Whole Genome Development of Specific Alien-Chromosome Oligo (SAO) Markers for Wild Peanut Chromosomes Based on Chorus2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Development of PCR-Based SAO Markers on Chromosomes Adu01 and Adu04 in A. duranensis
2.2. Validation and the Efficiency of SAO Markers Development by PCR
2.3. Development of SAO Markers in Five Wild Peanut Species
2.4. The Efficiency of the SAO Markers’ Development by PCR in Five Wild Peanut Species
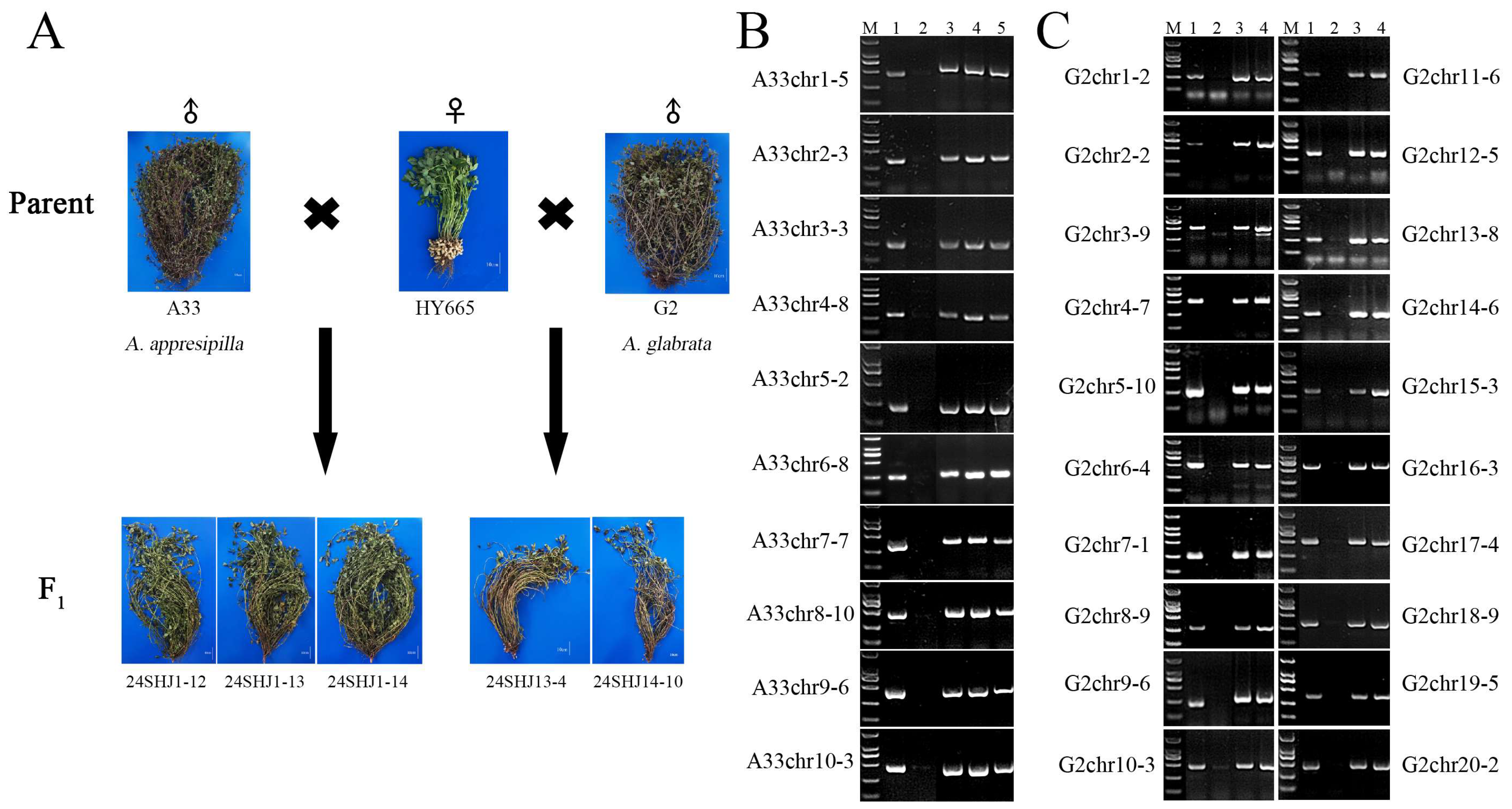
2.5. Identification of the Chromosomal Composition of Wild Peanut and Cultivated Peanut Hybrid F1 Generation Using SAO Markers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. DNA Extraction and Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
4.3. Specific Loci Calculation
4.4. Primer Design
4.5. PCR Amplification and Products Visualization
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friend, S.A.; Quandt, D.; Tallury, S.P.; Stalker, H.T.; Hilu, K.W. Species, genomes, and section relationships in the genus Arachis (Fabaceae): A molecular phylogeny. Plant Syst. Evol. 2010, 290, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio, K.; Gregory, W.C. Taxonomy of the genus Arachis (Leguminosae). Bonplandia 2007, 16, 7–205. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, D.E. Global Strategy for the Conservation and Use of Peanut Genetic Resources; Global Crop Diversity Trust: Bonn, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Robledo, G.; Lavia, G.I.; Seijo, G. Species relations among wild Arachis species with the A genome as revealed by FISH mapping of rDNA loci and heterochromatin detection. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 118, 1295–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robledo, G.; Seijo, G. Species relationships among the wild B genome of Arachis species (section Arachis) based on FISH mapping of rDNA loci and heterochromatin detection: A new proposal for genome arrangement. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2010, 121, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallury, S.P.; Hilu, K.W.; Milla, S.R.; Friend, S.A.; Alsaghir, M.; Stalker, H.T.; Quandt, D. Genomic affinities in Arachis section Arachis (Fabaceae): Molecular and cytogenetic evidence. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 111, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Bertioli, S.C.M.; de Blas, F.J.; Chavarro, M.C.; Simpson, C.E.; Valls, J.F.M.; Tallury, S.P.; Moretzsohn, M.C.; Custodio, A.R.; Stalker, H.T.; Seijo, G.; et al. Relationships of the wild peanut species, section Arachis: A resource for botanical classification, crop improvement, and germplasm management. Am. J. Bot. 2024, 111, e16357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallikarjuna, N.; Varshney, R.K.; Mallikarjuna, N.; Varshney, R.K. Genetics, Genomics and Breeding of Peanuts; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hammons, R.O. Peanuts: Genetic vulnerability and breeding strategy. Crop Sci. 1976, 16, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, J.P. Potential sources of peanut seed proteins and oil in the genus Arachis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1976, 25, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, S.N.; Dwivedi, S.L.; Gibbons, R.W. Groundnut breeding: Constraints, achievements and future possibilities. Plant Breed Abstr. 1991, 61, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Du, P.; Zeng, F.; Wang, Q.; Miao, L.; Qi, F.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, G.; Fu, L.; et al. Development and characterization of bacterial wilt-resistant synthetic polyploid peanuts. Crop J. 2025, 13, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.J.; Sun, H.J.; Li, J.K.; Qi, W.J.; Yuan, G.D.; Wang, Z.W.; Zhang, M.J.; Liang, X.Q.; Wang, C.T. Overcoming cross-incompatibility in genus Arachis via in situ embryo rescue. Breeding Sci. 2024, 74, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.J.; Sun, H.J.; Yu, J.; Jiang, C.J.; Yuan, G.D.; Li, S.X.; Xu, C.Y.; Wang, C.T. First report on trait segregation in F1 hybrids between the cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) and the wild incompatible species A. glabrata Benth. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2025, 72, 8567–8581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Brenneman, T.B.; Gao, D.; Chu, Y.; Lamon, S.; Bertioli, D.J.; Lealbertioli, S.C.M. The identification of the peanut wild relative Arachis stenosperma as a source of resistance to stem rot and analyses of genomic regions conferring disease resistance through QTL mapping. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Dai, K.L.; Xiao, J.; Yuan, C.X.; Zhao, R.H.; Dolezer, J.; Wu, Y.F.; Cao, A.Z.; Chen, P.D.; Zhang, S.Z.; et al. Development of intron targeting (IT) markers specific for chromosome arm 4VS of Haynaldia villosa by chromosome sorting and next-generation sequencing. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.D.; Wei, X.; Xiao, J.; Yuan, C.X.; Wu, Y.F.; Cao, A.Z.; Xing, L.P.; Chen, P.D.; Zhang, S.Z.; Wang, X.E.; et al. Whole genome development of intron targeting (IT) markers specific for Dasypyrum villosum chromosomes based on next-generation sequencing technology. Mol. Breed. 2017, 37, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Xiao, J.; Bie, T.D.; Cheng, S.H.; Jia, Q.; Yuan, C.X.; Zhang, R.Q.; Cao, A.Z.; Chen, P.D.; et al. Induction of 4VS chromosome recombinants using the CS ph1b mutant and mapping of the wheat yellow mosaic virus resistance gene from Hynaldia villosa. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 2921–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.J.; Song, J.J.; Xiao, J.; Xu, T.; Wei, X.; Yuan, C.X.; Cao, A.Z.; Xing, L.P.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, X.E. Development of EST-PCR markers specific to the long arm of chromosome 6V of Dasypyrum villosum. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 1720–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, G.Q.; Zhao, H.N.; Braz, G.T.; Jiang, J.M. Chorus2: Design of genome-scale oligonucleotide-based probes for fluorescence in situ hybridization. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 1967–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.H.; Zhang, T.; Thammapichai, P.; Weng, Y.Q.; Jiang, J.M. Chromosome-specific painting in Cucumis species using bulked oligonucleotides. Genetics 2015, 200, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.F.; Zhao, Q.Z.; Yan, W.K.; Li, M.X.; Liu, Y.X.; Cheng, C.Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, X.Q.; Li, J.; Qian, C.T.; et al. Flexible chromosome painting based on multiplex PCR of oligonucleotides and its application for comparative chromosome analyses in Cucumis. Plant J. 2020, 102, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimoníková, D.; Němečková, A.; Karafiátová, M.; Uwimana, B.; Swennen, R.; Doležel, J.; Hřibová, E. Chromosome painting facilitates anchoring reference genome sequence to chromosomes in situ and integrated karyotyping in Banana (Musa Spp.). Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, M.; Li, K.; Han, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, Z.Y.; Han, Y.H. Integrated karyotyping of woodland strawberry (Fragaria vesca) with oligopaint FISH probes. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2017, 153, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braz, G.T.; He, L.; Zhao, H.N.; Zhang, T.; Semrau, K.; Rouillard, J.M.; Torres, G.A.; Jiang, J.M. Comparative Oligo-FISH mapping: An efficient and powerful methodology to reveal karyotypic and chromosomal evolution. Genetics 2018, 208, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Braz, G.T.; Torres, G.A.; Jiang, J.M. Chromosome painting in meiosis reveals pairing of specific chromosomes in polyploid Solanum species. Chromosoma 2018, 127, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.Y.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Y.F.; Zhang, W.L.; Zhang, P.D.; Xi, M.L.; Jiang, J.M. An extraordinarily stable karyotype of the woody Populus species revealed by chromosome painting. Plant J. 2020, 101, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.; Zhang, Z.L.; Yan, T.Y.; Lin, Q.F.; Wang, Y.; Huang, W.Y.; Huang, Y.J.; Li, Z.J.; Yu, Q.Y.; Wang, J.P.; et al. Comprehensively characterizing the cytological features of Saccharum spontaneous by the development of a complete set of chromosome-specific oligoprobes. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1624. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Zhao, X.W.; Chai, J.; Ding, X.; Li, X.T.; Huang, Y.J.; Wang, X.H.; Wu, J.Y.; Zhang, M.Q.; Yang, Q.H.; et al. Chromosome-specific painting unveils chromosomal fusions and distinct allopolyploid species in the Saccharum complex. New Phytol. 