Depth and Seasonality of Soil Respiration in Caragana korshinskii Plantation on the Loess Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Measurements of Soil Moisture, Soil CO2 Concentration, and Soil Temperature
2.3. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.4. Calculations
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
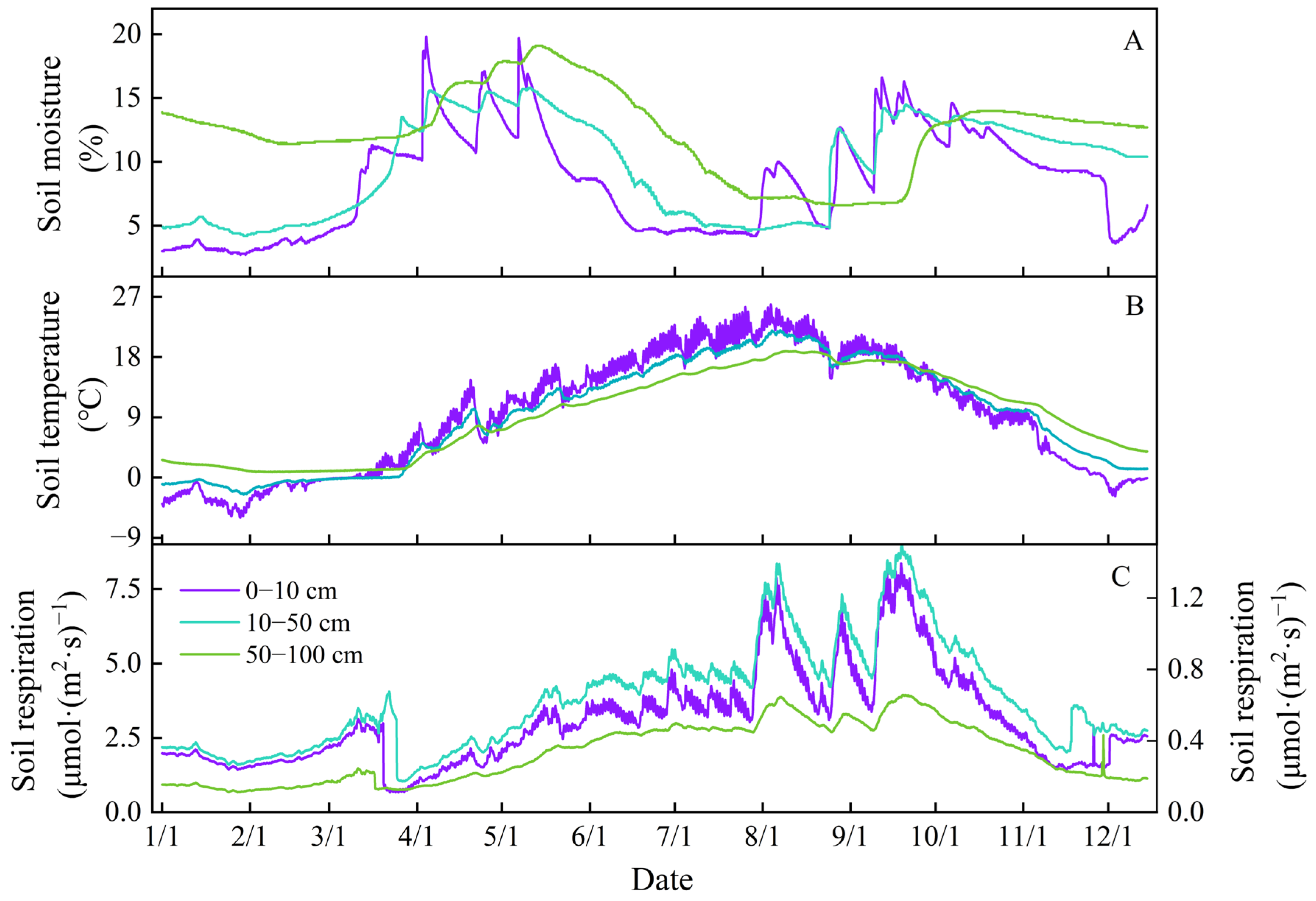
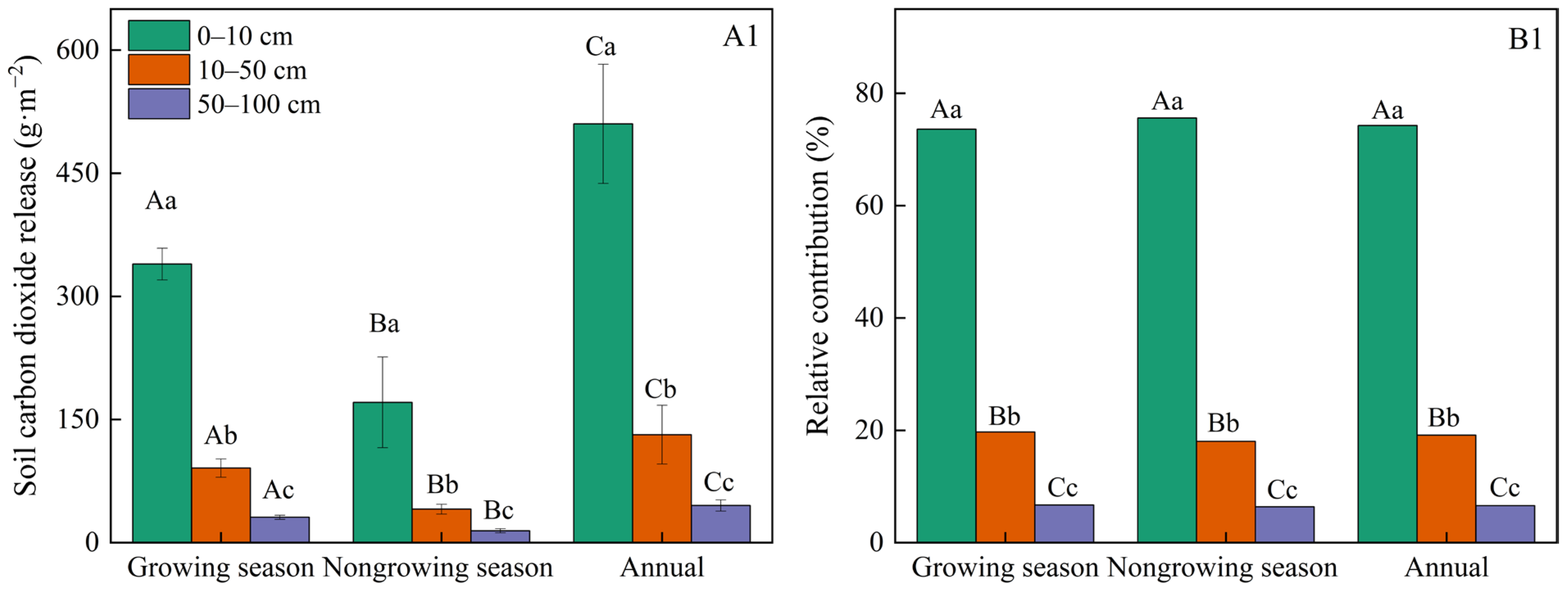
3.1. Variations in Soil Respiration
3.2. Soil Temperature and Moisture Regulating Soil Respiration
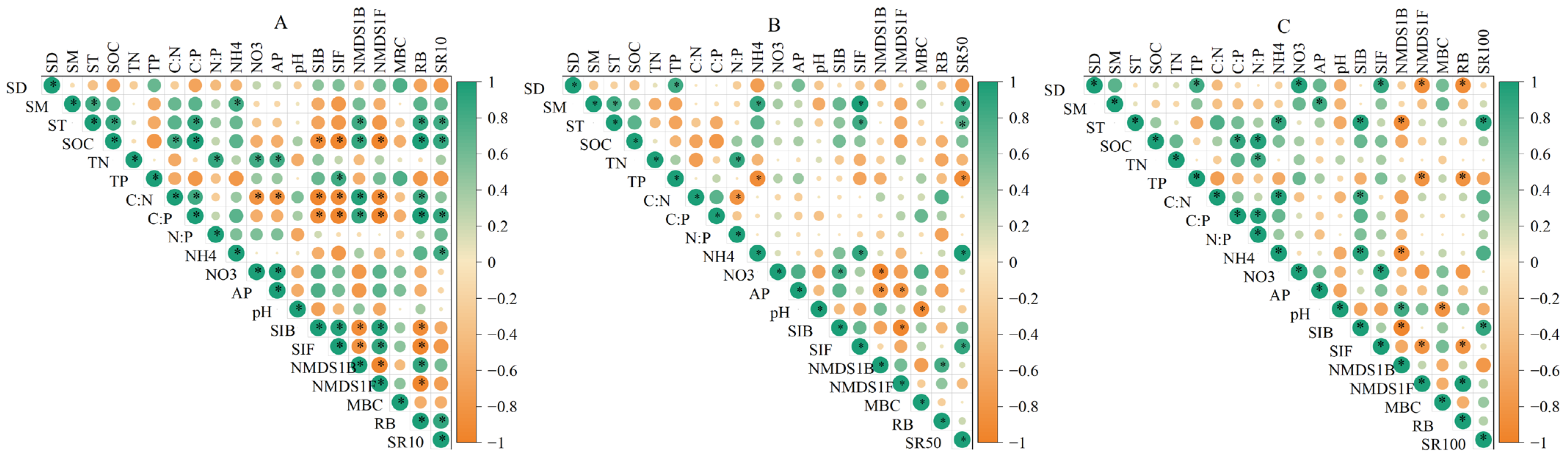
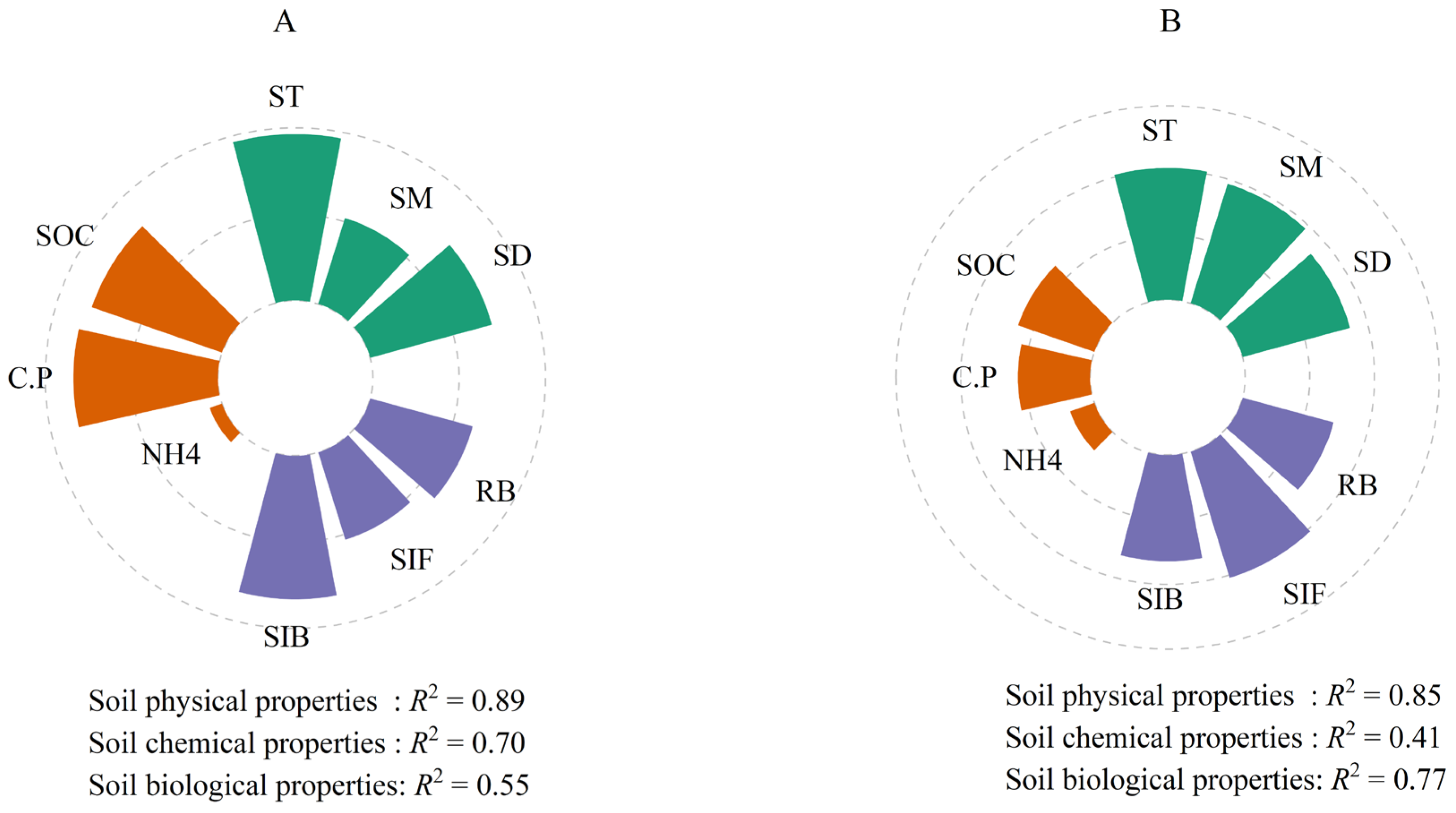
3.3. Environmental Influences on Soil Respiration During Two Seasons
3.4. Environmental Influences on Soil Respiration at Three Depths
4. Discussion
4.1. The Soil Respiration During the Nongrowing Season Is Not Negligible
4.2. Limited Effect of Soil Depths of Soil Respiration
4.3. Uncertainty Consideration
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Li, P.K.; Li, L.; Zhao, M.N.; Yan, P.S.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Ding, S.Y.; Zhao, Q.H. Soil respiration and carbon sequestration response to short-term fertilization in wheat-maize cropping system in the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 251, 106536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Huang, F.Y.; Wang, B.F.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhao, C.X.; Ding, R.X.; Yang, B.P.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Z.K. Soil respiration in response to biotic and abiotic factors under different mulching measures on rain-fed farmland. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 232, 105749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.H.; Luo, X.R.; Shi, Y.H.; Zhou, T.; Luo, K.; Lai, Y.S.; Yu, P.; Liu, L.; Olchev, A.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; et al. Controls and variability of soil respiration temperature sensitivity across China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 161974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Gou, M.M.; Hu, J.W.; Lei, L.; Zhu, S.F.; Hu, R.Y.; Zhao, H.P.; Xiao, W.F.; Liu, C.F. Seasonal variations in soil enzyme activity and nutrient limitations of differently aged Pinus massoniana plantation. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.J.; Wang, G.S.; Zhou, S.H.; Li, W.Y.; Xiong, L.H. Day-night discrepancy in soil respiration varies with seasons in a temperate forest. Funct. Ecol. 2024, 37, 2002–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laza, H.E.; Acosta-Martinez, V.; Cano, A.; Baker, J.; Mahan, J.; Gitz, D.; Emendack, Y.; Slaughter, L.; Lascano, R.; Tissue, D.; et al. Elevated [CO2] enhances soil respiration and AMF abundance in a semiarid peanut agroecosystem. