Meta-Analysis of Mixed Sowing Effects on Forage Yield and Water Use Efficiency in China: Influencing Factors and Optimal Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Analysis
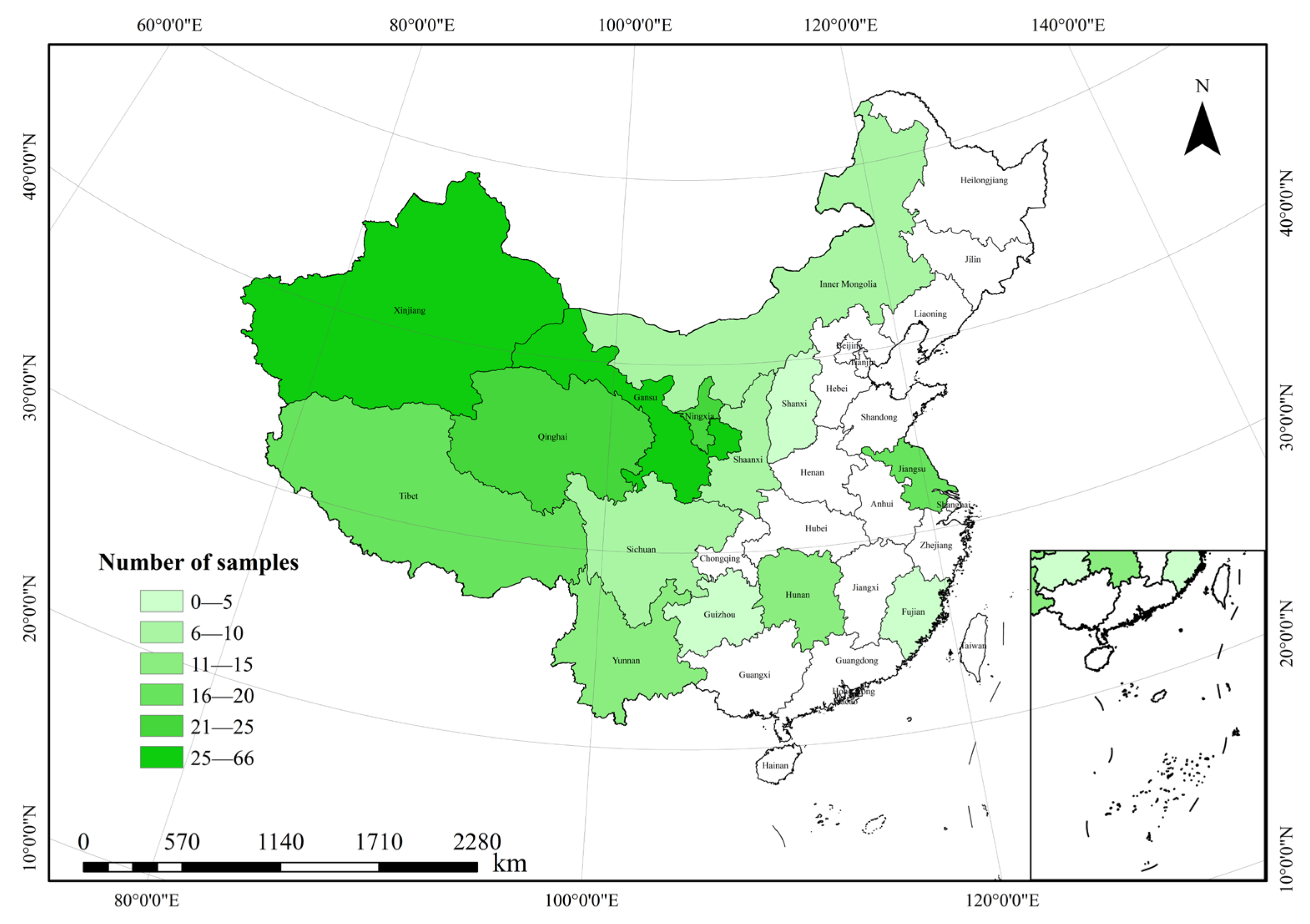
2.1. Sample Distribution of Forage Yield and Water Use Efficiency
2.2. Overall Effects of Mixed Sowing on Forage Yield and Water Use Efficiency
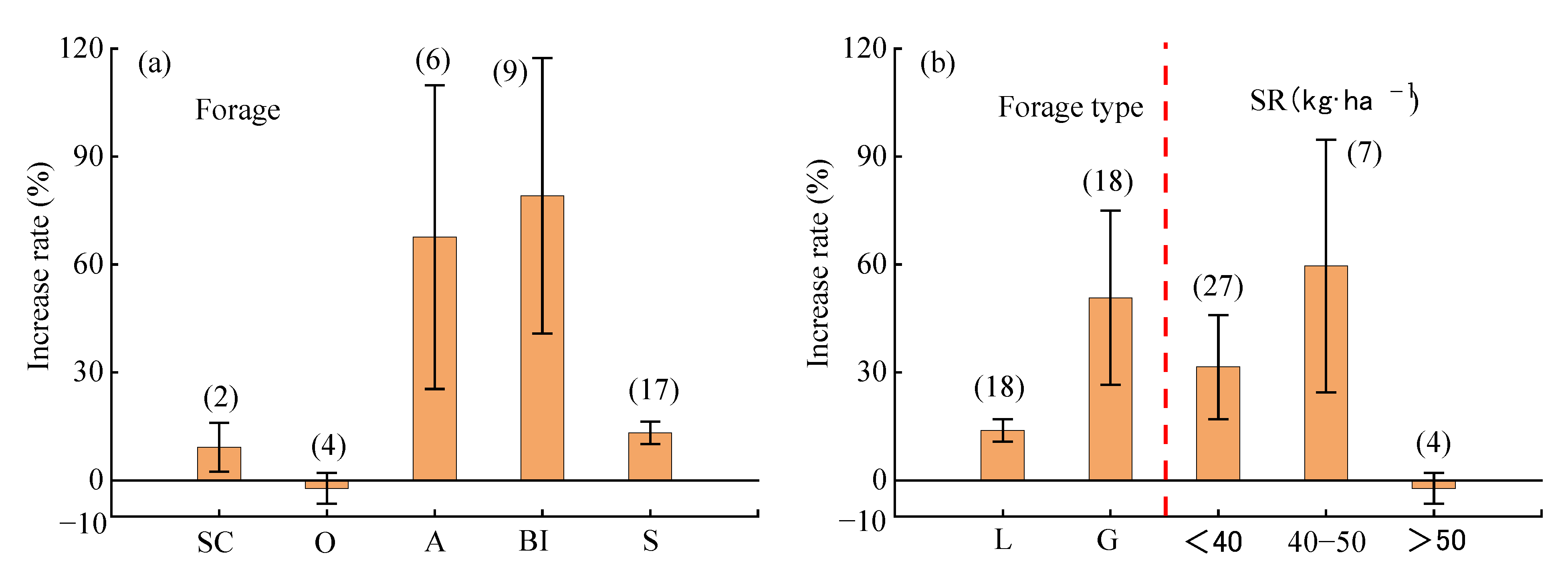
2.3. Factors Influencing Forage Yield Under Mixed Sowing
2.3.1. Regional Factors
2.3.2. Mixed Sowing Factors
2.3.3. Monoculture Factors
2.3.4. Other Factors
2.4. Factors Influencing Water Use Efficiency of Mixed Sowing
2.4.1. Regional Factors
2.4.2. Mixed Sowing Factors
2.4.3. Monoculture Factors
2.4.4. Other Factors
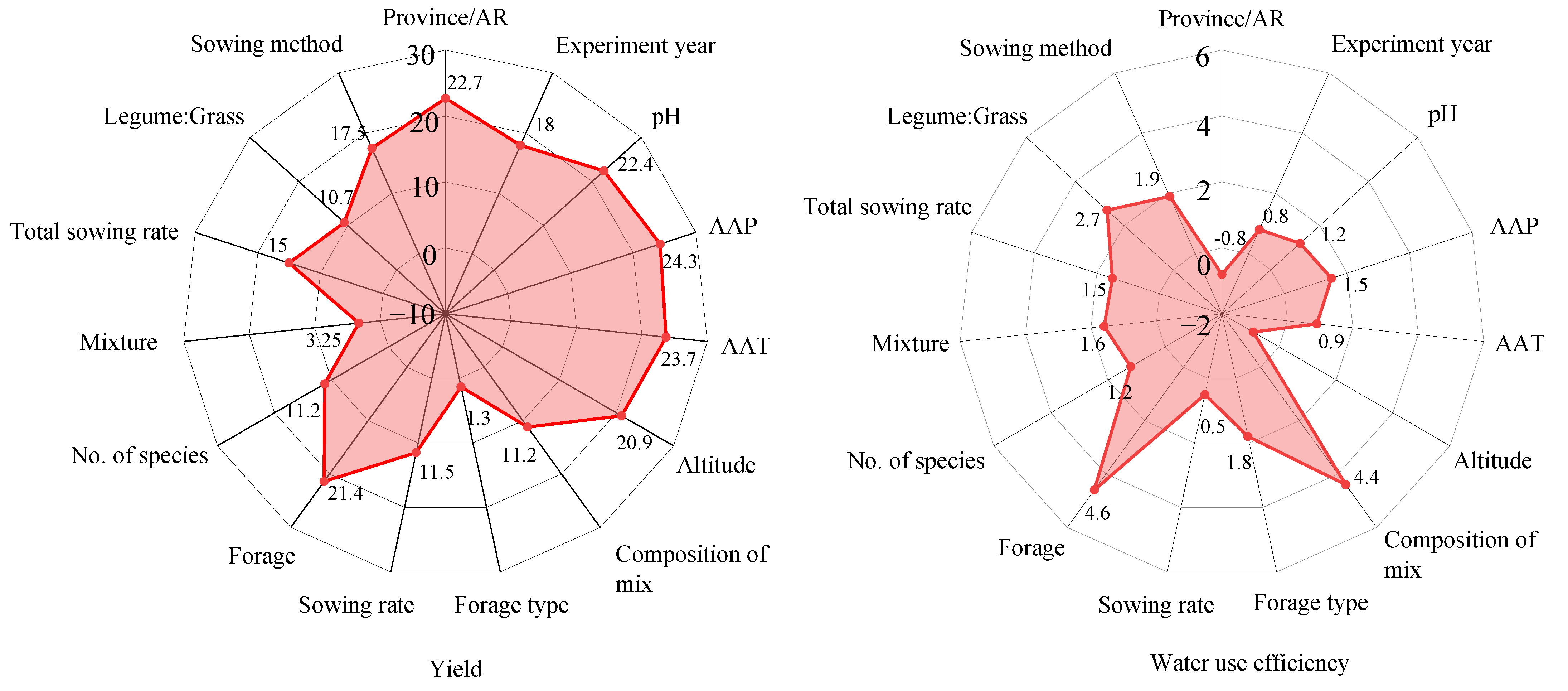
2.5. Importance of Mixed Sowing for Forage Yield and Water Use Efficiency
3. Discussion
3.1. Effects of Mixed Sowing on Forage Yield and Water Use Efficiency
3.2. Influence of Regional Factors on Forage Yield and Water Use Efficiency in Mixed Sowing
3.3. Influence of Mixed Sowing and Monocultureg Factors on Forage Yield and Water Use Efficiency
3.4. Influence of Other Factors on Forage Yield and Water Use Efficiency
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Sources
4.2. Data Classification
4.3. Data Analysis
4.3.1. Calculation of Effect Size
4.3.2. Heterogeneity Test
4.3.3. Model Verification
4.4. Data Processing
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Compared with monoculture, mixed sowing significantly increased forage yield and water use efficiency (WUE) by an average of 58.3% and 32.0%, respectively.
- (2)
- In regions such as Shaanxi and Fujian, with an average annual precipitation of 200–600 mm, an average annual temperature of 10–15 °C, and altitudes below 2000 m, the following conditions were conducive to improving the yield effect of mixed sowing: alfalfa + Bromus inermis, a two-forage allocation, a mixture with Leguminosae and Gramineae with a species ratio of Leguminosae to Gramineae of 1:1, mixed sowing in the same rows, monoculture of Gramineae such as Agropyron cristatum, soil pH of 4–5, and a total sowing rate of 50–100 kg·ha−1.
