Integrated Moldboard Ploughing and Organic–Inorganic Fertilization Enhances Maize Yield and Soil Fertility in a Semi-Arid Region of North China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Influence of Tillage and Fertilizer Practices on Plant Height, Ear Height and Stem Thickness
2.2. Effects of Tillage and Fertilizer Practices on Maize Grain Yield and Its Compositions
2.3. Effects of Tillage and Fertilizer Practices on Soil Bulk Density, Total Porosity and Soil Respiration Rate
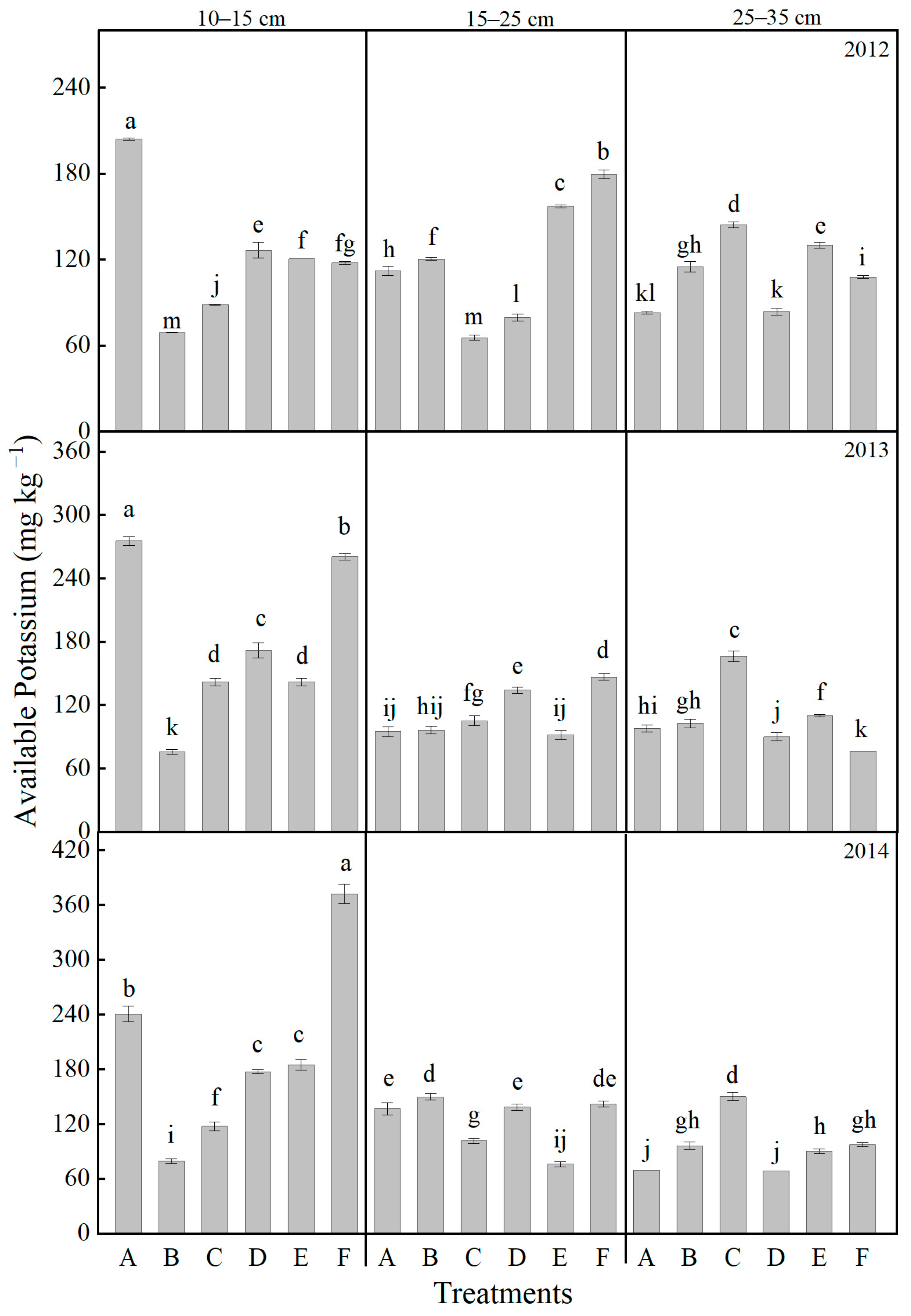
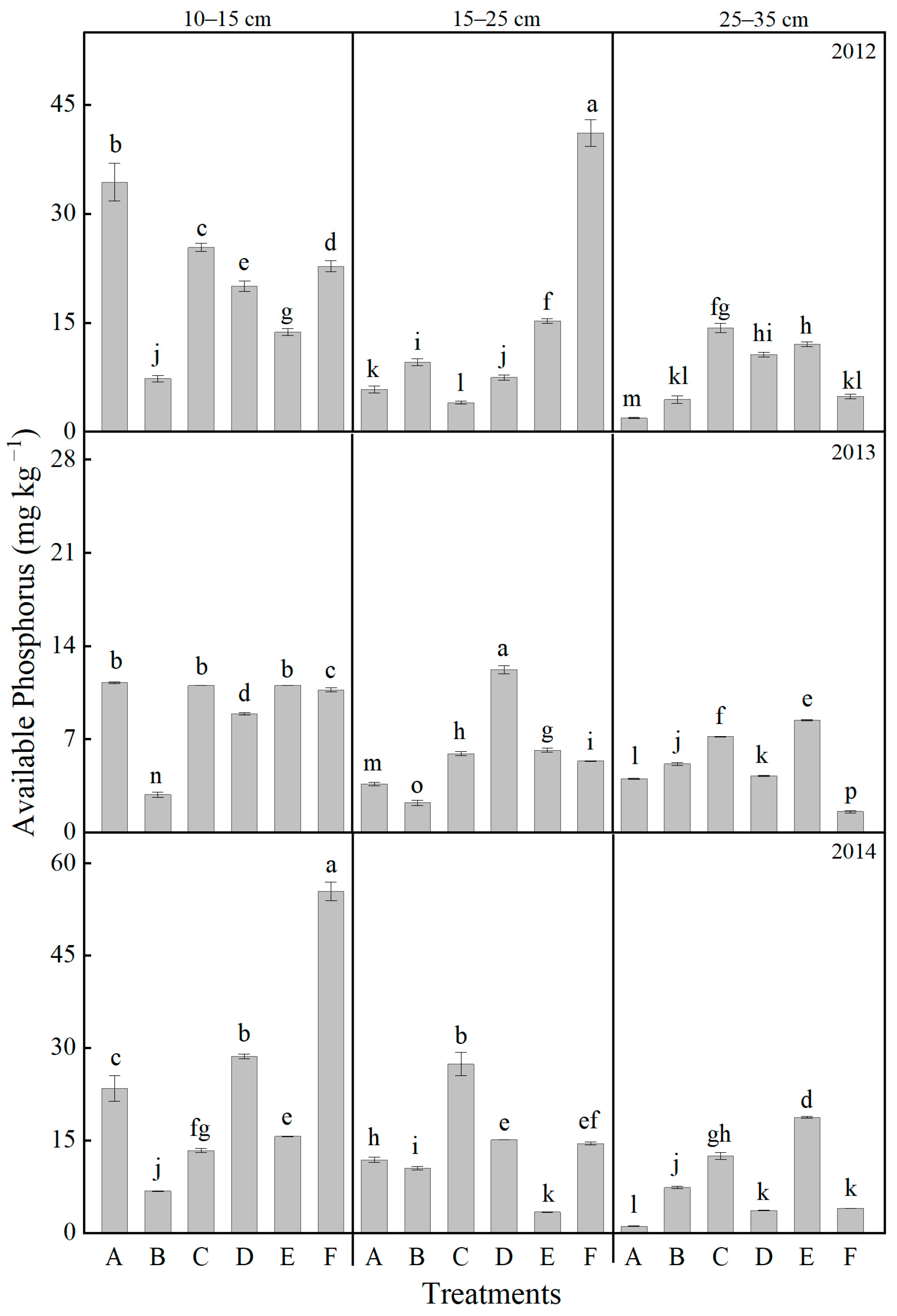
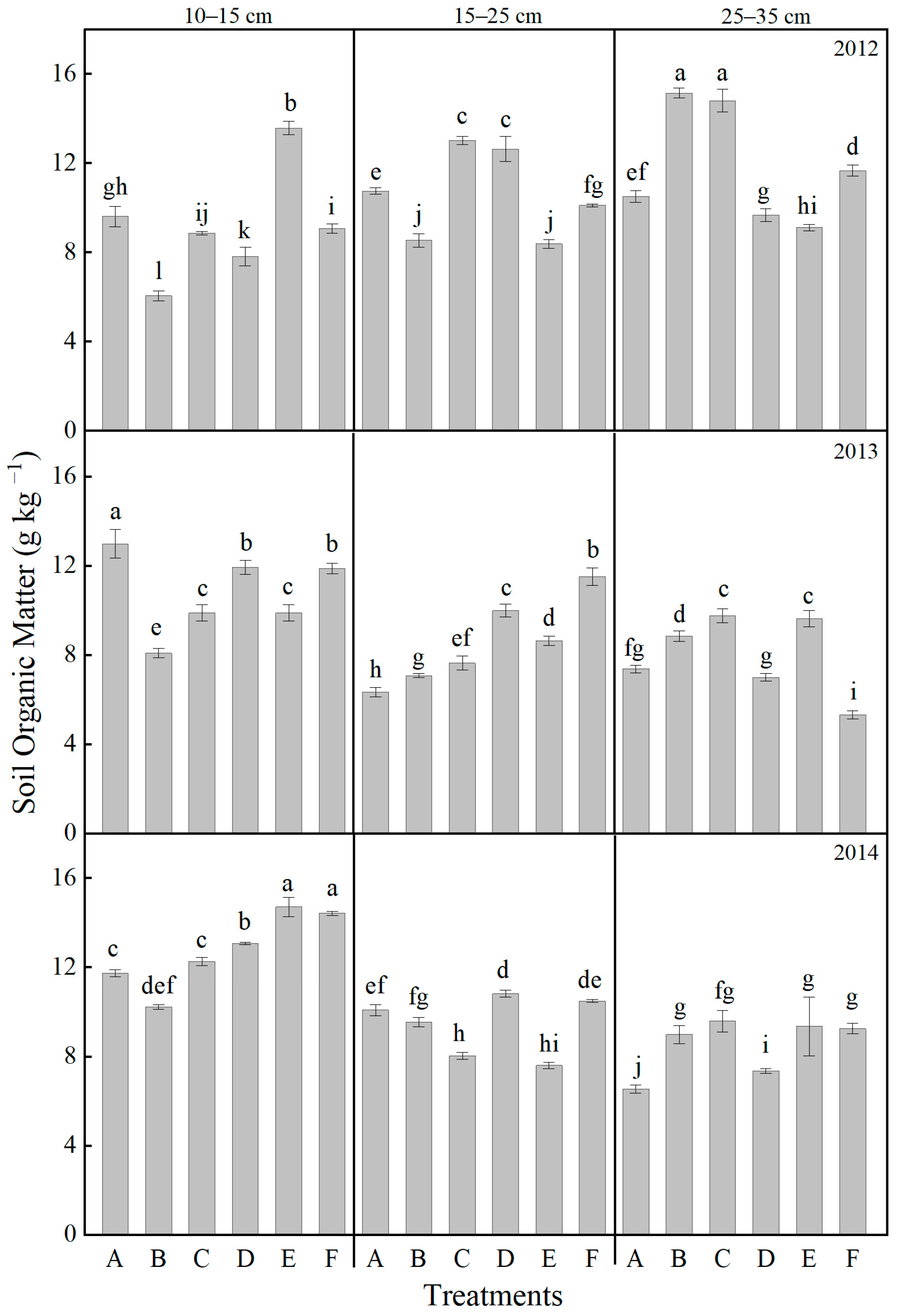
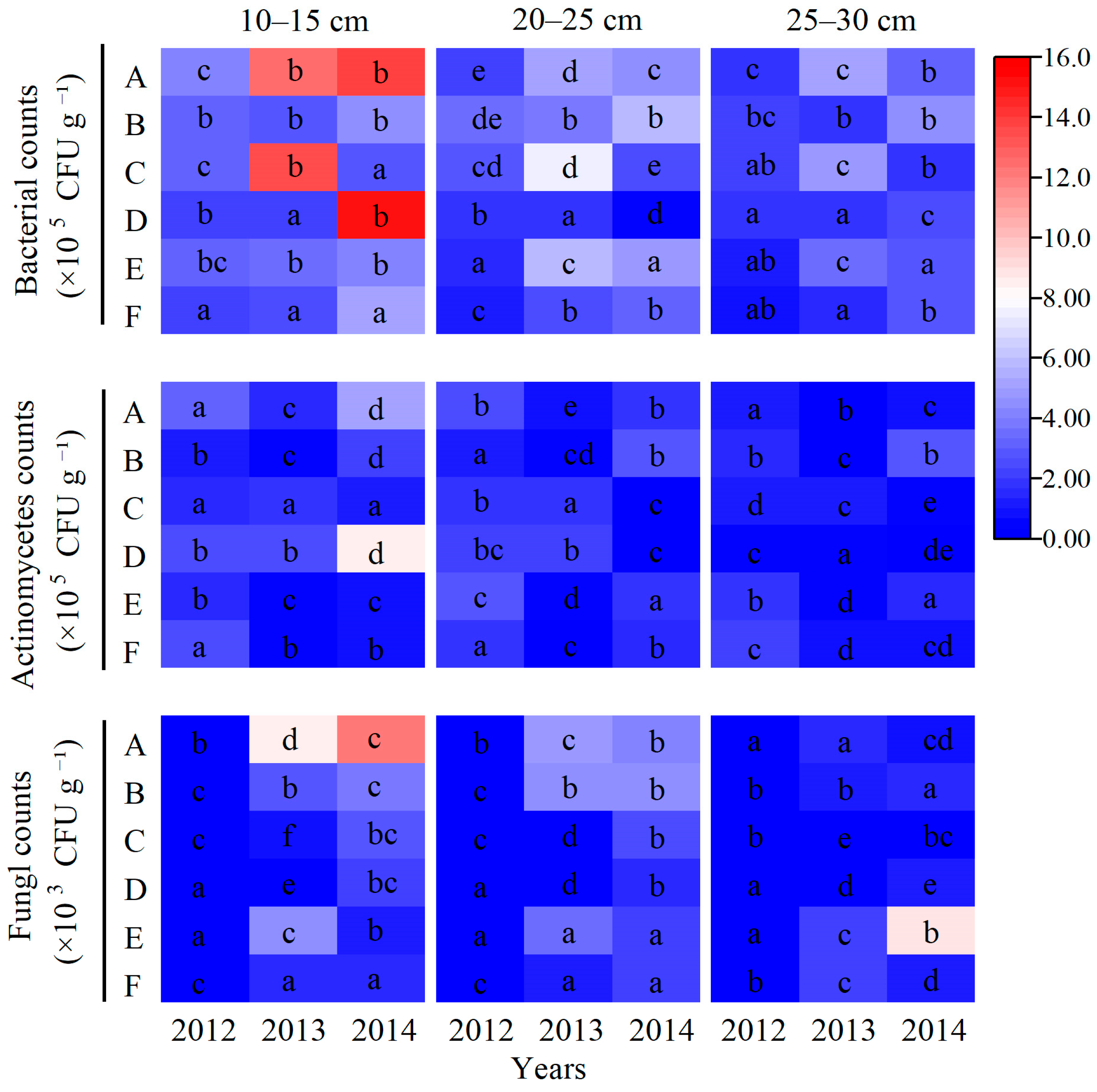
2.4. Effects of Tillage and Fertilizer Practices on Soil Nutrients at Different Soil Layers
3. Discussion
3.1. Effects of Tillage and Fertilization Treatments on the Formation and Stability of Maize Yield
3.2. Synergistic Effects of Tillage and Fertilization on Soil Physical Properties, Nutrient Distribution, and Microbial Profiles
4. Materials and Methods
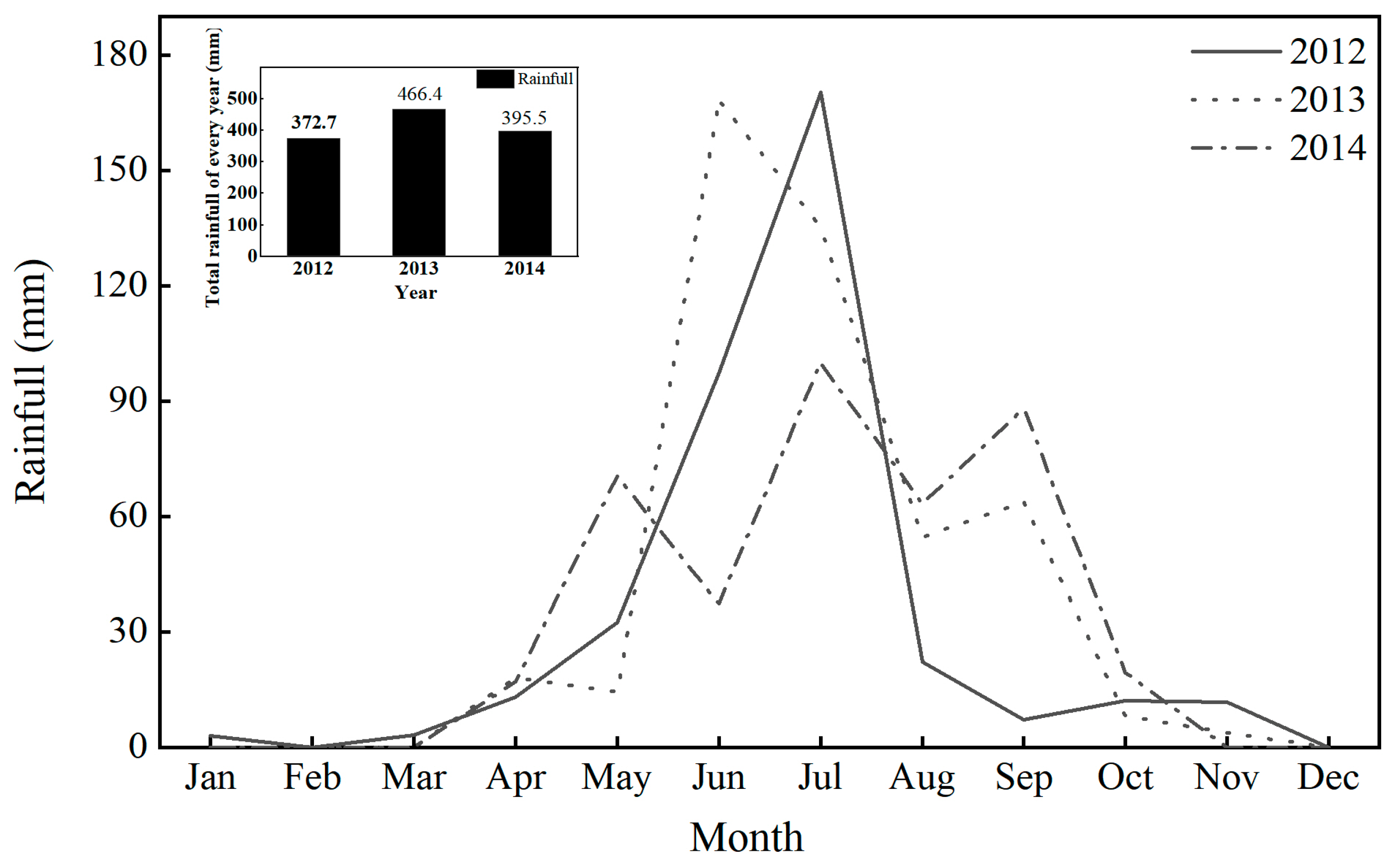
4.1. Plant Sites and Environmental Conditions
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Determination of Maize Biomass and Yield
4.4. Measurement of Soil Bulk Density, Total Porosity and Soil Respiration Rate
4.5. Determination of Soil Nutrient Content and Soil Microflora
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Treatments | Descriptions | Tillage Depth (cm) | Tillage Years | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | |||
| A (CK) | Continuous R + 750 kg ha−1 CF | 10–15 | √ | √ | √ |
| B | Continuous P + 750 kg ha−1 CF | 15–25 | √ | √ | √ |
| C | Continuous P + 750 kg ha−1 CF | 25–35 | √ | √ | √ |
| D | Continuous R + 1200 kg ha−1 MC + 375 kg ha−1 CF | 10–15 | √ | √ | √ |
| E | R + 1200 kg ha−1 MC + 375 kg ha−1 CF | 10–15 | √ | ||
| MP + 1200 kg ha−1 MC + 375 kg ha−1 CF | 15–25 | √ | |||
| MP + 1200 kg ha−1 MC + 375 kg ha−1 CF | 25–35 | √ | |||
| F | MP + 1200 kg ha−1 MC + 375 kg ha−1 CF | 25–35 | √ | ||
| MP + 1200 kg ha−1 MC + 375 kg ha−1 CF | 15–25 | √ | |||
| R + 1200 kg ha−1 MC + 375 kg ha−1 CF | 10–15 | √ | |||
References
- Tilman, D.; Balzer, C.; Hill, J.; Befort, B.L. Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20260–20264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray, H.C.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food security: The challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shun Chan, F.K.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Johnson, M.F.; Li, G.; Chen, W.-Q.; Wang, L.; Li, P.; Wang, J. Food security in climatic extremes: Challenges and opportunities for China. Cell Rep. Sustain. 2024, 1, 100013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, R.; Ye, X.; Ma, C.; Wang, Q.; Tu, R.; Zhang, L.; Gao, H. Greenhouse gas emissions from synthetic nitrogen manufacture and fertilization for main upland crops in China. Carbon Balance Manag. 2019, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, Y.; Shen, X.; Xia, X. Responses of soil microbial community to global climate change: A review. Microbiol. China 2023, 50, 1700–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Dong, C.; Bian, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y. Effects of different fertilization practices on maize yield, soil nutrients, soil moisture, and water use efficiency in northern China based on a meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashidi, M.; Keshavarzpour, F. Effect of different tillage methods on soil physical properties and crop yield of melon (Cucumis melo). ARPN J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2008, 3, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Aikins, S.; Afuakwa, J. Effect of four different tillage practices on maize performance under rainfed conditions. Agric. Biol. J. N. Am. 