Synergistic Remediation of Eutrophic Rural Pond Water Using Submerged Macrophytes and Daphnia magna
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
2.1.1. Test Water
2.1.2. Tested Submerged Plants
2.1.3. Tested D. magna
2.2. Experiment Designs
2.3. Tested Methods
2.3.1. Determination of Water Quality
2.3.2. Determination of Phytoplankton
2.3.3. D. magna Density and Plants Wet Weight
2.4. Data Analysis and Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Different Daphnia magna Densities on Water Quality and Algal Suppression
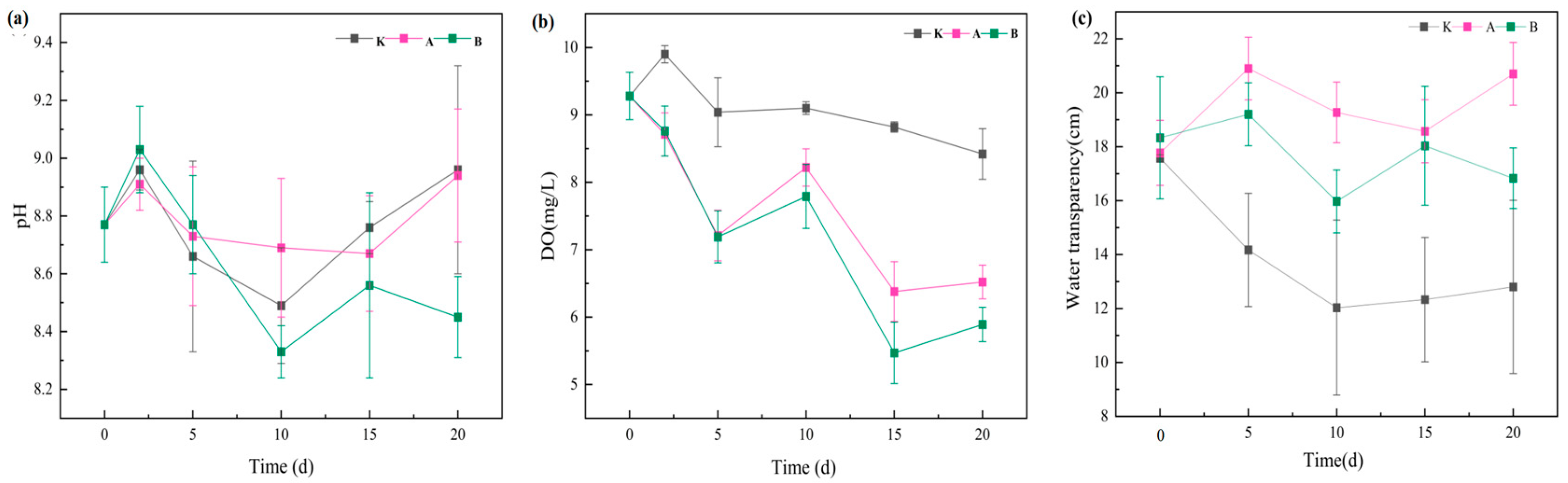
3.1.1. Effects on pH, Dissolved Oxygen (DO), and Water Transparency
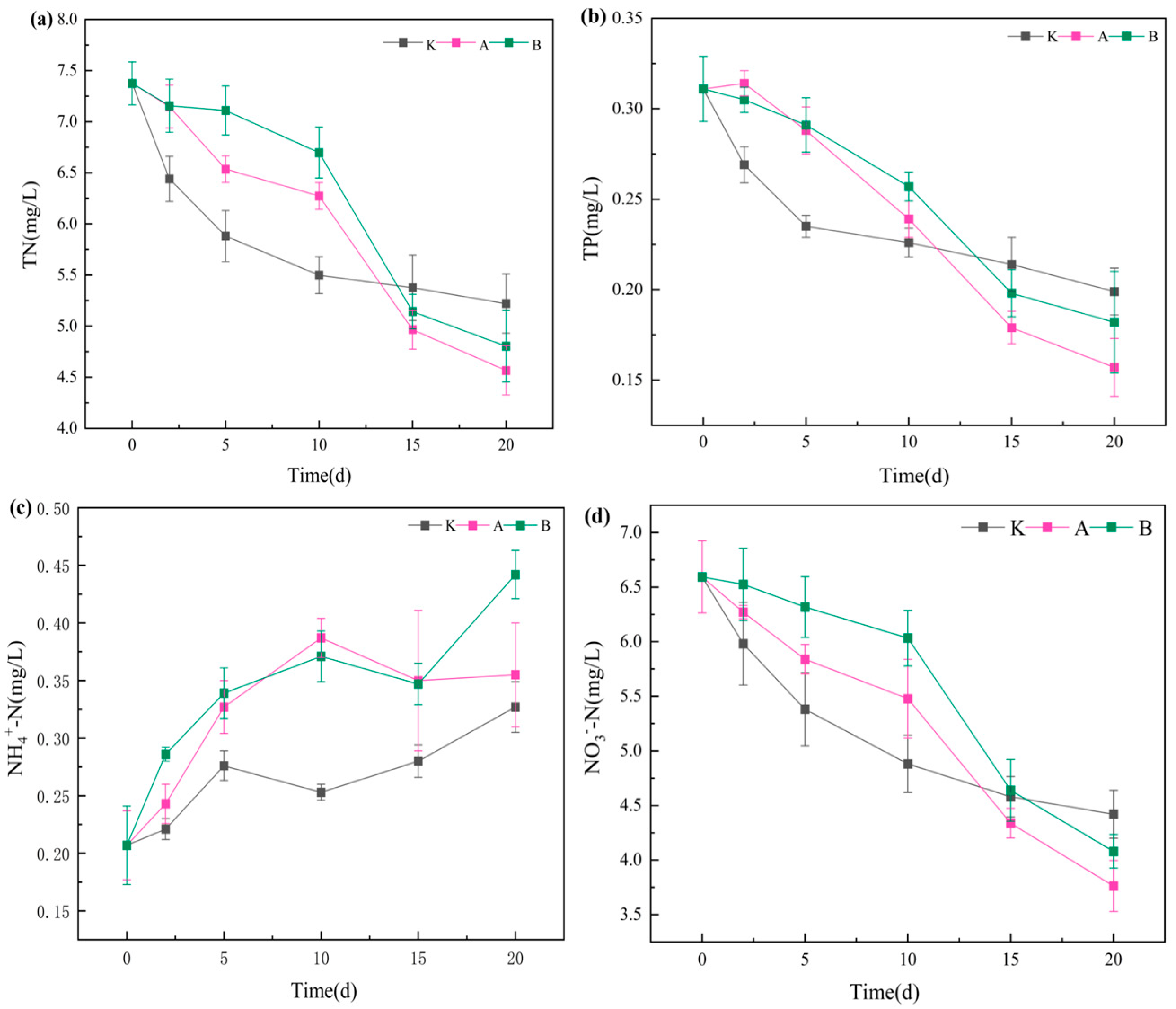
3.1.2. Variations in Nutrient Concentrations
3.1.3. Effects on Phytoplankton and Microcystins
3.2. Effects of Two Submerged Macrophytes on Water Quality
3.2.1. Variations in pH, Dissolved Oxygen (DO), and Water Transparency
3.2.2. Changes in Nitrogen and Phosphorus Concentrations
3.2.3. Dynamics of Phytoplankton Communities and Microcystin-LR (MC-LR) Concentrations
3.3. Effects of Two Submerged Macrophytes with Different Daphnia magna Densities on Water Quality
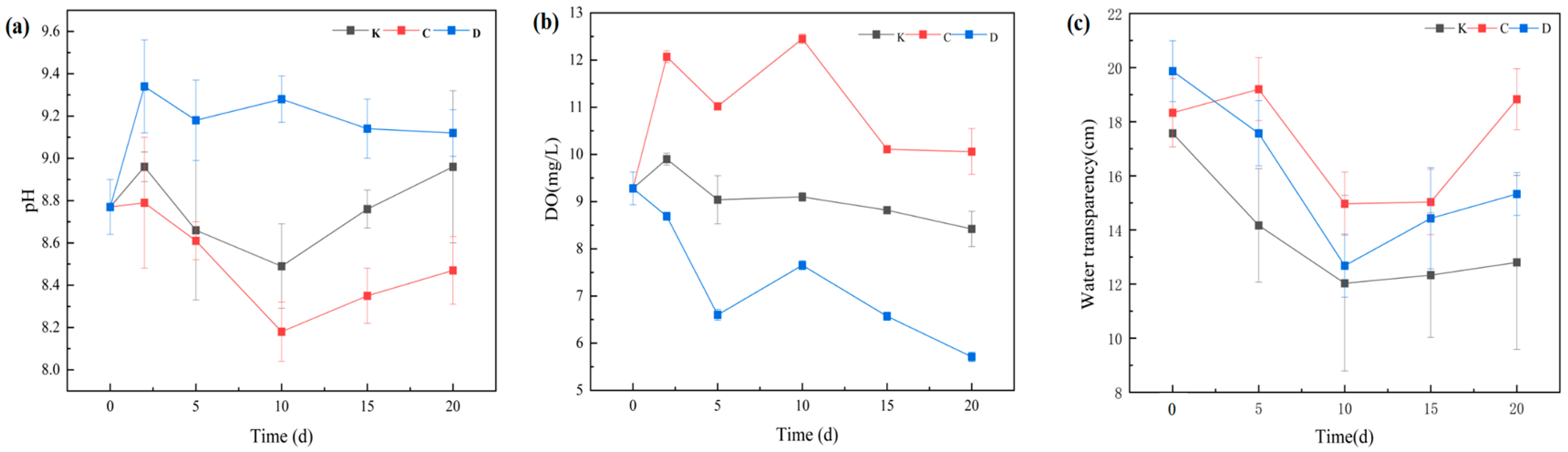
3.3.1. Variations in pH, Dissolved Oxygen (DO), and Water Transparency
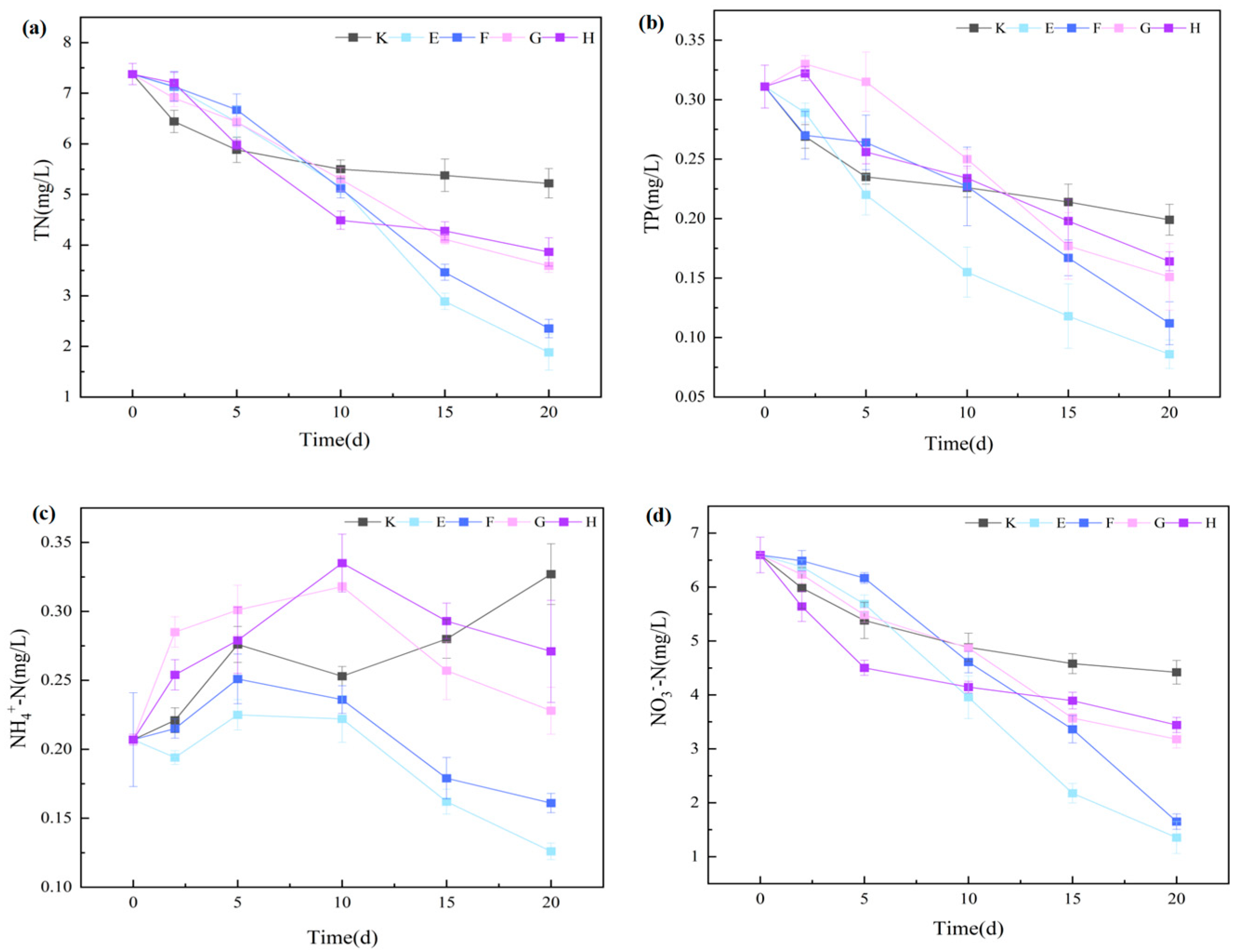
3.3.2. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal Characteristics and Synergistic Mechanisms
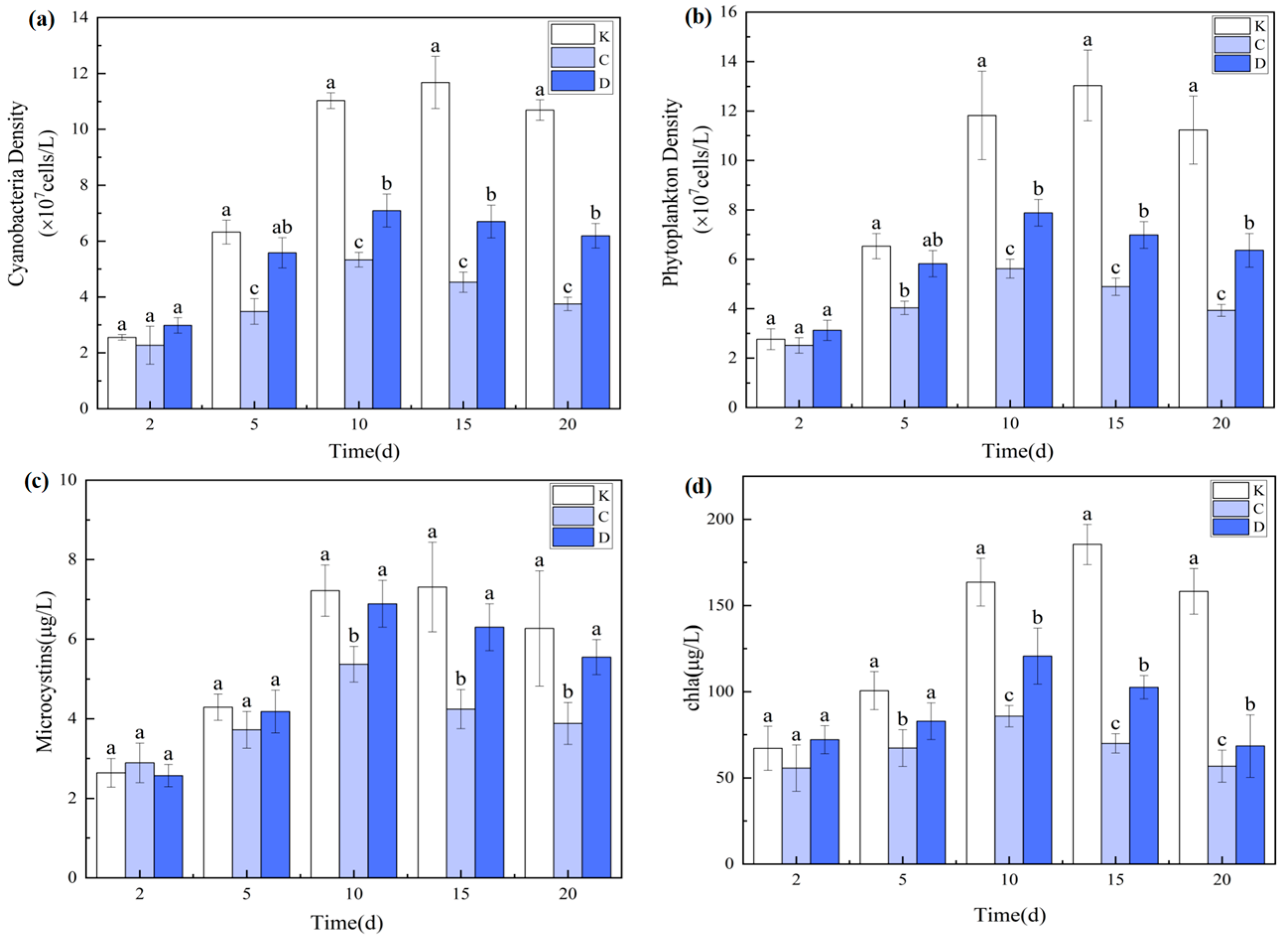
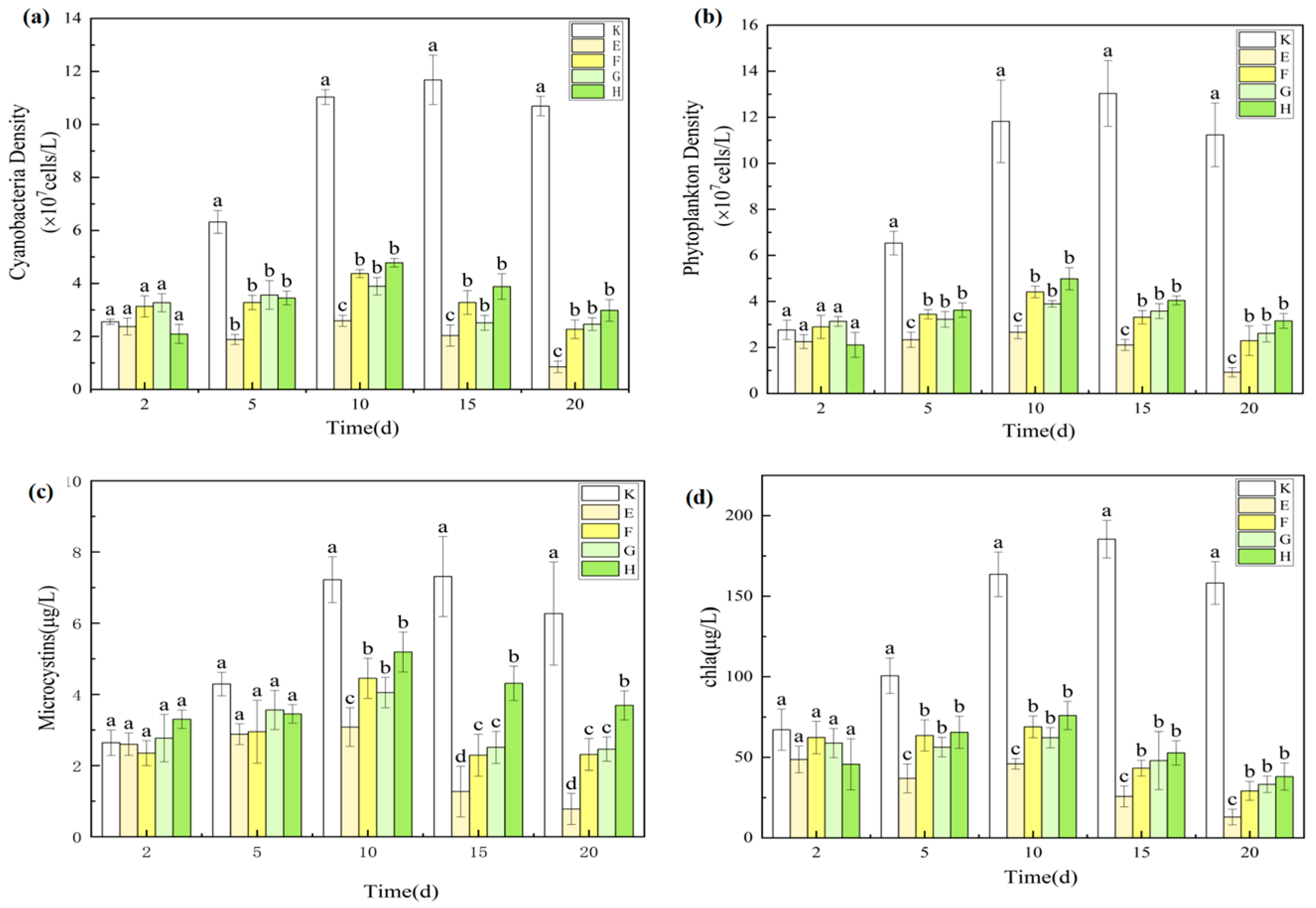
3.3.3. Synergistic Suppression of Phytoplankton and Microcystins
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Tian, K.; Liang, Q.; Liu, H. Study on the Application of Phoslock in Purifying Eutrophic Water in Dianchi Lake. Meteorol. Environ. Res. 2010, 1, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Luo, W.; Wu, X.; Wei, H.; Wang, B.; Phyoe, W.; Wang, F. Historical record of nutrients inputs into the Xin’an Reservoir and its potential environmental implication. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 20330–20341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, E.; Michalak, A.M.; Balaji, V. Eutrophication will increase during the 21st century as a result of precipitation changes. Science 2017, 357, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvie, H.P.; Smith, D.R.; Norton, L.R.; Edwards, F.K.; Bowes, M.J.; King, S.M.; Scarlett, P.; Davies, S.; Dils, R.M.; Bachiller-Jareno, N. Phosphorus and nitrogen limitation and impairment of headwater streams relative to rivers in Great Britain: A national perspective on eutrophication. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Yang, J.R.; Xiao, P.; Wilkinson, D.M.; Yang, J. Response of the eukaryotic plankton community to the cyanobacterial biomass cycle over 6 years in two subtropical reservoirs. ISME J. 2019, 13, 2196–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Geng, Y.; Liang, W.; Wang, H. Effect of aquatic macrophyte growth on landscape water quality improvement. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 33791–33803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferr O-Filho, A.D.S.; Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B. Cyanotoxins: Bioaccumulation and Effects on Aquatic Animals. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2729–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Harmful Cyanobacterial Blooms: Causes, Consequences, and Controls. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paskerova, H.; Hilscherova, K.; Blaha, L. Oxidative stress and detoxification biomarker responses in aquatic freshwater vertebrates exposed to microcystins and cyanobacterial biomass. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 2024–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geletu, T.T. Lake eutrophication: Control of phytoplankton overgrowth and invasive aquatic weeds. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2023, 28, e12425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.H.; Li, Q.; Cai, Q.; Ding, Y.R.; Zhao, T.T.; Luo, Y.; Pan, X.J. Effects of pH and Illumination on Removing Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Eutrophic Water by Purple-Root Water Hyacinth. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 807, 1690–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.S.; Eom, C.; Kim, W.; Kim, P.I.; Ju, S.Y.; Ryu, J.; Han, G.H.; Oh, J.; Cho, H.; Baek, S.H.; et al. Construction of target-specific virus-like particles for the delivery of algicidal compounds to harmful algae. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.T.; Yin, L.Y.; Chang, F.Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Li, W. Response of Vallisneria spinulosa (Hydrocharitaceae) to contrasting nitrogen loadings in controlled lake mesocosms. Hydrobiologia 2016, 776, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chislock, M.F.; Sarnelle, O.; Jernigan, L.M.; Wilson, A.E. Do high concentrations of microcystin prevent Daphnia control of phytoplankton? Water Res. 2013, 47, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, T.; Wang, H. Stress of algicidal substances from a bacterium Exiguobacterium sp. h10 on Microcystis aeruginosa. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 64, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtal-Frankiewicz, A.; Frankiewicz, P. The impact of pelagic (Daphnia longispina) and benthic (Dreissena polymorpha) filter feeders on chlorophyll and nutrient concentration. Limnologica 2011, 41, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gremberghe, I.; Vanormelingen, P.; Van der Gucht, K.; Mancheva, A.; D’hondt, S.; De Meester, L.; Vyverman, W. Influence of Daphnia infochemicals on functional traits of Microcystis strains (Cyanobacteria). Hydrobiologia 2009, 635, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Xiu, P.; Chai, F. Physical and biological controls on the summer chlorophyll bloom to the east of Vietnam. J. Oceanogr. 