Assessment of the N-Alkylamide Content and Volatile Profiles in Two Cultivars of Acmella oleracea (L.) R.K. Jansen Grown in Aquaponics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Nutrients, pH, and Conductivity of Water
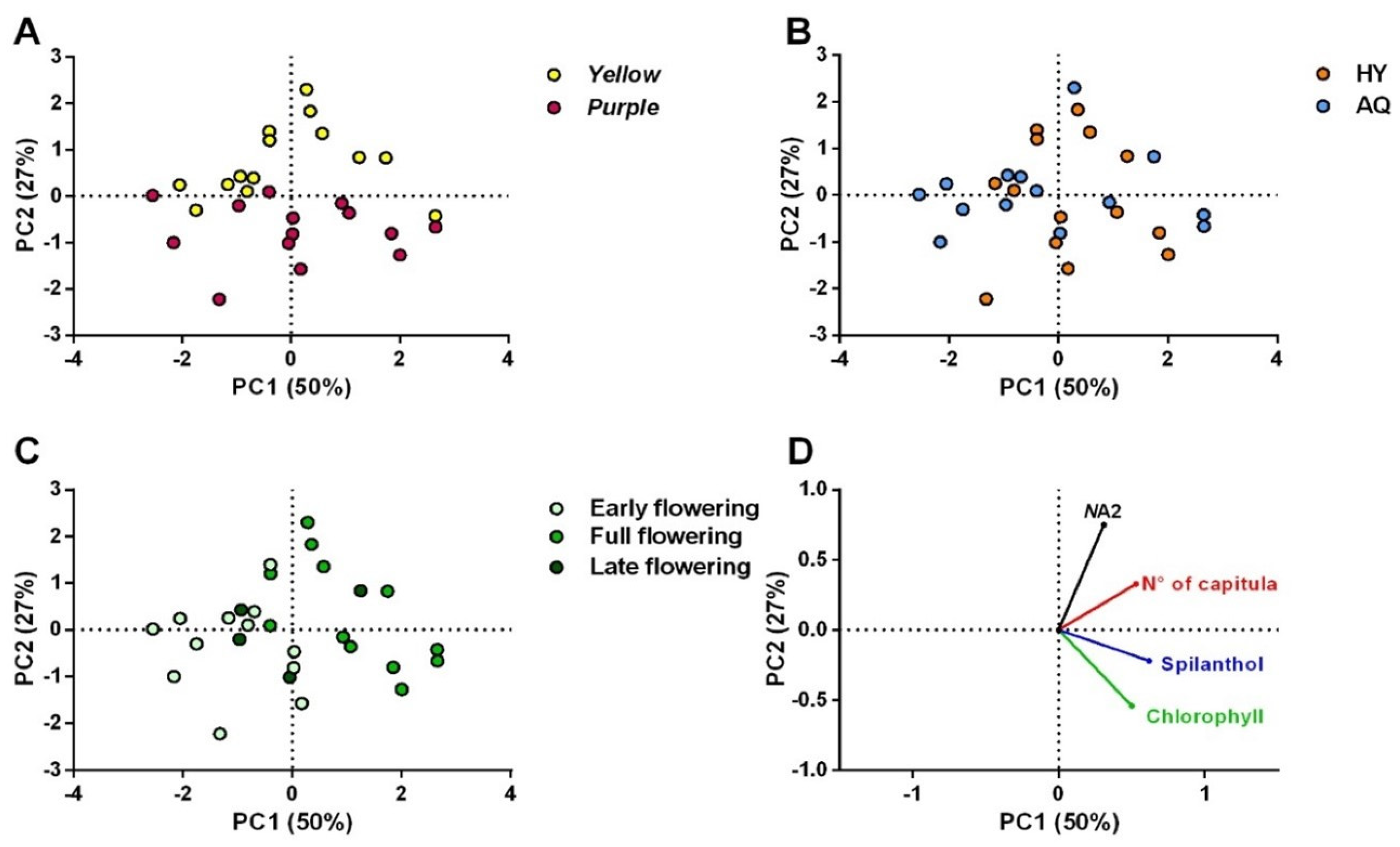
