Integrative Omics Analysis Reveals Mechanisms of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Djulis Spikes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
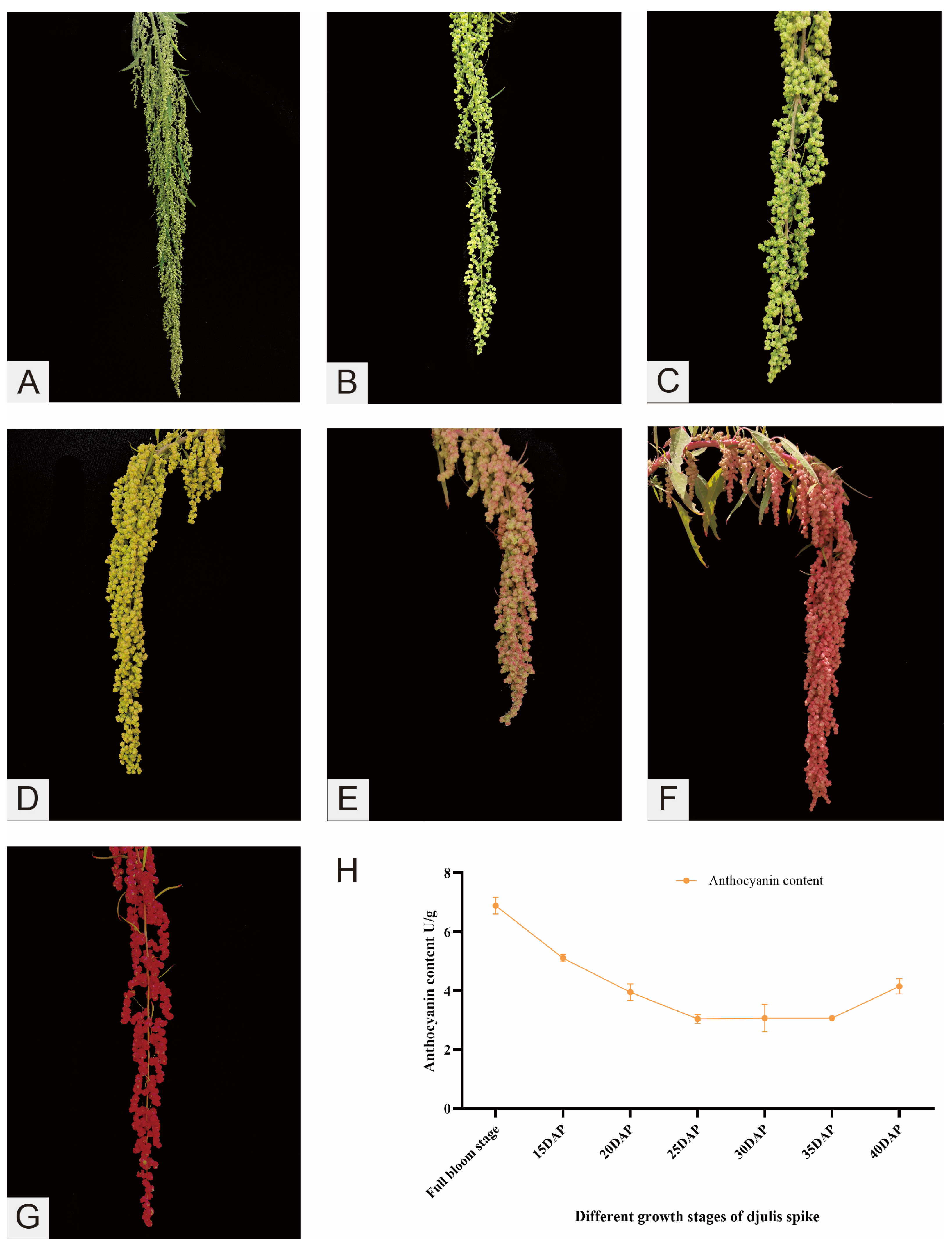
2.1. Changes in Anthocyanin Content During Spike Development
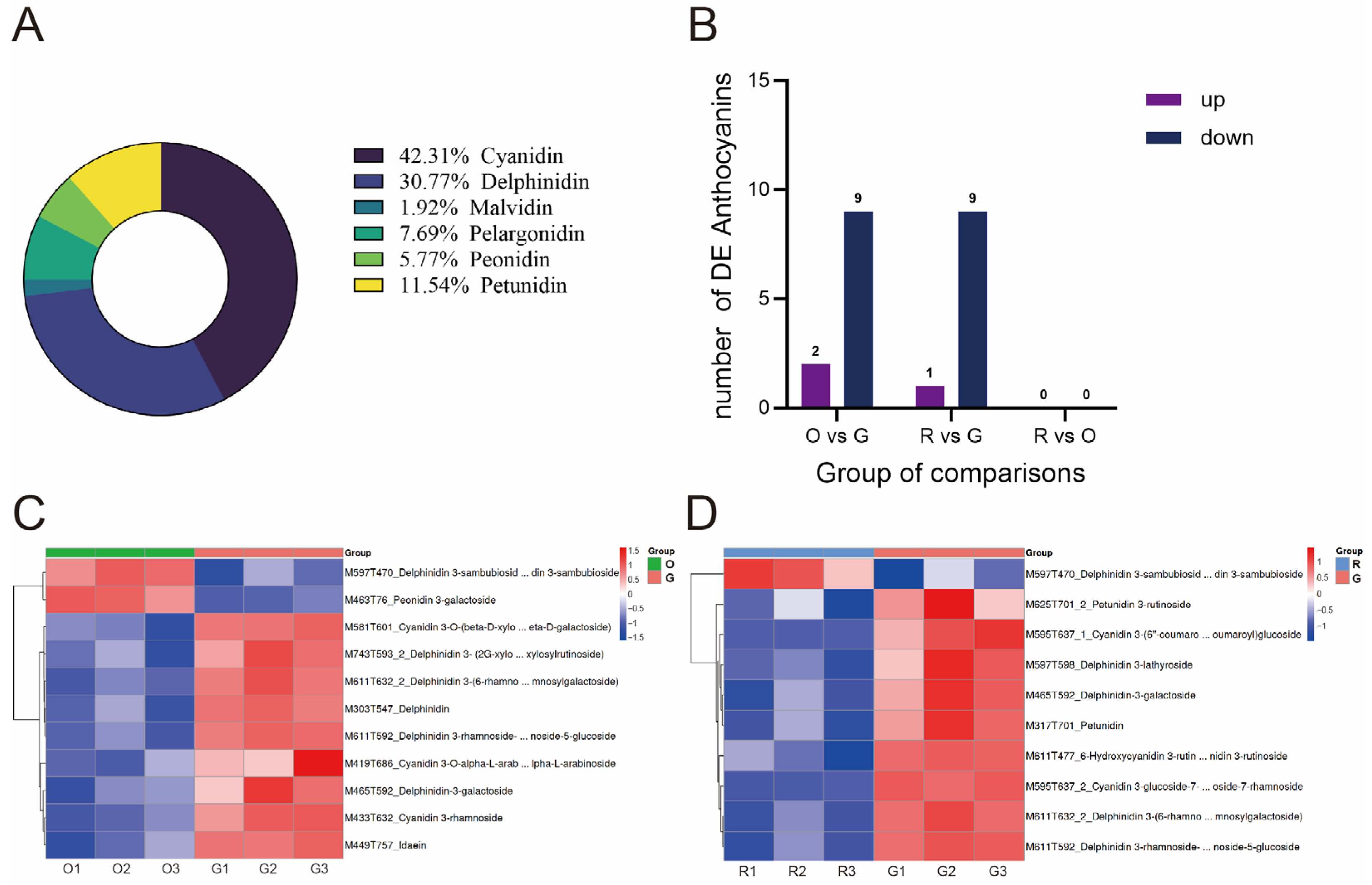
2.2. Non-Targeted Metabolomics
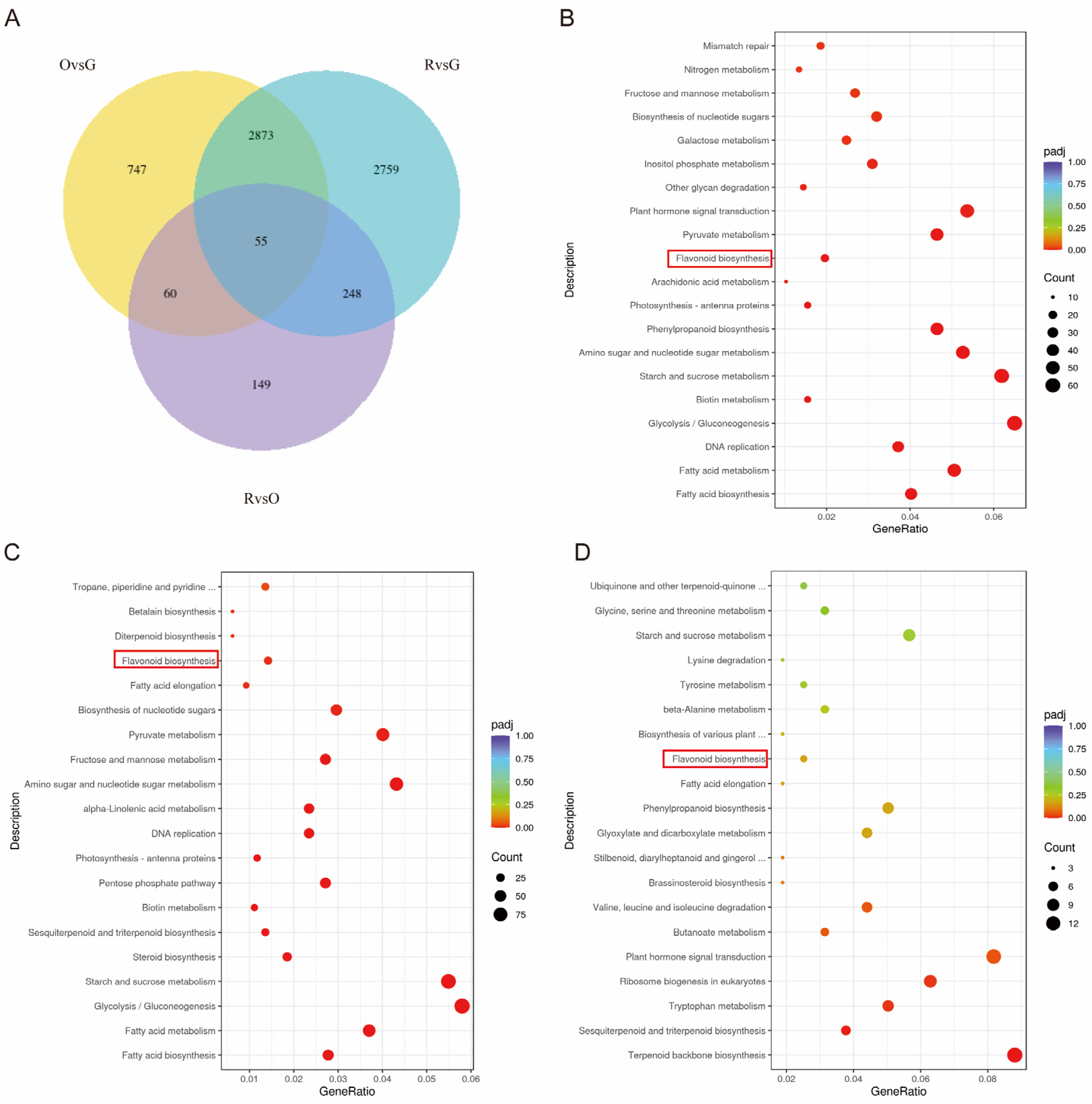
2.3. Transcriptomics, GO, and KEGG Enrichment Analysis
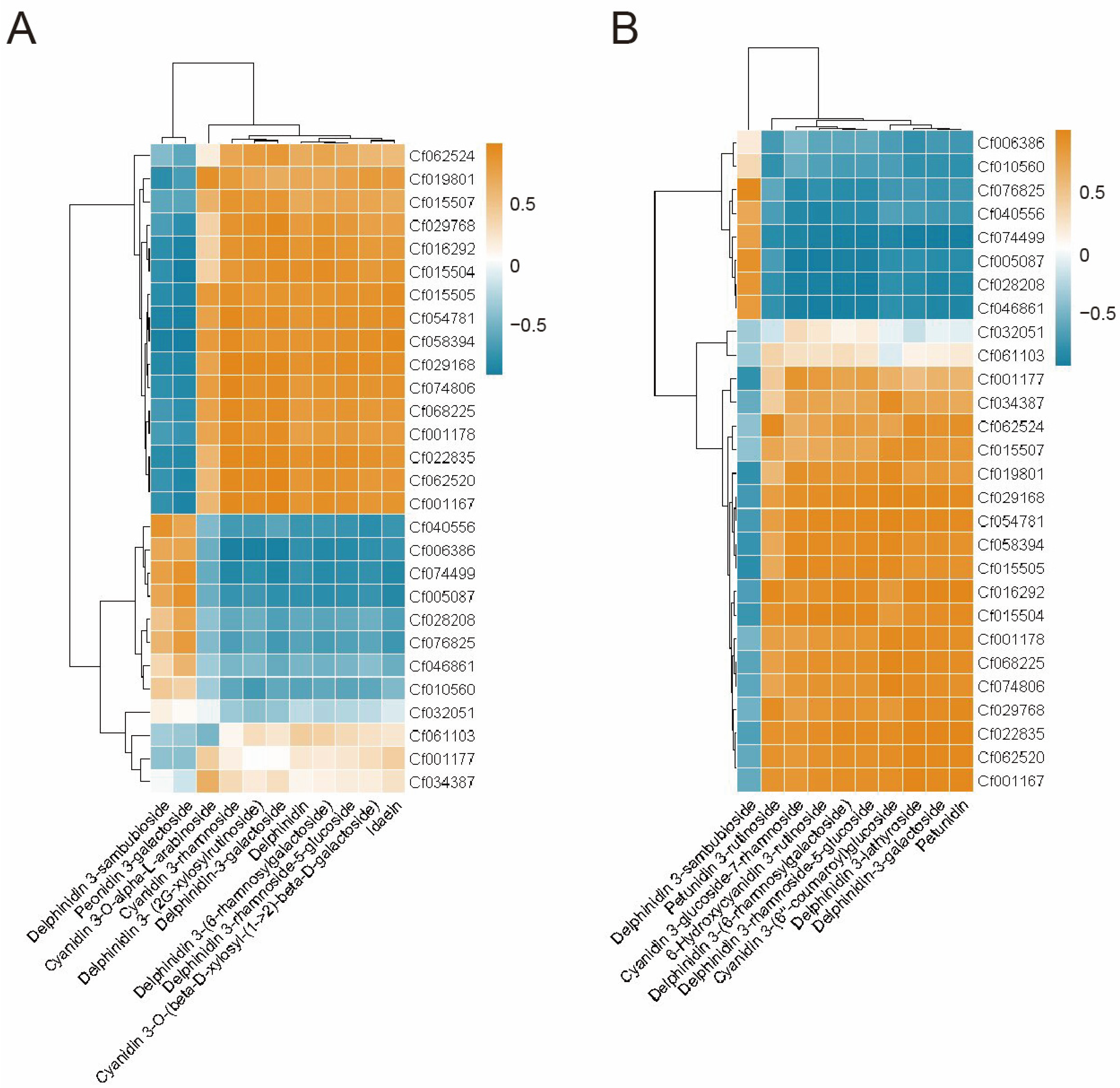
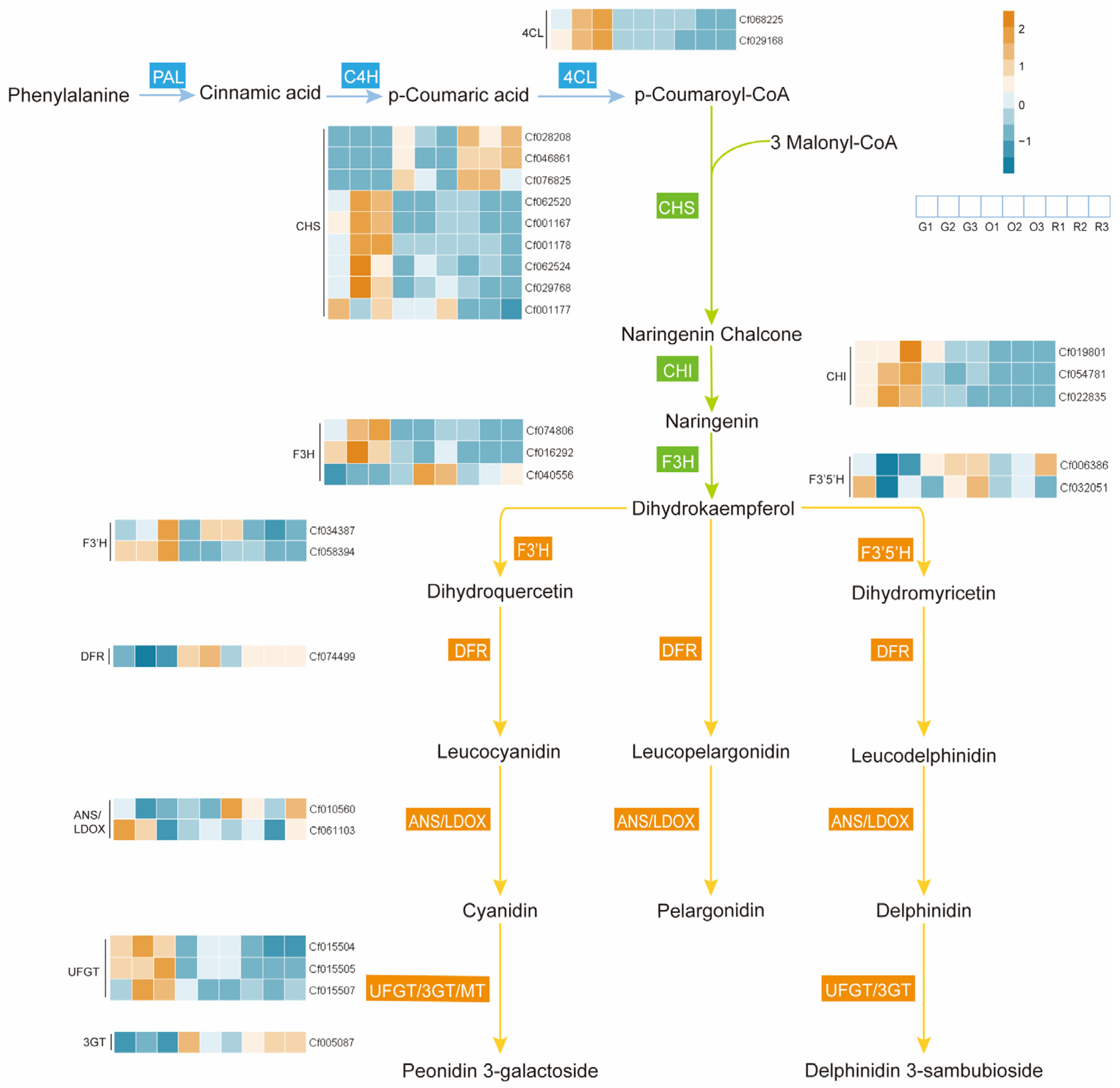
2.4. Combined Analysis of Integrated Transcriptomics and Metabolomics
2.5. qRT-PCR Validation Results
3. Discussion
3.1. The Biosynthesis of Anthocyanins in the Spike of Djulis
3.2. The Change in Spike Color May Be the Result of the Combined Action of Anthocyanins and Betalains
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Determination of Anthocyanin Content
4.3. Anthocyanins Targeted Metabolomics Analysis
4.4. Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis
4.5. Transcriptomics Analysis
4.6. Differential Genes Identification, GO, and KEGG Enrichment Analysis
4.7. Combined Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Analysis
4.8. qRT-PCR Validation
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, B.-Y.; Cheng, M.-H.; Ko, C.-H.; Wang, Y.-N.; Chen, W.-H.; Hwang, W.-S.; Yang, Y.-P.; Chen, H.-T.; Chang, F.-C. Potential bioethanol production from Taiwanese chenopods (Chenopodium formosanum). Energy 2014, 76, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.W.; Cheng, M.C.; Chen, B.Y.; Wang, C.Y. Effects of high pressure extraction on the extraction yield, phenolic compounds, antioxidant and anti-tyrosinase activity of Djulis hull. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 4016–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.-H.; Chan, Y.-J.; Lu, W.-C.; Huang, D.-W.; Chang, T.-C.; Chang, W.-H.; Nie, X.-B.; Jiang, C.-X.; Zhang, X.-L. Bioresource Utilization of Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum) Biomass as Natural Antioxidants. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y.-Y.; Hsueh, I.E. Insights into Physiological Mechanisms of Salt Stress Tolerance in Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum Koidz.) Sprouts. J. Plant Biol. 2019, 62, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.H.; Chao, Y.Y. Different Drought-Tolerant Mechanisms in Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) and Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum Koidz.) Based on Physiological Analysis. Plants 2021, 10, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, P.-J.; Chen, Y.-S.; Sheu, C.-H.; Chen, C.-Y. Effect of Nanogrinding on the Pigment and Bioactivity of Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum Koidz.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.H.; Huang, Y.L.; Liu, Y.C.; Tsai, P.J. Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum Koidz.) Water Extract and Its Bioactive Components Ameliorate Dermal Damage in UVB-Irradiated Skin Models. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7368797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, B.Y.; Lin, S.W.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Chen, B.H. Simultaneous determination of phenolic acids and flavonoids in Chenopodium formosanum Koidz. (djulis) by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 132, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, Y.-Y.; Wang, W.-J.; Liu, Y.-T. Effect of Calcium on the Growth of Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum Koidz.) Sprouts. Agronomy 2021, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, B.-Y.; Pan, S.-Y.; Wu, L.-Y.; Ho, C.-T.; Hwang, L.S. Hypoglycemic activity of Chenopodium formosanum Koidz. components using a glucose uptake assay with 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Food Biosci. 2018, 24, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.H.; Chan, Y.J.; Hou, Y.W.; Lu, W.C.; Chen, W.H.; Tseng, J.Y.; Mulio, A.T. Functionality of Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum) By-Products and In Vivo Anti-Diabetes Effect in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Biology 2021, 10, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, Y.T.; Zeng, J.L.; Ho, S.T.; Xu, J.W.; Li, S.; Wu, J.H. Anti-NAFLD Effect of Djulis Hull and Its Major Compound, Rutin, in Mice with High-Fat Diet (HFD)-Induced Obesity. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-Y.; Chu, C.-C.; Chyau, C.-C.; Yang, J.-W.; Duh, P.-D. Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum) and its bioactive compounds affect vasodilation, angiotensin converting enzyme activity, and hypertension. Food Biosci. 2019, 32, 100469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyau, C.C.; Chu, C.C.; Chen, S.Y.; Duh, P.D. The Inhibitory Effects of Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum) and Its Bioactive Compounds on Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Molecules 2018, 23, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-Y.; Chu, C.-C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Duh, P.-D. Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum) and Its Bioactive Compounds for Management of Hyperlipidemia and Hyperglycemia in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2019, 7, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.W.; Chen, H.J.; Xie, G.R.; Shih, C.K. Djulis (Chenopodium Formosanum) Prevents Colon Carcinogenesis via Regulating Antioxidative and Apoptotic Pathways in Rats. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.-C.; Chen, S.-Y.; Chyau, C.-C.; Fu, Z.-H.; Liu, C.-C.; Duh, P.-D. Protective effect of Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum) and its bioactive compounds against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury, in vivo. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 26, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.A.; Ke, B.J.; Cheng, C.S.; Wang, J.J.; Wei, B.L.; Lee, C.L. Red Quinoa Bran Extracts Protects against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury and Fibrosis in Mice via Activation of Antioxidative Enzyme Systems and Blocking TGF-β1 Pathway. Nutrients 2019, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.-C.; Chen, S.-Y.; Chyau, C.-C.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chu, H.-L.; Duh, P.-D. Anticancer activity and mediation of apoptosis in hepatoma carcinoma cells induced by djulis and its bioactive compounds. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, D.G.; Chyau, C.C.; Chen, S.Y.; Chu, H.L.; Wang, S.C.; Duh, P.D. Antiproliferative Effect and Mediation of Apoptosis in Human Hepatoma HepG2 Cells Induced by Djulis Husk and Its Bioactive Compounds. Foods 2020, 9, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-K.; Chan, S.-T.; Chun, Y.-M.; Lin, Y.-T.; Kan, K.-W.; Yu, C.-H. Anti Cutaneous Aging Effect of Red Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum) Extract on Gene Expression of Human Dermal Fibroblast. Preprints 2019, 2019090028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-M.; Chung, Y.-C.; Chen, P.-Y.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chen, W.-L. Fermentation of Chenopodium formosanum Leaf Extract with Aspergillus oryzae Significantly Enhanced Its Physiological Activities. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.J.; Sheu, C.H.; Wu, P.H.; Sun, Y.F. Thermal and pH stability of betacyanin pigment of Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum) in Taiwan and their relation to antioxidant activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chio, E.H.; Yang, E.-C.; Huang, H.-T.; Hsu, E.-L.; Chen, C.-R.; Huang, C.-G.; Huang, R.-N. Toxicity and repellence of Taiwanese indigenous djulis, Chenopodium formosaneum, against Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) and Forcipomyia taiwana (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae). J. Pest Sci. 2013, 86, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, K.J.; Chen, Z.J.; Cheng, C.L.; Hong, G.B. Investigation of the Antioxidant Capacity, Insecticidal Ability and Oxidation Stability of Chenopodium formosanum Seed Extract. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaakola, L. New insights into the regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in fruits. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spelt, C.; Quattrocchio, F.; Mol, J.N.; Koes, R. anthocyanin1 of Petunia Encodes a Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Protein That Directly Activates Transcription of Structural Anthocyanin Genes. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 1619–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.-c.; Zhang, X.-d.; Gao, Z.-q.; Hu, T.; Liu, Y. The Research Progress of Chalcone Isomerase (CHI) in Plants. Mol. Biotechnol. 2018, 61, 32–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Wu, Z.; Ma, J.; Gu, C. Decoding the formation of diverse petal colors of Lagerstroemia indica by integrating the data from transcriptome and metabolome. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 970023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Han, T.; Lyu, L.; Li, W.; Wu, W. Research progress in understanding the biosynthesis and regulation of plant anthocyanins. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 321, 112374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Lei, Y.; Yan, L.; Liu, Y.; Pandey, M.K.; Wan, X.; Varshney, R.K.; Fang, J.; Liao, B. Transcriptome and metabolome reveal redirection of flavonoids in a white testa peanut mutant. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, A.; Xiao, S.; Dai, X.; Yuan, R.; Zhou, Z.; Cao, Q. Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses of the Flavonoid Biosynthetic Pathway for the Accumulation of Anthocyanins and Other Flavonoids in Sweetpotato Root Skin and Leaf Vein Base. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 2574–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoeva, O.Y.; Glagoleva, A.Y.; Khlestkina, E.K. The factors affecting the evolution of the anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway genes in monocot and dicot plant species. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tikunov, Y.; Schouten, R.E.; Marcelis, L.F.M.; Visser, R.G.F.; Bovy, A. Anthocyanin Biosynthesis and Degradation Mechanisms in Solanaceous Vegetables: A Review. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Sasaki, N.; Ohmiya, A. Biosynthesis of plant pigments: Anthocyanins, betalains and carotenoids. Plant J. 2008, 54, 733–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Du, J.; Zhu, D.; Li, X.; Li, X. Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis Mechanisms in the Color Mutant Ziziphus jujuba cv. Tailihong. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 15186–15198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Chen, C.; Gong, X.; Luan, X.; Wu, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, Q.; Xu, M.; Yu, F. Transcriptome and metabolome analyses reveal a key role of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway cascade in the pigmentation of a Cinnamomum camphora red bark mutant (‘Gantong 1’). Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 175, 114236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, S.; Peng, D.; Wu, Q.; Liao, X.; Xiang, K.; Wang, Z.; Tembrock, L.R.; Bendahmane, M.; Bao, M.; et al. Integrated multi-omic data and analyses reveal the pathways underlying key ornamental traits in carnation flowers. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1182–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Kong, Y.; Dou, X.; Yang, Y.; Chi, X.; Lang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, H.; Bai, J. Integrative Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses Reveal the Mechanism of Petal Blotch Formation in Rosa persica. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Han, H.; Ma, Y.; Xie, X.