Functional 14-3-3 Proteins: Master Regulators in Plant Responses to Salt Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
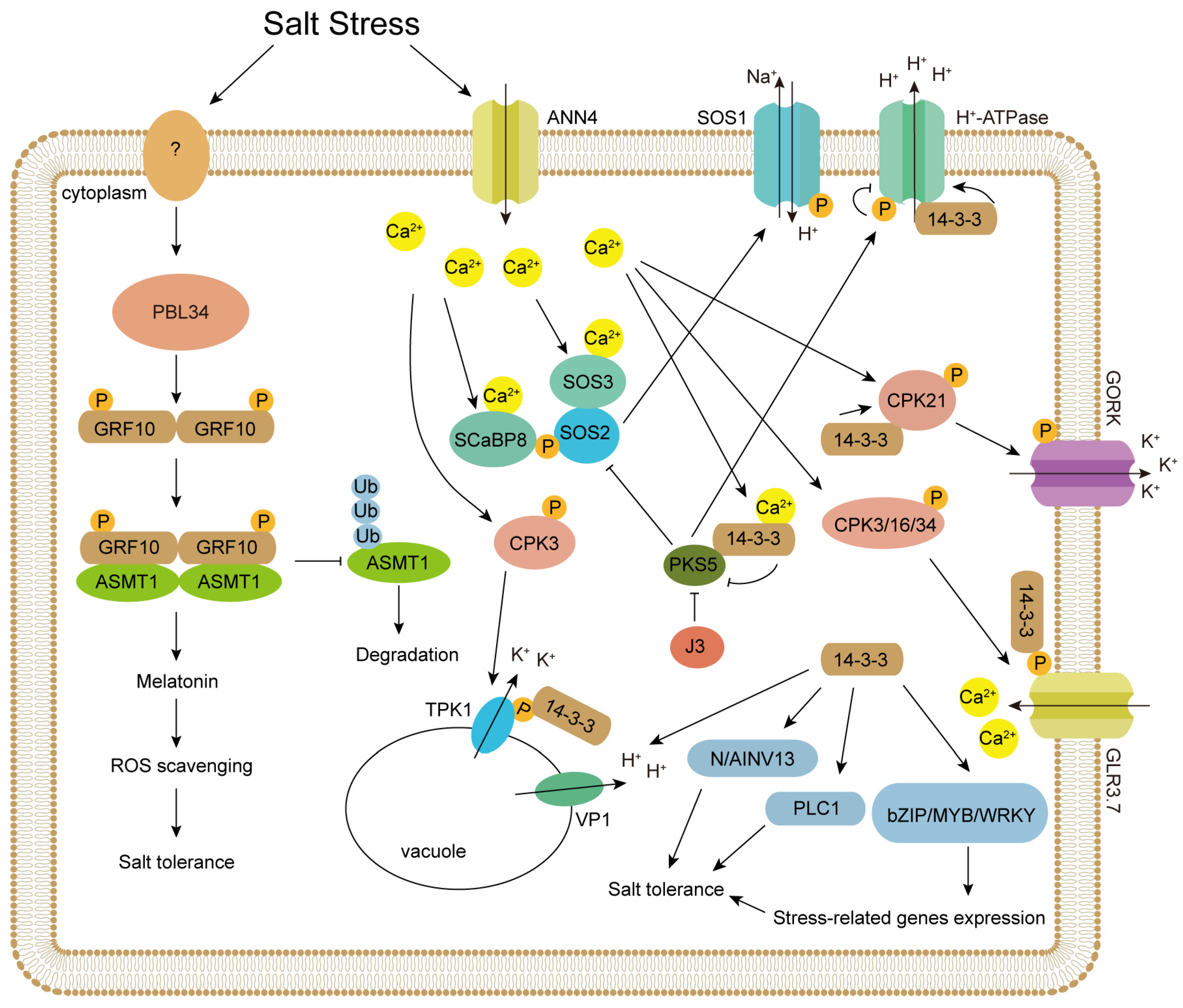
2. 14-3-3 Proteins Regulate Salt Stress-Related Proteins
| Proteins | Key Regulatory Features | Species | Stress | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOS2 | Context-dependent: Binding inhibits kinase activity normally. Salt stress induces 14-3-3 degradation, releasing SOS2 for activation. | Arabidopsis thaliana | Salt stress | [36,37] |
| PKS5 | Direct Inhibition: Ca2+-activated 14-3-3 binds and represses PKS5 kinase activity, releasing its inhibition of SOS2. | Arabidopsis thaliana | Salt and alkaline stresses | [37,38] |
| CPK21 | Positive Feedback: Salt-induced Ca2+ and autophosphorylation enhance 14-3-3 binding, which further amplifies kinase activity. | Arabidopsis thaliana | Salt stress | [39] |
| TMKP1 | Direct Activation: 14-3-3 binding to phosphorylated C-terminus stimulates phosphatase activity, boosting antioxidant defense. | Triticum durum | Salt stress | [40] |
| GORK | Indirect Activation: Activated by CPK21 (which is enhanced by 14-3-3). 14-3-3 may stabilize the CPK21-GORK complex. | Arabidopsis thaliana | Salt stress | [39] |
| TPK1/KCO1 | Phospho-Dependent: Phosphorylation (e.g., by CPK3) enhances 14-3-3 binding, increasing channel activity for vacuolar K+ release. | Arabidopsis thaliana | Salt stress | [41,42] |
| GLR3.7 | Phospho-Switched: Normally inhibited. Salt-induced phosphorylation enhances 14-3-3 binding, modulating its Ca2+ channel activity. | Arabidopsis thaliana | Salt stress | [43] |
| SOS1 | Direct inhibition: via binding to SOS1 C-terminal. | Arabidopsis thaliana | Salt stress | [44] |
| H+-ATPase | Phospho-Binding: 14-3-3 binds phosphorylated C-terminal autoinhibitory domain, displacing it to activate H+ pumping. | Arabidopsis thaliana | Salt and alkaline stresses | [38,45,46,47] |
| N/AINV | Enzyme Activation: Interaction enhances sucrose hydrolase activity, increasing osmolyte (glucose/fructose) production. | Gossypium hirsutum | Salt and drought stresses | [48] |
| PLC1 | Dual Role: 14-3-3 binding both activates enzyme activity and stabilizes the protein by inhibiting its ubiquitination. | Oryza sativa | Salt stress | [49] |
| VP1 | Pump Activation: Interaction enhances H+-pyrophosphatase activity, strengthening the proton gradient for vacuolar Na+ sequestration. | Nitraria sibirica | Salt stress | [14] |
| bZIP23/62/71 | TF Co-activator: Binding enhances transcription factor stability/DNA-binding, upregulating ABA-responsive genes. | Oryza sativa/ Brachypodium distachyon | Salt, drought, osmotic stresses | [50,51,52] |
| AREB | ABA Signaling: Interacts with AREB transcription factors to strengthen ABA signaling and stress-responsive gene expression. | Malus domestica | Salt, drought stresses | [53] |
| VSF-1 | Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Shuttling: Binding retains TF in cytoplasm. Dephosphorylation under stress releases it for nuclear translocation. | Solanum lycopersicum | Hypo-osmotic stress | [54,55,56,57,58] |
| MYB64 | TF Co-activator: Interaction enhances the transcriptional activation function of MYB64. | Triticum aestivum | Salt stress | [59] |
| WRKY18 | Stability and Activity: Phospho-dependent interaction enhances TF stability and transcriptional activity of SOS pathway genes. | Malus domestica | Salt stress | [60] |
| ASMT1 | Enzyme Recruitment: Phosphorylated 14-3-3 shows enhanced association with ASMT1, promoting melatonin biosynthesis. | Malus domestica | Salt stress | [61] |
| GCN4 | Proteasomal Degradation: GCN4 promotes the degradation of specific 14-3-3 isoforms, inhibiting H+-ATPase and closing stomata. | Arabidopsis thaliana | Drought stress | [62] |
| RNF1/2 | Ubiquitination Link: 14-3-3 protein interacts with E3 ubiquitin ligases RNF1 and RNF2, suggesting potential regulation of 14-3-3 stability. | Setaria italica | Salt stress | [63] |
2.1. Reprogramming Stress Responses by Regulating Signaling Components
2.1.1. Regulation of Protein Kinases
2.1.2. Regulation of Protein Phosphatases
2.2. Maintaining Cellular Balance by Regulating Ion Homeostasis and Membrane Transport
2.2.1. Regulation of Ion Channels
2.2.2. Regulation of Proton Pumps
2.3. Coordinating Metabolism and Gene Expression by Regulating Metabolic Enzymes and Transcription Factors
2.3.1. Regulation of Key Metabolic Enzymes
