Noise Was Obviously Reduced by Both Leaf Texture and Surface Roughness in Leaf Scale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
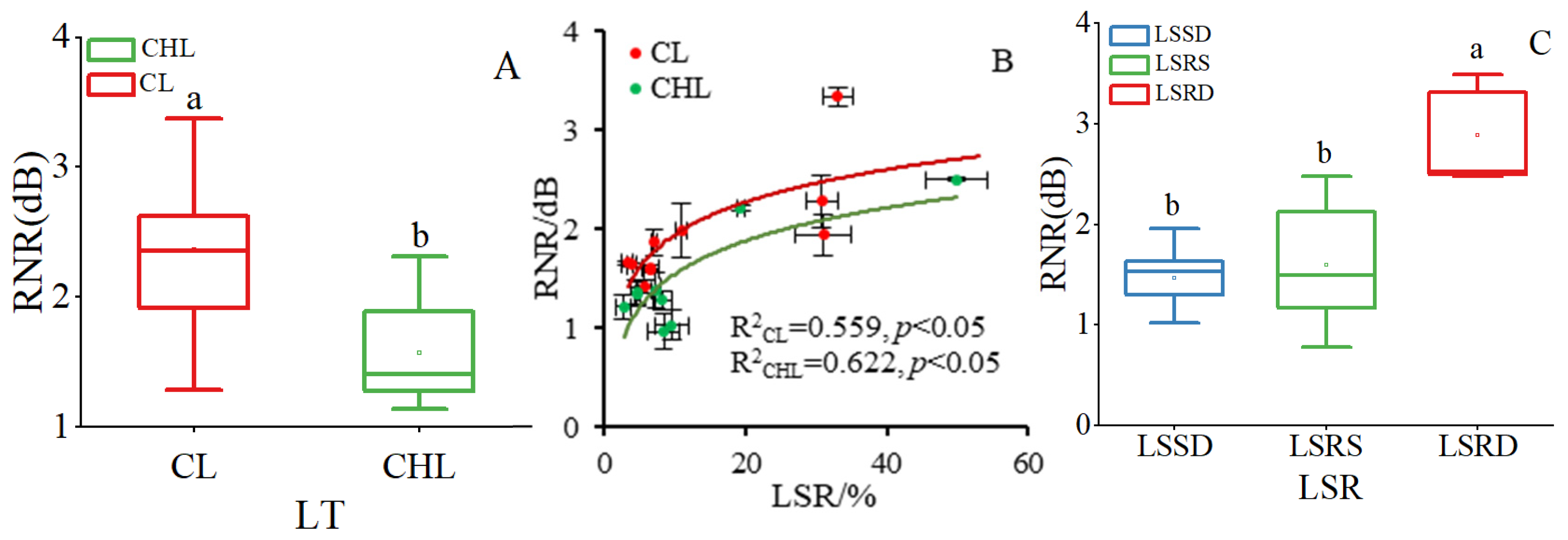
2.1. Effects of Leaf Texture and Surface Roughness of Leaf on Noise Reduction
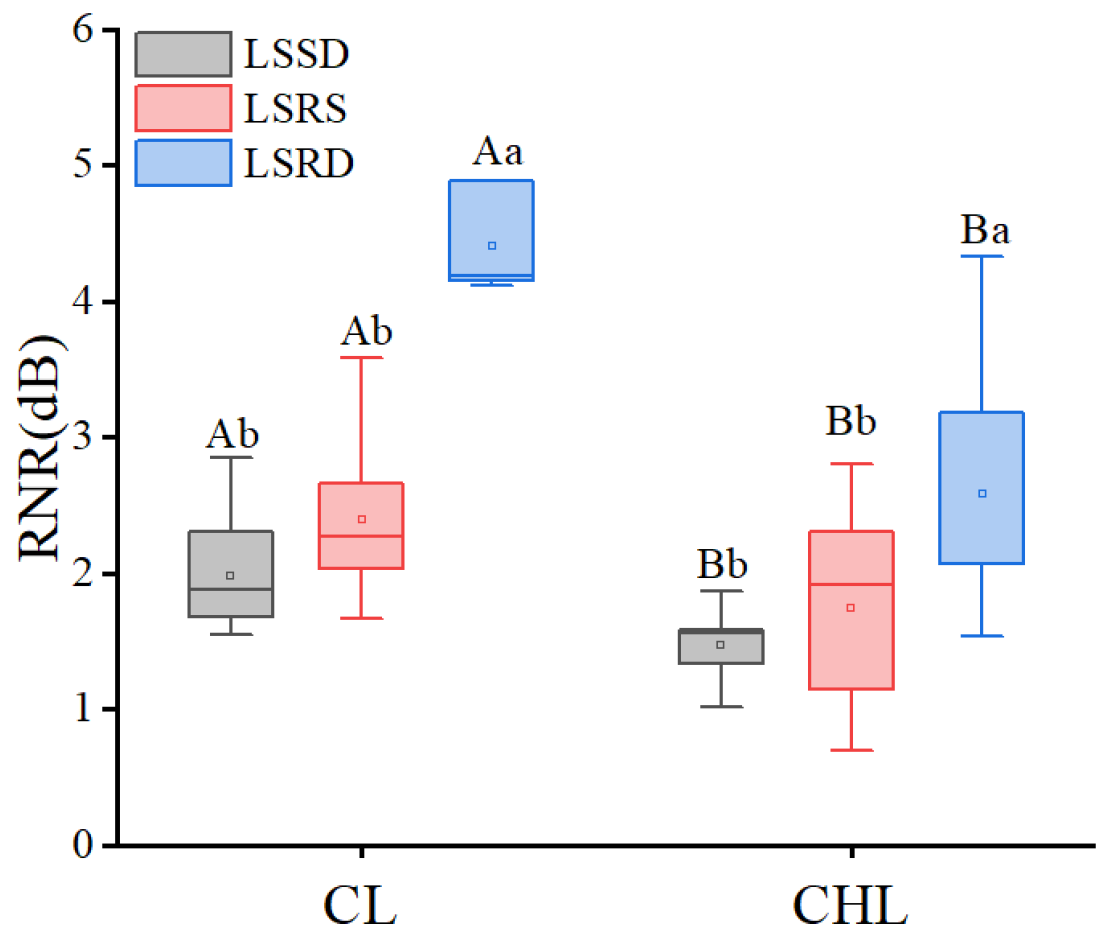
2.2. Interactive Effects of Leaf Texture and Leaf Surface Roughness on Noise Reduction
3. Discussion
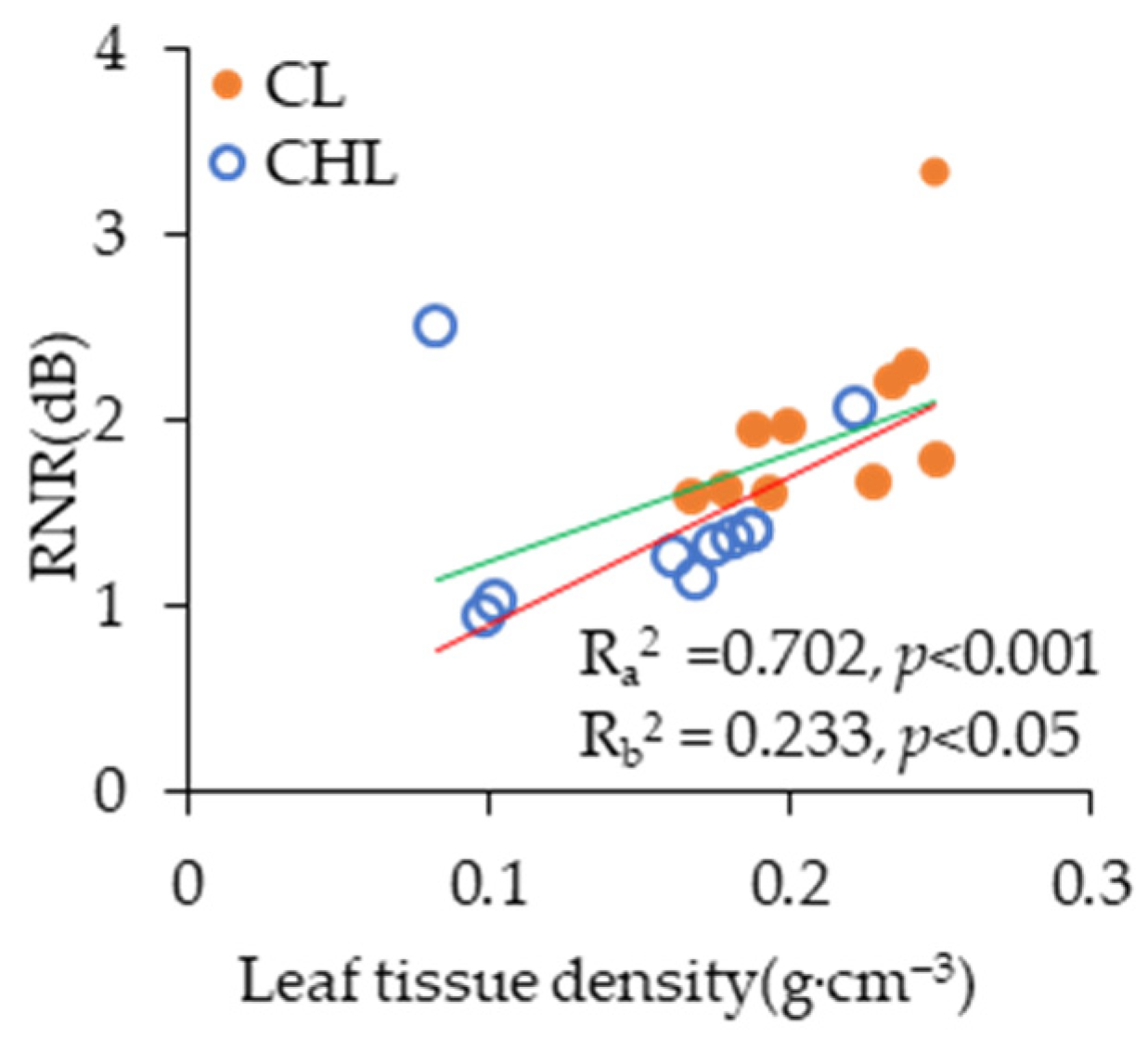
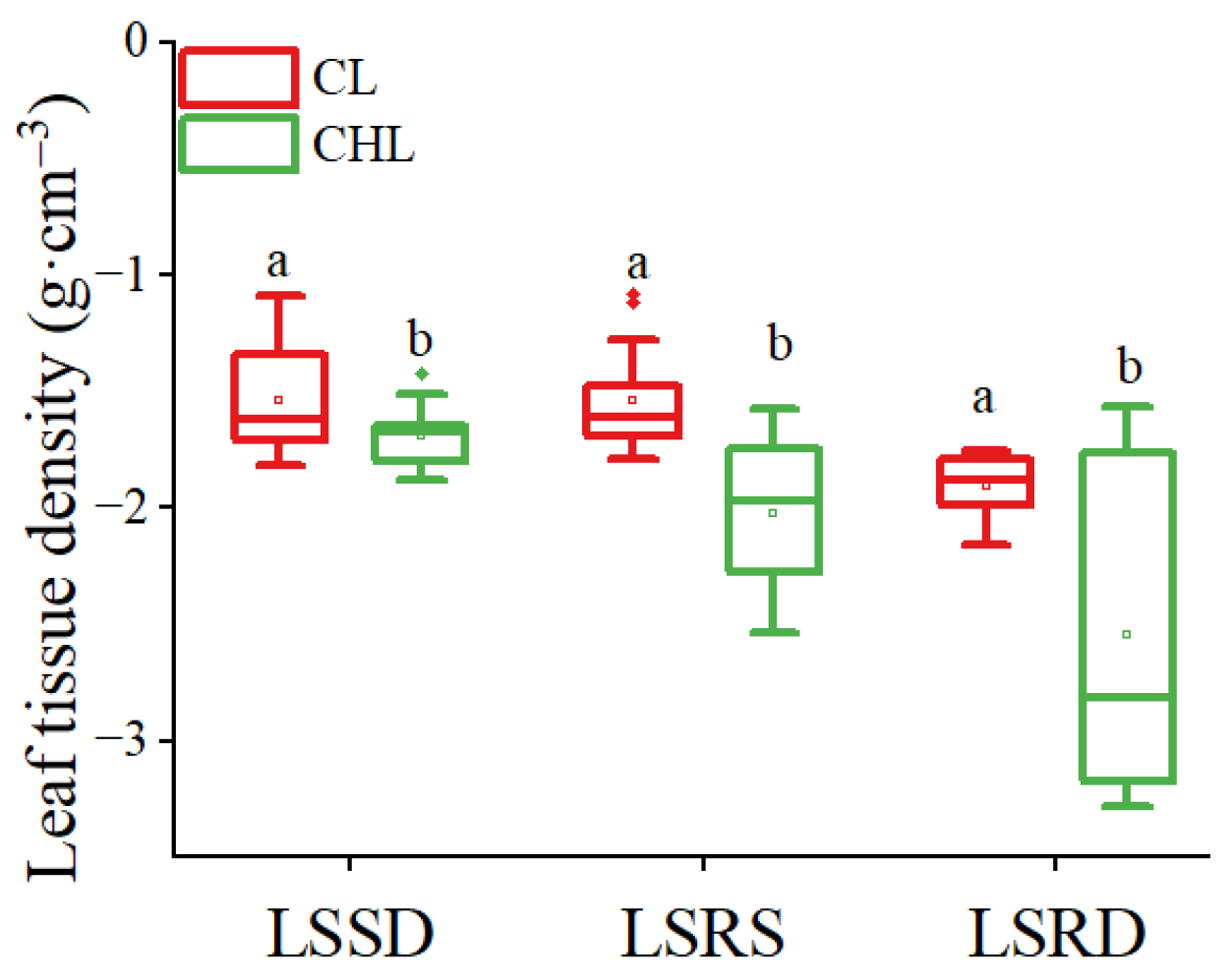
3.1. Effects of Noise Reduction Caused by Leaf Texture Linked with Physical Blocking
3.2. The Effects of Noise Reduction Caused by Leaf Surface Roughness Linked with Refraction and Interference
3.3. Research Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Tree Species and Individual Choice
4.2. Leaves Sampling
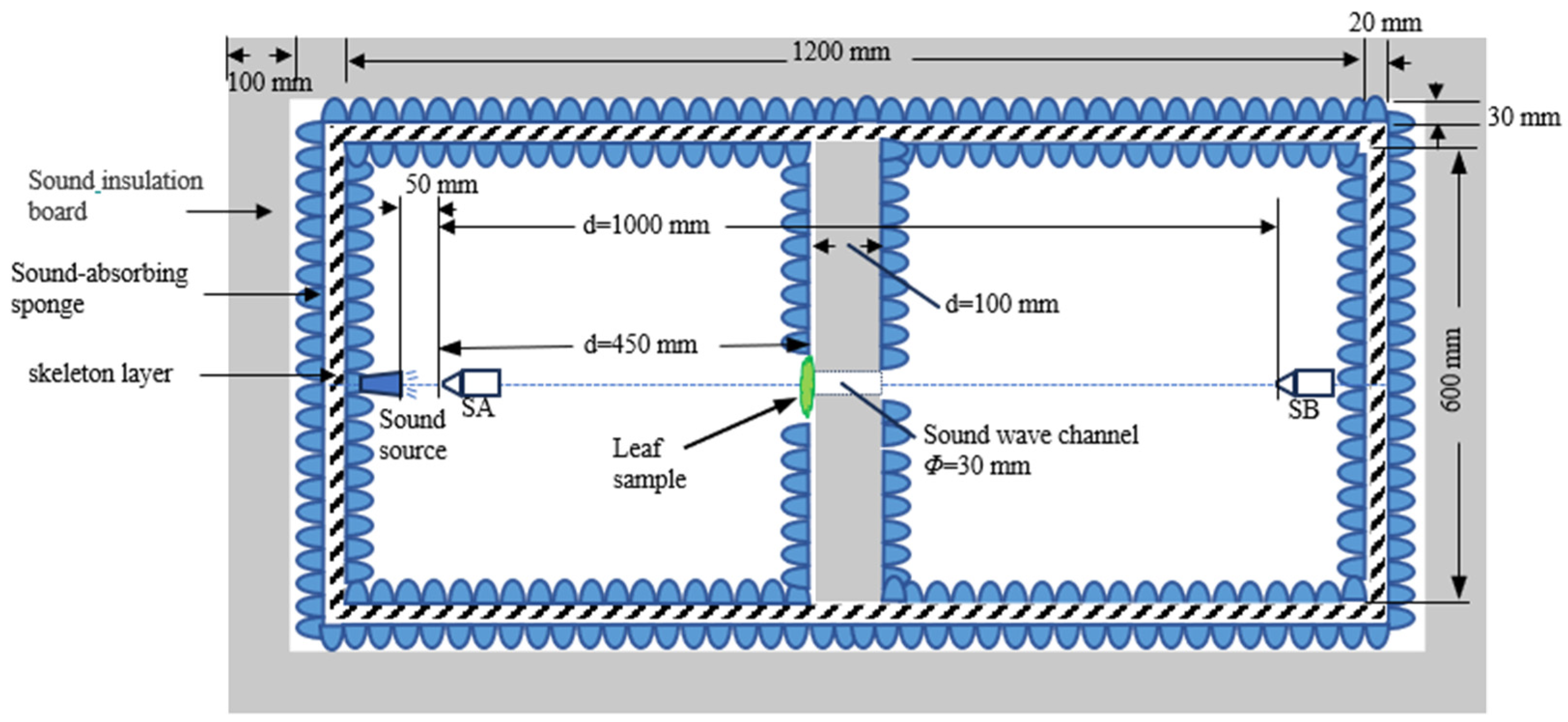
4.3. Indoor Noise Reduction Test System
4.4. Noise Reduction Measurement and Calculation
4.5. Determination of Leaf Characteristics
4.5.1. Leaf Segment Sampling for Data Extraction of Surface Characteristics
4.5.2. Determination of Leaf Texture
4.5.3. Data Extraction of Leaf Surface Roughness
4.5.4. Leaf Dry Mass per Area
4.5.5. Leaf Tissue Density
4.6. Data Collection and Analysis
4.6.1. Expression of Noise Reduction
4.6.2. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LT | leaf texture |
| LSR | leaf surface roughness |
| CL | coriaceous leaf |
| CHL | chartaceous leaf |
| LSSD | leaf surface with smooth on double epidermis |
| LSRS | leaf surface with roughness on single epidermis |
| LSRD | leaf surface with roughness on double epidermis |
| SA | sound level meter A |
| SB | sound level meter B |
| EJ | Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. |
| HN | Hedera nepalensis var. sinensis (Tobler) Rehder |
| BP | Broussonetia papyrifera (L.) L’Hér. ex Vent. |
| MG | Magnolia grandiflora L. |
| CP | Chimonanthus praecox (L.) Link |
| DC | Daphniphyllum calycinum Benth. |
| MC | Michelia cavaleriei Finet & Gagnep. |
| AC | Aesculus chinensis Bunge |
| MA | Michelia maudiae Dunn |
| GB | Ginkgo biloba L. |
| SO | Syringa oblata Lindl. |
| DL | Diospyros lotus L. |
| CR | Chionanthus retusus Lindl. & Paxton |
| DG | Deutzia grandiflora Bunge |
| PO | Platanus orientalis L. |
| EU | Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. |
| WF | Weigela florida (Bunge) A. DC. |
