Current Status of Studying on Physiological Mechanisms of Rice Response to Flooding Stress and Flooding-Resistant Cultivation Regulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Concept, Type, and Occurrence Characteristics of Rice Flooding
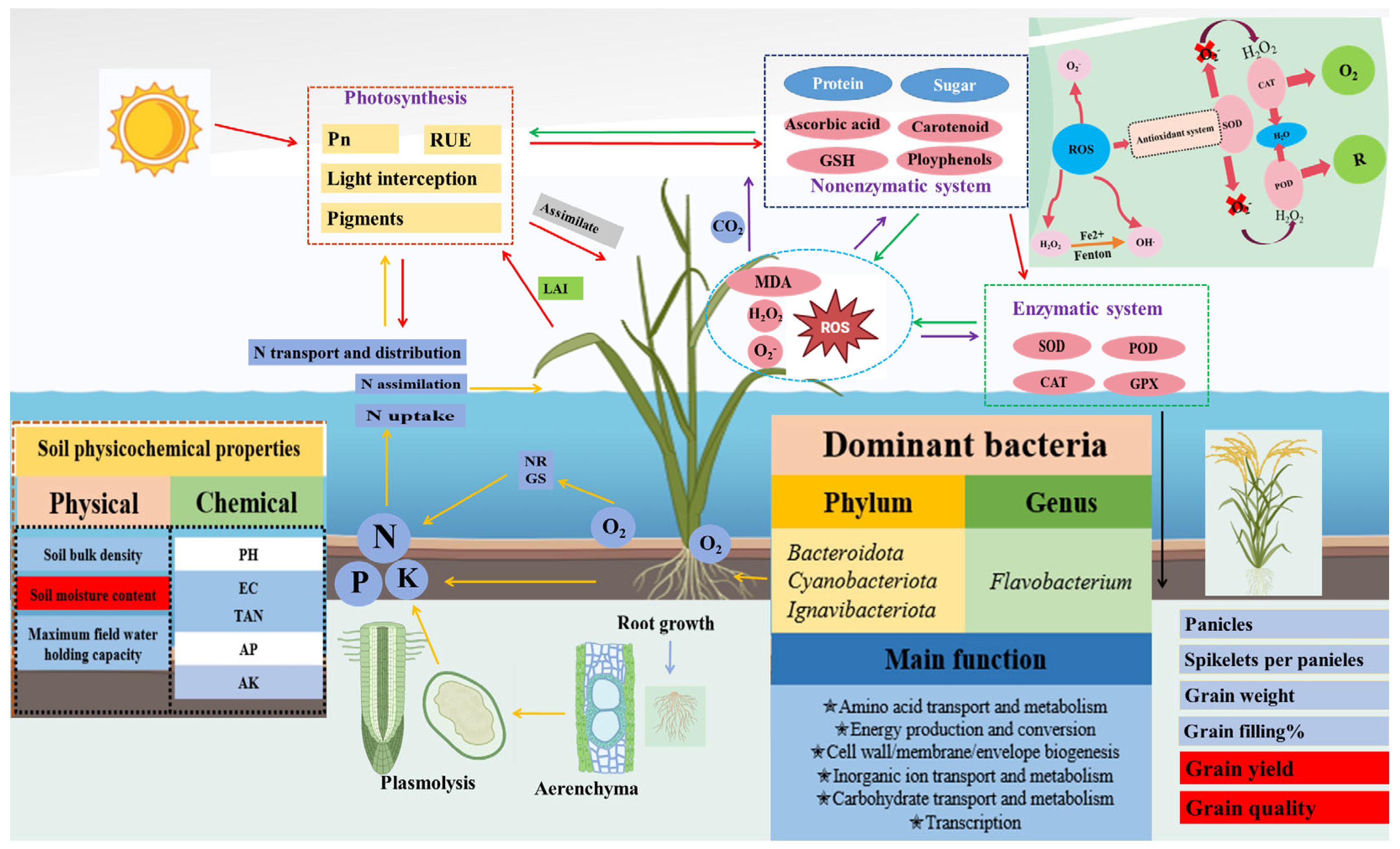
3. Effects of Flooding Stress on Growth, Physiology, and Yield
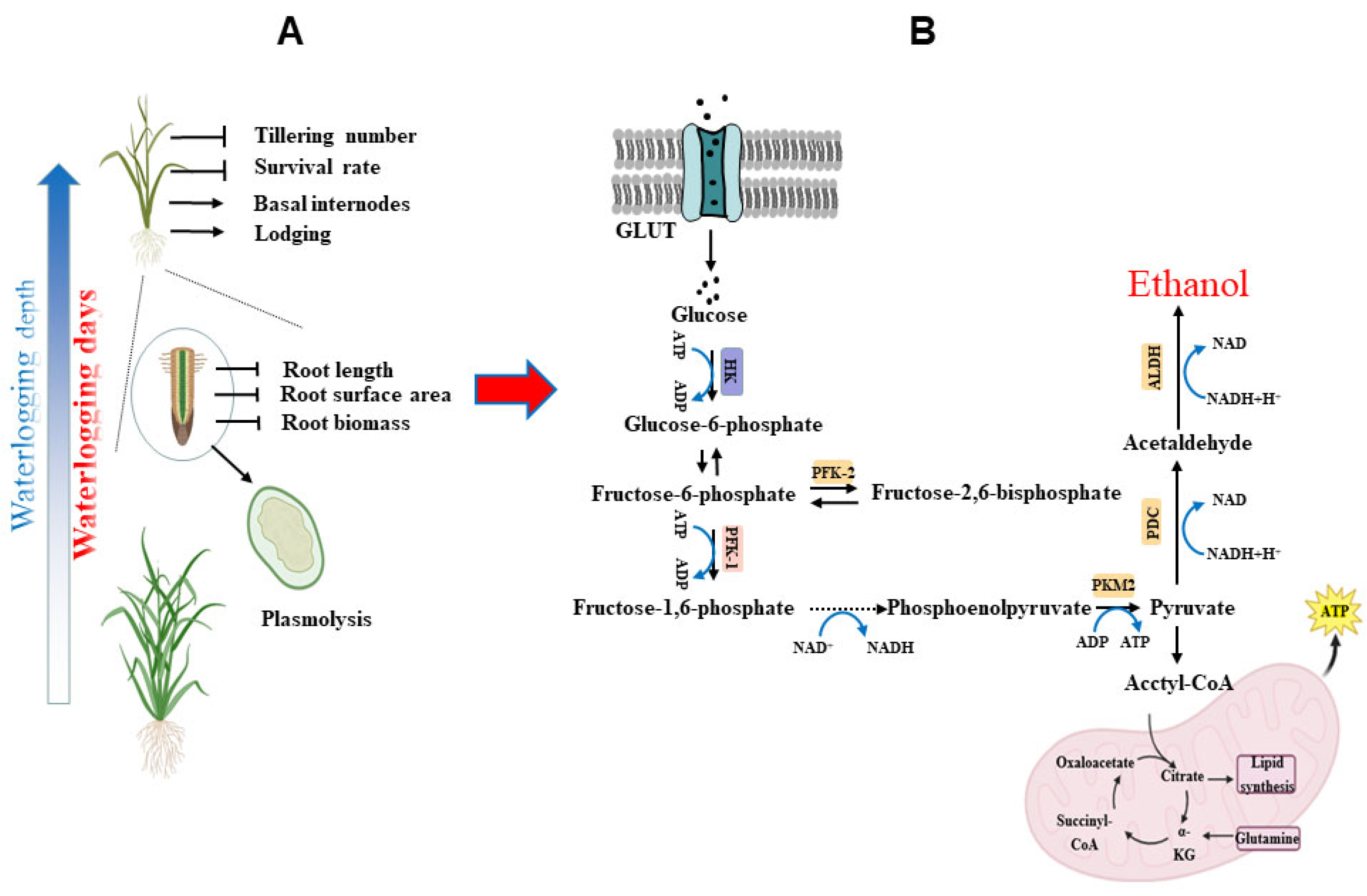
3.1. The Effect of Flooding Stress on Rice Plant Growth Traits
3.2. The Effects of Flooding Stress on Rice Roots’ Growth Traits
3.3. Effects of Flooding Stress on Reactive Oxygen Metabolism
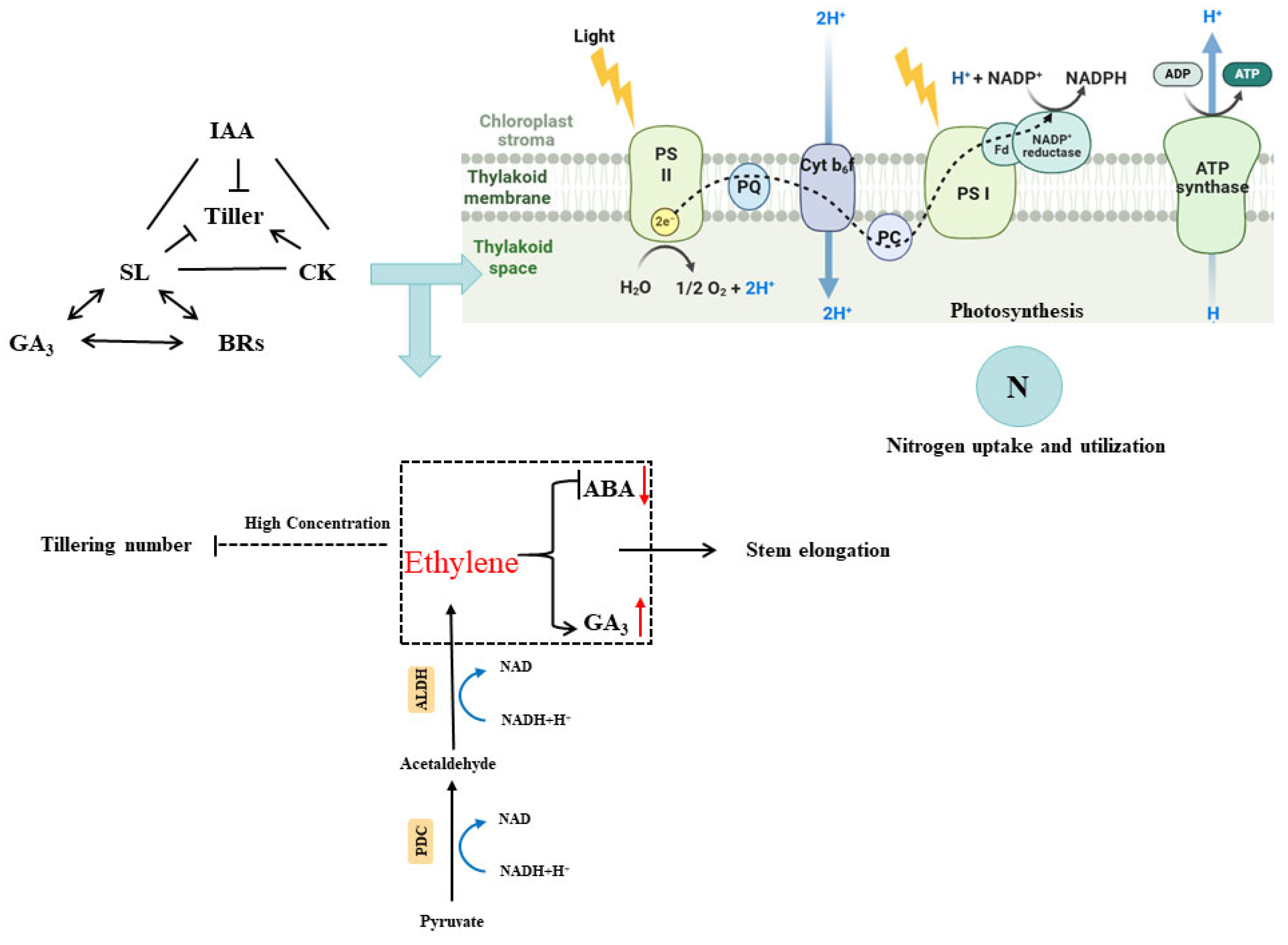
3.4. The Effects of Flooding Stress on Radiation Use Efficiency
3.5. Effects of Flooding Stress on Endogenous Hormones Balance
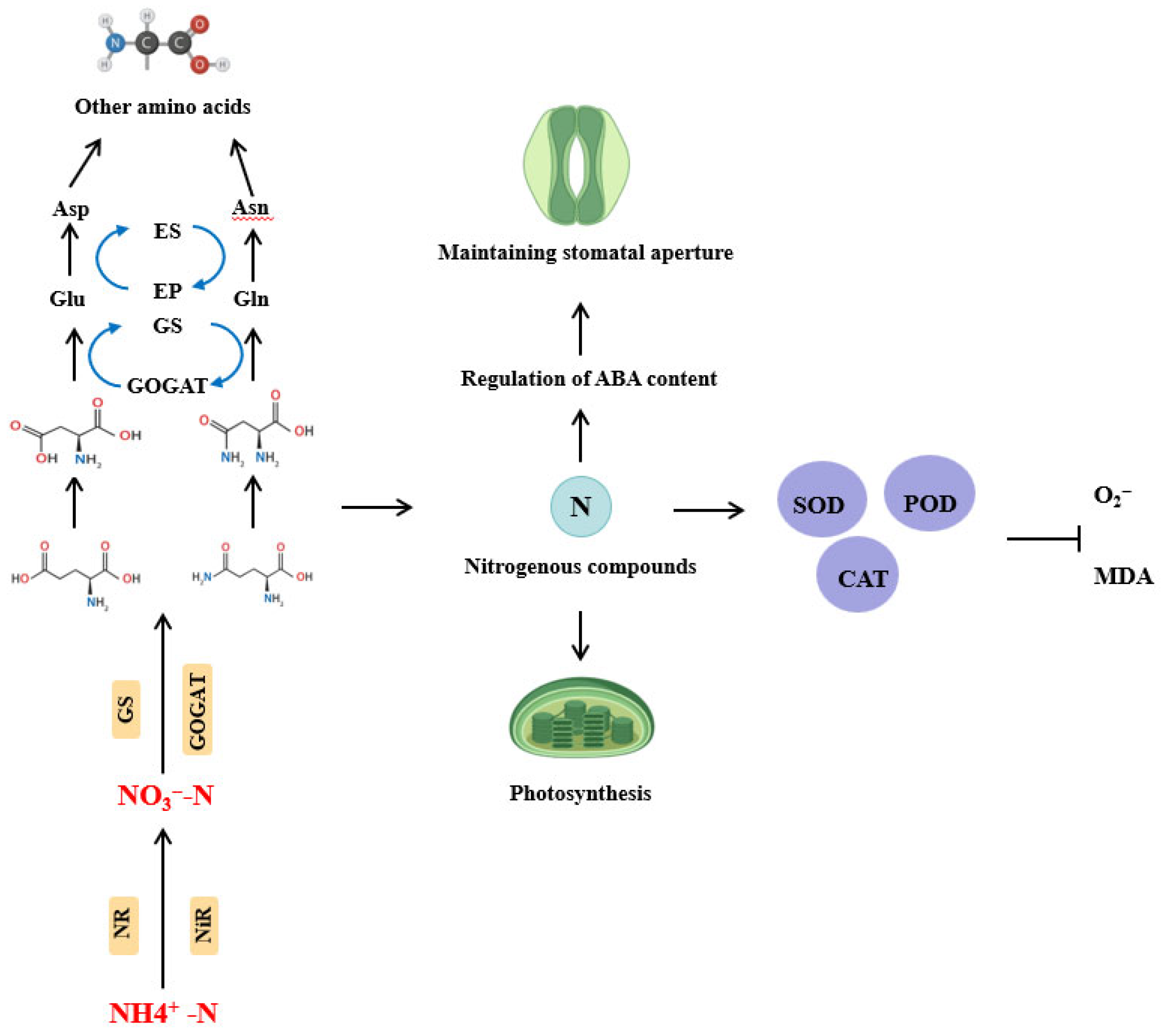
3.6. Effect of Flooding Stress on Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency
3.7. The Impact of Flooding Stress on Rice Grain Yield
4. Rice Stress-Resistant Breeding and Cultivation Regulation Methods
4.1. Breeding Strategies to Reduce the Stress of Rice Flooding
4.2. Cultivation and Regulation Methods to Alleviate Flooding Stress in Rice
4.2.1. Drainage and Disaster Reduction
4.2.2. Optimize Fertilizer Management
4.2.3. Exogenous Growth Regulatory Substances
5. Conclusions and Prospective
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, G.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Ma, Z.S.; Shi, C.M. The unevenness in observed daily precipitation in mainland China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 146, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Jian, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Ciais, P.; Zscheischler, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Müller, C.; Webber, H.; et al. Extreme rainfall reduces one-twelfth of china’s rice yield over the last two decades. Nat. Food. 2023, 4, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultgren, A.; Carleton, T.; Delgado, M.; Gergel, D.R.; Greenstone, M.; Houser, T.; Hsiang, S.; Jina, A.; Kopp, R.E.; Malevich, S.B.; et al. Impacts of climate change on global agriculture accounting for adaptation. Nature 2025, 642, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Collard, B.C.Y.; Septiningsih, E.M.; Ismail, A.M. Increasing Flooding Tolerance in Rice: Combining Tolerance of Submergence and of Stagnant Flooding. Ann. Bot. 2020, 124, 1199–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proctor, J. Extreme Rainfall Reduces Rice Yields in China. Nat. Food. 2023, 4, 360–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Chen, X. The 1998 Flood on the Yangtze, China. Nat. Hazards 2000, 22, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Cheng, X.; Huang, Q.; Chen, R.; Ward, P.J.; Aerts, J.C.J.H. Brief communication: Rethinking the 1998 China floods to prepare for a nonstationary future. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 19, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Yan, C.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, Z. Advances and perspectives in research about mechanism and assessment methods of crop flood disaster. Torrential Rain Disasters 2023, 42, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.H.; de Janvry, A.; Emerick, K.; Raitzer, D.; Sadoulet, E. Flood-tolerant rice reduces yield variability and raises expected yield, differentially benefitting socially disadvantaged groups. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Liu, K.; Tian, N.; Feng, X.