- (3)
- In regions such as Gansu, with an average annual precipitation of 400–600 mm, an annual average temperature of 5–10 °C, and altitudes of 1000–2000 m, the following conditions were conducive to improving WUE: oats + peas, a two-forage allocation, a mixture of Leguminosae and Gramineae with a species ratio of Leguminosae to Gramineae of 1:1, mixed sowing in different rows, monoculture of Gramineae such as Bromus inermis, sowing rate of 40–50 kg·ha−1, soil pH of 8–9, and a total sowing rate of <50 kg·ha−1.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huo, L.X.; Hong, M.; Zhao, B.; Gao, H.Y.; Ye, H. Decomposition of Litter in desert grassland. Chin. J. Grassl. 2018, 40, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; Bullock, J.M.; Lavorel, S.; Manning, P.; Schaffner, U.; Ostle, N.; Chomel, M.; Durigan, G.; Fry, E.L.; Johnson, D.; et al. Combatting global grassland degradation. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 720–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.H.; Ma, Y.L.; Kang, Y.X.; Jia, Q.; Qi, G.P.; Wang, J.H. Effects of nitrogen application on alfalfa yield and quality in China—A Meta-analysis. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2022, 31, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J. Grassland ecosystem services: A systematic review of research advances and future directions. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 793–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Lee, T.M.; Nie, X.; Wang, T.; Liang, E.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Piao, S.; et al. Nature-based Solutions can help restore degraded grasslands and increase carbon sequestration in the Tibetan Plateau. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.H.; Zhu, Y.K.; Zhao, X.; Geng, X.Q.; Gao, S.Q.; Fang, J.Y. Analysis of current grassland resources in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.C.; Wu, R.H.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, S.R.T.L.T.; Wang, Q.; Li, P.; Zhao, H.X. Contribution rate of scientific and technological progress to the grass industry under the background of high-quality development of grassland-based livestock husbandry in Inner Mongolia. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2023, 31, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.F.; Yu, Z.; Yang, Q.C.; Wan, H.W.; Huang, J.H.; Ji, B.M.; Li, A. Mechanisms requlating the productivity and stability of artificial grasslandsin China: Lssues, progress, and prospects. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.F.; Wang, M.L. The Change Trend and Comparative Analysis of Forage Production in the Perspective of Cost-Benefit. Chin J. Grassl. 2024, 46, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oweis, T.Y. Improving Agricultural Water Productivity: A Viable Response to Water Scarcity in the Dry Areas. In Integrated Water Resources Management in the Mediterranean Region; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.X.; Yang, G.W.; Wei, Y.Q.; Wilson, G.W.T.; Wei, B.; He, Y.J.; Yu, H.Q.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Y.J. Low legume-grass seeding ratio combined with phosphorus fertilization promotes forage yield and soil quality in managed grasslands. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 44, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocira, A.; Staniak, M.; Tomaszewska, M.; Kornas, R.; Cymerman, J.; Panasiewicz, K.; Lipińska, H. Legume cover crops as one of the elements of strategic weed management and soil quality improvement. A review. Agriculture 2020, 10, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambalvo, D.; Amato, G.; Di, M.G.; Sain, S.; Uros, V.; Frenda, A.S.; Ruisi, P. Mediterranean forage Leguminosae grown alone or in mixture with annual ryegrass: Biomass production, n-2 fixation, and indices of intercrop efficiency. Plant Soil 2016, 402, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Gu, S.; Li, S.; Shen, W.; Zhou, X.; Yu, H.; Ma, K.