Functional Characterization of Pomegranate CAMTA3 in Cold Stress Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of CAMTA Genes in Pomegranate
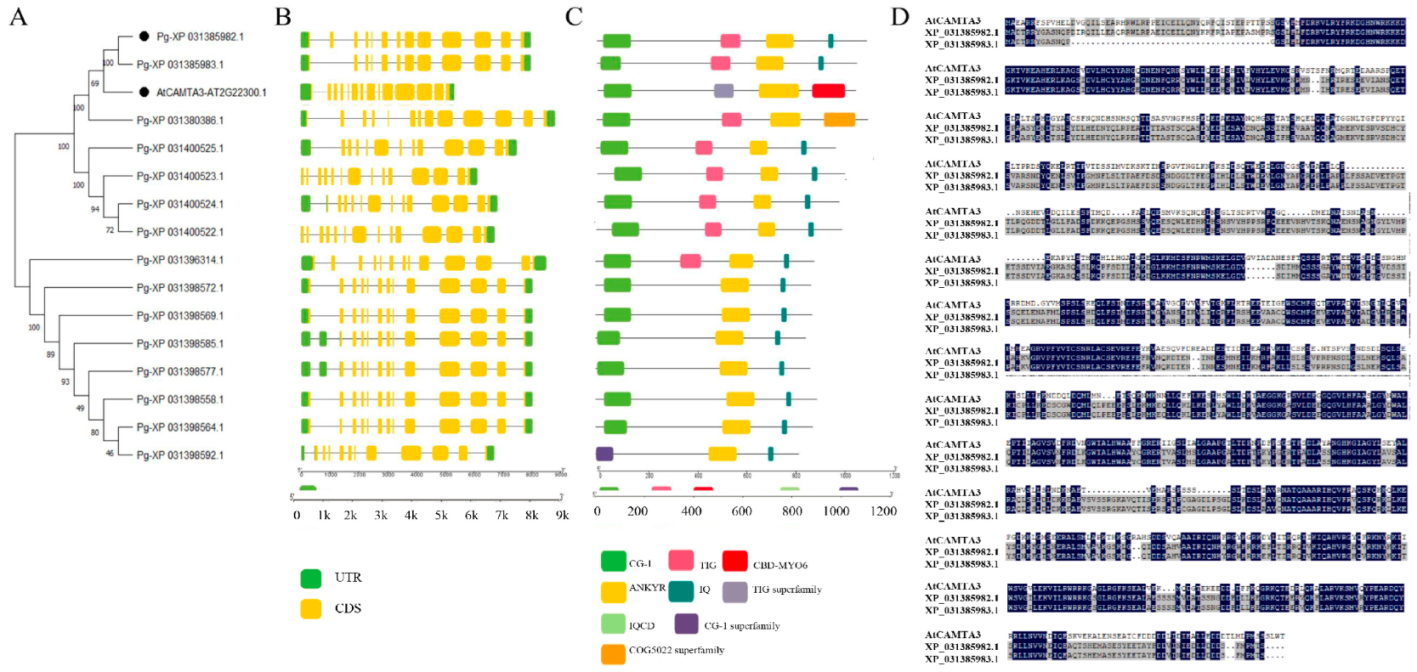
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of CAMTA Genes
2.3. Gene Structure Analysis of the CAMTA Genes in Pomegranate
2.4. Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements in the Promoter Regions of PgCAMTA3 Genes
2.5. The Expression of PgCAMTA3 Genes Under ABA and Cold Stress
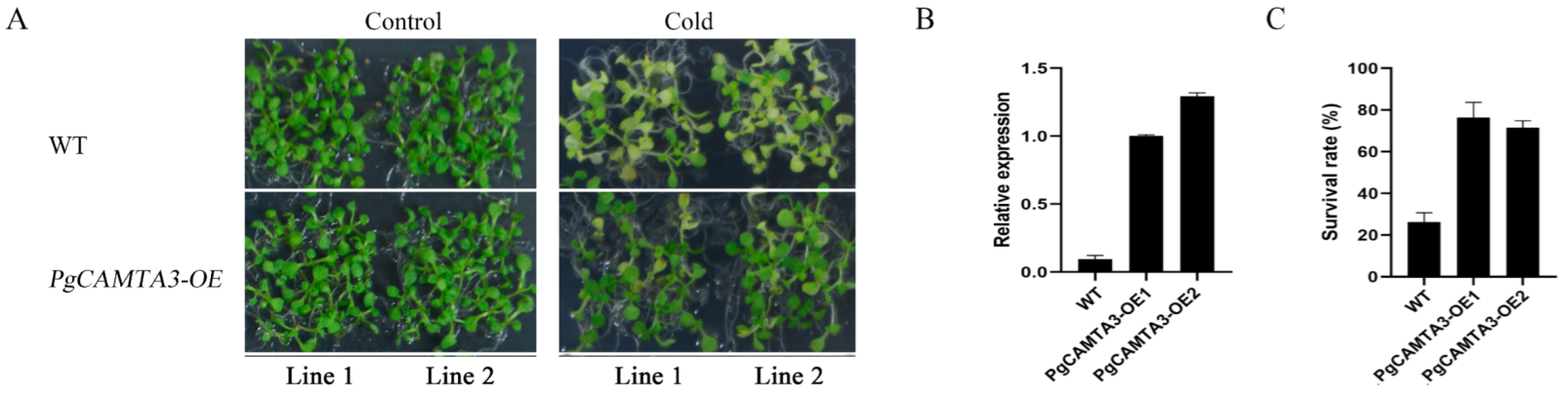
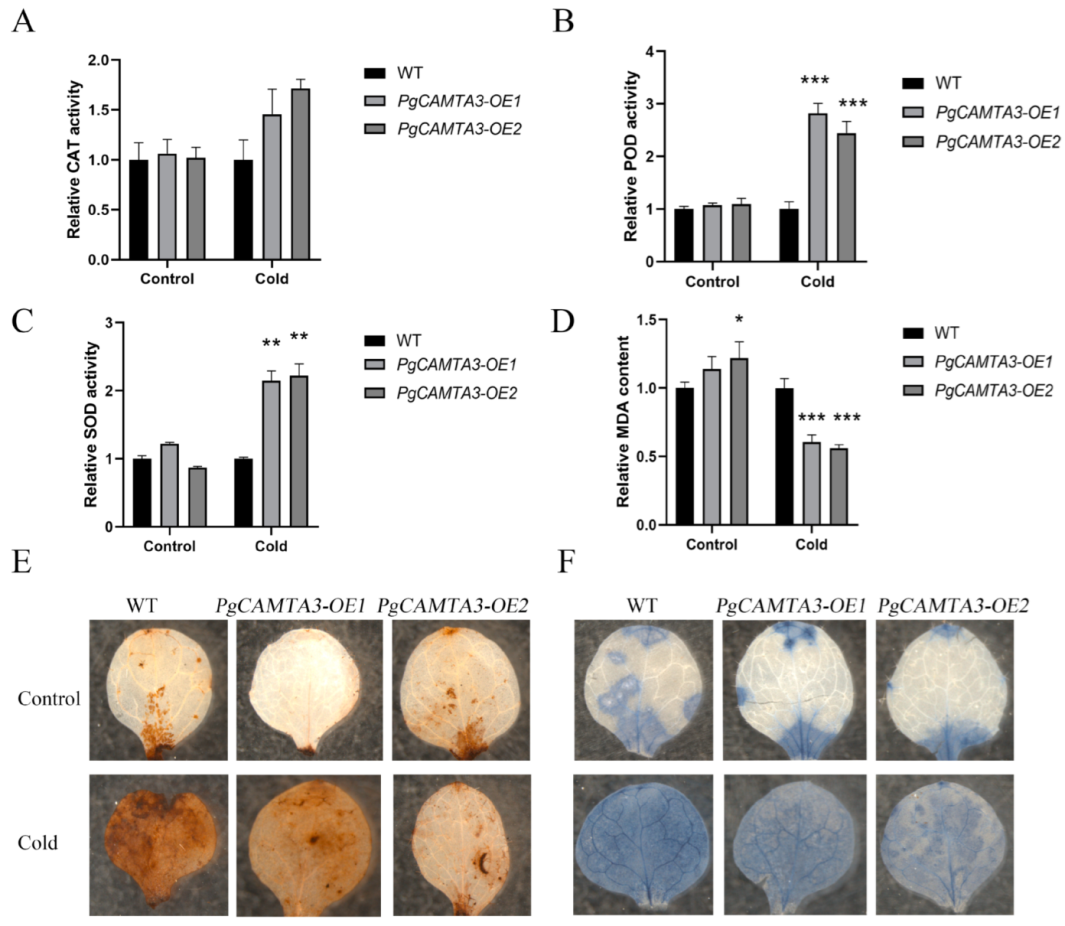
2.6. Overexpression of PgCAMTA3 Enhanced Freezing Tolerance in A. thaliana
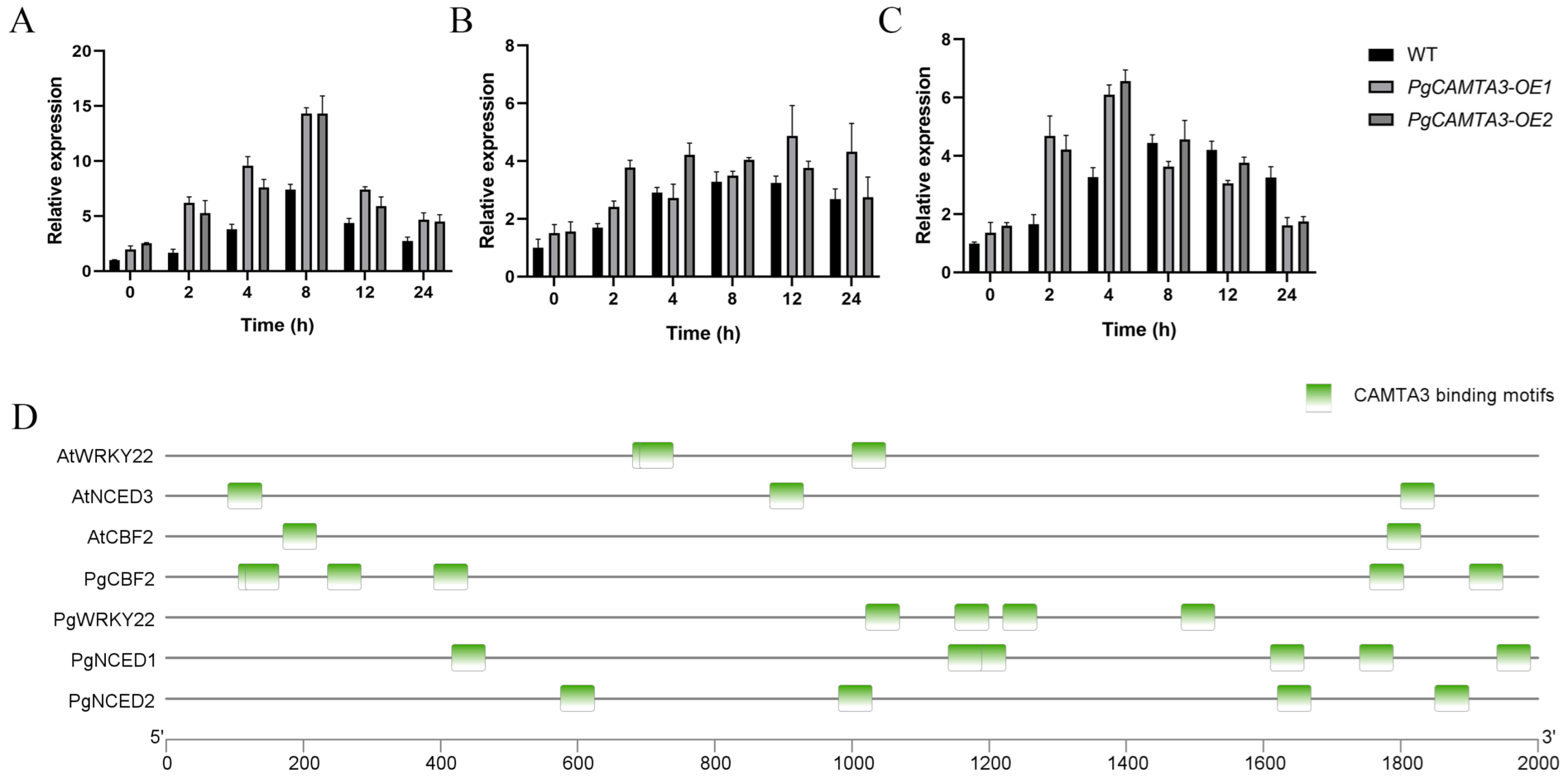
2.7. PgCAMTA3 Activated Downstream Genes in Transgenic A. thaliana
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material, Growth Conditions
4.2. Identification of CAMTA Genes
4.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.4. Prediction of the Motifs/Domains of CAMTA Genes
4.5. Recombination Vector Construction and Transgenic Plant Generation
4.6. Cold Tolerance Assays
4.7. RNA Isolation and qPCR Analysis
4.8. Determination of MDA Content and Enzyme Activities
4.9. Histochemical Staining
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, Z.; Xiong, L.; Shi, H.; Yang, S.; Herrera-Estrella, L.R.; Xu, G.; Chao, D.; Li, J.; Wang, P.; Qin, F.; et al. Plant abiotic stres response and nutrient use efficiency. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 635–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.K. Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidokoro, S.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Transcriptional regulatory network of plant cold-stress responses. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 922–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnusamy, V.; Zhu, J.H.; Zhu, J. Cold stress regulation of gene expression in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2007, 12, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Kidokoro, S.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. Regultory networks in plant response to drought and cold stress. Plant Physiol. 2024, 195, 170–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yang, S. Regulatory networks underlying plant responses and adaptation to cold stress. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2024, 58, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Li, Q.; Jiang, W.; Chen, G.; Xue, D.; Deng, F.; Zeng, F.; Chen, Z.H. Molecular evolution of calcium signaling and transport in plant adaption to abiotic stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Zhu, Q.; Yuan, P.; Yan, Y.; Yi, K.; Du, L. Calmodulin and calmodulin-like protein-mediated plant response to biotic stresses. Plant Cell Environ. 2023, 46, 3680–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkler, A.; Ashery-Padan, R.; Fromm, H. CAMTAs: Calmodulin-binding transcription activators from plants to human. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 3893–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Whalley, H.J.; Knight, M.R. Combining modelling and experimental approaches to explain how calcium signatures are decoded by calmodulin-binding transcription activators (CAMTAs) to produce specific gene expression responses. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, M.; Aysha, J.; Ketehouli, T.; Yang, J.; Du, L.; Wang, F.; Li, H. Calmodulin binding transcription activators: An interplay between calcium signaling and plant stress tolerance. Plant Physiol. 2021, 256, 153327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.B.; Peng, H.; Whitaker, B.D.; Jurick, W.M. Differential expression of calcium/calmodulin-regulated SISRs in response to abitotic and biotic stresses in tomato fruit. Physiol. Plant. 2013, 148, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shkolnik, D.; Finkler, A.; Pasmanik-Chor, M.; Fromm, H. Calmodulin-binding transcription activatior 6: A key regulator of Na(+) homeostasis during germination. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 1101–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, B.; Davydov, O.; Knight, H.; Galon, Y.; Knight, M.R.; Fluhr, R.; Fromm, H. Rapid transcriptome changes induced bycytosolic Ca2+ transients reveal ABRE-related sequences as Ca2+-responsive cis elements in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 2733–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Poovaiah, B.W. A calmodulin-binding/CGCG box DNA-binding protein family involved in multiple signaling pathways in plants. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 45049–45058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galon, Y.; Snir, O.; Fromm, H. How calmodulin binding transcription activators (CAMTAs) mediate auxin responses. Plant Signal. Behav. 2010, 5, 1311–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Doherty, C.J.; Van Buskirk, H.A.; Myers, S.J.; Thomashow, M.F. Roles for Arabidopsis CAMTA Transcription Factors in Cold-Regulated Gene Expression and Freezing Tolerance. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 972–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, N.; Ranjan, A.; Pant, P.; Tripathi, R.K.; Ateek, F.; Pandey, H.P.; Patre, U.V.; Sawant, S.V. CAMTA 1 regulates drought responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, K.J.; Vogel, M.O.; Viehhauser, A. AP2/EREBP transcription factors are part of gene regulatory networks and integrate metabolic, hormonal and environmental signals in stress acclimation and retrograde signalling. Protoplasma 2010, 245, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, S.; Thomashow, M.F. Arabidopsis transcriptome profiling indicates that multiple regulatory pathways are activated during cold acclimation in addition to the CBF cold response pathway. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 1675–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, S.J.; Zarka, D.G.; Stockinger, E.J.; Salazar, M.P.; Houghton, J.M.; Thomashow, M.F. Low temperature regulation of the Arabidopsis CBF family of AP2 transcriptional activators as an early step in cold-induced COR gene expression. Plant J. 1998, 16, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, T.H.; Lee, J.; Yang, P.T.; Chiu, L.H.; Charng, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Chan, M.T. Heterology expression of the Arabidopsis C-repeat/dehydration response element binding factor 1 gene confers elevated tolerance to chilling and oxidative stresses in transgenic tomato. Plant Physiol. 2002, 135, 1145. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Dong, F.S.; Hu, F.H.; Liu, Y.W.; Chai, J.F.; Zhao, H.; Lv, M.Y.; Zhou, S. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the calmodulin-binding transcription activator (CAMTA) gene family in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Genet. 2020, 21, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhao, M.; Xing, F.; Mao, G.; Wang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Niu, M.; Yuan, H. Identification and Expression Analysis of CAMTA Genes in Tea Plant Reveal Their Complex Regulatory Role in Stress Responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 910768. [Google Scholar]