2.3.2. Regulation of Transcription Factors
3. Regulation of 14-3-3 Proteins in Response to Salt Stress
3.1. Regulation of 14-3-3 Proteins by Phosphorylation
3.2. The Regulation of 14-3-3s by Ubiquitination
3.3. Concluding Remarks on 14-3-3 Regulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeLille, J.M.; Sehnke, P.C.; Ferl, R.J. The Arabidopsis 14-3-3 Family of Signaling Regulators. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Du, Y.; Jiang, L.; Liu, J.Y. Molecular Analysis and Expression Patterns of the 14-3-3 Gene Family from Oryza sativa. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 40, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Xie, F.; Zhang, B. Transcriptome-Wide Identification and Stress Properties of the 14-3-3 Gene Family in Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Funct. Integr. Genom. 2011, 11, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dhaubhadel, S. Soybean 14-3-3 Gene Family: Identification and Molecular Characterization. Planta 2011, 233, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.P.; Li, H.L.; Guo, D.; Tang, X.; Peng, S.Q. Identification and Characterization of the 14-3-3 Gene Family in Hevea brasiliensis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 80, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Wang, T.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, J. Genome-Wide Identification, Classification, and Expression Analysis of 14-3-3 Gene Family in Populus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Muthamilarasan, M.; Bonthala, V.S.; Roy, R.; Prasad, M. Unraveling 14-3-3 Proteins in C4 Panicoids with Emphasis on Model Plant Setaria italica Reveals Phosphorylation-Dependent Subcellular Localization of RS Splicing Factor. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Jiang, X.; Jin, D.; Dhaubhadel, S.; Bian, S.; Li, X. Identification of 14-3-3 Family in Common Bean and Their Response to Abiotic Stress. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Shi, W. Profiling of the 14-3-3 Gene Family in Response to Salt Stress and Potassium and Iron Deficiencies in Young Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) Roots: Analysis by Real-Time RT–PCR. Ann. Bot. 2006, 98, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandna, R.; Augustine, R.; Kanchupati, P.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, P.; Arya, G.C.; Bisht, N.C. Class-Specific Evolution and Transcriptional Differentiation of 14-3-3 Family Members in Mesohexaploid Brassica rapa. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Bian, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhen, S.; Hu, Y.; Yan, Y. Molecular Characterization of the 14-3-3 Gene Family in Brachypodium distachyon L. Reveals High Evolutionary Conservation and Diverse Responses to Abiotic Stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ren, L.; Xu, B.; Yang, X.; Xia, Q.; He, P.; Xiao, S.; Guo, A.; Hu, W.; Jin, Z. Genome-Wide Identification, Phylogeny, and Expression Analyses of the 14-3-3 Family Reveal Their Involvement in the Development, Ripening, and Abiotic Stress Response in Banana. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Shan, H.; Ni, Y.; Xu, M.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, B.; Li, X. Genome-Wide Analysis of 14-3-3 Gene Family in Four Gramineae and Its Response to Mycorrhizal Symbiosis in Maize. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1117879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Duan, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X. Genome-Wide Identification of the 14-3-3 Gene Family and Its Involvement in Salt Stress Response through Interaction with NsVP1 in Nitraria sibirica Pall. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, D.; Morris, E.R.; Walker, J.C. 14-3-3 and FHA Domains Mediate Phosphoprotein Interactions. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009, 60, 67–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denison, F.C.; Paul, A.L.; Zupanska, A.K.; Ferl, R.J. 14-3-3 Proteins in Plant Physiology. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.J.; Freitas, T.A.; Wallick, C.J.; Guyette, C.V.; Warn-Cramer, B.J. Molecular Dynamics and In Vitro Analysis of Connexin43: A New 14-3-3 Mode-1 Interacting Protein. Protein Sci. 2006, 15, 2344–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuasa, K.; Ota, R.; Matsuda, S.; Isshiki, K.; Inoue, M.; Tsuji, A. Suppression of Death-Associated Protein Kinase 2 by Interaction with 14-3-3 Proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 464, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kumagai, A.; Dunphy, W.G. Positive Regulation of Wee1 by Chk1 and 14-3-3 Proteins. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalle, M.; Visconti, S.; Marra, M.; Camoni, L.; Velasco, R.; Aducci, P. ZmMPK6, a Novel Maize MAP Kinase that Interacts with 14-3-3 Proteins. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 59, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Koizumi, N.; Kusano, T.; Sano, H. Specific Binding of a 14-3-3 Protein to Autophosphorylated WPK4, an SNF1-Related Wheat Protein Kinase, and to WPK4-Phosphorylated Nitrate Reductase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 41528–41530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Peng, T.; Xue, S. Mechanisms of Plant Saline-Alkaline Tolerance. J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 281, 153916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhou, H.; Ma, C.; Wang, P. Regulation of Plant Responses to Salt Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R. Genes and Salt Tolerance: Bringing Them Together. New Phytol. 2005, 167, 645–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Guo, Y. Designing Salt Stress-Resilient Crops: Current Progress and Future Challenges. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2024, 66, 303–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Shi, H.; Yang, Y.; Feng, X.; Chen, X.; Xiao, F.; Lin, H.; Guo, Y. Insights into Plant Salt Stress Signaling and Tolerance. J. Genet. Genom. 2024, 51, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.K. Abiotic Stress Signaling and Responses in Plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Zhu, J.K. Molecular and Genetic Aspects of Plant Responses to Osmotic Stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2002, 25, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Schumaker, K.S.; Zhu, J.K. Cell Signaling during Cold, Drought, and Salt Stress. Plant Cell 2002, 14, S165–S183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, S.; Wang, C. Calcium Signaling Mechanisms Across Kingdoms. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 37, 311–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibesigwa, D.G.; Zhuang, W.; Matola, S.H.; Zhao, H.; Li, W.; Yang, L.; Ren, J.; Liu, Q.; Yang, J. Molecular Insights Into Salt Stress Adaptation in Plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2025, 48, 5604–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishitani, M.; Liu, J.; Halfter, U.; Kim, C.S.; Shi, W.; Zhu, J.K. SOS3 Function in Plant Salt Tolerance Requires N-Myristoylation and Calcium Binding. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, R.; Lin, H.; Mendoza, I.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, W.; Yang, Y.; Shang, M.; Chen, S.; Pardo, J.M.; Guo, Y. SCABP8/CBL10, a Putative Calcium Sensor, Interacts with the Protein Kinase SOS2 to Protect Arabidopsis Shoots from Salt Stress. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1415–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Yang, Y.; Quan, R.; Mendoza, I.; Wu, Y.; Du, W.; Zhao, S.; Schumaker, K.S.; Pardo, J.M.; Guo, Y. Phosphorylation of SOS3-Like Calcium Binding Protein8 by SOS2 Protein Kinase Stabilizes Their Protein Complex and Regulates Salt Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 1607–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, Y. Unraveling Salt Stress Signaling in Plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2018, 60, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Lin, H.; Chen, S.; Becker, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Kudla, J.; Schumaker, K.S.; Guo, Y. Inhibition of the Arabidopsis Salt Overly Sensitive Pathway by 14-3-3 Proteins. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 1166–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, C.; Xue, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Song, C.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Y. Calcium-Activated 14-3-3 Proteins as a Molecular Switch in Salt Stress Tolerance. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuglsang, A.T.; Guo, Y.; Cuin, T.A.; Qiu, Q.; Song, C.; Kristiansen, K.A.; Bych, K.; Schulz, A.; Shabala, S.; Schumaker, K.S.; et al. Arabidopsis Protein Kinase PKS5 Inhibits the Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase by Preventing Interaction with 14-3-3 Protein. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1617–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kleeff, P.J.M.; Gao, J.; Mol, S.; Zwart, N.; Zhang, H.; Li, K.W.; de Boer, A.H. The Arabidopsis GORK K+-Channel Is Phosphorylated by Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinase 21 (CPK21), Which in Turn Is Activated by 14-3-3 Proteins. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 125, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbel, M.; Cotelle, V.; Ebel, C.; Zaidi, I.; Ormancey, M.; Galaud, J.-P.; Hanin, M. Regulation of the Wheat MAP Kinase Phosphatase 1 by 14-3-3 Proteins. Plant Sci. 2017, 257, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latz, A.; Becker, D.; Hekman, M.; Müller, T.; Beyhl, D.; Marten, I.; Eing, C.; Fischer, A.; Dunkel, M.; Bertl, A.; et al. TPK1, a Ca2+-Regulated Arabidopsis Vacuole Two-Pore K+ Channel Is Activated by 14-3-3 Proteins. Plant J. 2007, 52, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latz, A.; Mehlmer, N.; Zapf, S.; Mueller, T.D.; Wurzinger, B.; Pfister, B.; Csaszar, E.; Hedrich, R.; Teige, M.; Becker, D. Salt Stress Triggers Phosphorylation of the Arabidopsis Vacuolar K+ Channel TPK1 by Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinases (CDPKs). Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1274–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.H.; Lee, C.E.; Lin, Y.S.; Lee, M.H.; Chen, P.Y.; Chang, H.C.; Chang, I.F. The Glutamate Receptor-Like Protein GLR3.7 Interacts with 14-3-3ω and Participates in Salt Stress Response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duscha, K.; Martins Rodrigues, C.; Müller, M.; Wartenberg, R.; Fliegel, L.; Deitmer, J.W.; Jung, M.; Zimmermann, R.; Neuhaus, H.E. 14-3-3 Proteins and Other Candidates form Protein-Protein Interactions with the Cytosolic C-terminal End of SOS1 Affecting Its Transport Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahn, T.; Fuglsang, A.T.; Olsson, A.; Brüntrup, I.M.; Collinge, D.B.; Volkmann, D.; Sommarin, M.; Palmgren, M.G.; Larsson, C. The 14-3-3 Protein Interacts Directly with the C-Terminal Region of the Plant Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 1805–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falhof, J.; Pedersen, J.T.; Fuglsang, A.T.; Palmgren, M. Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase Regulation in the Center of Plant Physiology. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Chai, X.; Mei, Y.; Du, J.; Du, H.; Shi, H.; Zhu, J.-K.; Zhang, H. Acetylproteomics Analyses Reveal Critical Features of Lysine-ε-Acetylation in Arabidopsis and a Role of 14-3-3 Protein Acetylation in Alkaline Response. Stress Biol. 2022, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, X.; Lv, J.; Ge, M.; Qiao, K.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Fan, S.; Ma, Q. GhN/AINV13 Positively Regulates Cotton Stress Tolerance by Interacting with the 14-3-3 Protein. Genomics 2021, 113, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Li, H.; Fan, W.; Feng, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, B.; Lin, F.; Jing, W.; et al. A 14-3-3 Protein Positively Regulates Rice Salt Tolerance by Stabilizing Phospholipase C1. Plant Cell Environ. 2023, 46, 1232–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, C.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, F.; Wei, Q.; Li, K.; Chang, J.; Yang, G.; et al. A Member of the 14-3-3 Gene Family in Brachypodium distachyon, BdGF14d, Confers Salt Tolerance in Transgenic Tobacco Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, H.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ou, X. The 14-3-3 Protein BdGF14a Increases the Transcriptional Regulation Activity of BdbZIP62 to Confer Drought and Salt Resistance in Tobacco. Plants 2024, 13, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, X.; Liao, W.; Zhang, J.; Liang, J.; Xu, W. Involvement of OsGF14b Adaptation in the Drought Resistance of Rice Plants. Rice 2019, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.R.; Yang, Y.Y.; Zhang, R.; You, C.X.; Zhao, Q.; Hao, Y.J. MdGRF11, an Apple 14-3-3 Protein, Acts as a Positive Regulator of Drought and Salt Tolerance. Plant Sci. 2019, 288, 110219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeo, K.; Ito, T. Subcellular Localization of VIP1 Is Regulated by Phosphorylation and 14-3-3 Proteins. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 1972–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugama, D.; Liu, S.; Fujino, K.; Takano, T. Calcium Signalling Regulates the Functions of the bZIP Protein VIP1 in Touch Responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Ann. Bot. 2018, 122, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugama, D.; Yoon, H.S.; Fujino, K.; Liu, S.; Takano, T. Protein Phosphatase 2A Regulates the Nuclear Accumulation of the Arabidopsis bZIP Protein VIP1 under Hypo-Osmotic Stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 6101–6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.S.; Fujino, K.; Liu, S.; Takano, T.; Tsugama, D. The B″-Family Subunits of Protein Phosphatase 2A Are Necessary for In Vitro Dephosphorylation of the Arabidopsis Mechanosensory Transcription Factor VIP1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 534, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.S.; Tsugama, D. Overexpression of the Tomato Nuclear-Cytoplasmic Shuttling bZIP Transcription Factor VSF-1 in Arabidopsis Retards Plant Development under Mannitol-Stressed Conditions. J. Plant Physiol. 2025, 308, 154476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, W.; Chen, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, X.; Jin, Y.; Zhan, C.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.; Ma, D.; Qiao, Y. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Wheat 14-3-3 Genes Unravels the Role of TaGRF6-A in Salt Stress Tolerance by Binding MYB Transcription Factor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Kuang, W.; Leng, J.; Wang, X.; Qiu, L.; Nie, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, R.-F.; Wang, Y.; et al. The 14-3-3 Protein GRF8 Modulates Salt Stress Tolerance in Apple via the WRKY18-SOS Pathway. Plant Physiol. 2023, 194, 1906–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Yan, T.; Zhang, T.; Dong, S.; Bai, Y.; Song, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Li, R.; Zhao, H.; et al. MdGRF10 Phosphorylation Stabilizes MdASMT1 for Melatonin-Mediated Salt Tolerance in Apple. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2025, 67, 2863–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaundal, A.; Ramu, V.S.; Oh, S.; Lee, S.; Pant, B.; Lee, H.K.; Rojas, C.M.; Senthil-Kumar, M.; Mysore, K.S. GENERAL CONTROL NONREPRESSIBLE4 Degrades 14-3-3 and the RIN4 Complex to Regulate Stomatal Aperture with Implications on Nonhost Disease Resistance and Drought Tolerance. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 2233–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, C.; Kang, L.; Zhang, H.; Song, Y.; Zou, Z.; Zheng, W. Over-Expression of a 14-3-3 Protein from Foxtail Millet Improves Plant Tolerance to Salinity Stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, M.A.; Yamamoto, R.T.; Hanks, S.K.; Lamb, C.J. Molecular Cloning of Plant Transcripts Encoding Protein Kinase Homologs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 3140–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Y.; Song, C.; Wang, B.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y.; Gong, Z. Protein Kinases in Plant Responses to Drought, Salt, and Cold Stress. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 53–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ye, J.; Yang, Y.; Lin, H.; Yue, L.; Luo, J.; Long, Y.; Fu, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The SOS2-SCaBP8 Complex Generates and Fine-Tunes an AtANN4-Dependent Calcium Signature under Salt Stress. Dev. Cell 2019, 48, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.; Cai, J.; Zhan, E.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, H. Stability and Localization of 14-3-3 Proteins Are Involved in Salt Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 92, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, G.; Li, Y.; Sun, W.; He, X.; Li, R.; Jin, D.; Qi, X.; Liu, Z.; Bian, S. Functional Roles of Two 14-3-3s in Response to Salt Stress in Common Bean. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2018, 40, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumwald, E. Sodium Transport and Salt Tolerance in Plants. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2000, 12, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, M.; Bressan, R.; Pardo, J. The Dawn of Plant Salt Tolerance Genetics. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozdowicz, Y.M.; Rea, P.A. Vacuolar H+ Pyrophosphatases: From the Evolutionary Backwaters into the Mainstream. Trends Plant Sci. 2001, 6, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brini, F.; Masmoudi, K. Ion Transporters and Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants. ISRN Mol. Biol. 2012, 2012, 927436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Xie, C.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, J.; Liu, D.; Chen, S.; Fuglsang, A.T.; Palmgren, M.G.; Schumaker, K.S.; et al. The Arabidopsis Chaperone J3 Regulates the Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase through Interaction with the PKS5 Kinase. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 1313–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Jia, L.; Shi, W.; Balu¡ka, F.e.; Kronzucker, H.J.; Liang, J.; Zhang, J. The Tomato 14-3-3 Protein TFT4 Modulates H+ Efflux, Basipetal Auxin Transport, and the PKS5-J3 Pathway in the Root Growth Response to Alkaline Stress. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 1817–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, S.; Ehlert, B.; Liese, A.; Kurth, J.; Cazalé, A.C.; Romeis, T. Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinase CPK21 Functions in Abiotic Stress Response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.Y.; Yu, X.C.; Wang, X.J.; Zhao, R.; Li, Y.; Fan, R.C.; Shang, Y.; Du, S.Y.; Wang, X.F.; Wu, F.Q.; et al. Two Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinases, CPK4 and CPK11, Regulate Abscisic Acid Signal Transduction in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 3019–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrabak, E.M.; Chan, C.W.M.; Gribskov, M.; Harper, J.F.; Choi, J.H.; Halford, N.; Kudla, J.r.; Luan, S.; Nimmo, H.G.; Sussman, M.R.; et al. The Arabidopsis CDPK-SnRK Superfamily of Protein Kinases. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 666–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulm, R.; Ichimura, K.; Mizoguchi, T.; Peck, S.C.; Zhu, T.; Wang, X.; Shinozaki, K.; Paszkowski, J. Distinct Regulation of Salinity and Genotoxic Stress Responses by Arabidopsis MAP Kinase Phosphatase 1. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 6483–6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Wang, S.; Sritubtim, S.; Chen, J.-G.; Ellis, B.E. Arabidopsis Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase MPK12 Interacts with the MAPK Phosphatase IBR5 and Regulates Auxin Signaling. Plant J. 2009, 57, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaïdi, I.; Ebel, C.; Touzri, M.; Herzog, E.; Evrard, J.L.; Schmit, A.C.; Masmoudi, K.; Hanin, M. TMKP1 Is a Novel Wheat Stress Responsive MAP Kinase Phosphatase Localized in the Nucleus. Plant Mol. Biol. 2010, 73, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, I.; Ebel, C.; Belgaroui, N.; Ghorbel, M.; Amara, I.; Hanin, M. The Wheat MAP Kinase Phosphatase 1 Alleviates Salt Stress and Increases Antioxidant Activities in Arabidopsis. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 193, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.J.; Leigh, R.A.; Miller, A.J. Potassium Homeostasis in Vacuolate Plant Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 10510–10514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuin, T.A.; Miller, A.J.; Laurie, S.A.; Leigh, R.A. Potassium Activities in Cell Compartments of Salt--Grown Barley Leaves. J. Exp. Bot. 2003, 54, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adem, G.D.; Chen, G.; Shabala, L.; Chen, Z.H.; Shabala, S. GORK Channel: A Master Switch of Plant Metabolism? Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapken, D.; Hollmann, M. Arabidopsis thaliana Glutamate Receptor Ion Channel Function Demonstrated by Ion Pore Transplantation. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 383, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, F.J.; Martinez-Atienza, J.; Villalta, I.; Jiang, X.; Kim, W.Y.; Ali, Z.; Fujii, H.; Mendoza, I.; Yun, D.J.; Zhu, J.K.; et al. Activation of the Plasma Membrane Na/H Antiporter Salt-Overly-Sensitive 1 (SOS1) by Phosphorylation of an Auto-Inhibitory C-Terminal Domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2611–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baunsgaard, L.; Fuglsang, A.T.; Jahn, T.; Korthout, H.A.A.J.; De Boer, A.H.; Palmgren, M.G. The 14-3-3 Proteins Associate with the Plant Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase to Generate a Fusicoccin Binding Complex and a Fusicoccin Responsive System. Plant J. 1998, 13, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svennelid, F.; Olsson, A.; Piotrowski, M.; Rosenquist, M.; Ottman, C.; Larsson, C.; Oecking, C.; Sommarin, M. Phosphorylation of Thr-948 at the C Terminus of the Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase Creates a Binding Site for the Regulatory 14-3-3 Protein. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 2379–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Tu, B.P. Acetyl-CoA and the Regulation of Metabolism: Mechanisms and Consequences. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 33, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, H.; Shabala, S.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H. Tissue Tolerance Mechanisms Conferring Salinity Tolerance in a Halophytic Perennial Species Nitraria sibirica Pall. Tree Physiol. 2021, 41, 1264–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.D.; Huang, Y.F.; Pan, Y.J.; Huang, L.K.; Liao, Y.Y.; Lin, W.H.; Liu, T.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Pan, R.L. Regulation of H+-Pyrophosphatase by 14-3-3 Proteins from Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Membr. Biol. 2018, 251, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinoia, E.; Maeshima, M.; Neuhaus, H.E. Vacuolar Transporters and Their Essential Role in Plant Metabolism. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zeng, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Jiang, L.; Guo, Y. SOS2 Phosphorylates FREE1 to Regulate Multi-Vesicular Body Trafficking and Vacuolar Dynamics under Salt Stress. Plant Cell 2025, 37, koaf012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, W.A.; Pontis, H.G.; Salerno, G.L. Differential Expression of Alkaline and Neutral Invertases in Response to Environmental Stresses: Characterization of an Alkaline Isoform as a Stress-Response Enzyme in Wheat Leaves. Planta 2007, 226, 1535–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Mo, X.; Wu, S.; Chu, J.; Wu, P. AtCYT-INV1, a Neutral Invertase, Is Involved in Osmotic Stress-Induced Inhibition on Lateral Root Growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 64, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Han, X.; Yu, S.; Liu, Z.; Guo, D.; He, Y.; Li, W.; Tao, Y.; Sun, C.; Xu, P.; et al. OsINV3 and Its Homolog, OsINV2, Control Grain Size in Rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; van Kleeff, P.J.M.; Oecking, C.; Li, K.W.; Erban, A.; Kopka, J.; Hincha, D.K.; de Boer, A.H. Light Modulated Activity of Root Alkaline/Neutral Invertase Involves the Interaction with 14-3-3 Proteins. Plant J. 2014, 80, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.; Wu, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Ruan, Y.L. Evolution of Sucrose Metabolism: The Dichotomy of Invertases and Beyond. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-El-Haliem, A.M.; Joosten, M.H.A.J. Plant Phosphatidylinositol-Specific Phospholipase C at the Center of Plant Innate Immunity. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2017, 59, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ried, M.K.; Wild, R.; Zhu, J.; Pipercevic, J.; Sturm, K.; Broger, L.; Harmel, R.K.; Abriata, L.A.; Hothorn, L.A.; Fiedler, D.; et al. Inositol Pyrophosphates Promote the Interaction of SPX Domains with the Coiled-Coil Motif of PHR Transcription Factors to Regulate Plant Phosphate Homeostasis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, R.; Gerasimaite, R.; Jung, J.Y.; Truffault, V.; Pavlovic, I.; Schmidt, A.; Saiardi, A.; Jessen, H.J.; Poirier, Y.; Hothorn, M.; et al. Control of Eukaryotic Phosphate Homeostasis by Inositol Polyphosphate Sensor Domains. Science 2016, 352, 986–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, F.; Yan, P.; Jing, W.; Zhang, C.; Kudla, J.; Zhang, W. A Phosphoinositide-Specific Phospholipase C Pathway Elicits Stress-Induced Ca2+ Signals and Confers Salt Tolerance to Rice. New Phytol. 2017, 214, 1172–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Yuan, S.; Cao, H.; Lam, S.M.; Shui, G.; Hong, Y.; Wang, X. Phosphatidylinositol-Hydrolyzing Phospholipase C4 Modulates Rice Response to Salt and Drought. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 536–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wu, Z.; Dong, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, J.; Yang, T.; Yang, W.