2022, 233, 1953–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, P.S.; Zhang, T.; Semrau, K.; Rouillard, J.M.; Kao, Y.H.; Wang, C.J.R.; Danilova, T.V.; Jiang, J.M.; Birchler, J.A. Whole chromosome paints in maize reveal rearrangements, nuclear domains, and chromosomal relationships. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1679–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braz, G.T.; Martins, L.D.V.; Zhang, T.; Albert, P.S.; Birchler, J.A.; Jiang, J.M. A universal chromosome identification system for maize and wild Zea species. Chromosome Res. 2020, 28, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhao, H.N.; He, J.; Yang, Z.J.; Guan, B.; Chen, K.L.; Hong, Q.B.; Wang, J.H.; Liu, J.J.; Jiang, J.M. Extraordinarily conserved chromosomal synteny of Citrus species revealed by chromosome-specific painting. Plant J. 2020, 103, 2225–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Y.; Song, R.R.; Zhou, J.W.; Yan, W.K.; Zhang, T.; Sun, H.J.; Xiao, J.; Wu, Y.F.; Xi, M.L.; Lou, Q.F.; et al. Development and application of oligonucleotide-based chromosome painting for chromosome 4D of Triticum aestivum L. Chromosome Res. 2020, 28, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.Y.; Sun, H.J.; Liu, G.Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.W.; Song, R.R.; Xiao, J.; Yuan, C.X.; Sun, L.; Wang, Z.K.; et al. Chromosome painting reveals inter-chromosomal rearrangements and evolution of the subgenome D of wheat. Plant J. 2022, 112, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.Y. Creation, identification and genetic analysis of alien chromosome lines between cultivatied peanut and diploid wild species Arachis duranensis. Master’s Thesis, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bertioli, D.J.; Cannon, S.B.; Froenicke, L.; Huang, G.D.; Farmer, A.; Cannon, E.K.S.; Liu, X.; Gao, D.Y.; Clevenger, J.; Dash, S.; et al. The genome sequences of Arachis duranensis and Arachis ipaensis, the diploid ancestors of cultivated peanut. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertioli, D.J.; Jenkins, J.; Clevenger, J.; Dudchenko, O.; Gao, D.Y.; Seijo, G.; Leal-Bertioli, S.C.M.; Ren, L.H.; Farmer, A.; Pandey, M.K.; et al. The genome sequence of segmental allotetraploid peanut Arachis hypogaea. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, M.D.; Moretzsohn, M.C.; Palmieri, D.A.; Monteiro, J.P.; Bacci, M.J.; Martins, J.J.; Valls, J.F.; Lopes, C.R.; Gimenes, M.A. Phylogenetic relationships in genus Arachis based on ITS and 5.8S rDNA sequences. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppolu, R.; Upadhyaya, H.D.; Dwivedi, S.L.; Hoisington, D.A.; Varshney, R.K. Genetic relationships among seven sections of genus Arachis studied by using SSR markers. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Barkley, N.A.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, M.; Prakash, C.S. Phylogenetic relationships of species of genus Arachis based on genic sequences. Genome 2014, 57, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Z.; He, L.Q.; Xia, H.; Zhou, X.M.; Geng, Y.; Hou, L.; Li, P.C.; Li, G.H.; Zhao, S.Z.; Ma, C.L.; et al. De novo full length transcriptome analysis of Arachis glabrata provides insights into gene expression dynamics in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Genomics 2021, 113, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voichek, Y.; Weigel, D. Identifying genetic variants underlying phenotypic variation in plants without complete genomes. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaegle, B.; Voichek, Y.; Haupt, M.; Sotiropoulos, A.G.; Gauthier, K.; Heuberger, M.; Jung, E.; Herren, G.; Widrig, V.; Leber, R.; et al. k-mer-based GWAS in a wheat collection reveals novel and diverse sources of powdery mildew resistance. Genome Biol. 2025, 26, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Q.; Zhang, T. Bioinformatic Prediction of Bulked Oligonucleotide Probes for FISH Using Chorus2. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2672, 389–408. [Google Scholar]
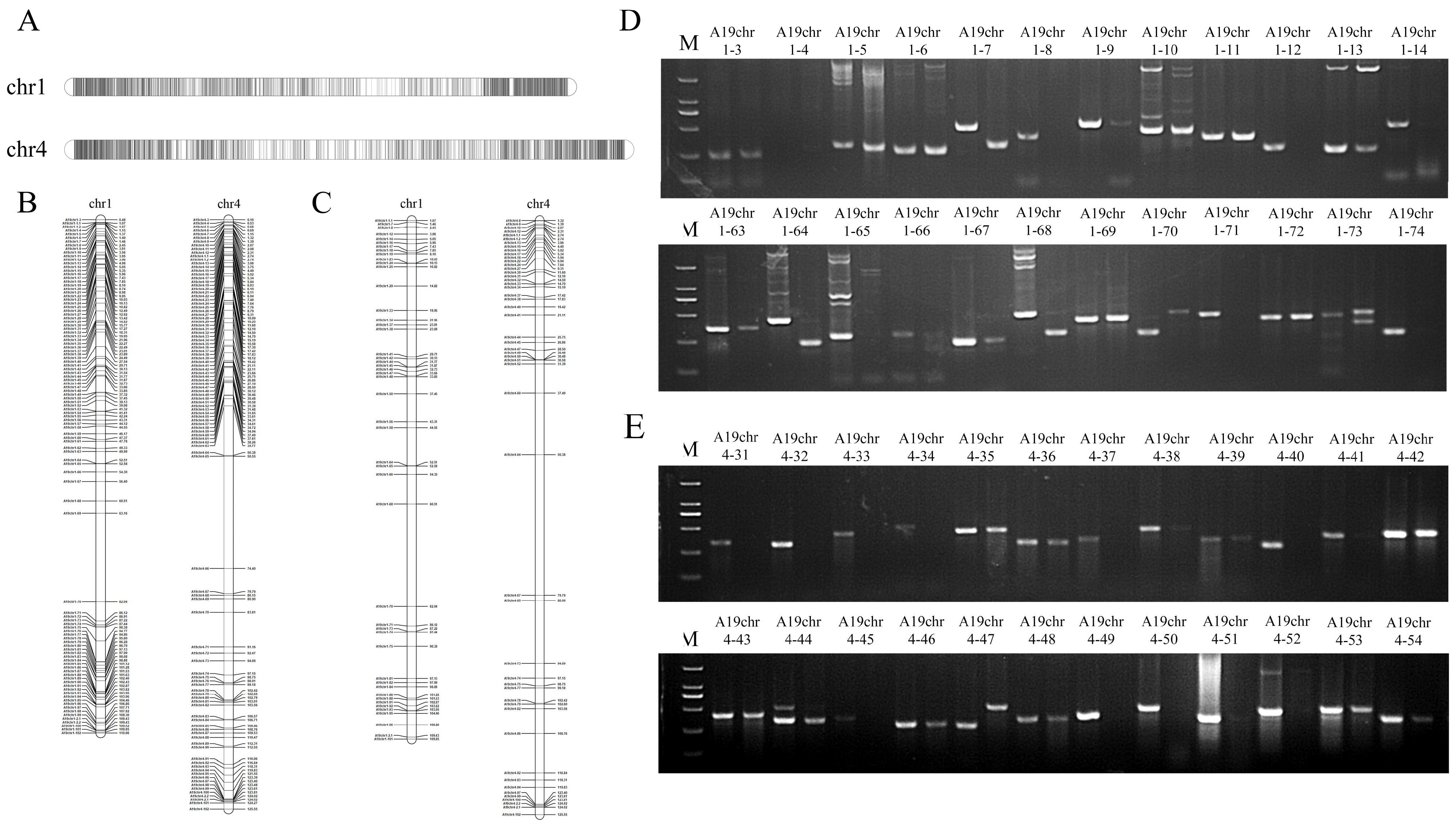
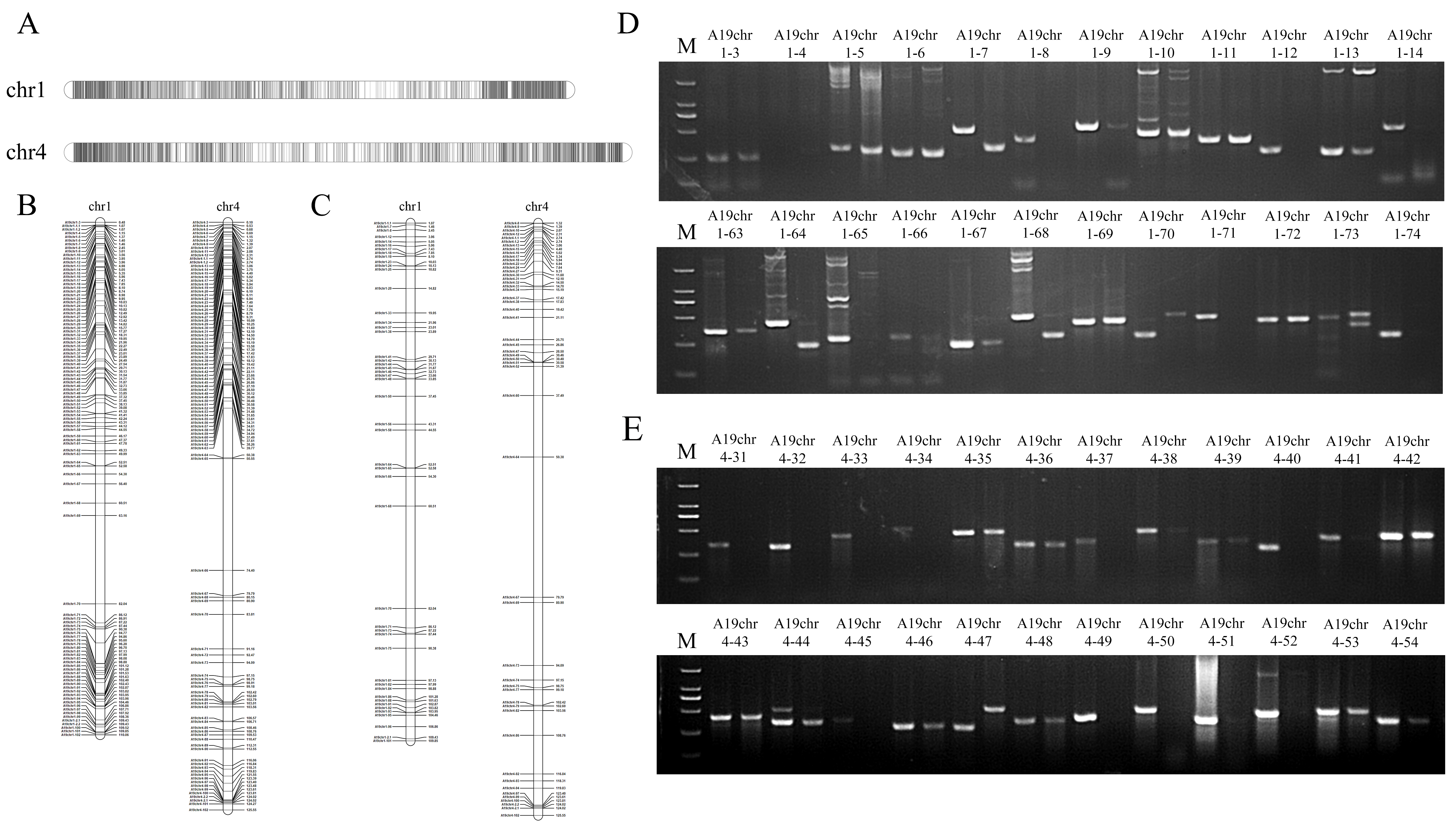

| Peanut Wild Species/Chromosome | Number of Indel Positions | Number of Design Markers | Number of Specific Markers | Marker Polymorphism Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A19 chromosomeAdu01 | 3551 | 104 | 48 | 46.2% |
| A19 chromosomeAdu04 | 3153 | 104 | 51 | 49.0% |
| A19 (Excluding chromosomeAdu01 and Adu04) | 25,872 | 192 | 121 | 63.0% |