- Noman, M.; Jameel, A.; Qiang, W.D.; Ahmad, N.; Liu, W.C.; Wang, F.W.; Li, H.Y. Overexpression of GmCAMTA12 Enhanced Drought Tolerance in Arabidopsis and Soybean. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tang, D. Comprehensive identiffcation and expression analysis of CAMTA gene family in Phyllostachys edulis under abiotic stress. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Li, M.; Yang, Z.; He, C.; Wu, Z.; Tong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, S. The Vital Role of the CAMTA Gene Family in Phoebe bournei in Response to Drought, Heat, and Light Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshirsagar, K.R.; Pathak, S.S.; Patil, S.M. Pomegranate (Punica granatum L): A fruitful fountain of remedial potential. Cureus 2023, 15, e45677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Xu, C.; Ming, R.; Tang, H.; Guyot, R.; Kramer, E.M.; Hu, Y. The pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) genome and the genomics of punicalagin biosynthesis. Plant J. 2017, 91, 1108–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumawat, S.; Sharma, Y.; Vats, S.; Sudhakaran, S.; Sharma, S.; Mandlik, R.; Raturi, G.; Kumar, V.; Rana, N.; Kumar, A.; et al. Understanding the role of SWEET genes in fruit development and abiotic stress in pomegranate (Punica granatum L.). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, S.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, J. A genome-wide analysis of the BAM gene family and identification of the cold-responsive genes in Pomegrnate (Punica granatum L.). Plants 2024, 13, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doddaraju, P.; Kumar, P.; Dashyal, M.S.; Girigowda, M. Identification of suitable reference genes for expression studies in pomegranate under different biotic and abiotic stress conditions. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 3935–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouché, N.; Scharlat, A.; Snedden, W.; Bouchez, D.; Fromm, H. A novel family of calmodulin-binding transcription activators in multicellular organisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 21851–21861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.S.; Kim, M.C.; Yoo, J.H.; Moon, B.C.; Koo, S.C.; Park, B.O.; Lee, J.H.; Koo, Y.D.; Han, H.J.; Lee, S.Y. Isolation of a calmodulin-binding transcription factor from rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 40820–40831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, R.; Lu, C.; Sun, T.; Peng, T.; Han, X.; Qi, J.; Yan, S.; Tie, S. Identification and expression profiling analysis of calmodulin-binding transcription activator genes in maize (Zea mays L.) under abiotic and biotic stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Dai, X.; Xu, Y.; Luo, W.; Zheng, X.; Zeng, D.; Pan, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, D.; et al. COLD1 confers chilling tolerance in rice. Cell 2015, 160, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Jiang, X.; Zhong, G.; Wang, W.; Hake, K.; Matschi, S.; Lederer, S.; Hoehenwarter, W.; Sun, Q.; Lee, J.; et al. CAMTA3 repressor destabilization triggers TIR domain protein TN2-mediated autoimmunity in the Arabidopsis exo70B1 mutant. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 2021–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Shi, A.; Mou, B. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the CBF/DREB1 gene family in lettuce. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riechmann, J.L.; Meyerowitz, E.M. The AP2/EREBP family of plant transcription factors. Biol. Chem. 1998, 379, 633–646. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Du, J.; Jiao, R.; Wang, X.; Fang, T.; Huang, G. Genome-wide identification of CAMTA gene family in teak (Tectona grandis) and functional characterization of TgCAMTA1 and TgCAMTA3 in cold tolerance. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Xie, B.; Hou, Y.; Zhao Li Hu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, P.; Jin, P. PpCaM7 and PpCAMTA5 synergistically mitigate chilling-induced browning by suppressing reactive oxygen species synthesis in peach fruit. Postharvest Biol. Tec. 2024, 214, 112978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, K.; Ivanov, R.; Eutebach, M.; Büsra Acaroglu Mohr, I.; Bauer, P. Mobility and localization of the iron deficiency-induced transcription factor bHLH039 change in the presence of FIT. Plant Direct 2019, 3, e00190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Mora-Garcia, S.; Li, J.; Yoshida, S.; Asami, T.; Chory, J. BES1 accumulates in the nucleus in response to brassinosteroids to regulate gene expression and promote stem elongation. Cell 2002, 109, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio, M.B.; Ng, S.; Berkowitz, O.; De Clercq, I.; Mao, C.; Shou, H.; Jost, R. SPX4 acts on PHR1-dependent and -independent regulation of shoot phosphorus status in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2019, 181, 332–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ye, K.Y.; Shi, Y.T.; Cheng, J.K.