Lambertianic Acid from Platycladus orientalis Inhibits Muscle Atrophy in Dexamethasone-Induced C2C12 Muscle Atrophy Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
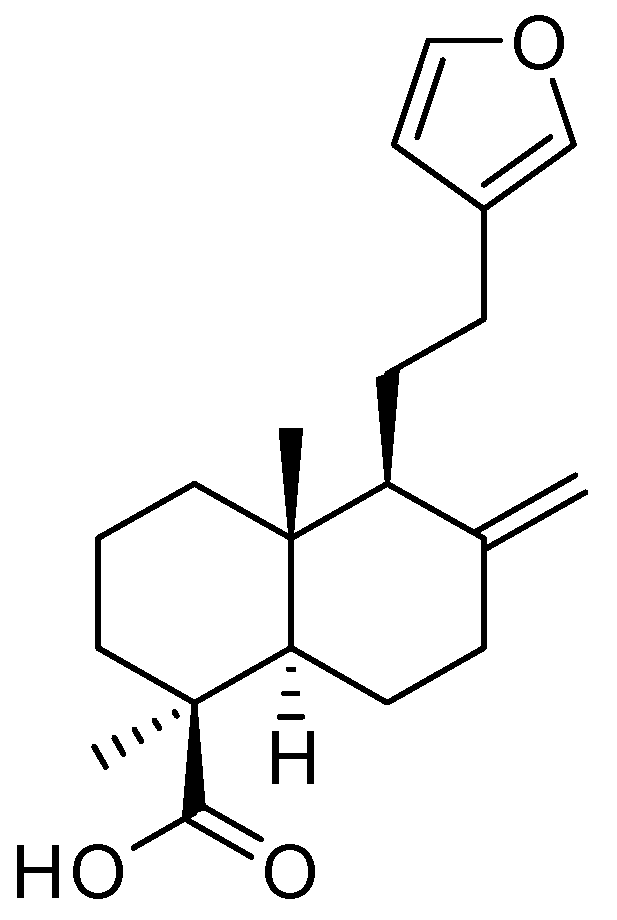
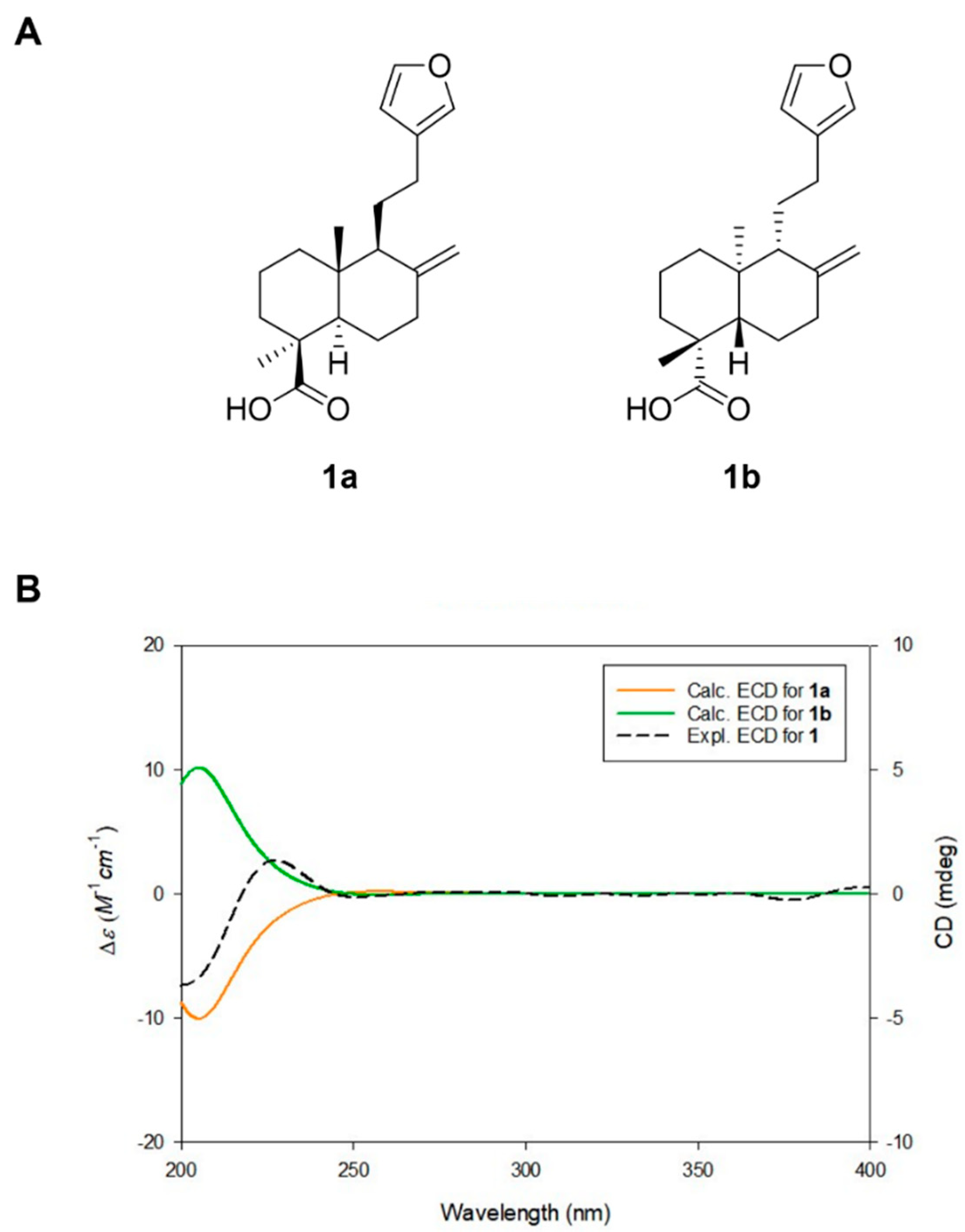
2.1. Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Lambertianic Acid
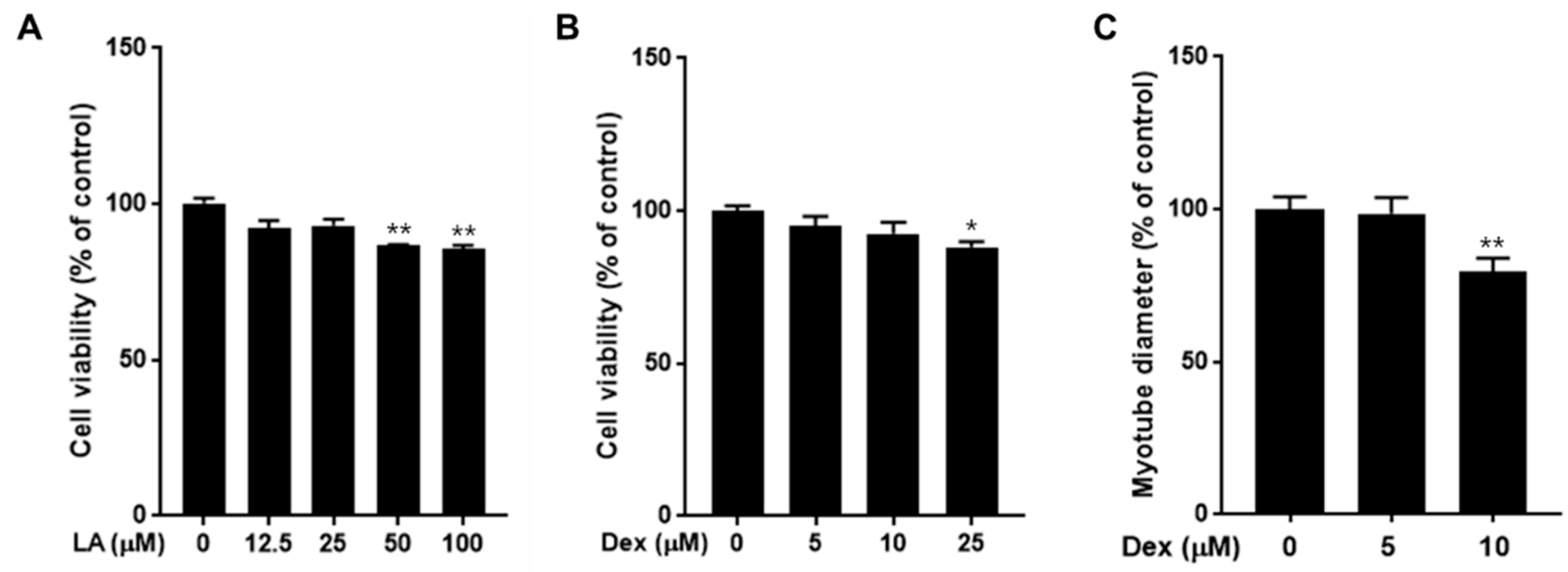
2.2. Effect of LA and Dexamethasone on C2C12 Cell Viability
2.3. Effect of LA on C2C12 Myotubes Fiber Diameter
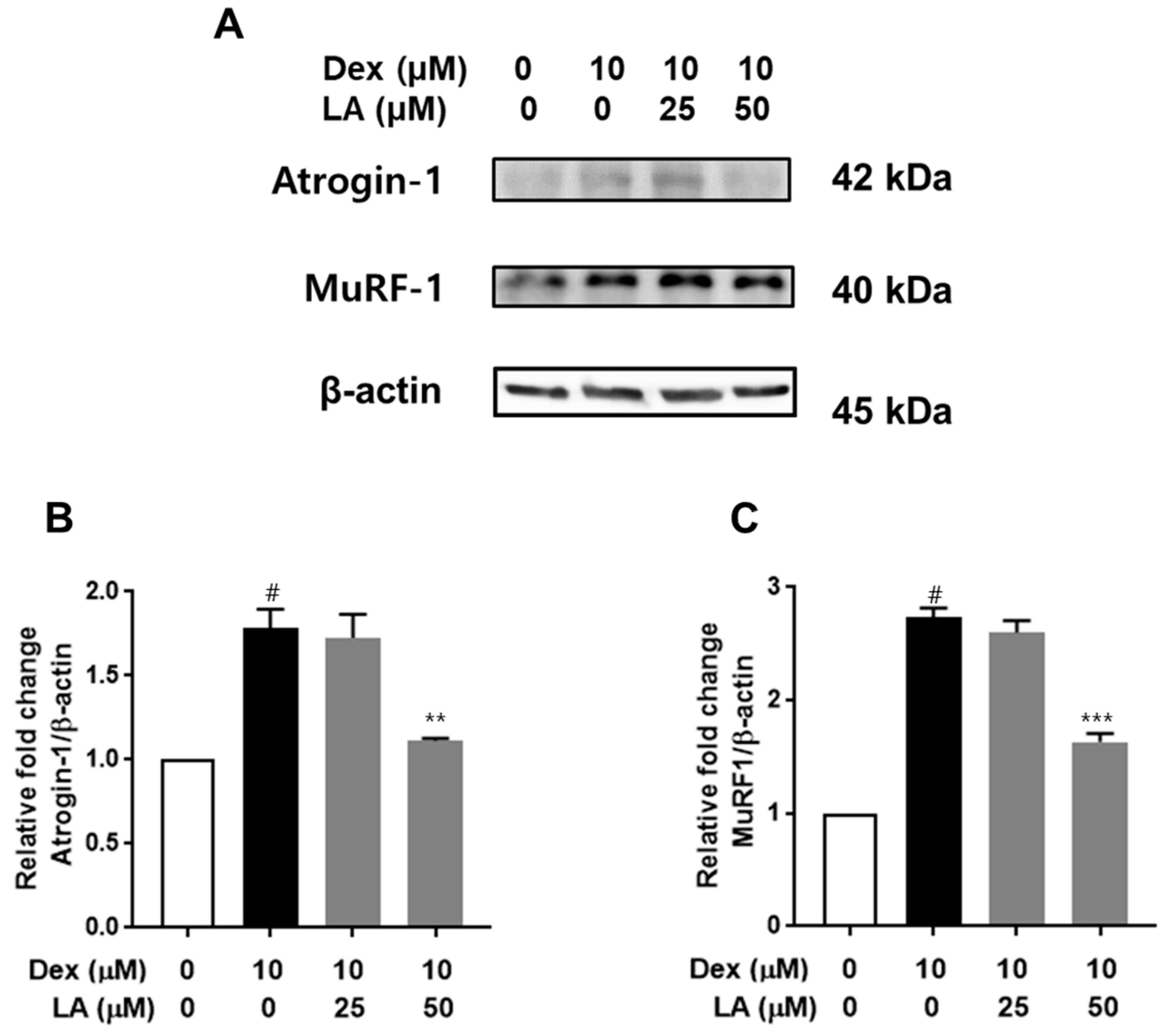
2.4. Effect of LA on Atrogin-1 and MuRF-1 Expression in Dex-Treated C2C12 Myotubes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.2. Plant Material
4.3. Extraction and Isolation
Lambertianic Acid (LA)
4.4. DFT Based ECD Calculations of LA
4.5. Cell Culture
4.6. Cell Viability
4.7. Muscle Atrophy Determination
4.8. Western Blot
4.9. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, L.; Li, M.; Deng, C.; Qiu, J.; Wang, K.; Chang, M.; Zhou, S.; Gu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Potential Therapeutic Strategies for Skeletal Muscle Atrophy. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Tao, J.; Qian, Y.; Feng, F.; Hu, X.; Xu, T.; Jin, H.; Ruan, H.; Zheng, H.F.; Tong, P. Morroniside ameliorates inflammatory skeletal muscle atrophy via inhibiting canonical and non-canonical NF-kappaB and regulating protein synthesis/degradation. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1056460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, C.; Pang, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, G. Advances in research on cell models for skeletal muscle atrophy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Koike, H.; Ono, T.; Hayashi, S.; Kudo, F.; Kaneda, A.; Kagechika, H.; Manabe, I.; Nakashima, T.; Oishi, Y. Identification of a KLF5-dependent program and drug development for skeletal muscle atrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2102895118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, M.K.; Rahimizadeh, M.; Bazzaz, B.S.F.; Emami, S.A.; Assili, J. Chemical and Antimicrobial Studies of Platycladus orientalis Essential Oils. Pharm. Biol. 2008, 39, 388–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, Y.; El-Sharkawy, E.; Abd El-Azim, M.H.M. New cytotoxic flavonoids from aerial parts of Platycladus orientalis L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, M.Q.; Shang, J.; Ding, A.W. Platycladus orientalis leaves: A systemic review on botany, phytochemistry and pharmacology. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 523–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, R.S.; Hammoda, H.M.; Ghareeb, D.A.; Abdelhamid, A.S.A.; Harraz, F.M.; Shawky, E. Seasonal dynamics of the phenolic constituents of the cones and leaves of oriental Thuja (Platycladus orientalis L.) reveal their anti-inflammatory biomarkers. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 24624–24635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, A.K.; Mishra, J.; Dash, D.K. Antidiabetic along with antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant activity of aqueous extract of Platycladus orientalis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Curr. Med. Res. Pract. 2014, 4, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, E.; Elsharkawy, E. Antibacterial Activity of Ethyl Acetate Extract of Platycladus orientalis against Staphylococcus saprophyticus. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 13, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; Choi, S.U.; Lee, K.R. Three New Diterpenoids from the Leaves of Thuja orientalis. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, L.; Chen, S.S.; Guan, J.; Qu, F.Z.; Zhao, Y.Q. Hair growth promoting activity of cedrol isolated from the leaves of Platycladus orientalis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Joo, J.H.; Kim, J.; Rim, H.; Shin, J.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Min, K.; Lee, S.Y.; Jun, S.H.; Kang, N.G. Platycladus orientalis Leaf Extract Promotes Hair Growth via Non-Receptor Tyrosine Kinase ACK1 Activation. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 11207–11219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, K.A.; Sung, S.H.; Kim, Y.C. A new neuroprotective pinusolide derivative from the leaves of Biota orientalis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 834–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.Y.; Zeng, H.W.; Pei, Y.H.; Li, L.; Ye, J.; Pan, Y.X.; Zhang, J.G.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, W.D. The anti-inflammatory activities of an extract and compounds isolated from Platycladus orientalis (Linnaeus) Franco in vitro and ex vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 141, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.Y.; Pei, Y.H.; Zeng, H.W.; Zhang, S.D.; Li, Y.L.; Li, L.; Ye, J.; Pan, Y.X.; Li, H.L.; Zhang, W.D. Compounds from Platycladus orientalis and their inhibitory effects on nitric oxide and TNF-alpha production. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 1623–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetzos, C.; Dimas, K.S. Labdane-type diterpenes: Chemistry and biological activity. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2001, 25, 235–292. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.S.; Lee, S.O.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, E.O.; Lee, H.J. Anti-Cancer Effect of Lambertianic Acid by Inhibiting the AR in LNCaP Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.K.; Yang, H.; Yoon, J.S.; Jeong, E.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Ha, N.R.; Sung, S.H.; Kim, Y.C. Antifibrotic activity of diterpenes from Biota orientalis leaves on hepatic stellate cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2008, 31, 866–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jang, M.; Ryoo, R.; Roh, J.; Ko, S.K.; Kim, K.H. New autophagy-modulating lanostane-type triterpenoids from a hallucinogenic poisonous mushroom Gymnopilus orientispectabilis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2024, 47, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.E.; Park, K.H.; Hong, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Park, K.M.; Kim, K.H. Anti-osteoporosis effects of triterpenoids from the fruit of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) through the promotion of osteoblast differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells, C3H10T1/2. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2023, 46, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, T.-Y.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, H.-M.; Sim, H.-Y.; Choi, W.; Lee, B.S.; Kim, K.H.; An, H.-J. Aster glehni Ethanol Extract Inhibits Inflammatory Responses Regulating Skin Barrier Molecules in Human Keratinocytes. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2024, 30, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.H.; Chae, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.H. Phenolic Compounds Isolated from Juncus decipiens and Their Effects on Osteoblast Differentiation in the Mouse Mesenchymal Stem Cell Line C3H10T1/2. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2024, 30, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Jeong, S.Y.; Li, Z.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, H.W.; Yoo, M.J.; Jang, H.J.; Kim, D.K.; Cho, N.; Yoo, H.M.; et al. Development of a screening platform to discover natural products active against SARS-CoV-2 infection using lung organoid models. Biomater. Res. 2023, 27, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.L.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.; Vuong, T.A.; Lee, H.Y.; Jeong, S.Y.; Alishir, A.; Walker, A.S.; Bae, G.U.; Kim, K.H.; et al. Inonotus obliquus upregulates muscle regeneration and augments function through muscle oxidative metabolism. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 4898–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asili, J.; Lambert, M.; Ziegler, H.L.; Stærk, D.; Sairafianpour, M.; Witt, M.; Asghari, G.; Ibrahimi, I.S.; Jaroszewski, J.W. Labdanes and Isopimaranes from Platycladus orientalis and Their Effects on Erythrocyte Membrane and on Plasmodium falciparum Growth in the Erythrocyte Host Cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodine, S.C.; Baehr, L.M. Skeletal muscle atrophy and the E3 ubiquitin ligases MuRF1 and MAFbx/atrogin-1. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 307, E469–E484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahinozzaman, M.; Islam, M.; Basak, B.; Sultana, A.; Emran, R.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Islam, A. A review on chemistry, source and therapeutic potential of lambertianic acid. Z. Naturforsch C J. Biosci. 2021, 76, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Sim, D.Y.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, K.R.; Kim, S.H. Apoptotic effect of lambertianic acid through AMPK/FOXM1 signaling in MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, A.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, S.-H. Reactive oxygen species dependent phosphorylation of the liver kinase B1/AMP activated protein kinase/acetyl-CoA carboxylase signaling is critically involved in apoptotic effect of lambertianic acid in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 70116–70129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, D.S.; Lee, H.J.; Hwang, J.; Han, H.; Kim, B.; Shim, B.; Kim, S.H. Lambertianic Acid Sensitizes Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers to TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis via Inhibition of XIAP/NF-kappaB and Activation of Caspases and Death Receptor 4. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauben, W.G.; German, V.F. The structure of lamertianic acid: A new diterpenic acid. Tetrahedron 1966, 22, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, H.S.; Chin, Y.W. Anti-allergic effect of lambertianic acid from Thuja orientalis in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2012, 34, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Cho, S.M.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, E.O.