Characterization of Grain Structure Using Micro-CT and Identification of Related Candidate Genes by QTL Mapping in Foxtail Millet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Three-Dimensional Structure of All Tested Grains
2.2. Relationship Between Different Traits of All Tested Grains
2.3. Phenotypic Analysis for Foxtail Millet Grains
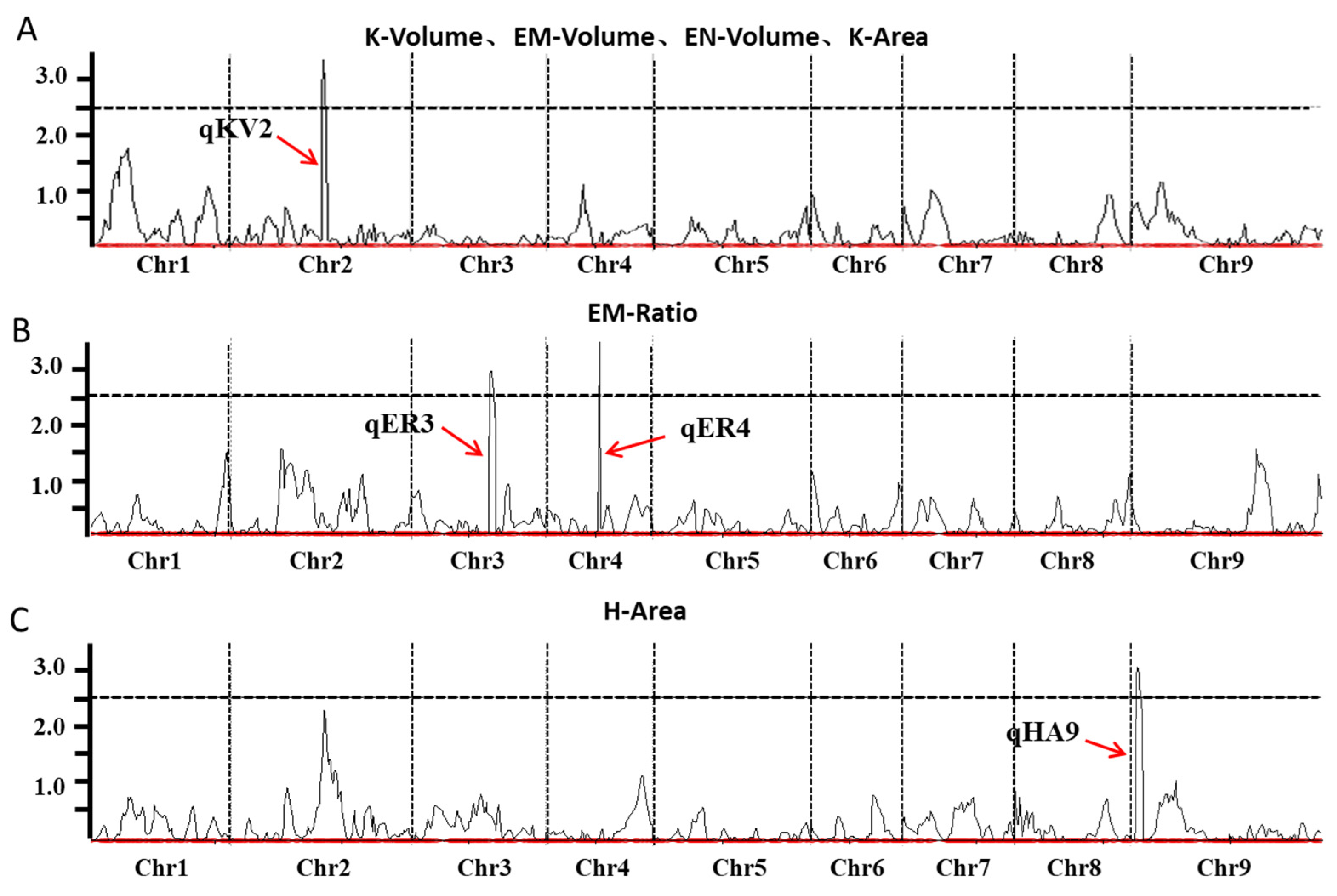
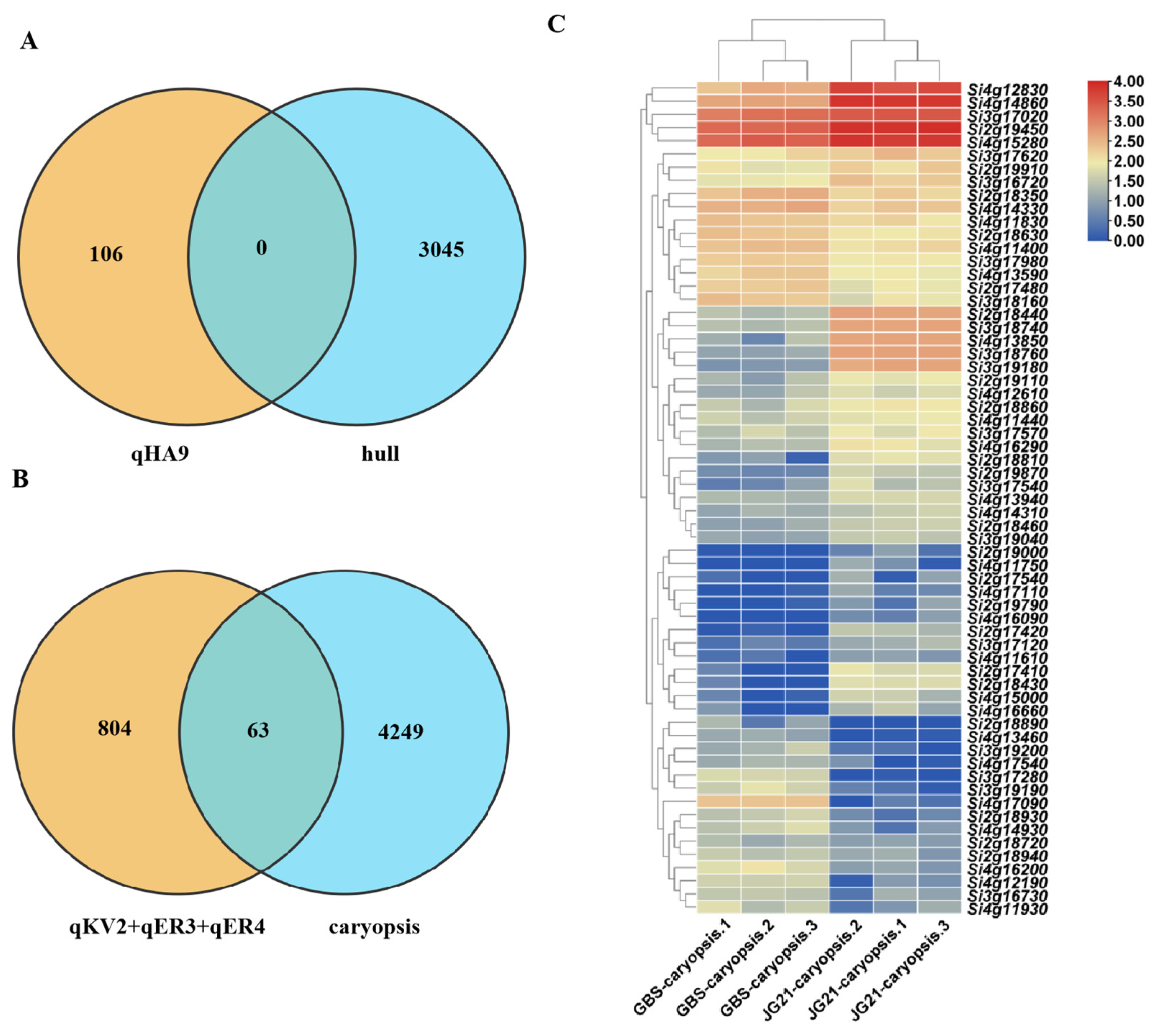
2.4. Identification of QTLs Related to Grain Structures in Foxtail Millet
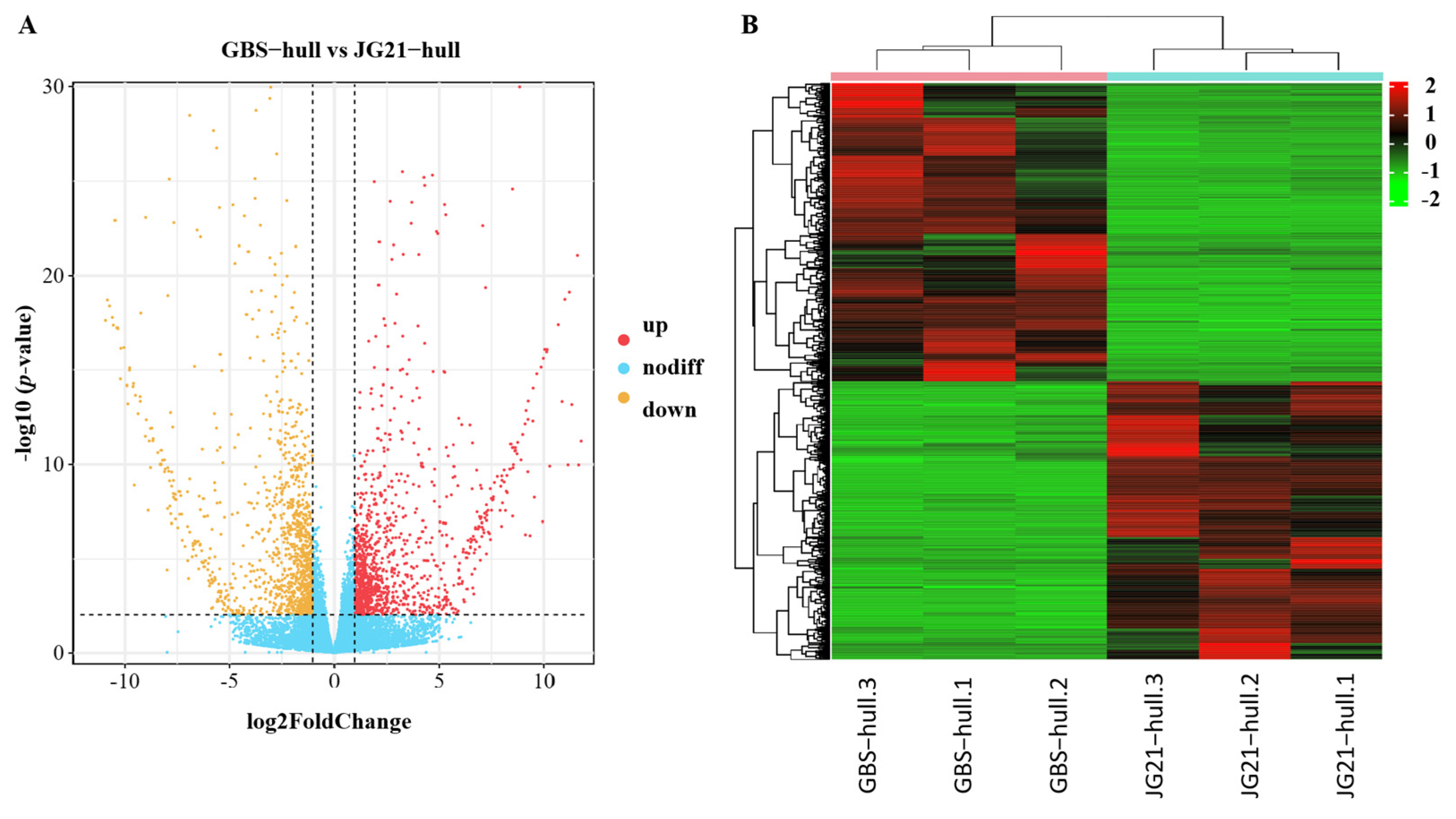
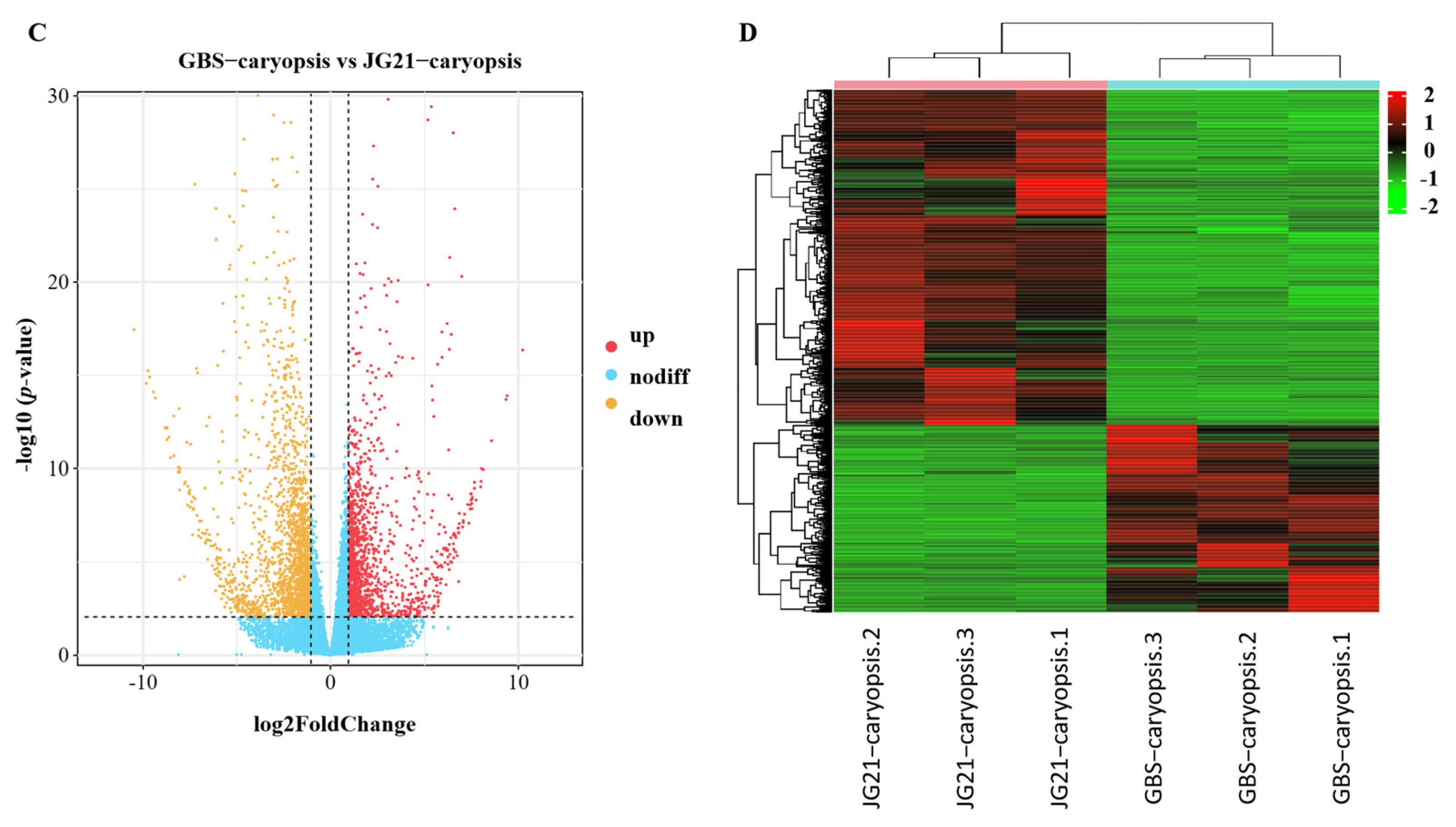
2.5. Differentially Expressed Genes During Grain Development Between Varieties with Different Grain Structures
2.6. Expression Analysis of Candidate Genes Related to Grain Structure
2.7. Functional Prediction of Candidate Genes for Grain Structure
3. Discussion
3.1. Grain Structure Characteristics
3.2. QTL Mapping and Identification of Candidate Genes in Combination with Transcriptome Profiling
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Data Acquisition and Analysis
4.3. QTL Mapping and Transcriptome Analysis
4.4. Functional Analysis of Candidate Genes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| QTL | Quantitative trait loci |
| RILs | Recombination inbred lines |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscope |
| CV | Coefficient of phenotypic variation |
| PVE | Phenotypic variation |
| LOD | Logarithm of odds scores |
| Add | Additive effects |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
References
- Lu, H.Y.; Zhang, J.P.; Liu, K.B.; Wu, N.Q.; Li, Y.M.; Zhao, K.S.; Ye, M.L.; Zhang, T.Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Yang, X.Y.; et al. Earliest domestication of common millet in East Asia extended to 10,000 years ago. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7367–7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.X.; Tian, G.; Wang, Y.W.; Liu, X.; Liu, H. Genetic correlation coefficients of foxtail millet traits between parents and hybrids. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2020, 53, 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, G.Q.; Huang, X.H.; Zhi, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, W.J.; Chai, Y.; Yang, L.F.; Liu, K.Y.; Lu, H.Y.; et al. A haplotype map of genomic variations and genome-wide association studies of agronomic traits in foxtail millet (Setaria italica). Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, X.M.; Wang, L.W.; Zhi, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.G.; Cheng, R.H. Development, genetic deciphering and breeding utilization of dwarf lines in foxtail millet. Acta Agron. Sin. 2024, 50, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Gong, X.; Ma, F.; Duan, M.; Wang, L.; Han, Y. Identification of candidate genes related to the husk papillae in foxtail millet (Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv). Plants 2025, 14, 2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.H.; Sami, A.; Chen, Z.P.; Fatima, M.; Zheng, W.Y.; Xu, Q.Q.; Lei, Y.H.; Jin, X.Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; et al. Effects of microscopic testa color and morphology on the water uptake ability and drought tolerance of germination-stage rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Bioengineered 2021, 12, 9341–9355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloetens, P.; Mache, R.; Schlenker, M.; Lerbs-Mache, S. Quantitative phase tomography of Arabidopsis seeds reveals intercellular void network. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14626–14630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.H.; Wei, C.X. Comprehensive comparison and applications of different sections in investigating the microstructure and histochemistry of cereal kernels. Plant Methods 2020, 16, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.B.; Liu, J.X.; Li, D.Q.; Liu, C.M. Rice caryopsis development I: Dynamic changes in different cell layers. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2016, 58, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prunet, N.; Duncan, K. Imaging flowers: A guide to current microscopy and tomography techniques to study flower development. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 2898–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawson, S.D.; Maksimcuka, J.; Withers, P.J.; Cartmell, S.H. X-ray computed tomography in life sciences. BMC Biol. 2020, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littlejohn, G.R.; Gouveia, J.D.; Edner, C.; Smirnoff, N.; Love, J. Perfluorodecalin enhances in vivo confocal microscopy resolution of Arabidopsis thaliana mesophyll. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, D.; Mizuta, Y.; Sato, Y.; Higashiyama, T. ClearSee: A rapid optical clearing reagent for whole-plant fluorescence imaging. Development 2015, 142, 4168–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhawana; Miller, J.L.; Cahoon, A.B. 3D plant cell architecture of Arabidopsis thaliana (Brassicaceae) using focused ion beam-scanning electron microscopy. Appl. Plant Sci. 2014, 2, 1300090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittelmann, M.; Hawes, C.; Hughes, L. Serial block face scanning electron microscopy and the reconstruction of plant cell membrane systems. J. Microsc. 2016, 263, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czymmek, K.; Sawant, A.; Goodman, K.; Pennington, J.; Pedersen, P.; Hoon, M.; Otegui, M.S. Imaging plant cells by high-pressure freezing and serial block-face scanning electron microscopy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2177, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwood, R.; Goodman, E.; Gudmundsdottir, M.; Huynh, M.; Musulin, Q.; Song, M.; Barbour, M.M. Cell and chloroplast anatomical features are poorly estimated from 2D cross-sections. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 2567–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, K.E.; Czymmek, K.J.; Jiang, N.; Thies, A.C.; Topp, C.N. X-ray microscopy enables multiscale high-resolution 3D imaging of plant cells, tissues, and organs. Plant Physiol. 2022, 188, 831–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Z.; Wang, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.J.; Du, J.J.; Guo, X.Y. CT-based phenotyping and genome-wide association analysis of the internal structure and components of maize kernels. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunishima, N.; Takeda, Y.; Hirose, R.; Kalasová, D.; Šalplachta, J.; Omote, K. Visualization of internal 3D structure of small live seed on germination by laboratory-based X-ray microscopy with phase contrast computed tomography. Plant Methods 2020, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, S.R.; Gómez, J.F.; Sturrock, C.J.; Wilson, Z.A.; Ferguson, A.C. Non-destructive determination of floral staging in cereals using X-ray micro-computed tomography (µCT). Plant Methods 2017, 13, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers, A.W.; Hepworth, C.; Baillie, A.L.; Sloan, J.; Jones, H.; Lundgren, M.; Fleming, A.J.; Mooney, S.J.; Sturrock, C.J. Investigating the microstructure of plant leaves in 3D with lab-based X-ray computed tomography. Plant Methods 2018, 14, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Nagato, Y. Flower development in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 4719–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasu, H.; Momohara, A.; Yasuda, Y.; Jie, H. The occurrence and identification of Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv. (foxtail millet) grains from the Chengtoushan site (ca. 5800 cal B.P.) in central China, with reference to the domestication centre in Asia. Veg. Hist. Archaeobotany 2007, 16, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmency, H.; Dekker, J. Setaria. In Wild Crop Relatives: Genomic and Breeding Resources; Kole, C., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 275–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, J. The foxtail (Setaria) species-group. Weed Sci. 2003, 51, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.M.; Dong, K.J.; Wang, X.Q.; Liu, T.P.; He, J.H.; Ren, R.Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, R.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, M.; et al. A high density genetic map and QTL for agronomic and yield traits in foxtail millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.]. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.Q.; Chai, S.H.; Guo, Y.; Shi, X.; Han, F.; Qu, T.; Xing, L.; Yang, Q.H.; Gao, J.F.; Gao, X.L.; et al. Mapping of major QTL and candidate gene analysis for hull colour in foxtail millet (Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.). BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Liu, D.C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.Z.; Yang, W.L.; Yang, W.; Yin, L.X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, S.C.; Sun, J.Z.; et al. Unraveling the genetic architecture of grain size in einkorn wheat through linkage and homology mapping and transcriptomic profiling. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 4671–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.M.; Wang, B.; Xie, F.G.; Zhang, L.P.; Gong, J.; Zhu, W.; Li, X.Q.; Feng, F.Q.; Huang, J. QTL mapping and transcriptome analysis identify candidate genes regulating pericarp thickness in sweet corn. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.Q.; Sun, Y.W.; Guo, T.; Shi, C.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Kan, Y.; Xiang, Y.H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.B.; Li, Y.C.; et al. UDP-glucosyltransferase regulates grain size and abiotic stress tolerance associated with metabolic flux redirection in rice. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.H.; Zhang, X.; Chang, G.M.; Yang, J.; Wan, J.P.; Wang, F.J.; Tao, D.Y.; Zhou, J.W.; Shang, L.G.; Xu, P.; et al. Natural alleles of a uridine 5′-diphospho-glucosyltransferase gene responsible for differential endosperm development between upland rice and paddy rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranocha, P.; Dima, O.; Nagy, R.; Felten, J.; Corratgé-Faillie, C.; Novák, O.; Morreel, K.; Lacombe, B.; Martinez, Y.; Pfrunder, S.; et al. Arabidopsis WAT1 is a vacuolar auxin transport facilitator requireed for auxin homoeostasis. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.C.; Ma, J.J.; Zhou, X.M.; Li, G.H.; Zhao, C.Z.; Xia, H.; Fan, S.J.; Wang, X.J. Arabidopsis MDN1 is involved in the establishment of a normal seed proteome and seed germination. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohto, M.A.; Fischer, R.L.; Goldberg, R.B.; Nakamura, K.; Harada, J.J. Control of seed mass by APETALA2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3123–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukail, S.; Macharia, M.; Miculan, M.; Masoni, A.; Calamai, A.; Palchetti, E.; Dell’Acqua, M. Genome wide association study of agronomic and seed traits in a world collection of proso millet (Panicum miliaceum L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.R.; Li, J.Y. Molecular genetic dissection of quantitative trait loci regulating rice grain size. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2014, 48, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.F.; Wang, Y.J.; Han, S.L.; Han, Y.H.; Li, H.Y.; Hou, S.Y. Correlation analysis of grain episperm color and main agronomic traits in hybrid population from a famous foxtail millet cultivar Jingu 21. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 2020, 48, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Wang, R.; Jing, Z.; Wang, K.; Tan, M.; Li, F.; Zhang, W.; Han, J.; Han, Y. CT image segmentation of foxtail millet seeds based on semantic segmentation model VGG16-UNet. Plant Methods. 2024, 20, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, N.; Sun, Y.R.; Fu, Z.X.; Han, Y.H.; Yang, Y.; Jia, J.C.; Hou, S.Y.; Zhang, B.J. QTL mapping of downy mildew resistance in foxtail millet by SLAF-seq and BSR-seq analysis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2024, 137, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, B.; Agrawal, P.; Saha, S.; Gupta, H. Mapping QTLs for opaque2 modifiers influencing the tryptophan content in quality protein maize using genomic and candidate gene-based SSRs of lysine and tryptophan metabolic pathway. Plant Cell Rep. 2015, 34, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

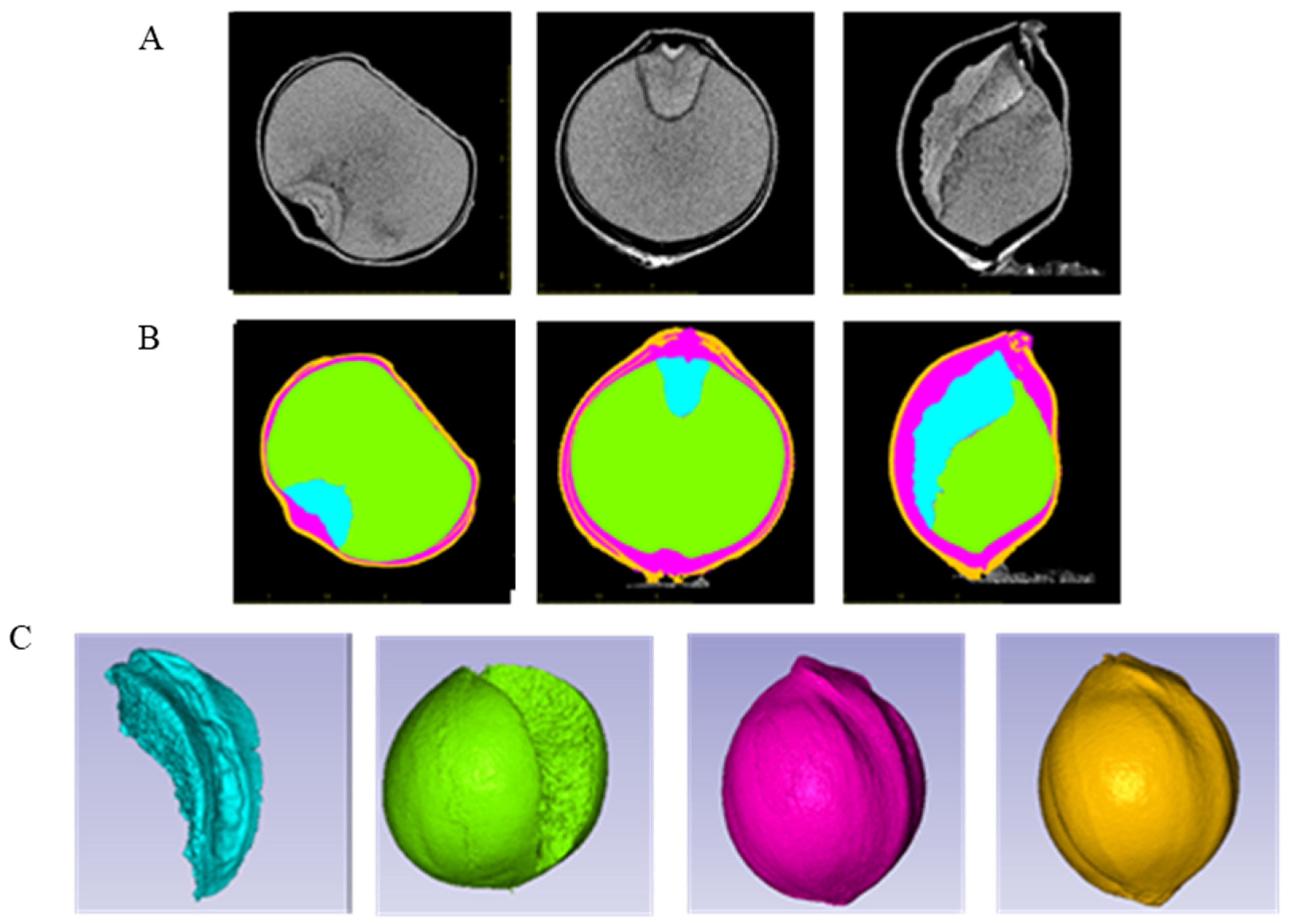
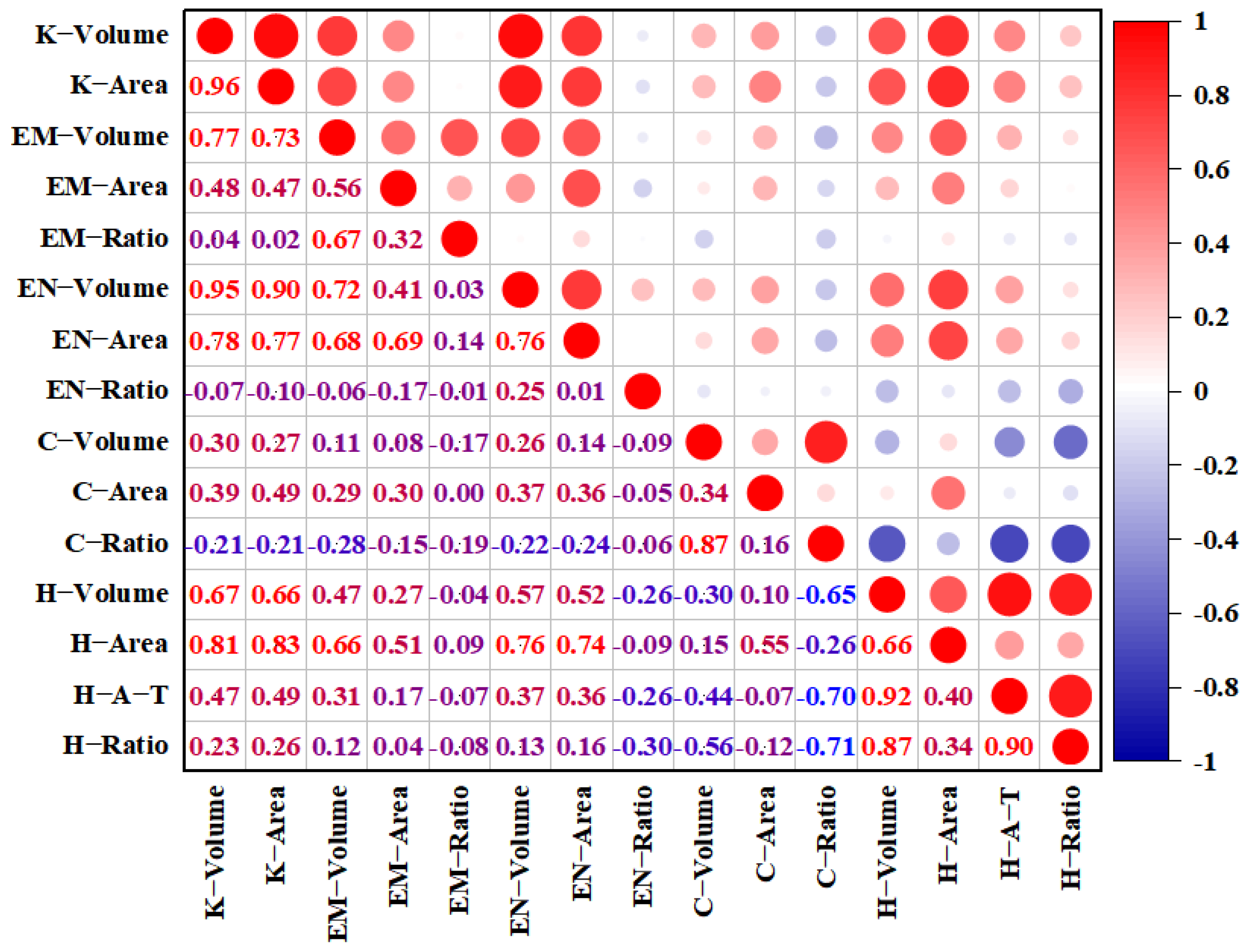
| Trait | Parents | RIL Population | CV (%) | Skewness | Kurtosis | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GBS | JG21 | Minimum | Maximum | Mean ± SD | |||||