| FC | Fraxinus chinensis Roxb. |
| LHP | leaf hair proportion |
| LMA | leaf dry mass per area |
| LTD | leaf tissue density |
| DW | dry weight |
| V | leaf volume |
| PA | the area of lamina surface protrusion |
| HA | the area of hair patches |
| SHA | the area of the leaf surface where the hairs are located |
| VA | the area of leaf vein |
| LA | the leaf area |
| RNR | relative noise reduction |
| SPLA | sound pressure level A |
| SPLA0 | sound pressure level A0 |
| SPLB | sound pressure level B |
| SPLB0 | sound pressure level B0 |
| SRBE | surface roughness on abaxial epidermis |
| SRDE | surface roughness on abaxial epidermis |
| CLSSD | coriaceous leaf with smooth on double epidermis |
| CLSRS | coriaceous leaf with roughness on single epidermis |
| CLSRD | coriaceous leaf with roughness on double epidermis |
| CHLSSD | chartaceous leaf with smooth on double epidermis |
| CHLSRS | chartaceous leaf with roughness on single epidermis |
| CHLSRD | chartaceous leaf with roughness on double epidermis |
| BE | abaxial epidermis |
| DE | adaxial epidermis |
| PABE | Protrusion area on abaxial epidermis |
| HABE | Hair area on abaxial epidermis |
| VABE | Vein area on abaxial epidermis |
| PADE | Protrusion area on adaxial epidermis |
| HADE | Hair area on adaxial epidermis |
| VADE | Vein area on adaxial epidermis |
References
- Terzakis, M.E.; Dohmen, M.; van Kamp, I.; Hornikx, M. Noise Indicators Relating to Non-Auditory Health Effects in Children—A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, G.A.P.; Souza, L.C.L.d. Urban Green Spaces and the Influence on Vehicular Traffic Noise Control. Ambiente Construído 2018, 18, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Aletta, F.; Oberman, T.; Mitchell, A.; Erfanian, M.; Tong, H.; Torresin, S.; Xu, C.; Yang, T.; Chen, X. Supportive Soundscapes Are Crucial for Sustainable Environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basner, M.; Babisch, W.; Davis, A.; Brink, M.; Clark, C.; Janssen, S.; Stansfeld, S. Auditory and Non-Auditory Effects of Noise on Health. Lancet 2014, 383, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatappa, K.G.; Shankar, V.M. Effect of Road Traffic Noise on Auditory Threshold in Traffic Policemen. Int. J. Curr. Res. Biol. Med. 2018, 3, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirrera, S.; De Valck, E.; Cluydts, R. Nocturnal Road Traffic Noise: A Review on Its Assessment and Consequences on Sleep and Health. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.M.O.; Paleologos, E.K.; Howari, F.M. Noise Pollution and Its Impact on Human Health and the Environment. In Pollution Assessment for Sustainable Practices in Applied Sciences and Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 975–1026. ISBN 9780128095829. [Google Scholar]
- Nadri, F.; Khavanin, A.; Mazaheri, Z.; Soleimanian, A. Effect of Noise Pollution on Male Fertility (Review). J. Occup. Health Epidemiol. 2016, 5, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sina, O.J.; Ayodele, I.M.; Augustine, I.O. The Effect of Noise Pollution on Physical and Mental Health of Pregnant Women in Ekiti State, Nigeria. Eur. J. Pharm. Med. Res. 2017, 4, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Echerbaoui, I.; El Malki, I.C.; Ahami, A.O.T.; Mottier, C.; Wallon, P. Professional Stress Factor of Vulnerability in Which Has Occurred of the Road Traffic Accidents at a Sample of Drivers in Morocco. Open J. Med. Psychol. 2017, 06, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadiri Khanaposhtani, M.; Gasc, A.; Francomano, D.; Villanueva-Rivera, L.J.; Jung, J.; Mossman, M.J.; Pijanowski, B.C. Effects of Highways on Bird Distribution and Soundscape Diversity around Aldo Leopold’s Shack in Baraboo, Wisconsin, USA. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 192, 103666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, G.; McKenna, M.F.; Angeloni, L.M.; Crooks, K.R.; Fristrup, K.M.; Brown, E.; Warner, K.A.; Nelson, M.D.; White, C.; Briggs, J.; et al. A Synthesis of Two Decades of Research Documenting the Effects of Noise on Wildlife. Biol. Rev. 2016, 91, 982–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Q.; Ren, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, L.; Yu, J.; Yu, Z. Bird Risk Assessment in Urban Ecological Patch under Light Pollution and Noise Pollution Stress. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 2186–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, W.; Steinle, S.; Pärkkä, J.; Parmes, E.; Liedes, H.; Kuijpers, E.; Pronk, A.; Sarigiannis, D.; Karakitsios, S.; Chapizanis, D.; et al. Urban Greenspace and the Indoor Environment: Pathways to Health via Indoor Particulate Matter, Noise, and Road Noise Annoyance. Environ. Res. 2020, 180, 108850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillaume, G.; Gauvreau, B.; L’Hermite, P. Numerical Study of the Impact of Vegetation Coverings on Sound Levels and Time Decays in a Canyon Street Model. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.F.; Lau, S.K.; Lu, Z.; Ow, L.F. Enhancement of Sound Absorption via Vegetation with a Metasurface Substrate. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 165, 107309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, A.; Önder, S. An Acoustical Landscaping Study: The Impact of Distance between the Sound Source and the Landscape Plants on Traffic Noise Reduction. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 12036–12058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Renterghem, T.; Huyghe, F.; Verheyen, K. Effect of Tree Species and Season on the Ability of Forest Floors to Abate Environmental Noise. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 184, 108349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wang, M.; Chen, R.; Li, Z. Correlation Analysis between Noise Reduction Function and Biological Structure of Acer Truncatum Crown. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1171, 012040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ow, L.F.; Ghosh, S. Urban Cities and Road Traffic Noise: Reduction through Vegetation. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morihara, T.; Sato, T.; Yano, T. Re-Analysis of Socio-Acoustic Survey Data in Tomakomai: Seasonal Effects of a Tree Belt on Road Traffic Noise Annoyance. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 196, 108861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Xu, L.; Ma, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Comparison on the Noise Reduction of Plant Community in Expressway, Primary and Secondary Road of Hangzhou. Chin. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 10, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekeykhah, J.; Hosseini, S.M.; Jalali, G.; Alavi, J.; Sari, A.E. Species-Related Difference to Noise Reduction between Trees in Urban Forest: The Abidar Forest Park (Case Study). Sound Vib. 2019, 53, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.F.; Ling, D.L. Investigation of the Noise Reduction Provided by Tree Belts. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2003, 63, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, K.; Hosseini, S.M.; Nasiri, P. The Effect of Pure and Mixed Plantations of Robinia pseudoacasia and Pinus eldarica on Traffic Noise Decrease. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 1, 213–224. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.H.; Ong, P.P.; Woon, H.S. Monte Carlo Simulation of Sound Propagation through Leafy Foliage Using Experimentally Obtained Leaf Resonance Parameters. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1986, 80, 1740–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, M.J.M.; Severens, P.P.J.; Van Wissen, H.A.W.M.; Van Der Heijden, L.A.M. Acoustic Reflection Characteristics of Deciduous Plant Leaves. Environ. Exp. Bot. 1985, 25, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens; Maurice, J.M. Absorption of Acoustic Energy by Plant Leaves. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1981, 69, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Renterghem, T.; Botteldooren, D.; Verheyen, K. Road Traffic Noise Shielding by Vegetation Belts of Limited Depth. J. Sound. Vib. 2012, 331, 2404–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Feng, Z.; Du, X.; Xu, C.; Qiao, Q.; An, K.; Ren, H. Noise-Reducing Capability of 13 Kinds of Color-Leaf Plants in Rizhao. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2016, 17, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Y.; Li, Q.-M.; Nan, H.-L.; Yang, X.-H. Study on Noise Attenuation of Green Belts in Plain Area. For. Res. 2017, 30, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attenborough, K.; Van Renterghem, T. (Eds.) Predicting Outdoor Sound; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; ISBN 9780429470806. [Google Scholar]
- D’Alessandro, F.; Asdrubali, F.; Mencarelli, N. Experimental Evaluation and Modelling of the Sound Absorption Properties of Plants for Indoor Acoustic Applications. Build. Environ. 2015, 94, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldauf, R. Roadside Vegetation Design Characteristics That Can Improve Local, near-Road Air Quality. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2017, 52, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Van Rentgem, T.; Qi, M.; Botteldooren, D.; Kang, J. Tree Species Selection and Planting Strategy for Reducing Urban Traffic Noise. J. Appl. Acoust. 