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, X.; Gu, H.; et al. Transcriptome and metabolite profiling analyses reveal the molecular mechanism underlying the characteristic accumulation of anthocyanins and flavonols in Fritillaria unibracteata and F. delavayi. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 186, 115183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koes, R.; Verweij, W.; Quattrocchio, F. Flavonoids: A colorful model for the regulation and evolution of biochemical pathways. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lv, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, B.; Chen, W.; Ou, L.; Dai, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, X. Integrative analysis of metabolome and transcriptome reveals the mechanism of color formation in pepper fruit (Capsicum annuum L.). Food Chem. 2020, 306, 125629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Wang, T.; Gan, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Jin, B. Plant flavonoids: Classification, distribution, biosynthesis, and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Li, H.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, F.; Wan, Y.; Filiz, E. Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis Unveil Anthocyanin Metabolism in Pink and Red Testa of Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Int. J. Genom. 2021, 2021, 5883901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Yoon, Y.; Yoon, H.; Park, H.-M.; Song, S.; Yeum, K.-J. Dietary Anthocyanins against Obesity and Inflammation. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, H.E.; Azlan, A.; Tang, S.T.; Lim, S.M. Anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: Colored pigments as food, pharmaceutical ingredients, and the potential health benefits. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61, 1361779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Yi, H.; Lee, M.; Han, C.-T.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Park, J.-I.; Nou, I.-S.; Kim, S.-J.; Hur, Y. Purple Brassica oleracea var. capitata F. rubra is due to the loss of BoMYBL2–1 expression. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Chen, S.; Hou, B.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, L.; Duan, H. Anthocyanins inhibit high glucose-induced renal tubular cell apoptosis caused by oxidative stress in db/db mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, R.; Francioso, A.; Mosca, L.; Silva, P. Anthocyanins: A Comprehensive Review of Their Chemical Properties and Health Effects on Cardiovascular and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2020, 25, 3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazafa, A.; Rehman, K.-U.; Jahan, N.; Jabeen, Z. The Role of Polyphenol (Flavonoids) Compounds in the Treatment of Cancer Cells. Nutr. Cancer 2019, 72, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockington, S.F.; Walker, R.H.; Glover, B.J.; Soltis, P.S.; Soltis, D.E. Complex pigment evolution in the Caryophyllales. New Phytol. 