| A19 (total) | 32,576 | 400 | 220 | 55.0% |
| A10 | 32,392 | 200 | 77 | 38.5% |
| A33 | 44,495 | 215 | 112 | 52.1% |
| G2 | 1893 | 200 | 69 | 34.5% |
| G3 | 25,191 | 151 | 59 | 39.1% |
| Material No. | Chromosomal Constitutions | Species | Section |
|---|---|---|---|
| HY665 | 2n = 4x = 40, AABB | A. hypogaea | Arachis |
| A10 | 2n = 2x = 20, HH | A. pusilla | Heteranthae |
| A19 | 2n = 2x = 20, AA | A. duranensis | Arachis |
| A33 | 2n = 2x = 20, PRPR | A. appresipilla | Procumbentes |
| G2 | 2n = 4x = 40, R1R1R2R2 | A. glabrata | Rhizomatosae |
| G3 | 2n = 4x = 40, R1R1R2R2 | A. glabrata | Rhizomatosae |
| 24SHJ1-12 | n = 3x = 30, ABPR | A. hypogaea-A. appresipilla | - |
| 24SHJ1-13 | n = 3x = 30, ABPR | A. hypogaea-A. appresipilla | - |
| 24SHJ1-14 | n = 3x = 30, ABPR | A. hypogaea-A. appresipilla | - |
| 24SHJ13-4 | n = 4x = 40, ABR1R2 | A. hypogaea-A. glabrata | - |
| 24SHJ14-10 | n = 4x = 40, ABR1R2 | A. hypogaea-A. glabrata | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, H.; Jiang, C.; Qi, W.; Chen, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, C.; Yu, J.; Yuan, G. Whole Genome Development of Specific Alien-Chromosome Oligo (SAO) Markers for Wild Peanut Chromosomes Based on Chorus2. Plants 2025, 14, 3114. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193114
Sun H, Jiang C, Qi W, Chen Y, Song X, Wang C, Yu J, Yuan G. Whole Genome Development of Specific Alien-Chromosome Oligo (SAO) Markers for Wild Peanut Chromosomes Based on Chorus2. Plants. 2025; 14(19):3114. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193114
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Haojie, Chunjiao Jiang, Weijie Qi, Yan Chen, Xinying Song, Chuantang Wang, Jing Yu, and Guangdi Yuan. 2025. "Whole Genome Development of Specific Alien-Chromosome Oligo (SAO) Markers for Wild Peanut Chromosomes Based on Chorus2" Plants 14, no. 19: 3114. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193114
APA StyleSun, H., Jiang, C., Qi, W., Chen, Y., Song, X., Wang, C., Yu, J., & Yuan, G. (2025). Whole Genome Development of Specific Alien-Chromosome Oligo (SAO) Markers for Wild Peanut Chromosomes Based on Chorus2. Plants, 14(19), 3114. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193114