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yang, S.H. BZR1 positively regulates dreezing tolerance via CBF-dependent and CBF-independent pathways in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, C.M.; Doherty, C.J.; Gilmour, S.J.; Kim, Y.; Thomashow, M.F. Regulation of the Arabidopsis CBF regulon by a complex low temperature regulatory network. Plant J. 2015, 82, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, S.J.; Bent, A.F. Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998, 16, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Ban, Q.; Hao, J.; Zhu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Mao, J.; Lin, M.; Xia, E.; Li, Y. Genome-wide characterization of the C-repeat binding factor (CBF) gene family involved in the response to abiotic stresses in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Huang, C.; Deng, X.; Zhou, S.; Chen, L.; Li, Y. TaASR1, a transcription factor gene in wheat, confers drought stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Environ. 2013, 36, 1449–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, L.; Li, X.; Ouyang, Z.G.; Yu, Y.M.; Li, D.Y. Overexpression of a rice long-chain base kinase gene OsLCBK1 in tobacco improves oxidative stress tolerance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2013, 30, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwarari, D.; Guan, Y.; Ahmad, B.; Movahedi, A.; Min, T.; Hao, Z.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, L. ICE-CBF-COR signaling cascade and its regulation in plants responding to cold stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, S.; Lu, R.; Feng, L.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, H.; Yin, Y.; Zheng, L. Functional Characterization of Pomegranate CAMTA3 in Cold Stress Responses. Plants 2025, 14, 813. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050813
Zhao S, Lu R, Feng L, Zheng M, Zhang H, Yin Y, Zheng L. Functional Characterization of Pomegranate CAMTA3 in Cold Stress Responses. Plants. 2025; 14(5):813. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050813
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Shuangshuang, Rui Lu, Lijuan Feng, Mengyu Zheng, Han Zhang, Yanlei Yin, and Ling Zheng. 2025. "Functional Characterization of Pomegranate CAMTA3 in Cold Stress Responses" Plants 14, no. 5: 813. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050813
APA StyleZhao, S., Lu, R., Feng, L., Zheng, M., Zhang, H., Yin, Y., & Zheng, L. (2025). Functional Characterization of Pomegranate CAMTA3 in Cold Stress Responses. Plants, 14(5), 813. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050813