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, H.; et al. Grass-legume mixtures enhance forage production via the bacterial community. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 338, 108087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousselin, X.; Cassagne, N.; Baux, A.; Valantin-Morison, M.; Herrera, J.M.; Lorin, M.; Hédan, M.; Fustec, J. Interactions between plants and plant-soil in functionally complex mixtures including grass pea, faba bean and niger, intercropped with oilseed rape. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulwa, U.; Mgujulwa, N.; Beyene, S.T. Benefits of grass-legume inter-crop in livestock systems. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 13, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Shi, J.M.; Wang, T.F.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Ma, J.P.; Li, J.W.; Wang, X.B.; Deng, J.Q.; Lan, J. Effect of nitrogen application on production performance and nitrogen fertilizer contribution of forage sorghum/lablab mixed cropping. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2024, 34, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussana, J.F.; Tallec, T.; Blanfort, V. Mitigating the greenhouse gas balance of ruminant production systems through carbon sequestration in grasslands. Animal 2010, 4, 334–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, D.A.; Beacom, S.E.; Dawley, W.K. Pasture productivity of two grass-alfalfa mixtures in northeastern Saskatchewan. Can. J. Plant. Sci. 1965, 45, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Liu, J.; Wu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Nimir, N.E.A.; Zhou, G. The Optimum Mixed Cropping Ratio of Oat and Alfalfa Enhanced Plant Growth, Forage Yield, and Forage Quality in Saline Soil. Plants 2024, 13, 3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniak, M.; Bojarszczuk, J.; Księżak, J. Changes in yield and gas exchange parameters in Festulolium and alfalfa grown in pure sowing and in mixture under drought stress. Acta Agric. Scand. B-Soil Plant Sci. 2018, 68, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Tian, X.H.; Du, W.H. Effects of mixed sowing of rye and common vetch on forage yield and nutrient quality in alpine pastoral areas. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2021, 30, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangi, S. Oat as Green Fodder and Its Intercropping Benefits: A Review. Agric. Rev. 2021, 42, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.X.; Li, R.Z.; Tian, X.H.; Du, W.H. Effects of Sowing Method on the Production Performance and Nutrient Composition of Timothy Grass Genotypes in Alpine and Shaded Areas of Gansu. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2023, 45, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Ma, H.C.; Ma, J.L.; Chen, Y.W.; Ma, W.L.; Sun, Q. Analysis of production performance and economic benefit of different forage multiple cropping modes in Ningxia irrigation area. Pratac. Sci. 2024, 41, 2458–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, K.; Vanek, S.J.; Sueldo, Y.; Olivera, E.; Ccanto, R.; Scurrah, M.; Fonte, S.J. Grass–legume mixtures show potential to increase above-and belowground biomass production for Andean forage-based fallows. Agronomy 2022, 12, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Gong, J.R.; Pan, Y.; Luo, Q.P.; Zhai, Z.W.; Xu, S.; Yang, L.L. Effects of grass–legume mixtures on the production and photosynthetic capacity of constructed grasslands in Inner Mongolia, China. Crop Pasture Sci. 2016, 67, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Wang, B.; Wang, T.F.; Ni, W.; Deng, J.G.; Lan, J. Effects of mixed sowing of vetch and oat on production performance and nutrient quality of grassland. J. Acta Agrest. Sin. 2022, 30, 3439–3446. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, Z.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.X.; Yu, T.F.; Chen, W.D.; Sun, H.; Liu, H.; Tang, Y.T. The density of alfalfa and the production performance and photosynthetic characteristics of grassland under the mixed sowing method of rice and beans. Pratac. Sci. 2022, 39, 1618–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Yi, T.F.; Hao, F.; Cheng, M. Effects of fertilization and mixed sowing ratio on the production. Performance of grass-alfalfa mixed forage. Chin J. Grassl. 2020, 42, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte, A.; Samarappuli, D.; Berti, M.T. Alfalfa–grass mixtures in comparison to grass and alfalfa monocultures. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Struik, P.C.; Zhang, Y.; Stomph, T.J. Forage quality in cereal/legume intercrop: A meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2023, 304, 109174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeder, A.; Schweingruber, F.H.; Ebeling, A.; Eisenhauer, N.; Fischer, M.; Roscher, C. Plant diversity effects on plant longevity and their relationships to population stability in experimental grasslands. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 2566–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.j.; Baima, G.W.; Wei, W.; De, K.J. The effects of grass-legume mixing farming on forage nutritional quality and soil nutrient in alpine zone of Tibet. ARAA 2021, 39, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.S.; Qi, J.; Li, X.; Lu, X.; Jia, Y.W.; Sai, N.G. Effect of Alfalfa and Elymus sibiricus Mixture on Forage Yield and Soi Nutrients. Chin J. Grassl. 2024, 46, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Gao, K.; Yu, T.F.; Zhang, L.J.; Cheng, M. Effects of Sowing Patterns on Productivity and Interspecific Relationship of Alfalfa-Grass Mixture System. Chin J. Grassl. 2020, 42, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.Q.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yan, J.C. Influence of mixed sowing of Alfalfa and Grass onsoluble sugar content in root. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2019, 21, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govaert, L.; Hendry, A.P.; Fattahi, F.; Mst, M. Quantifying interspecific and intraspecific diversity effects on ecosystem functioning. Ecology 2024, 105, e4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X. Countermeasures for the development of alfalfa planting industry in China. J. Beijing Univ. Agric. 2022, 37, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Bai, H.Y.; Li, J.Q.; Ma, Q.; Wang, P.T. Changes of vegetation potential distribution pattern in the Qinling Mountains in Shaanxi Province in the context of climate warming. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.Y.; Meng, X.; Xu, Z.Z.; Zhang, L.W.; Wan, J.C.; Yan, A.; Li, C.J. Study on forage yield and nutritional value of mixed-culture grassland of different legume and grass forage in semi-arid Area of Xinjiang. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2021, 9, 1835–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, E.S.; Bork, E.W.; Willms, W. D Soil moisture and plant growth responses to litter and defoliation impacts in Parkland grasslands. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 135, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporte, M.F.; Duchesne, L.C.; Wetzel, S. Effect of rainfall patterns on soil surface CO2 efflux, soil moisture, soil temperature and plant growth in a grassland ecosystem of northern Ontario, Canada: Implications for climate change. BMC Ecol. 2002, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, N.G.; Jeffrey, S.D. Plant respiration and photosynthesis in global-scale models: Incorporating acclimation to temperature and CO2. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, E.E.; Siebert, S.; Manderscheid, R. Quantifying the response of wheat yields to heat stress: The role of the experimental setup. J. Field Crops Res. 2018, 217, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangchuk, K.; Darabant, A.; Nirola, H.; Wangdi, J.; Gratzer, G. Climate warming decreases plant diversity but increases community biomass in high-altitude grasslands. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 75, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Li, Y.; Biswas, A.; Holden, N.M.; Adamowski, J.F.; Wang, F. Grassland biomass allocation across continents and grazing practices and its response to climate and altitude. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Gong, L.; Lian, L. Effect of altitude and mixed-sowing ratio on forage production and quality of oat and common vetch. Pratac. Sci. 2018, 35, 2438–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santala, K.; Cardou, F.; Yemshanov, D.; Campioni, F.; Simpson, M.; Handa, I.T.; Aubin, I. Finding the perfect mix: An applied model that integrates multiple ecosystem functions when designing restoration programs. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 180, 106646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.Y.; Zheng, W.H.; Tian, Y.Y.; Li, S.S.; Ma, Y.X.; Zheng, W. Comprehensive comparison of production performance of annual soybean grass mixed sowing grassland. Pratac. Sci. 2023, 40, 2639–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, F.; Bai, Y. Multiple global changes drive grassland productivity and stability: A meta-analysis. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 2850–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhang, L.P.; Zhang, H.H.; Zhang, X.F.; Ma, H.Y.; Li, X.S. Analysis of interspecific competition in community of mixedly-sown Alfalfa and Awnless Brome. Acta Agric. Jiangxi 2016, 8, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.H.; Han, J.G.; Li, H.X.; Mao, P.S.; Rong, Y.P. Dynamic study on biomass, quality and interspecific competition of annual mixed grassland. Acta Agrest. Sin. 1999, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhu, J.Z. Comprehensive evaluation of the performance of mixed sowing grassland with different mixed sowing methods. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2012, 21, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barillot, R.; Louarn, G.; Escobar-Gutiérrez, A.J.; Huynh, P.; Combes, D. How good is the turbid medium-based approach for accounting for light partitioning in contrasted grass–legume intercropping systems. Ann. Bot. 2011, 108, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauk, R.; Lauk, E. Pea-oat intercrops are superior to pea-wheat and pea-barley intercrops. Acta Agric. Scand. B Soil Plant Sci. 2008, 58, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.Q.; Yu, H.; Zheng, W.; Li, S.S. Effects of different planting configurations on yield of Avena sativa and Vicia sativa mixed plantings with soybean in alpine pastures. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2020, 29, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.S.; Zhu, L.; Xu, X. Effects of mixed combination and proportion between leguminous and graminaceous forages grown in Ningxia desert steppe. Pratac. Sci. 2015, 32, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.F.; Wang, B.; Deng, J.Q.; Li, M.Y.; Ni, W.; Feng, Q.; Tuo, Y.Y.; Lan, J. Effect of sowing rate on yield and forage quality of a dolichos lablab. dorghum bicolor mixture under drip irrigation in arid areas of Ningxia. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2023, 32, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, M.J. The influence of sowing date, harvest date and seed rate on the yield of forage peas. Grass Forage Sci 2010, 35, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, K.T.; Graham, J.H. Nutrient Status and Root Density of Huanglongbing-Affected Trees: Consequences of Irrigation Water Bicarbonate and Soil pH Mitigation with Acidification. Agronomy 2019, 9, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencel, J.; Mocek-Płóciniak, A.; Kryszak, A. Soil microbial community and enzymatic activity of grasslands under different use practices: A review. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Ma, Y.; Kang, Y.; Jia, Q.; Qi, G.; Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Yu, J. Optimized farmland mulching improves alfalfa yield and water use efficiency based on meta-analysis and regression analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 267, 107617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.Z.; Deng, Q.; Guo, Y. Effects of biochar application on root traits: A meta-analysis. GCB Bioenergy 2017, 9, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
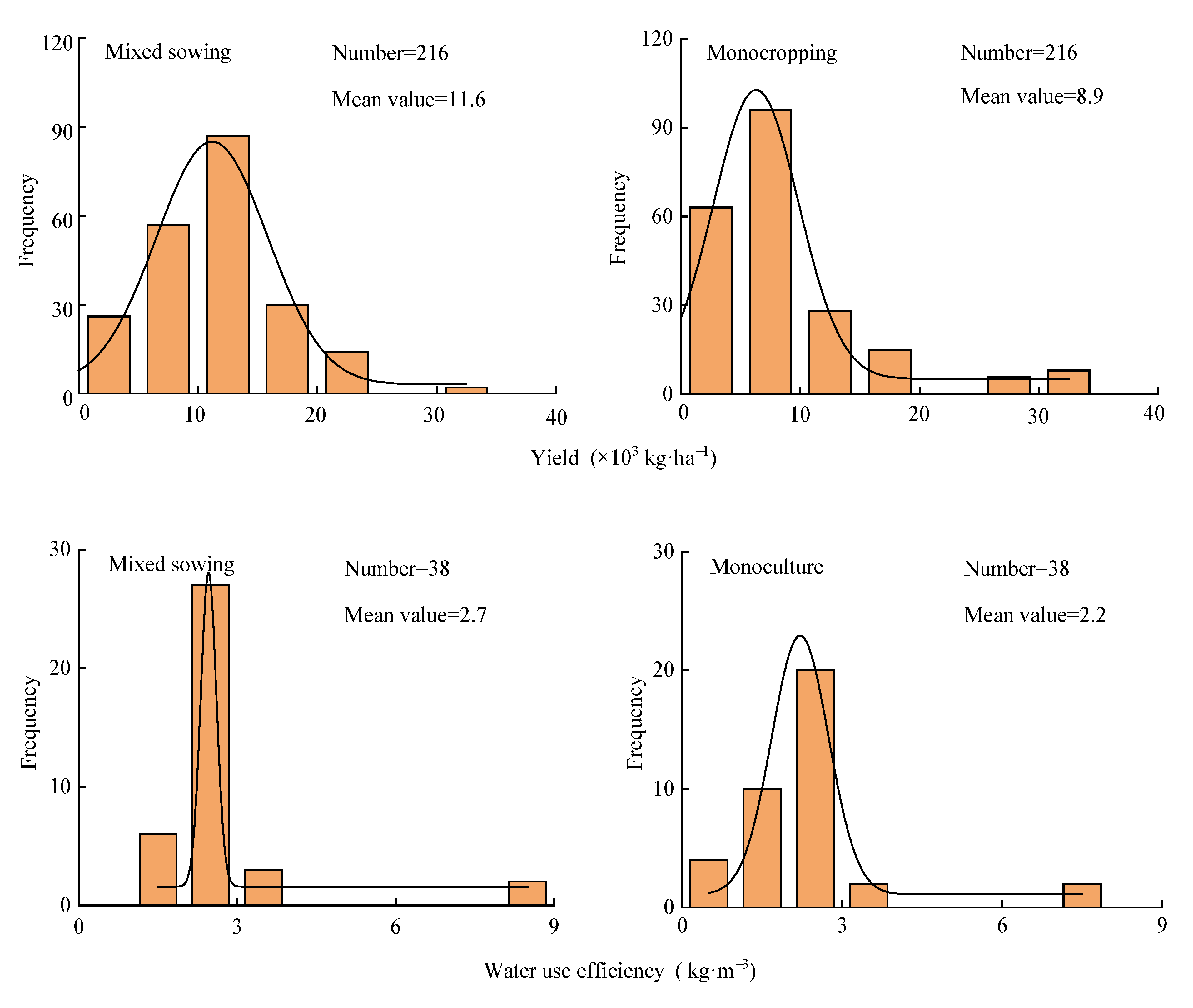
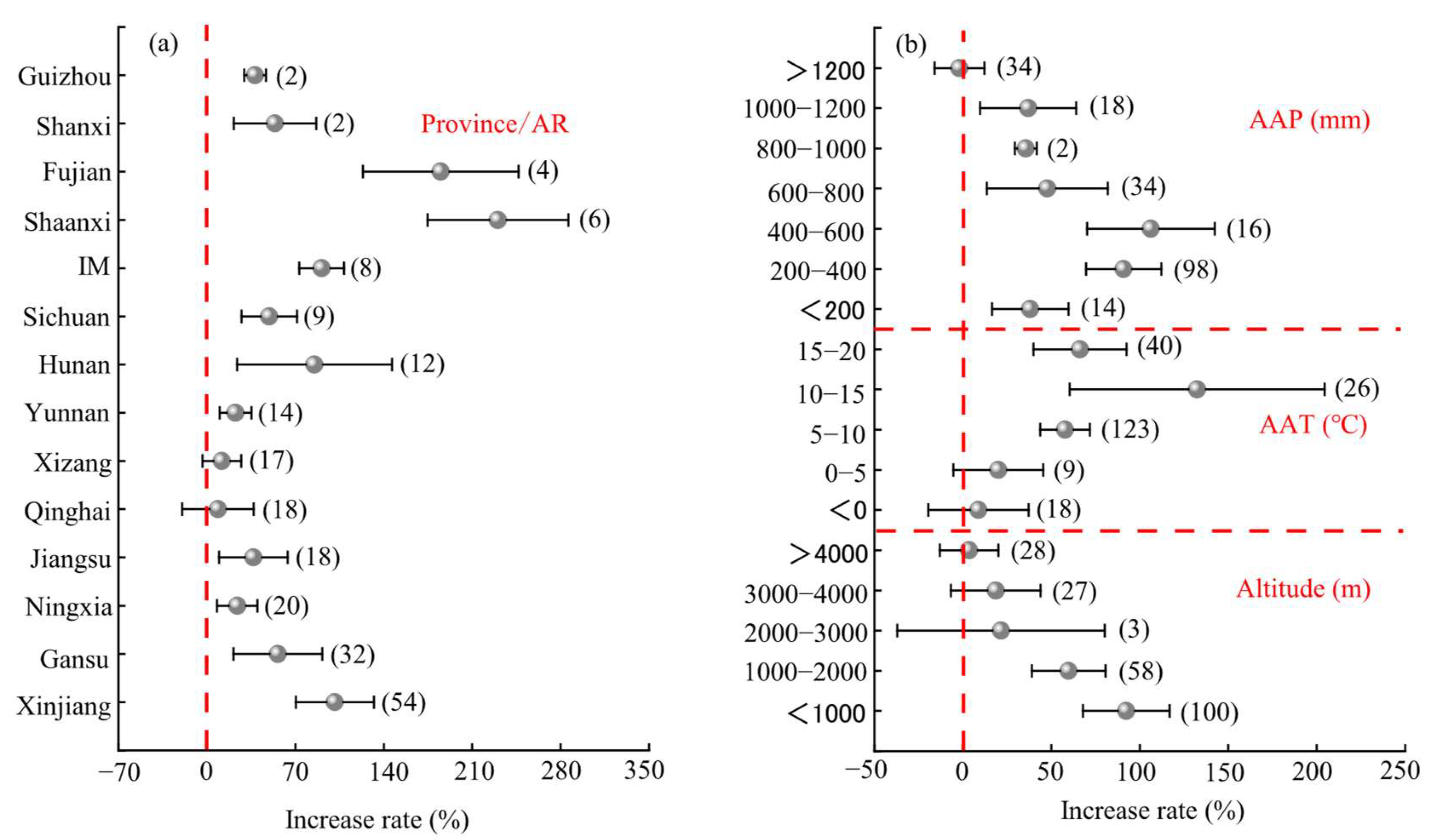
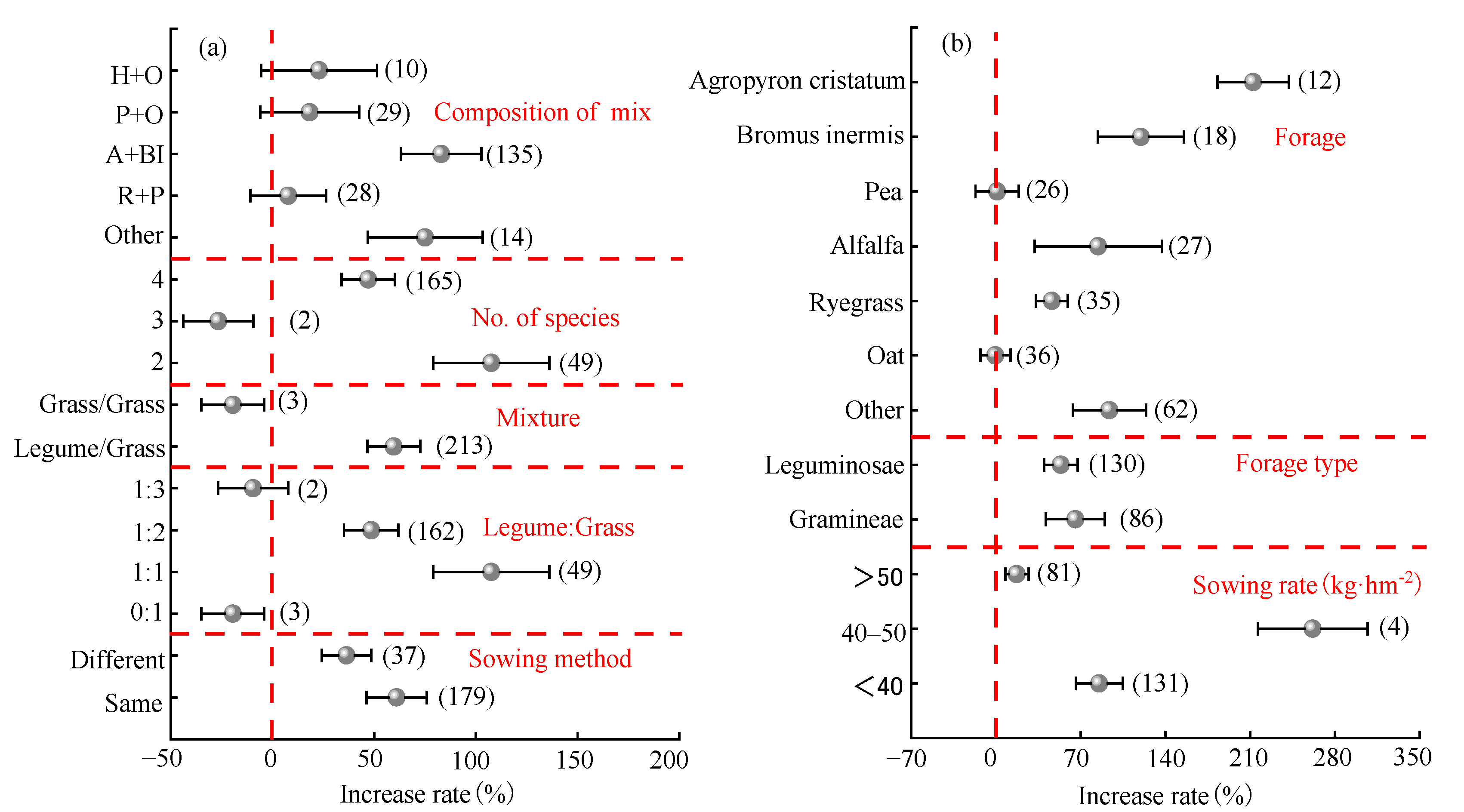


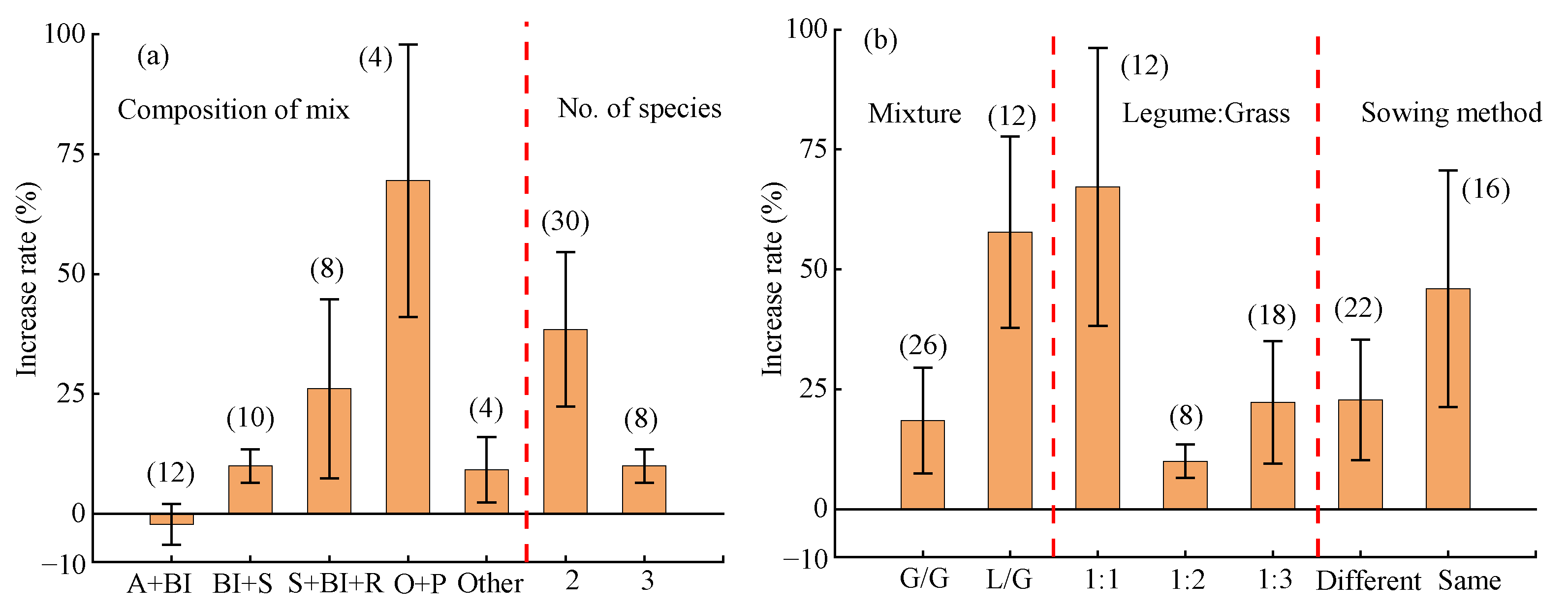

| Index | Model | Increase Rate (%) | 95% CI (%) | Effect Size Test | Heterogeneity Test | Safety Factor Against Failure | 5k + 10 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LL | UL | Z | P | Q | PQ | |||||
| Yield | REM | 58.3 | 45.5 | 72.3 | 10.63 | 0.000 | 45,412 | 0.000 | 794,737 | 1090 |
| Water use efficiency | REM | 32.0 | 19.2 | 46.1 | 5.33 | 0.000 | 42,313 | 0.000 | 4626 | 200 |
| Primary Factors | Secondary Factors | Grouping | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | ||
| Regional Factors | Provinces/AR | Xinjiang | Gansu | Ningxia | Jiangsu | Qinghai | Tibet | Others |
| Annual average precipitation (mm) | <200 | 200–400 | 400–600 | 600–800 | 800–1000 | 1000–2000 | >1200 | |
| Annual average temp (°C) | <0 | 0–5 | 5–10 | 10–15 | 15–20 | − | − | |
| Altitude (m) | <1000 | 1000–2000 | 2000–3000 | 3000–4000 | >4000 | − | − | |
| Mixed Sowing Factors | Composition of mix | H + O | P + O | A + BI | R + P | Others | − | − |
| No. of species | 2 | 3 | 4 | − | − | − | − | |
| Mixture | Legume/Grass | Grass/Grass | − | − | − | − | − | |
| Legume–Grass | 1:1 | 1:2 | 1:3 | 0:1 | − | − | − | |
| Sowing method | Different rows | Same rows | − | − | − | − | − | |
| Monoculture Factors | Forage | AC | BI | Pea | Alfalfa | R | Oat | Others |
| Forage Type | Legume | Grass | − | − | − | − | − | |
| Sowing rate (kg·ha−1) | <40 | 40–50 | >50 | − | − | − | − | |
| Other Factors | Experimental Year | <2006 | 2006–2008 | 2009–2011 | 2012–2014 | 2015–2017 | 2018–2020 | >2020 |
| Soil pH | 4.0–5.0 | 5.0–6.0 | 6.0–7.0 | 7.0–8.0 | 8.0–9.0 | − | − | |
| Total sowing rate (kg·ha−1) | <50 | 50–100 | 100–150 | >150 | − | − | − |
| Primary Factors | Secondary Factors | Grouping | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Regional Factors | Provinces/AR | Gansu | Qinghai | − | − | − |
| Annual average precipitation (mm) | <200 | 200–400 | 400–600 | − | − | |
| Annual average temp (°C) | <0 | 0–5 | − | − | − | |
| Altitude (m) | 1000–2000 | 2000–3000 | − | − | − | |
| Mixed Sowing Factors | Composition of mix | P + O | S + BI + R | BI + S | A + BI | Others |
| No. of species | 2 | 3 | − | − | − | |
| Mixture | MLAG | MGAG | − | − | − | |
| Legume–Grass | 1:1 | 1:2 | 0:1 | − | − | |
| Sowing method | Different rows | Same rows | − | − | − | |
| Monoculture Factors | Forage | Silage Corn | Oat | Alfalfa | BI | Sainfoin |