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, H.J. Ethanol extract of Pinus koraiensis leaves containing lambertianic acid exerts anti-obesity and hypolipidemic effects by activating adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK). BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrinelli, V.; Rouault, C.; Rodriguez-Cuenca, S.; Albert, V.; Edom-Vovard, F.; Vidal-Puig, A.; Clément, K.; Butler-Browne, G.S.; Lacasa, D. Human Adipocytes Induce Inflammation and Atrophy in Muscle Cells During Obesity. Diabetes 2015, 64, 3121–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajita, K.; Mune, T.; Ikeda, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Uno, Y.; Sugiyama, C.; Matsubara, K.; Morita, H.; Takemura, M.; Seishima, M.; et al. Effect of fasting on PPARgamma and AMPK activity in adipocytes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2008, 81, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, M.; Sandri, C.; Gilbert, A.; Skurk, C.; Calabria, E.; Picard, A.; Walsh, K.; Schiaffino, S.; Lecker, S.H.; Goldberg, A.L. Foxo transcription factors induce the atrophy-related ubiquitin ligase atrogin-1 and cause skeletal muscle atrophy. Cell 2004, 117, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schakman, O.; Kalista, S.; Barbe, C.; Loumaye, A.; Thissen, J.P. Glucocorticoid-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2163–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Liao, Q.; Liu, J.; Pan, R.; Lee, S.M.; Lin, L. Myricanol rescues dexamethasone-induced muscle dysfunction via a sirtuin 1-dependent mechanism. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, Y.; Oishi, S.; Onoda, K.; Shibata, K.; Miyoshi, N. Diosgenin prevents dexamethasone-induced myotube atrophy in C2C12 cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2023, 747, 109759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.J.; An, J.S.; Bae, E.S.; Cho, E.; Hwang, S.; Nam, S.J.; Oh, K.B.; Lee, S.K.; Oh, D.C. Ligiamycins A and B, Decalin-Amino-Maleimides from the Co-Culture of Streptomyces sp. and Achromobacter sp. Isolated from the Marine Wharf Roach, Ligia exotica. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, D.; Youn, I.; Huynh, T.H.; Kim, H.W.; Noh, S.G.; Chung, H.Y.; Oh, D.C.; Seo, E.K. Identification of New Polyacetylenes from Dendropanax morbifera with PPAR-α Activity Study. Molecules 2024, 29, 5942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, R.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, H.; Oh, J.E.; Kim, T.H.; Go, G.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Bae, G.U. Ginsenoside Rg5 promotes muscle regeneration via p38MAPK and Akt/mTOR signaling. J. Ginseng Res. 2023, 47, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.K.S.; Nguyen, N.Q.