Screening of In Vitro Heavy Metal Tolerance in Tocoyena brasiliensis Mart. (Rubiaceae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
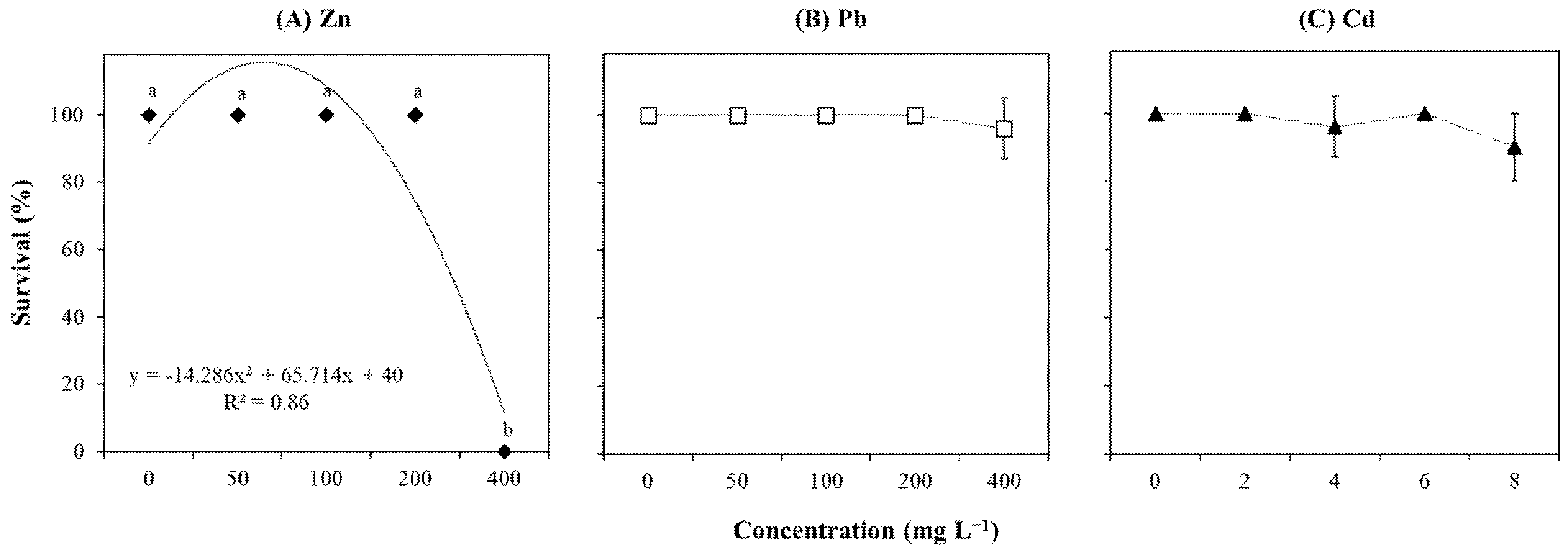
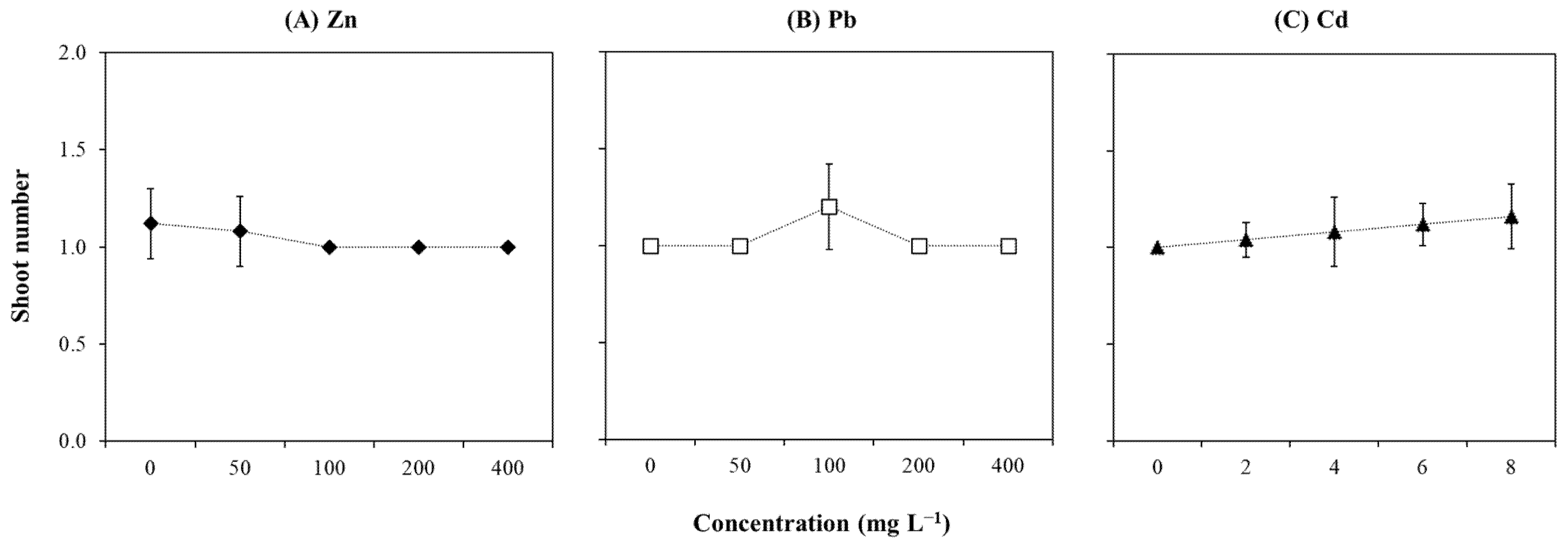
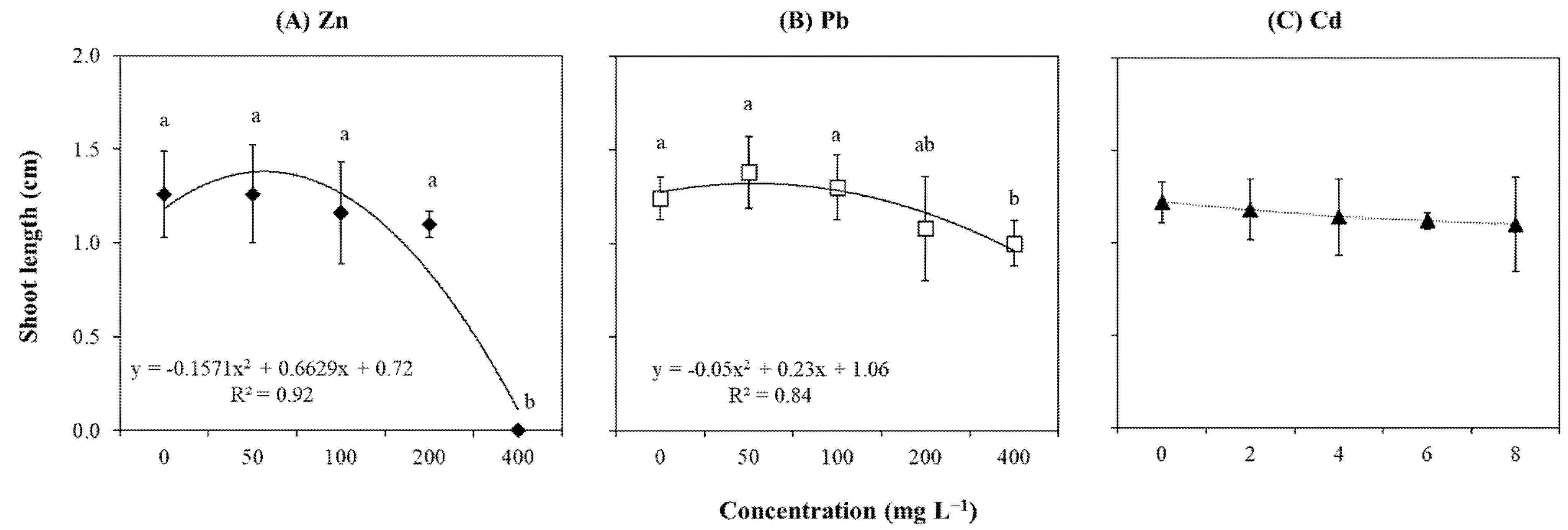
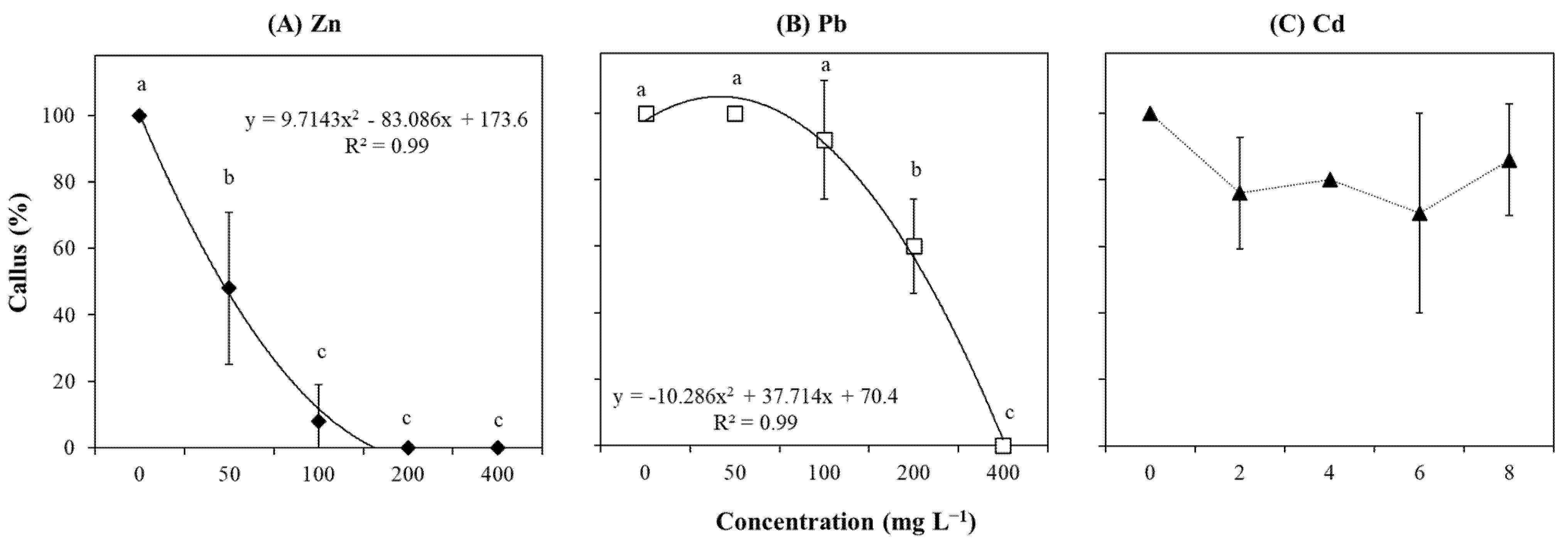
2. Results
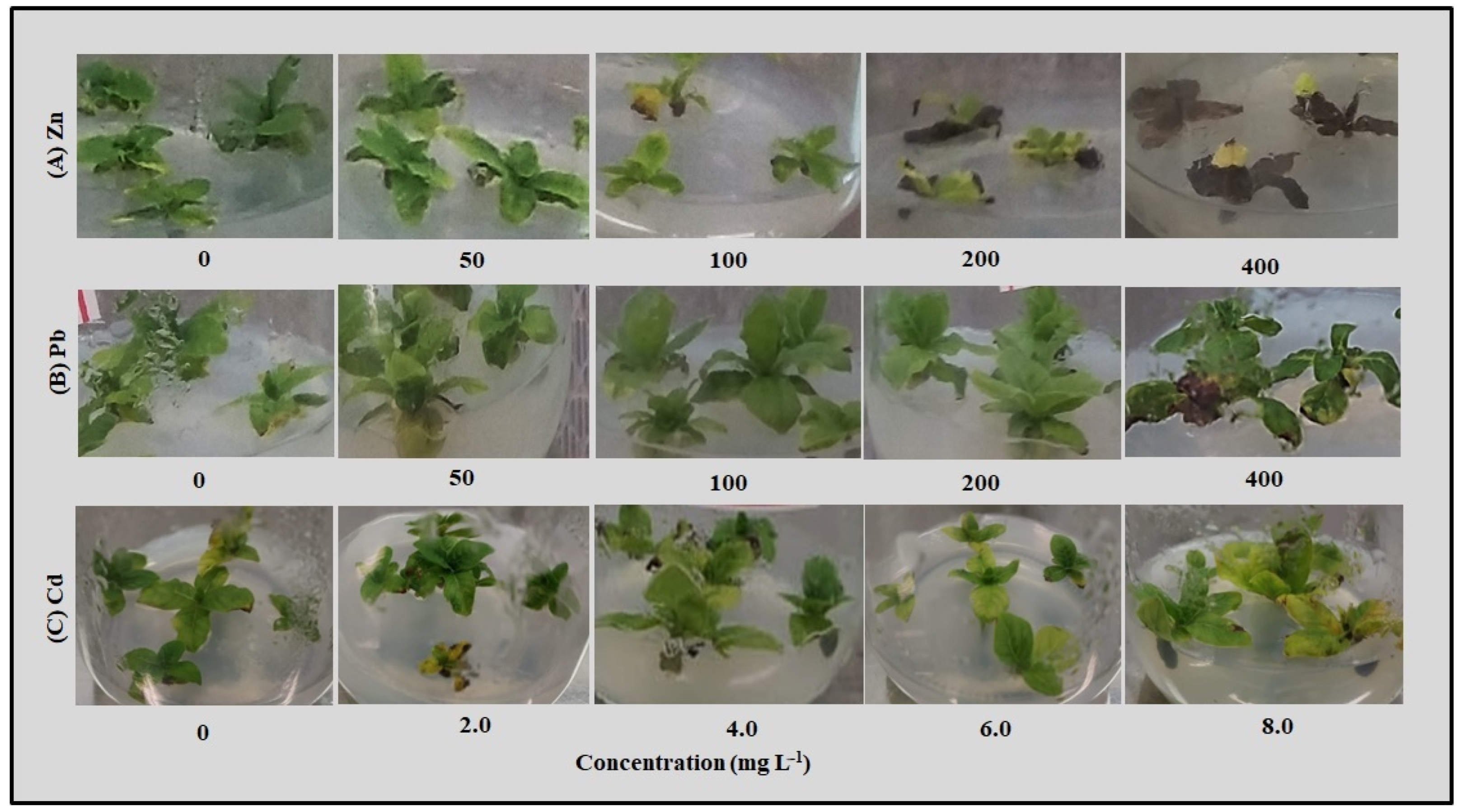
2.1. In Vitro Culture Establishment
2.2. Growth-Related Parameters
2.3. Callus Formation
3. Discussion
3.1. Explants Sensitivity to High Concentration of Zn
3.2. Explants Resistance to Cd
3.3. Explants Resistance to Pb
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
4.2. Heavy Metal Treatments
4.3. Data Collection
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Angon, P.B.; Islam, M.S.; KC, S.; Das, A.; Anjum, N.; Poudel, A.; Suchi, S.A. Sources, Effects and Present Perspectives of Heavy Metals Contamination: Soil, Plants and Human Food Chain. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, W.H.O. Evolution of Metal Tolerance in Higher Plants. For. Snow Landsc. Res. 2006, 80, 251–274. [Google Scholar]
- Angulo-Bejarano, P.I.; Puente-Rivera, J.; Cruz-Ortega, R. Metal and Metalloid Toxicity in Plants: An Overview on Molecular Aspects. Plants 2021, 10, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, M.; Ma, Y. Metal Tolerance Mechanisms in Plants and Microbe-Mediated Bioremediation. Environ. Res. 2023, 222, 115413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Parihar, P.; Singh, R.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Heavy Metal Tolerance in Plants: Role of Transcriptomics, Proteomics, Metabolomics, and Ionomics. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; Fatnani, D.; Parida, A.K. Uptake, Impact, Adaptive Mechanisms, and Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals by Plants: Role of Transporters in Heavy Metal Sequestration. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 221, 109578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asare, M.O.; Száková, J.; Tlustoš, P. Mechanisms of As, Cd, Pb, and Zn Hyperaccumulation by Plants and Their Effects on Soil Microbiome in the Rhizosphere. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1157415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuana, M. Heavy Metals and Woody Plants—Biotechnologies for Phytoremediation. iForest-Biogeosci. For. 2011, 4, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lonardo, S.; Capuana, M.; Arnetoli, M.; Gabbrielli, R.; Gonnelli, C. Exploring the Metal Phytoremediation Potential of Three Populus alba L. Clones Using an in Vitro Screening. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageria, N.K.; Nascente, A.S. Management of Soil Acidity of South American Soils for Sustainable Crop Production. In Advances in Agronomy; Donald, L.S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 221–275. ISBN 9780128021392. [Google Scholar]
- Bolfe, E.F.; Sano, E.E.; Campos, S.K. Dinâmica Agrícola no Cerrado: Análises e Projeções, 1st ed.; EMBRAPA: Brasília, Brazil, 2020; ISBN 978-85-7035-951-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, J.F.; Walter, B.M.T. Fitofisionomias Do Bioma Cerrado. In Cerrado: Ambiente e Flora; Sano, S.M., Almeida, S.P., Eds.; EMBRAPA-CPAC: Planaltina, Brazil, 1998; pp. 89–166. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, R.d.P.; Moreira, A.; Rassini, J.B. Toxidez de Alumínio em Culturas Anuais, 1st ed.; EMBRAPA Pecuária Sudeste: São Carlos, Brazil, 2006; ISBN 1980-6841. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, S.T.; Castro, S.R.; Fernandes, M.M.; Soares, A.C.; de Souza Freitas, G.A.; Ribeiro, E. Heavy Metal in Contaminated Industrial Soil: Uptake Assessment in Native Plant Species from Brazilian Cerrado. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2016, 18, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, R.L. Tocoyena in Flora e Funga do Brasil. Jardim Botânico do Rio de Janeiro. Available online: https://floradobrasil.jbrj.gov.br/FB14336 (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Hamerski, L.; Carbonezi, C.A.; Cavalheiro, A.J.; Bolzani, V.D.S.; Young, M.C.M. Saponinas Triterpênicas de Tocoyena Brasiliensis Mart. (Rubiaceae). Quim. Nova 2005, 28, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macêdo, B.R.M.d.; Calvente, A.D.M. List