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 355, 108592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, K.; Schierling, L.; Sun, Y.; Schuchardt, M.A.; Jentsch, A.; Deola, T.; Wolff, P.; Kiese, R.; Lehndorff, E.; Pausch, M.; et al. Temperature sensitivity of soil respiration declines with climate warming in subalpine and alpine grassland soils. Biogeochemistry 2024, 167, 1453–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, A.L.; Cusack, D.F.; Dietterich, L.H.; Hockaday, W.C.; Mcfarlane, K.J.; Sivapalan, V.; Hedgpeth, A.; Neupane, A.; Colburn, L.; Konwent, W.; et al. Root characteristics vary with depth across four lowland seasonal tropical forests. Ecosystems 2024, 27, 1104–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.F.; Qin, W.K.; Feng, J.G.; Li, X.J.; Zhang, Z.H.; He, J.S.; Schimel, J.P.; Zhu, B. Whole-soil-profile warming does not change microbial carbon use efficiency in surface and deep soils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 20, e2302190120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.R.; Lu, S.B.; Chen, Y.M. Variations and controlling factors of soil CO2 release at daytime and nighttime scales in the loess hilly regions of China. Geoderma 2025, 454, 117167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore, T.J.; Knorr, M.A.; Simpson, M.J.; Stephens, R.B.; Phillips, R.P.; Frey, S.D. Response of Root Respiration to Warming and Nitrogen Addition Depends on Tree Species. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Zhao, C.M.; Dacal, M.; Gozalo, B.; Ochoa, V.; Asensio, S.; Corrochano-Monsalve, M.; Chen, N.; Biancari, L.; Maestre, F.T. Biocrusts alter the effects of long-term warming on soil respiration in a dryland ecosystem. Geoderma 2025, 459, 117388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Fu, Y.J.; Li, P.; Qiao, J.; Li, H.; Wu, L.C.; Wang, B.P.; Lu, S. Exploring the effects of different fertilizer application durations on the functional microbial profiles of soil carbon and nitrogen cycling by using metagenomics in Paulownia plantations in a subtropical zone. Eur. J. For. Res. 2024, 143, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luboš, S.; Jindřich, N.; Radomír, U. Changes in the concentration of CO2 in forest soils resulting from the traffic of logging machines. J. For. Sci. 2025, 71, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podzikowski, L.Y.; Billings, S.A.; Bever, J.D. Plant functional diversity shapes soil respiration response to soil moisture availability. Ecosystems 2025, 28, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zveushe, O.K.; Sajid, S.; Dong, F.Q.; Han, Y.; Zeng, F.; Geng, Y.H.; Shen, S.R.; Xiang, Y.L.; Kang, Q.L.; Zhang, Y.Z. Different sex combinations of Populus cathayana affect soil respiration and tea litter decomposition by influencing plant growth and soil functional microbial diversity. Plant Soil 2025, 490, 631–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.H.