2.2. Capitula Production, N-Alkylamides, and Chlorophyll Content
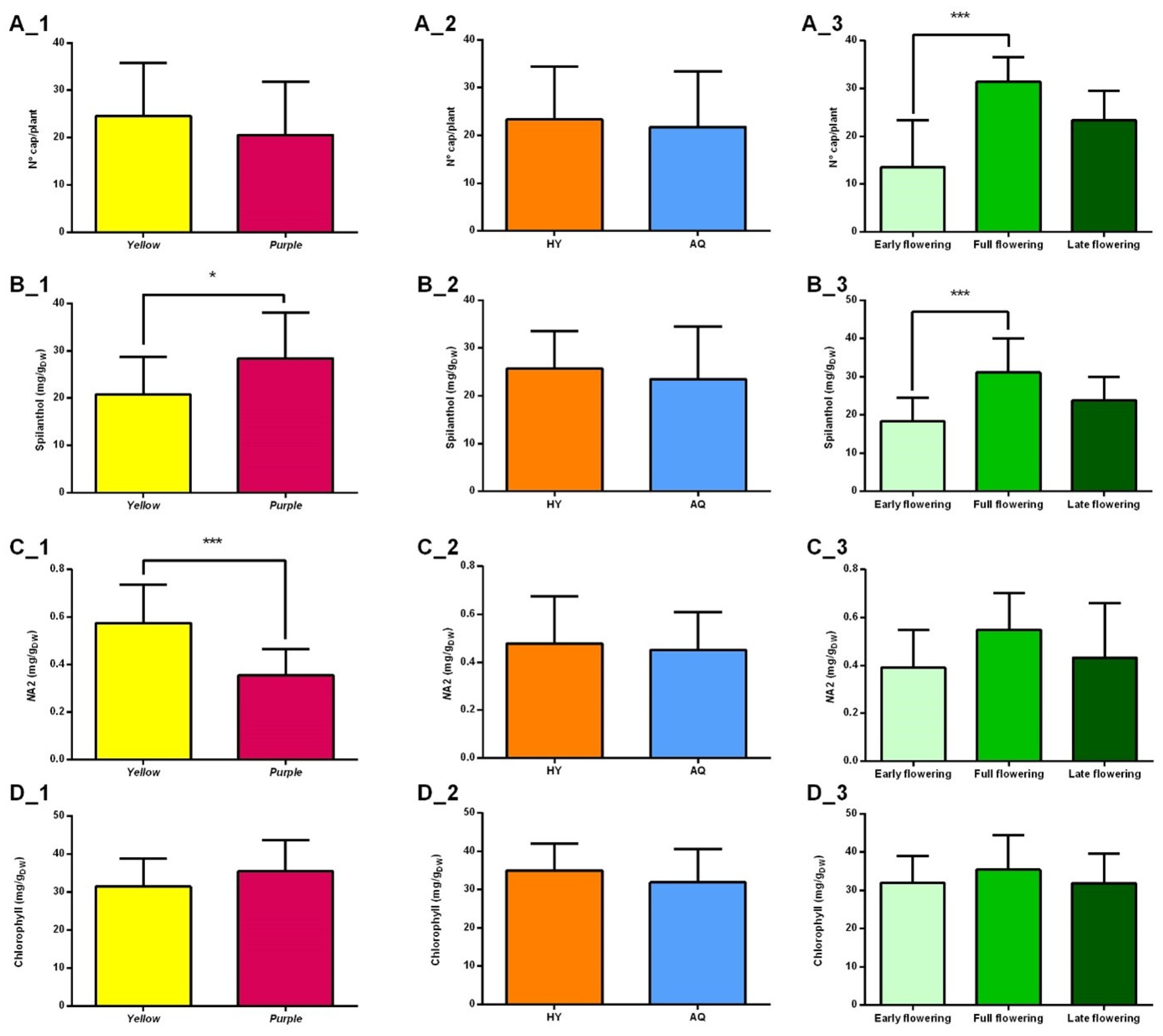
2.2.1. Production of Capitula
2.2.2. Spilanthol Content
2.2.3. (2E)-N-Isobutyl-2-undecene-8,10-diynamide (NA2) Content
2.2.4. Chlorophyll Content
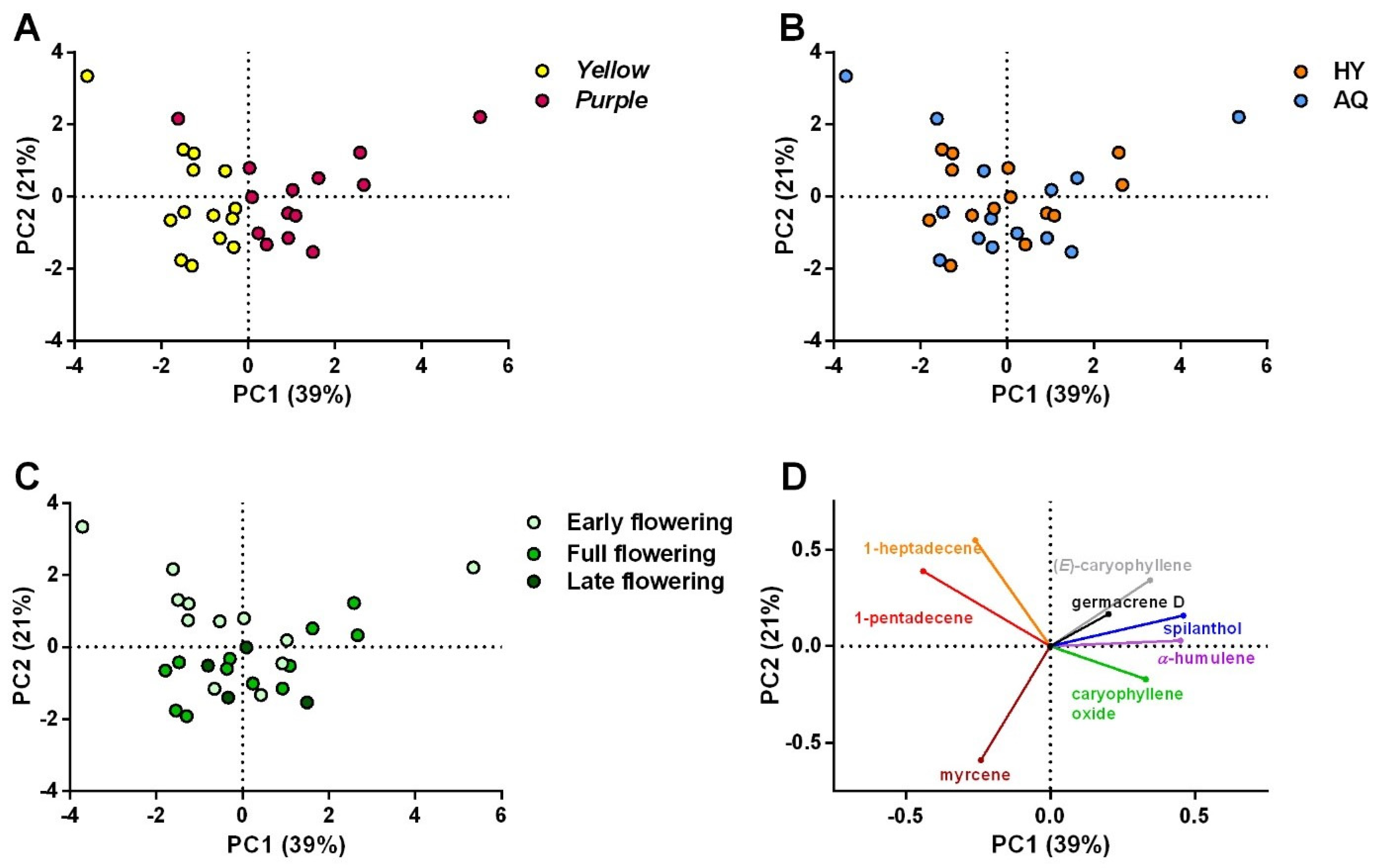
2.3. Volatile Profile
Influence of Cultivars, Cultivation Systems, and Harvesting Period
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Acmella oleracea Cultivation
3.1.1. Aquaponics
3.1.2. Hydroponics
3.2. Measurements of Water Parameters
3.2.1. Ammonium Test
- 2(HgI2 + KI) + 2NH3 → 2(NH3HgI2) + 2KI;
- 2(NH3HgI2) → NH2Hg2I3 + NH4I.