2014, 70, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, Q.; Xia, S.; Yan, C.; Pei, G. Response of benthic algae to environmental conditions in an urban lake recovered from eutrophication, China. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2020, 38, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waajen, G.W.A.M.; Van Bruggen, N.C.B.; Pires, L.M.D.; Lengkeek, W.; Lürling, M. Biomanipulation with quagga mussels (Dreissena rostriformis bugensis) to control harmful algal blooms in eutrophic urban ponds. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 90, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, X.F.; Mo, S.Q. Effects of mussel (Anodonta woodiana), submerged macrophyte (Vallisneria natans) and their coexistence on water quality. Chin. J. Ecol. 2016, 35, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y. Enhancement of Constructed Wetlands Performance by the Synergistic Effect of Submerged Plant and Benthic Fauna; Shandong University: Jinan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, Y.Z.; He, W.H.; Luo, K.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Tian, Q.T.; He, P.M. Bioremediation efficiency of applying Daphnia magna and submerged plants: A case study in Dishui lake of Shanghai China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecolog. 2010, 21, 495–499. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; He, W.H.; Peng, Z.R.; Hua, X.M.; Fenf, Y.; Huang, Z.Y.; Zhuo, S.; Zhou, L.L. Study on water eutrophication treatment with Daphnia magna and Vallisneria natans control system. J. Shanghai Ocean. Univ. 2018, 27, 515–521. [Google Scholar]