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Saez-Sandino, T.; Chen, J.Y.; Feng, J.; Huang, Q.Y.; Guirado, E.; Rillig, M.C.; Liu, Y.R. Negative impacts of global change stressors permeate into deep soils. Ecol. Lett. 2025, 28, e70143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.X.; Shi, J.; Fan, Z.M.; Peng, Y.M.; Wang, X. Changes in long-term land use alter deep soil microbial necromass and organic carbon stabilization. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 384, 125589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.L.; He, C.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhao, L.L.; He, X.L.; Sun, X. Soil variables driven by host plant and growth season affect soil microbial composition and metabolism in extremely arid desert ecosystems. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 269, 127315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gunina, A.; Chen, J.; Wang, B.R.; Cheng, H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Liang, C.; An, S.S.; Chang, S.X.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M. Unfolding the Potential of Soil Microbial Community Diversity for Accumulation of Necromass Carbon at Large Scale. Glob. Change Biol. 2025, 31, e70292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, C.X.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, J.J.; Xu, B.C. Variation Patterns and Affecting Factors of Plant Alpha Diversity, Beta Diversity and Its Components in Restoration Grasslands on Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 5162–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.J.; Chen, Z.F.; Jian, C.X.; Luo, Y.; Niu, F.R.; Palta, J.A.; Xu, B.C. Autotrophic Respiration Is More Sensitive to Nitrogen and Phosphorus Supply Than Heterotrophic Respiration in Semiarid Grassland. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2024, 129, e2024JG008230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jian, C.X.; Zhou, J.J.; Mou, Y.K.; Jin, Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Xu, B.C. Effects of surface vegetation and litter on rainfall redistribution during the rainy season in semiarid grasslands. J. Hydrol. 2025, 657, 133079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.R.; Liu, C.; Zhao, M.; Liu, L.; Liang, S.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Chen, Y.M. Influence of extreme rainfall events on soil carbon release in the Loess Hilly Region, China. Catena 2023, 220, 106652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Z.J.; Li, Y.; He, J.L.; Wu, X.D. Dynamic growth models for Caragana korshinskii shrub biomass in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 269, 110675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.F.; Xiong, P.F.; Zhou, J.J.; Lai, S.B.; Jian, C.X.; Xu, W.Z.; Xu, B.C. Effects of plant diversity on semiarid grassland stability depend on functional group composition and dynamics under N and P addition. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Global Forest Resources Assessment; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Wang, R.; Yang, M.D.; Liu, Q.F.; Zhang, W.J.; Guo, S.L. Differential responses of soil CO2 dynamics along soil depth to rainfall patterns in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 378, 109306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contosta, A.R.; Burakowski, E.A.; Varner, R.K.; Frey, S.D. Winter soil respiration in a humid temperate forest: The roles of moisture, temperature, and snowpack. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 3072–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.R.; Gregorich, E.G. Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor and Francis Group: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Sun, Y.R.; Liu, S.H.; Li, Y.C.; Chen, Y.M. Effects of stand density on the structure of soil microbial functional groups in Robinia pseudoacacia plantations in the hilly and gully region of the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, M.; Schack-Kirchner, H. Using the gradient method to determine soil gas flux: A review. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 192–193, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühlmann, J.; Körschens, M.; Graefe, J. A new approach to calculate the particle density of soils considering properties of the soil organic matter and the mineral matrix. Geoderma 2006, 130, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Phillips, R.P.; Manzoni, S.; Scott, R.L.; Oishi, A.C.; Finzi, A.C.; Daly, E.; Vargas, R.; Novick, K.A. Changes in photosynthesis and soil moisture drive the seasonal soil respiration-temperature hysteresis relationship. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 259, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Qi, Y. Soil-surface CO2 efflux and its spatial and temporal variations in a young ponderosa pine plantation in northern California. Glob. Change Biol. 2001, 7, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.Y.; Du, S.; Morina, J.C.; Guan, J.H.; Wang, K.B.; Ma, M.G.; Yamanaka, N.; Tateno, R. Physical and biogeochemical controls on soil respiration along a topographical gradient in a semiarid forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 247, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A.; Samanta, S.; Caramori, S.S.; Savage, K. The dual Arrhenius and Michaelis-Menten kinetics model for decomposition of soil organic matter at hourly to seasonal time scales. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.S.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Peres-Neto, P.R. Generalizing hierarchical and variation partitioning in multiple regression and canonical analyses using the rdacca.hp R package. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2022, 13, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.F.; Yang, S.P.; He, Z.B.; Zhao, W.Z.; Kong, J.Q.; Feng, X.Y.; Li, X.G. Divergent seasonal patterns and drivers of soil respiration in alpine forests of northwestern China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 343, 109787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.; Markewitz, D. Soil heterotrophic respiration: Measuring and modeling seasonal variation and silvicultural impacts. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 430, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Wang, H.; Schindlbacher, A.; Liu, S.R.; Yang, Y.J.; Tian, H.M.; Chen, L.; Ming, A.G.; Wang, J.; Li, J.C.; et al. Soil respiration related to the molecular composition of soil organic matter in subtropical and temperate forests under soil warming. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 201, 109661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacal, M.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Barquero, J.; Berhe, A.A.; Gallardo, A.; Maestre, F.T.; García-Palacios, P. Temperature increases soil respiration across ecosystem types and soil development, but soil properties determine the magnitude of this effect. Ecosystems 2022, 25, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Chen, B.B.; Dong, H.X.; Zhang, W.L.; Kumar, A.; Hui, D.F.; Zhang, C.G.; Shan, S.D.; Zhu, B. Effects of soil moisture fluctuation and microplastics types on soil organic matter decomposition and carbon dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 205, 109781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, J.L.; Marañon-Jimenez, S.; Cotrufo, M.F.; Boeckx, P.; Bodé, S.; Guenet, B.; Peñuelas, J.; Richter, A.; Stahl, C.; Verbruggen, E.; et al. Soil microbial CNP and respiration responses to organic matter and nutrient additions: Evidence from a tropical soil incubation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 122, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Marschner, P. Soil respiration, microbial biomass and nutrient availability in soil after repeated addition of low and high C/N plant residues. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.P.; Ge, X.G.; Lei, L.; Zhou, B.Z.; Li, M.H. Effects of phosphorus resorption on bioactive phosphorus of different-aged Pinus massoniana plantations. For. Ecosyst. 2024, 11, 100241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hursh, A.; Ballantyne, A.; Cooper, L.; Maneta, M.; Kimball, J.; Watts, J. The sensitivity of soil respiration to soil temperature, moisture, and carbon supply at the global scale. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 2090–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.P.; Fu, R.T.; Nottingham, A.T.; Domeignoz-Horta, L.A.; Yang, X.Y.; Du, H.; Wang, K.L.; Li, D.J. Tree species diversity increases soil microbial carbon use efficiency in a subtropical forest. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 7131–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Huang, W.D.; He, Y.Z.; Zhu, Y.Z. Effects of warming and precipitation reduction on soil respiration in Horqin sandy grassland, northern China. Catena 2023, 233, 107470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Song, X.Y.; Zhou, S.Y.; Jiang, Y.F.; Qiao, L.J.; Ma, X.J.; Chen, N.; Zhao, C.M. Divergent responses of soil respiration to biocrusts during the nongrowing and growing seasons in a dryland shrubland ecosystem. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 211, 106113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Mu, J.P.; Liu, Y.Z.; Smith, N.G.; Sun, S.C. Effect of microtopography on soil respiration in an alpine meadow of the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Plant Soil 2017, 421, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.Q.; Lyu, X. Identification of a novel cellobiose 2-epimerase from Acidobacteriota bacterium and its application for in-situ milk catalysis. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1575725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, O.S.; Fernandes, A.S.; Tupy, S.M.; Ferreira, T.G.; Almeida, L.N.; Creevey, C.J.; Santana, M.F. Insights into plant interactions and the biogeochemical role of the globally widespread Acidobacteriota phylum. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 192, 109369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.H.; Feng, F.J.; Cai, T.J.; Tang, S.J. Soil Microbial Community Response Differently to the Frequency and Strength of Freeze-Thaw Events in a Larix gmelinii Forest in the Daxing’an Mountains, China. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klink, S.; Keller, A.B.; Wild, A.J.; Baumert, V.L.; Gube, M.; Lehndorff, E.; Meyer, N.; Mueller, C.W.; Phillips, R.P.; Pausch, J. Stable isotopes reveal that fungal residues contribute more to mineral-associated organic matter pools than plant residues. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 168, 108634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, C.T.; Engel, K.; Hall, M.; Neufeld, J.D.; Walker, V.K.; Grogan, P. Arctic tundra soil depth, more than seasonality, determines active layer bacterial community variation down to the permafrost transition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 200, 109624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.F.; Zhou, L.H.; Zou, B.Z.; Wang, S.R.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, Z.Q.; He, J.Z. Soil Fungal Diversity and Functionality Changes Associated with Multispecies Restoration of Pinus massoniana Plantation in Subtropical China. Forests 2022, 13, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, V.; Henneron, L.; Ribémont, R.; Colin, Y.; Buquet, S.; Vincenot, L.; Aubert, M. Standing at the crossroads: Path analysis highlights potential levers to preserve fungal richness when shifting tree species for forest adaptation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2025, 589, 122772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yang, T.; Rinne-Garmston, K.T.; Ji, X.Y.; Xu, Q.; Xu, Z.Y.; Zheng, Y.X.