Functional Changes of Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soils Under the Decline of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Nutrient Content in Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soils of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantations at Different Stand Ages
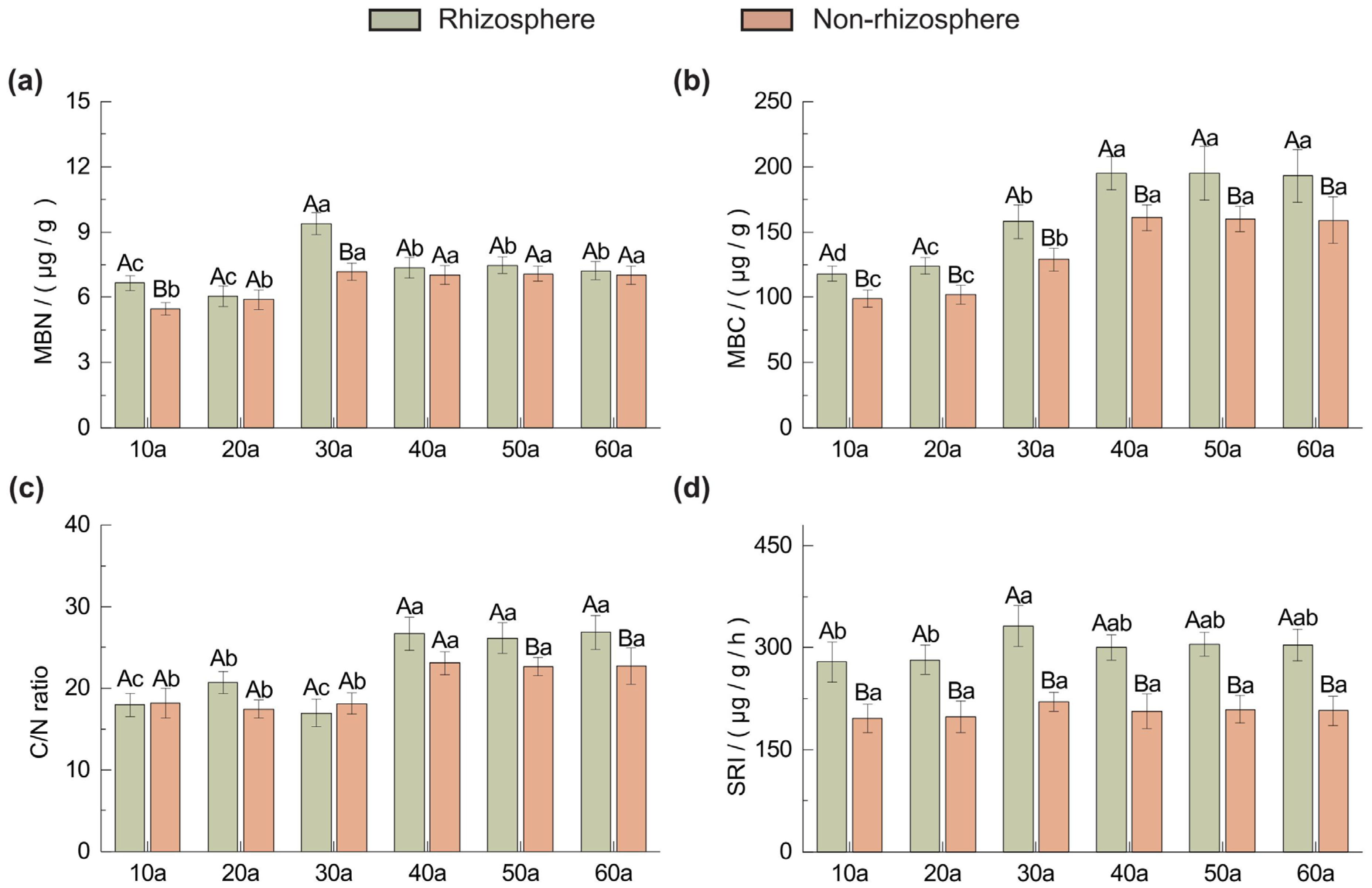
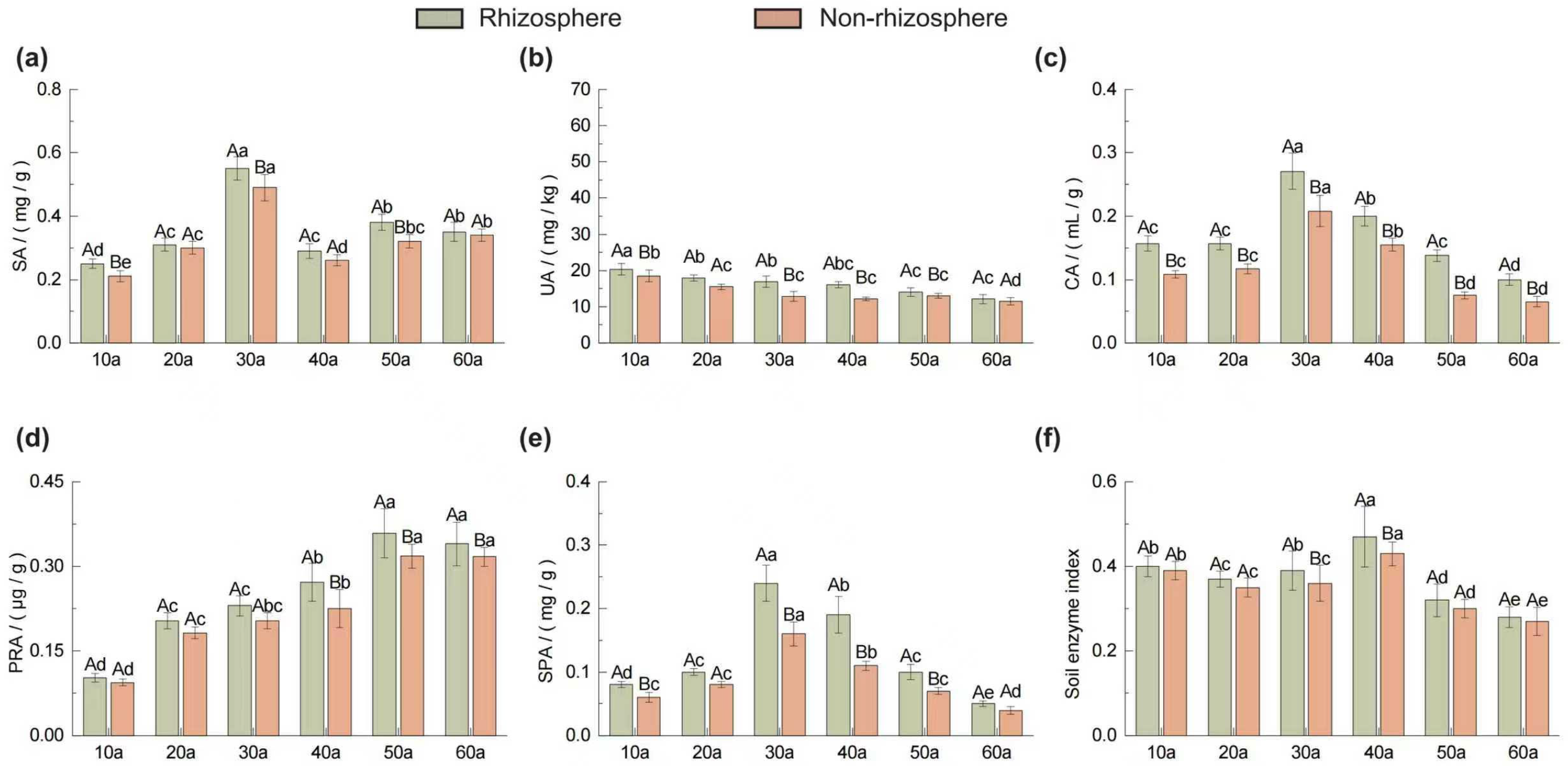
2.2. Variations in Microbial Biomass and Enzyme Activities in Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soils Across Stand Ages
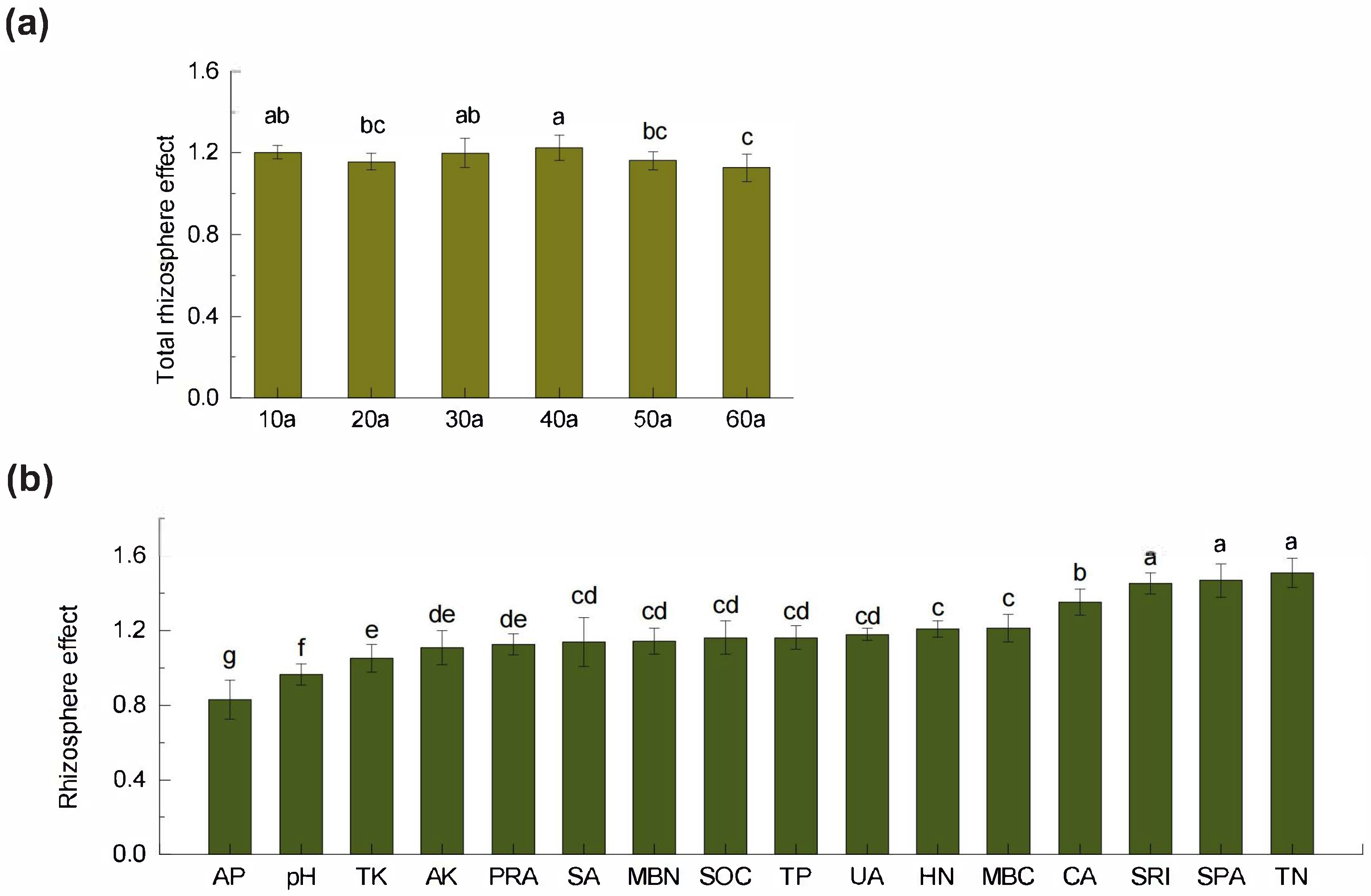
2.3. Dynamics of Rhizosphere Effects Across Stand Ages
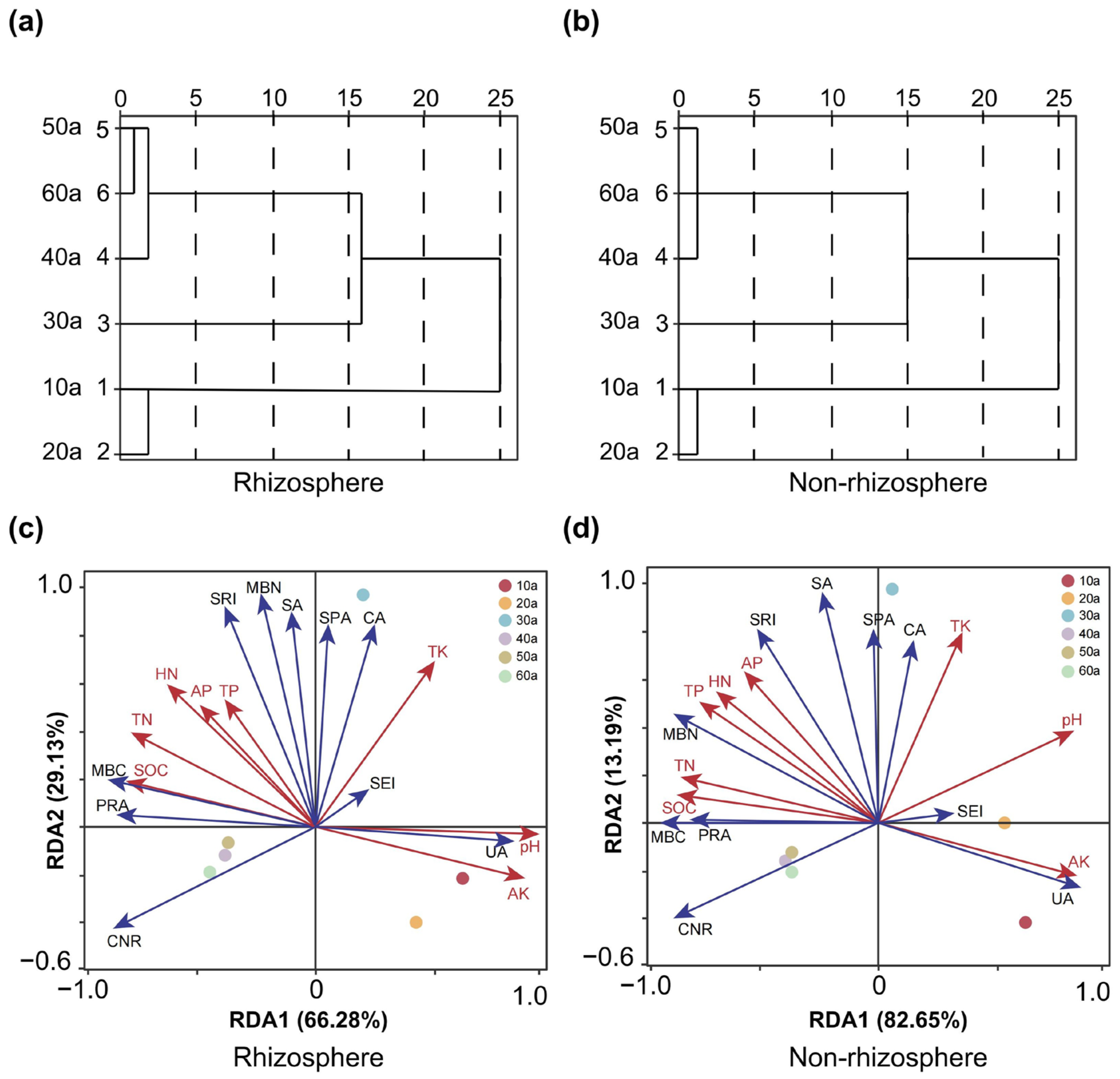
2.4. Linkages Between Soil Nutrients and Microbial Indicators Revealed by RDA and Clustering
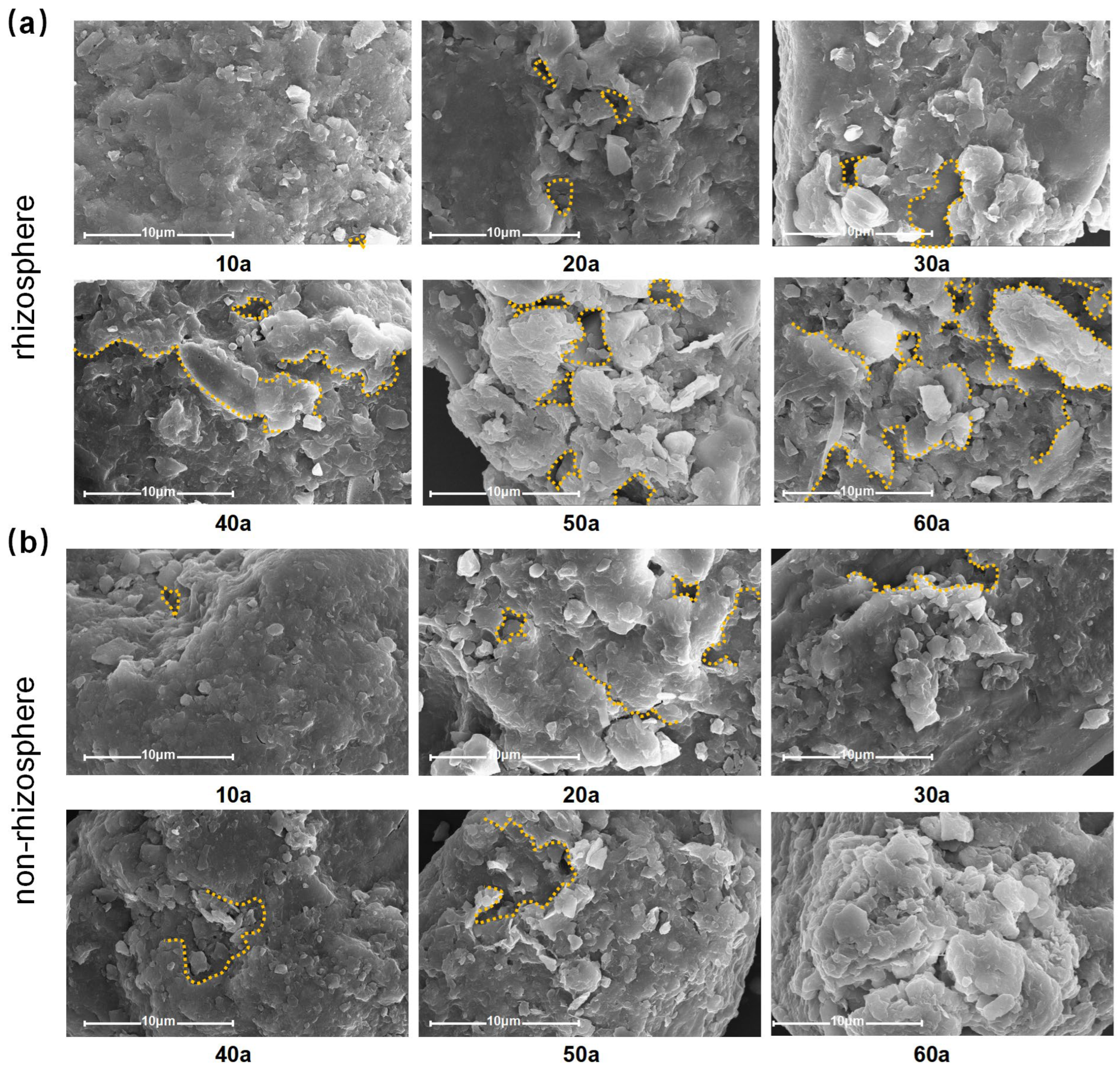
2.5. Characteristics of Soil Particle Morphology Changes with Tree Age
3. Discussion
3.1. Rhizosphere Differences in Soil Nutrients Across Different Stand Ages
3.2. Soil Microbial Biomass and Soil Respiration
3.3. Soil Enzyme Activities
3.4. Soil Particle Morphology
4. Materials and Methods
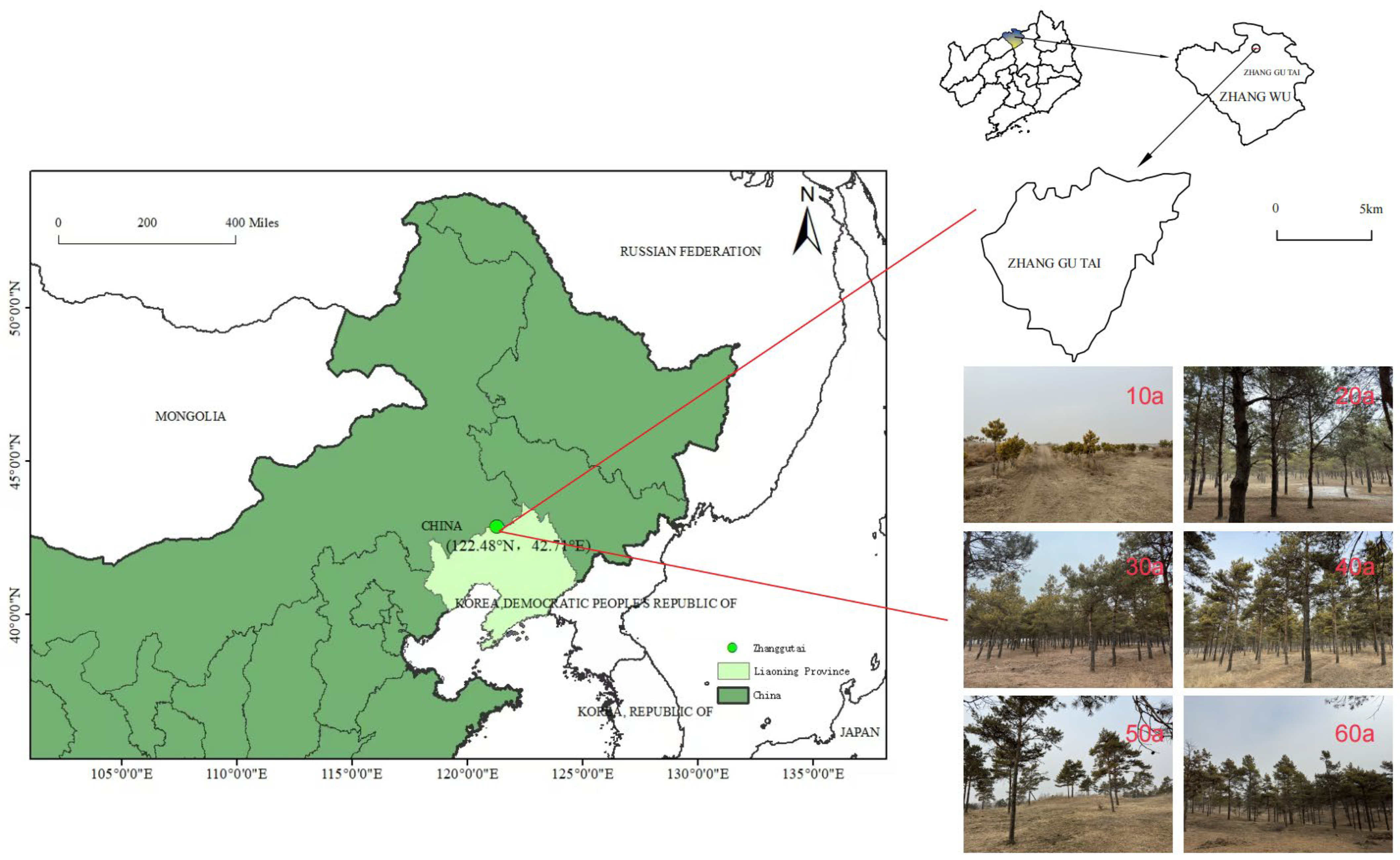
4.1. Study Area
4.2. Plot Selection and Sample Collection
4.3. Soil Properties and Enzyme Activity
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, F.; Letort, V.; Lu, Q.; Bai, X.; Guo, Y.; De Reffye, P.; Li, B. A Functional and Structural Mongolian Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica) Model Integrating Architecture, Biomass and Effects of Precipitation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halifu, S.; Deng, X.; Song, X.; An, Y.; Song, R. Effects of Sphaeropsis Blight on Rhizosphere Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Soil Physicochemical Properties of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica in Zhanggutai, China. Forests 2019, 10, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lei, Z.; Zhou, F.; Han, Y.