- Halpin, K. The Effect of Seed Mix Additions on Emergent Community Composition with Implications for Iowa CREP Wetland Restorations. Ph.D. Thesis, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Wei, X.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, B. D. magna in Combination with M. aquaticum Inhibited the Bacterioplankton in Eutrophic Water. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Tian, R.N. Purification Effect of Four Kinds of Aquatic Plants on Simulated Urban Landscape Polluted Water. Wetland Sci. 2018, 16, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, E.D.C.; Castelo-Branco, R.; Silva, L.; Silva, N.; Azevedo, J.; Vasconcelos, V.; Faustino, S.; Cunha, A. First Detection of Microcystin-LR in the Amazon River at the Drinking Water Treatment Plant of the Municipality of Macapá, Brazil. Toxins 2019, 11, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F. Study of Physicochemical Properties of Microenvironment in Cyanobacterial Granules and Water Layer and Their Influencing Factors; Nanjing University: Nanjing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, C.L.; Capps, K.A.; Rugenski, A.T.; Vanni, M.J. Consumer-driven nutrient dynamics in freshwater ecosystems: From individuals to ecosystems. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2017, 92, 2003–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Li, L.; Song, K.; Li, Y.; Lyu, H.; Wen, Z.; Fang, C.; Bi, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. Corrigendum to “An OLCI-based algorithm for semi-empirically partitioning absorption coefficient and estimating chlorophyll a concentration in various turbid case-2 waters”. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proulx, M.; Pick, F.R.; Mazumder, A.; Hamilton, P.B.; Lean, D.R.S. Effects of Nutrients and Planktivorous Fish on the Phytoplankton of Shallow and Deep Aquatic Systems. Ecology 1996, 77, 1556–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, S. Initial conditions mediate the interaction between Daphnia and bloom-forming cyanobacteria. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 2120–2127. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzenberger, A.; Sadler, T.; Von Elert, E. Effect of nutrient limitation of cyanobacteria on protease inhibitor production and fitness of Daphnia magna. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 3649–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Wu, X.F.; Li, W. Functions of submerged macrophytes in in-situ ecological restoration of eutrophic waters. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2018, 38, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.Z.; Song, D.J.; Wang, L.Y.; Liang, C.Y.; Sun, X.S.; Liu, Y.J. The control effects of Daphnia magna population on the phytoplankton in eutrophic water body. Ecol. Sci. 2015, 34, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.X.; Wei, X.C.; Wag, H.Y.; Zheng, X.Q.; Yang, B. Study on the effects of phytoplankton in eutrophic water around farmland by aquatic plants and Daphnia magna. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2021, 60, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, X.M.; Qu, C.; Zhi, Q.; Lin, D.J. Study of the in-situ repair on polluted water by aquatic plants. J. Hebei Univ. Eng. 2018, 35, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, W.; Wang, S.; Peng, C.; Chen, Z. Root features related to plant growth and nutrient removal of 35 wetland plants. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3941–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.F.; Liu, F.; Li, H.J.; Xiao, R.L.; He, Y.; Wang, D.; Wu, J.S. Combined Process of Biofilter, Constructed Wetland and Stabilization Pond for Treatment of Rural Decentralized