Comprehensive Phytohormone Analysis Reveals the Roles of Auxin, Cytokinin, and Gibberellin in Enhancing Seed Germination and Growth of Chimonobambusa utilis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material Collection and Preparation
2.2. Morphological and Nutritional Characterization
2.3. Phytohormone Preparation and Seed Treatment Procedures
2.4. Seed Germination and Seedling Development
2.5. Determination of Soluble Sugar and Starch Content
2.6. Enzyme Activity Assays
2.6.1. Sucrose-Metabolizing Enzyme Activities
2.6.2. Starch-Degrading Enzyme Activities
2.6.3. Starch-Synthesizing Enzyme Activities
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
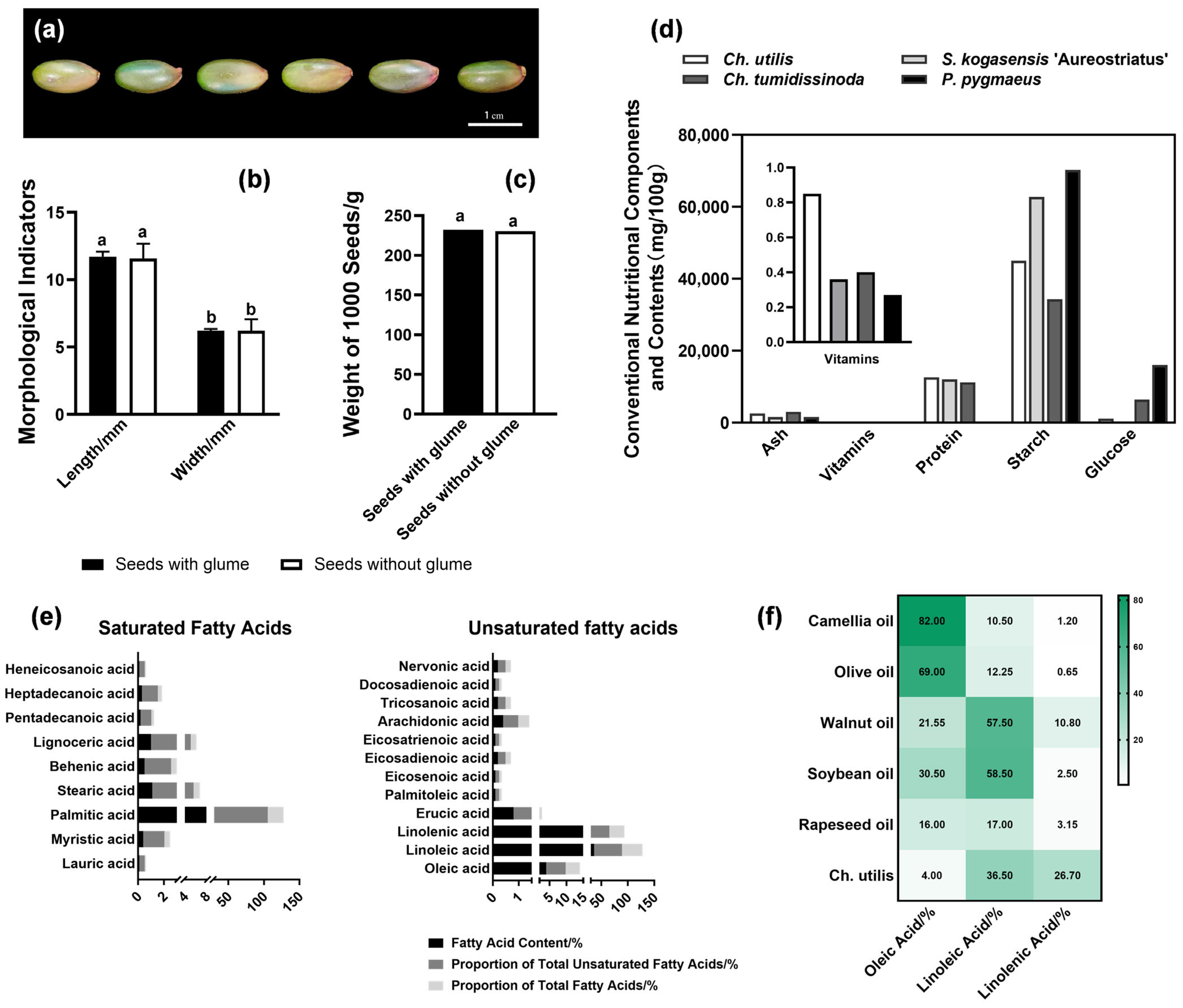
3.1. Nutritional Quality Assessment of Seeds in Ch. utilis
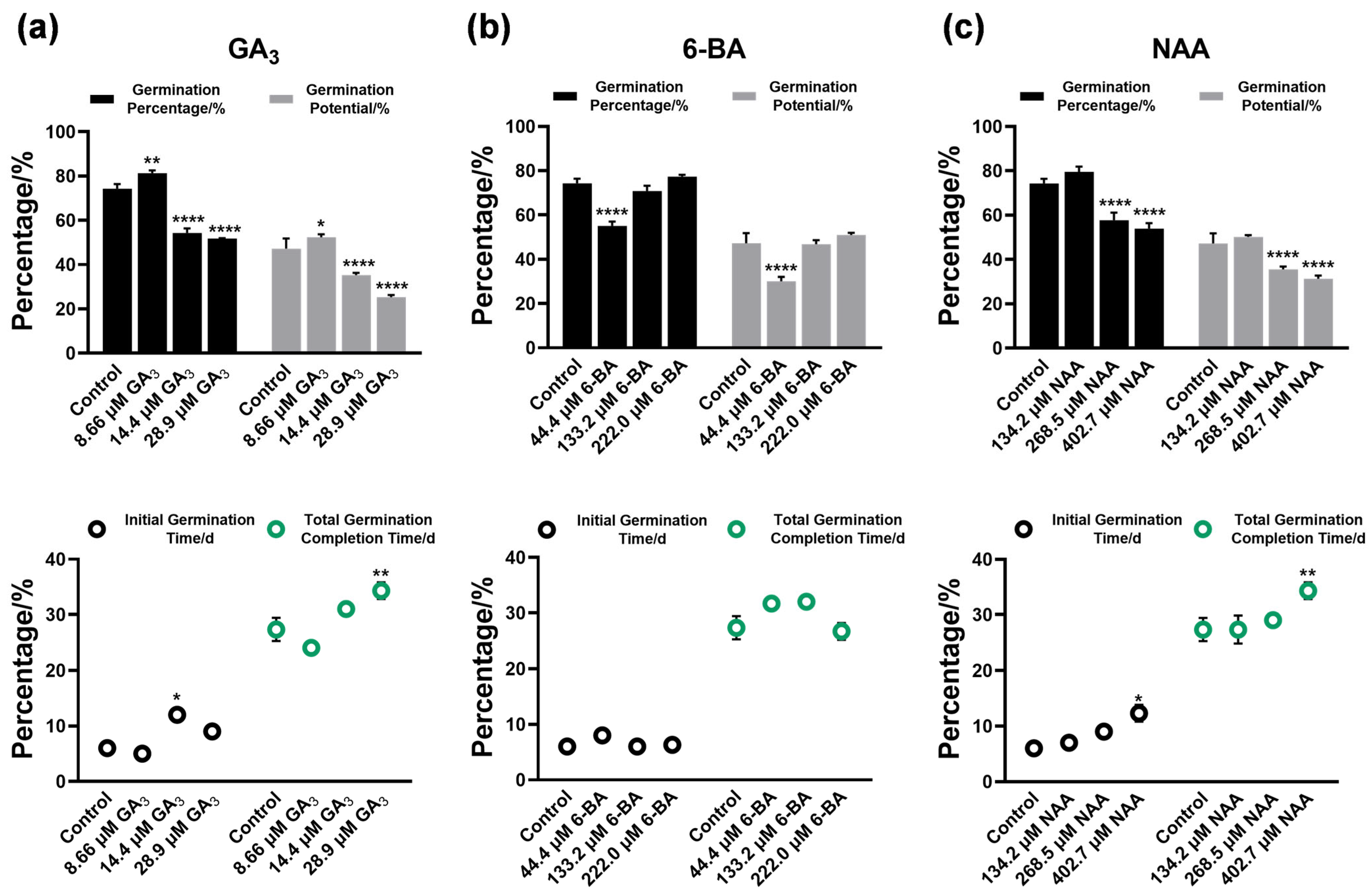
3.2. Regulatory Effects of Plant Growth Regulators on Seed Germination
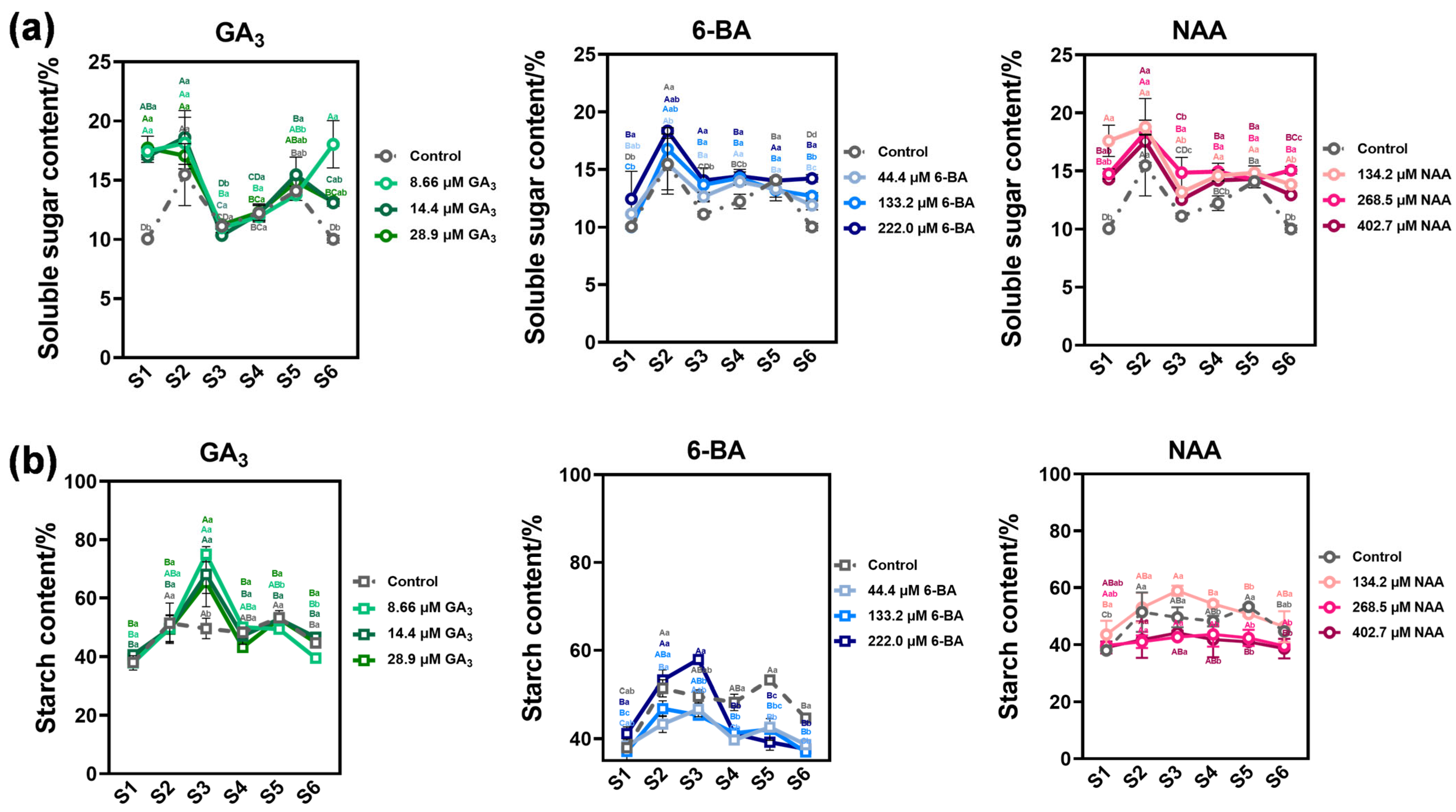
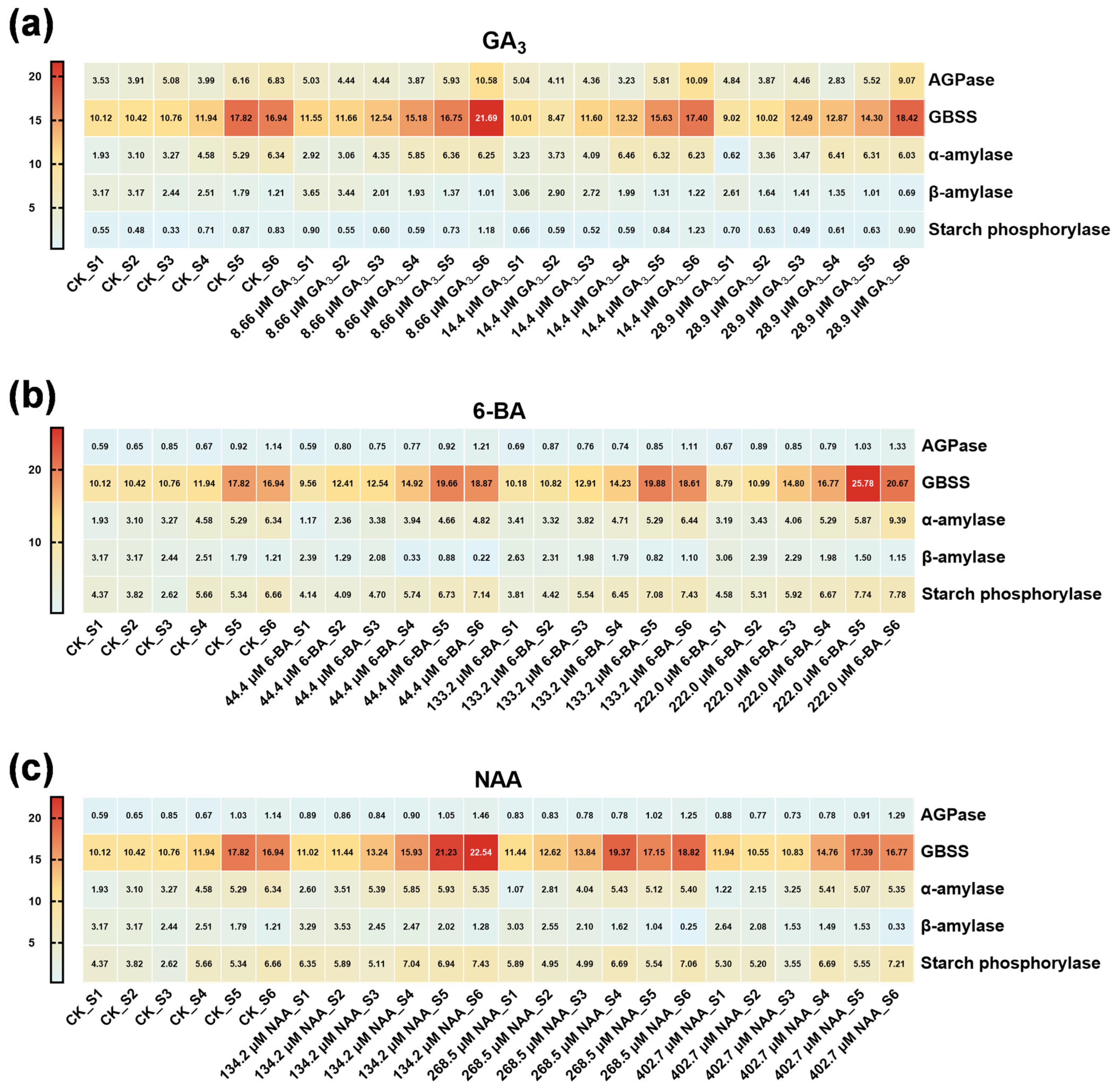
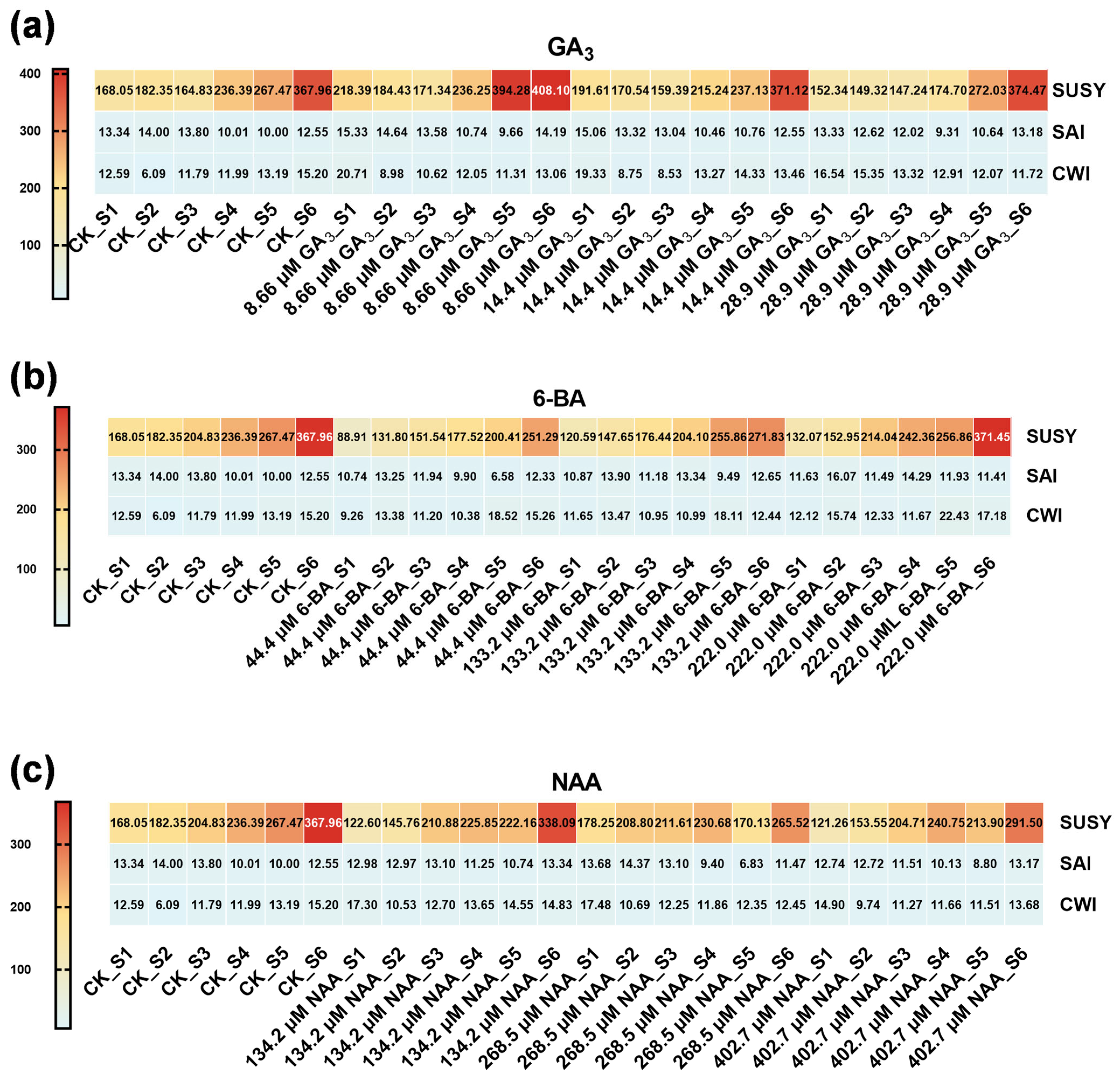
3.3. Phytohormone Regulation of Seed Storage Substance Dynamics in Ch. utilis Seeds
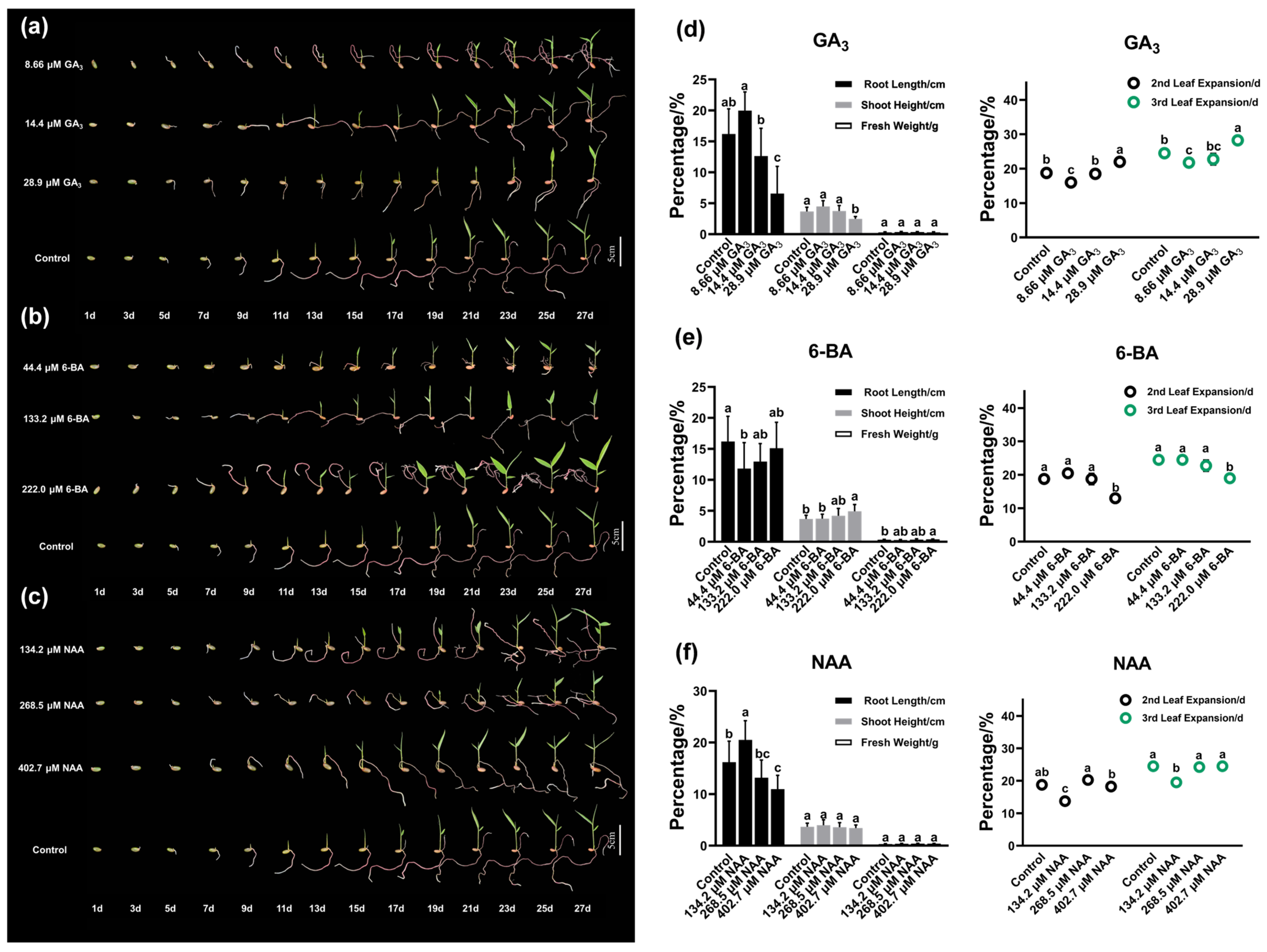
3.4. Effects of PGR on Growth Traits of Ch. utilis Seedling
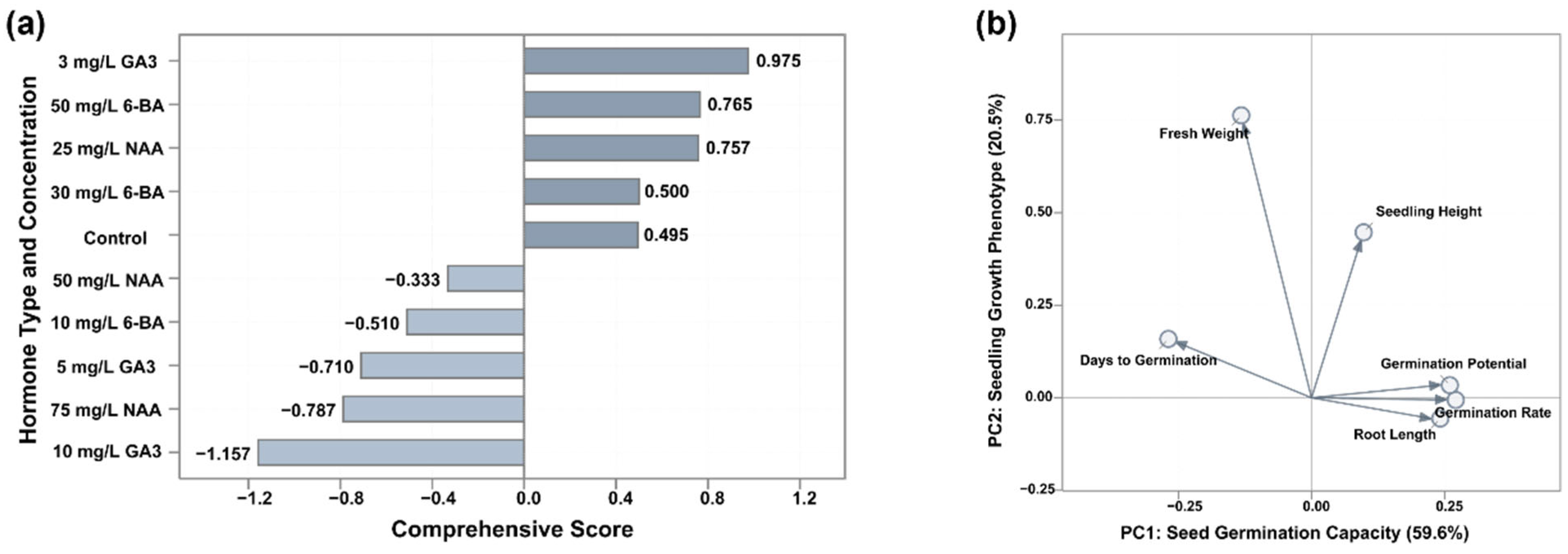
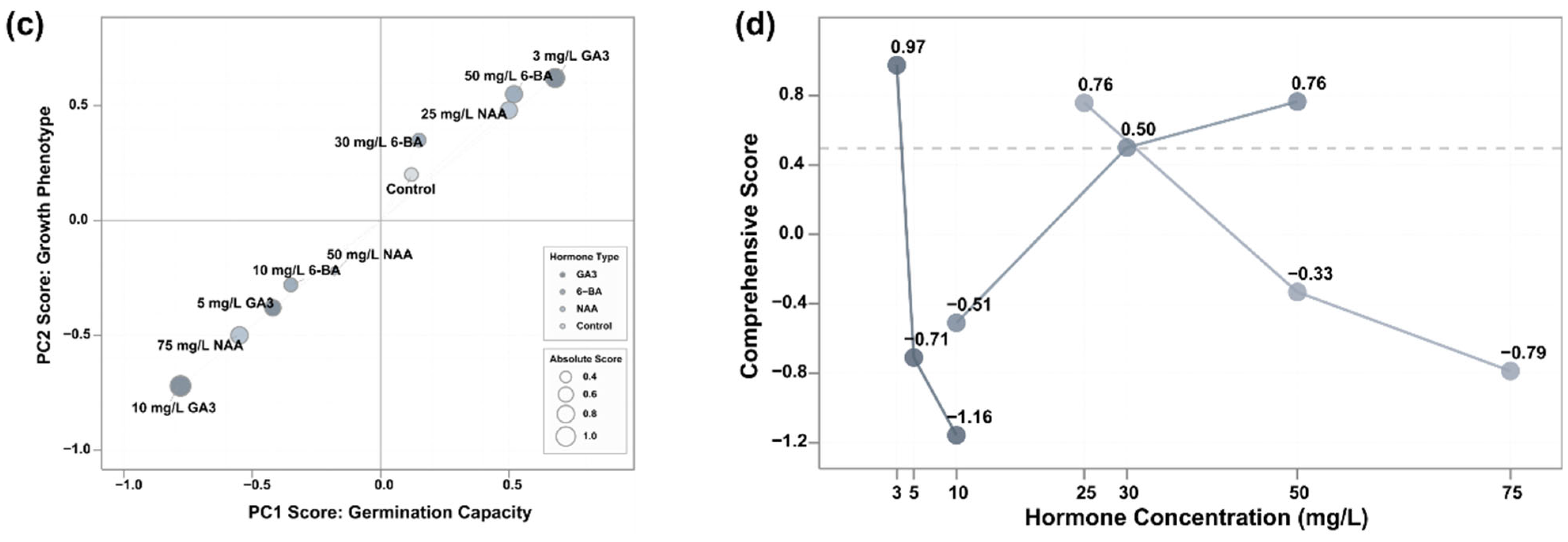
3.5. Multifactorial Comprehensive Evaluation
4. Discussion
4.1. Nutritional Advantages and Edible Potential of Ch. utilis Seeds
4.2. Differential Phytohormone Regulation Patterns and Physiological Mechanisms
4.3. Enzymatic Regulation of Starch and Sucrose Metabolism
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Linkies, A.; Graeber, K.; Knight, C.; Leubner-Metzger, G. The evolution of seeds. N. Phytol. 2010, 186, 817–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch-Savage, W.E.; Leubner-Metzger, G. Seed dormancy and the control of germination. N. Phytol. 2006, 171, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewley, J.D.; Bradford, K.J.; Hilhorst, H.W.M.; Nonogaki, H. Seeds: Physiology of Development, Germination and Dormancy; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajjou, L.; Duval, M.; Gallardo, K.; Catusse, J.; Bally, J.; Job, C.; Job, D. Seed germination and vigor. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2012, 63, 507–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitbrecht, K.; Müller, K.; Leubner-Metzger, G. First off the mark: Early seed germination. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 3289–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonogaki, H. Seed germination and dormancy: The classic story, new puzzles, and evolution. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2019, 61, 541–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Lin, S.Y.; Fu, H.J.; Wan, Y.W.; Ding, Y.L. The bamboo flowering cycle sheds light on flowering diversity. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.Q.; Guo, C.C.; Yao, W.J.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Y.L.; Yang, Z.Z.; Lin, S.Y. Comparative phylogenomic analyses and co-expression gene network reveal insights in flowering time and aborted meiosis in woody bamboo, Bambusa oldhamii ‘Xia Zao’ ZSX. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1023240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Xue, J.R.; Yang, Y.M.; Hui, Z.M.; Wang, J. Study on flowering phenomenon and its type of bamboo in yunnan in past fifteen years. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2000, 6, 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.Q.; Wu, Z.C.; Xiao, J.; Guo, C.C.; Yang, G.Y.; Yu, F. Flowering biological characteristics of Pseudosasa viridula. For. Res. 2020, 33, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.L.; Lin, S.Y.; Wei, Q.; Yao, W.J.; Que, F.; Li, L. Advances in developmental biology of bamboos. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 46, 23–40. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, C.J.; Peng, Z.H.; Gao, J.; Wang, H.X.; Liu, F. Seed germination characteristics of Phyllostachys edulis. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2008, 24, 163–167. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, L.J.; Wan, Y.W.; Su, J.L.; Yang, Y.Y.; Li, F.; Shi, P.J.; Ding, Y.L.; Lin, S.Y. Effect of temperature on seed germination and seedling growth of Qiongzhuea tumidinoda. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2019, 46, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, L.J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, J.P.; Lin, S.Y.; Ding, Y.L. The effect on the seed vitality of Pleioblastus pygmaeus under the conditions of different storage temperature and moisture content. Seed 2018, 37, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.Q.; Chen, L.N.; Cui, Y.Z.; Yang, H.Q. Optimum sterilization conditions and germination characteristics of dendrocalamus brandisii and D. membranaceus seeds. For. Res. 2018, 31, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Jiang, M.Y.; Zhang, L.; Lin, S.Y.; Ding, Y.L. Fruit morphological characteristics of thirteen bamboo species. J. Plant Resour. Environ. 2016, 25, 96–103. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.H.; Tao, X.L.; Tan, R.Q. A study of low temperature seeds storage conditions and seedling environment of 13 species of bamboos. World Bamboo Ratt. 2018, 16, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y.; Lin, S.Y.; Ding, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Qin, M.; Cai, O. Study on development characteristics and dynamic changes of starch granules in the fruit of Chimonobambusa utilis. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 47, 150–158. [Google Scholar]
- Miransari, M.; Smith, D.L. Plant hormones and seed germination. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 99, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, K.; Liu, X.D.; Xie, Q.; He, Z.H. Two faces of one seed: Hormonal regulation of dormancy and germination. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishal, B.; Kumar, P.P. Regulation of seed germination and abiotic stresses by gibberellins and abscisic acid. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, T.; Schmülling, T. Cytokinin action in plant development. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortleven, A.; Leuendorf, J.E.; Frank, M.; Pezzetta, D.; Bolt, S.; Schmülling, T. Cytokinin action in response to abiotic and biotic stresses in plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 998–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, A.W.; Bartel, B. Auxin: Regulation, action, and interaction. Ann. Bot. 2005, 95, 707–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunewald, W.; Friml, J. The march of the PINs: Developmental plasticity by dynamic polar targeting in plant cells. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 2700–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.C.; Ye, Y.X. Effects of different concentrations of GA3, IAA and 6-BA on seed germination of snake melon. J. Yangtze Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2011, 8, 229–232+216. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.J.; Qi, J.; Ma, H.P.; Wu, S.L.; Jin, X.; Sun, S.J.; Liu, W.H. Effect of 6-BA on the growth and physiological characteristics of Elymus sibiricus seedlings under salt stress. Pratacultural Sci. 2018, 35, 2174–2182. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.H.; Guan, X.L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S.Q. Effects of plant growth regulators GA3 and 6-BA on seed germination characteristic of Clematis glauca. Seed 2010, 29, 44–45+50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, S.H.; Jia, N. Effects of different concentrations of gibberellin on seed germination in Eucommia ulmoides. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2019, 47, 144–146+185. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S. Effect of NAA soaking on seed germination of Limonium anumerum. J. Green Sci. Technol. 2021, 23, 106–108+116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, T.; Dai, M.H.; Gu, F.P.; A, M.N.; Du, K.B. Effects of different reagents on seed germination of low-temperature stored Taiwania flousiana. J. Hubei Minzu Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 42, 11–17+25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, L.L.; Yang, L.; Wu, H.Y.; Yao, W.J.; Ding, Y.L.; Lin, S.Y. Comparisons of seedling growth traits in two leaf variation types of Chimonobambusa utilis. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2023, 51, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.L. Vertical distribution of Chimonobambusa utilis and its shoot yield and quality after introduced to different places at low elevation. World Bamboo Ratt. 2021, 19, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.L.; Gao, G.B.; Zhang, F.S.; Zheng, J.; Wu, L.R. Quality analysis and evaluation of five cultivars of Chimonobambusa quadrangularis shoots with color shell from jinfoshan mountain. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.X.; Long, Z.H. Research progress on nutritional value and storage technology of Chimonobambusa utilis bamboo shoots. China Food Saf. Mag. 2021, 26, 133–134+136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ying, J.Y.; Wu, L.R.; Zhou, C.P. Study on the nutritional components of mineral elements in Chimonobambusa utilis shoots. Stud. Trace Elem. Health 2008, 1, 27–28. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, L.L.; Qin, M.; Wang, F.S.; Ding, Y.L.; Yao, W.J.; Li, L.; Huang, F.Y.; Lin, S.Y. Nutrient composition and potential feeding value of Chimonobambusa utilis shoot sheath. World Bamboo Ratt. 2023, 21, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Y.L. Seed nutrients and seedling breeding of Chimonobambusa utilis in daloushan mountains. World Bamboo Ratt. 2021, 19, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- GB 5009.5-2016; Determination of Protein in Foods. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.6-2016; Determination of Fat in Foods. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.124-2016; Determination of Amino Acid in Foods. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.82-2016; Determination of Vitamins A, D and E in Foods. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.168-2016; Determination of Fatty Acid in Foods. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Harris, W.S.; Mozaffarian, D.; Rimm, E.; Kris-Etherton, P.; Rudel, L.L.; Appel, L.J.; Engler, M.M.; Engler, M.B.; Sacks, F. Omega-6 fatty acids and risk for cardiovascular disease: A science advisory from the American Heart Association Nutrition Subcommittee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation 2009, 119, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzmann-Petithory, D. Alpha-linolenic acid and cardiovascular diseases. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2001, 5, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawade, K.; Tabeta, H.; Ferjani, A.; Hirai, M.Y. The roles of functional amino acids in plant growth and development. Plant Cell Physiol. 2023, 64, 1482–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, S.A.; Tyerman, S.D.; Gilliham, M.; Xu, B. γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) signalling in plants. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 1577–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnersley, A.M.; Turano, F.J. Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) and plant responses to stress. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2000, 19, 479–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan-Wilson, A.L.; Wilson, K.A. Mobilization of seed protein reserves. Physiol. Plant. 