The Effect of Minerals and Hormones on the Nutrients in Chinese Fir Leaves and Seed Set
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
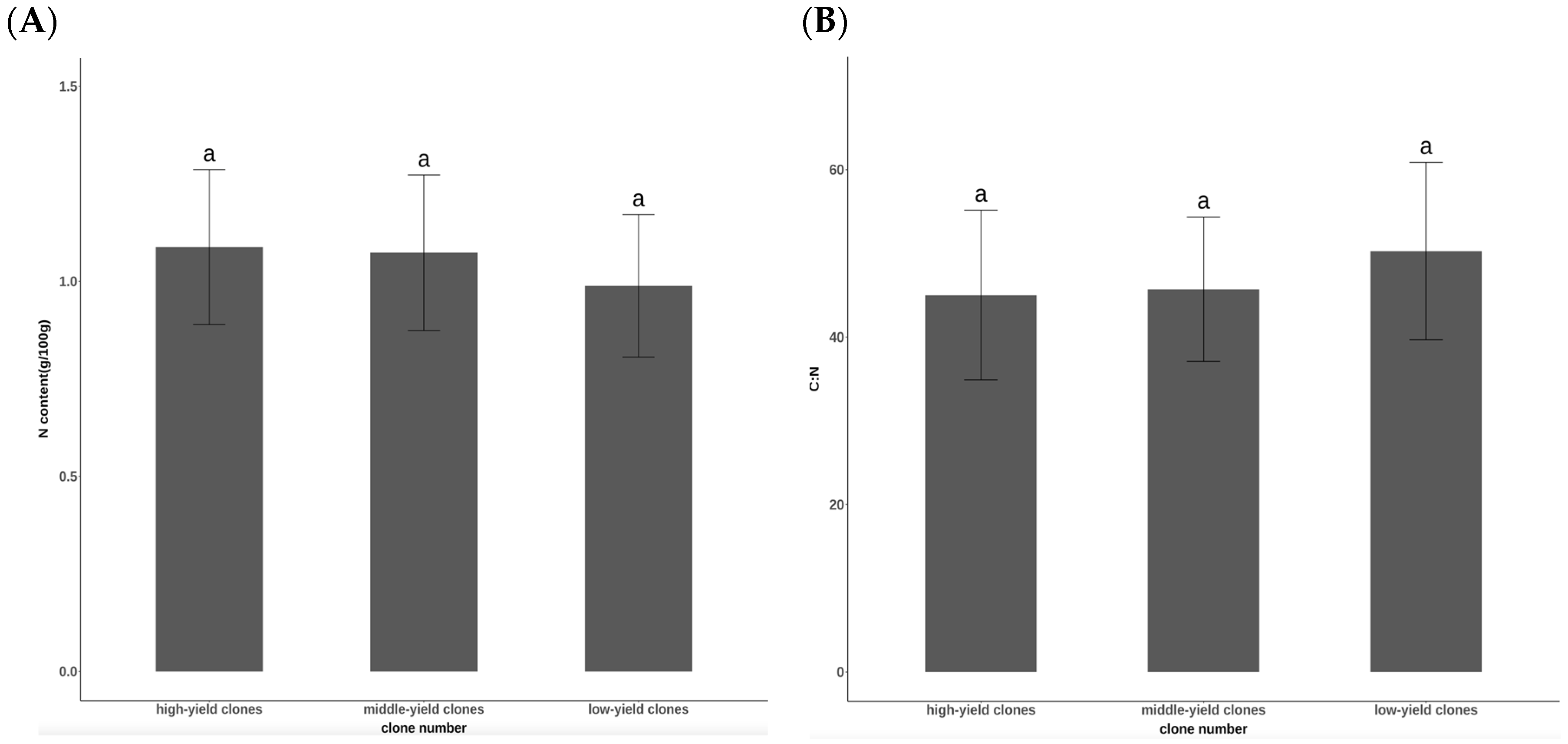
3.1. Comparison of Nutritional Conditions of Chinese Fir Clones with Different Seed-Setting Characteristics After Cutting
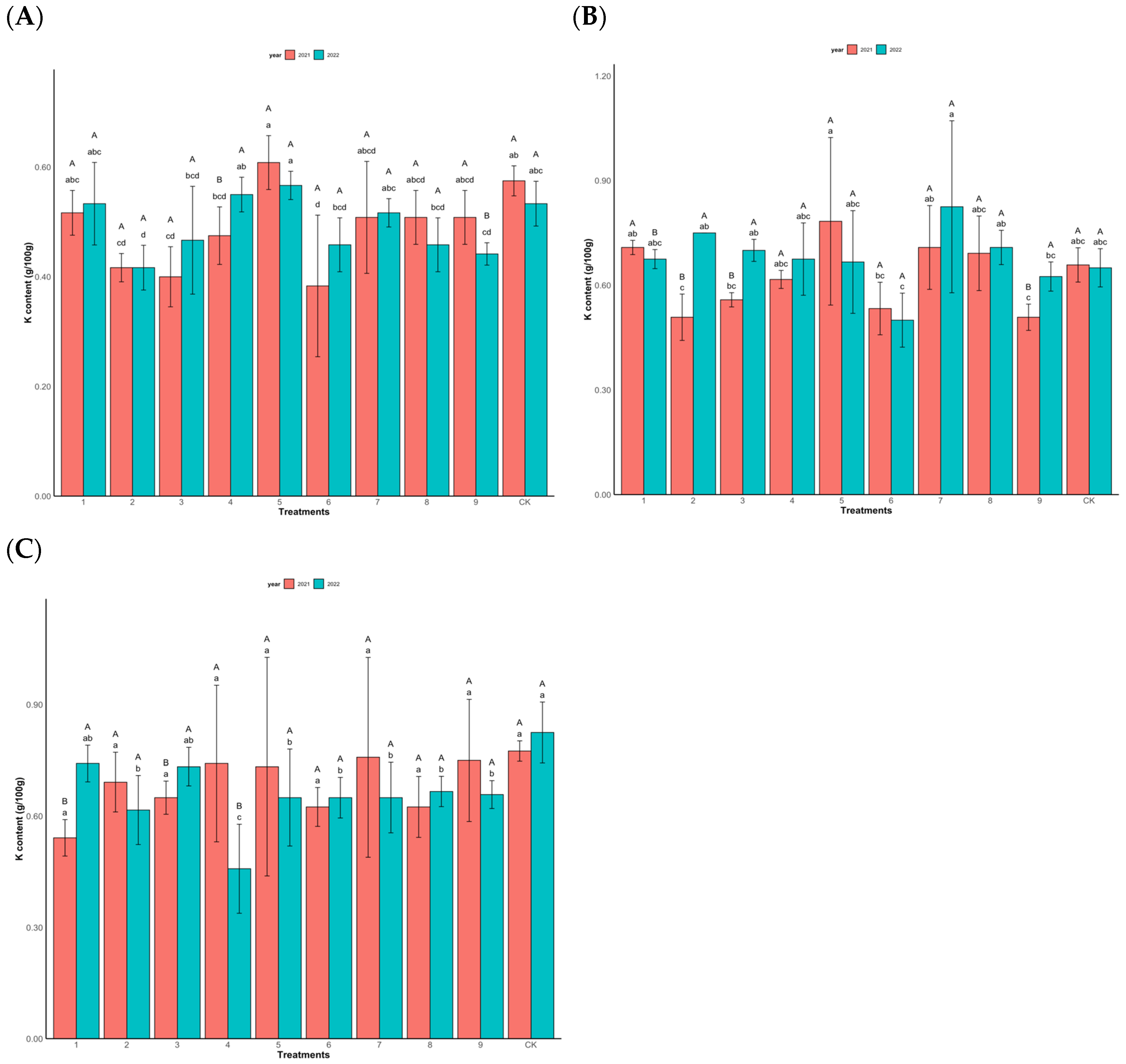