Sewage. China Water Wastewater 2015, 31, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Jabran, K. Manipulation of Allelopathic Crops for Weed Control; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, R. Acute animal and human poisonings from cyanotoxin exposure—A review of the literature. Environ. Int. 2016, 91, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qin, Y.J.; Qiu, Y.L.; Pan, W.B. Advances on Biomanipulation in Control of Eutrophic Lakes. Ecol. Sci. 2005, 24, 188–192. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, P.; Xu, T.T.; Yang, P.Y.; Gao, W.; Wang, Y.J.; Ma, J.M. Effects of phosphorus concentration on the interactions among Cyclotella, Daphnia magna and Myriophyllum verticillatum. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2016, 40, 103–108. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Burks, R.L.; Lodge, D.M.; Jeppesen, E.; Lauridsen, T.L. Diel horizontal migration of zooplankton: Costs and benefits of inhabiting the littoral. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 343–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, D.E. Prediction of Chlorophyll a Concentrations in Florida Lakes: The Importance of Phosphorus and Nitrogen. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2010, 19, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Carpenter, S.; Foley, J.A.; Folke, C.; Walker, B. Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Nature 2001, 413, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.J.; Jang, R.F.; Ran, W.M.; Dai, X.X.; Xiao, X.M.; Xie, H.Q. Ecological Mechanisms of Submerged Macrophytes in the Restoration of Eutrophic Shallow Lakes. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2016, 44, 58–61. [Google Scholar]



| Indexes. | Values | Indexes | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.77 | Nitrate nitrogen (mg/L) | 6.59 |