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Zhao, G.P.; Hu, Z.H. Wood-inhabiting fungal community characteristics responses to nutrient additions vary among tree taxonomic groups. J. Soil Sediments 2025, 25, 1497–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, Y.L.; Lou, J.W.; Wang, Y.K.; Kan, Z.R.; Neugschwandtner, R.W.; Li, F.M.; Liu, J.; Dong, K.; Xue, Y.G.; et al. Fungal Saprotrophic Promotion and Plant Pathogenic Suppression under Ditch-Buried Straw Return with Appropriate Burial Amount and Depth. Plant 2024, 13, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nola, P.; Bracco, F.; Assini, S.; von Arx, G.; Castagneri, D. Xylem anatomy of Robinia pseudoacacia L. and Quercus robur L. is differently affected by climate in a temperate alluvial forest. Ann. For. Sci. 2020, 77, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.G.; Qiao, Y.N.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y.M.; Wu, X.; Xue, W.Y. Seasonal variations in carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry of a Robinia pseudoacacia plantation on the Loess Hilly Region, China. Forests 2021, 12, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.R.; Zhao, M.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.H.; Dong, C.G.; Chen, Y.M. Plant carbon removal affects monthly temperature sensitivity of soil respiration during growing season in three typical plantations in the Loess Hilly Region, China. Catena 2024, 234, 107549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, M.A.; Classen, A.T.; English, M.E.; Frey, S.D.; Knorr, M.A.; Rand, K.; Adair, E.C. Soil microbial legacies influence freeze-thaw responses of soil. Funct. Ecol. 2023, 37, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


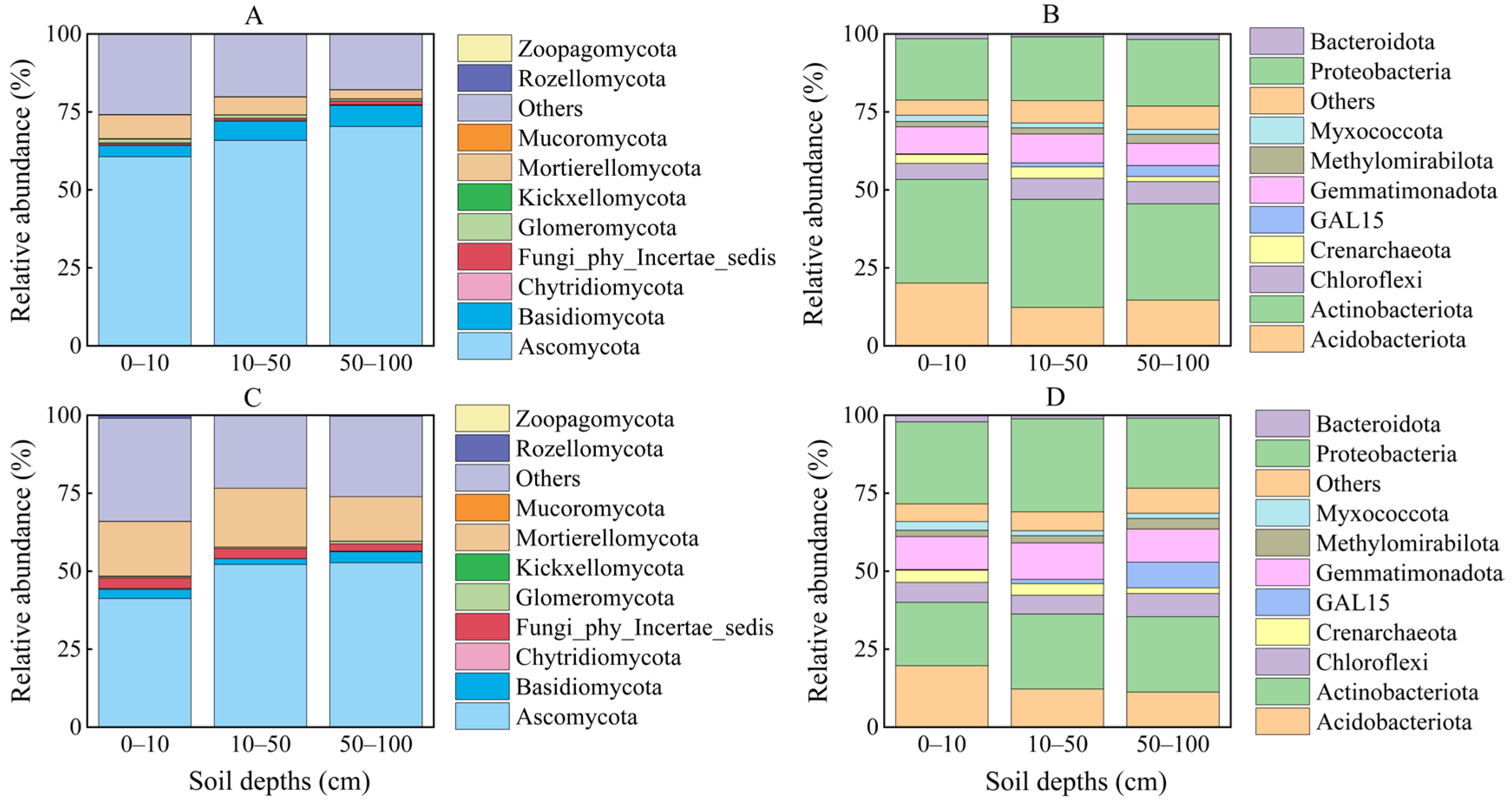
| Depth (cm) | Growing Season | Non-Growing Season | S | D | S × D | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 | 10–50 | 50–100 | 0–10 | 10–50 | 50–100 | p | |||
| TN (g·kg−1) | 0.97 ± 0.16 Aa | 0.34 ± 0.10 Ab | 0.29 ± 0.03 Ab | 0.97 ± 0.06 Aa | 0.34 ± 0.07 Ab | 0.30 ± 0.05 Ab | 0.24 | <0.01 | 0.87 |
| NH4+ (g·kg−1) | 0.10 ± 0.06 Aa | 0.09 ± 0.05 Aa | 0.08 ± 0.10 Aa | 0.07 ± 0.03 Ba | 0.054 ± 0.11 Ba | 0.05 ± 0.05 Ba | <0.01 | 0.43 | 0.38 |
| TP (g·kg−1) | 0.64 ± 0.00 Aa | 0.62 ± 0.00 Aa | 0.61 ± 0.00 Aa | 0.56 ± 0.01 Ba | 0.55 ± 0.02 Ba | 0.54 ± 0.00 Ba | <0.01 | 0.88 | 0.32 |
| pH | 8.45 ± 0.14 Aa | 8.49 ± 0.16 Aa | 8.6 ± 0.08 Aa | 8.43 ± 0.18 Aa | 8.57 ± 0.06 Aa | 8.72 ± 0.22 Aa | 0.41 | 0.13 | 0.73 |
| SOC (g·kg−1) | 5.64 ± 0.27 Aa | 3.88 ± 0.97 Ab | 2.92 ± 0.17 Ab | 4.68 ± 0.25 Aa | 3.59 ± 0.84 Ab | 2.91 ± 0.42 Ab | 0.31 | <0.05 | 0.78 |