2024, 43, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horoshenkov, K.; Khan, A.; Benkreira, H. Acoustic Properties of Low Growing Plants. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, 2554–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Prieur, J.-F.; Liu, Y.; Kneeshaw, D.; Lapointe, E.M.; Paquette, A.; Zinszer, K.; Dupras, J.; Villeneuve, P.J.; Rainham, D.G.; et al. Tree Characteristics and Environmental Noise in Complex Urban Settings—A Case Study from Montreal, Canada. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakor, S.; Chamani, A. Temporal Variability of Noise Pollution Attenuation by Vegetation in Urban Parks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 23143–23151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Kang, J. Influence of Leaf Physical Properties on Single-Leaf Vibrational Response to Sound. Forests 2020, 11, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Renterghem, T.; Van Ginderachter, I.; Thomas, P. Porous Stones Increase the Noise Shielding of a Gabion. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 145, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J. Optimization of Noise Reduction Performance of Upright Insert Noise Barrier Screen Panels. Tech. Acoustics. 2024, 43, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yang, W.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; An, S. Does Strategy of Resource Acquisition in Tropical Woody Species Vary with Life Form, Leaf Texture, and Canopy Gradient? Eur. J. Res. 2010, 129, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorter, H.; Niinemets, Ü.; Poorter, L.; Wright, I.J.; Villar, R. Causes and Consequences of Variation in Leaf Mass per Area (LMA): A Meta-Analysis. New Phytol. 2009, 182, 565–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhou, Z.; He, Y.; Fang, H. Roughness Measurement of Leaf Surface Based on Shape from Focus. Plant Methods 2021, 17, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoda, Y.; Westoby, M.; Adler, P.B.; Choong, A.M.F.; Clissold, F.J.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Díaz, S.; Dominy, N.J.; Elgart, A.; Enrico, L.; et al. Global Patterns of Leaf Mechanical Properties. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halashi, K.; Taban, E.; Soltani, P.; Amininasab, S.; Samaei, E.; Moghadam, D.N.; Khavanin, A. Acoustic and Thermal Performance of Luffa Fiber Panels for Sustainable Building Applications. Build. Environ. 