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Y. Impact of Climate Factors on Height Growth of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Han, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Li, M.; Liu, C. Key Strategies Underlying the Adaptation of Mongolian Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica) in Sandy Land under Climate Change: A Review. Forests 2022, 13, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Yao, Q.; Cooper, D.J.; Han, S.; Wang, X. Response of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica to Water Change and the Reconstruction of Drought History for the Past 260 Years in Northeast China. Clim. Past Discuss. 2018, 14, 1213–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Wang, S.; Chen, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Y.; Hu, M. Decreasing Productivity of Pine Forests on the Southern Edge of the Mongolian Plateau as Indicated by Tree Rings. J. For. Res. 2024, 35, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Tan, H.; Kang, H.; Xu, M. Comparison of Foliar Nutrient Concentrations between Natural and Artificial Forests of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica on Sandy Land, China. J. For. Res. 2006, 17, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fu, S.; Gao, H.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; You, C.; Liu, S.; Tan, B.; et al. Linking Fungal Community Structure with Soil Nitrogen Dynamics Following Forest Conversion in a Subalpine Forest in China. Geoderma 2023, 433, 116448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Six, J. Soil Structure and Microbiome Functions in Agroecosystems. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 4, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Deng, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, S.; Richter, A.; Shibistova, O.; Guggenberger, G.; et al. C:N:P Stoichiometry Regulates Soil Organic Carbon Mineralization and Concomitant Shifts in Microbial Community Composition in Paddy Soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2020, 56, 1093–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Wu, J. Soil pH and Potassium Drive Root Rot in Torreya Grandis via Direct Modulation and Microbial Taxa-Mediated Pathways. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 228, 120940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Huang, R.; Guan, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, Z.; Fang, H.; Zou, X.; Li, J.; Liu, P. Litter, Root, and Mycorrhiza Manipulations and Seasonal Effects on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Communities in a Subtropical Coniferous and Broad-Leaved Mixed Forest. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 204, 105721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, W.; Hu, W.; Hu, J.; Hu, M. Changes in Litter Traits Induced by Vegetation Restoration Accelerate Litter Decomposition in Robinia Pseudoacacia Plantations. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, X.; Qi, J.; Peng, Z.; Chen, B.; Pan, H.; Liang, C.; Liu, J.; et al. Agricultural Tillage Practice and Rhizosphere Selection Interactively Drive the Improvement of Soybean Plant Biomass. Plant Cell Environ. 2023, 46, 3542–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, D.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Gao, M. Changes in Rhizosphere Phosphorus Fractions and Phosphate-Mineralizing Microbial Populations in Acid Soil as Influenced by Organic Acid Exudation. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 225, 105543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, O.E.; Gios, E.; Close, M.; Weaver, L.; Daughney, C.; Handley, K.M. Nitrogen Cycling and Microbial Cooperation in the Terrestrial Subsurface. ISME J. 2022, 16, 2561–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iven, H.; Walker, T.W.N.; Anthony, M. Biotic Interactions in Soil Are Underestimated Drivers of Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Coventry, D.R.; Gupta, V.V.S.R.; Fuentes, D.; Merchant, A.; Kaiser, B.N.; Li, J.; Wei, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. The Preceding Root System Drives the Composition and Function of the Rhizosphere Microbiome. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Gube, M.; Holz, M.; Song, B.; Shan, I.; Shi, L.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Dippold, M.A.; Pausch, J. Ectomycorrhizal and Non-mycorrhizal Rhizosphere Fungi Increase Root-derived C Input to Soil and Modify Enzyme Activities: A 14C Pulse Labelling of Picea Abies Seedlings. Plant Cell Environ. 