Comprehensive Analysis of Miscanthus NF-YA Genes Reveals Potential Involvement in Drought Stress Adaptation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
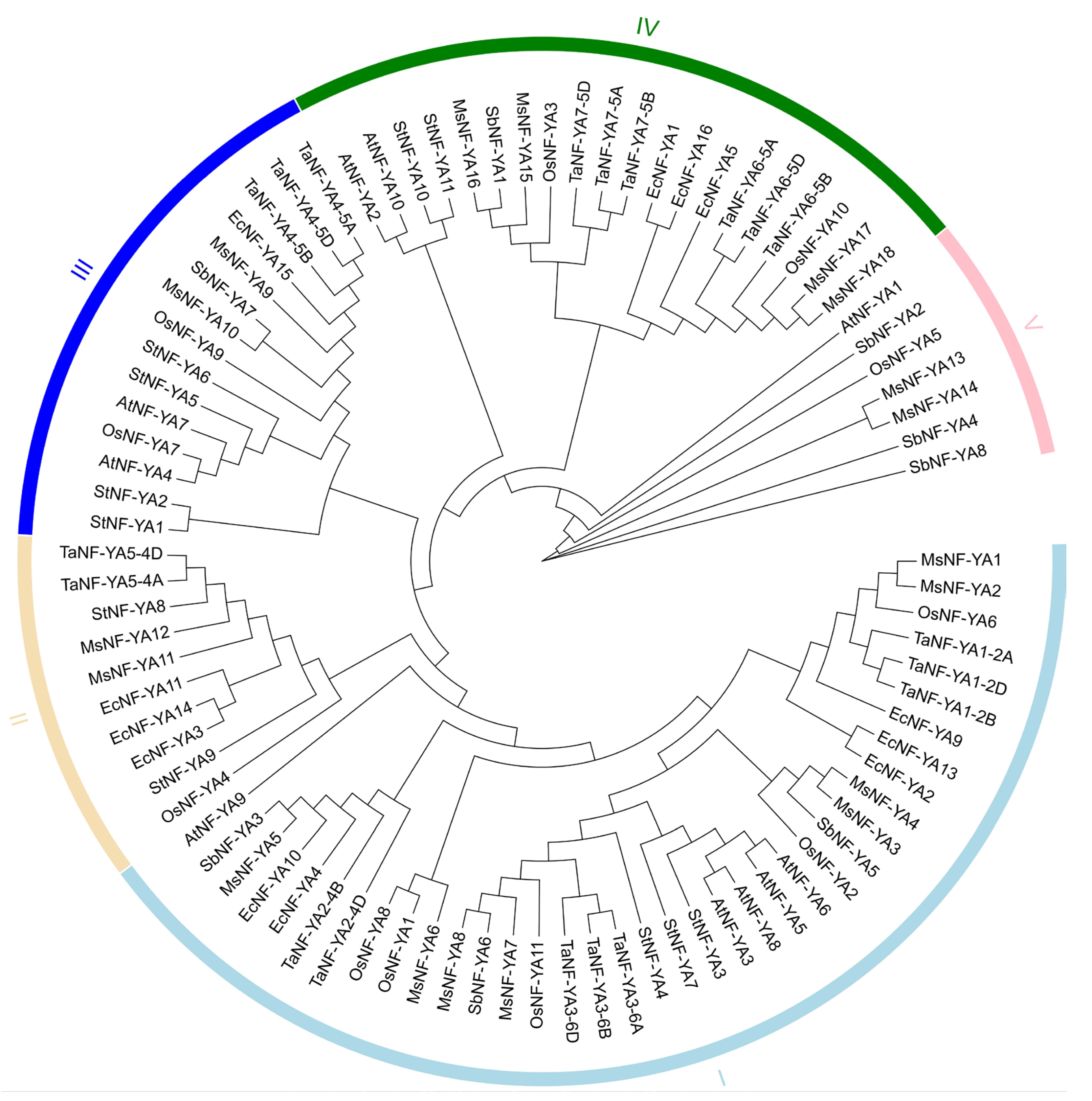
2.1. Characterization and Phylogenetic Relationship Assessment of Miscanthus NF-YAs
2.2. Exon–Intron Structure and Protein-Motif Analysis of MsNF-YAs
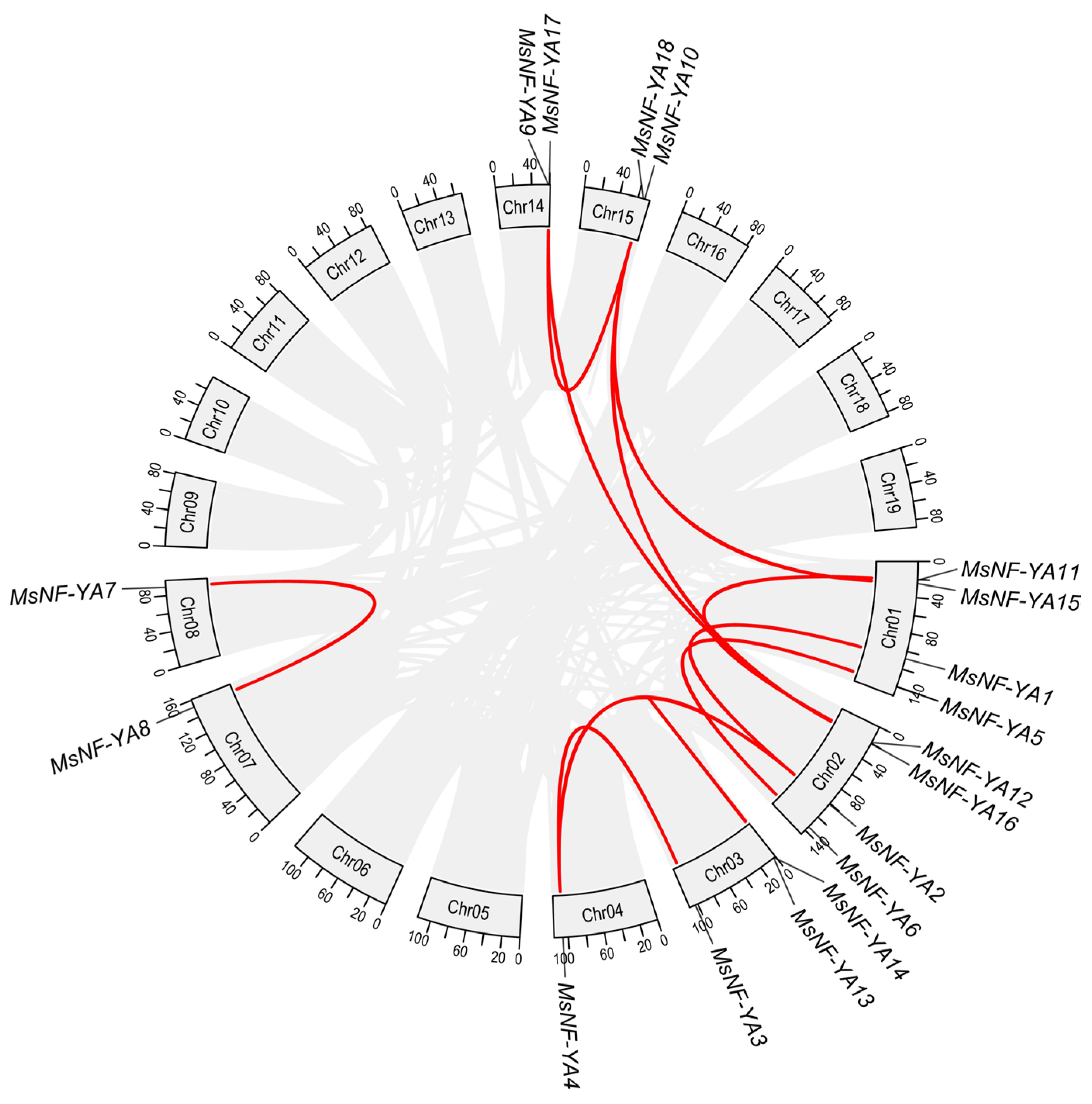
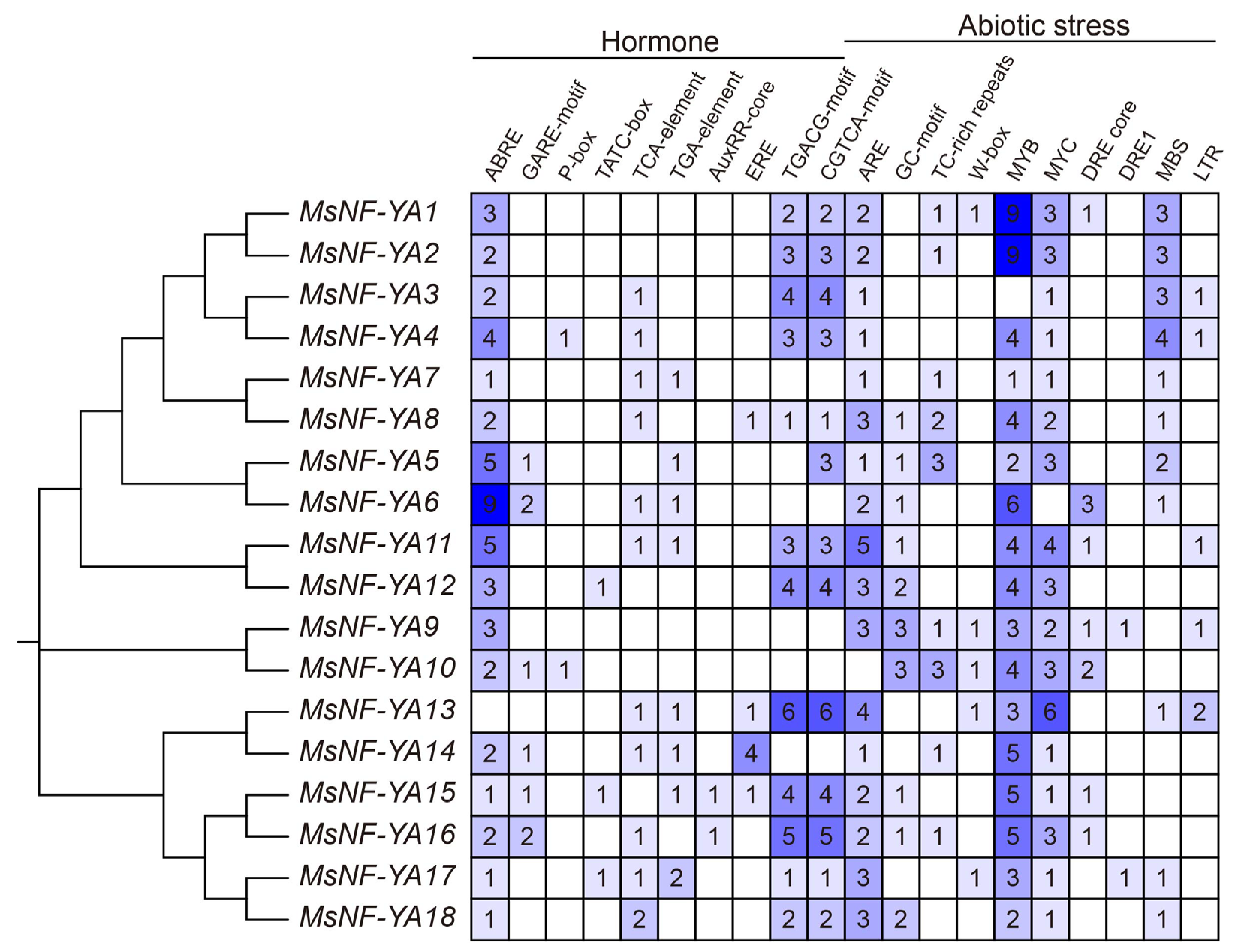
2.3. Synteny and Cis-Regulatory Element Analysis of MsNF-YA Members in Miscanthus
2.4. Effects of Dehydration/Osmotic Stress on the Relative Water Content (RWC) in Miscanthus
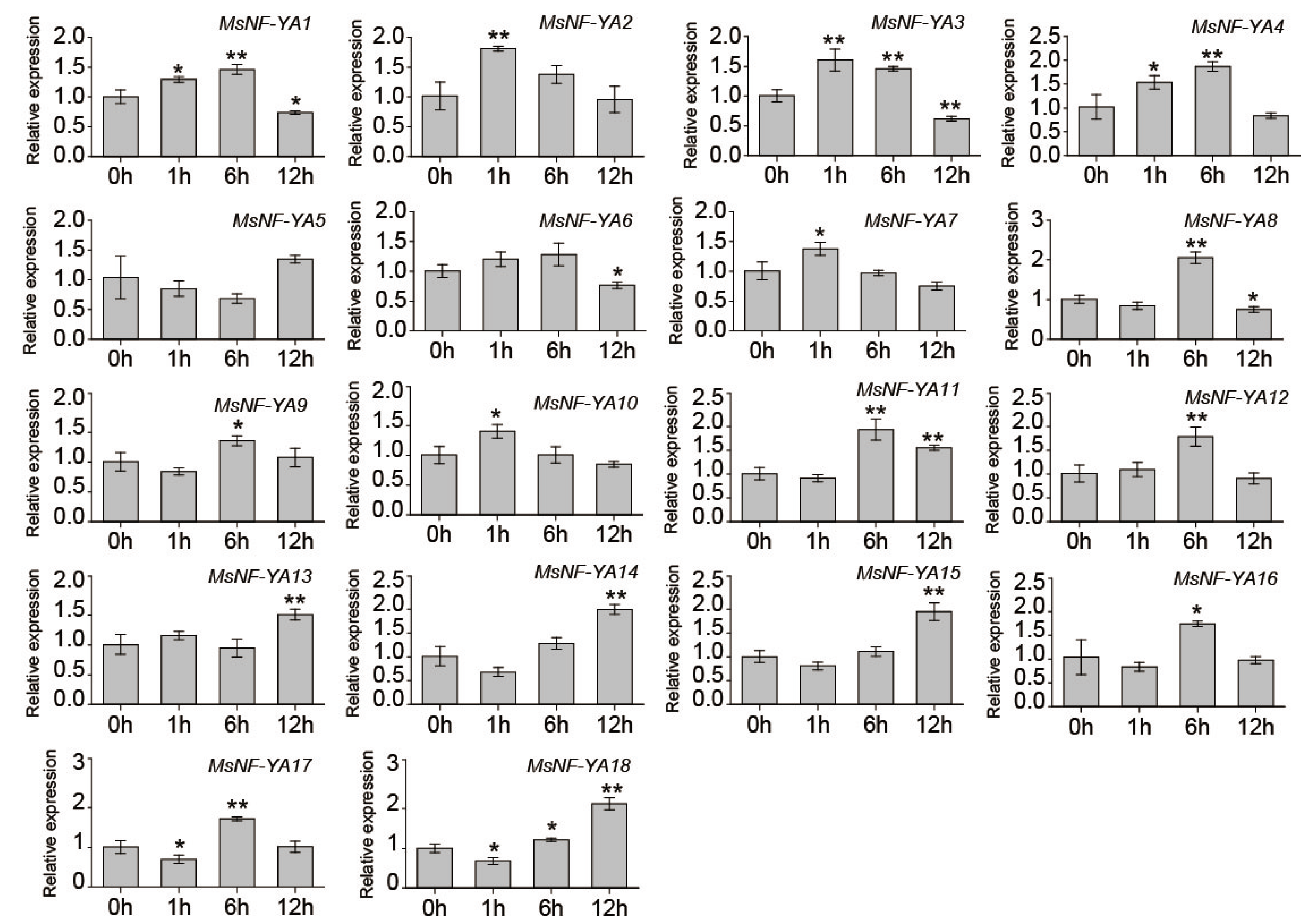
2.5. Investigation of Miscanthus NF-YA Members Under Dehydration/Osmotic Stress
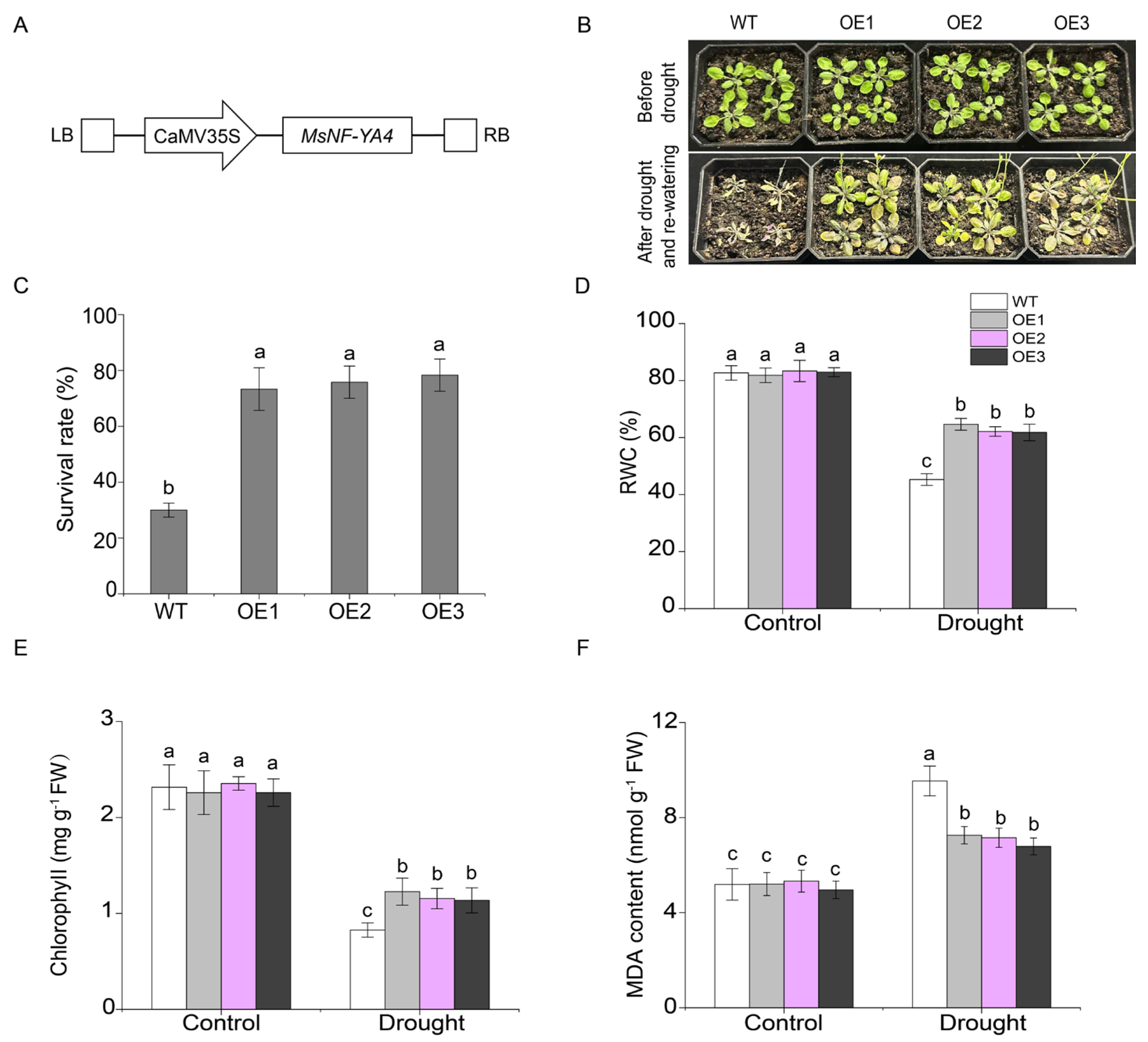
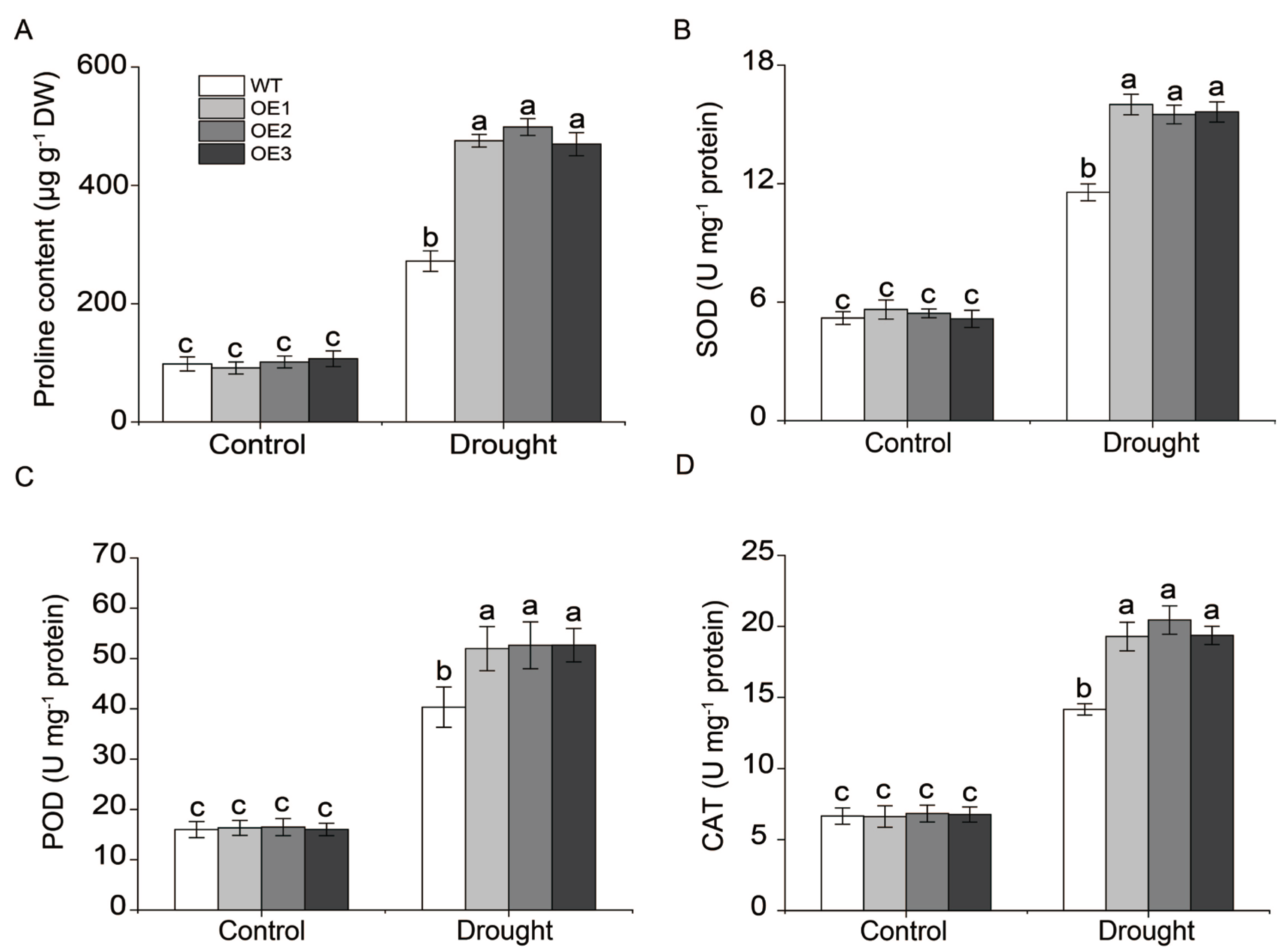
2.6. Functional Analysis of MsNF-YA4 Overexpression in Arabidopsis Under Drought Stress
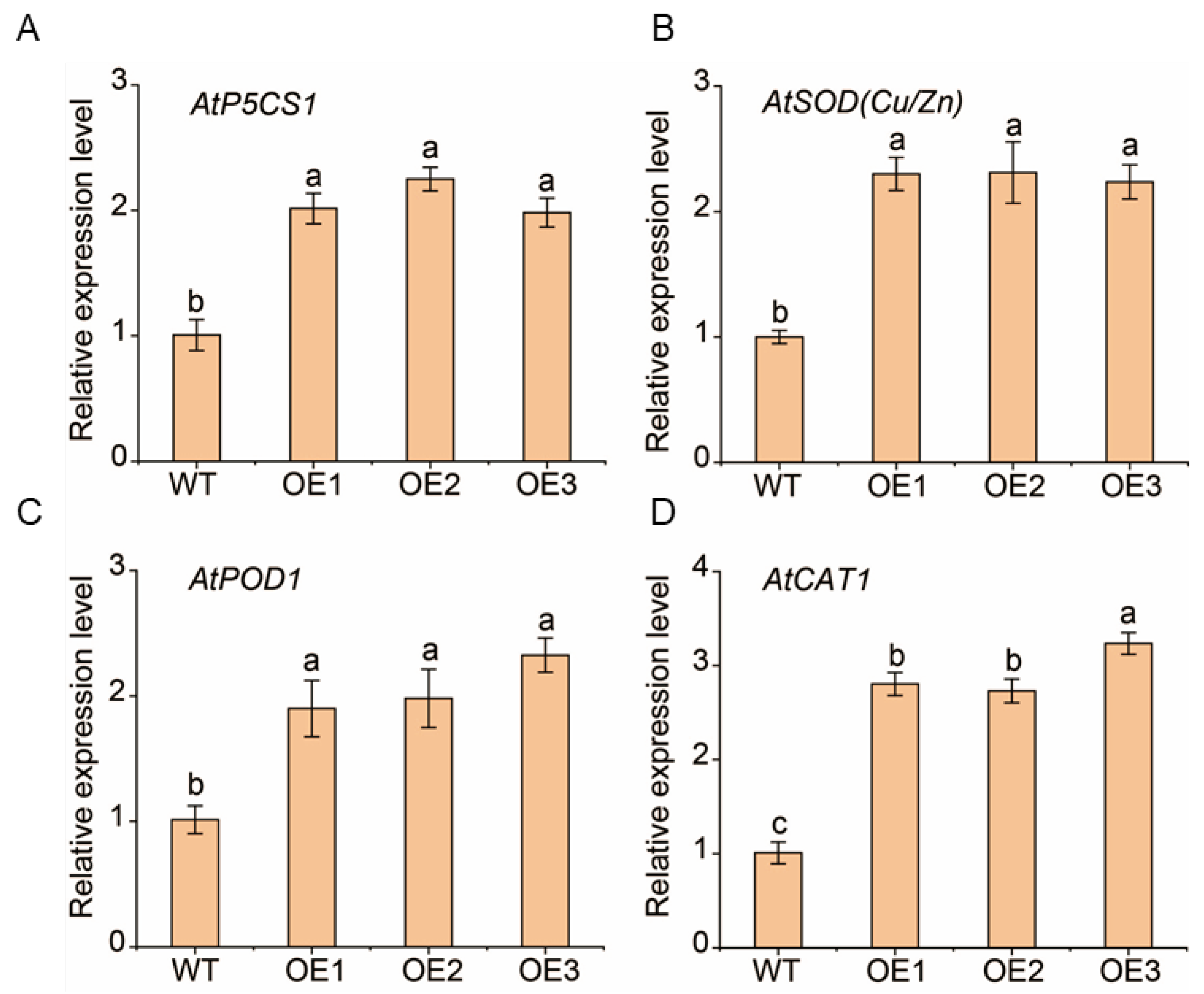
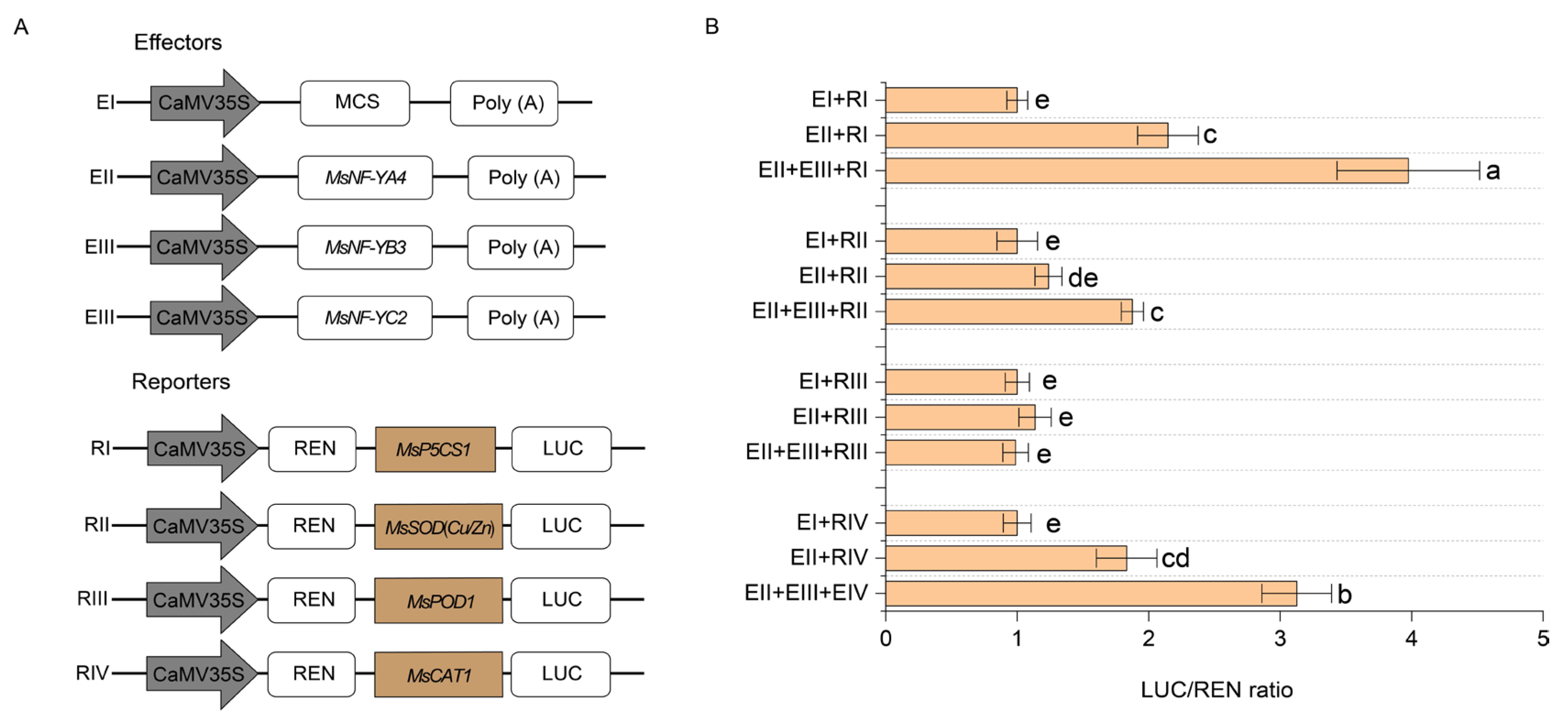
2.7. The Regulatory Role of the MsNF-YA4/MsNF-YB3/MsNF-YC2 Module on MsP5CS1, MsSOD (Cu/Zn), MsPOD1, and MsCAT1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Characterization and Phylogenetic Profiling of Miscanthus NF-YAs
4.2. Plant Material, and Dehydration/Osmotic Treatments
4.3. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR Analysis
4.4. Characterization of NF-YA Genes and Proteins in Miscanthus
4.5. Gene Duplication and Cis-Regulatory Element Analysis of Miscanthus NF-YAs
4.6. Creation of Transgenic Arabidopsis Lines and Evaluation of Physiological Characteristics
4.7. Yeast Two-Hybrid Assay
4.8. Transactivation of Promoters in the Transient System
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiong, H.; He, H.; Chang, Y.; Miao, B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Dong, F.; Xiong, L. Multiple roles of NAC transcription factors in plant development and stress responses. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2025, 67, 510–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Cao, X.; Yao, S.; Han, Y.; Chen, C.; Du, L.; Li, S.; et al. Perception of viral infections and initiation of antiviral defence in rice. Nature 2025, 641, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnaswamy, A.; Sakthivel, S.K.; Channappa, M.; Ramanathan, V.; Shivalingamurthy, S.G.; Peter, S.C.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, R.A.; Dhansu, P.; Meena, M.R.; et al. Overexpression of an NF-YB gene family member, EaNF-YB2, enhances drought tolerance in sugarcane (Saccharum Spp. Hybrid). BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Mao, L.; Li, Y.; Lu, K.; Qu, C.; Tang, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, L. Natural variation in BnaA9.NF-YA7 contributes to drought tolerance in Brassica napus L. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wei, H.; Zhang, N.; Li, S.; Si, H. StNF-YA8-YB20-YC5 module regulates potato tuber dormancy by modulating gibberellin and abscisic acid pathways. Plant J. 2025, 121, e70106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, B.; He, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Teng, W.; Shao, A.; Zhao, X.; Ma, W.; Wang, J.; Li, B.; et al. A wheat CCAAT box-binding transcription factor increases the grain yield of wheat with less fertilizer input. Plant physiol. 