2011, 190, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, D.E.; Sproul, J.S.; Navarro-Dominguez, B.; Krak, K.; Jaggi, K.; Huang, Y.F.; Huang, T.Y.; Lin, T.C.; Jellen, E.N.; Maughan, P.J. Chromosome-Scale Genome Assembly of the Hexaploid Taiwanese Goosefoot “Djulis” (Chenopodium formosanum). Genome Biol. Evol. 2022, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Bashandy, H.; Ainasoja, M.; Kontturi, J.; Pietiäinen, M.; Laitinen, R.A.E.; Albert, V.A.; Valkonen, J.P.T.; Elomaa, P.; Teeri, T.H. Functional diversification of duplicated chalcone synthase genes in anthocyanin biosynthesis of Gerbera hybrida. New Phytol. 2013, 201, 1469–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Tao, J. Recent advances on the development and regulation of flower color in ornamental plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.-H.; Park, B.; Kim, D.-H.; Park, S.; Yang, J.-H.; Jung, J.-A.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.-Y. Cloning and Functional Characterization of Dihydroflavonol 4-Reductase Gene Involved in Anthocyanin Biosynthesis of Chrysanthemum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Wei, G.; Zhou, H.; Gu, C.; Vimolmangkang, S.; Liao, L.; Han, Y. Unraveling the Mechanism Underlying the Glycosylation and Methylation of Anthocyanins in Peach. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 1044–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueyama, Y.; Katsumoto, Y.; Fukui, Y.; Mizutani, M.F.; Ohkawa, H.; Kusumi, T.; Iwashita, T.; Tanaka, Y. Molecular characterization of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway and flower color modification of Nierembergia sp. Plant Biotechnol. 2006, 23, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Suzuki, T.; Nakatsuka, T.; Dohra, H.; Yamagishi, M.; Matsuyama, K.; Matsuura, H. RNA-seq-based evaluation of bicolor tepal pigmentation in Asiatic hybrid lilies (Lilium spp.). BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Yin, W.; Feng, Y.; Xie, Q.; Chen, G. Anthocyanins and flavonols are responsible for purple color of Lablab purpureus (L.) sweet pods. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Luo, J.; Li, X.; Zhai, L.; He, L.; Zhang, Y. Biochemical and Comparative Transcriptomic Analyses Identify Candidate Genes Related to Variegation Formation in Paeonia Rockii. Molecules 2017, 22, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Xie, H.; Liu, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, S.; Wei, C. Metabolites and Transcriptional Profiling Analysis Reveal the Molecular Mechanisms of the Anthocyanin Metabolism in the “Zijuan” Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis var. assamica). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 69, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Shang, S.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Lu, C.; Wang, M.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.; et al. Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses reveals anthocyanin biosynthesis in leaf coloration of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolano, B.; McCann, J.; OskĘDra, M.; Chrapek, M.; Rojek, M.; Nobis, A.; Weiss-Schneeweiss, H. Parental origin and genome evolution of several Eurasian hexaploid species of Chenopodium (Chenopodiaceae). Phytotaxa 2019, 392, 163–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Chu, Y.L.; Sridhar, K.; Tsai, P.J. Analysis and determination of phytosterols and triterpenes in different inbred lines of Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum Koidz.) hull: A potential source of novel bioactive ingredients. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorinstein, S.; Vargas, O.J.M.; Jaramillo, N.O.; Salas, I.A.; Ayala, A.L.M.; Arancibia-Avila, P.; Toledo, F.; Katrich, E.; Trakhtenberg, S. The total polyphenols and the antioxidant potentials of some selected cereals and pseudocereals. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2006, 225, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paśko, P.; Bartoń, H.; Zagrodzki, P.; Gorinstein, S.; Fołta, M.; Zachwieja, Z. Anthocyanins, total polyphenols and antioxidant activity in amaranth and quinoa seeds and sprouts during their growth. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 994–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkprasom, K.; Wang, S.-P.; Hsiao, S.-M.; Tsai, P.-J. Kinetics of Color Loss of Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum Koidz.) Extracts during Storage in Different Concentrations of Alcohol and Temperature. APCBEE Procedia 2012, 2, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laqui-Vilca, C.; Aguilar-Tuesta, S.; Mamani-Navarro, W.; Montaño-Bustamante, J.; Condezo-Hoyos, L. Ultrasound-assisted optimal extraction and thermal stability of betalains from colored quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) hulls. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 111, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Niu, H.; Yun, Y.; Tian, J.; Lao, F.; Liao, X.; Gao, Z.; Ren, D.; Zhou, L. Analysis of coloration characteristics of Tunisian soft-seed pomegranate arils based on transcriptome and metabolome. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polturak, G.; Heinig, U.; Grossman, N.; Battat, M.; Leshkowitz, D.; Malitsky, S.; Rogachev, I.; Aharoni, A. Transcriptome and Metabolic Profiling Provides Insights into Betalain Biosynthesis and Evolution in Mirabilis jalapa. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucker, B.; Walker-Hale, N.; Dzurlic, J.; Yim, W.C.; Cushman, J.C.; Crum, A.; Yang, Y.; Brockington, S.F. Multiple mechanisms explain loss of anthocyanins from betalain-pigmented Caryophyllales, including repeated wholesale loss of a key anthocyanidin synthesis enzyme. New Phytol. 2023, 241, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.C.; Chan, Y.J.; Tseng, F.Y.; Chiang, P.Y.; Li, P.H. Production and Physicochemical Properties of Starch Isolated from Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum). Foods 2019, 8, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.-X.; Lin, F.-R.; Huang, P.; Guo, W.-Y.; Han, L.-B.; Zheng, Y.-Q. Seasonal variation of flavonoid metabolites in leaves of Liquidambar formosana ‘Nanlinhong’ trees revealed by UPLC-ESI–MS/MS. Braz. J. Bot. 2021, 44, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