2022, 45, 3122–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Tsujii, Y.; Xu, T.; Han, M.; Li, R.; Han, Y.; Gan, D.; Zhu, B. Species of Fast Bulk-Soil Nutrient Cycling Have Lower Rhizosphere Effects: A Nutrient Spectrum of Rhizosphere Effects. Ecology 2023, 104, e3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Bi, H.; Wang, N.; Liu, Z.; Hou, G.; Huang, J.; Song, Y. Does Increasing Forest Age Lead to Greater Trade-Offs in Ecosystem Services? A Study of a Robinia Pseudoacacia Artificial Forest on the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freschet, G.T.; Aerts, R.; Cornelissen, J.H.C. A Plant Economics Spectrum of Litter Decomposability. Funct. Ecol. 2012, 26, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyaschenko, J.; Ovaskainen, O.; Ekblad, A.; Hagenbo, A.; Karltun, E.; Clemmensen, K.E.; Lindahl, B.D. Soil Fertility in Boreal Forest Relates to Root-driven Nitrogen Retention and Carbon Sequestration in the Mor Layer. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 1492–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegretta, I.; Legrand, S.; Alfeld, M.; Gattullo, C.E.; Porfido, C.; Spagnuolo, M.; Janssens, K.; Terzano, R. SEM-EDX Hyperspectral Data Analysis for the Study of Soil Aggregates. Geoderma 2022, 406, 115540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Han, H.; Shi, Z.; Yang, X. Biomass Accumulation and Carbon Sequestration in an Age-Sequence of Mongolian Pine Plantations in Horqin Sandy Land, China. Forests 2019, 10, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; He, H.; Cheng, W.; Bai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. Factors Controlling Soil Organic Carbon Stability along a Temperate Forest Altitudinal Gradient. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Heal, K.V.; Liu, A.; Jarvis, P.G. Nutrient Cycling and Distribution in Different-Aged Plantations of Chinese Fir in Southern China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 243, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, Q.-Y.; Mao, B.; Zeng, D.-H. Understory Vegetation Interacts with Nitrogen Addition to Affect Soil Phosphorus Transformations in a Nutrient-Poor Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 507, 120026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, R. Strategies for Improving Potassium Use Efficiency in Plants. Mol. Cells 2014, 37, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; He, G.