3.2. Impact of Foliar Fertilization on the N, P, and K Contents of Chinese Fir Needles
- (1)
- Impact of foliar fertilization on total N in the needles of Chinese fir
- (2)
- Impact of foliar fertilization on total P in the needles of Chinese fir
- (3)
- Impact of foliar fertilization on total K in the needles of Chinese fir
3.3. Effects of Foliar Fertilization on the Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics of C, N, and P in Chinese Fir Needles
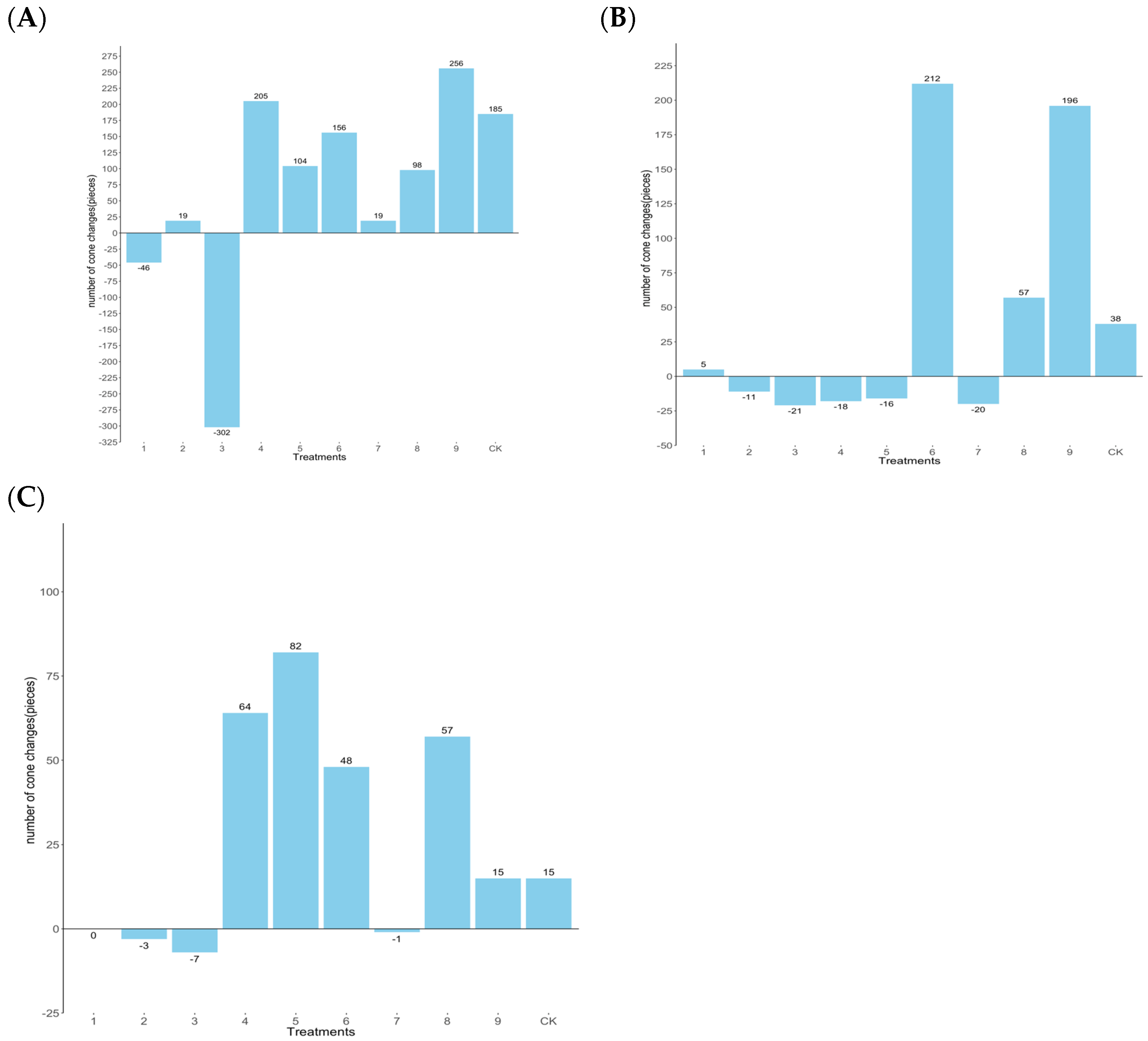
3.4. Analysis of Foliar Fertilization on the Yield and Quality of Chinese Fir Cones
- (1)
- Effect of foliar fertilization on cone number of clones with different seed-setting types
- (2)
- Correlation analysis between the number of Chinese fir cones with different fruiting characteristics and N, P, and K.
