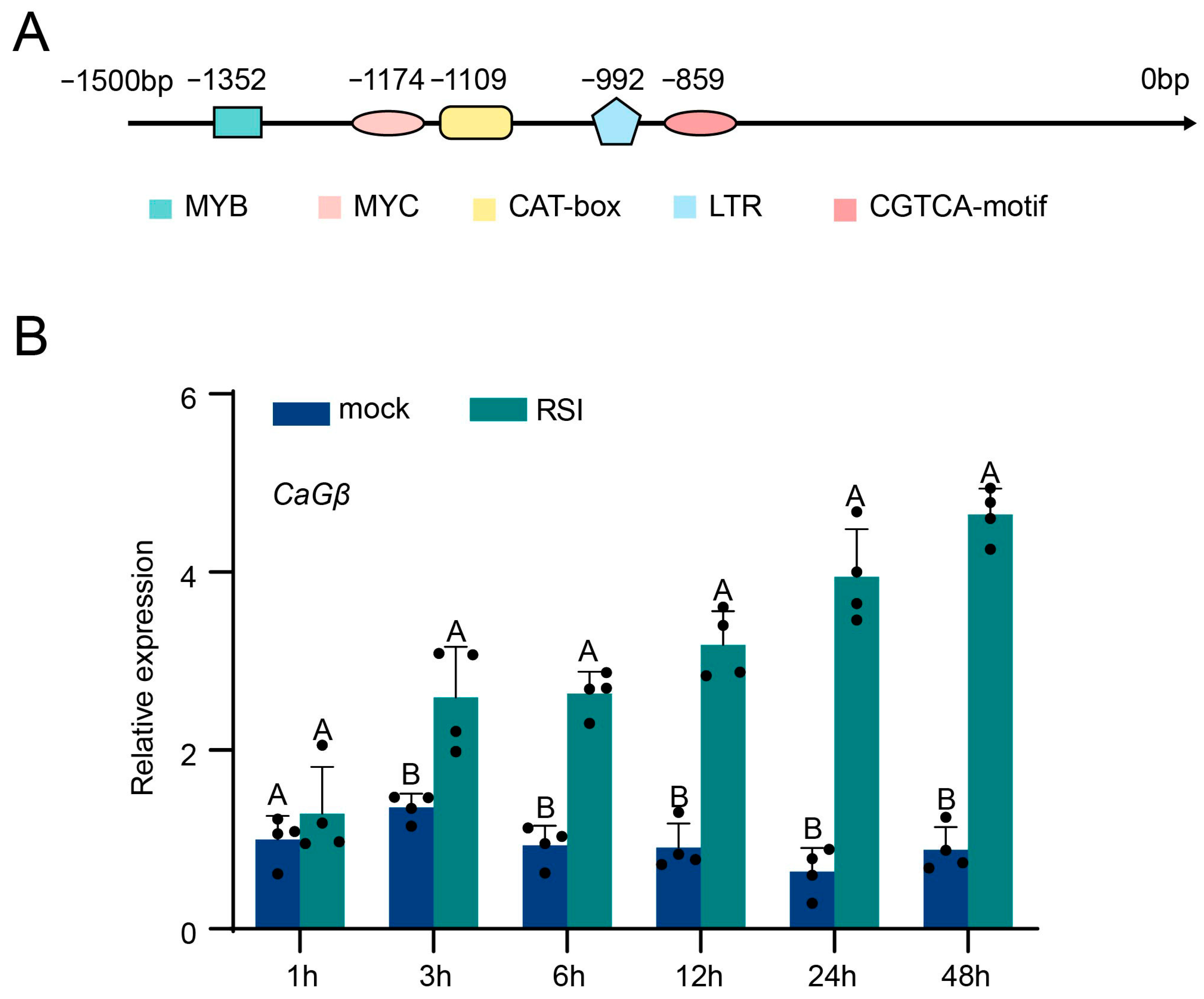
2.2. CaGβ Was Upregulated by R. solanacearum Infection in Pepper Plants
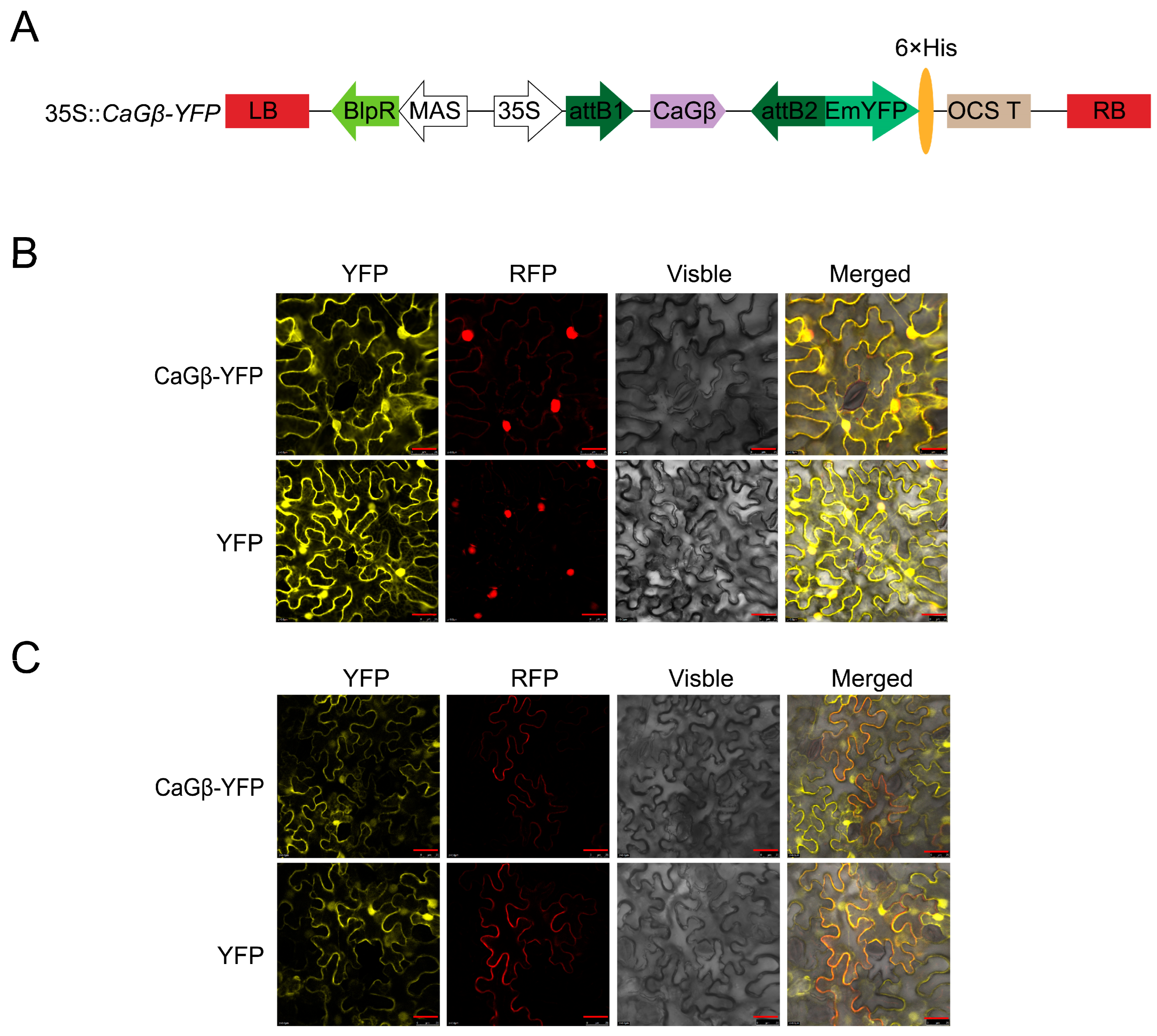
2.3. CaGβ Locates in Plasma Membrane, Cytoplasm and Also in the Nuclei
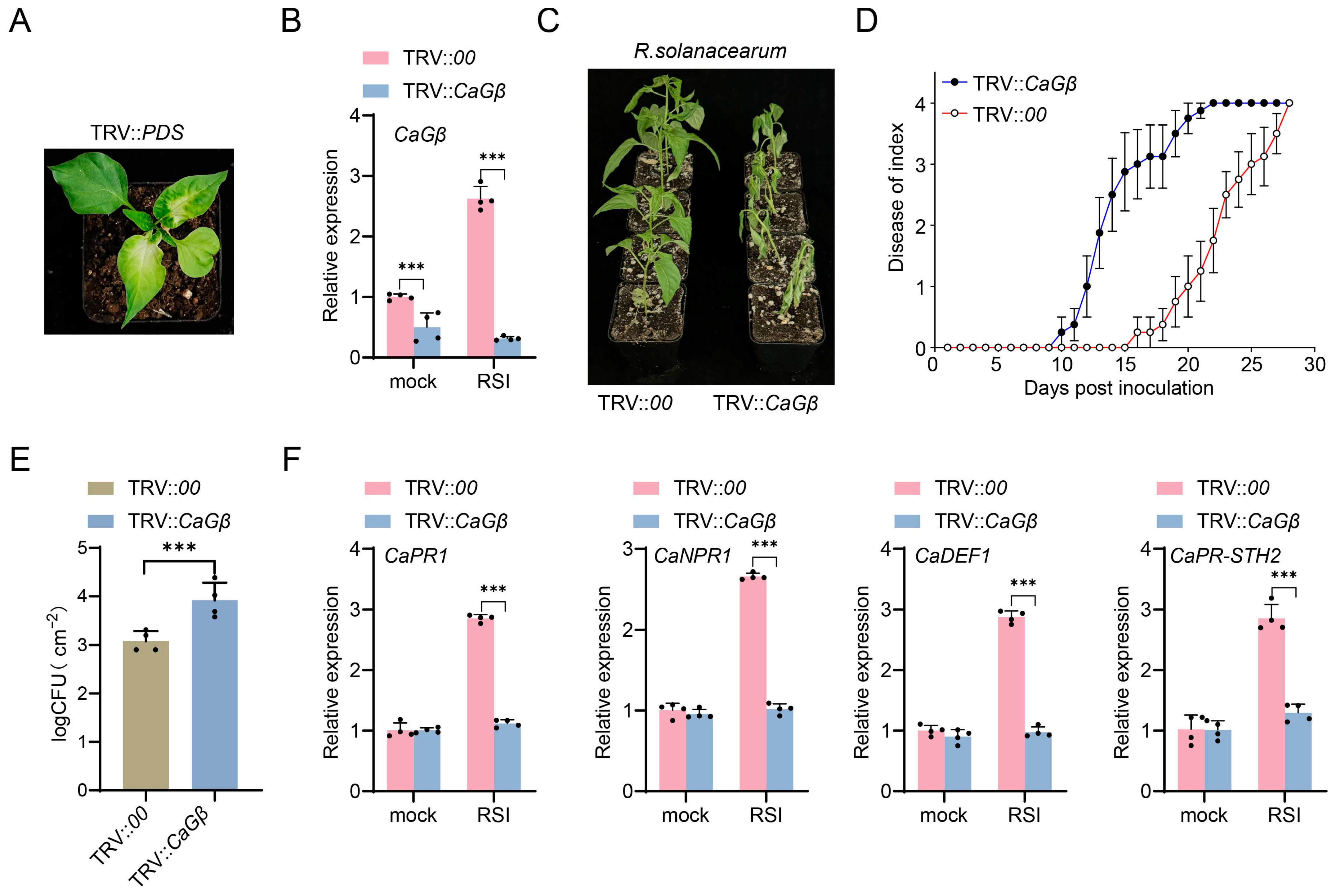
2.4. CaGβ Silencing by VIGS Significantly Increased Susceptibility of Pepper Plants to R. solanacearum Infection
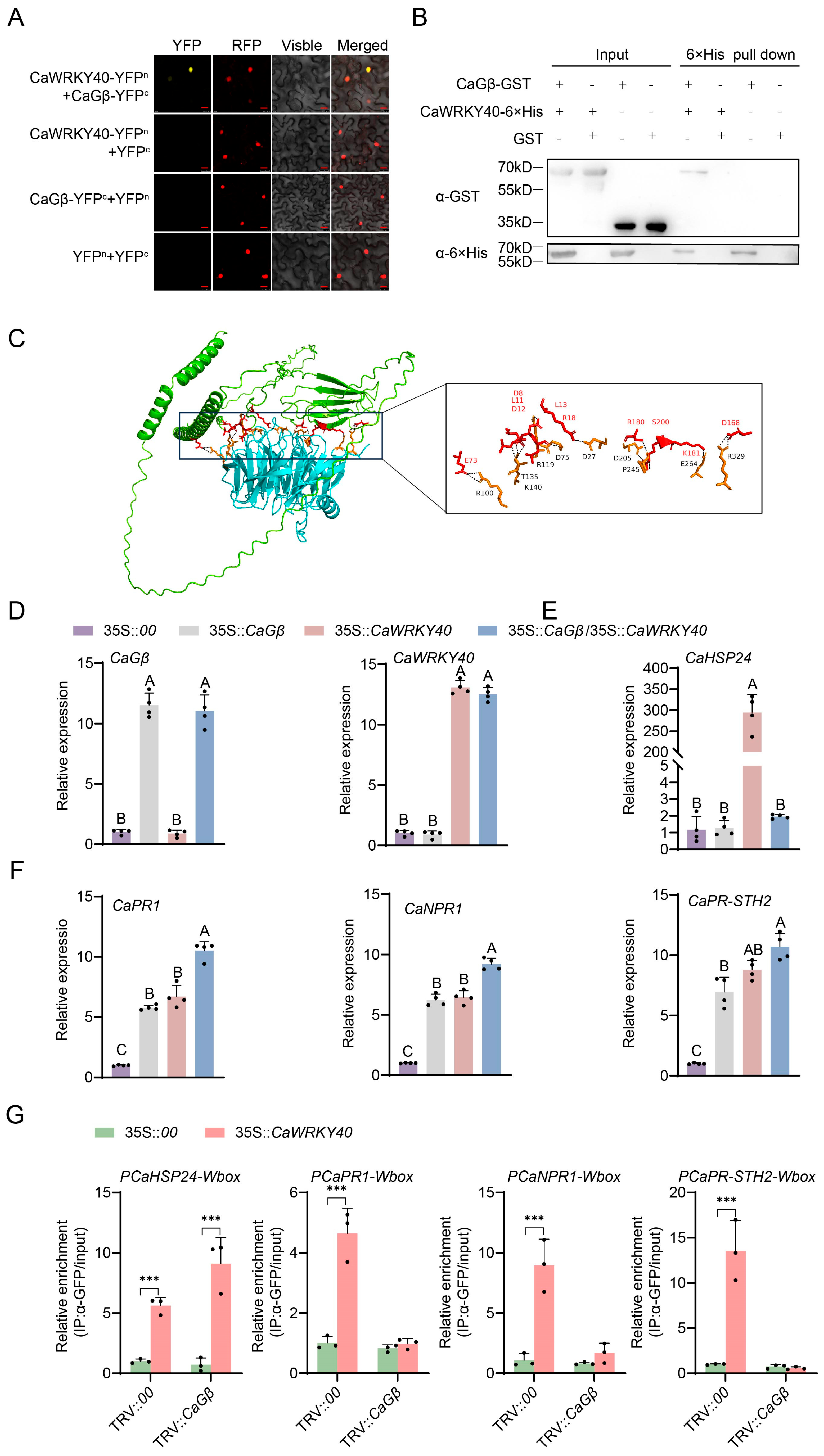
2.5. CaGβ Interacted with CaWRKY40 and Promoted CaWRKY40 in Activating Immunity by Blocking Its Activating Thermotolerance-Related CaHSP24
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Pathogen and Pathogen Inoculation
4.3. Vector Construction
4.4. Silencing of CaGβ by Virus-Induced Gene Silencing (VIGS) in Pepper Plants
4.5. Agrobacterium-Mediated Transient Overexpression and Subcellular Localization as Well as Bimolecular Fluorescent Complimentary (BiFC) Assay
4.6. Determination of CFU of Ralstonia solanacearum
4.7. Pull Down Assay and Western Blotting
4.8. RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, A.; Senthil-Kumar, M. Concurrent Stresses are Perceived as New State of Stress by the Plants Overview of Impact of Abiotic and Biotic Stress Combinations. In Concurrent Stresses Are Perceived as New State of Stress by the Plants: Overview of Impact of Abiotic and Biotic Stress Combinations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, N.; Rivero, R.M.; Shulaev, V.; Blumwald, E.; Mittler, R. Abiotic and biotic stress combinations. New Phytol. 2014, 203, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, R.N.; Martin, G.B.; Pombo, M.A.; Rosli, H.G. WRKY22 and WRKY25 transcription factors are positive regulators of defense responses in Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Mol. Biol. 2021, 105, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.H.; Anand, S.; Singh, B.; Bohra, A.; Joshi, R. WRKY transcription factors and plant defense responses: Latest discoveries and future prospects. Plant Cell Rep. 2021, 40, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh Tran, T.; MacIntyre, A.; Khokhani, D.; Hawes, M.; Allen, C. Extracellular DNases of Ralstonia solanacearum modulate biofilms and facilitate bacterial wilt virulence. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 4103–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vleesschauwer, D.; Filipe, O.; Hoffman, G.; Seifi, H.S.; Haeck, A.; Canlas, P.; Van Bockhaven, J.; De Waele, E.; Demeestere, K.; Ronald, P.; et al. Target of rapamycin signaling orchestrates growth-defense trade-offs in plants. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, F.; Kracher, B.; Mine, A.; Seyfferth, C.; Blanvillain-Baufumé, S.; Parker, J.E.; Tsuda, K.; Schulze-Lefert, P.; Maekawa, T. A dominant-interfering camta3 mutation compromises primary transcriptional outputs mediated by both cell surface and intracellular immune receptors in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 1667–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R.; Schwarze, J.; Sherwood, O.L.; Jnaid, Y.; McCabe, P.F.; Kacprzyk, J. Stressed to Death: The Role of Transcription Factors in Plant Programmed Cell Death Induced by Abiotic and Biotic Stimuli. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, P.; Devi, R.; Verma, B.; Hussain, S.; Arora, P.; Tabassum, R.; Gupta, S. WRKY transcription factors: Evolution, regulation, and functional diversity in plants. Protoplasma 2023, 260, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, T.; Gao, S.J. WRKY transcription factors in plant defense. Trends Genet. 