2024, 247, 111051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhu, H.C.; Qiu, X.J.; Du, G.H. Acoustic Theory and Engineering Applications; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Wang, R.; Wang, Z. A Method of Rough Pore Surface Model and Application in Elastic Wave Propagation. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 143, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Hou, L.; Zhou, W.; Chen, Y. Design, Fabrication and Sound Absorption Performance Investigation of Porous Copper Fiber Sintered Sheets with Rough Surface. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 170, 107525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Wei, L.; Xu, C.; Zhang, H. Response of Functional Characters of Street Trees with Different Leaf Textures to Impervious Land Coverage under Canopy. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2022, 44, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Bediaf, H.; Sabre, R.; Journaux, L.; Cointault, F. Comparison of Leaf Surface Roughness Analysis Methods by Sensitivity to Noise Analysis. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 136, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, T.; Olsen, H. Road Traffic Noise Sprectra-the Need for Updates. In Proceedings of the Baltic-Nordic Acoustics Meeting, Oslo, Norway, 3–5 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cointault, F.; Bédiaf, H.; Journaux, L.; Sabre, R. Measuring Vine Leaf Roughness by Image Processing. In Proceedings of the EFITA-WCCA-CIGR Conference “Sustainable Agriculture through ICT Innovation”, Torino, Italy, 23–27 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.; Zhang, M. Semantic Differential Analysis of the Soundscape in Urban Open Public Spaces. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xie, H.; Woodward, G. Soundscape Components, Perceptions, and EEG Reactions in Typical Mountainous Urban Parks. Urban Urban Green. 2021, 64, 127269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kight, C.R.; Swaddle, J.P. How and Why Environmental Noise Impacts Animals: An Integrative, Mechanistic Review. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 3785.1-2010; Electroacoustics—Sound Level Meters—Part 1 Specifications. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2010.