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; et al. The 14-3-3 Protein OsGF14f Interacts with OsbZIP23 and Enhances Its Activity to Confer Osmotic Stress Tolerance in Rice. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 4173–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Ou, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Q. A 14-3-3 Protein-Encoding Gene, BdGF14g, Confers Better Drought Tolerance by Regulating ABA Biosynthesis and Signaling. Plants 2023, 12, 3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chang, S.; Chu, Z.; Wang, H.; Han, S.; Wang, Y. Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinase 21 Phosphorylates 14-3-3 Proteins in Response to ABA Signaling and Salt Stress in Rice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 1450–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.L.; Huang, L.F.; Lu, C.A.; He, S.L.; Wang, C.C.; Yu, S.P.; Chen, J.; Yu, S.M. Sugar Starvation- and GA-Inducible Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinase 1 Feedback Regulates GA Biosynthesis and Activates a 14-3-3 Protein to Confer Drought Tolerance in Rice Seedlings. Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 81, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailemariam, S.; Liao, C.J.; Mengiste, T. Receptor-Like Cytoplasmic Kinases: Orchestrating Plant Cellular Communication. Trends Plant Sci. 2024, 29, 1113–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Back, K. Melatonin Metabolism, Signaling and Possible Roles in Plants. Plant J. 2021, 105, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.A.; Saleem, M.; Fariduddin, Q. Recent Advances and Mechanistic Insights on Melatonin-Mediated Salt Stress Signaling in Plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 188, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.-W.; Liu, M.; Zhao, D.; Du, P.; Yan, L.; Liu, D.; Shi, Q.; Yang, C.; Qin, G.; Gong, B. Melatonin Confers Saline-Alkali Tolerance in Tomato by Alleviating Nitrosative Damage and S-Nitrosylation of H+-ATPase 2. Plant Cell 2025, 37, koaf035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhaylova, Y.V.; Puzanskiy, R.K.; Shishova, M.F. Evolution of 14-3-3 Proteins in Angiosperm Plants: Recurring Gene Duplication and Loss. Plants 2021, 10, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; He, J.; Babla, M.; Wu, T.; Tong, T.; Riaz, A.; Zeng, F.; Qin, Y.; Chen, G.; Deng, F.; et al. Molecular Evolution and Interaction of 14-3-3 Proteins with H+-ATPases in Plant Abiotic Stresses. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 75, 689–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, S.; Ren, H.; Afriyie, O.E.; Zhang, M.; Xu, D.; Huang, X. Genome-Wide Identification and Comparative Evolution of 14-3-3 Gene Family Members in Five Brassicaceae species. BMC Genom. 2025, 26, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Ye, G.; Liu, T.; Chen, C.; Yang, X.; Wan, B.; Pan, Y.; Yu, L. Functional Identification of a Novel 14-3-3 Epsilon Splicing Variant Suggests Dimerization is Not Necessary for 14-3-3 Epsilon to Inhibit UV-Induced Apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 396, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanna, W.; Thipwong, J.; Mahakaew, W.; Phongdara, A. Identification and Expression Analysis of Two Splice Variants of the 14-3-3 Epsilon from Litopenaeus Vannamei during WSSV Infections. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 5487–5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Kong, J.; Dong, N.; Zheng, L.; Zhao, S. Functional 14-3-3 Proteins: Master Regulators in Plant Responses to Salt Stress. Plants 2025, 14, 3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233568
Tang D, Zhao Y, Wang Z, Kong J, Dong N, Zheng L, Zhao S. Functional 14-3-3 Proteins: Master Regulators in Plant Responses to Salt Stress. Plants. 2025; 14(23):3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233568
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Dongxue, Yiwu Zhao, Zhongliang Wang, Junwen Kong, Naiqing Dong, Ling Zheng, and Shuangshuang Zhao. 2025. "Functional 14-3-3 Proteins: Master Regulators in Plant Responses to Salt Stress" Plants 14, no. 23: 3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233568
APA StyleTang, D., Zhao, Y., Wang, Z., Kong, J., Dong, N., Zheng, L., & Zhao, S. (2025). Functional 14-3-3 Proteins: Master Regulators in Plant Responses to Salt Stress. Plants, 14(23), 3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233568