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Peng, T.; Harrison, M.T.; Huang, L.; et al. The tradeoff between increasing productivity and environmental sustainability in super hybrid rice breeding. npj Sustain. Agric. 2025, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhou, Y.J.; Xu, Y.Z.; Chen, G.; Hu, Q.F.; Wu, W.G.; Qu, X.M. Effects of Waterlogging Stress on Growth and Yield of Middle Season Rice at the Tillering Stage. J. Plant Physiol. Ecol. 2014, 20, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.L.; Chen, Y.T.; Evangelina, E.S.; Ismail, A.M. Mechanisms associated with tiller suppression under stagnant flooding in rice. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2019, 205, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Zhu, J.; Yan, J. Response of Middle-season Hybrid Rice to Flooding Stress at the Booting Stage. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2023, 37, 642–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Hill, C.B.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, X.Q.; Jia, Y.; Li, C. Opportunities for Improving Waterlogging Tolerance in Cereal Crops-Physiological Traits and Genetic Mechanisms. Plants 2021, 10, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phukan, U.J.; Jindal, S.; Laldinsangi, C.; Singh, P.K.; Longchar, B. A microscopic scenario on recovery mechanisms under waterlogging and submergence stress in rice. Planta 2023, 259, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talpur, M.A.; Changying, J.; Junejo, S.A.; Tagar, A.A.; Ram, B.K. Effect of different water depths on growth and yield of rice crop. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 8, 4654–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiuchi, S.; Yamauchi, T.; Takahashi, H.; Kotula, L.; Nakazono, M. Mechanisms for coping with submergence and waterlogging in rice. Rice 2012, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.E.; Humphreys, E. Enhancing the productivity and sustainability of cropping systems in the coastal zones of tropical deltas of Asia. Field Crops Res. 2021, 263, 108059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowdra, V.M.G.; Lalitha, B.S.; Halli, H.M.; Senthamil, E.; Negi, P.; Jayadeva, H.M.; Basavaraj, P.S.; Harisha, C.B.; Boraiah, K.M.; Adavi, S.B.; et al. Root growth, yield and stress tolerance of soybean to transient waterlogging under different climatic regimes. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hu, T.; Li, P.; Qi, X. The Interaction Effects of Drought–Flood Abrupt Alternation on Rice Yield and Dry Matter Partitioning. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohilla, M.; Mazumder, A.; Chakraborty, K.; Chowdhury, D.; Prakash, N.; Mondal, T.K. The Private Life of Deepwater Rice: Unravelling Exclusive Features and Unexplored Mechanisms. Plant Stress 2025, 17, 100910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladosu, Y.; Rafii, M.Y.; Arolu, F.; Chukwu, S.C.; Muhammad, I.; Kareem, I.; Salisu, M.A.; Arolu, I.W. Submergence Tolerance in Rice: Review of Mechanism, Breeding and, Future Prospects. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Zhao, X.Y.; Liu, F.P.; Zhu, L.D.; Fu, T.X.; Liu, J.C. Flood Tolerance Test of Major Early Rice Varieties in the Poyang Lake Basin. China Rural. Water Hydropower 2023, 244–249, 255, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukao, T.; Xiong, L. Genetic mechanisms conferring adaptation to submergence and drought in rice: Simple or complex? Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2013, 16, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustroph, A.; Boamfa, E.I.; Laarhoven, L.J.J.; Harren, F.J.M.; Albrecht, G.; Grimm, B. Organ-specific analysis of the anaerobic primary metabolism in rice and wheat seedlings. I: Dark ethanol production is dominated by the shoots. Planta 2006, 225, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Sharif, R.; Xu, X.; Chen, X. Mechanisms of Waterlogging Tolerance in Plants: Research Progress and Prospects. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 627331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Han, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y. Flooding Tolerance of Rice: Regulatory Pathways and Adaptive Mechanisms. Plants 2024, 13, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Guo, X. Stem Characteristic Associated with Lodging Resistance of Rice Changes with Varied Alternating Drought and Flooding Stress. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Gao, Y.; Xu, K.; Sun, X.; Huo, L. The role of ethylene in the regulation of plant response mechanisms to waterlogging stress. Plant Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, A.; Mahmood, A.; Ur-Rehman, H.; Li, C.; Liang, X.; Shao, J.; Negm, S.; Moustafa, M.; Aamer, M.; Hassan, M.U. Plant Adaptation to Flooding Stress under Changing Climate Conditions: Ongoing Breakthroughs and Future Challenges. Plants 2023, 12, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thepbandit, W.; Athinuwat, D. Rhizosphere Microorganisms Supply Availability of Soil Nutrients and Induce Plant Defense. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Colmer, T.D.; Pedersen, O.; Nakazono, M. Regulation of Root Traits for Internal Aeration and Tolerance to Soil Waterlogging-Flooding Stress. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 1118–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Robles, M.J.; Bernal, M.P.; Sánchez-Guerrero, A.; Sevilla, F.; Clemente, R. Major As species, lipid peroxidation and protein carbonylation in rice plants exposed to increasing As(V) concentrations. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Hong, H.; Liu, Y.; Luo, S.; Zou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Z.; et al. Deciphering Seed Deterioration: Molecular Insights and Priming Strategies for Revitalizing Aged Seeds. Plants 2025, 14, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.H.; Zhou, W.X.; Yu, W.Q.; Liu, F.P.; Xu, T.; Su, T. Effects of Flood Stress with Different Sediment Contents on Growth and Yield of Double-Season Rice in the Poyang Lake Plain. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2024, 55, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, X.H.; Shi, F.Z.; Ruan, X.M.; Luo, Y.X.; Wang, Y.L.; Luo, Z.X. Physiological Differences in Response to Waterlogging Stress during Tillering Stage among Different Submergence-Tolerant Genotypes of Rice. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2018, 46, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, V.D.; Harish; Singh, R.K.; Verma, K.K.; Sharma, L.; Quiroz-Figueroa, F.R.; Meena, M.; Gour, V.S.; Minkina, T.; Sushkova, S.; et al. Recent Developments in Enzymatic Antioxidant Defence Mechanism in Plants with Special Reference to Abiotic Stress. Biology 2021, 10, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.; Hertz, D.L.; Morales, M.; Adams, E.J.; Gordon, S.; Tan, C.J.; Staff, N.P.; Kamath, J.; Oh, J.; Shinde, S.; et al. Biological predictors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN): MASCC neurological complications working group overview. Support Care Cancer 2019, 27, 3729–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mattos, E.M.; Binkley, D.; Campoe, O.C.; Alvares, C.A.; Stape, J.L. Variation in canopy structure, leaf area, light interception and light use efficiency among Eucalyptus clones. For. Ecol. Management. 