3.2.2. Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) Analyses
3.2.3. Ion Chromatography
3.3. Plant Collection and Labeling
3.4. HPLC-DAD-MS Analysis
3.4.1. Preparation of Samples and Standard Solutions
3.4.2. Analytical Conditions
3.5. Chlorophyll Measurement
3.6. Solid-Phase Microextraction–Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (SPME-GC/MS)
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EC | electrical conductivity |
| EF | early flowering |
| FF | full flowering |
| LF | late flowering |
| NA1 | (2Z)-N-isobutyl-2-nonene-6,8-diynamide |
| NA2 | (2E)-N-isobutyl-2-undecene-8,10-diynamide |
| NA4/5 | (2E,7Z)-N-isobutyl-2,7-decadienamide and (2E)-N-(2-methylbutyl)-2-undecene-8,10-diynamide |
| NA6 | (2E,6Z,8E)-N-(2-methylbutyl)-2,6,8 decatrienamide |
| EO | essential oil |
References
- Ibrahim, L.A.; Shaghaleh, H.; El-Kassar, G.M.; Abu-Hashim, M.; Elsadek, E.A.; Alhaj Hamoud, Y. Aquaponics: A sustainable path to food sovereignty and enhanced water use efficiency. Water 2023, 15, 4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baganz, G.F.; Junge, R.; Portella, M.C.; Goddek, S.; Keesman, K.J.; Baganz, D.; Staaks, G.; Shaw, C.; Lohrberg, F.; Kloas, W. The aquaponic principle—It is all about coupling. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreejana, K.C.; Thapa, R.; Lamsal, A.; Ghimire, S.; Kurunju, K.; Shrestha, P. Aquaponics a modern approach for integrated farming and wise utilization of components for sustainability of food security: A review. Arch. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2022, 7, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.K.; Chandrakant, M.H.; John, V.C.; Peter, R.M.; John, I.E. Aquaponics as an integrated agri-aquaculture system (IAAS): Emerging trends and future prospects. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 194, 122709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, H.W.; Knaus, U.; Appelbaum, S.; Goddek, S.; Strauch, S.M.; Vermeulen, T.; Haïssam Jijakli, M.; Kotzen, B. Towards commercial aquaponics: A review of systems, designs, scales and nomenclature. Aquac. Int. 2018, 26, 813–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yep, B.; Zheng, Y. Aquaponic trends and challenges—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 1586–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasozi, N.; Abraham, B.; Kaiser, H.; Wilhelmi, B. The complex microbiome in aquaponics: Significance of the bacterial ecosystem. Ann. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondanelli, M.; Fossari, F.; Vecchio, V.; Braschi, V.; Riva, A.; Allegrini, P.; Petrangolini, G.; Iannello, G.; Faliva, M.A.; Peroni, G.; et al. Acmella oleracea for pain management. Fitoterapia 2020, 140, 104419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinozzi, E.; Ferrati, M.; Baldassarri, C.; Cappellacci, L.; Marmugi, M.; Caselli, A.; Benelli, G.; Maggi, F.; Petrelli, R. A review of the chemistry and biological activities of Acmella oleracea (“jambù”, Asteraceae), with a view to the development of bioinsecticides and acaricides. Plants 2022, 11, 2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, N.; Sandjo, L.P.; Biavatti, M.W. Spilanthol-containing products: A patent review (1996–2016). Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 74, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusmão, M.T.A.; Gusmão, S.A.L. Jambu da amazônia (Acmella oleracea): Características gerais, cultivo convencional, orgânico e hidropônico; EDUFRA: Belém, Brazil, 2013; p. 135. [Google Scholar]