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, S.; Yang, X.; Yang, L.; Ji, L. Nitrogen Enrichment Stimulates Nutrient Cycling Genes of Rhizosphere Soil Bacteria in the Phoebe Bournei Young Plantations. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Cui, Z.; Cao, C. Sand-Fixation Plantation Type Affects Soil Phosphorus Transformation Microbial Community in a Revegetation Area of Horqin Sandy Land, Northeast China. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 180, 106644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staszel-Szlachta, K.; Lasota, J.; Szlachta, A.; Błońska, E. The Impact of Root Systems and Their Exudates in Different Tree Species on Soil Properties and Microorganisms in a Temperate Forest Ecosystem. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Masto, R.E.; Cerdà, A.; Ram, L.C. Rhizosphere Soil Indicators for Carbon Sequestration in a Reclaimed Coal Mine Spoil. Catena 2016, 141, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.R.; Gregorich, E.G.; Angers, D.A.; Beare, M.H.; Sparling, G.P.; Wardle, D.A.; Voroney, R.P. Interpretation of Microbial Biomass Measurements for Soil Quality Assessment in Humid Temperate Regions. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1999, 79, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, X.; Weng, B.; Su, J.; Nie, S.; Gilbert, J.A.; Zhu, Y.-G. The Phenological Stage of Rice Growth Determines Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidation Activity in Rhizosphere Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 100, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, K.R.; Mooney, S.J.; Bennett, M.J.; Crout, N.M.J.; Roose, T.; Tracy, S.R. Assessing the Influence of the Rhizosphere on Soil Hydraulic Properties Using X-Ray Computed Tomography and Numerical Modelling. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 2305–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. Effect of Changes in Throughfall on Soil Respiration in Global Forest Ecosystems: A Meta-Analysis. Forests 2023, 14, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Jin, G. Variability of Soil Respiration at Different Spatial Scales in Temperate Forests. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.S.; Mack, R.; Castillo, X.; Kaiser, M.; Joergensen, R.G. Microbial Biomass, Fungal and Bacterial Residues, and Their Relationships to the Soil Organic Matter C/N/P/S Ratios. Geoderma 2016, 271, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, M.S.; Rousk, J. Considering Fungal:Bacterial Dominance in Soils—Methods, Controls, and Ecosystem Implications. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.H.; Wang, C.K. Soil Resources and Climate Jointly Drive Variations in Microbial Biomass Carbon and Nitrogen in China’s Forest Ecosystems. Biogeosciences Discuss. 2015, 12, 6751–6760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousk, J.; Brookes, P.C.; Bååth, E. The Microbial PLFA Composition as Affected by pH in an Arable Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Zhuang, S.; Gao, J.; Tang, L.; Harindintwali, J.D.; Wang, F. Aeration Increases Soil Bacterial Diversity and Nutrient Transformation under Mulching-Induced Hypoxic Conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 153017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeler, E.; Gerber, H. Short-Term Assay of Soil Urease Activity Using Colorimetric Determination of Ammonium. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1988, 6, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, G.; Xue, S.; Song, Z. Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Activity under Different Vegetation Types on the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 2011, 161, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Vitousek, P.M. Responses of Extracellular Enzymes to Simple and Complex Nutrient Inputs. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Razavi, B.S. Rhizosphere Size and Shape: Temporal Dynamics and Spatial Stationarity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, P.G.; Miller, A.J.; Hirsch, P.R. Are Root Exudates More Important than Other Sources of Rhizodeposits in Structuring Rhizosphere Bacterial Communities?: Root Exudates and Rhizosphere Bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 72, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Hodge, A.; Kuzyakov, Y. Plant and Mycorrhizal Regulation of Rhizodeposition. New Phytol. 