2020, 463, 118038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Keira, M.; Yoon, D.K.; Mae, T.; Ishida, H.; Makino, A.; Ishiyama, K. Photosynthetic Enhancement, Lifespan Extension, and Leaf Area Enlargement in Flag Leaves Increased the Yield of Transgenic Rice Plants Overproducing Rubisco Under Sufficient N Fertilization. Rice 2022, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Mackill, D.J.; Ismail, A.M. Physiological Basis of Tolerance to Complete Submergence in Rice Involves Genetic Factors in Addition to the SUB1 Gene. AoB Plants 2014, 6, plu060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Meng, Y.; Chen, P.; Cao, K. Submergence Stress Reduces the Ability of Rice to Regulate Recovery after Disaster. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Chen, K.C.; Cheng, T.S.; Lee, C.; Lin, S.H.; Tung, C.W. Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis in diverse rice varieties reveals the positive correlation between the seedlings salt tolerance and photosynthetic efficiency. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Gu, X.; Sun, L.; Yang, G.; Zhou, L.; Guo, W. Dynamic change in rice leaf area index and spectral response under flooding stress. Paddy Water Environ. 2020, 18, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaduri, D.; Chakraborty, K.; Nayak, A.K.; Mohammad, S.; Tripathi, R.; Behera, R.; Singh, S.; Srivastava, A.K. Alteration in plant spacing improves submergence tolerance in Sub1 and non-Sub1 rice (cv. IR64) by better light interception and effective carbohydrate utilization under stress. Funct. Plant Biol. 2020, 47, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Ma, M.; Chen, J.; Wu, S. Plant Morphological, Physiological and anatomical adaption to flooding stress and the underlying molecular mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Wu, M.; Ye, M.; Zhang, Z. The formation of rice tillers and factors influencing it. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.M.; Johnson, D.E.; Ella, E.S.; Vergara, G.V.; Baltazar, A.M. Adaptation to flooding during emergence and seedling growth in rice and weeds, and implications for crop establishment. AoB Plants 2012, 2012, pls019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhou, J.; Lin, J.; Chen, M.; Liu, F.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, R.; Xiao, L.; Liu, Y. Perception of strigolactones and the coordinated phytohormonal regulation on rice (Oryza sativa) tillering is affected by endogenous ascorbic acid. Funct. Plant Biol. 2024, 51, FP23148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Feng, X.; Ding, H.; Lin, D.; Lan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Akbar, S.; Shi, H.; Li, Z.; Gao, R.; et al. Identification and functional analysis of strigolactone pathway genes regulating tillering traits in sugarcane. Plant Cell Physiol. 2025, 66, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Friml, J. Tale of cAMP as a second messenger in auxin signaling and beyond. New Phytol. 