2012, 3, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R. Soil carbon sequestration to mitigate climate change. Geoderma 2004, 123, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, G.; Yang, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, R.; Liu, F.; Jie, X.; Liu, S. Differentiation in nitrogen transformations and crop yield as affected by tillage modes in a Fluvo-Aquic soil. Plants 2023, 12, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, P.; Li, F.; Xi, J.; Han, Y. Effects of tillage and biochar on soil physiochemical and microbial properties and its linkage with crop yield. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 929725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, J.; Dai, Y. Analysis of conservation practices for black soil based on organic matter and nitrogen contents in the black soil region of Northeast China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 23989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y. Long-term no-tillage and organic input management enhanced the diversity and stability of soil microbial community. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beylich, A.; Oberholzer, H.-R.; Schrader, S.; Höper, H.; Wilke, B.-M. Evaluation of soil compaction effects on soil biota and soil biological processes in soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 109, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varsa, E.C.; Chong, S.K.; Abolaji, J.O.; Farquhar, D.A.; Olsen, F.J. Effect of deep tillage on soil physical characteristics and corn (Zea mays L.) root growth and production. Soil Tillage Res. 1997, 43, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Ma, D.; Lei, T.; Hu, S.; Yu, X.; Gao, J. Subsoil tillage improved the maize stalk lodging resistance under high planting density. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1396182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, O.D. Land-use change: Impacts of climate variations and policies among small-scale farmers in the Loess Plateau, China. Land Use Policy 2006, 23, 361–371. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, L.; Zhang, X.P.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, J.J.; Ma, T.Y.; Sun, Y.P. Spatiotemporal characteristics of precipitation and extreme events on the Loess Plateau of China between 1957 and 2009. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 28, 4971–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, N.; Xing, Y.; Mohamed, B.E.C. Synergetic effects of plastic mulching and nitrogen application rates on grain yield, nitrogen uptake and translocation of maize planted in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Huang, G. The effect of nitrogen rates on yields and nitrogen use efficiencies during four years of wheat–maize rotation cropping seasons. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 2076–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, C.; Xu, X.; Sun, M.; Zhang, L. Farmland scale and chemical fertilizer use in rural China: New evidence from the perspective of nutrient elements. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Qin, H.; Wang, J.; Yao, D.; Zhang, L.; Guo, J.; Zhu, B. Immediate response of paddy soil microbial community and structure to moisture changes and nitrogen fertilizer application. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1130298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Zhao, W.; Lv, Z.; Xu, B.; Hu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y. Optimal rate of nitrogen fertilizer improves maize grain yield by delaying the senescence of ear leaves and thereby altering their nitrogen remobilization. Field Crops Res. 2024, 310, 109359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddech, N.; Theerakulpisut, P.; Ma, Y.N.; Sarin, P. Bioorganic fertilizers from agricultural waste enhance rice growth under saline soil conditions. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmeades, D.C. The long-term effects of manures and fertilisers on soil productivity and quality: A review. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2003, 66, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.W.I.; Torn, M.S.; Abiven, S.; Dittmar, T.; Guggenberger, G.; Janssens, I.A.; Kleber, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Lehmann, J.; Manning, D.A.C.; et al. Persistence of soil organic matter as an ecosystem property. Nature 2011, 478, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratibha, G.; Manjunath, M.; Raju, B.M.K.; Srinivas, I.; Rao, K.V.; Shanker, A.K.; Prasad, J.; Rao, M.S.; Kundu, S.; Indoria, A.K.; et al. Soil bacterial community structure and functioning in a long-term conservation agriculture experiment under semi-arid rainfed production system. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1102682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Wang, X.; Li, R.; Jia, Z.; Liang, L.; Wang, J.; Nie, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z. Effects of different manure application rates on soil properties, nutrient use, and crop yield during dryland maize farming. Soil Res. 2012, 50, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, J.; Pan, X.; Gao, C.; Tang, D. Impact of combining long-term subsoiling and organic fertilizer on soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen, soil enzyme activity, and water use of winter wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 788651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Parihar, C.M.; Nayak, H.S.; Sena, D.R.; Godara, S.; Dhakar, R.; Patra, K.; Sarkar, A.; Bharadwaj, S.; Ghasal, P.C.; et al. Modeling maize growth and nitrogen dynamics using CERES-Maize (DSSAT) under diverse nitrogen management options in a conservation agriculture-based maize-wheat system. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Xu, X.; Zhu, Y. Long-term straw mulching with nitrogen fertilization increases nutrient and microbial determinants of soil quality in a maize—Wheat rotation on China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljubičić, N.; Popović, V.; Kostić, M.; Pajić, M.; Buđen, M.; Gligorević, K.; Dražić, M.; Bižić, M.; Crnojević, V. Multivariate interaction analysis of Zea mays L. genotypes growth productivity in different environmental conditions. Plants 2023, 12, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; He, W.; He, L.; Yang, J.Y.; Qian, B.; Zhou, W.; He, P. Modelling adaptation strategies to reduce adverse impacts of climate change on maize cropping system in Northeast China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekiya, A.O.; Ogunboye, O.I.; Ewulo, B.S.; Olayanju, A. Effects of different rates of poultry manure and split applications of urea fertilizer on soil chemical properties, growth, and yield of maize. Sci. World J. 2020, 2020, 4610515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Xing, Z.; Ni, C.; Ye, M.; Zhang, Z. Optimizing controlled-release urea and urea combinations for sustainable rice-wheat production under nitrogen reduction. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1576049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuku, G.; Onwonga, R.; Chepkemoi, J.; Kathumo, V. Effects of tillage practices, cropping systems and organic inputs on soil nutrient content in Machakos County. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 13, 2618–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, S.T.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.W.; Zhao, B. Effects of long-term mixed application of organic and inorganic fertilizers on canopy apparent photosynthesis and yield of winter wheat. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 26, 2362–2370. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Jin, Y.; Qi, Y.; Huang, R.; Wang, F. Combination of nitrogen and organic fertilizer practices increased rice yields and quality with lower CH(4) emissions in a subtropical rice cropping system. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1613163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, N.; Pang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Lin, W.; Mbuya, S.N.; Abubakar, A.Y.; Fabrice, K.M.A.; Zhang, H. Plant growth and stress-regulating metabolite response to biochar utilization boost crop traits and soil health. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1271490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinapriya, P.; Maharajan, T.; Jothi, R.; Prabakaran, M.; Lee, I.B.; Yi, P.H.; Jeong, S.T. Unlocking biochar impacts on abiotic stress dynamics: A systematic review of soil quality and crop improvement. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1479925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Qi, B.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, H. Research progress and prospects of intelligent measurement and control technology for tillage depth in subsoiling operations. Sensors 2025, 25, 3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Niu, Z.; Guo, Z.; Li, J.; Ye, S.; Hua, D. Improving soil water dynamics and crop productivity through conservation tillage in arid regions. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 25242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiping, L.; Ruizhi, X.; Yang, L.; Pengxiang, S.; Hongbing, Z.; Bo, M.; Hao, W.; Wuren, L.; Jinyu, Z.; Shaokun, L. Effects of conservation tillage methods on maize growth and yields in a typical black soil region. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2024, 32, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, N.; Angelidakis, V.; Luli, S.; Nadimi, S. How Do Roots Interact with Layered Soils? J. Imaging 2022, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, R. Soil organic matter and water retention. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 3265–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezhadahmadi, A.; Prodhan, M.Z.; Faruq, G. Drought tolerance in wheat. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 610721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redding, M.R.; Lewis, R.; Kearton, T.; Smith, O. Manure and sorbent fertilisers increase on-going nutrient availability relative to conventional fertilisers. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Li, G.; Lu, W.; Lu, D. Effects of different fertilizer combinations on the yield and nitrogen use efficiency of summer maize in Jiangsu Province, China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peladarinos, N.; Piromalis, D.; Cheimaras, V.; Tserepas, E.; Munteanu, R.A.; Papageorgas, P. Enhancing smart agriculture by implementing digital twins: A comprehensive review. Sensors 2023, 23, 7128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risman, R.D.S.; Nonkhonman, C.; Sungthongwises, K. Integrating vermicompost, black soldier fly, and inorganic fertilizers enhances corn growth and yield. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, D.A.; Fleming, P.; Davis, D.D.; Horton, R.; Wang, B.; Karlen, D.L. Impact of biochar amendments on the quality of a typical Midwestern agricultural soil. Geoderma 2010, 158, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, B.; Sun, X.; Yue, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhao, M. Soil tillage management affects maize grain yield by regulating spatial distribution coordination of roots, soil moisture and nitrogen status. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Li, R.; Jia, Z.; Han, Q.; Wang, W.; Yang, B. Effects of rotational tillage practices on soil properties, winter wheat yields and water-use efficiency in semi-arid areas of north-west China. Field Crops Res. 2012, 129, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.J.; Zhang, X.C.; Yu, X.F.; Hou, H.Z.; Wang, W.; Ma, Y.F.; Zhang, G.P.; Lei, K.N.; Yin, J.D. Effects of vertical rotary subsoiling with combined organic and inorganic fertilization on water use efficiency and yield of forage maize in a semi-arid area. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiecher, T.; Gatiboni, L.; Filippi, D.; Osmond, D.; Hardy, D. Effect of P rates in long-term conservation agriculture trials on the vertical distribution of soil acidity and nutrient availability. J. Environ. Qual. 2025, 54, 1187–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, K.; Ji, B.; Guo, H.; Xue, Z.; Li, C. Responses of soil properties, root growth and crop yield to tillage and crop residue management in a wheat–maize cropping system on the North China Plain. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 78, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linh, T.B.; Sleutel, S.; Vo, T.G.; Le Van, K.; Cornelis, W.M. Deeper tillage and root growth in annual rice-upland cropping systems result in improved rice yield and economic profit relative to rice monoculture. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 154, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Chen, P.; Zhang, C.; Liang, M.; Xie, G.; Zhao, L.; Wang, C. Effects of combined application of slow-release nitrogen fertilizer and urea on nitrogen uptake, utilization and yield of maize under two tillage methods. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, S.; Xiang, Q.; Yu, X.; Zhao, K.; Zou, L.; Chen, Q.; Tu, S.; Zhang, X. Long-term Fertilization Structures Bacterial and Archaeal Communities along Soil Depth Gradient in a Paddy Soil. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautz, T.; Amelung, W.; Ewert, F.; Gaiser, T.; Horn, R.; Jahn, R.; Javaux, M.; Kemna, A.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Munch, J.-C.; et al. Nutrient acquisition from arable subsoils in temperate climates: A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 1003–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Al-Kaisi, M.M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z. Tillage practices effect on root distribution and water use efficiency of winter wheat under rain-fed condition in the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 146, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasal, M.C.; Andriulo, A.E.; Taboada, M.A. Soil porosity characteristics and water movement under zero tillage in silty soils in Argentinian Pampas. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 87, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ding, Z.; Wang, X.; Hou, H.; Zhou, B.; Yue, Y.; Ma, W.; Ge, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, M. Subsoiling practices change root distribution and increase post-anthesis dry matter accumulation and yield in summer maize. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.; Recous, S.; Stockdale, E.; Fillery, I.R.P.; Jensen, L.; Hatch, D.J.; Goulding, K. Gross nitrogen fluxes in soil: Theory, measurement and application of 15N pool dilution techniques. Adv. Agron. 2003, 79, 69–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, W.; Xu, Z.; Li, W.; Ren, Y.; Huang, T.; Ran, W.; Wang, B.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R. Long-term organic-inorganic fertilization ensures great soil productivity and bacterial diversity after natural-to-agricultural ecosystem conversion. J. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassini, P.; You, J.; Hubbard, K.G.; Cassman, K.G. Soil water recharge in a semi-arid temperate climate of the Central U.S. Great Plains. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak-Mensah, E.; Obour, P.B.; Essel, E.; Wang, Q.; Ahiakpa, J.K. Influence of plastic film mulch with biochar application on crop yield, evapotranspiration, and water use efficiency in northern China: A meta-analysis. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Chai, Q.; Feng, F.; Zhao, C.; Yu, A. Interspecies interactions in relation to root distribution across the rooting profile in wheat-maize intercropping under different plant densities. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, D.; Bardgett, R.D.; Finlay, R.D.; Jones, D.L.; Philippot, L. A plant perspective on nitrogen cycling in the rhizosphere. Funct. Ecol. 2019, 33, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Ma, X.; Sun, L.; Liu, S.; Ji, J.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Kuang, E.; Liu, Y.; et al. High ratio of manure substitution enhanced soil organic carbon storage via increasing particulate organic carbon and nutrient availability. Plants 2025, 14, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koza, N.A.; Adedayo, A.A.; Babalola, O.O.; Kappo, A.P. Microorganisms in plant growth and development: Roles in abiotic stress tolerance and secondary metabolites secretion. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Pandey, R.; Chauhan, N.S. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia promotes wheat growth by enhancing nutrient assimilation and rhizosphere microbiota modulation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2025, 13, 1563670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Gao, P.; Lai, K.; Binbin, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wan, X.; Lyu, C.; Kang, C.; Guo, L.; et al. Mechanistic insights from metagenomics into the early-stage quality improvement of licorice under partial replacement of chemical by organic fertilizers. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1613771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Zhu, R.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Ai, C.; He, P.; Liang, G.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, P. Effect of high soil C/N ratio and nitrogen limitation caused by the long-term combined organic-inorganic fertilization on the soil microbial community structure and its dominated SOC decomposition. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 303, 114155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagar, S.; Bhatti, A. Physical properties of soil. In Soil Science, 2nd ed.; National Book Foundation: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2001; pp. 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Shu-Tao, C.; Zheng-Hua, H.U.; Jing-Quan, R.; Xiao-Shuai, S. Effects of simulated warming on soil respiration in a cropland under winter wheat-soybean rotation. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 4205–4211. [Google Scholar]
- He, G.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Ji, T.; Yang, Z.; Qi, H.; Ma, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; et al. Recovery in soil carbon stocks but reduced carbon stabilization after near-natural restoration in degraded alpine meadows. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 31124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathania, S.; Dhiman, S.R.; Kashyap, B.; Kumar, A.; Kaushal, R.; Gupta, R.K.; Saleh, I.A.; Okla, M.K.; Elshikh, M.S. Influence of planting dates and fertilizer modules on yield of chrysanthemum and soil health. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
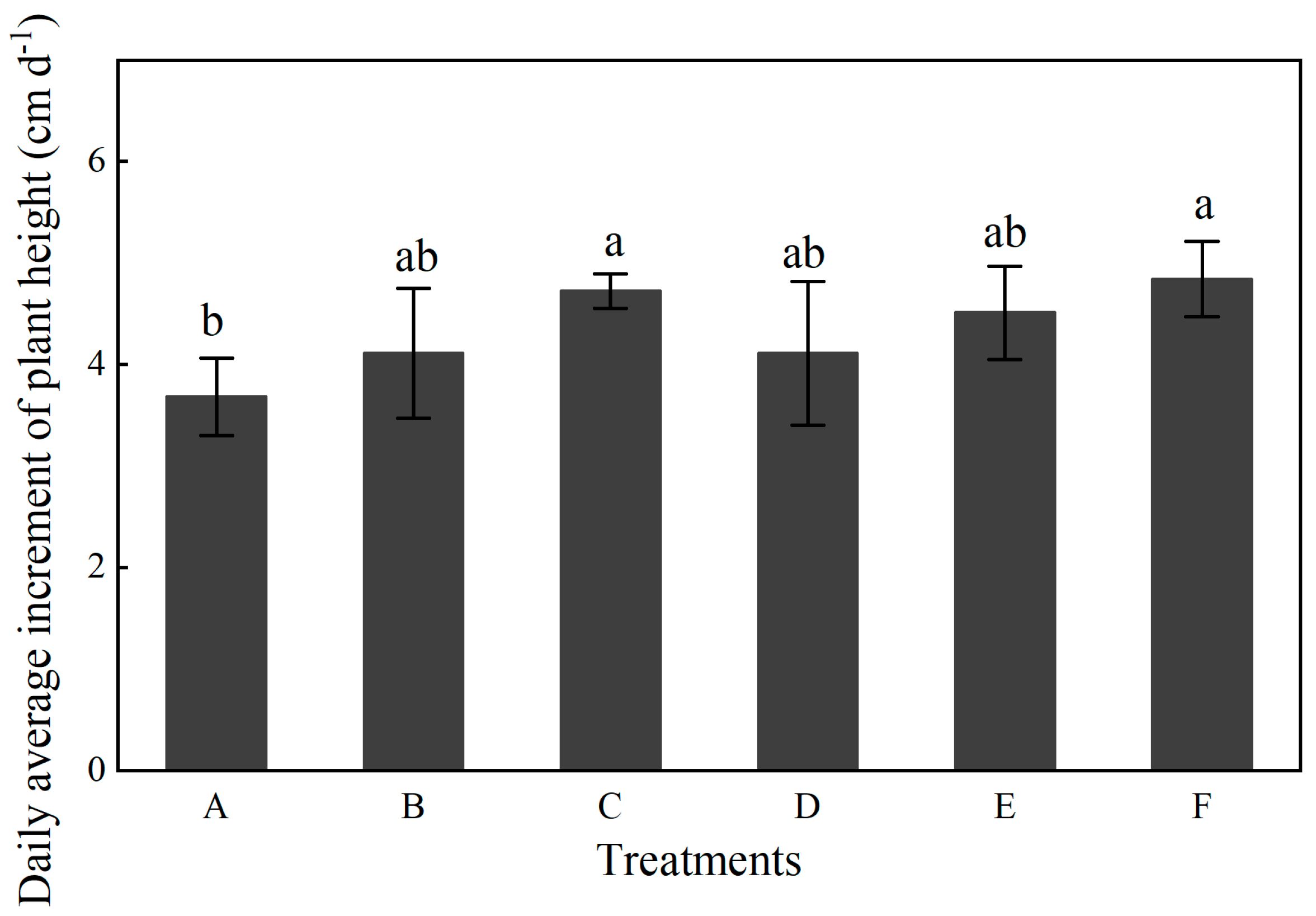
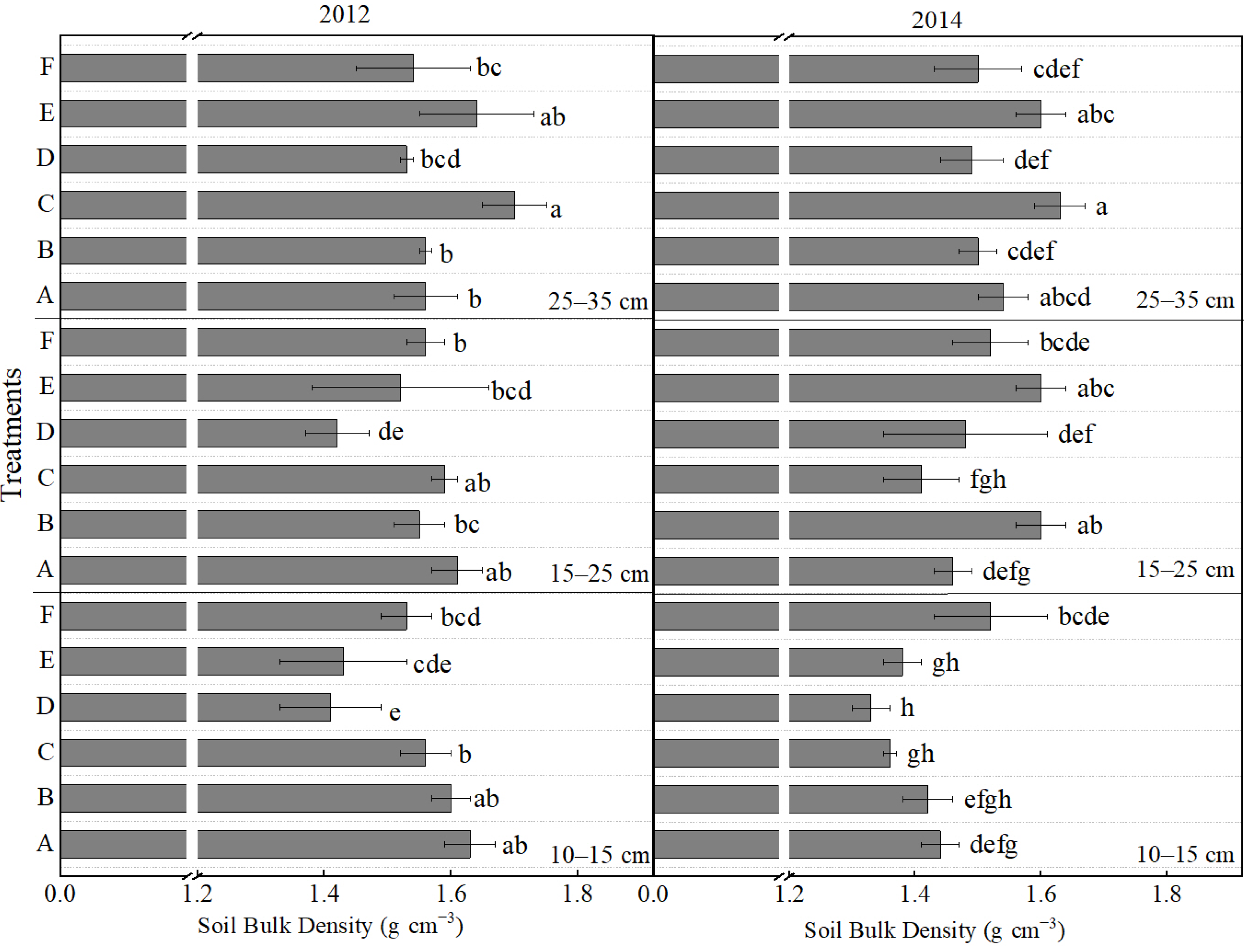

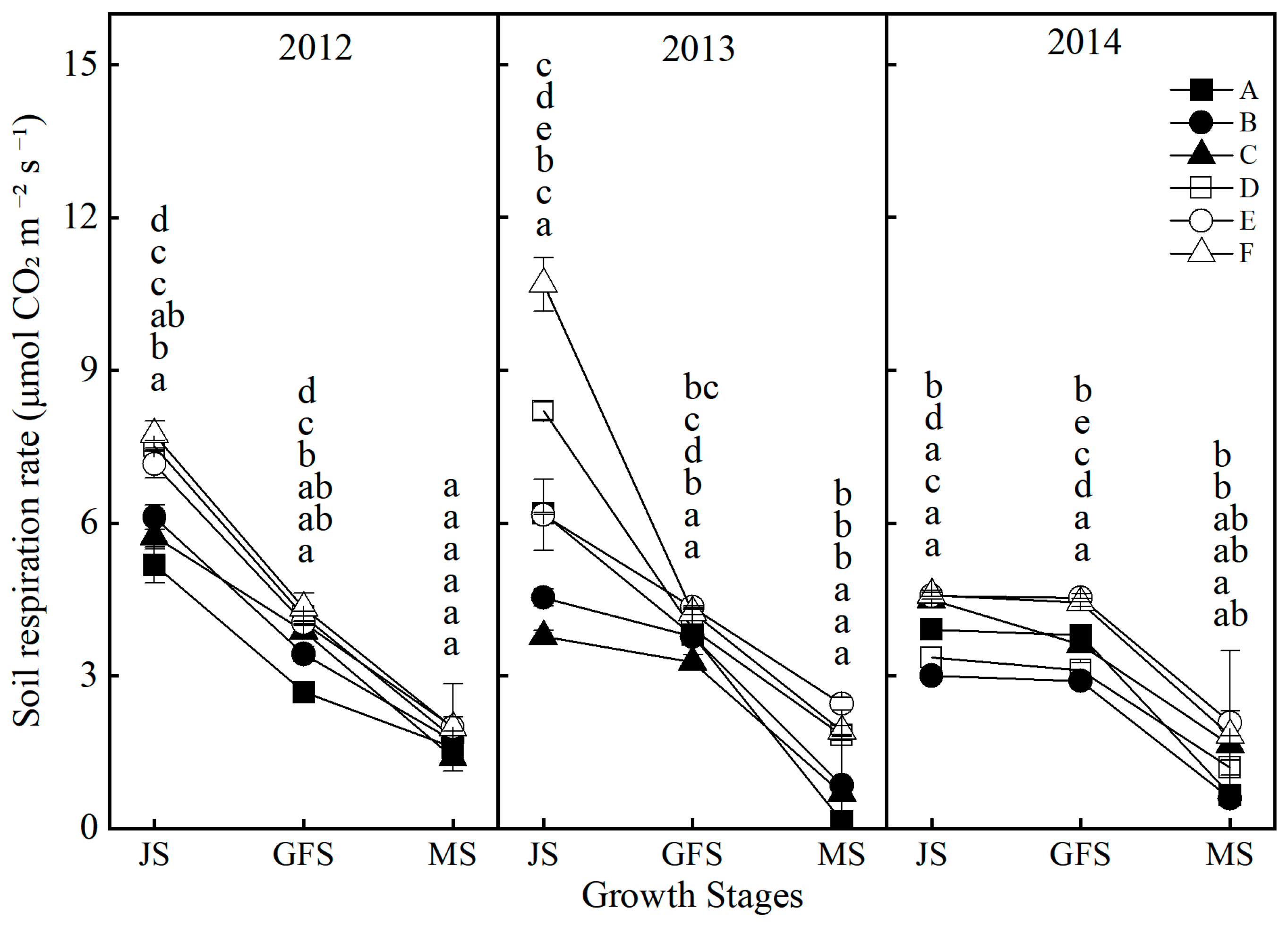
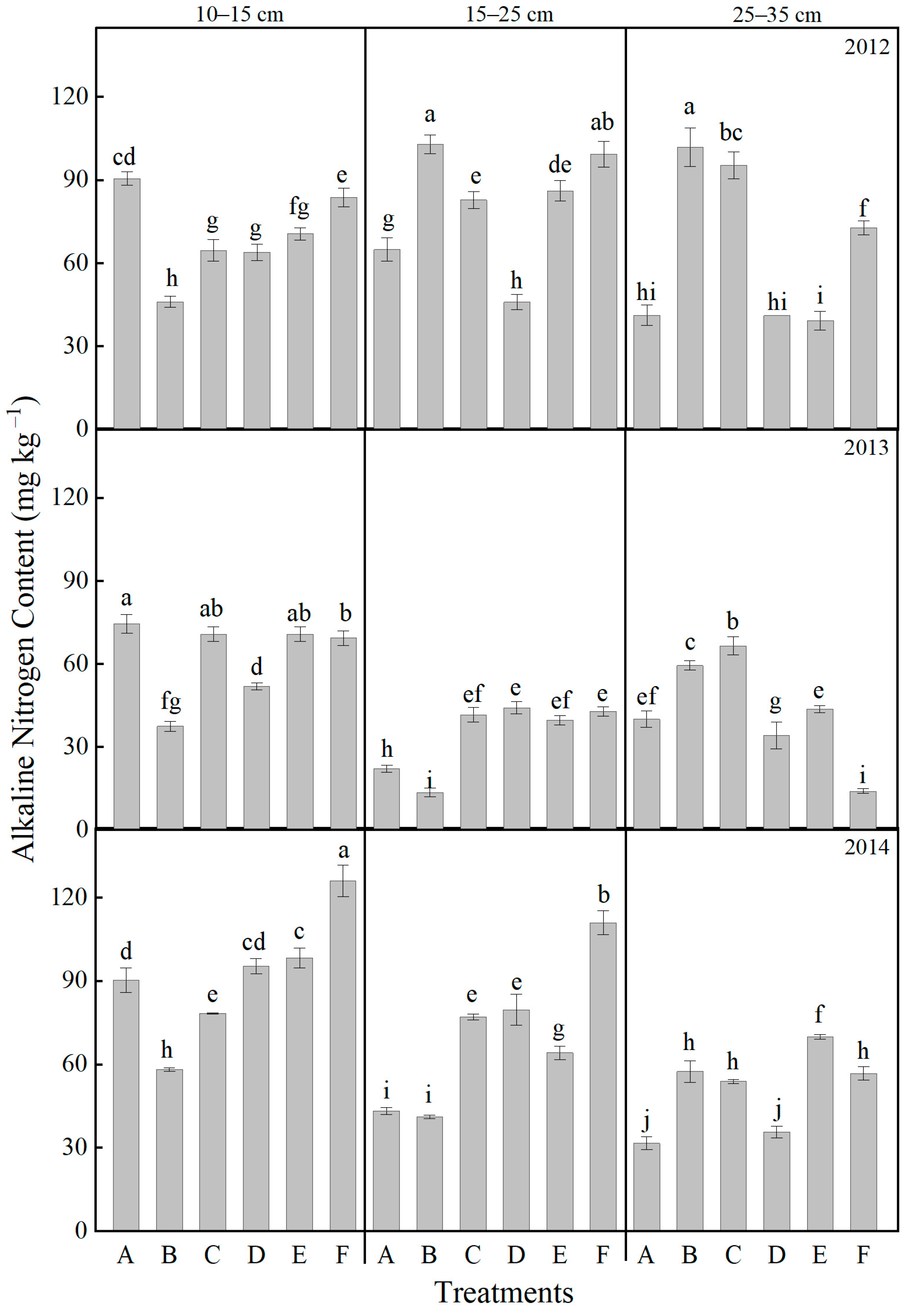

| Years | Treatments | Plant Height (cm) | Ear Height (cm) | Stem Diameter (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jointing Stage | Tasseling Stage | ||||
