Subsurface Drip Irrigation Combined with Ammonium Enhances Root Growth in Rice (Oryza sativa L.), Leading to Improved N Uptake and Higher Yield Formation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
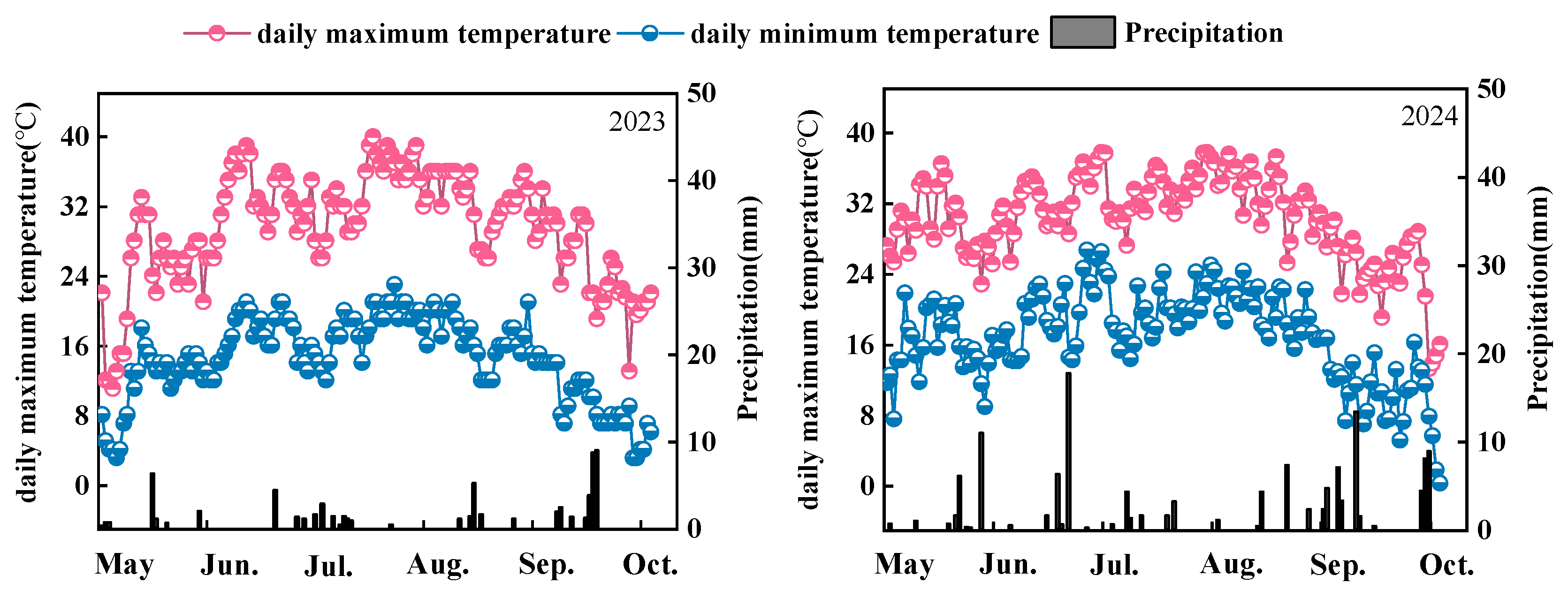
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design and Materials
2.2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Processing
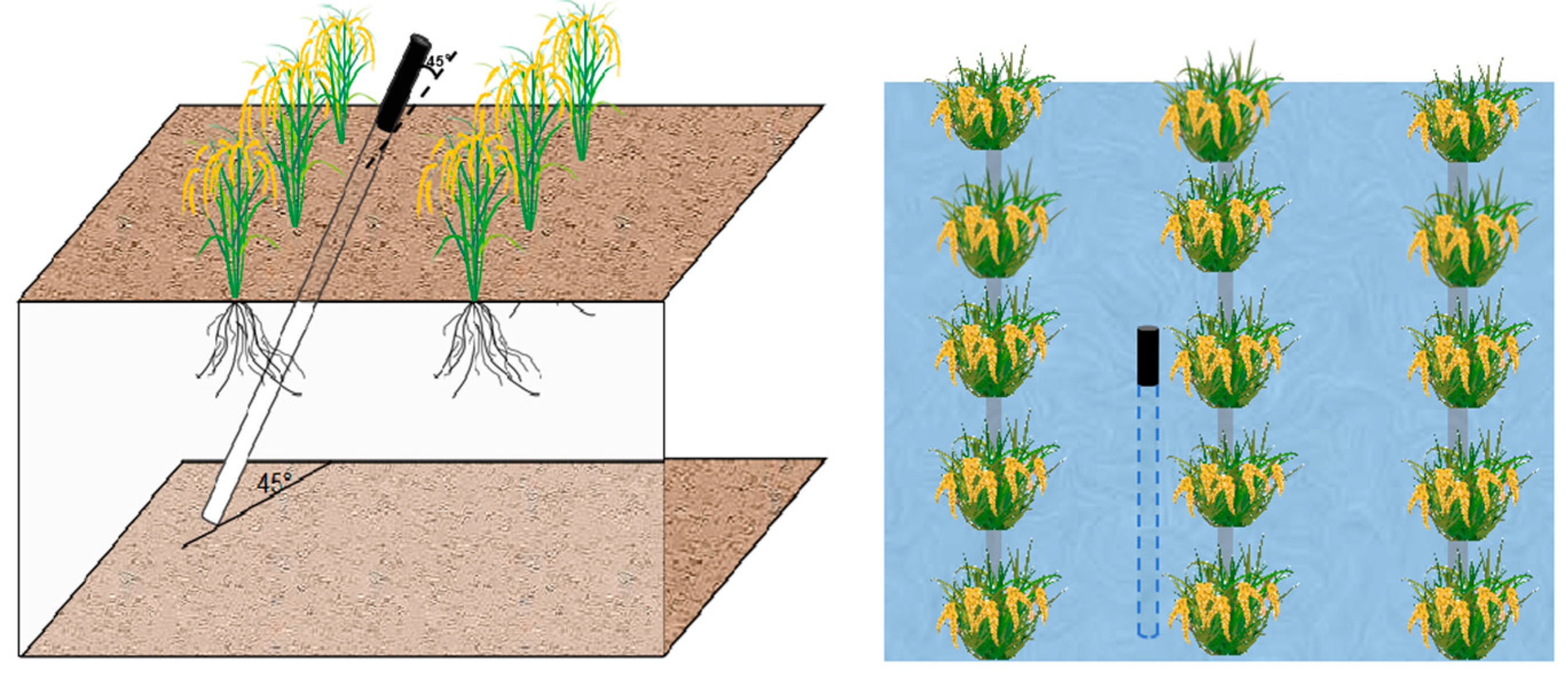
2.3.1. Installation of Root Tubes and Collection of Root Parameters
- (i)
- Acquisition of Root Morphological Parameters
- (ii)
- Calculation of Root Architectural Parameters
- (iii)
- Daily Root Elongation Rate
2.3.2. Root Biomass
2.3.3. Measurement of Root Activity
2.3.4. Leaf Photosynthetic Characteristics
2.3.5. Dry Matter Accumulation and N Uptake
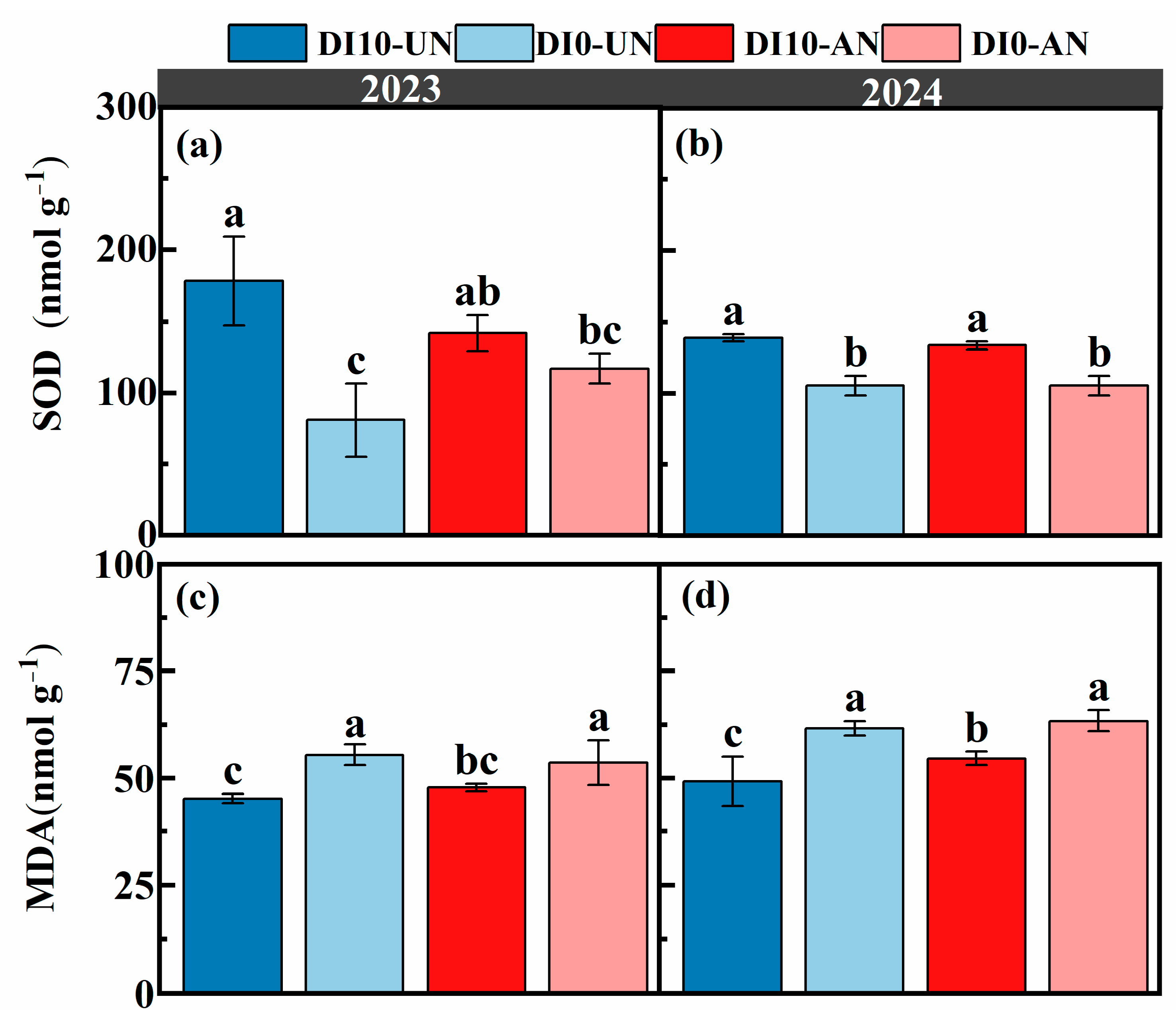
2.3.6. Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) and Malondialdehyde (MDA)
2.3.7. Yield
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Drip Irrigation Depth and N Forms on Rice Yield Formation and N Uptake
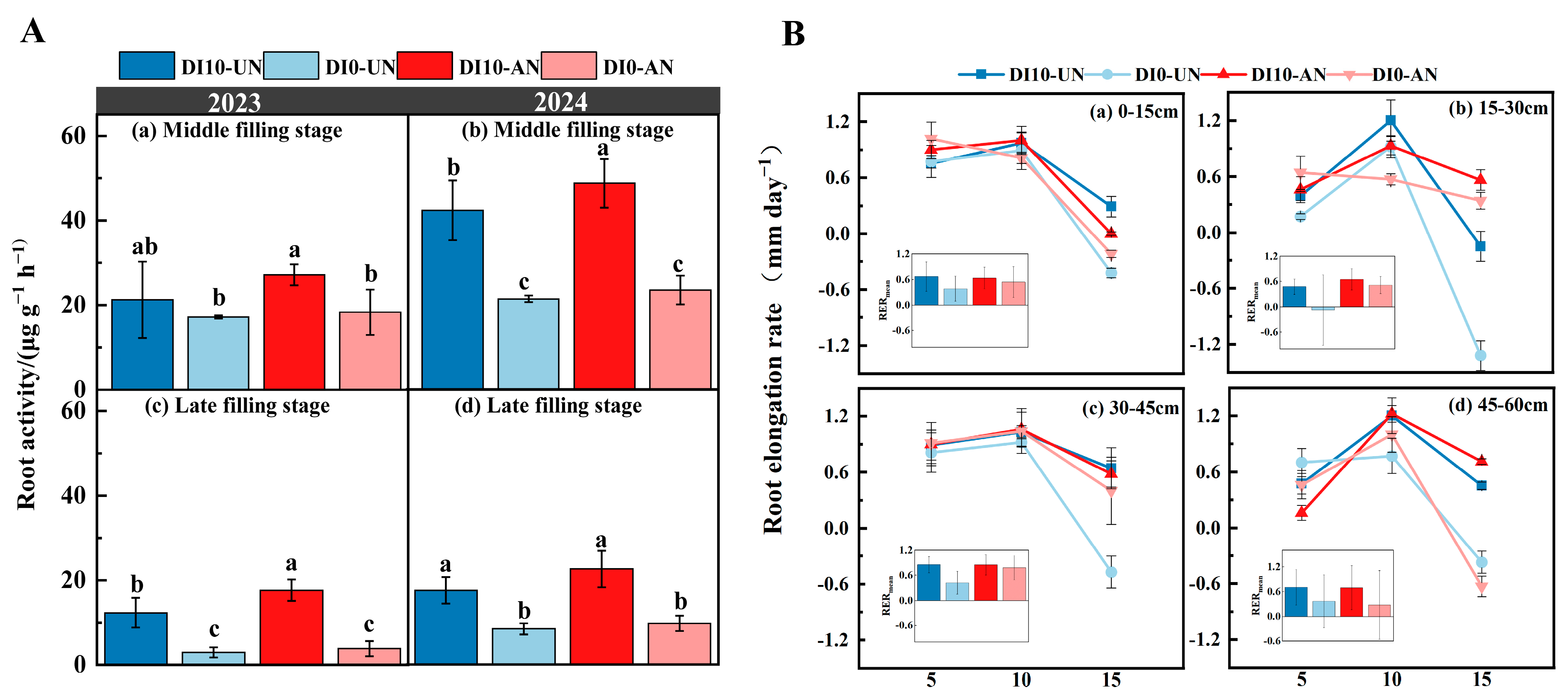
3.2. Effects of N Forms and Drip Irrigation Depths on Leaf Enzyme Activity and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Rice
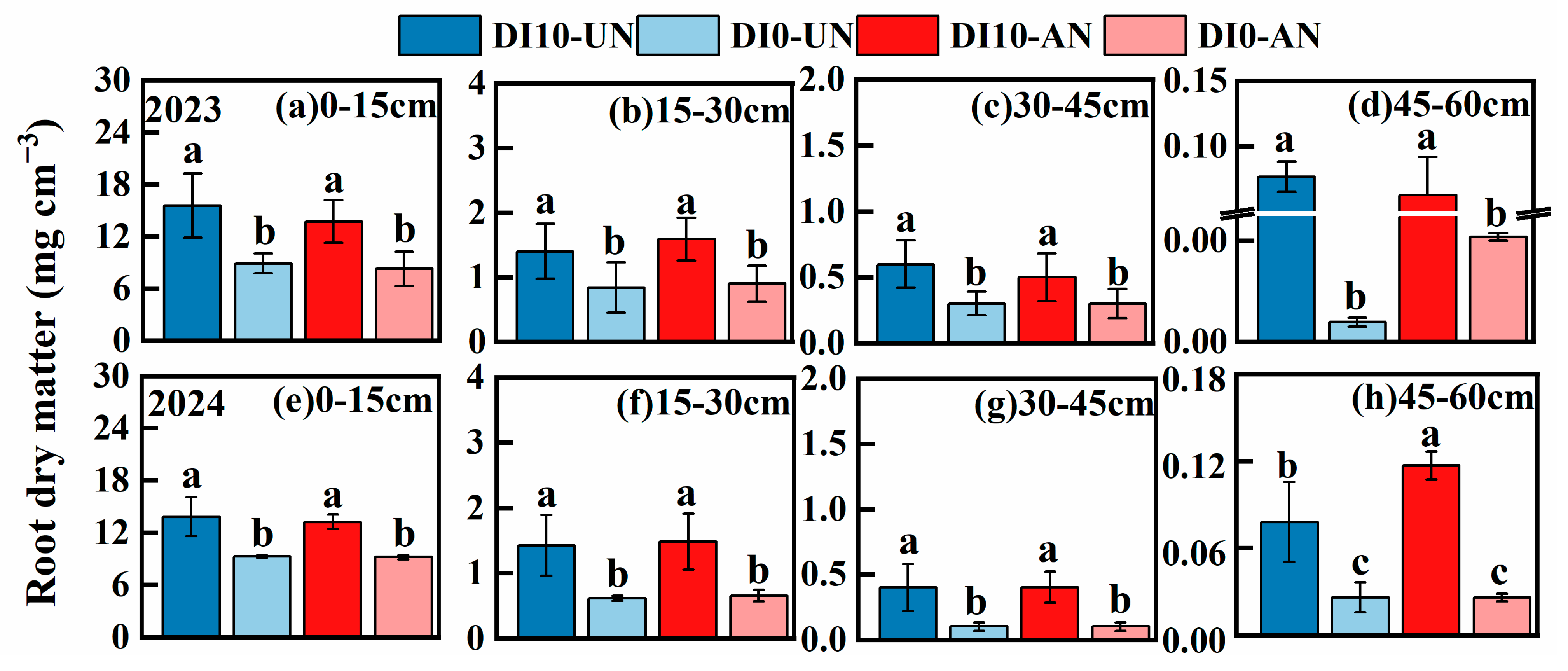
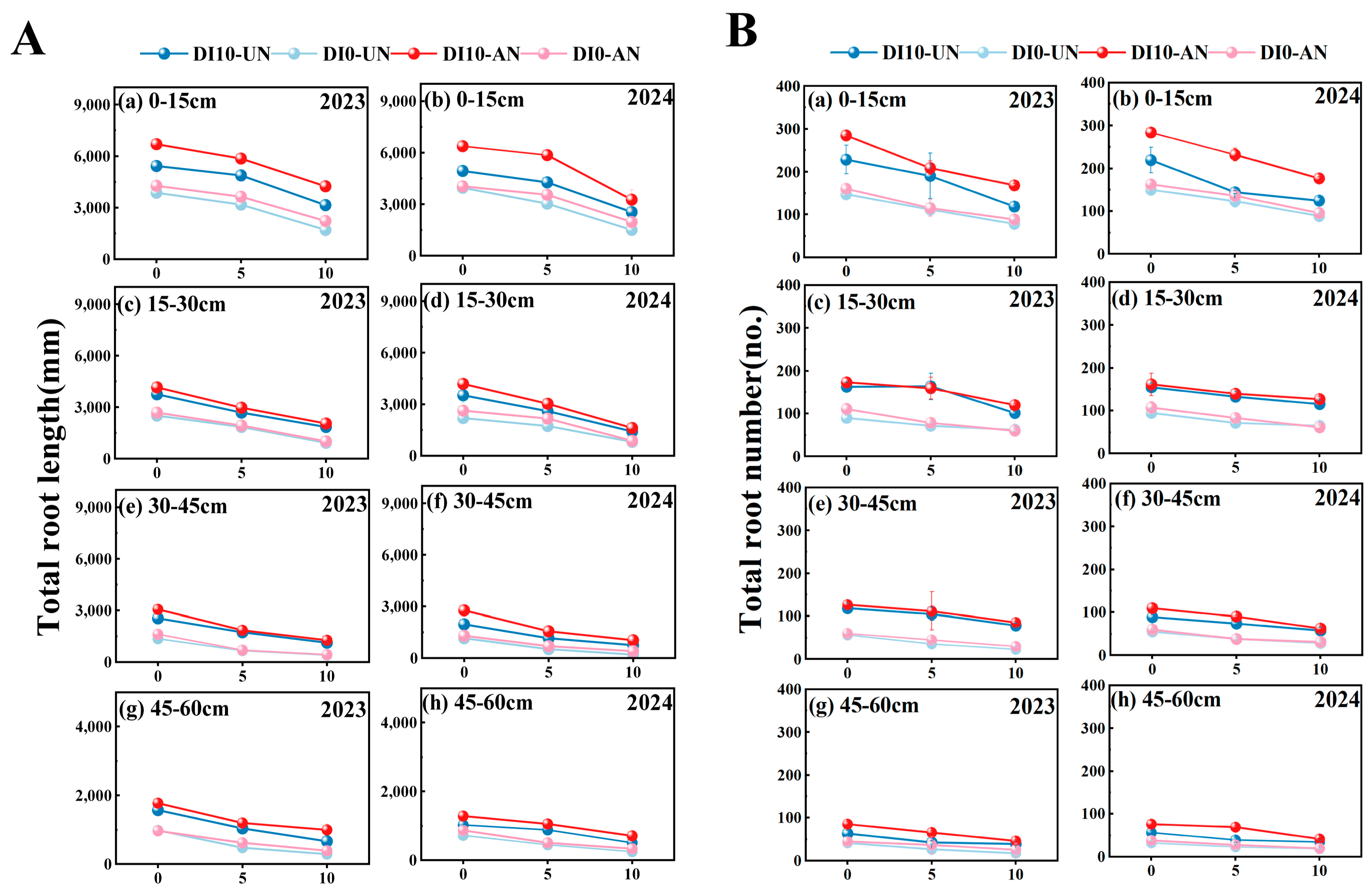
3.3. Spatial Dynamic Distribution of Rice Root Morphology and Root Architecture (Root Biomass, Root Number, and Root Length)
3.3.1. Root Biomass
3.3.2. Root Length
3.3.3. Root Number
3.3.4. Distribution of Root Architecture β Values
3.4. Effects of Subsurface Drip Irrigation and N Forms on Daily RER and Ra in Rice
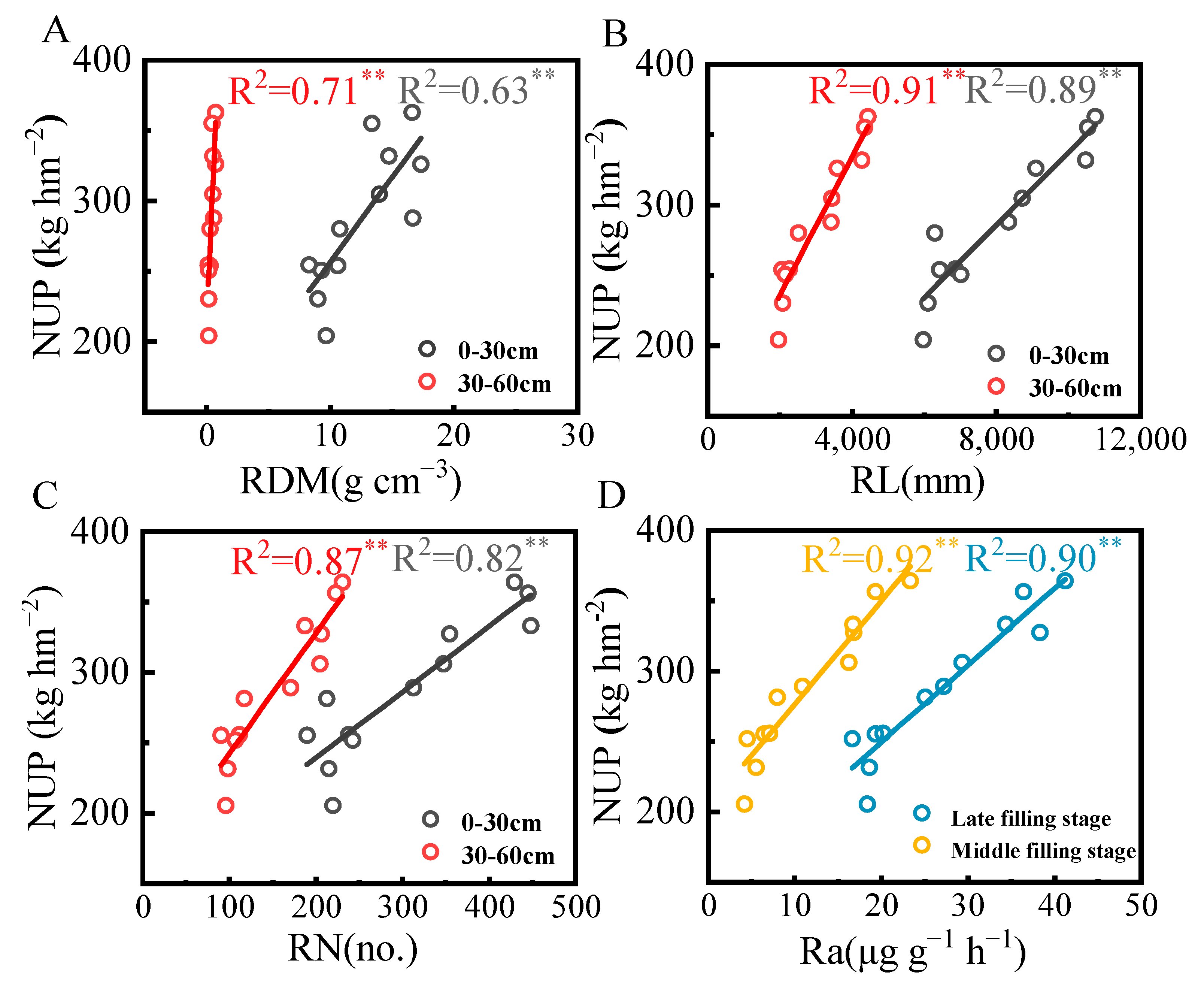
3.5. Correlation Between Subsurface Drip Irrigation, Ammonium N, Root Morphological Parameters, and N Uptake