2023, 240, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, N.; Hu, C.; Wan, L.; Hu, Q.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, C. Strigolactones improve plant growth, photosynthesis, and alleviate oxidative stress under salinity in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) by regulating gene expression. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.; Munné-Bosch, S. Hormonal impact on photosynthesis and photoprotection in plants. Plant Physiol. 2021, 185, 1500–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, J.; Gao, J.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Q. Nitrogen fertilization application strategies improve yield of the rice cultivars with different yield types by regulating phytohormones. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, H.E.; Park, E.; Jung, M. Age-Related difference in the relationship between age stereotypes and health behavior in midlife koreans. Innov. Aging 2020, 4, 447–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Qi, S.; Wang, Y.; Jia, J. Integration of Nitrate and Abscisic Acid Signaling in Plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2024, 75, 3259–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, X.; Deng, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, C.; Zhao, L. Study on the mechanism of slow-release fertilizer and nitrogen fertilizer on the senescence characteristics of quinoa leaves. Agronomy 2024, 14, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, S.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Zheng, S.; Shen, X.; Wang, C.; Yang, Z.; Liu, D. Effects of supplemental nitrogen application on physiological characteristics, dry matter and nitrogen accumulation of winter rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) under waterlogging stress. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, L.; Song, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, Y. Effects of Water and Nitrogen Management on Root Morphology, Nitrogen Metabolism Enzymes, and Yield of Rice under Drip Irrigation. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, A.; Asano, K.; Sugiura, D.; Kano-Nakata, M.; Ehara, H. Waterlogged conditions influence the nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and sugar distribution in sago palm (Metroxylon sagu Rottb.) at seedling stages. Plants 2022, 11, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Kim, M.; Geem, K.R.; Sung, J. Improving nutrient use efficiency of rice under alternative wetting and drying irrigation combined with slow-release nitrogen fertilization. Plants 2025, 14, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, S.; Nigro, D.; Lasorella, C.; Marcotuli, I.; Gadaleta, A.; de Pinto, M.C. The role of glutamine synthetase (gs) and glutamate synthase (gogat) in the improvement of nitrogen use efficiency in cereals. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikanth, B.; Subrahmanyam, D.; Rao, D.S.; Reddy, S.N.; Supriya, K.; Rao, P.R.; Surekha, K.; Sundaram, R.M.; Neeraja, C.N. Promising physiological traits associated with nitrogen use efficiency in rice under reduced n application. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1268739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, S.S.; Siddiqi, T.O.; Kumar, D.; Ahmad, A.; Bhat, M.A.; Wani, S.A.; Rather, A.H. Physio-biochemical, agronomical, and gene expression analysis reveals different responsive approach to low nitrogen in contrasting rice cultivars for nitrogen use efficiency. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 1575–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Vila, M.; dos Santos Vianna, M.; Harrison, M.T.; Bindi, M.; Ceglar, A.; Donat, M.G.; Dorigo, W.; Eklundh, L.; Gentine, P.; Kerr, G.; et al. Gaps and strategies for accurate simulation of waterlogging impacts on crop productivity. Nat. Food 2025, 6, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashikari, M.; Nagai, K.; Bailey-Serres, J. Surviving Floods: Escape and quiescence strategies of rice coping with submergence. Plant Physiol. 2025, 197, kiaf029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, B.; Zhou, X.; Lu, H.; Li, H. Effects of Waterlogging on rice growth at jointing–booting stage. Water 2024, 16, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, D.; Barik, J.; Sarkar, R.K. Recent advances of genetic resources, genes and genetic approaches for flooding tolerance in rice. Curr. Genom. 2021, 22, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toojinda, T.; Siangliw, M.; Tragoonrung, S.; Vanavichit, A. Molecular genetics of submergence tolerance in rice: QTL analysis of key traits. Ann. Bot. 2003, 91, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septiningsih, E.M.; Pamplona, A.M.; Sanchez, D.L.; Neeraja, C.N.; Vergara, G.V.; Heuer, S.; Ismail, A.M.; Mackill, D.J. Development of Submergence-Tolerant Rice Cultivars: The Sub1 Locus and Beyond. Ann. Bot. 2009, 103, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Singh, Y.; Mahato, A.K.; Jayaswal, P.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, R.; Yadav, N.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, R.; et al. Allelic Sequence Variation in the Sub1A, Sub1B and Sub1C Genes Among Diverse Rice Cultivars and Its Association with Submergence Tolerance. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukao, T.; Bailey-Serres, J. Submergence Tolerance Conferred by Sub1A Is Mediated by SLR1 and SLRL1 Restriction of Gibberellin Responses in Rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16814–16819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Geng, S.; Zhang, X. A Review of Soil Waterlogging Impacts, Mechanisms, and Adaptive Strategies. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1545912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukao, T.; Yeung, E.; Bailey-Serres, J. The Submergence Tolerance Regulator SUB1A Mediates Crosstalk Between Submergence and Drought Tolerance in Rice. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 412–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, X.; Jin, S.; Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, X. Overexpression of Rice NAC Gene SNAC1 Improves Drought and Salt Tolerance by Enhancing Root Development and Reducing Transpiration Rate in Transgenic Cotton. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Khan, M.I.R.; Dixit, S.; Cruz, P.C.S.; Septiningsih, E.M.; Ismail, A.M. Growth, productivity and grain quality of AG1 and AG2 QTLs introgression lines under flooding in direct-seeded rice system. Field Crops Res. 2020, 248, 107713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, Y.; Nagai, K.; Furukawa, S.; Song, X.J.; Kawano, R.; Sakakibara, H.; Wu, J.; Matsumoto, T.; Yoshimura, A.; Kitano, H.; et al. The ethylene response factors SNORKEL1 and SNORKEL2 allow rice to adapt to deep water. Nature 2009, 460, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Feng, Q.; Lu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, A.; Tian, Q.; Zhan, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, T.; et al. Pan-genome analysis highlights the extent of genomic variation in cultivated and wild rice. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Xu, X.; Fukao, T.; Canalas, P.; Maghirang-Rodriguez, R.; Heuer, S.; Mackill, D.J. Sub1A is an ethylene responsive-factor-like gene that confers submergence tolerance to rice. Nature 2006, 442, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroha, T.; Nagai, K.; Gamuyao, R.; Wang, D.R.; Furuta, T.; Nakamori, M.; Kitaoka, T.; Adachi, K.; Minami, A.; Mori, Y.; et al. Ethylene-gibberellin signaling underlies adaptation of rice to periodic flooding. Science 2018, 361, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuanar, S.R.; Sarkar, R.K.; Panigrahi, R.; Mohapatra, P.K. Introgression of SUB1 Aggravates the Susceptibility of the Popular Rice Cultivars Swarna and Savitri to Stagnant Flooding. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, D.; Sarkar, R.K. Role of Non-Structural Carbohydrate and Its Catabolism Associated with Sub1 QTL in Rice Subjected to Complete Submergence. Exp. Agric. 2012, 48, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhu, P.; Liu, Y.; Kong, D.; Wang, J.; Luo, L.; Yu, X. Molecular Marker-Assisted Selection of a New Water-Saving and Drought-Resistant Rice (WDR) Restoration Line, Hanhui 8200, for Enhanced Resistance to Rice Blast. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Tong, J.; Xu, R.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Nadeem, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, F.; et al. Identification of Stable Quantitative Trait Loci Underlying Waterlogging Tolerance Post-Anthesis in Common Wheat (Triticum aestivum). Crop J. 2023, 11, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, N.; Choudhary, S.; Naaz, N.; Sharma, N.; Laskar, R.A. Recent Advancements in Molecular Marker-Assisted Selection and Applications in Plant Breeding Programmes. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escamilla, D.M.; Li, D.; Negus, K.L.; Kappelmann, K.L.; Kusmec, A.; Vanous, A.E.; Schnable, P.S.; Li, X.; Yu, J. Genomic Selection: Essence, Applications, and Prospects. Plant Genome 2025, 18, e70053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.C.P.; Latif, M.A.; Rafii, M.Y.; Ismail, M.R.; Puteh, A. Advances to Improve the Eating and Cooking Qualities of Rice by Marker-Assisted Breeding. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2014, 36, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Guo, Q.; Dai, Y.; Gong, L.; Shi, H. Effects of Sediment Content, Flooding, and Drainage Process on Rice Growth and Leaf Physiology of Early Rice During Heading–Flowering Stage. Agronomy 2025, 15, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, P.; Lal, B.; Tripathi, R.; Baig, M.J.; Shahid, M.; Maharana, S.; Bihari, P.; Nayak, A.K. Impact of Seedling Age and Nitrogen Application on Submergence Tolerance of Sub1 and Non-Sub1 Cultivars of Rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Plant Growth Regul. 2017, 36, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.D.; Sharma, A.R.; Panda, M.M. Flood Tolerance of Rice Grown under Intermediate Deepwater Conditions (15–50 cm) as Affected by Phosphorus Fertilization. J. Agric. Sci. 1991, 117, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Lu, H.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhi, W.