| Forage Type | Leguminosae | Gramineae | − | − | − | |
| Sowing rate (kg·ha−1) | <40 | 40–50 | >50 | − | − | |
| Other Factors | Experimental Year | 2015–2017 | 2018–2020 | − | − | − |
| Soil pH | 6.0–7.0 | 7.0–8.0 | 8.0–9.0 | − | − | |
| Total sowing rate (kg·ha−1) | <50 | 50–100 | 100–150 | >150 | − |
| Provinces/AR | Ningxia | Tibet | Qinghai | Jiangsu | Guizhou | Xinjiang | Hunan | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average yield (×103 kg·ha−1) | Mixed Sowing | Mono- culture | Mixed Sowing | Mono- culture | Mixed Sowing | Mono- culture | Mixed Sowing | Mono- culture | Mixed Sowing | Mono- culture | Mixed Sowing | Mono- culture | Mixed Sowing | Mono- culture |
| 14.3 | 12.2 | 7.6 | 7.0 | 17.4 | 15.2 | 14.8 | 11.7 | 14.7 | 10.9 | 12.8 | 7.4 | 4.3 | 2.8 | |
| Provinces/AR | Shanxi | Inner Mongolia | Shaanxi | Sichuan | Fujian | Yunnan | Gansu | |||||||
| Average yield (×103 kg·ha−1) | Mixed Sowing | Mono- culture | Mixed Sowing | Mono- culture | Mixed Sowing | Mono- culture | Mixed Sowing | Mono- culture | Mixed Sowing | Mono- culture | Mixed Sowing | Mono- culture | Mixed Sowing | Mono- culture |
| 10.5 | 6.4 | 15.9 | 8.2 | 2.9 | 1.9 | 16.7 | 11.2 | 4.9 | 1.7 | 10.1 | 8.2 | 10.7 | 8.8 | |
| Provinces/AR | Gansu | Ningxia | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average WUE (kg·m−3) | Mixed Sowing | Monoculture | Mixed Sowing | Monoculture |
| 2.7 | 2.2 | 2.6 | 2.7 | |
| Provinces/AR | Ningxia | Tibet | Qinghai | Jiangsu | Guizhou | Xinjiang | Hunan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Altitude (m) | 1454.1 | 4148.0 | 4112.6 | 5.0 | 1468.0 | 592.0 | 44.9 |
| Annual average precipitation (mm) | 312.8 | 476.8 | 598.3 | 1030.0 | 1121.4 | 208.1 | 1422.4 |
| Annual average temp (°C) | 8.4 | 6.3 | −4.6 | 15.0 | 12.6 | 7.9 | 17.0 |
| Average Soil pH | 8.4 | 7.9 | 6.9 | 7.3 | 5.8 | 8.6 | 4.7 |
| Total sowing rate (kg·ha−1) | 105.2 | 95.2 | 182.4 | 11 | 2.5 | 29.8 | 64.3 |
| Provinces/AR | Shanxi | Inner Mongolia | Shaanxi | Sichuan | Fujian | Yunnan | Gansu |
| Altitude (m) | 1016.1 | 1800.0 | 454.8 | 1118.1 | 314 | 187.7 | 1807.3 |
| Annual average precipitation (mm) | 390.0 | 375 | 635.1 | 250.4 | 1600.5 | 650.0 | 282.6 |
| Annual average temp (°C) | 6.4 | 6.2 | 12.9 | 11.8 | 19.2 | 5.8 | 7.9 |
| Soil pH | 6.8 | 8.5 | 8.4 | 6.1 | 4.8 | 6.1 | 7.5 |
| Total sowing rate (kg·ha−1) | 28.5 | 105 | 12.5 | 161.1 | 27.9 | 187.7 | 65.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, W.; Jiang, Y.; Yin, M.; Ling, Y.; Kang, Y.; Qi, G.; Duan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ling, G.; et al. Meta-Analysis of Mixed Sowing Effects on Forage Yield and Water Use Efficiency in China: Influencing Factors and Optimal Conditions. Plants 2025, 14, 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091283
Guo W, Jiang Y, Yin M, Ling Y, Kang Y, Qi G, Duan Y, Ma Y, Liu Y, Ling G, et al. Meta-Analysis of Mixed Sowing Effects on Forage Yield and Water Use Efficiency in China: Influencing Factors and Optimal Conditions. Plants. 2025; 14(9):1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091283
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Weiqiang, Yuanbo Jiang, Minhua Yin, Yi Ling, Yanxia Kang, Guangping Qi, Yaya Duan, Yanlin Ma, Yushuo Liu, Gen Ling, and et al. 2025. "Meta-Analysis of Mixed Sowing Effects on Forage Yield and Water Use Efficiency in China: Influencing Factors and Optimal Conditions" Plants 14, no. 9: 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091283
APA StyleGuo, W., Jiang, Y., Yin, M., Ling, Y., Kang, Y., Qi, G., Duan, Y., Ma, Y., Liu, Y., Ling, G., & Pan, K. (2025). Meta-Analysis of Mixed Sowing Effects on Forage Yield and Water Use Efficiency in China: Influencing Factors and Optimal Conditions. Plants, 14(9), 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091283