- Tyson, R.V.; Treadwell, D.D.; Simonne, E.H. Opportunities and challenges to sustainability in aquaponic systems. HortTechnology 2011, 21, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derikvand, P.; Sauter, B.; Stein, L.Y. Development of an aquaponics microbial inoculum for efficient nitrification at acidic pH. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 7009–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xie, H.; Guimbaud, C.; Fang, Y. Effects of pH on nitrogen transformations in media-based aquaponics. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 210, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- do Carmo, A.P.M.; Freitas, M.S.M.; Machado, L.C.; dos Santos Silva, L.; Petri, D.J.C.; Vimercati, J.C.; Ribeiro Matos, C.A.; Mathias, L.; Curcino Vieira, I.J.; de Carvalho, A.J.C. Electrical conductivity of nutrient solutions affects the growth, nutrient levels, and content and composition of essential oils of Acmella oleracea (L.) RK Jansen from southeastern Brazil. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 15, 100968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroel, M.; Mariscal-Legarda, M.M.; Franco, E.G. Tilapia production in aquaponics. In Biology and Aquaculture of Tilapia; López-Olmeda, J.F., Sánchez-Vázquez, J., Fortes-Silva, R., Eds.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 244–257. [Google Scholar]
- Wongkiew, S.; Hu, Z.; Chandran, K.; Lee, J.W.; Khanal, S.K. Nitrogen transformations in aquaponic systems: A review. Aquac. Eng. 2017, 76, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, P.E.M.; Che-Othman, M.H.; Al-Tawaha, A.R.M. Managing Nitrogen Toxicity in the Soilless Culture System: A Review. J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutra, F.M.; Rönnau, M.; Sponchiado, D.; Forneck, S.C.; Freire, C.A.; Ballester, E.L.C. Histological alterations in gills of Macrobrachium amazonicum juveniles exposed to ammonia and nitrite. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 187, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzortzakis, N.G. Potassium and calcium enrichment alleviate salinity-induced stress in hydroponically grown endives. Hortic. Sci. 2010, 37, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelme, R.P.; Oyserman, B.O.; Blom, J.E.; Sepulveda-Villet, O.J.; Newton, R.J. Stripping away the soil: Plant growth promoting microbiology opportunities in aquaponics. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthpala, T.G.G.; Navaratne, S.B. Acmella oleracea plant; identification, applications and use as an emerging food source–review. Food Rev. Int. 2021, 37, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, L.E.S.; Arriola, N.D.A.; da Silva, L.A.L.; Faqueti, L.G.; Sandjo, L.P.; de Araújo, C.E.S.; Biavatti, M.W.; Barcelos-Oliveira, J.L.; Amboni, R.D.D.M.C. Phytochemical profile of different anatomical parts of jambu (Acmella oleracea (L.) RK Jansen): A comparison between hydroponic and conventional cultivation using PCA and cluster analysis. Food Chem. 2020, 332, 127393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampaio, I.M.G.; Silva Júnior, M.L.D.; Bittencourt, R.F.D.M.P.; Santos, G.A.M.D.; Lemos Neto, H.D.S. Production and postharvest quality of jambu in hydroponics under nitrogen application in nutrient solution. Rev. Ciência Agronômica 2021, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.M.A.; Santos, P.; Seabra, I.J.; Júnior, R.N.C.; Braga, M.E.M.; De Sousa, H.C. Spilanthol from Spilanthes acmella flowers, leaves and stems obtained by selective supercritical carbon dioxide extraction. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2012, 61, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.; Maity, S.; Singh, M.; Saraf, S.A.; Saha, S. Phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of Spilanthes acmella: A review. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 1, 423750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Volk, T.A.; Quackenbush, L.J.; Stehman, S.V. Estimation of shrub willow leaf chlorophyll concentration across different growth stages using a hand-held chlorophyll meter to monitor plant health and production. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 150, 106132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, F.L.D. Agronomic performance of jambu (Acmella oleracea) using organic fertilization. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2018, 12, 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- Sut, S.; Ferrarese, I.; Shrestha, S.S.; Kumar, G.; Slaviero, A.; Sello, S.; Altissimo, A.; Pagni, L.; Gattesco, F.; Dall’Acqua, S. Comparison of biostimulant treatments in Acmella oleracea cultivation for alkylamides production. Plants 2020, 9, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, F.; Shen, S.; Wang, X.; Nihmot Ibrahim, A.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, J.; Ji, X.; Liao, X.; Zhang, Y. Natural chlorophyll: A review of analysis methods, health benefits, and stabilization strategies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Niu, D.; Liu, X. Effects of abiotic stress on chlorophyll metabolism. Plant Sci. 2024, 342, 112030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninkuu, V.; Zhang, L.; Yan, J.; Fu, Z.; Yang, T.; Zeng, H. Biochemistry of terpenes and recent advances in plant protection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, Y.; Kunoh, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Akimitsu, K. Biological roles of monoterpene volatiles derived from rough lemon (Citrus jambhiri Lush) in citrus defense. J. Gent. Plant. Pathol. 2007, 73, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrabal, C.; García, F.M.; Arraiza, M.P.; García, S.G. Chemical composition of essential oil of Senecio coincyi, an endemic species of the Central Iberian Peninsula. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benelli, G.; Pavela, R.; Drenaggi, E.; Maggi, F. Insecticidal efficacy of the essential oil of jambú (Acmella oleracea (L.) RK Jansen) cultivated in central Italy against filariasis mosquito vectors, houseflies and moth pests. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 229, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinozzi, E.; Pavela, R.; Bonacucina, G.; Perinelli, D.R.; Cespi, M.; Petrelli, R.; Cappellacci, L.; Fiorini, D.; Scortichini, S.; Garzoli, S.; et al. Spilanthol-rich essential oil obtained by microwave-assisted extraction from Acmella oleracea (L.) RK Jansen and its nanoemulsion: Insecticidal, cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory activities. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 172, 114027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerônimo, L.B.; Santos, P.V.L.; Pinto, L.C.; da Costa, J.S.; de Aguiar Andrade, E.H.; Setzer, W.N.; do Rosário da Silva, J.K.; de Araújo, J.A.C.; Figueiredo, P.L.B. Acmella oleracea (L.) RK Jansen essential oils: Chemical composition, antioxidant, and cytotoxic activities. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2024, 112, 104775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiestl, F.P.; Ayasse, M.; Paulus, H.F.; Löfstedt, C.; Hansson, B.S.; Ibarra, F.; Francke, W. Orchid pollination by sexual swindle. Nature 1999, 399, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohman, B.; Weinstein, A.M.; Mozuraitis, R.; Flematti, G.R.; Borg-Karlson, A.K. Identification of (Z)-8-heptadecene and n-pentadecane as electrophysiologically active compounds in Ophrys insectifera and its Argogorytes pollinator. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoagland, D.R.; Arnon, D.I. The Water-Culture Method for Growing Plants Without Soil, 2nd ed.; College of Agriculture, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1950; p. 347. [Google Scholar]
- IRSA. Criteri e Limiti per il Controllo dell’Inquinamento delle Acque; Quaderni IRSA, Istituto di Ricerca Sulle Acque: Rome, Italy, 1986; pp. 495–497. [Google Scholar]
- Kavallieratos, N.G.; Spinozzi, E.; Filintas, C.S.; Nika, E.P.; Skourti, A.; Panariti, A.M.E.; Ferrati, M.; Petrelli, R.; Ricciutelli, M.; Angeloni, S.; et al. Acmella oleracea extracts as green pesticides against eight arthropods attacking stored products. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 94904–94927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.P. Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry, 5th ed.; R.P. Adams: Gruver, TX, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- NIST/EPA/NIH Mass Spectral Library with Search Program; Data Version 17, Software Version 2.3; National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2017.
- Mondello, L. FFNSC 2: Flavors and Fragrances of Natural and Synthetic Compounds, Mass Spectral Database; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 1118145836. [Google Scholar]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation coefficients: Appropriate use and interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
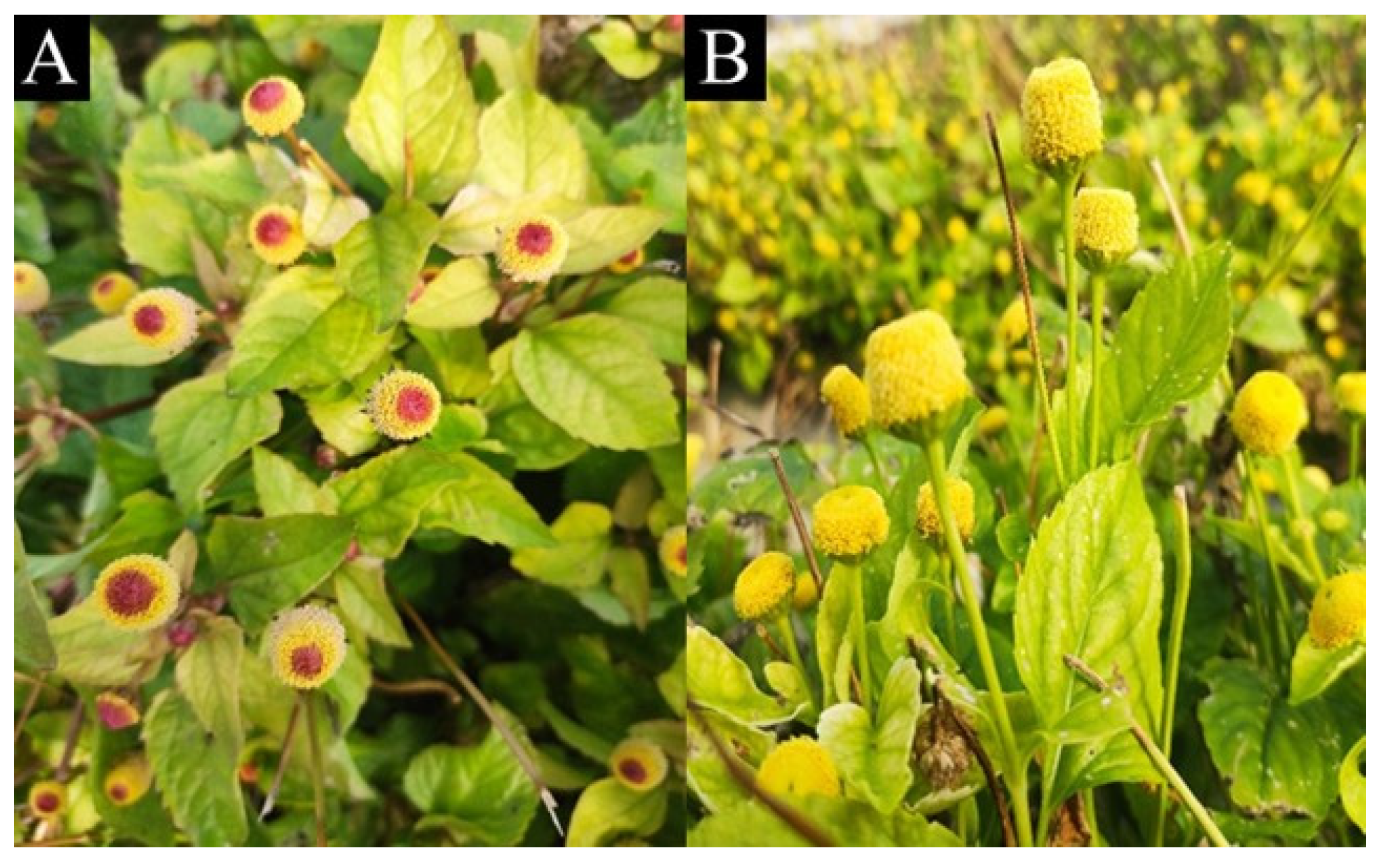