- (3)
- Path analysis of N, P, and K content in China fir needles on cone quantity
- (4)
- Comprehensive evaluation of foliar fertilization on needle nutrition and fruiting
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Nutrition Status of Chinese Fir Clones with Different Seed-Setting Characteristics After Cutting
4.2. Effects of Fertilization Treatments on the Ecological Stoichiometry Characteristics of Chinese Fir Needles
4.3. Analysis of Seed Yield and Quality of Chinese Fir Treated with Fertilizer
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- After pruning, the Chinese fir cones exhibited notable variations. In July, there were no significant differences in total N content and C:N ratio among the different seed-setting characteristics. However, the P content in the high-yield clones was markedly higher than that in the middle-yield and low-yield clones, while the K content was notably lower. This demonstrated the significance of July in cone and seed development, which required P and K supplementation. Attention to these indicators can be crucial to scientifically enhancing seed orchard yields.
- (2)
- Fertilization could be a vital strategy for enhancing the nutritional growth of Chinese fir and increasing seed yield. Strategic fertilization not only conserved costs, but also boosted yields. To elevate Chinese fir seed yield post-stem cutting and dwarfing and to mitigate on-and-off-year fluctuations, various fertilizer and hormone ratios were designed through orthogonal design. The objective was to identify the optimal fertilization scheme for different seed-setting characteristics. For the high-yield clones, four formulations such as Treatment 5, Treatment 6, Treatment 8, and Treatment 9 can be applied, which can enhance the nutrient level of branches and increase the number of cones. For the middle-yield clones, three formulations like Treatment 3, Treatment 6, and Treatment 9 can be used to improve needle nutrition and the number of cones. For the low-yield clones, applying three formulations including Treatment 3, Treatment 4, and Treatment 5 can increase the nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium contents by 18.54%, 36.57%, and 26.56%, respectively, and increase the number of cones by 82. Therefore, during fertilization, tailored formulas should be employed according to the specific seed-setting characteristics of Chinese fir and management objectives to effectively enhance yield.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jing, Y.L.; Bian, L.M.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhao, B.; Zheng, R.; Su, S.; Ye, D.; Zheng, X.; El-Kassaby, Y.A.; Shi, J. Genetic diversity and structure of the 4th cycle breeding population of Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata (lamb.) hook). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1106615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.S.; Luo, Y.L. A Study on the effect of top cutting of mother trees in camphor Pine seed orchard on cone setting. For. Technol. 2021, 46, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.Y.; Zhou, G.J.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhang, Q.J.; Sun, H.L. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on stoichiometry characteristics of leaf, fine root and soil of Fraxinus mandshurica plantation. For. Eng. 2023, 39, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batjer, G.L.P.B. Tree fruit nutrition in central Washington. Proc. Wash State Hort. Assoc. 1996, 62, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.J.; Wang, J.; Dang, X.H.; Han, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, P. Contents and stoichiometric characteristics of C, N, P and K in leaves process of Nitraria tangutorum succession. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2021, 41, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro Marín, I.; Loef, I.; Bartetzko, L.; Searle, I.; Coupland, G.; Stitt, M.; Osuna, D. Nitrate regulates floral induction in Arabidopsis, acting independently of light, gibberellin and autonomous pathways. Planta 2011, 233, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.R.; Li, X.Y.; Quan, X.Q.; Liang, H.; Wang, L.; Yan, X. Effects of nitrogen stress and nitrogen form ratios on the bacterial community and diversity in the root surface and rhizosphere of Cunninghamia lanceolata and Schima superba. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1240675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zihan, L.; Shufang, Z.; Peirong, Y.; Ningning, L.; Yiquan, Y.; Jinhua, H.; Xueyan, Z.; Yin, T.; Shanshan, X. Interactive effects of light intensity and nitrogen supply onphotosynthetic physiology of Cunninghamia lanceolata seedlings. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2024, 20, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, G.; Dechen, A.R. Long-term annual fertilization with nitrogen and potassium affect yield and mineral composition of “Fuji” apple. Sci. Agr. 2009, 66, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, J.G.; Tong, Q.-Y.; Chen, S.-L.; Xu, Z.-Q.; Zhou, Z.-C. Effects of P fertilizer on female strobilus and needle N and P nutrition of Pinus massoniana clones with different fruiting abilities. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 1184–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.M.; Liu, Y.Q.; Ruan, Y.J. Research progress on plant potassium. Chin. Hortic. Dig. 2015, 31, 71–148. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Han, D.; Wang, J.; Guo, D.; Li, J. Floral induction of Longan (Dimocarpus longan) by potassium chlorate: Application, mechanism, and future perspectives. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 670587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sublett, W.L.; Barickman, T.C.; Sams, C.E. Effects of elevated temperature and potassium on biomass and quality of dark red ‘Lollo Rosso’ lettuce. Horticulturae 2018, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahe, S.; Shirin, S. Investigating of N and K fertilizers on yield and components of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.). J. Agr. Sci.-Camb. 2017, 9, 85. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.; Ren, B. The mechanism of action of several plant growth regulators and their application in grapes. Grapes Wines China Abroad 2008, 40–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciniak, K.; Przedniczek, K. Anther dehiscence is regulated by gibberellic acid in yellow lupine (Lupinus luteus L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Tang, S.; Meng, X.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, D.; Shen, Q. Proteomic analysis demonstrates a molecular dialog between trichoderma guizhouense njau 4742 and Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) roots: Role in promoting plant growth. Mol. Plant Microbe. Interact. 2021, 34, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Chang, Z. The effects of sludge and auxin addition on the growth of Poa pratensis and soil microorganisms. Grassl. Lawn 2021, 41, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Li, X.Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, B.Q.; Wang, L.X. Advances in study on mechanism of foliar nutrition and development of foliar fertilizer application. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2009, 42, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Chen, L.Y.; Lu, Z.J.; Jie, M.; Lianhong, W.; Xiaohui, S.; Baojin, L. Effects of formula fertilization on seed yield and quality in primary seed orchard of Pinus thunbergii. Guangxi For. Sci. 2022, 51, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, P.B.; Tjoelker, M.G.; Machado, J.; Oleksyn, J. Universal scaling of respiratory metabolism, size and nitrogen in plants. Nature 2006, 439, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Yang, Z.J.; Yang, L.; Li, Z.; Wei, W.; Zhang, Q. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of plants and soil under different vegetation types in the semi-arid loess small watershed. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 1824–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.F.; Shu, X.Y.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Tang, X.; Gu, Y.; Lan, T.; Xia, J.; Ling, J.; et al. Storage of C, N, and P affected by afforestation with Salix cupularis in an alpine semiarid desert ecosystem. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Yan, Z.B.; Fang, J.Y. Review on characteristics and main hypotheses of plant ecological stoichiometry. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2021, 45, 682–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, Y.H.; Jiang, T.; Yao, H.J.; Zhan, S.T. Effects of drought stress on N and P stoichiometry and allocation of poplar seedlings. Chin. J. Ecol. 2017, 36, 3116–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güsewell, S. N: P ratios in terrestrial plants: Variation and functional significance. New Phytol. 2004, 164, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.T.; Song, A.Y.; Zhao, X.M.; Peng, L.; Zhou, F. C, N and P stoichiometry of Zizyphus jujuba Mill var.inermis dongzao during the growing season. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2020, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.K. Soil Agrochemical Analysis Methods; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 308–315. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X. The Influence of Fertilization on Growth and Flowering in Pinus massoniana Seed Orchard. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.F.; Wu, N.; Liu, J.L.; Xu, X. Effects of phosphorus application levelson the ecological stoichiometric characteristics of carbon nitrogen and phosphorus of Switchgrass (Panicum virgatum) in saline-alkali land. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2024, 32, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.F.; Li, Y.Y.; Wu, J.P.; Fan, H.; Xu, L.; Yuan, Y. Study on the relationship between the seed yield and nutrient factors in the 3rd generation seed orchard of Cunninghamia lanceolata. J. Fujian For. Coll. 2013, 33, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J. Photosynthetic and Nutrition Physiology of Korean Pine with Different Fruit Characteristics During Flower Bud Differentiation. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y. Analysis of the Effects of Stem-Cutting Dwarfing and Phosphorus Fertilizer Application on Female Strobilus of Pinus massoniana Clones. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Yu, C.; Yang, Z.A.; Wang, H.; Deng, F.; Bai, Z.; Gong, W.; Wang, J. Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilization promotes Zanthoxylum armatum‘Hanyuan Putao Qingjiao’ flower bud differentiation in Sichuan, China. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2021, 61, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, Y.; Xi, R.C.; Huang, R.; Xu, Y. Flower bud differentiation and development characteristics of Camellia gauchowensis Chang. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2018, 45, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Qi, G.H.; Li, B.G.; Guo, S.P.; Zhang, X.M.; Qi, K. Female flower bud differentiation in Pistacia chinensis Bunge. J. Hebei Agric. Univ. 2011, 34, 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q. Dynamic Analysis of Needle C and N, NSC and Terminal bud Hormones in Pinus koraiensis Trees with Different Seed Setting Situations. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.Y.; Liu, X.J.; Xu, D.P.; Chen, C.; Nie, G.; Xiang, B. Research progress on nutritional and reproductive growth control techniques of forest trees. World For. Res. 2019, 32, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.S.; Jiang, H.; Ma, J.L.; Shu, H.Y.; Chen, X.F. Variations of net ecosystem carbon exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Phyllostachys edulis forest in Anji. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2016, 28, 1003–1008. Available online: http://www.zjnyxb.cn/CN/Y2016/V28/I6/1003 (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Zhang, L.; Guo, S.J.; Song, Y.; Sun, H.; Xie, M.; Wu, Y. Effects of spraying fertilizer on N and P distribution in above-ground organs of Chinese Chestnut. J. Northeast. For. Univ. 2017, 45, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.W.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, D.Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Q.Y. The effect of phosphorus on the fruiting performance and yield of chestnut. Acta Hortic. Sin. 1991, 18, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.Y.; Hu, D.N.; Guo, X.M.; Lei, X.; Yan, Y.; He, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Weng, X. Effect of KH2PO4 on blossom and fruit-protecting of Camellia oleifera. Non-Wood For. Res. 2022, 40, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, A. Vine growth, yield, berry quality attributes and leaf nutrient content of grapevines as influenced by seaweed extract (Ascophyllum nodosum) and nanosize fertilizer pulverizations. Sci Hortic-Amst. 2014, 175, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.Y.; Liu, B.X.; Li, Y.N.; Liu, H. Effect of fertilization on the growth and fruiting of Pinus koraiensis clonal orchards. For. Sci. Technol. 2023, 48, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ågren, G.I. The C:N:P stoichiometry of autotrophs-theory and observations. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenxuan, H.; Jingyun, F.; Dali, G.; Yan, Z. Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across 753 terrestrial plant species in China. New Phytol. 2005, 168, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, N.J.; Edward, C.D. N, P, and C stoichiometry of Eranthis hyemalis (Ranunculaceae) and the allometry of plant growth. Am J Bot 2005, 92, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rez-Harguindeguy, N.P.; Az, S.D.; Garnier, E.; Lavorel, S.; Poorter, H.; Jaureguiberry, P.; Bret-Harte, M.S.; Cornwell, W.K.; Craine, J.M.; Gurvich, D.E. New handbook for standardised measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Aust. J. Bot. 2013, 61, 167–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardle, D.A.; Walker, L.R.; Bardgett, R.D. Ecosystem properties and forest decline in contrasting long-term chronosequences. Science 2004, 305, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, P.B.; Oleksyn, J. Global patterns of plant leaf N and P in relation to temperature and latitude. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11001–11006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, R.; Hannie, D.C.; Beltman, B. Is the relation between nutrient supply and biodiversity co-determined by the type of nutrient limitation? Oikos 2003, 101, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jin, B.J.; Zhong, Q.L.; Ma, Y.Z.; Lu, H.D.; Guo, B.Q.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, D.L. Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization on leaf N and P stoichiometric ffect of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization on leaf N and P stoichiometric characteristics of haracteristics of Machilus pauhoi achilus pauhoi seedlings. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2016, 22, 285–291. Available online: http://www.cibj.com//#/digest?ArticleID=3220 (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Lu, X.; Hu, M.H. Response of seed characteristics of seed-bearing mother plant of Larix kaempferi Seed orchard to nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium proportional fertilization. Engl. J. Southwest For. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2020, 40, 6–11. Available online: http://xnldxb.ns.swfu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11929/j.swfu.201909004 (accessed on 6 March 2025).