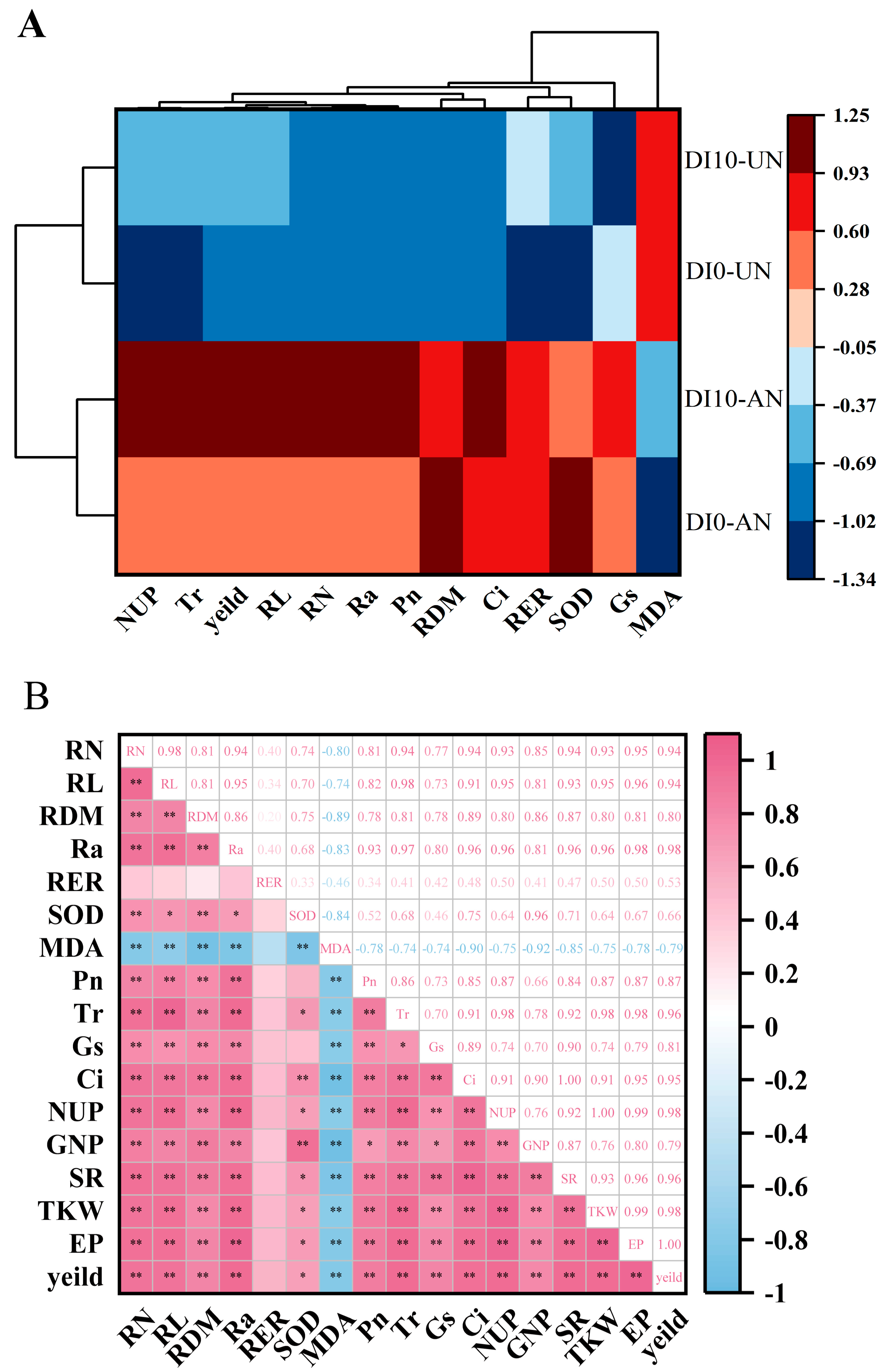
3.6. Cluster Analysis and Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Subsurface Drip Irrigation Combined with Ammonium N Effectively Maintains Root Activity in the Late Growth Stage of Drip-Irrigated Rice
4.2. Subsurface Drip Irrigation Combined with Ammonium N Promotes Root Growth and Proper Distribution in Drip-Irrigated Rice
4.3. Subsurface Drip Irrigation Combined with Ammonium N Promotes N Accumulation and Yield Formation in Drip-Irrigated Rice
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RL | Total root length |
| RDM | Root dry matter |
| Ra | Root activity |
| RN | Total root number |
| RER | Root elongation rate |
| SOD | Superoxide Dismutase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| Pn | Net photosynthetic rate |
| Tr | Transpiration rate |
| Gs | Gas conductance |
| Ci | Intercellular CO2 concentration |
| NUP | N uptake |
| GNP | Grain number per panicle |
| SR | Seed setting rate |
| TKW | 1000-kernel weight |
| EP | Efficient panicle |
References
- Li, J.; Yang, C.N.; Zhang, X.Z.; Wu, S.B.; Chi, H.L.; Zhang, X.J.; Wei, C.Z. Soil N distribution affects N utilization and yield of drip-irrigated rice. Agronomy 2024, 14, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, M.; Craine, J.M. Competition for nutrients and optimal root allocation. Plant Soil 2006, 285, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, M.R.; Grigal, D.F. Vertical root distributions of northern tree species about successional status. Can. J. For. Res. 1987, 17, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Z.; Wang, X.P. Root architecture and adaptive strategy of two desert plants in the Alxa Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 6001–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yan, H.; Xu, S.; Lin, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, D. Moderately deep banding of phosphorus enhanced winter wheat yield by improving phosphorus availability, root spatial distribution, and growth. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 220, 105388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetgin, A. Exploring the dynamic nature of root plasticity and morphology in the face of changing environments. Ecol. Front. 2024, 44, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, J.; Robinson, D.; Yang, Z.; Yao, X.; Wang, X.; Dai, X.; Chen, T.; Wu, D.; et al. Contrasting depth-related fine root plastic responses to soil warming in a subtropical Chinese fir plantation. J. Ecol. 2024, 112, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D. Timely supplemental irrigation changed N use of wheat by regulating root vertical distribution. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2018, 181, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, H.A.; DaMatta, F.M.; Chaves, A.R.M.; Loureiro, M.E.; Ducatti, C. Drought Tolerance Is Associated with Rooting Depth and Stomatal Control of Water Use in Clones of Coffea canephora. Ann. Bot. 2005, 96, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freschet, T.; Roumet, C.; Comas, L.H.; Weemstra, M.; Bengough, A.G.; Rewald, B.; Bardgett, R.D.; De Deyn, G.B.; Johnson, D.; Klimešová, J.; et al. Root Traits as Drivers of Plant and Ecosystem Functioning: Current Understanding, Pitfalls and Future Research Needs. New Phytol. 2021, 232, 1123–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresbøll, D.B.; Thorup-Kristensen, K.; McKenzie, B.M.; Dupuy, L.X.; Bengough, A.G. Timelapse scanning reveals spatial variation in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) root elongation rates during partial waterlogging. Plant Soil 2013, 369, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Rasmussen, C.R.; Dresboell, D.B.; Smith, A.G.; Thorup-Kristensen, K. Dynamics of deep water and N uptake under varied N and water supply. Plants 2021, 10, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, L.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, N.; Chen, J.; Zhang, K.; Bai, Z.; Wang, G.; et al. The responses of lateral roots and root hairs to N stress in cotton based on daily root measurements. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2021, 208, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulugalle, N.R.; Broughton, K.J.; Tan, D.K.Y. Fine root production and mortality in irrigated cotton, maize and sorghum sown in vertisols of northern New South Wales, Australia. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 146, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chen, F.; Lai, S.; Jin, M.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Ferré, T.P. Spatial distribution and dynamics of cotton fine root under film-mulched drip irrigation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 179, 114693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y. Fine root and root hair morphology of cotton under drought stress revealed with RhizoPot. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2020, 206, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ji, Z.; Tao, Y. Improving rice nitrogen-use efficiency by modulating a novel monoubiquitination machinery for optimal root plasticity response to nitrogen. Nat. Plants 2023, 9, 1902–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xu, X.; Shen, Q.; Guo, S. Root ABA Accumulation Enhances Rice Seedling Drought Tolerance