- Bambil, D.; Pistori, H.; Bao, F.; Weber, V.; Alves, F.M.; Gonçalves, E.G.; de Alencar Figueiredo, L.F.; Abreu, U.G.P.; Arruda, R.; Bortolotto, I.M. Plant Species Identification Using Color Learning Resources, Shape, Texture, through Machine Learning and Artificial Neural Networks. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2020, 40, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.T.; Entrenas, J.A.; Torres, I.; Vega, M.; Pérez-Marín, D. Monitoring Texture and Other Quality Parameters in Spinach Plants Using NIR Spectroscopy. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 155, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, J.R.; Zhu, H. 3D Optical Surface Profiler for Quantifying Leaf Surface Roughness. Surf. Topogr. 2019, 7, 045016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.D.; Noble, S.D. Characterization of Leaf Surface Phenotypes Based on Light Interaction. Plant Methods 2023, 19, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coste, S.; Roggy, J.C.; Sonnier, G.; Dreyer, E. Similar Irradiance-Elicited Plasticity of Leaf Traits in Saplings of 12 Tropical Rainforest Tree Species with Highly Different Leaf Mass to Area Ratio. Funct. Plant Biol. 2010, 37, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Lavorel, S.; Garnier, E.; Díaz, S.; Buchmann, N.; Gurvich, D.E.; Reich, P.B.; ter Steege, H.; Morgan, H.D.; van der Heijden, M.G.A.; et al. A Handbook of Protocols for Standardised and Easy Measurement of Plant Functional Traits Worldwide. Aust. J. Bot. 2003, 51, 335–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyka, T.P.; Oleksyn, J.; Żytkowiak, R.; Karolewski, P.; Jagodziński, A.M.; Reich, P.B. Responses of Leaf Structure and Photosynthetic Properties to Intra-Canopy Light Gradients: A Common Garden Test with Four Broadleaf Deciduous Angiosperm and Seven Evergreen Conifer Tree Species. Oecologia 2012, 170, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sources of Variations | RNR | |
|---|---|---|
| F | p | |
| LT | 118.813 | <0.001 |
| LSR | 77.776 | <0.001 |
| LT × LSR | 3.717 | 0.025 |
| CL | CHL | LT | All Data | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSSD | LSRS | LSRD | LSSD | LSRS | LSRD | CL | CHL | ||
| SRDE | 0.083 ns | 0.389 ns | 0.881 *** | 0.248 ns | 0.250 ns | 0.977 *** | 0.748 *** | 0.668 *** | 0.645 *** |
| SRBE | 0.026 ns | 0.496 ns | 0.922 *** | 0.237 ns | 0.648 *** | 0.852 *** | 0.731 *** | 0.883 *** | 0.771 *** |
| LSR | —— | 0.150 ns | 0.790 * | —— | 0.529 * | 0.758 *** | 0.793 *** | 0.845 *** | 0.754 *** |
| LMA | 0.479 * | 0.564 ns | 0.948 *** | 0.776 *** | 0.962 ** | 0.517 ns | 0.646 *** | 0.052 ns | 0.500 *** |
| LTD | 0.882 ** | 0.851 ** | 0.858 *** | 0.753 *** | 0.959 ** | 0.816 *** | 0.689 *** | 0.322 * | 0.349 *** |
| n | 20 | 15 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 10 | 45 | 45 | 90 |
| Leaf Texture (LT) | Leaf Surface Roughness (LSR) | Scientific Names of Tree and Shrub Species | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Code for Types of LT | Description | Code for Types of LSR | |
| Coriaceous leaf | CL | smooth on double epidermis | LSSD | Hedera nepalensis var. sinensis (Tobler) Rehder, Epipremnum aureum (Linden & André) Bunting, Michelia cavaleriei Finet & Gagnep., Aesculus chinensis Bunge, Michelia maudiae Dunn, Syringa oblata Lindl. |
| Chartaceous leaf | CHL | smooth on double epidermis | LSSD | Daphniphyllum calycinum Benth., Ginkgo biloba L. |
| Coriaceous leaf | CL | roughness on single epidermis | LSRS | Magnolia grandiflora L., Diospyros lotus L., Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl., Chionanthus retusus Lindl. & Paxton |
| Chartaceous leaf | CHL | roughness on single epidermis | LSRS | Weigela florida (Bunge) A. DC., Chimonanthus praecox (L.) Link, Deutzia grandiflora Bunge, Fraxinus chinensis Roxb., Platanus orientalis L. |
| Coriaceous leaf | CL | roughness on double epidermis | LSRD | Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. |
| Chartaceous leaf | CHL | roughness on double epidermis | LSRD | Broussonetia papyrifera (L.) L’Hér. ex Vent. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, G.; Ma, B.; Li, X.; Liao, J.; Wei, L.; Guo, X.; Xu, C.; Kong, X.; Jin, G.; Jin, Y. Noise Was Obviously Reduced by Both Leaf Texture and Surface Roughness in Leaf Scale. Plants 2025, 14, 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091363
Sun G, Ma B, Li X, Liao J, Wei L, Guo X, Xu C, Kong X, Jin G, Jin Y. Noise Was Obviously Reduced by Both Leaf Texture and Surface Roughness in Leaf Scale. Plants. 2025; 14(9):1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091363
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Guangpeng, Bingqian Ma, Xianwen Li, Juyang Liao, Liuduan Wei, Xuan Guo, Chengyang Xu, Xiangqi Kong, Guixiang Jin, and Yingshan Jin. 2025. "Noise Was Obviously Reduced by Both Leaf Texture and Surface Roughness in Leaf Scale" Plants 14, no. 9: 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091363
APA StyleSun, G., Ma, B., Li, X., Liao, J., Wei, L., Guo, X., Xu, C., Kong, X., Jin, G., & Jin, Y. (2025). Noise Was Obviously Reduced by Both Leaf Texture and Surface Roughness in Leaf Scale. Plants, 14(9), 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091363