2023, 39, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoso, M.A.; Hussain, A.; Ritonga, F.N.; Ali, Q.; Channa, M.M.; Alshegaihi, R.M.; Meng, Q.; Ali, M.; Zaman, W.; Brohi, R.D.; et al. WRKY transcription factors (TFs): Molecular switches to regulate drought, temperature, and salinity stresses in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1039329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nievola, C.C.; Carvalho, C.P.; Carvalho, V.; Rodrigues, E. Rapid responses of plants to temperature changes. Temperature 2017, 4, 371–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Cai, W.; Shen, L.; Cao, J.; Liu, C.; Hu, J.; Guan, D.; He, S. A CaCDPK29-CaWRKY27b module promotes CaWRKY40-mediated thermotolerance and immunity to Ralstonia solanacearum in pepper. New Phytol. 2022, 233, 1843–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Siyu, F.; Lei, L.; Lirong, Z.; Wanqin, C.; Xia, L.; Zhiyu, X.; Shidie, C.; Houping, W.; Diqiu, Y. WRKY transcription factors: Hubs for regulating plant growth and stress responses. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2025, 67, 488–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Meiyun, W.; Xingge, C.; Qing, C.; Huolin, S. A 14-3-3 Protein Ca16R Acts Positively in Pepper Immunity against Ralstonia solanacearum by Interacting with CaASR1. Plants 2024, 13, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Shen, L.; Yang, S.; Guan, D.; He, S. CaASR1 promotes salicylic acid- but represses jasmonic acid-dependent signaling to enhance the resistance of Capsicum annuum to bacterial wilt by modulating CabZIP63. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 6538–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navjyoti, C.; Nandula, R. Life, death and resurrection of plant GPCRs. Plant Mol. Biol. 2022, 111, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Nguyen Minh, D.; Søren, G.F.R.; Daniel, H.; Xavier, K.; Liwen, W.; Jennifer, B.; Hee Ryung, K.; Marcin, W.; Awuri, A.; et al. Assembly of a GPCR-G Protein Complex. Cell 2019, 177, 1232–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, F.; Liu, L.; Char, S.N.; Ding, Y.; Je, B.I.; Schmelz, E.; Yang, B.; Jackson, D. The maize heterotrimeric G protein beta subunit controls shoot meristem development and immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 117, 1799–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Tabata, R.; Yamada, M.; Aida, M.; Mitsumasu, K.; Fujiwara, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Shigenobu, S.; Higuchi, M.; Tsuji, H.; et al. Heterotrimeric G proteins control stem cell proliferation through CLAVATA signaling in Arabidopsis. EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsunomiya, Y.; Samejima, C.; Takayanagi, Y.; Izawa, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Sawada, Y.; Fujisawa, Y.; Kato, H.; Iwasaki, Y. Suppression of the rice heterotrimeric G protein beta-subunit gene, RGB1, causes dwarfism and browning of internodes and lamina joint regions. Plant J. 2011, 67, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, M.; Liang, J. RGB1 Regulates Grain Development and Starch Accumulation Through Its Effect on OsYUC11-Mediated Auxin Biosynthesis in Rice Endosperm Cells. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 585174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Qian, Q.; Wu, K.; Luo, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Q.; Huang, X.; Yuan, Q.; et al. Heterotrimeric G proteins regulate nitrogen-use efficiency in rice. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, S.; Wu, Y.; Venkataraman, G.; Sopory, S.K.; Tuteja, N. Heterotrimeric G-protein complex and G-protein-coupled receptor from a legume (Pisum sativum): Role in salinity and heat stress and cross-talk with phospholipase C. Plant J. 2007, 51, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Assmann, S.M. The heterotrimeric G-protein β subunit, AGB1, plays multiple roles in the Arabidopsis salinity response. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 2143–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifnan Khan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Hu, J.; Liu, C.; Yang, S.; Hussain, A.; Furqan Ashraf, M.; Noman, A.; Shen, L.; et al. CaWRKY40b in Pepper Acts as a Negative Regulator in Response to Ralstonia solanacearum by Directly Modulating Defense Genes Including CaWRKY40. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiyan, J.; Natalie, H.; Lucía, J.; Tigran, M.A.; Josh, T.; Janice, L.J.; Kinya, N.; Jing, Y.; Sheng-Yang, H.; Alexander, T.; et al. Phosphorylation-activated G protein signaling stabilizes TCP14 and JAZ3 to repress JA signaling and enhance plant immunity. Mol. Plant 2025, 18, 1171–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justin, M.W.; Christian, M.; Natalie, M.C.; Gaoyuan, S.; Celio Cabral, O.; Bharat, M.; Libuse, B.; Clara, M.S.; Malek, S.M.; Jing, Y.; et al. Phosphorylation Dynamics in a flg22-Induced, G Protein-Dependent Network Reveals the AtRGS1 Phosphatase. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2023, 23, 100705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulab Chand, A.; Ruchi, T.; Bisht, N.C. A complex interplay of Gβ and Gγ proteins regulates plant growth and defence traits in the allotetraploid Brassica juncea. Plant Mol. Biol. 2021, 106, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo-Liang, Y.; Hong-Ju, L.; Wei-Cai, Y. The integration of Gβ and MAPK signaling cascade in zygote development. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Liu, Z.; Yang, S.; Yang, T.; Liang, J.; Wen, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Shi, L.; Tang, Q.; et al. Pepper CabZIP63 acts as a positive regulator during Ralstonia solanacearum or high temperature-high humidity challenge in a positive feedback loop with CaWRKY40. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 2439–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Yang, S.; Wu, R.; Cao, J.; Shen, L.; Guan, D.; Shuilin, H. Pepper NAC-type transcription factor NAC2c balances the trade-off between growth and defense responses. Plant Physiol. 2021, 186, 2169–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Yang, S.; Yan, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Cheng, J.; Wu, J.; Qiu, A.; Lai, Y.; Mou, S.; Guan, D.; et al. CaWRKY6 transcriptionally activates CaWRKY40, regulates Ralstonia solanacearum resistance, and confers high-temperature and high-humidity tolerance in pepper. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 3163–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Yang, S.; Yang, T.; Liang, J.; Cheng, W.; Wen, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Shi, L.; Tang, Q.; et al. CaCDPK15 positively regulates pepper responses to Ralstonia solanacearum inoculation and forms a positive-feedback loop with CaWRKY40 to amplify defense signaling. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Wan, M.; Song, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hu, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, R.; Lu, Q.; et al. CaSTH2 disables CaWRKY40 from activating pepper thermotolerance and immunity against Ralstonia solanacearum via physical interaction. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, uhae066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Yang, S.; Wu, R.; Zheng, Y.; He, S.; Shen, L.; Guan, D.; He, S. CaSWC4 regulates the immunity-thermotolerance tradeoff by recruiting CabZIP63/CaWRKY40 to target genes and activating chromatin in pepper. PLoS Genet. 2022, 18, e1010023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
He, L.; Wan, M.; Cheng, X.; Chen, X.; Duan, C.; He, S.; Wu, Y.; Yang, S.; Qiu, A. CaGβ Promotes CaWRKY40 to Activate Immunity Against Ralstonia solanacearum but Disables It from Activating Thermotolerance. Plants 2026, 15, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants15010101
He L, Wan M, Cheng X, Chen X, Duan C, He S, Wu Y, Yang S, Qiu A. CaGβ Promotes CaWRKY40 to Activate Immunity Against Ralstonia solanacearum but Disables It from Activating Thermotolerance. Plants. 2026; 15(1):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants15010101
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Li, Meiyun Wan, Xingge Cheng, Xueqiong Chen, Chenfeng Duan, Shuilin He, Yang Wu, Sheng Yang, and Ailian Qiu. 2026. "CaGβ Promotes CaWRKY40 to Activate Immunity Against Ralstonia solanacearum but Disables It from Activating Thermotolerance" Plants 15, no. 1: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants15010101
APA StyleHe, L., Wan, M., Cheng, X., Chen, X., Duan, C., He, S., Wu, Y., Yang, S., & Qiu, A. (2026). CaGβ Promotes CaWRKY40 to Activate Immunity Against Ralstonia solanacearum but Disables It from Activating Thermotolerance. Plants, 15(1), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants15010101