| Dissolved oxygen (mg/L) | 9.28 | Chlorophyll a (μg/L) | 68.59 |
| Water transparency (cm) | 17.20 | Phytoplankton density (cells/L) | 2.80 × 107 |
| Total nitrogen (mg/L) | 7.38 | Cyanobacteria density (cells/L) | 2.52 × 107 |
| Total phosphorus (mg/L) | 0.31 | Microcystin concentration (μg/L) | 2.77 |
| Ammonia-nitrogen (mg/L) | 0.21 |
| Groups | D. magna | M. aquaticum | C. demersum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control K | / | / | / | |
| D. magna | A | 25 ind·L−1 | / | / |
| B | 100 ind·L−1 | / | / | |
| submerged plants | C | / | 3 g·L−1 | / |
| D | / | / | 3 g·L−1 | |
| D. magna + submerged plants | E | 25 ind·L−1 | 3 g·L−1 | / |
| F | 100 ind·L−1 | 3 g·L−1 | / | |
| G | 25 ind·L−1 | / | 3 g·L−1 | |
| H | 100 ind·L−1 | / | 3 g·L−1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, H.; Zhang, C.; Yang, B.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X. Synergistic Remediation of Eutrophic Rural Pond Water Using Submerged Macrophytes and Daphnia magna. Plants 2025, 14, 3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14203136
Cao H, Zhang C, Yang B, Liu L, Wang J, Zheng X. Synergistic Remediation of Eutrophic Rural Pond Water Using Submerged Macrophytes and Daphnia magna. Plants. 2025; 14(20):3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14203136
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Haoyu, Chunxue Zhang, Bo Yang, Liyuan Liu, Jiarui Wang, and Xiangqun Zheng. 2025. "Synergistic Remediation of Eutrophic Rural Pond Water Using Submerged Macrophytes and Daphnia magna" Plants 14, no. 20: 3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14203136
APA StyleCao, H., Zhang, C., Yang, B., Liu, L., Wang, J., & Zheng, X. (2025). Synergistic Remediation of Eutrophic Rural Pond Water Using Submerged Macrophytes and Daphnia magna. Plants, 14(20), 3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14203136