| K-Volume | 2.344 | 3.516 | 2.229 | 3.714 | 3.023 ± 0.305 | 10.1 | −0.301 | 0.483 | 0.042 * |
| K-Area | 9.255 | 11.634 | 8.832 | 12.525 | 10.950 ± 0.735 | 6.71 | −0.464 | 0.703 | 0.454 |
| EM-Volume | 0.200 | 0.359 | 0.178 | 0.361 | 0.259 ± 0.035 | 13.602 | 0.389 | 0.33 | 0.989 |
| EM-Area | 3.159 | 5.468 | 2.603 | 5.468 | 3.502 ± 0.475 | 13.555 | 1.271 | 2.981 | 0.000 ** |
| EM-Ratio | 0.081 | 0.110 | 0.068 | 0.113 | 0.086 ± 0.007 | 8.544 | 0.718 | 1.532 | 0.231 |
| EN-Volume | 0.840 | 1.940 | 0.840 | 2.241 | 1.759 ± 0.210 | 15.335 | −0.123 | 0.301 | 0.557 |
| EN-Area | 7.27 | 12.673 | 7.150 | 12.673 | 9.151 ± 0.945 | 11.932 | 1.174 | 3.426 | 0.000 ** |
| EN-Ratio | 0.561 | 0.555 | 0.512 | 0.619 | 0.585 ± 0.034 | 10.324 | −1.112 | 2.092 | 0.007 ** |
| C-Volume | 0.632 | 0.485 | 0.375 | 1.048 | 0.563 ± 0.111 | 19.665 | 1.023 | 3.483 | 0.369 |
| C-Area | 27.55 | 27.456 | 18.112 | 44.842 | 25.769 ± 3.497 | 13.571 | 1.59 | 7.695 | 0.208 |
| C-Ratio | 0.230 | 0.146 | 0.109 | 0.33 | 0.187 ± 0.035 | 18.739 | 0.845 | 2.676 | 0.168 |
| H-Volume | 0.345 | 0.543 | 0.244 | 0.603 | 0.410 ± 0.084 | 20.568 | 0.112 | −0.456 | 0.812 |
| H-Area | 22.17 | 28.259 | 18.174 | 28.259 | 23.596 ± 1.928 | 8.172 | 0.056 | 0.512 | 0.149 |
| H-Ratio | 0.126 | 0.164 | 0.09 | 0.212 | 0.135 ± 0.022 | 16.724 | 0.319 | 0.811 | 0.908 |
| H-A-T | 35.46 | 43.380 | 26.16 | 56.29 | 38.966 ± 6.517 | 16.074 | 0.221 | −0.445 | 0.900 |
| QTL | Chromosome | Physical Interval (Mb) | Traits | LOD | PVE (%) | Add |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qKV2 | 2 | 25.180–28.330 | K-Volume | 3.352 | 17.087 | 0.120 |
| EM-Volume | 3.376 | 15.961 | 0.014 | |||
| EN-Volume | 3.007 | 14.513 | 0.069 | |||
| K-Area | 2.663 | 16.719 | 0.262 | |||
| qER3 | 3 | 12.320–14.800 | EM-Ratio | 2.955 | 11.398 | 0.003 |
| qER4 | 4 | 12.960–30.600 | EM-Ratio | 2.818 | 13.170 | −0.005 |
| qHA9 | 9 | 57.300–58.220 | H-Area | 3.045 | 13.792 | −0.701 |