2015, 167, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Sanjuan, A.; Gnesutta, N.; Gobbini, A.; Martignago, D.; Bernardini, A.; Fornara, F.; Mantovani, R.; Nardini, M. Structural determinants for NF-Y subunit organization and NF-Y/DNA association in plants. Plant J. 2021, 105, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Shen, J.; Niu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Guo, Y.; Sun, P.; Yang, T.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Z.; et al. Cucumber NUCLEAR FACTOR-YC2/-YC9 target translocon component CsTIC21 in chloroplast photomorphogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2023, 192, 2822–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laloum, T.; De Mita, S.; Gamas, P.; Baudin, M.; Niebel, A. CCAAT-box binding transcription factors in plants: Y so many? Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Cui, L.; Ai, G.; Wang, X.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, D.; Larkin, R.M.; et al. NF-Y plays essential roles in flavonoid biosynthesis by modulating histone modifications in tomato. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 3237–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Martínez, H.H. Get two for the price of one: GmNF-YC4 factor mediates GmEXP7-induced root developmental changes and phosphorus starvation response in soybean. Plant Physiol. 2024, 197, kiae554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cai, Y.; Yao, W.; Chen, L.; Hou, W. The soybean NUCLEAR FACTOR-Y C4 and α-EXPANSIN 7 module influences phosphorus uptake by regulating root morphology. Plant Physiol. 2025, 197, kiae478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Hu, X.; Zhu, M.; Xu, M.; Wang, L. Transcription factors NF-YA2 and NF-YA10 regulate leaf growth via auxin signaling in Arabidopsis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lin, S.; Ouvrard, S.; Sirguey, C.; Qiu, R.; Wu, B. Environmental remediation potential of a pioneer plant (Miscanthus sp.) from abandoned mine into biochar: Heavy metal stabilization and environmental application. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ma, Z.; He, D.; Han, X.; Liu, X.; Dong, Q.; Tan, C.; Yu, B.; Sun, T.; Nordenskiöld, L.; et al. Molecular condensation of the CO/NF-YB/NF-YC/FT complex gates floral transition in Arabidopsis. EMBO J. 2025, 44, 225–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Wei, P.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, P.; Tahir, M.M.; Toktonazarovich, T.K.; Shen, Y.; Zuo, X.; Mao, J.; Zhang, D.; et al. Genomic identification of the NF-Y gene family in apple and functional analysis of MdNF-YB18 involved in flowering transition. Mol. Breed. 2025, 45, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Lin, K.; Ma, L.; Chen, Q.; Gan, S.; Li, G. Arabidopsis NUCLEAR FACTOR Y A8 inhibits the juvenile-to-adult transition by activating transcription of MIR156s. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 4890–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, X.; Cui, T.; Han, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C. Expression patterns of the poplar NF-Y gene family in response to Alternaria alternata and hormone treatment and the role of PdbNF-YA11 in disease resistance. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 956271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Li, W.; Jin, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, P.; Huang, J.; Hu, T. OsNF-YA8 promotes starch accumulation and influences seed traits by positively regulating starch biosynthesis in rice. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 171, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Cheng, Y.; Jiang, N.; Jiang, T.; Wei, Z. Overexpression of the PtrNF-YA6 gene inhibits secondary cell wall thickening in poplar. Plant Sci. 2024, 343, 112058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Du, P.; Liu, X.; Hou, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, Y. Identification of nuclear factor YA6 genes in sorghum and characterization of their involvement in drought tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1524066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Mei, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, R.; Ma, C.; Song, J.; Cui, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, D. Nuclear factor NF-YA4a regulates salt stress tolerance and juvenile-adult phase transition in Pyrus. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2025, 66, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiao, P.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Shi, K.; Gao, X.; Guan, S.; Ma, Y. ZmNF-YB10, a maize NF-Y transcription factor, positively regulates drought and salt stress response in Arabidopsis thaliana. GM Crops Food 2025, 16, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Ma, C.; Ye, F.; Pang, Y.; Wang, G.; Fahim, A.M.; Lu, X. Genome-wide identification of NF-Y gene family in maize (Zea mays L.) and the positive role of ZmNF-YC12 in drought resistance and recovery ability. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1159955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.F.; Liu, Y.; Fu, J.D.; Ma, J.; Fang, Z.W.; Chen, J.; Zheng, L.; Lu, Z.W.; Zhou, Y.B.; Chen, M.; et al. The NF-Y-PYR module integrates the abscisic acid signal pathway to regulate plant stress tolerance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 2589–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Guan, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, R.; Qin, L.; Chen, E.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Li, F. SiNF-YC2 Regulates Early Maturity and Salt Tolerance in Setaria italica. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yu, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, Z.; Ding, X.; Yang, S. Overexpression of GmNF-YA14 produced multiple phenotypes in soybean. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2023, 210, 105316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, L.; Ma, X.; Yu, Q.; Jia, Z.; Wu, J.; Wei, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Overexpressing OsNF-YB12 elevated the content of jasmonic acid and impaired drought tolerance in rice. Plant Sci. 2025, 352, 112397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-González, M.A.; Ibarra-Laclette, E.; Cruz-Ramírez, A.; Herrera-Estrella, L. Functional and transcriptome analysis reveals an acclimatization strategy for abiotic stress tolerance mediated by Arabidopsis NF-YA family members. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Ye, T.; Zhong, B.; Liu, X.; Jin, R.; Chan, Z. AtHAP5A modulates freezing stress resistance in Arabidopsis through binding to CCAAT motif of AtXTH21. New Phytol. 2014, 203, 554–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Lv, J.; Sadeghnezhad, E.; Cheng, J.; Jia, H. Transcriptomic and metabolomic profiling of strawberry during postharvest cooling and heat storage. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1009747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Yuan, H.; Gu, C. The I1NF-YC6 transcription factor of Iris lactea var. chinensis (Fisch.) activates the llCDT1 gene and enhances tolerance to cadmium stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 197, 116558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, C.; Zhao, Z.; Feng, B.; Zhang, X.; An, K.; et al. Populus euphratica CPK21 interacts with NF-YC3 to enhance cadmium tolerance in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroni, K.; Kumimoto, R.W.; Gnesutta, N.; Calvenzani, V.; Fornari, M.; Tonelli, C.; Holt, B.F.; Mantovani, R. The promiscuous life of plant NUCLEAR FACTOR Y transcription factors. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 4777–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Lu, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Yao, J. Genome-wide identification and co-expression network analysis of the OsNF-Y gene family in rice. Crop J. 2017, 5, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, G.; Liu, W.; Dong, X.; Zhang, A. Genome-wide analysis of the NF-Y gene family in peach (Prunus persica L.). BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wu, M.; Liu, H.L.; Gao, Y.M.; Chen, J.; Yan, H.W.; Xiang, Y. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the NF-Y transcription factor family in populus. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 171, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Luo, L.; Zhang, X.; Lv, Y.; Zhu, S.; Kong, L.; Wan, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, K. Genome-wide identification and abiotic stress response pattern analysis of NF-Y gene family in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Trop. Plant Biol. 2021, 14, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tao, Y.; Bai, A.; Wang, H.; Yu, Z.; Liu, T.; Hou, X.; Li, Y. Genome-wide analysis of the NF-Y gene family in non-heading Chinese cabbage and the involvement of BcNF-YA8 in ABA-mediated flowering regulation. Hort. Plant J. 2025, 2, 661–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Song, K.; Li, B.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Yang, L. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of NF-Y gene family in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Sci. Rep. 2025, 14, 5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafat, A.A.; Verdía Barbará, P.; Ullah, A.; Kontturi, E.; Law, R.V.; Hallett, J.P. Efficient extraction of carboxylated nanocellulose from ionoSolv pulps with alkaline H2O2 assisted oxidation. Cellulose 2025, 32, 853–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Lu, Y.; Xiao, L.; Xue, S.; Yi, Z.; Li, M.; Hou, W. Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Miscanthus and its relative genera (Poaceae) in China. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 192, 116113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzegórska, A.; Czaplicka, N.; Antonkiewicz, J.; Rybarczyk, P.; Baran, A.; Dobrzyński, K.; Zabrocki, D.; Rogala, A. Remediation of soils on municipal rendering plant territories using Miscanthus × giganteus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 22305–22318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, E.M.; McCalmont, J.; Rowe, R.; Whitaker, J.; Holder, A.; Clifton-Brown, J.C.; Thornton, J.; Hastings, A.; Robson, P.R.H.; Webster, R.J.; et al. Upscaling miscanthus production in the United Kingdom: The benefits, challenges, and trade-offs. GCB Bioenergy 2024, 16, e13177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruett, J.; Abdelshafy, A.; Walther, G. Using miscanthus and biochar as sustainable substrates in horticulture: An economic and carbon footprint assessment of their primary and cascading value chains. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 49, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironova, G.F.; Budaeva, V.V.; Skiba, E.A.; Gismatulina, Y.A.; Kashcheyeva, E.I.; Sakovich, G.V. Recent Advances in Miscanthus Macromolecule Conversion: A Brief Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, P.; Kaur, A.; Kumar, P. Phytoremediation of metal contaminated soil using energy crops: Soil health maintenance along with biofuel production. In Bioremediation of Emerging Contaminants from Soils; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 307–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Tian, H.; Cheng, H.; Xuan, Y.; Shang, L.; Yang, Y. The economic and environmental sustainability of converting Miscanthus to hydrocarbon biofuel by pyrolysis and catalytic hydrotreatment. Biomass Bioenergy 2024, 181, 107041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavyrkina, N.A.; Budaeva, V.V.; Skiba, E.A.; Gismatulina, Y.A.; Sakovich, G.V. Review of current prospects for using Miscanthus-based polymers. Polymers 2023, 15, 3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Ma, Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y. Techno-economic analysis of developing miscanthus biorefinery for the production of platform chemicals and renewable resins. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 427, 139172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Yan, Z.; Zhao, G. Genome-wide identification of WRKY transcription factor family members in Miscanthus sinensis (Miscanthus sinensis Anderss). Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Zhou, H.F.; Chen, W.L.; Yan, J.; Cai, Z.; Wei, R.X.; Chen, C.H.; Han, B.; Li, J.Q.; Sang, T.; et al. Population genetics and evolutionary history of Miscanthus species in China. J. Syst. Evol. 2019, 57, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Yi, Z. Heterosis for biomass yield and quality traits in a reciprocal cross population between Miscanthus sinensis and Miscanthus lutarioriparius. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 205, 117451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Wu, S.; Fu, T.; Xu, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, M.; Yi, Z.; Xue, S. Unlocking the potential of Dongting Lake-grown Miscanthus lutarioriparius biomass: A comprehensive quality analysis and bioproduct application study. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 896, 165276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafeez, A.; Rasheed, R.; Ashraf, M.A.; Qureshi, F.F.; Hussain, I.; Iqbal, M. Effect of heavy metals on growth, physiological and biochemical responses of plants. In Plants and Their Interaction to Environmental Pollution; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Jiang, C.; Tang, C.; Nie, X.; Du, L.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, P.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Kang, Z.; et al. Wheat adaptation to environmental stresses under climate change: Molecular basis and genetic improvement. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1564–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakespear, S.; Sivaji, M.; Kumar, V.; Arumugam Pillai, M.; Wani, S.H.; Penna, S.; Yasin, J.K. Navigating through harsh conditions: Coordinated networks of plant adaptation to abiotic stress. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 44, 1396–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wei, H.; Fu, X.; Ma, L.; Lu, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, S. Genome-wide identification of NF-YA gene family in cotton and the positive role of GhNF-YA10 and GhNF-YA23 in salt tolerance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 2103–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.J.; Fu, J.D.; Tang, Y.M.; Yu, T.F.; Yin, Z.G.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.B.; Chen, M.; Xu, Z.S.; Ma, Y.Z. GmNFYA13 improves salt and drought tolerance in transgenic soybean plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 587244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, C.; Wang, M. Wheat NF-YA10 functions independently in salinity and drought stress. Bioengineered 2015, 6, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Ni, C.; Bai, X.; Lin, R.; Xiao, K. TaNF-YA7-5B, a gene encoding nuclear factor Y (NF-Y) subunit A in Triticum aestivum, confers plant tolerance to PEG-inducing dehydration simulating drought through modulating osmotic stress-associated physiological processes. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 188, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, D.; Behera, J.R.; Shinde, S.; Pattada, S.D.; Roth, M.; Yao, L.; Welti, R.; Kilaru, A. Dynamic membrane lipid changes in Physcomitrium patens reveal developmental and environmental adaptations. Biology 2024, 13, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.Y.; Wu, Z.G.; Li, H.Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, W.H.; Yuan, P.R.; Zhu, Z.H.; Yang, X.; Li, H.H.; Huang, P.; et al. Heterologous expression of heat-shock protein PpHSP70 improves high temperature and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Stress 2023, 10, 100273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Feng, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, C.; Lu, H.; Fan, D.; Yan, J.; Lu, Y.; Tian, Q.; et al. Chromosome-scale assembly and analysis of biomass crop Miscanthus lutarioriparius genome. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Noor, M.; Zhang, J.; Yan, X. Progress and prospects of bermudagrass research in the last decade. Grass Res. 2024, 4, e017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhuo, C.; Lu, S.; Guo, Z. Overexpression of a NF-YC transcription factor from bermudagrass confers tolerance to drought and salinity in transgenic rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiruvengadam, R.; Venkidasamy, B.; Easwaran, M.; Chi, H.Y.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Kim, S.H. Dynamic interplay of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS and RNS) in plant resilience: Unveiling the signaling pathways and metabolic responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, S.V. Molecular targets of oxidative stress. Biochem. J. 2011, 434, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negre-Salvayre, A.; Auge, N.; Ayala, V.; Basaga, H.; Boada, J.; Brenke, R.; Chapple, S.; Cohen, G.; Feher, J.; Grune, T.; et al. Pathological aspects of lipid peroxidation. Free Radic. Res. 2010, 44, 1125–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, V.D.; Harish; Singh, R.K.; Verma, K.K.; Sharma, L.; Quiroz-Figueroa, F.R.; Meena, M.; Gour, V.S.; Minkina, T.; Sushkova, S.; et al. Recent developments in enzymatic antioxidant defence mechanism in plants with special reference to abiotic stress. Biology 2021, 10, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Approaches to enhancing antioxidant defense in plants. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Niu, D.; Liu, X. Effects of abiotic stress on chlorophyll metabolism. Plant Sci. 2024, 342, 112030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, A.; Kandpal, G.; Kumar, P. Proline accumulation and its defensive role under diverse stress condition in plants: An overview. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 12, 1655–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, A.; Zahoor, I.; Mushtaq, U. Proline accumulation and oxidative stress: Diverse roles and mechanism of tolerance and adaptation under salinity stress. In Salt Stress, Microbes, and Plant Interactions: Mechanisms and Molecular Approaches; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 269–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylyshbayeva, G.; Bishimbayeva, N.; Jatayev, S.; Eliby, S.; Shavrukov, Y. Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) Application Triggers Plant Dehydration but Does Not Accurately Simulate Drought. Plants 2024, 14, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A. Effect of Soil Water Deficit on Growth and Development of Plants: A Review. In Soil Water Deficit and Physiological Issues in Plants; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brázda, V.; Bartas, M.; Bowater, R.P. Evolution of diverse strategies for promoter regulation. Trends Genet. 2021, 37, 730–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xu, Y.; He, G.; He, K.; Xiao, L.; Hu, R.; Li, S. Genome-wide C characterization and expression profiling of the GRAS gene family in salt and alkali stresses in Miscanthus sinensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Hu, R.; Jiang, J.; Qi, G.; Yang, X.; Zhu, M.; Fu, C.; Zhou, G.; Yi, Z. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of 13 NAC transcription factors in Miscanthus lutarioriparius. Plant Cell Rep. 2014, 33, 2077–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, M.; Yang, X.; Hu, Y.; Huang, L.; Peng, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Nie, G. Identification of candidate reference genes for quantitative RT-PCR in Miscanthus sinensis subjected to various abiotic stresses. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 2913–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Li, M.; Song, T.; Zhang, S.; Wang, T. Genome-wide identification of Miscanthus ASR gene family reveals that MsASR4 is linked to NaCl tolerance. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 219, 119113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zhang, M.; Shang, J.; Liu, Z.; Weng, Y.; Yue, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, P. A 5.5-kb LTR-retrotransposon insertion inside phytochrome B gene (CsPHYB) results in long hypocotyl and early flowering in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2023, 136, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Yang, T.; Li, Q.; Chang, Z.; Sun, C.; Jiang, H.; Meng, X.; Huang, T.; Li, C.B.; Zhong, S.; et al. Tomato MED25 regulates fruit ripening by interacting with EIN3-like transcription factors. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 1038–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Chong, Z.; Lu, C.; Li, K.; Liang, C.; Meng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, S.; He, L.; Zhang, R. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the cotton patatin-related phospholipase A genes and response to stress tolerance. Planta 2023, 257, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Song, T.; Zhang, D.; Shi, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W.; Chen, D.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, X. The transcription factor TabZIP156 acts as a positive regulator in response to drought tolerance in Arabidopsis and wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2024, 216, 109086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Li, M.; Yu, M.; Wang, T. Comprehensive Analysis of Miscanthus NF-YA Genes Reveals Potential Involvement in Drought Stress Adaptation. Plants 2025, 14, 3100. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193100
Yu Y, Li M, Yu M, Wang T. Comprehensive Analysis of Miscanthus NF-YA Genes Reveals Potential Involvement in Drought Stress Adaptation. Plants. 2025; 14(19):3100. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193100
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yang, Mengting Li, Ming Yu, and Tingting Wang. 2025. "Comprehensive Analysis of Miscanthus NF-YA Genes Reveals Potential Involvement in Drought Stress Adaptation" Plants 14, no. 19: 3100. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193100
APA StyleYu, Y., Li, M., Yu, M., & Wang, T. (2025). Comprehensive Analysis of Miscanthus NF-YA Genes Reveals Potential Involvement in Drought Stress Adaptation. Plants, 14(19), 3100. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193100