2012, 145, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, B.; Cohn, M.A.; Leubner-Metzger, G. Plant hormone interactions during seed dormancy release and germination. Seed Sci. Res. 2005, 15, 281–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdsworth, M.J.; Bentsink, L.; Soppe, W.J. Molecular networks regulating Arabidopsis seed maturation, after-ripening, dormancy and germination. N. Phytol. 2008, 179, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.D.; Gao, X.; He, P.; Xiao, G.H. Origin, evolution, and molecular function of DELLA proteins in plants. Crop J. 2022, 10, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hou, X. Antagonistic regulation of ABA and GA in metabolism and signaling pathways. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ildoo, H.; Jen, S.; Bruno, M. Cytokinin signaling networks. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2012, 63, 353–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Rovere, F.; Fattorini, L.; D’Angeli, S.; Veloccia, A.; Falasca, G.; Altamura, M.M. Auxin and cytokinin control formation of the quiescent centre in the adventitious root apex of Arabidopsis. Ann. Bot. 2013, 112, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, J.L.; Li, X.F.; Guo, G.Q. Cytokinin-controlled gradient distribution of auxin in Arabidopsis root tip. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, T.; Motyka, V.; Laucou, V.; Smets, R.; Van Onckelen, H.; Schmülling, T. Cytokinin-deficient transgenic Arabidopsis plants show multiple developmental alterations indicating opposite functions of cytokinins in the regulation of shoot and root meristem activity. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2532–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overvoorde, P.; Fukaki, H.; Beeckman, T. Auxin control of root development. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a001537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanova, A.N.; Robertson-Hoyt, J.; Yun, J.; Benavente, L.M.; Xie, D.Y.; Doleža, K.; Schlereth, A.; Jürgens, G.; Alonso, J.M. TAA1-mediated auxin biosynthesis is essential for hormone crosstalk and plant development. Cell 2008, 133, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Wysocka-Diller, J. Phytohormone signalling pathways interact with sugars during seed germination and seedling development. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 3359–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Wen, X.X.; Liao, Y.C. Effect of polyamine on seed germination of wheat under drought stress is related to changes in hormones and carbohydrates. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 2759–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, H.X.; Yan, H.; Qiu, L.; Baskin, C.C. Mobilization and role of starch, protein, and fat reserves during seed germination of six wild grassland species. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.J.; Jiang, W.; Wu, K.J.; Chen, J.D.; Li, Y.P.; Tao, Z.M. Integrating transcriptomics and hormones dynamics reveal seed germination and emergence process in Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, J.M.; Sorooshzadeh, A.; Modarres Sanavy, S.A.M.; Allahdadi, I.; Moradi, F. Effects of the exogenous application of auxin and cytokinin on carbohydrate accumulation in grains of rice under salt stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2011, 65, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Stitt, M. Coordination of carbon supply and demand during growth. Plant Cell Environ. 2007, 30, 1126–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Street, H.E.; Cockburn, W. Plant metabolism, the diverse chemistry set of the future. Science 2014, 353, 1232–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Ortiz, F.A.; Castro-Rosas, J.; Gómez-Aldapa, C.A.; Mora-Escobedo, R.; Rojas-León, A.; Rodríguez-Marín, M.L.; Román-Gutiérrez, A.D. Enzyme activity during germination of different cereals: A review. Food Rev. Int. 2019, 35, 177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.W.; Hannah, L.C. Adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase, a rate-limiting step in starch biosynthesis. Physiol. Plant. 1998, 103, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M. The biosynthesis of starch granules. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Henson, C.A. A quantitative assessment of the importance of barley seed α-amylase, β-amylase, debranching enzyme, and α-glucosidase in starch degradation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1991, 284, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.L. Sucrose metabolism: Gateway to diverse carbon use and sugar signaling. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 33–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, H.; Scofield, G.N.; Badger, M.R.; Chow, W.S.; Furbank, R.T.; Ruan, Y.L. Localization of sucrose synthase in developing seed and siliques of Arabidopsis thaliana reveals diverse roles for SUS during development. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 3283–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourey, P.S.; Nelson, O.E. The enzymatic deficiency conditioned by the shrunken-1 mutations of maize. Biochem. Genet. 1976, 14, 1041–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, J.; Barratt, P.; Tatge, H.; Dejardin, A.; Handley, L.; Gardner, C.D.; Barber, L.; Wang, T.; Hedley, C.; Martin, C.; et al. Mutations at the rug4 locus alter the carbon and nitrogen metabolism of pea plants through an effect on sucrose synthase. Plant J. 1999, 17, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Counce, P.A.; Gravois, K.A. Sucrose synthase activity as a potential indicator of high rice grain yield. Crop Sci. 2006, 46, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, W.; Ai, S.; Yuan, H.; Lv, M.; Lin, S. Comprehensive Phytohormone Analysis Reveals the Roles of Auxin, Cytokinin, and Gibberellin in Enhancing Seed Germination and Growth of Chimonobambusa utilis. Plants 2025, 14, 3780. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14243780
Zhao W, Ai S, Yuan H, Lv M, Lin S. Comprehensive Phytohormone Analysis Reveals the Roles of Auxin, Cytokinin, and Gibberellin in Enhancing Seed Germination and Growth of Chimonobambusa utilis. Plants. 2025; 14(24):3780. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14243780
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Wanqi, Simei Ai, Haixiang Yuan, Mingzhen Lv, and Shuyan Lin. 2025. "Comprehensive Phytohormone Analysis Reveals the Roles of Auxin, Cytokinin, and Gibberellin in Enhancing Seed Germination and Growth of Chimonobambusa utilis" Plants 14, no. 24: 3780. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14243780
APA StyleZhao, W., Ai, S., Yuan, H., Lv, M., & Lin, S. (2025). Comprehensive Phytohormone Analysis Reveals the Roles of Auxin, Cytokinin, and Gibberellin in Enhancing Seed Germination and Growth of Chimonobambusa utilis. Plants, 14(24), 3780. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14243780