under Ammonium Supply: Interaction with Aquaporins. Plants 2016, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Dang, X.; Lin, X.; Gao, G.; Liu, Y.; Ma, F. Combining base to topdressing ratio and layered application of phosphorus fertilizer enhanced cotton yield by regulating root distribution and activity. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 241, 105956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Liu, P.; Jia, L.; Wu, L.; Qin, Y.; Shi, X.; Fan, M. Shallow burial of drip irrigation tape improves the water use efficiency of potatoes in semi-arid areas. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, T. Effects of Drip Irrigation Combined with Ammonium Nitrogen on Rice Growth and Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Plants 2020, 12, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Liu, F.; Chen, G.Z.; Wang, J.Y.; Huang, F.Y.; Cai, T.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Z.K. Can deep fertilizer application enhance maize productivity by delaying leaf senescence and decreasing nitrate residue levels? Field Crops Res. 2022, 277, 108417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ren, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B.; Ren, B.; Wan, Y.; Liu, P. Deep phosphorus fertilizer placement increases maize productivity by improving root-shoot coordination and photosynthetic performance. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 235, 105915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.M.; Wang, M.; Ding, L.; Chen, Y.P.; Guo, S.W. High water uptake ability was associated with root aerenchyma formation in rice: Evidence from local ammonium supply under osmotic stress conditions. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 150, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, S.; Ma, H.; Wang, Y.; He, H.; Fang, C. Spatial-Temporal distribution of allelopathic rice roots in paddy soil and its impact on weed-suppressive activity at the seedling stages. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 940218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Yuan, W.; Li, G.; Petropoulos, E.; Xue, L.; Feng, Y.; Xue, L.; Yang, L.; Ding, Y. Deep fertilization with controlled-release fertilizer for higher cereal yield and N utilization in paddies: The optimal fertilization depth. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 5027–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Chen, G.; Liu, F.; Cai, T.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Z. How does deep-band fertilizer placement reduce N2O emissions and increase maize yields? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 322, 107672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, A.M.; Gaihre, Y.K.; Hunter, G.; Singh, U.; Hossain, S.A. Fertilizer deep placement increases rice production: Evidence from farmers’ fields in fouthern bangladesh. Agronomy 2016, 108, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, B.; Tian, Y.; Yin, B.; Zhu, Z. Integration of urea deep placement and organic addition for improving yield and soil properties and decreasing N loss in paddy field. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 247, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrick, R.L.; Pregitzer, K.S. The demography of fine roots in a northern hardwood Forest. Ecology 1992, 73, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunlong Medical. Plant Root Vitality Assay Kit (TTC Method). Sunlong Medical 2021. Available online: https://www.sunlongmedical.com (accessed on 22 February 2025).