of Native Trees Used as Ornamental and Selection of New Species from the Caatinga and Atlantic Forest of Rio Grande Do Norte, Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Arborização Urbana 2023, 18, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadley, M.R.; White, P.J.; Hammond, J.P.; Zelko, I.; Lux, A. Zinc in Plants. New Phytol. 2007, 173, 677–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Baccio, D.; Tognetti, R.; Sebastiani, L.; Vitagliano, C. Responses of Populus deltoides × Populus nigra (Populus × Euramericana) Clone I-214 to High Zinc Concentrations. New Phytol. 2003, 159, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateos-Naranjo, E.; Redondo-Gómez, S.; Cambrollé, J.; Luque, T.; Figueroa, M.E. Growth and Photosynthetic Responses to Zinc Stress of an Invasive Cordgrass, Spartina Densiflora. Plant Biol. 2008, 10, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchin, C.; Fossati, T.; Pasquini, E.; Lingua, G.; Castiglione, S.; Torrigiani, P.; Biondi, S. High Concentrations of Zinc and Copper Induce Differential Polyamine Responses in Micropropagated White Poplar (Populus alba). Physiol. Plant. 2007, 130, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, A.P.C.; dos Santos, D.S.; Vieira, E.A. Effects of Zinc Excess on Antioxidant Metabolism, Mineral Content and Initial Growth of Handroanthus impetiginosus (Mart. Ex DC.) Mattos and Tabebuia Roseoalba (Ridl.) Sandwith. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2017, 144, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghori, N.H.; Ghori, T.; Hayat, M.Q.; Imadi, S.R.; Gul, A.; Altay, V.; Ozturk, M. Heavy Metal Stress and Responses in Plants. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1807–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeen-ud-din, M.; Wang, S.; Yang, S.; Wang, J. The Combined Effects of Copper and Zinc on Arabidopsis Involve Differential Regulation of Chlorophyll Synthesis and Photosystem Function. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 216, 109160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.F.; Aarts, M.G.M. The Molecular Mechanism of Zinc and Cadmium Stress Response in Plants. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 3187–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglione, S.; Franchin, C.; Fossati, T.; Lingua, G.; Torrigiani, P.; Biondi, S. High Zinc Concentrations Reduce Rooting Capacity and Alter Metallothionein Gene Expression in White Poplar (Populus alba L. Cv. Villafranca). Chemosphere 2007, 67, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeuchi, M.; Sugimoto, K.; Iwase, A. Plant Callus: Mechanisms of Induction and Repression. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 3159–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Moeen-ud-din, M.; Yang, S. Dose-Dependent Responses of Arabidopsis Thaliana to Zinc Are Mediated by Auxin Homeostasis and Transport. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 189, 104554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaan, I.; Sharma, P.; Singh, A.D.; Dhiman, S.; Kour, J.; Kumar, P.; Kaur, G.; Sharma, I.; Gautam, V.; Kaur, R.; et al. Zinc and Plant Hormones: An Updated Review. In Zinc in Plants; Tripathi, D.K., Singh, V.P., Pandey, S., Sharma, S., Chauhan, D.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 193–223. ISBN 9780323913140. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, H.; Naidu, R.; Sarkar, B.; Lamb, D.T.; Liu, Y.; Megharaj, M.; Sparks, D. Competitive Sorption of Cadmium and Zinc in Contrasting Soils. Geoderma 2016, 268, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, V.L.; De Almeida, A.A.F.; Lima, S.G.C.; Júlio, J.C.; da C. Silva, D.; Mangabeira, P.A.O.; Gomes, F.P. Morphophysiological Responses and Programmed Cell Death Induced by Cadmium in Genipa americana L. (Rubiaceae). BioMetals 2011, 24, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, D.; Ma, J.; Gao, R.; Bai, J.; Hou, Q. Transcriptomic and Physiological Analyses of Symphytum officinale L. in Response to Multiple Heavy Metal Stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 277, 116361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Shen, J.; Zhang, L.; Wei, P.; Liu, A.; Song, H. The Alleviating Effect on the Growth, Chlorophyll Synthesis, and Biochemical Defense System in Sunflowers under Cadmium Stress Achieved through Foliar Application of Humic Acid. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmaja, K.; Prasad, D.D.K.; Prasad, A.R.K. Inhibition of Chlorophyll Synthesis in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Seedlings by Cadmium Acetate. Photosynthetica 1990, 24, 399–405. [Google Scholar]
- Grajek, H.; Rydzyński, D.; Piotrowicz-Cieślak, A.; Herman, A.; Maciejczyk, M.; Wieczorek, Z. Cadmium Ion-Chlorophyll Interaction—Examination of Spectral Properties and Structure of the Cadmium-Chlorophyll Complex and Their Relevance to Photosynthesis Inhibition. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelssohn, I.; McKee, K.; Kong, T. A Comparison of Physiological Indicators of Sublethal Cadmium Stress in Wetland Plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2001, 46, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.G.d.; Melo, V.d.F.; Souza, L.C.d.P.; Gabardo, J.; Reissmann, C.B. Metais Pesados Em Solos de Área de Mineração e Metalurgia de Chumbo: II—Formas e Disponibilidade Para Plantas. Rev. Bras. Ciência Solo 2009, 33, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, S.M.; Pena, L.B.; Barcia, R.A.; Azpilicueta, C.E.; Iannone, M.F.; Rosales, E.P.; Zawoznik, M.S.; Groppa, M.D.; Benavides, M.P. Unravelling Cadmium Toxicity and Tolerance in Plants: Insight into Regulatory Mechanisms. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2012, 83, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, S.; Baskar, A.; Geevarghese, D.M.; Ali, M.N.V.S.; Bahubali, P.; Choudhary, R.; Lvov, V.; Tovar, G.I.; Senatov, F.; Koppala, S.; et al. Bioaccumulation of Lead (Pb) and Its Effects in Plants: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2022, 3, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.; Aslam, A.; Sheraz, M.; Ali, B.; Ulhassan, Z.; Najeeb, U.; Zhou, W.; Gill, R.A. Lead Toxicity in Cereals: Mechanistic Insight into Toxicity, Mode of Action, and Management. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 587785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, E.P.D.; França, I.D.; Ferreira, L.E. Mecanismos de Tolerância a Estresses Por Metais Pesados Em Plantas. Rev. Bras. Agrociência 2011, 17, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Prasad, M.N.V. Plant-Lead Interactions: Transport, Toxicity, Tolerance, and Detoxification Mechanisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 166, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kališová-Špirochová, I.; Punčochářová, J.; Kafka, Z.; Kubal, M.; Soudek, P.; Vanek, T. Accumulation of Heavy Metals by in Vitro Cultures of Plants. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2003, 3, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, R.; Ahmad, P.; Gadgil, K.; Sharma, S. Effect of Cadmium and Lead on Growth, Biochemical Parameters and Uptake in Lemna polyrrhiza L. Plant Soil Environ. 2008, 54, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, T.; Khan, N.; Wahab, M.; Okla, M.K.; Abdel-Maksoud, M.A.; Saleh, I.A.; Abu-Harirah, H.A.; AlRamadneh, T.N.; AbdElgawad, H. Assessing Lead and Cadmium Tolerance of Chenopodium Ambrosioides during Micropropagation: An in-Depth Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.C.; Mariz-Ponte, N.; Santos, C. Lead Induces Oxidative Stress in Pisum Sativum Plants and Changes the Levels of Phytohormones with Antioxidant Role. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 137, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albacete, A.; Ghanem, M.E.; Martínez-Andújar, C.; Acosta, M.; Sánchez-Bravo, J.; Martínez, V.; Lutts, S.; Dodd, I.C.; Pérez-Alfocea, F. Hormonal Changes in Relation to Biomass Partitioning and Shoot Growth Impairment in Salinized Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 4119–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amdoun, R.; Sahli, F.; Hamadache, K.; Ouzzane, A.H.; Khelifi-Slaoui, M.; Moustafa, K.; Hefferon, K.; Makhzoum, A.; Khelifi, L. Optimization of Caulogenesis in Populus nigra under Lead (Pb) Stress via Response Surface Methodology (RSM) and Desirability Function Analysis. Plant Cell. Tissue Organ Cult. 