2004, 163, 459–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Yun, W.; Luo, B.; Chai, R.; Zhang, C.; Xiang, X.; Su, X. Changes in Phosphorus Mobilization and Community Assembly of Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Rice Rhizosphere Under Phosphate Deficiency. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 953340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Jarvie, S.; Yan, Y.; Han, P.; Liu, T.; Guo, K.; Ren, L.; Yue, K.; Wu, H.; et al. Ecosystem Restoration through Aerial Seeding: Interacting Plant–Soil Microbiome Effects on Soil Multifunctionality. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 5334–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingorance, M.D.; Peña, A. A Methodological Approach to Measure Soil Respiration. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 169, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamer Vestlund, A.; Al-Ashaab, R.; Tyrrel, S.F.; Longhurst, P.J.; Pollard, S.J.T.; Drew, G.H. Morphological Classification of Bioaerosols from Composting Using Scanning Electron Microscopy. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, P.; Falsone, G.; Wilson, C.; Cavani, L.; Ciavatta, C.; Marzadori, C. New Insights into Organic Carbon Stabilization in Soil Macroaggregates: An In Situ Study by Optical Microscopy and SEM-EDS Technique. Geoderma 2021, 397, 115101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, K.; Wang, W.; Ren, G.; Khan, A.; Feng, Y.; Yang, G. Changes in Soil Enzymes, Soil Properties, and Maize Crop Productivity under Wheat Straw Mulching in Guanzhong, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 182, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Lauber, C.L.; Weintraub, M.N.; Ahmed, B.; Allison, S.D.; Crenshaw, C.; Contosta, A.R.; Cusack, D.; Frey, S.; Gallo, M.E.; et al. Stoichiometry of Soil Enzyme Activity at Global Scale. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Fu, S.; Yan, S.; Ren, C.; Wu, S.; Deng, J.; Li, B.; Han, X.; Yang, G. Responses of Plant Community to the Linkages in Plant-Soil C:N:P Stoichiometry during Secondary Succession of Abandoned Farmlands, China. J. Arid. Land 2020, 12, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Sun, H.; Yang, W.; Gao, M.; Zhao, X.; Xu, H. Harnessing Vitamin C Industrial Byproducts for Sustainable Agriculture: Improved Soil Quality and Maize Production in Degraded Semi-Arid Farmlands. Agronomy 2025, 15, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Site No. | Stand Age/a | Mean Canopy Height/m | Mean Diameter/cm | Average Crown width (East, West)/m | Average Crown Width (South, North)/m | Soil Bulk Density/(g·cm−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10a | 3.28 | 7.50 | 2.59 | 2.42 | 1.67 |
| 2 | 20a | 7.80 | 13.31 | 3.60 | 4.21 | 1.64 |
| 3 | 30a | 9.25 | 16.69 | 4.01 | 4.10 | 1.60 |
| 4 | 40a | 11.27 | 20.92 | 4.30 | 4.69 | 1.56 |
| 5 | 50a | 11.01 | 19.61 | 4.59 | 4.72 | 1.60 |
| 6 | 60a | 13.04 | 20.59 | 4.62 | 4.92 | 1.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, T.; Zeng, Z.; Cheng, H.; Bao, S.; Xiao, L.; Liu, T.; Zhao, X. Functional Changes of Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soils Under the Decline of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantations. Plants 2025, 14, 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182819
Kong T, Zeng Z, Cheng H, Bao S, Xiao L, Liu T, Zhao X. Functional Changes of Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soils Under the Decline of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantations. Plants. 2025; 14(18):2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182819
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Tao, Zeyu Zeng, Haotian Cheng, Sinuo Bao, Lin Xiao, Tong Liu, and Xiaoliang Zhao. 2025. "Functional Changes of Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soils Under the Decline of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantations" Plants 14, no. 18: 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182819
APA StyleKong, T., Zeng, Z., Cheng, H., Bao, S., Xiao, L., Liu, T., & Zhao, X. (2025). Functional Changes of Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soils Under the Decline of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantations. Plants, 14(18), 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182819