- Clemensson-Lindell, A. Triphenyl tetrazolium chloride as an indicator of fine-root vitality and environmental stress in coniferous forest stands: Applications and limitations. Plant Soil 1994, 159, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Meng, Z.; He, D. Soil water effect on root activity, root weight density, and grain yield in winter wheat. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanello, D.D.; Kelly, S.J.; Bartoli, C.G.; Cano, M.G.; Guiamet, J.J. Plasticity of root growth and respiratory activity: Root responses to above-ground senescence, fruit removal or partial root pruning in soybean. Plant Sci. 2019, 290, 110296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaume, A.; Mächler, F.; De León, C.; Narro, L.; Frossard, E. Low-P tolerance by maize (Zea mays L.) genotypes: Significance of root growth, and organic acids and acid phosphatase root exudation. Plant Soil 2001, 228, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Bai, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.F. Phosphorus dynamics: From soil to plant. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pregitzer, K.S.; Laskowski, M.J.; Burton, A.J.; Lessard, V.C.; Zak, D.R. Variation in sugar maple root respiration with root diameter and soil depth. Tree Physiol. 1998, 18, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadelhoffer, K.J. The potential effects of nitrogen deposition on fine-root production in forest ecosystems. New Phytol. 2000, 147, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, B.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Xu, Z.W.; Zhang, X.Q. Research progress on plant root systems. Tianjin Agric. Sci. 2016, 22, 11–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Padilla, F.M.; Pugnaire, F.I. Rooting depth and soil moisture control Mediterranean woody seedling survival during drought. Funct. Ecol. 2007, 21, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.B.; Sperry, J.S.; Dawson, T.E. Root water uptake and transport: Using physiological processes in global predictions. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumet, C.; Birouste, M.; Picon-Cochard, C.; Ghestem, M.; Osman, N.; Vrignon-Brenas, S.; Cao, K.; Stokes, A. Root Structure–Function Relationships in 74 Species: Evidence of a Root Economics Spectrum Related to Carbon Economy. New Phytol. 2016, 210, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germon, A.; Cardinael, R.; Prieto, I.; Mao, Z.; Kim, J.; Stokes, A.; Dupraz, C.; Laclau, J.-P.; Jourdan, C. Unexpected Phenology and Lifespan of Shallow and Deep Fine Roots of Walnut Trees Grown in a Silvoarable Mediterranean Agroforestry System. Plant Soil 2016, 401, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornish, P.S. Research directions: Improving plant uptake of soil phosphorus, and reducing dependency on input of phosphorus fertiliser. Crop Pasture Sci. 2009, 60, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, W.; Xue, X.; Feng, G.; Yang, R.; Tian, C. Can optimization of phosphorus input lead to high productivity and high phosphorus use efficiency of cotton through maximization of root/mycorrhizal efficiency in phosphorus acquisition? Field Crop Res. 2018, 216, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ma, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, F.; Rengel, Z.; Shen, J. Root morphological responses to localized nutrient supply differ among crop species with contrasting root traits. Plant Soil 2014, 376, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Qi, Y.; Yin, C.; Liu, X. Effects of nitrogen reduction at different growth stages on maize water and nitrogen utilization under shallow buried drip fertigated irrigation. Agronomy 2024, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Song, H.; Jiang, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J. Managing fertiliser placement locations and source types to improve rice yield and the use efficiency of nitrogen and phosphorus. Field Crop Res. 2019, 231, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piovesan, A.; Vancauwenberghe, V.; Van De Looverbosch, T.; Verboven, P.; Nicolaï, B. X-ray computed tomography for 3D plant imaging. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtahina, N.; Matsuoka, A.; Yoshinaga, K.; Moriwaki, A.; Uemura, M.; Shimono, H.; Matsunami, M. Deep placement of fertilizer enhances mineral uptake through changes in the root system architecture in rice. Plant Soil 2023, 490, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, A. The plastic plant: Root responses to heterogeneous supplies of nutrients. New Phytol. 2004, 162, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikawa, H.; Chen, C.P.; Sikma, M.; Yoshimoto, M.; Sakai, H.; Tokida, T.; Usui, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Ono, K.; Maruyama, A.; et al. Increasing Canopy Photosynthesis in Rice Can Be Achieved Without a Large Increase in Water Use—A Model Based on Free-Air CO2 Enrichment. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 1321–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, X.; Zuo, W.; Lei, Z.; Sui, L.; Zhang, W. Characters in Light-Response Curves of Canopy Photosynthetic Use Efficiency of Light and N in Responses to Plant Density in Field-Grown Cotton. Field Crops Res. 2017, 203, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wu, X.; Lei, D.; Chen, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, Y.; Deng, H. Relationship between photosynthetic characteristics at late growth stage and yield of super large panicle rice R1126 and its combinations. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2023, 21, 19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Yang, L.; Yang, Y.X.; Zhu, O.Y. Rice root growth and nutrient uptake as influenced by organic manure in continuously and alternately flooded paddy soils. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 70, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, M.; Shinano, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Zheng, T.; Tadano, T. A root-shoot interaction hypothesis for high productivity of field crops. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1997, 43, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year | Treatment | Efficient Panicle 104 ha−1 | Seed Setting Rate (%) | Grain Number per Panicle | 1000-Kernel Weight (g) | Yield (t ha−1) | N Uptake (kg ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | DI10-UN | 360.82 ± 2.2.9 a | 76.79 ± 3.74 a | 86.57 ± 1.03 a | 32.17 ± 0.71 ab | 7.72 ± 0.59 ab | 149.38 ± 6.54 b |
| DI0-UN | 367.32 ± 14.99 a | 76.35 ± 1.11 a | 78.93 ± 0.19 c | 31.01 ± 1.56 ab | 6.86 ± 0.44 b | 108.28 ± 16.80 c | |
| DI10-AN | 376.31 ± 10.49 a | 81.15 ± 5.63 a | 84.22 ± 0.67 b | 33.08 ± 0.18 a | 8.51 ± 0.59 a | 179.59 ± 5.23 a | |
| DI0-AN | 336.33 ± 15.31 b | 80.73 ± 7.12 a | 84.17 ± 0.88 b | 30.04 ± 0.78 b | 6.87 ± 0.73 b | 121.77 ± 6.39 c | |
| 2024 | DI10-UN | 365.82 ± 6.87 a | 79.09 ± 2.56 ab | 82.66 ± 0.82 a | 31.88 ± 0.36 a | 7.62 ± 0.27 b | 156.40 ± 12.73 ab |
| DI0-UN | 320.84 ± 17.68 b | 72.21 ± 1.21 b | 71.89 ± 0.73 c | 30.12 ± 1.49 b | 5.02 ± 0.45 c | 120.47 ± 8.27 c | |
| DI10-AN | 369.82 ± 8.26 a | 85.42 ± 5.10 a | 84.84 ± 0.80 a | 33.11 ± 0.53 a | 8.88 ± 0.75 a | 170.14 ± 11.20 a | |
| DI0-AN | 336.83 ± 5.27 b | 73.36 ± 0.99 b | 77.02 ± 0.72 b | 30.01 ± 0.71 b | 5.72 ± 0.44 c | 139.36 ± 9.58 bc |
| Year | Treatment | Pn (mmol CO2 m−2s−1) | Tr (mmol H2 Om−2s−1) | Gs (mmol m−2s−1) | Ci (μmol CO2 m−2s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | DI10-UN | 7.19 ± 0.54 a | 5.26 ± 0.22 b | 124.97 ± 12.71 ab | 183.7 ± 17.76 b |
| DI0-UN | 6.47 ± 0.78 b | 4.32 ± 0.13 c | 124.2 ± 24.88 ab | 130.72 ± 31.00 c | |
| DI10-AN | 7.41 ± 0.35 a | 6.1 ± 0.13 a | 136.63 ± 10.99 a | 217.12 ± 11.76 a | |
| DI0-AN | 6.55 ± 0.22 b | 5.10 ± 0.13 b | 105.7 ± 5.91 b | 122.97 ± 21.50 c | |
| 2024 | DI10-UN | 6.75 ± 1.09 ab | 5.67 ± 0.11 a | 120.58 ± 10.78 a | 147.68 ± 24.38 a |
| DI0-UN | 5.82 ± 0.54 b | 5.16 ± 0.09 b | 104.27 ± 7.82 bc | 111.5 ± 37.31 a | |
| DI10-AN | 7.11 ± 1.00 a | 5.71 ± 0.45 a | 115.75 ± 11.25 ab | 130.87 ± 14.51 a | |
| DI0-AN | 5.92 ± 0.74 b | 4.95 ± 0.09 b | 96.47 ± 7.25 c | 107.68 ± 37.59 a |
| Year | Treatment | RDM β | RL β | RN β |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | DI10-UN | 0.900 ± 0.001 a | 0.958 ± 0.002 a | 0.963 ± 0.002 a |
| DI0-UN | 0.891 ± 0.004 b | 0.951 ± 0.004 b | 0.955 ± 0.004 b | |
| DI10-AN | 0.908 ± 0.005 a | 0.958 ± 0.001 a | 0.963 ± 0.001 a | |
| DI0-AN | 0.889 ± 0.004 b | 0.951 ± 0.001 b | 0.959 ± 0.001 ab | |
| 2024 | DI10-UN | 0.890 ± 0.009 b | 0.954 ± 0.002 a | 0.959 ± 0.001 a |
| DI0-UN | 0.864 ± 0.010 d | 0.945 ± 0.006 b | 0.954 ± 0.002 b | |
| DI10-AN | 0.896 ± 0.006 a | 0.955 ± 0.003 a | 0.959 ± 0.003 a | |
| DI0-AN | 0.870 ± 0.005 c | 0.947 ± 0.005 b | 0.955 ± 0.00 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, Y.; Ma, W.; Yang, C.; Bai, R.; Xia, T.; Wei, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, G. Subsurface Drip Irrigation Combined with Ammonium Enhances Root Growth in Rice (Oryza sativa L.), Leading to Improved N Uptake and Higher Yield Formation. Plants 2025, 14, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060891
Cui Y, Ma W, Yang C, Bai R, Xia T, Wei C, Zhang X, Zhou G. Subsurface Drip Irrigation Combined with Ammonium Enhances Root Growth in Rice (Oryza sativa L.), Leading to Improved N Uptake and Higher Yield Formation. Plants. 2025; 14(6):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060891
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Yuman, Weidong Ma, Changnan Yang, Ruxiao Bai, Tianze Xia, Changzhou Wei, Xinjiang Zhang, and Guangwei Zhou. 2025. "Subsurface Drip Irrigation Combined with Ammonium Enhances Root Growth in Rice (Oryza sativa L.), Leading to Improved N Uptake and Higher Yield Formation" Plants 14, no. 6: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060891
APA StyleCui, Y., Ma, W., Yang, C., Bai, R., Xia, T., Wei, C., Zhang, X., & Zhou, G. (2025). Subsurface Drip Irrigation Combined with Ammonium Enhances Root Growth in Rice (Oryza sativa L.), Leading to Improved N Uptake and Higher Yield Formation. Plants, 14(6), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060891