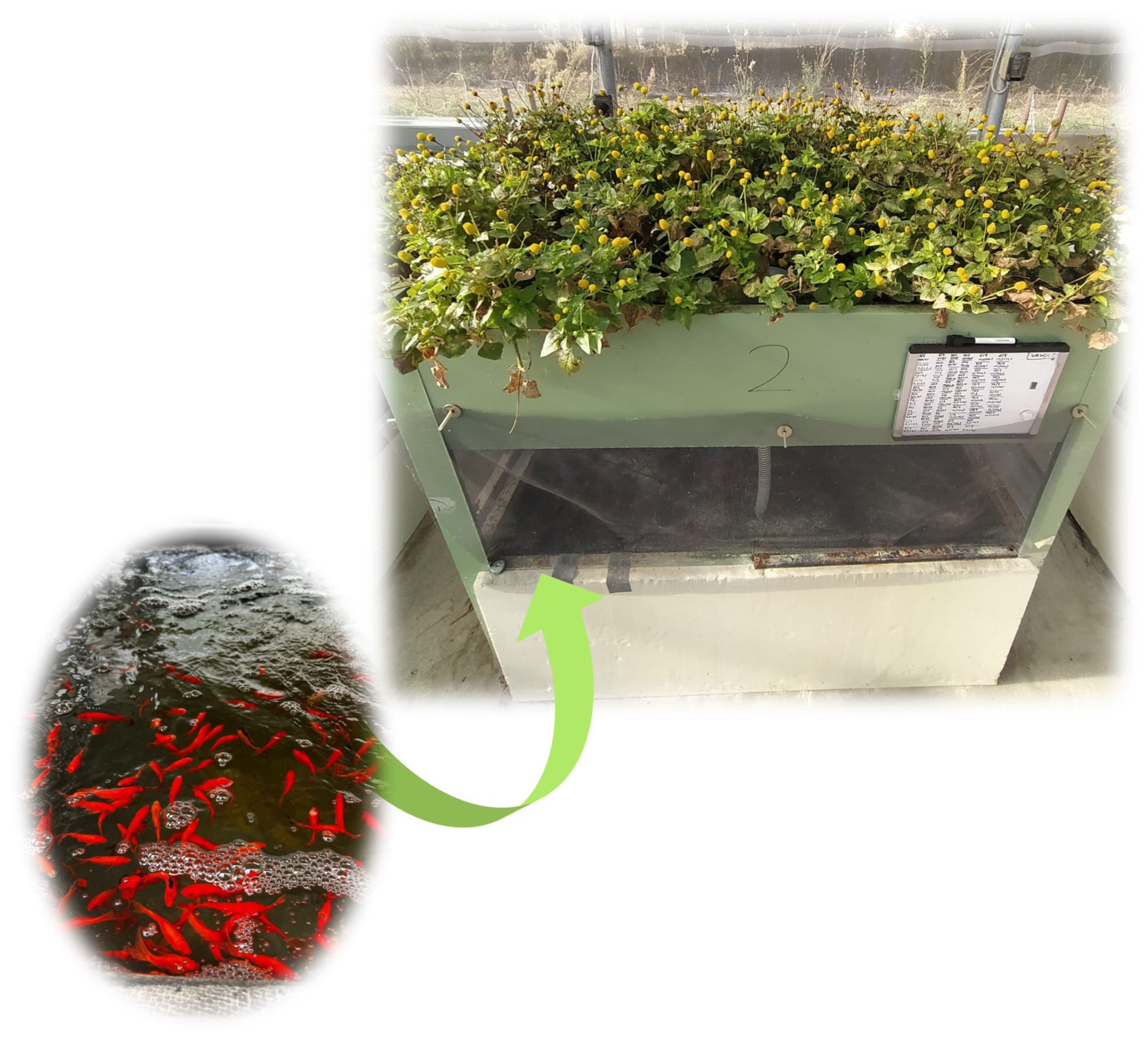



| Code | Cultivar | Cultivation System | Harvesting Date | Flowering Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YEAQ7J | yellow | Aquaponic | 7 July | EF a |
| YEHY7J | yellow | Hydroponic | 7 July | EF |
| YEAQ21J | yellow | Aquaponic | 21 July | EF |
| YEHY21J | yellow | Hydroponic | 21 July | EF |
| YEAQ4A | yellow | Aquaponic | 4 August | EF |
| YEHY4A | yellow | Hydroponic | 4 August | EF |
| YEAQ18A | yellow | Aquaponic | 18 August | FF b |
| YEHY18A | yellow | Hydroponic | 18 August | FF |
| YEAQ1S | yellow | Aquaponic | 1 September | FF |
| YEHY1S | yellow | Hydroponic | 1 September | FF |
| YEAQ15S | yellow | Aquaponic | 15 September | FF |
| YEHY15S | yellow | Hydroponic | 15 September | FF |
| YEAQ29S | yellow | Aquaponic | 29 September | LF c |
| YEHY29S | yellow | Hydroponic | 29 September | LF |
| PUAQ7J | purple | Aquaponic | 7 July | EF |
| PUHY7J | purple | Hydroponic | 7 July | EF |
| PUAQ21J | purple | Aquaponic | 21 July | EF |
| PUHY21J | purple | Hydroponic | 21 July | EF |
| PUAQ4A | purple | Aquaponic | 4 August | EF |
| PUHY4A | purple | Hydroponic | 4 August | EF |
| PUAQ18A | purple | Aquaponic | 18 August | FF |
| PUHY18A | purple | Hydroponic | 18 August | FF |
| PUAQ1S | purple | Aquaponic | 1 September | FF |
| PUHY1S | purple | Hydroponic | 1 September | FF |
| PUAQ15S | purple | Aquaponic | 15 September | FF |
| PUHY15S | purple | Hydroponic | 15 September | FF |
| PUAQ29S | purple | Aquaponic | 29 September | LF |
| PUHY29S | purple | Hydroponic | 29 September | LF |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferrati, M.; Bartolini, B.; Lupidi, G.; Freddi, L.; Bolletta, V.; Cespi, M.; Giovannetti, R.; Zannotti, M.; Petrelli, R.; Maggi, F.; et al. Assessment of the N-Alkylamide Content and Volatile Profiles in Two Cultivars of Acmella oleracea (L.) R.K. Jansen Grown in Aquaponics. Plants 2025, 14, 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091401
Ferrati M, Bartolini B, Lupidi G, Freddi L, Bolletta V, Cespi M, Giovannetti R, Zannotti M, Petrelli R, Maggi F, et al. Assessment of the N-Alkylamide Content and Volatile Profiles in Two Cultivars of Acmella oleracea (L.) R.K. Jansen Grown in Aquaponics. Plants. 2025; 14(9):1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091401
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerrati, Marta, Beatrice Bartolini, Giulio Lupidi, Lorenzo Freddi, Valentina Bolletta, Marco Cespi, Rita Giovannetti, Marco Zannotti, Riccardo Petrelli, Filippo Maggi, and et al. 2025. "Assessment of the N-Alkylamide Content and Volatile Profiles in Two Cultivars of Acmella oleracea (L.) R.K. Jansen Grown in Aquaponics" Plants 14, no. 9: 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091401
APA StyleFerrati, M., Bartolini, B., Lupidi, G., Freddi, L., Bolletta, V., Cespi, M., Giovannetti, R., Zannotti, M., Petrelli, R., Maggi, F., & Spinozzi, E. (2025). Assessment of the N-Alkylamide Content and Volatile Profiles in Two Cultivars of Acmella oleracea (L.) R.K. Jansen Grown in Aquaponics. Plants, 14(9), 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091401














