Optimizing Water–Fertilizer Coupling Across Different Growth Stages of Tomato in Yellow Sand Substrate: Toward Enhanced Yield, Quality, and Resource Use Efficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.1. Plot Specifications and Isolation Measures
2.2.2. Evapotranspiration (ETc) Calculation and Irrigation Amount Determination
2.3. Water–Fertilizer Integration System and Fertilizer Ratio
2.3.1. Management of Intelligent Drip Irrigation and Fertilization System
2.3.2. Fertilizer Ratio
2.4. Measurement Results
2.4.1. Physical and Chemical Properties of Yellow Sand Substrate
2.4.2. Tomato Fruit Yield
2.4.3. Tomato Fruit Quality
2.4.4. Water–Fertilizer Use Efficiency
2.5. Data Analysis and Statistics
2.5.1. Comprehensive Scoring Method Based on the Improved Entropy Method for Determining Evaluation Factor Weights
2.5.2. Improved TOPSIS Method Based on Virtual Ideal Solution
3. Results
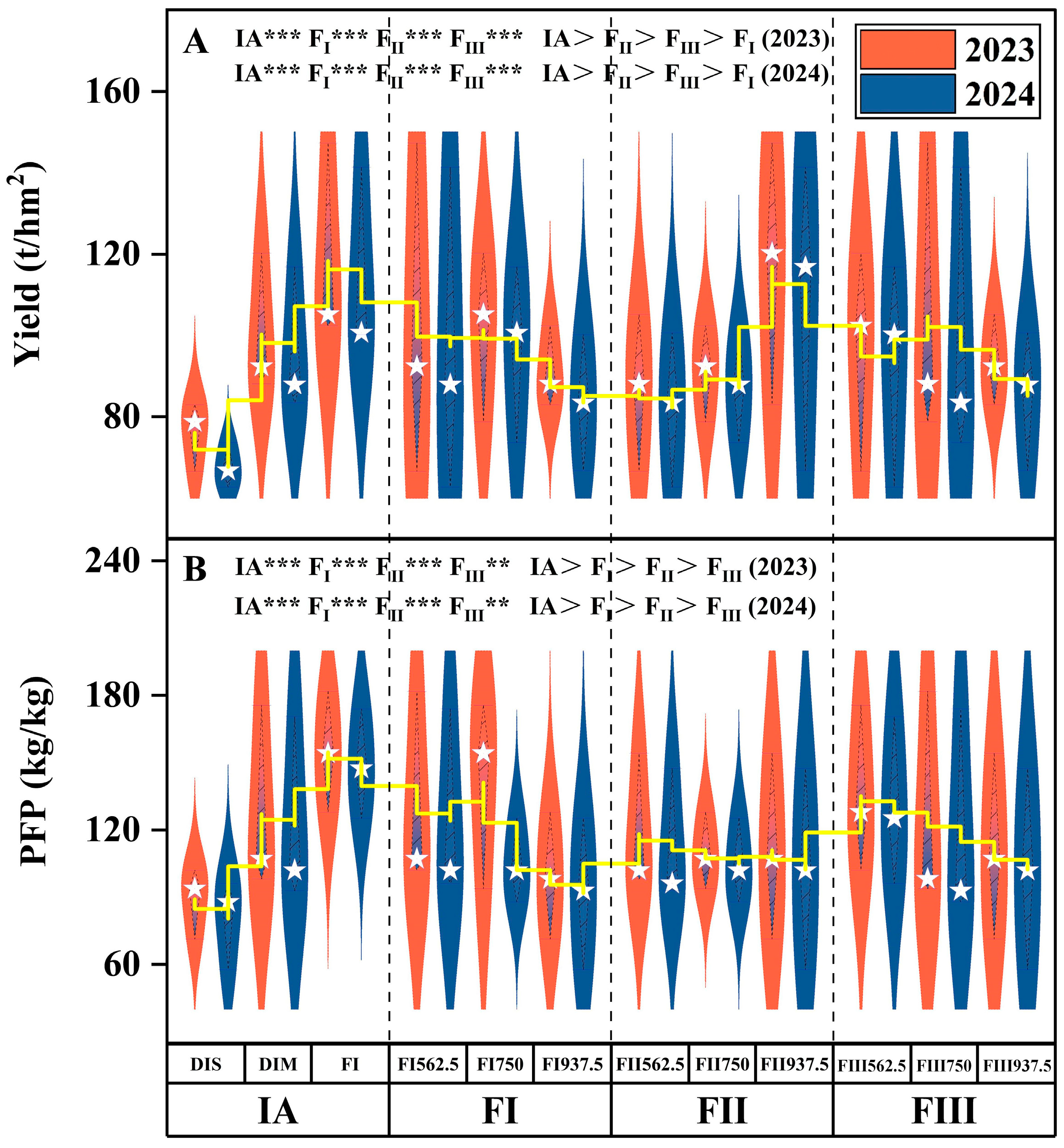
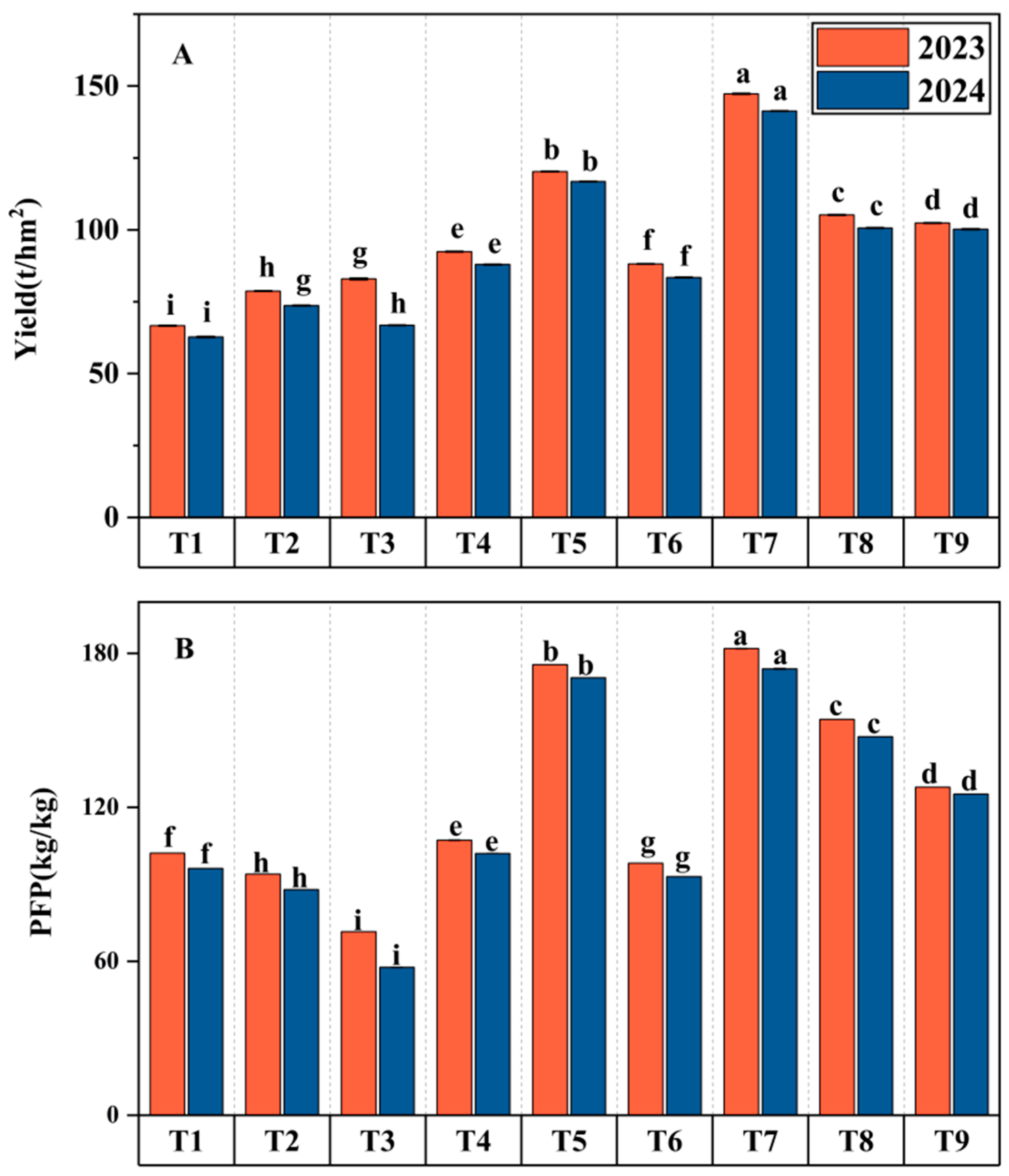
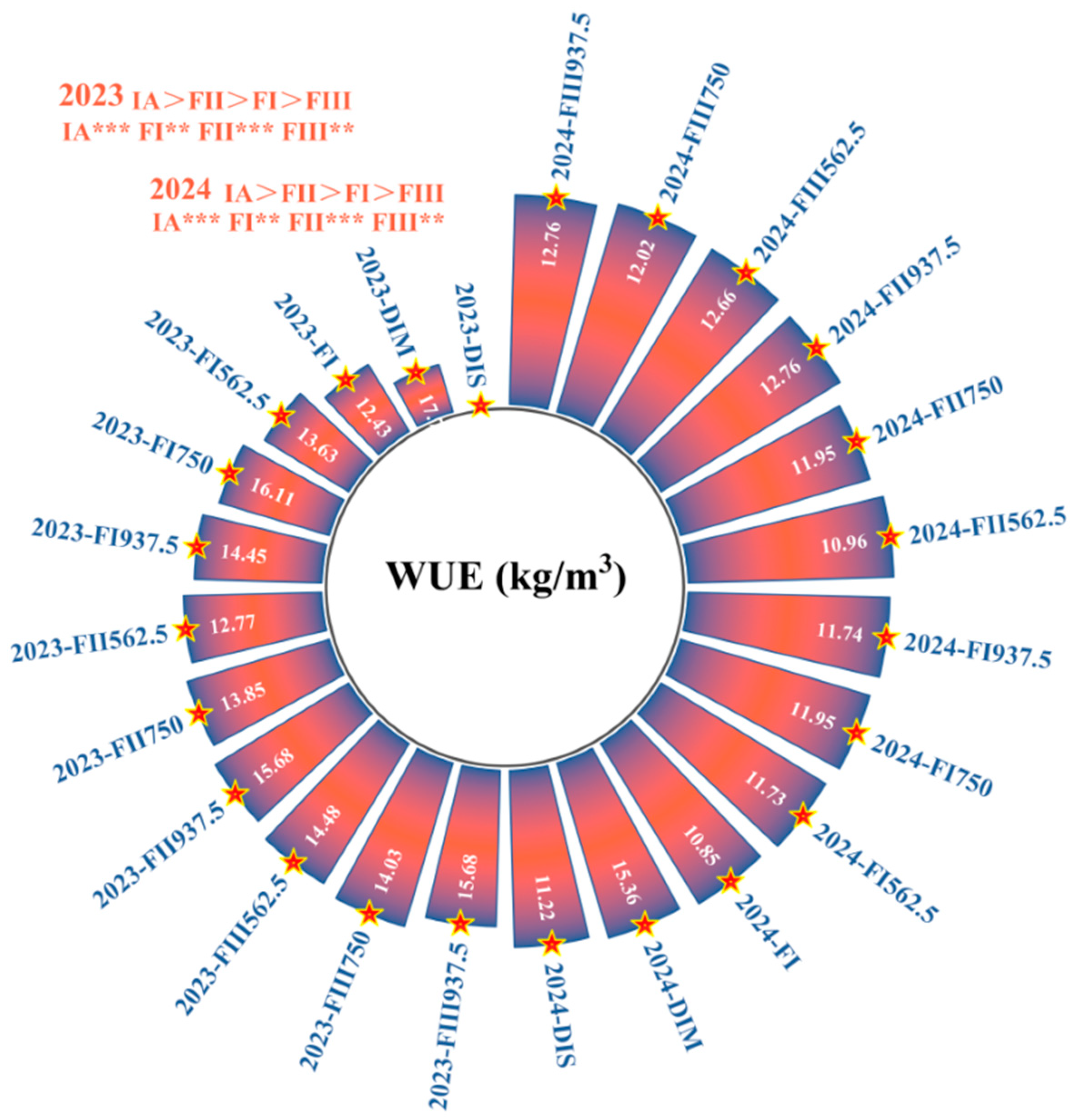
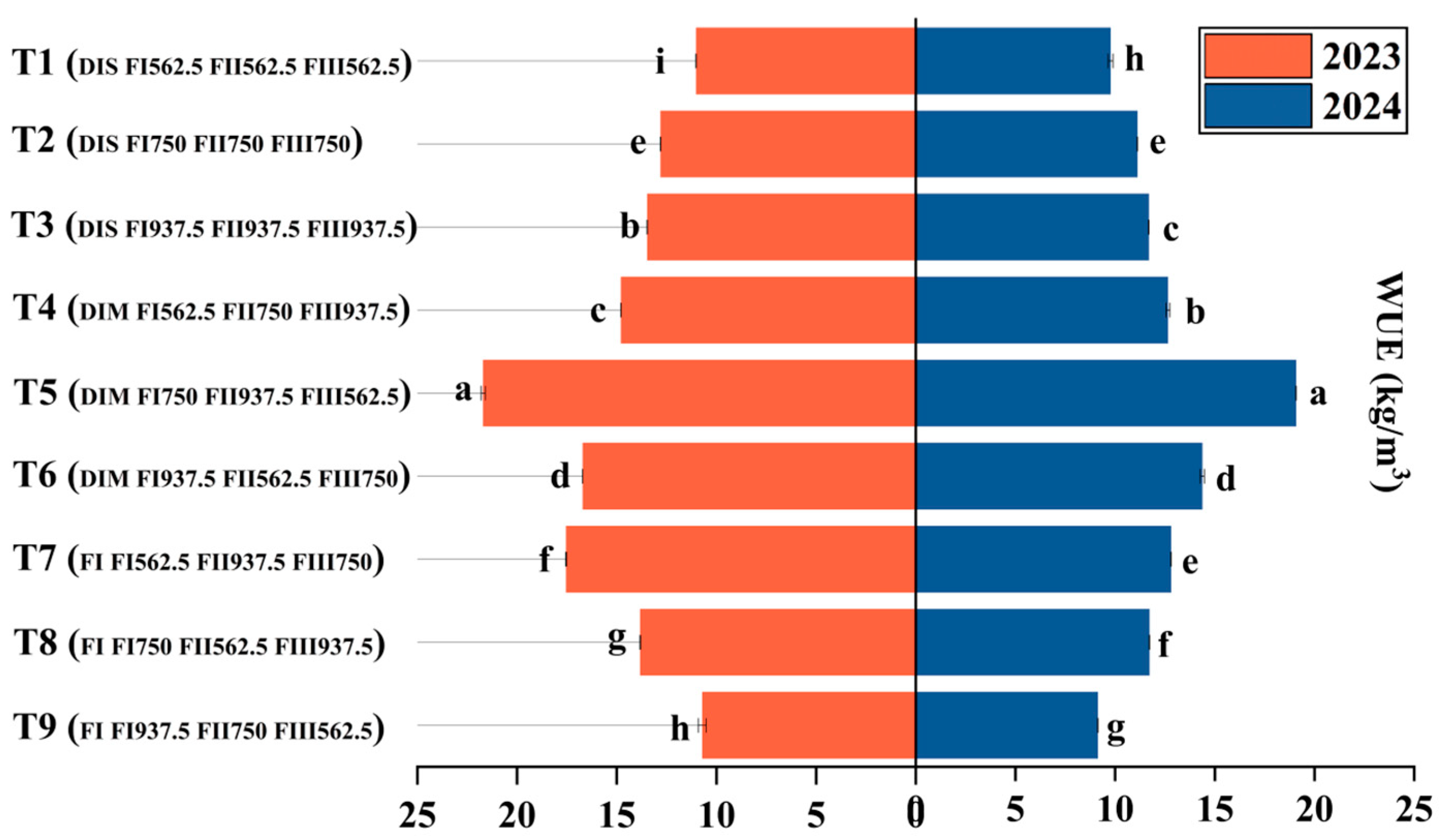
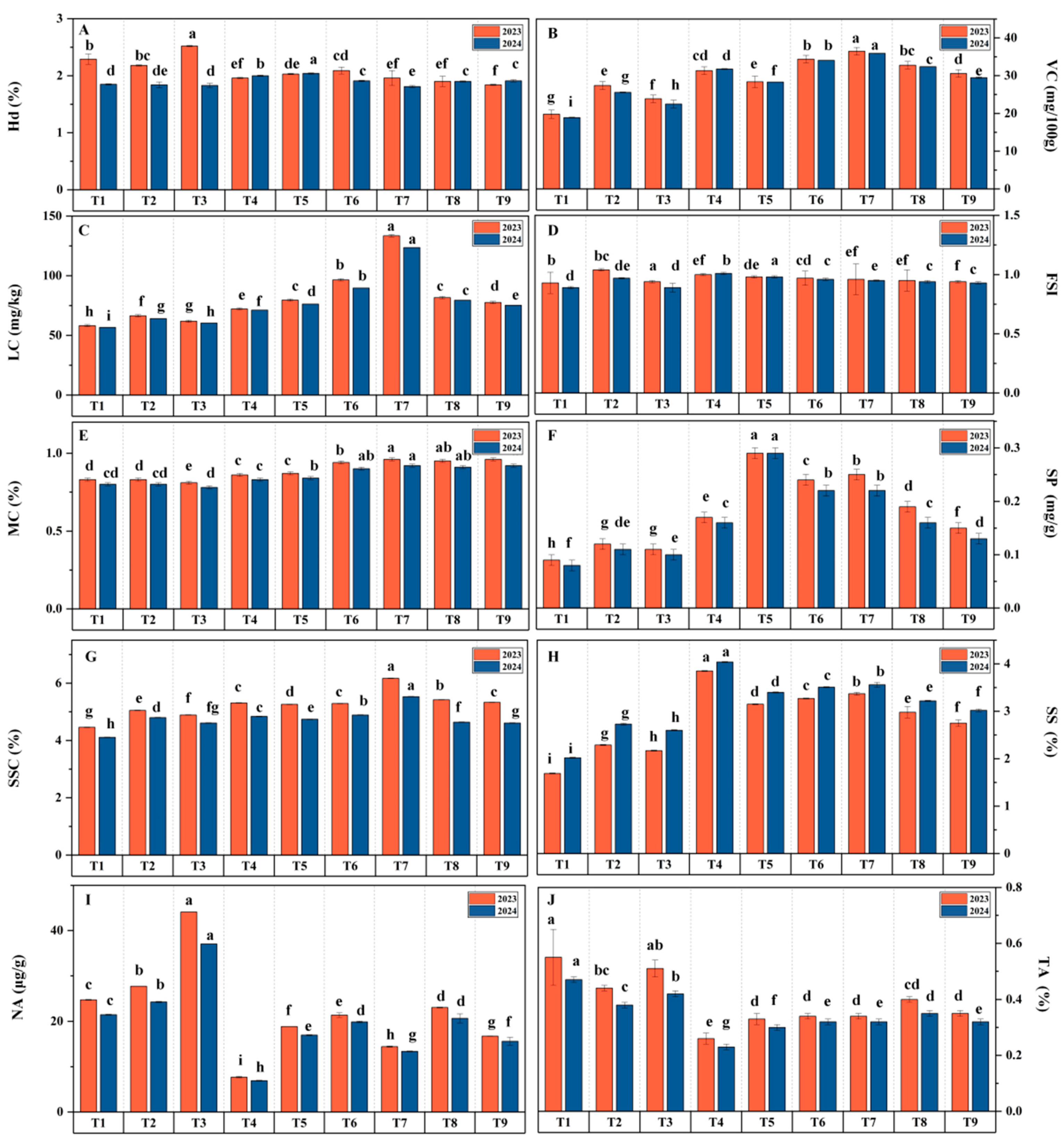
3.1. Effects of Water–Fertilizer Coupling on Tomato Yield and Water–Fertilizer Use Efficiency
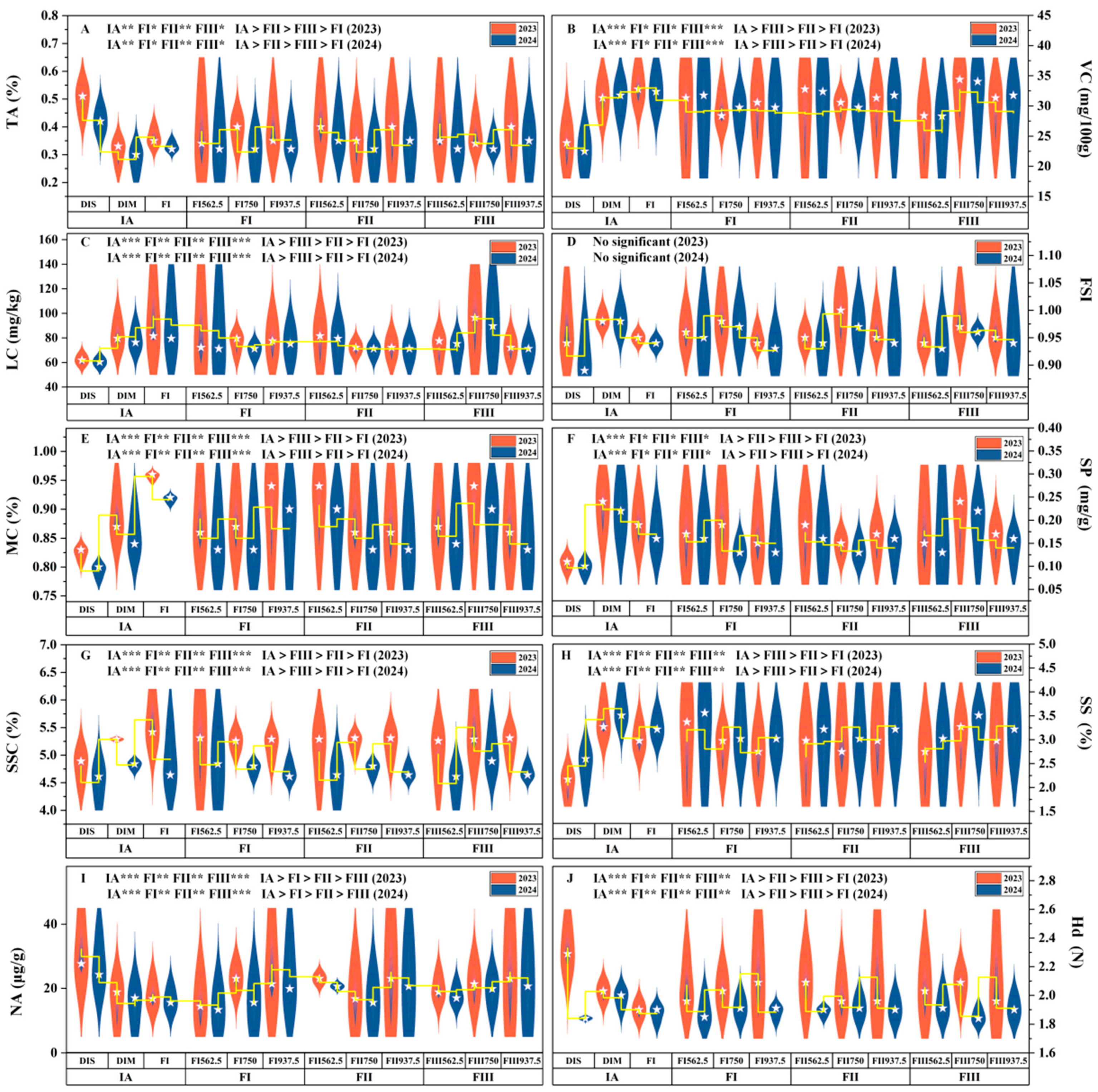
3.2. Effects of Water–Fertilizer Coupling on Tomato Fruit Quality
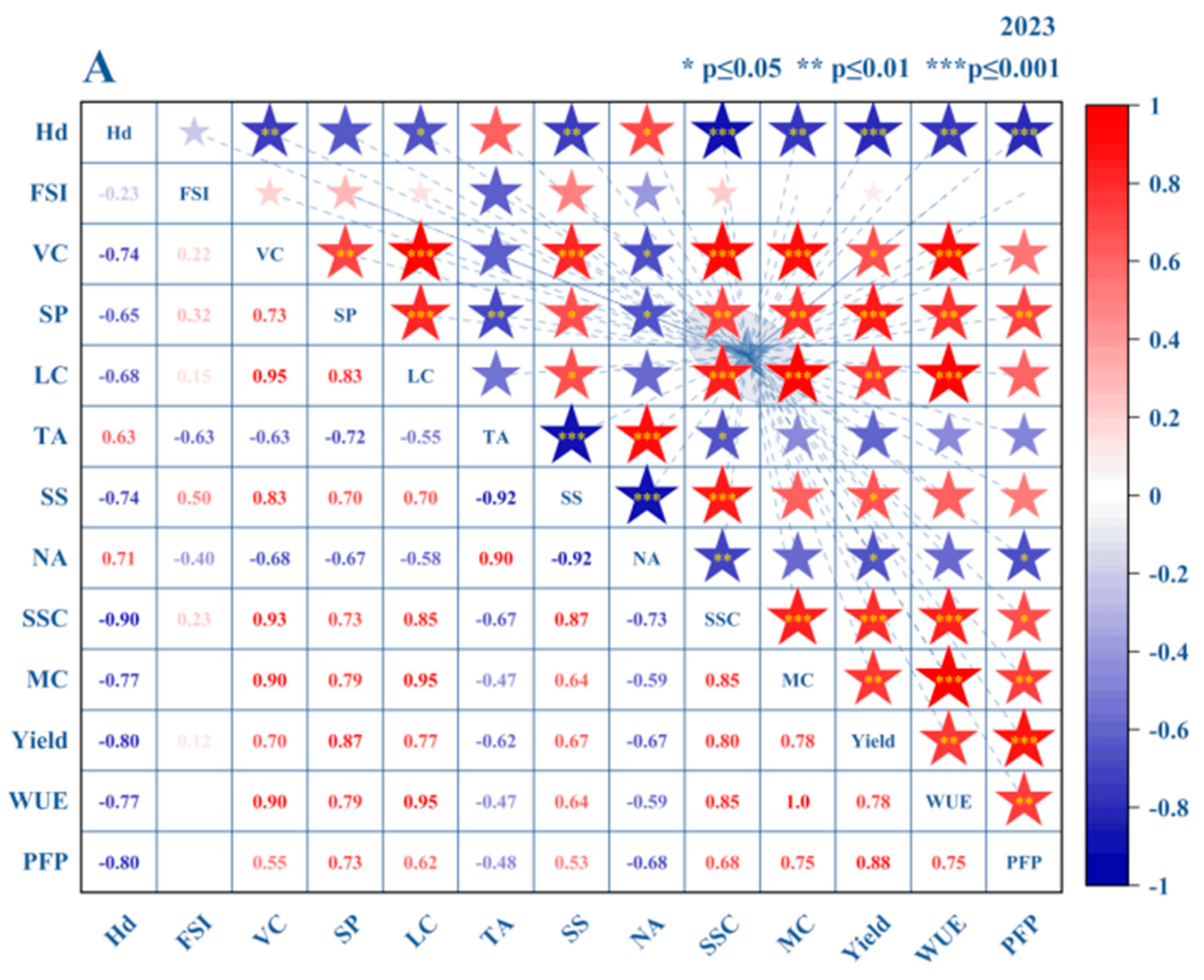
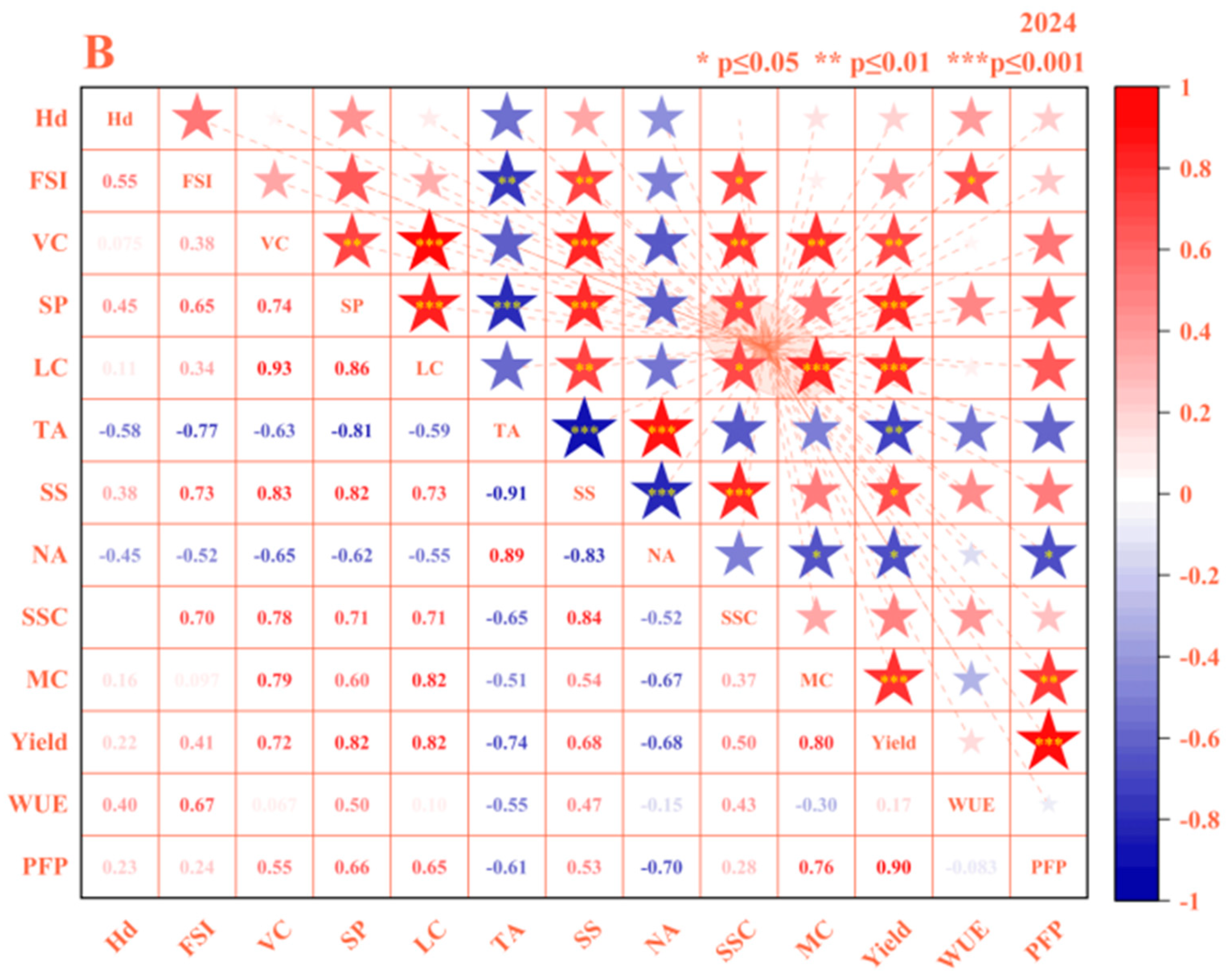
3.3. Comprehensive Evaluation of Tomatoes
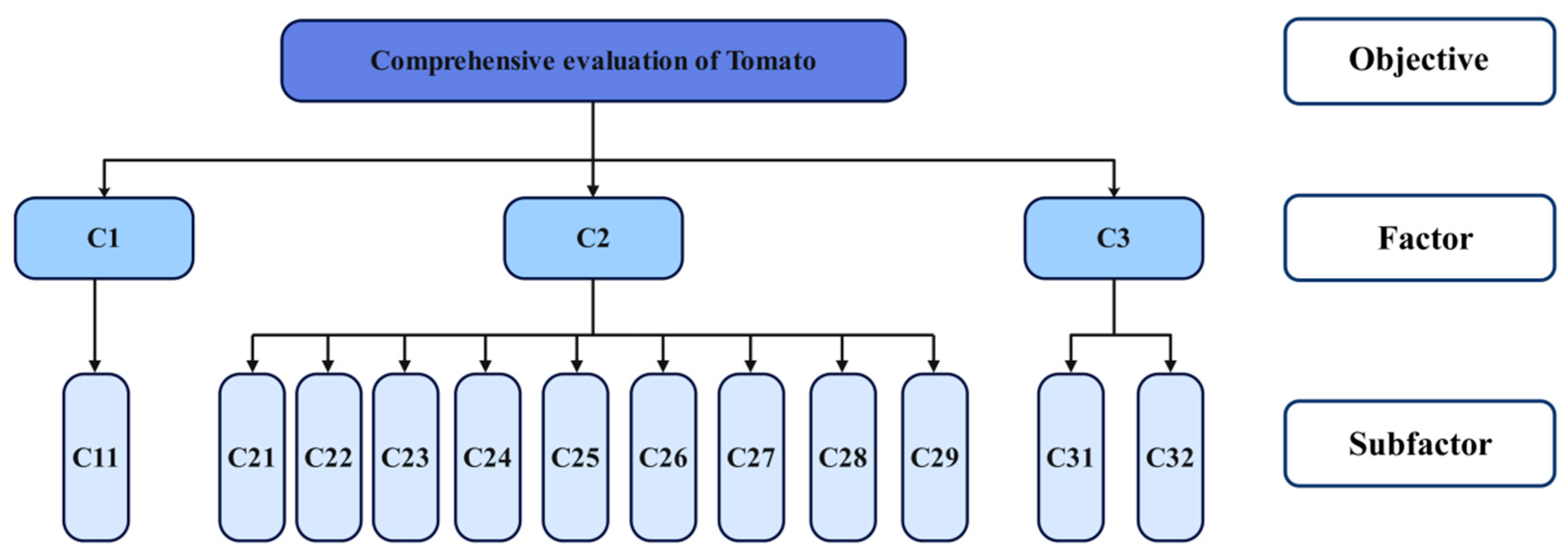
3.3.1. Construction of the Comprehensive Evaluation Model for Tomatoes
3.3.2. Analysis of the Comprehensive Scoring Method Based on the Improved Entropy Weight Method
3.3.3. Multi-Objective Decision Making and Evaluation Using an Improved TOPSIS Method with a Virtual Ideal Solution
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Irrigation and Fertilization on Tomato Yield, Water Use Efficiency (WUE), and Fertilizer Use Efficiency Under Yellow Sand Substrate Cultivation
4.2. Effects of Irrigation and Fertilization on Tomato Fruit Quality Under Yellow Sand Substrate Cultivation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rai, G.K.; Kumar, P.; Choudhary, S.M.; Kosser, R.; Khanday, D.M.; Choudhary, S.; Kumar, B.; Magotra, I.; Kumar, R.R.; Ram, C.; et al. Biomimetic Strategies for Developing Abiotic Stress-Tolerant Tomato Cultivars: An Overview. Plants 2023, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.G.; Liu, M.J.; Ding, W.C. Study on intelligent fertilization recommendation methods for tomatoes based on yield response and agronomic efficiency. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2024, 30, 2296–2306. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Wei, K.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Deng, M.; Tao, W. Effects of Organic Fertilizer on Photosynthesis, Yield, and Quality of Pakchoi Under Different Irrigation Conditions. Plants 2024, 13, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, Z. Optimized single irrigation can achieve high corn yield and water use efficiency in the Corn Belt of Northeast China. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 75, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Wang, L.; Lv, G.; Gao, C.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; He, L.; Sun, W. Deficit Irrigation Effects on Cotton Growth Cycle and Preliminary Optimization of Irrigation Strategies in Arid Environment. Plants 2024, 13, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toumi, I.; Zarrouk, O.; Ghrab, M.; Nagaz, K. Improving Peach Fruit Quality Traits Using Deficit Irrigation Strategies in Southern Tunisia Arid Area. Plants 2022, 11, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Bai, J.; Li, D.; Ren, X.; He, D.; Du, R.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, Z. Water and fertilizer decision model for synergistic optimization of yield, quality and efficiency of cherry tomato based on combination evaluation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 224, 109224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Q.; Liu, X.; Yang, Z.; Han, P.; Li, J.; Wei, Z.; Hu, T.; Liu, F. The Interactive Effects of Deficit Irrigation and Bacillus pumilus Inoculation on Growth and Physiology of Tomato Plant. Plants 2023, 12, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hueso, A.; Camacho, G.; Gomez-Del-Campo, M. Spring deficit irrigation promotes significant reduction on vegetative growth, flowering, fruit growth and production in hedgerow olive orchards (cv. Arbequina). Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 248, 106695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa e Vila, V.; Marques, P.A.A.; Rezende, R.; Wenneck, G.S.; Terassi, D.S.; Andrean, A.F.B.A.; Nocchi, R.C.F.; Matumoto-Pintro, P.T. Deficit irrigation with Ascophyllum nodosum extract application as a strategy to increase tomato yield and quality. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Li, J. Long-term effects of optimized fertilization, tillage and crop rotation on soil fertility, crop yield and economic profit on the Loess Plateau. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 143, 126731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Luo, H.; Li, H.; Bao, M.; Liu, E.; Shan, W.; Ren, X.; Jia, Z.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Zhang, P. Maximizing potato tuber yields and nitrogen use efficiency in semi-arid environments by precision fertilizer depth application. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 156, 127147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Dou, Z.; Jiang, W.; Mahmood, H.; Liao, Z.; Li, Z.; Fan, J. Optimal water and nitrogen regimes increased fruit yield and water use efficiency by improving root characteristics of drip-fertigated greenhouse tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Agronomy 2024, 14, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Sha, C.; Shu, Q. Integrated Physiological and Metabolomic Analyses of the Effect of Potassium Fertilizer on Citrus Fruit Splitting. Plants 2022, 11, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, W.; Liu, C.; Xu, C.; Wei, G.; Cui, B.; Hou, J.; Wan, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Effect of CO2 elevation on tomato gas exchange, root morphology and water use efficiency under two N-fertigation levels. Plants 2024, 13, 2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Yao, W.; Ji, H.; Xu, Y.; Jia, R.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, A.R.; Shen, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Optimizing nitrogen fertilization and irrigation strategies to balance agroecosystem services in the wheat-maize double cropping system: A 21-year field study. Field Crops Res. 2024, 322, 109706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhu, H.; Shi, A.; Wang, X. Optimizing nitrogen fertilizer management enhances rice yield, dry matter, and nitrogen use efficiency. Agronomy 2024, 14, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, H.; Zhang, W.; Siddique, K.H.M. Response of plastic film mulched maize to soil and atmospheric water stresses in an arid irrigation area. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 154, 127080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, T.; Yang, L.; He, T.; Liang, S. Climate-smart drip irrigation with fertilizer coupling strategies to improve tomato yield, quality, resources use efficiency and mitigate greenhouse gases emissions. Land 2024, 13, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Yu, X.; Luo, Y.; Chang, Y.; Lu, C.; Chen, X. Prediction model of greenhouse tomato yield using data based on different soil fertility conditions. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramniwas, R.A.; Kaushik, R.A.; Pareek, S.; Sarolia, D.K.; Singh, V. Effect of drip fertigation scheduling on fertilizer use efficiency, leaf nutrient status, yield and quality of ‘Shweta’ guava (Psidium guajava L.) under meadow orcharding. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2013, 36, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, Q. Effect of pore water velocities and solute input methods on chloride transport in the undisturbed soil columns of Loess Plateau. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2321–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Li, Y.; Gong, X.; Li, Y. Parameterization of Four Models to Estimate Crop Evapotranspiration in a Solar Greenhouse. Plants 2024, 13, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Xiao, S.; Yan, G.L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.; Su, F.; Chen, Y.B.; Zhou, R.M.; Zhang, Y.T. High-efficiency cultivation techniques for greenhouse-based tomato–onion intercropping. China Veg. 2019, 9, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Tan, Z.M.; Cheng, Y.X.; Shu, S.; Ma, Q. Effects of water-fertilizer coupling on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and yield in sand-cultured tomato. Mol. Plant Breeding 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.J. Cultivation techniques for high-quality cherry tomatoes. Modern Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 22, 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.T. Green tomato cultivation technology. Agric. Technol. Equip. 2020, 1, 148–149. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.G.; Peng, Y.L.; Yang, Q.L.; Wang, X.K.; Cui, N.B. Determining optimal deficit irrigation and fertilization to increase mango yield, quality, and WUE in a dry hot environment based on TOPSIS. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 245, 106650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Lin, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhai, Y.; Jin, Q.; Zhong, F. Optimization on the Buried Depth of Subsurface Drainage Under Greenhouse Condition Based on Entropy Evaluation Method. Entropy 2018, 20, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Guan, T.; Yan, X.B.; Li, Y.J. Supplier selection decision model based on hybrid VIKOR method. Control Decis. 2014, 29, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Li, R.; Feng, Z.; Li, D.; Yang, T.; Chen, J.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, Z. Effects of combined nitrogen and potassium application on cherry tomato production efficiency under deficit irrigation. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 328, 112958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, K.; Jalilian, J.; Pirzad, A. Nano-fertilizers improved drought tolerance in wheat under deficit irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz Gómez, N.; Poza-Carrión, C.; Del Castillo-González, L.; Martínez Sánchez, Á.I.; Moliner, A.; Aranaz, I.; Berrocal-Lobo, M. Enhancing Solanum lycopersicum Resilience: Bacterial Cellulose Alleviates Low Irrigation Stress and Boosts Nutrient Uptake. Plants 2024, 13, 2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basyal, B.; Emery, S.M. An arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus alters switchgrass growth, root architecture, and cell wall chemistry across a soil moisture gradient. Mycorrhiza 2021, 31, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Xu, S.; He, N.; Zhan, Z.; Dai, J.; Li, C.; Li, W.; et al. Plant pruning affects photosynthesis and photoassimilate partitioning in relation to the yield formation of field-grown cotton. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 173, 114087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Li, Y.; Nai, G.; Liang, G.; Ma, Z.; Chen, B.; Mao, J. Changes and response mechanism of sugar and organic acids in fruits under water deficit stress. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbarian-Alavijeh, B.; Millán, H. The relationship between surface fractal dimension and soil water content at permanent wilting point. Geoderma 2009, 151, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peco, J.D.; Rapoport, H.F.; Centeno, A.; Pérez-López, D. Does regulated deficit irrigation affect pear fruit texture by modifying the stone cells? Plants 2023, 12, 4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamzelou, S.; Kamath, K.S.; Masoomi-Aladizgeh, F.; Johnsen, M.M.; Atwell, B.J.; Haynes, P.A. Wild and cultivated species of rice have distinctive proteomic responses to drought. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.G. Effect of partial root-zone drying irrigation (PRDI) on soil C: N: P stoichiometry in N-fixing crops: Insights from a three-year field study with alfalfa. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 307, 109258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Meng, F.; Qi, H.; Mo, F.; Wang, P.; Chen, X.; Wang, A. Escaping drought: The pectin methylesterase inhibitor gene Slpmei27 can significantly change drought resistance in tomato. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 192, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, E.C.; Messias, R.S.; Borowski, J.M.; Crizel, R.L.; Schott, I.B.; Carvalho, I.R.; Rombaldi, C.V.; Galli, V. ABA-dependent salt and drought stress improve strawberry fruit quality. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Du, T. Osmotic adjustment of tomato under mild soil salinity can enhance drought resistance. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2022, 202, 105004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.-C.; Rasheed, A.; Wang, Y.-P.; Wu, Z.-F.; Tang, S.-Q.; Pan, X.-H.; Shi, Q.-H.; Wu, Z.-M. Silencing of OsXDH reveals the role of purine metabolism in dark tolerance in rice seedlings. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 1736–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Arie, R.; Kislev, N.; Frenkel, C. Ultrastructural changes in the cell walls of ripening apple and pear fruit. Plant Physiol. 1979, 64, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.Q.; Sun, X.J.; Liu, X.L.; Lin, H. Feasibility study of using blast furnace slag as a soilless cultivation substrate. Mod. Hortic. 2025, 48, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Cui, K.; Tang, S.; Li, G.; Wang, S.; Fahad, S.; Nie, L.; Huang, J.; Peng, S.; Ding, Y. Intensified pollination and fertilization ameliorate heat injury in rice (Oryza sativa L.) during the flowering stage. Field Crops Res. 2020, 252, 107795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.K.; Mei, X.R.; Yan, C.R.; Gong, D.Z.; Zhang, Y.Q. Effects of water stress on photosynthetic characteristics, dry matter translocation and WUE in two winter wheat genotypes. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 167, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotarelli, L.; Dukes, M.D.; Scholberg, J.M.S.; Muñoz-Carpena, R.; Icerman, J. Tomato nitrogen accumulation and fertilizer use efficiency on a sandy soil, as affected by nitrogen rate and irrigation scheduling. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisseler, D.; Linquist, B.A.; Lazicki, P.A. Effect of fertilization on soil microorganisms in paddy rice systems—A meta-analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temporiti, M.E.E.; Nicola, L.; Girometta, C.E.; Roversi, A.; Daccò, C.; Tosi, S. The analysis of the mycobiota in plastic polluted soil reveals a reduction in metabolic ability. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.; Lim, S.; Yi, G.; Lee, J.G.; Lee, E.J. Integrated transcriptomic-metabolomic analysis reveals cellular responses of harvested strawberry fruit subjected to short-term exposure to high levels of carbon dioxide. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 148, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupitu, A.; Moisa, C.; Bortes, F.; Peteleu, D.; Dochia, M.; Chambre, D.; Ciutină, V.; Copolovici, D.M.; Copolovici, L. The Impact of Increased CO2 and Drought Stress on the Secondary Metabolites of Cauliflower (Brassica oleracea var. botrytis) and Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata). Plants 2023, 12, 3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Sagar, G.R. Alteration of the pattern of distribution of photosynthetic products in the tomato by manipulation of the plant. Ann. Bot. 1969, 33, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharred, J.; Derbali, W.; Derbali, I.; Badri, M.; Abdelly, C.; Slama, I.; Koyro, H.-W. Impact of biochar application at water shortage on biochemical and physiological processes in Medicago ciliaris. Plants 2022, 11, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Peng, Q.; Li, K.; Mohammat, A.; Han, W. Nitrogen and phosphorus resorption of desert plants with various degree of propensity to salt in response to drought and saline stress. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatment | Irrigation (m3 ha−1) | Fertilization Rate (kg ha−1)—FI | Fertilization Rate (kg ha−1)—FII | Fertilization Rate (kg ha−1)—FIII | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 2024 | ||||
| T1 (DISFI562.5FII562.5FIII562.5) | 1525 | 1475 | 562.5 | 562.5 | 562.5 |
| T2 (DISFI750FII750FIII750) | 1525 | 1475 | 750 | 750 | 750 |