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Ren, Z.; Shi, Y.; Ji, Z.; et al. Nitrogen Management Enhanced Plant Growth, Antioxidant Ability, and Grain Yield of Rice under Salinity Stress. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Bhakta, N.; Srivastava, A.K.; Mishra, J.S.; Kumar, V.; Kumara, B.H.; Bhatt, B.P.; Singh, S. Physiological Mechanism and Nutrient Management Strategies for Flood Tolerance in Rice Grown in Lowland Flood Prone Ecosystem. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 21, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Miao, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Guo, J.; Shao, R.; Yang, Q. L-Arginine Alleviates the Reduction in Photosynthesis and Antioxidant Activity Induced by Drought Stress in Maize Seedlings. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janah, I.; Elhasnaoui, A.; Laouane, R.B.; Ait-El-Mokhtar, M.; Anli, M. Exploring Seed Priming as a Strategy for Enhancing Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Cereal Crops. Stresses 2025, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, A.; Xue, Z.; Tazein, S.; Arshad, A.; Zhu, Z.H.; Chen, Y.P.; Hong, Y.; Zhu, X.T.; Zhou, K.J. CRISPR-Cas9-based Genetic Engineering for Crop Improvement under Drought Stress. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 5814–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marthandan, V.; Geetha, R.; Kumutha, K.; Renganathan, V.G.; Karthikeyan, A.; Ramalingam, J. Seed Priming: A Feasible Strategy to Enhance Drought Tolerance in Crop Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantoja-Benavides, A.D.; Garces-Varon, G.; Restrepo-Díaz, H. Foliar Growth Regulator Sprays Induced Tolerance to Combined Heat Stress by Enhancing Physiological and Biochemical Responses in Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 702892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, H.J.; Hu, W.C.; Jia, Y.; Wang, X.P.; Tian, X.F.; Yu, M.F.; Zhao, H.W. Effect of Exogenous Salicylic Acid, Proline and γ-Aminobutyric Acid on Yield of Rice under Salt Stress. Acta Agron. Sinica 2017, 43, 1677–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bu, W.; Ahmad, I.; Fei, H.; Ibrahim, M.E.H.; Xu, Y.; Meng, T.; Zuo, Q.; Lei, T.; Zhou, G.; Zhu, G. Current Status of Studying on Physiological Mechanisms of Rice Response to Flooding Stress and Flooding-Resistant Cultivation Regulation. Plants 2025, 14, 2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182863
Bu W, Ahmad I, Fei H, Ibrahim MEH, Xu Y, Meng T, Zuo Q, Lei T, Zhou G, Zhu G. Current Status of Studying on Physiological Mechanisms of Rice Response to Flooding Stress and Flooding-Resistant Cultivation Regulation. Plants. 2025; 14(18):2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182863
Chicago/Turabian StyleBu, Weicheng, Irshad Ahmad, Han Fei, Muhi Eldeen Hussien Ibrahim, Yunji Xu, Tianyao Meng, Qingsong Zuo, Tianjie Lei, Guisheng Zhou, and Guanglong Zhu. 2025. "Current Status of Studying on Physiological Mechanisms of Rice Response to Flooding Stress and Flooding-Resistant Cultivation Regulation" Plants 14, no. 18: 2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182863
APA StyleBu, W., Ahmad, I., Fei, H., Ibrahim, M. E. H., Xu, Y., Meng, T., Zuo, Q., Lei, T., Zhou, G., & Zhu, G. (2025). Current Status of Studying on Physiological Mechanisms of Rice Response to Flooding Stress and Flooding-Resistant Cultivation Regulation. Plants, 14(18), 2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182863