| 2012 | A | 85.5 a | 138.2 d | 98.4 c | 22.3 ab |
| B | 76.4 b | 149.1 bc | 110.6 ab | 22.7 ab | |
| C | 78.3 b | 156.4 ab | 112.7 ab | 23.6 ab | |
| D | 78.0 b | 154.5 ab | 104.1 bc | 24.3 a | |
| E | 78.7 b | 158.4 a | 106.1 abc | 23.2 ab | |
| F | 69.6 c | 148.2 c | 114.1 a | 21.3 b | |
| 2013 | A | 57.2 ab | 166.8 b | 111.0 ab | 18.0 b |
| B | 58.2 a | 177.3 a | 114.6 ab | 19.9 ab | |
| C | 54.7 c | 182.5 a | 116.7 a | 20.3 a | |
| D | 51.7 d | 164.8 b | 115.0 ab | 21.3 a | |
| E | 56.9 ab | 178.2 a | 107.7 b | 19.7 ab | |
| F | 55.9 bc | 175.7 a | 116.5 a | 19.6 ab | |
| 2014 | A | 100.7 a | 174.5 c | 87.7 cd | 21.5 ab |
| B | 100.1 ab | 167.5 c | 82.5 d | 19.3 c | |
| C | 95.1 bc | 185.8 b | 95.5 b | 22.9 ab | |
| D | 102.7 a | 169.9 c | 90.7 bc | 21.2 abc | |
| E | 101.2 a | 182.5 b | 82.9 d | 20.9 bc | |
| F | 92.7 c | 195.8 a | 101.3 a | 23.0 a | |
| Y | 1169.421 ** | 195.430 ** | 151.250 ** | 28.333 ** | |
| T | 10.225 ** | 17.183 ** | 11.780 ** | 3.188 * | |
| Y × T | 4.863 ** | 6.716 ** | 2.753 ** | 2.475 * | |
| Years | Treatments | Ear Length (cm) | Ear Diameter (cm) | Row Number Per Ear | Grain Numbers Per Ear | Ear Tip Barrenness (cm) | 100-Grain Weight (g) | Grain Yield (kg ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | A | 19.5 b | 5.2 c | 15.3 a | 566.9 a | 0.63 c | 41.7 a | 5809 d |
| B | 19.8 ab | 5.3 ab | 15.3 a | 561.0 a | 0.90 ab | 41.4 a | 6283 c | |
| C | 20.2 ab | 5.3 abc | 16.7 a | 622.5 a | 0.80 abc | 40.0 b | 5887 d | |
| D | 20.4 a | 5.4 a | 16.0 a | 621.2 a | 0.80 abc | 41.0 ab | 6338 c | |
| E | 19.8 ab | 5.4 a | 16.0 a | 579.8 a | 0.73 bc | 40.8 ab | 6855 b | |
| F | 19.5 b | 5.2 bc | 16.2 a | 565.6 a | 0.93 a | 39.9 b | 7479 a | |
| 2013 | A | 18.8 a | 5.1 a | 17.6 a | 565.0 a | 0.86 ab | 33.0 d | 5592 f |
| B | 19.9 a | 5.3 a | 16.8 a | 621.0 a | 0.68 b | 36.9 c | 6313 e | |
| C | 18.9 a | 5.0 a | 17.2 a | 636.0 a | 0.87 ab | 35.9 c | 7270 d | |
| D | 19.1 a | 5.2 a | 17.2 a | 608.2 a | 0.87 ab | 41.4 ab | 8240 c | |
| E | 17.9 a | 5.0 a | 17.2 a | 636.2 a | 0.98 a | 40.2 b | 8690 b | |
| F | 18.2 a | 5.0 a | 17.6 a | 643.4 a | 0.74 ab | 42.5 a | 8953 a | |
| 2014 | A | 16.6 a | 4.6 a | 17.2 a | 526.8 a | 0.88 bc | 28.1 d | 5994 c |
| B | 16.1 a | 4.6 a | 16.8 a | 522.0 a | 1.12 a | 27.0 c | 5970 c | |
| C | 17.8 a | 4.8 a | 18.0 a | 570.5 a | 0.90 bc | 31.7 c | 6306 bc | |
| D | 16.6 a | 4.8 a | 17.0 a | 507.0 a | 0.82 c | 34.3 ab | 6639 ab | |
| E | 17.6 a | 4.6 a | 16.0 a | 552.3 a | 0.99 b | 29.5 b | 6792 a | |
| F | 17.4 a | 4.7 a | 17.0 a | 552.2 a | 0.97 b | 31.6 a | 6999 a | |
| Y | 13.917 ** | 62.117 ** | 6.939 ** | 9.276 | 10.268 ** | 45.242 ** | 304.106 ** | |
| T | 0.198 | 1.530 | 0.882 | 1.089 | 1.619 | 58.006 ** | 240.839 ** | |
| Y × T | 0.497 | 1.058 | 0.450 | 0.513 | 4.141 ** | 19.914 ** | 41.941 ** | |
| Treatments | Years | Inputs | Total Inputs | Yield | Unit Price | Yield Income | Net Income | Annual Average Income | Cost–Benefit Ratio | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ploughing Cost | Rotary Tillage Cost | Sowing Cost | Seed Cost | Mature Compost Cost | Compound Fertilizer Cost | Pesticide Cost | Harvesting Cost | |||||||||
| CNY ha−1 | CNY ha−1 | CNY ha−1 | CNY ha−1 | CNY ha−1 | CNY ha−1 | CNY ha−1 | CNY ha−1 | CNY ha−1 | Kg ha−1 | CNY kg−1 | CNY ha−1 | CNY ha−1 | CNY ha−1 | |||
| A | 2012 | 0 | 225 | 150 | 870 | 0 | 3975.0 | 225 | 1500 | 6945.0 | 5809.1 | 2.2 | 12,779.9 | 5834.9 | 5810.9 | 1.8 |
| 2013 | 0 | 225 | 150 | 870 | 0 | 3975.0 | 225 | 1500 | 6945.0 | 5591.9 | 2.2 | 12,302.1 | 5357.1 | |||
| 2014 | 0 | 225 | 150 | 870 | 0 | 3975.0 | 225 | 1500 | 6945.0 | 5993.6 | 2.2 | 13,185.8 | 6240.8 | |||
| B | 2012 | 300 | 225 | 150 | 870 | 0 | 3975.0 | 225 | 1500 | 7245.0 | 6283.1 | 2.2 | 13,822.7 | 6577.7 | 6369.3 | 1.9 |