| Genes ID | Gene Names | Homologous Gene | Function Annotation of Homologous Genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Si2g18440 | SiUDP82A1 | LOC_Os04g44354 | UDP-glycosyltransferases affect cell proliferation and expansion by regulating auxin transport, thereby regulating seed development [31,32]. |
| Si3g18740 | SiUDP | LOC_Os05g42020 | |
| Si3g18760 | SiUDP73E1 | LOC_Os05g42040 | |
| Si3g19180 | SiWAT1 | LOC_Os05g41420 | Regulating auxin exporting affects the elongation and division of cells [33]. |
| Si4g12830 | SiLEA1 | LOC_Os06g21910 | The mutant mdn1-1 exhibits an increased seed size and late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) proteins are over-accumulated in the dry seeds of mdn1-1 [34]. |
| Si4g14860 | SiLEA31 | LOC_Os06g23350 | |
| Si4g17090 | SiAP2 | LOC_Os06g36000 | The mutants exhibited larger seed size and increased seed mass [35]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, D.; Lei, B.; Miao, Y.; Ma, F.; Hou, S.; Han, J.; Liu, X.; et al. Characterization of Grain Structure Using Micro-CT and Identification of Related Candidate Genes by QTL Mapping in Foxtail Millet. Plants 2025, 14, 3603. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233603
Tan M, Yang Y, Zhang J, Guo D, Lei B, Miao Y, Ma F, Hou S, Han J, Liu X, et al. Characterization of Grain Structure Using Micro-CT and Identification of Related Candidate Genes by QTL Mapping in Foxtail Millet. Plants. 2025; 14(23):3603. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233603
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Meixia, Yang Yang, Jiarong Zhang, Dake Guo, Biao Lei, Yuyuan Miao, Fangfang Ma, Siyu Hou, Jiwan Han, Xiaodong Liu, and et al. 2025. "Characterization of Grain Structure Using Micro-CT and Identification of Related Candidate Genes by QTL Mapping in Foxtail Millet" Plants 14, no. 23: 3603. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233603
APA StyleTan, M., Yang, Y., Zhang, J., Guo, D., Lei, B., Miao, Y., Ma, F., Hou, S., Han, J., Liu, X., & Han, Y. (2025). Characterization of Grain Structure Using Micro-CT and Identification of Related Candidate Genes by QTL Mapping in Foxtail Millet. Plants, 14(23), 3603. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233603