| N:P | 1.52 ± 0.25 Aa | 0.55 ± 0.03 Ab | 0.48 ± 0.17 Ab | 1.73 ± 0.11 Aa | 0.62 ± 0.13 Ab | 0.56 ± 0.09 Ab | 0.7 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| NO3− (g·kg−1) | 0.58 ± 0.11 Aa | 0.47 ± 0.63 Aa | 0.27 ± 0.31 Aa | 0.53 ± 0.67 Aa | 0.30 ± 0.25 Aa | 0.23 ± 0.20 Aa | 0.62 | 0.85 | 0.34 |
| C:P | 8.81 ± 0.71 Aa | 6.25 ± 1.63 Ab | 4.79 ± 0.48 Ab | 8.38 ± 0.36 Ba | 6.53 ± 1.37 Ab | 5.39 ± 0.67 Ab | 0.21 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| C:N | 5.81 ± 1.17 Aa | 11.4 ± 1.58 Ab | 10.1 ± 0.29 Ab | 4.81 ± 0.53 Aa | 10.6 ± 4.64 Ab | 9.7 ± 0.70 Ab | 0.448 | <0.01 | 0.08 |
| SD (g·cm−3) | 1.35 ± 0.03 Aa | 1.45 ± 0.03 Ab | 1.58 ± 0.01 Ac | 1.37 ± 0.03 Aa | 1.47 ± 0.03 Ab | 1.60 ± 0.01 Ac | 0.27 | <0.05 | 0.51 |
| ST (°C) | 15.9 ± 0.33 Aa | 14.9 ± 0.40 Ab | 13.6 ± 0.33 Ac | −0.3 ± 0.21 Ba | 0.93 ± 0.15 Bb | 3.12 ± 0.20 Bc | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| SM (cm3·cm−3) | 0.10 ± 0.00 Aa | 0.12 ± 0.02 Aa | 0.12 ± 0.01 Aa | 0.05 ± 0.00 Ba | 0.09 ± 0.01 Ba | 0.12 ± 0.01 Ba | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| RB | 943.15 ± 59.9 Aa | 563.12 ± 69.0 Ab | 409.42 ± 77.1 Ac | 754.91 ± 87.5 Ba | 532.85 ± 6.50 Bb | 370.73 ± 61.1 Bc | <0.01 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| MBC (g·kg−1) | 14.46 ± 0.894 Aa | 9.53 ± 6.38 Ab | 8.23 ± 5.97 Ac | 13.09 ± 1.58 Aa | 8.67 ± 4.26 Ab | 6.46 ± 0.43 Ac | 0.43 | <0.05 | 0.91 |
| SIF | 5.98 ± 0.02 Aa | 5.38 ± 0.02 Ab | 4.95 ± 0.01 Ac | 7.14 ± 0.02 Ba | 5.11 ± 0.01 Bb | 4.95 ± 0.00 Bc | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.12 |
| SIB | 10.4 ± 0.11 Aa | 9.75 ± 0.10 Ab | 9.54 ± 0.11 Ac | 10.2 ± 0.10 Aa | 9.73 ± 0.08 Ab | 9.04 ± 0.07 Ac | 0.81 | <0.05 | 0.63 |
| NMDS1B | −0.10 ± 0.02 Aa | −0.05 ± 0.14 Ab | 0.01 ± 0.11 Ab | −0.10 ± 0.07 Aa | 0.00 ± 0.07 Ab | 0.06 ± 0.018 Ab | 0.31 | <0.05 | 0.07 |
| NMDS1F | −0.49 ± 0.17 Aa | −0.25 ± 0.14 Ab | −0.12 ± 0.18 Ac | −0.20 ± 0.03 Ba | −0.13 ± 0.27 Bb | 0.66 ± 0.082 Bc | <0.05 | <0.01 | <0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Chen, Y. Depth and Seasonality of Soil Respiration in Caragana korshinskii Plantation on the Loess Plateau. Plants 2025, 14, 3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193038
Sun Y, Chen Y. Depth and Seasonality of Soil Respiration in Caragana korshinskii Plantation on the Loess Plateau. Plants. 2025; 14(19):3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193038
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yarong, and Yunming Chen. 2025. "Depth and Seasonality of Soil Respiration in Caragana korshinskii Plantation on the Loess Plateau" Plants 14, no. 19: 3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193038
APA StyleSun, Y., & Chen, Y. (2025). Depth and Seasonality of Soil Respiration in Caragana korshinskii Plantation on the Loess Plateau. Plants, 14(19), 3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14193038