| 2013 | 300 | 225 | 150 | 870 | 0 | 3975.0 | 225 | 1500 | 7245.0 | 6312.6 | 2.2 | 13,887.7 | 6642.7 | |||
| 2014 | 300 | 225 | 150 | 870 | 0 | 3975.0 | 225 | 1500 | 7245.0 | 5969.3 | 2.2 | 13,132.4 | 5887.4 | |||
| C | 2012 | 330 | 225 | 150 | 870 | 0 | 3975.0 | 225 | 1500 | 7275.0 | 5886.9 | 2.2 | 12,951.2 | 5676.2 | 6997.4 | 2.0 |
| 2013 | 330 | 225 | 150 | 870 | 0 | 3975.0 | 225 | 1500 | 7275.0 | 7269.5 | 2.2 | 15,992.8 | 8717.8 | |||
| 2014 | 330 | 225 | 150 | 870 | 0 | 3975.0 | 225 | 1500 | 7275.0 | 6306.0 | 2.2 | 13,873.2 | 6598.2 | |||
| D | 2012 | 0 | 225 | 150 | 870 | 1500 | 1987.5 | 225 | 1500 | 6457.5 | 6338.3 | 2.2 | 13,944.2 | 7486.7 | 9101.6 | 2.4 |
| 2013 | 0 | 225 | 150 | 870 | 1500 | 1987.5 | 225 | 1500 | 6457.5 | 8240.0 | 2.2 | 18,127.9 | 11,670.4 | |||
| 2014 | 0 | 225 | 150 | 870 | 1500 | 1987.5 | 225 | 1500 | 6457.5 | 6638.7 | 2.2 | 14,605.1 | 8147.6 | |||
| E | 2012 | 0 | 225 | 150 | 870 | 1500 | 1987.5 | 225 | 1500 | 6457.5 | 6854.6 | 2.2 | 15,080.0 | 8622.5 | 9712.7 | 2.5 |
| 2013 | 300 | 225 | 150 | 870 | 1500 | 1987.5 | 225 | 1500 | 6757.5 | 8690.0 | 2.2 | 19,117.9 | 12,360.4 | |||
| 2014 | 330 | 225 | 150 | 870 | 1500 | 1987.5 | 225 | 1500 | 6787.5 | 6792.2 | 2.2 | 14,942.7 | 8155.2 | |||
| F | 2012 | 330 | 225 | 150 | 870 | 1500 | 1987.5 | 225 | 1500 | 6787.5 | 7478.7 | 2.2 | 16,453.1 | 9665.6 | 10,515.2 | 2.6 |
| 2013 | 300 | 225 | 150 | 870 | 1500 | 1987.5 | 225 | 1500 | 6757.5 | 8953.1 | 2.2 | 19,696.7 | 12,939.2 | |||
| 2014 | 0 | 225 | 150 | 870 | 1500 | 1987.5 | 225 | 1500 | 6457.5 | 6999.2 | 2.2 | 15,398.1 | 8940.6 | |||
| Soil Depths (cm) | Total Nitrogen (g kg−1) | Available Nitrogen (mg kg−1) | Available Phosphorus (mg kg−1) | Available Potassium (mg kg−1) | Organic Matter (g kg−1) | Bulk Density (g cm−3) | C/N Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10–15 | 0.49 | 61.5 | 1.73 | 79.0 | 6.56 | 1.54 | 7.76 |
| 15–25 | 0.61 | 24.2 | 3.71 | 102.0 | 7.98 | 1.58 | 7.59 |
| 25–35 | 0.41 | 35.7 | 1.76 | 82.7 | 5.24 | 1.62 | 7.41 |
| Total Nutrient Content (N + P2O5 + K2O, on Dry Basis) (%) | N (%) | P2O5 (%) | K2O (%) | Organic Matter Content (on Dry Basis) (%) | Moisture Content (Fresh Sample) (%) | Alkali-Hydrolyzable Nitrogen (mg kg−1) | Available Potassium (mg kg−1) | Available Potassium (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.2 | 1.29 | 0.53 | 1.34 | 55.04 | 3.6 | 2485 | 689.6 | 5068 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, M.; Zhen, Q.; Duan, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Shi, X. Integrated Moldboard Ploughing and Organic–Inorganic Fertilization Enhances Maize Yield and Soil Fertility in a Semi-Arid Region of North China. Plants 2025, 14, 3594. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233594
Gao M, Zhen Q, Duan Y, Liu C, Zhou J, Li Y, Zhang X, Wang X, Shi X. Integrated Moldboard Ploughing and Organic–Inorganic Fertilization Enhances Maize Yield and Soil Fertility in a Semi-Arid Region of North China. Plants. 2025; 14(23):3594. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233594
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Min, Qingmiao Zhen, Yafeng Duan, Chao Liu, Jing Zhou, Yongping Li, Xiaochen Zhang, Xiuhong Wang, and Xiangyuan Shi. 2025. "Integrated Moldboard Ploughing and Organic–Inorganic Fertilization Enhances Maize Yield and Soil Fertility in a Semi-Arid Region of North China" Plants 14, no. 23: 3594. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233594
APA StyleGao, M., Zhen, Q., Duan, Y., Liu, C., Zhou, J., Li, Y., Zhang, X., Wang, X., & Shi, X. (2025). Integrated Moldboard Ploughing and Organic–Inorganic Fertilization Enhances Maize Yield and Soil Fertility in a Semi-Arid Region of North China. Plants, 14(23), 3594. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233594