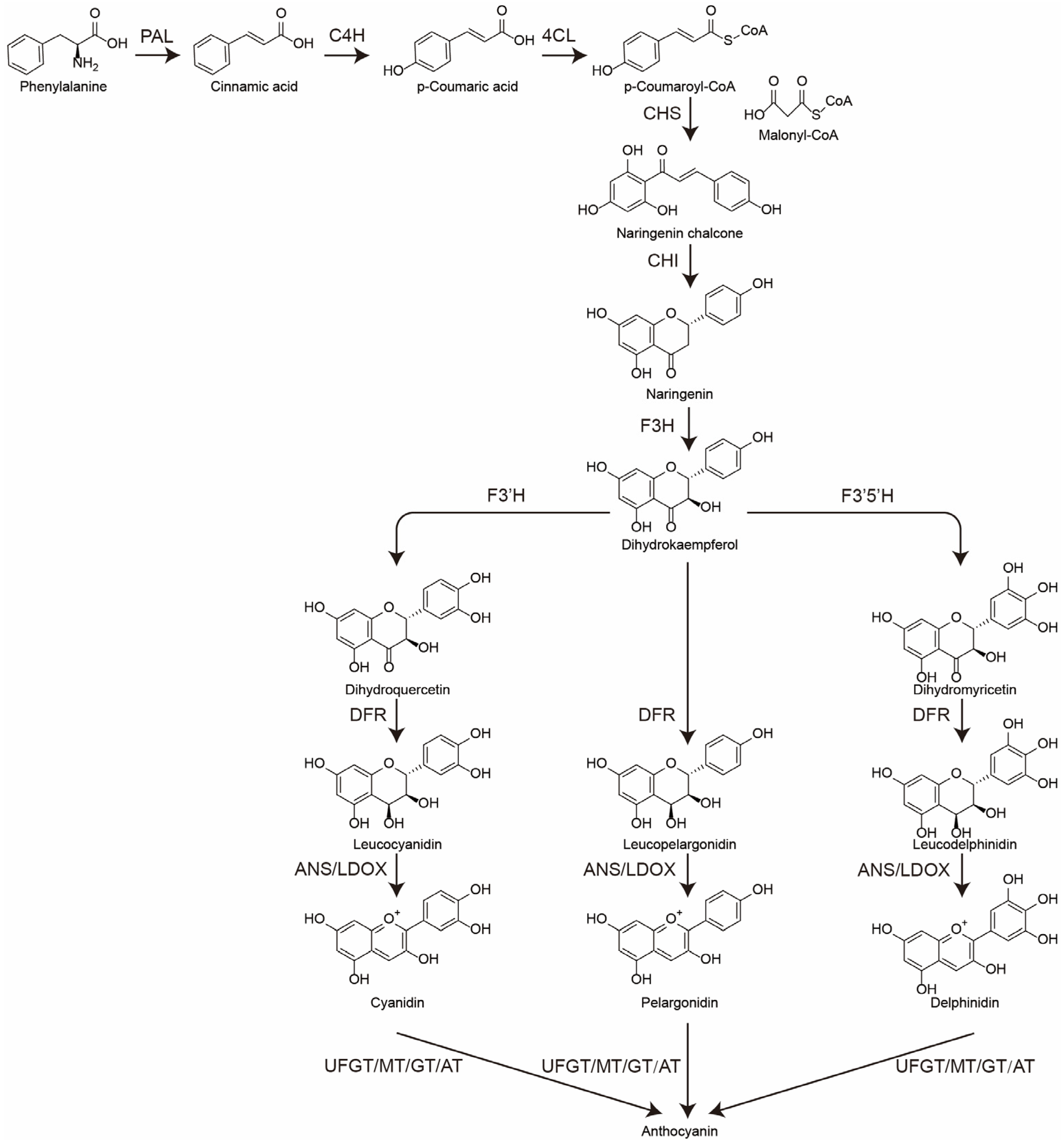



| Unigene_Id | Short Gene Name | Full Gene Name |
|---|---|---|
| Cf068225 | Cf4CL2_1 | 4-Coumarate-CoA ligase 2 |
| Cf029168 | Cf4CL2_2 | 4-Coumarate-CoA ligase 2 |
| Cf062520 | CfCHS_1 | Chalcone synthase |
| Cf001167 | CfCHS_2 | Chalcone synthase |
| Cf001178 | CfCHS_3 | Chalcone synthase |
| Cf062524 | CfCHS_4 | Chalcone synthase |
| Cf029768 | CfCHS_5 | Chalcone synthase |
| Cf028208 | CfCHS3_1 | Chalcone synthase 3 |
| Cf046861 | CfCHS3_2 | Chalcone synthase 3 |
| Cf076825 | CfCHS3_3 | Chalcone synthase 3 |
| Cf001177 | CfCHS3_4 | Chalcone synthase 3 |
| Cf019801 | CfCHI_1 | Chalcone-flavanone isomerase |
| Cf054781 | CfCHI2_1 | Chalcone isomerase |
| Cf022835 | CfCHI2_2 | Chalcone isomerase |
| Cf074806 | CfF3H_1 | Flavanone 3-hydroxylase |
| Cf016292 | CfF3H_2 | Flavanone 3-hydroxylase |
| Cf040556 | CfF3H_3 | Flavanone 3-hydroxylase |
| Cf034387 | CfCYP75B2_1 | Flavonoid 3′-monooxygenase |
| Cf058394 | CfCYP75B2_2 | Flavonoid 3′-monooxygenase |
| Cf006386 | CfCYP75A6_1 | Flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase |
| Cf032051 | CfCYP75A6_2 | Flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase |
| Cf074499 | CfDFRA | Dihydroflavonol 4-reductase |
| Cf010560 | CfANS | Anthocyanidin synthase |
| Cf061103 | CfLDOX | Leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase |
| Cf015504 | CfUFGT_1 | Anthocyanidin 3-O-glucosyltransferase |
| Cf015505 | CfUFGT_2 | Anthocyanidin 3-O-glucosyltransferase |
| Cf015507 | CfUFGT_3 | Anthocyanidin 3-O-glucosyltransferase |
| Cf005087 | Cf3GGT | Anthocyanidin 3-O-glucoside 2″-O-glucosyltransferase |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, C.; Ge, W.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Wu, X. Integrative Omics Analysis Reveals Mechanisms of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Djulis Spikes. Plants 2025, 14, 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14020197
Zheng C, Ge W, Li X, Wang X, Sun Y, Wu X. Integrative Omics Analysis Reveals Mechanisms of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Djulis Spikes. Plants. 2025; 14(2):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14020197
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Chunmei, Wenxuan Ge, Xueying Li, Xiuzhang Wang, Yanxia Sun, and Xiaoyong Wu. 2025. "Integrative Omics Analysis Reveals Mechanisms of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Djulis Spikes" Plants 14, no. 2: 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14020197
APA StyleZheng, C., Ge, W., Li, X., Wang, X., Sun, Y., & Wu, X. (2025). Integrative Omics Analysis Reveals Mechanisms of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Djulis Spikes. Plants, 14(2), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14020197