| T3 (DISFI937.5FII937.5FIII937.5) | 1525 | 1475 | 937.5 | 937.5 | 937.5 |
| T4 (DIMFI562.5FII750FIII937.5) | 2287.5 | 2212.5 | 562.5 | 750 | 937.5 |
| T5 (DIMFI750FII937.5FIII562.5) | 2287.5 | 2212.5 | 750 | 937.5 | 562.5 |
| T6 (DIMFI937.5FII562.5FIII750) | 2287.5 | 2212.5 | 937.5 | 562.5 | 750 |
| T7 (FIFI562.5FII937.5FIII750) | 3050 | 2950 | 562.5 | 937.5 | 750 |
| T8 (FIFI750FII562.5FIII937.5) | 3050 | 2950 | 750 | 562.5 | 937.5 |
| T9 (FIFI937.5FII750FIII562.5) | 3050 | 2950 | 937.5 | 750 | 562.5 |
| Year | Ammonium Nitrogen (mg/kg) | Available Phosphorus (mg/kg) | Available Potassium (mg/kg) | Maximum Field Capacity (%) | Yellow Sand Substrate Porosity (%) | Water-Holding Porosity (%) | Soil Bulk Density (g/cm3) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 108.24 | 93.57 | 236.77 | 18.3 | 37.1 | 17.6 | 1.61 | 7.82 |
| 2024 | 101.37 | 91.52 | 258.6 | 17.6 | 36.7 | 18.1 | 1.53 | 7.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S.; Xing, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, C.; Li, W.; Tan, Z.; Cheng, Y. Optimizing Water–Fertilizer Coupling Across Different Growth Stages of Tomato in Yellow Sand Substrate: Toward Enhanced Yield, Quality, and Resource Use Efficiency. Plants 2025, 14, 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060936
Song Y, Xu J, Zhang S, Xing J, Wang L, Wang X, Hu C, Li W, Tan Z, Cheng Y. Optimizing Water–Fertilizer Coupling Across Different Growth Stages of Tomato in Yellow Sand Substrate: Toward Enhanced Yield, Quality, and Resource Use Efficiency. Plants. 2025; 14(6):936. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060936
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yalong, Jiahui Xu, Shuo Zhang, Jianfei Xing, Long Wang, Xufeng Wang, Can Hu, Wentao Li, Zhanming Tan, and Yunxia Cheng. 2025. "Optimizing Water–Fertilizer Coupling Across Different Growth Stages of Tomato in Yellow Sand Substrate: Toward Enhanced Yield, Quality, and Resource Use Efficiency" Plants 14, no. 6: 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060936
APA StyleSong, Y., Xu, J., Zhang, S., Xing, J., Wang, L., Wang, X., Hu, C., Li, W., Tan, Z., & Cheng, Y. (2025). Optimizing Water–Fertilizer Coupling Across Different Growth Stages of Tomato in Yellow Sand Substrate: Toward Enhanced Yield, Quality, and Resource Use Efficiency. Plants, 14(6), 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060936