| Treatments | N (mg/L) | P (mg/L) | K (mg/L) | GA3 (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 (N0P2K2GA3 2) | 10,000 | 1300 | 2000 | 100 |
| T2 (N0P2K3GA3 1) | 10,000 | 1300 | 2500 | 50 |
| T3 (N0P2K1GA3 3) | 10,000 | 1300 | 1500 | 150 |
| T4 (N0P1K2GA3 3) | 10,000 | 800 | 2000 | 150 |
| T5 (N0P3K2GA3 1) | 10,000 | 1800 | 2000 | 50 |
| T6 (N0P3K1GA3 2) | 10,000 | 1800 | 1500 | 100 |
| T7 (N0P3K3GA3 3) | 10,000 | 1800 | 2500 | 150 |
| T8 (N0P1K3GA3 2) | 10,000 | 800 | 2500 | 100 |
| T9 (N0P1K1GA3 1) | 10,000 | 800 | 1500 | 50 |
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Treatments | Comprehensive Score | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fertilization Treatment in 2021 | Fertilization Treatment in 2022 | |||||
| High-Yield Clone | Middle-Yield Clone | Low-Yield Clone | High-Yield Clone | Middle-Yield Clone | Low-Yield Clone | |
| T1 | 0.2483 | 0.2306 | 0.2875 | 0.2597 | 0.2272 | 0.2609 |
| T2 | 0.2812 | 0.2446 | 0.2866 | 0.2544 | 0.2804 | 0.2598 |
| T3 | 0.2777 | 0.2967 | 0.2975 | 0.2409 | 0.2305 | 0.2599 |
| T4 | 0.2841 | 0.2488 | 0.2192 | 0.4315 | 0.2608 | 0.2885 |
| T5 | 0.2901 | 0.2608 | 0.2667 | 0.2098 | 0.2670 | 0.2779 |
| T6 | 0.2866 | 0.2012 | 0.2879 | 0.2469 | 0.2617 | 0.2600 |
| T7 | 0.2421 | 0.2492 | 0.2076 | 0.1552 | 0.2804 | 0.1746 |
| T8 | 0.2838 | 0.2198 | 0.2914 | 0.4627 | 0.296 | 0.2598 |
| T9 | 0.2842 | 0.2539 | 0.2826 | 0.1610 | 0.2849 | 0.2629 |
| CK | 0.2757 | 0.2760 | 0.2339 | 0.0753 | 0.2721 | 0.0772 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ye, D.; Zhou, J. The Effect of Minerals and Hormones on the Nutrients in Chinese Fir Leaves and Seed Set. Plants 2025, 14, 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060887
Duan Y, Zhao L, Ye D, Zhou J. The Effect of Minerals and Hormones on the Nutrients in Chinese Fir Leaves and Seed Set. Plants. 2025; 14(6):887. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060887
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Yu, Linying Zhao, Daiquan Ye, and Jian Zhou. 2025. "The Effect of Minerals and Hormones on the Nutrients in Chinese Fir Leaves and Seed Set" Plants 14, no. 6: 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060887
APA StyleDuan, Y., Zhao, L., Ye, D., & Zhou, J. (2025). The Effect of Minerals and Hormones on the Nutrients in Chinese Fir Leaves and Seed Set. Plants, 14(6), 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060887