2020, 142, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Dubey, R.S. Lead Toxicity in Plants. Brazilian J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 17, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, G.; McCown, B.H. Commercially Feasible Micropropagation of Mountain Laurel Kalmia Latifolia by Use of Shoot-Tip Culture. Comb. Proc. Int. Plant Propagators Soc. 1980, 30, 421–427. [Google Scholar]
- Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente. CONAMA Resolução No 420 de 28 de Dezembro de 2009; Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente: Brasília, Brazil, 2009. Available online: https://cetesb.sp.gov.br/areas-contaminadas/wp-content/uploads/sites/17/2017/09/resolucao-conama-420-2009-gerenciamento-de-acs.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Fageria, N.K. Adequate and Toxic Levels of Zinc for Rice, Common Bean, Corn, Soybean and Wheat Production in Cerrado Soil. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agrícola Ambient. 2000, 4, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martins, A.S.D.; Huarancca Reyes, T.; Guglielminetti, L.; Damiani, C.R. Screening of In Vitro Heavy Metal Tolerance in Tocoyena brasiliensis Mart. (Rubiaceae). Plants 2025, 14, 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091331
Martins ASD, Huarancca Reyes T, Guglielminetti L, Damiani CR. Screening of In Vitro Heavy Metal Tolerance in Tocoyena brasiliensis Mart. (Rubiaceae). Plants. 2025; 14(9):1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091331
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartins, Allex Sandro Durão, Thais Huarancca Reyes, Lorenzo Guglielminetti, and Cláudia Roberta Damiani. 2025. "Screening of In Vitro Heavy Metal Tolerance in Tocoyena brasiliensis Mart. (Rubiaceae)" Plants 14, no. 9: 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091331
APA StyleMartins, A. S. D., Huarancca Reyes, T., Guglielminetti, L., & Damiani, C. R. (2025). Screening of In Vitro Heavy Metal Tolerance in Tocoyena brasiliensis Mart. (Rubiaceae). Plants, 14(9), 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091331