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.H.; Jeong, D.; Seo, E.J.; Park, J.S.; Cho, J.; Kang, K.S. Anticancer effects of aloe-emodin from Rheum undulatum L. through activation of the p53 pathway in human prostate cancer cells. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2024, 67, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardiff, R.D.; Miller, C.H.; Munn, R.J. Manual hematoxylin and eosin staining of mouse tissue sections. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2014, 2014, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-R.; Eom, D.H.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, J.-C.; Shin, M.-S.; Shin, K.-S. Composition analysis and oral administered effects on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis of galactooligosaccharides bioconverted by Bacillus circulans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 270, 118389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, E.; Choi, J.G.; Choi, Y.; Ju, I.G.; Kim, B.; Shin, Y.J.; An, J.M.; Park, M.G.; Yim, S.V.; Chung, S.J.; et al. mirabilis- derived pore-forming haemolysin, HpmA drives intestinal alpha-synuclein aggregation in a mouse model of neurodegeneration. EBioMedicine 2023, 98, 104887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, C.H.; Chae, S.H.; Thi, N.H.L.; Um, S.H.; Lee, S.; Yu, J.S.; Kang, K.S.; Kim, K.H. Lambertianic Acid from Platycladus orientalis Inhibits Muscle Atrophy in Dexamethasone-Induced C2C12 Muscle Atrophy Cells. Plants 2025, 14, 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091357
Cho CH, Chae SH, Thi NHL, Um SH, Lee S, Yu JS, Kang KS, Kim KH. Lambertianic Acid from Platycladus orientalis Inhibits Muscle Atrophy in Dexamethasone-Induced C2C12 Muscle Atrophy Cells. Plants. 2025; 14(9):1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091357
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Chan Hee, Si Hyeon Chae, Ngoc Han Le Thi, Sung Hee Um, Seulah Lee, Jae Sik Yu, Ki Sung Kang, and Ki Hyun Kim. 2025. "Lambertianic Acid from Platycladus orientalis Inhibits Muscle Atrophy in Dexamethasone-Induced C2C12 Muscle Atrophy Cells" Plants 14, no. 9: 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091357
APA StyleCho, C. H., Chae, S. H., Thi, N. H. L., Um, S. H., Lee, S., Yu, J. S., Kang, K. S., & Kim, K. H. (2025). Lambertianic Acid from Platycladus orientalis Inhibits Muscle Atrophy in Dexamethasone-Induced C2C12 Muscle Atrophy Cells. Plants, 14(9), 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091357










