Corn Stover Biochar Amendment Enhances Nitrogen and Phosphorus Transformations, Microbial Community Diversity, and Enzyme Activities in Agricultural Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Biochar Amendment on Vertical Transport of Soil-Available P, Nitrate N, and Ammonium N
2.2. Effect of Biochar Amendment on Soil-Available P, Nitrate N, and Ammonium N Content
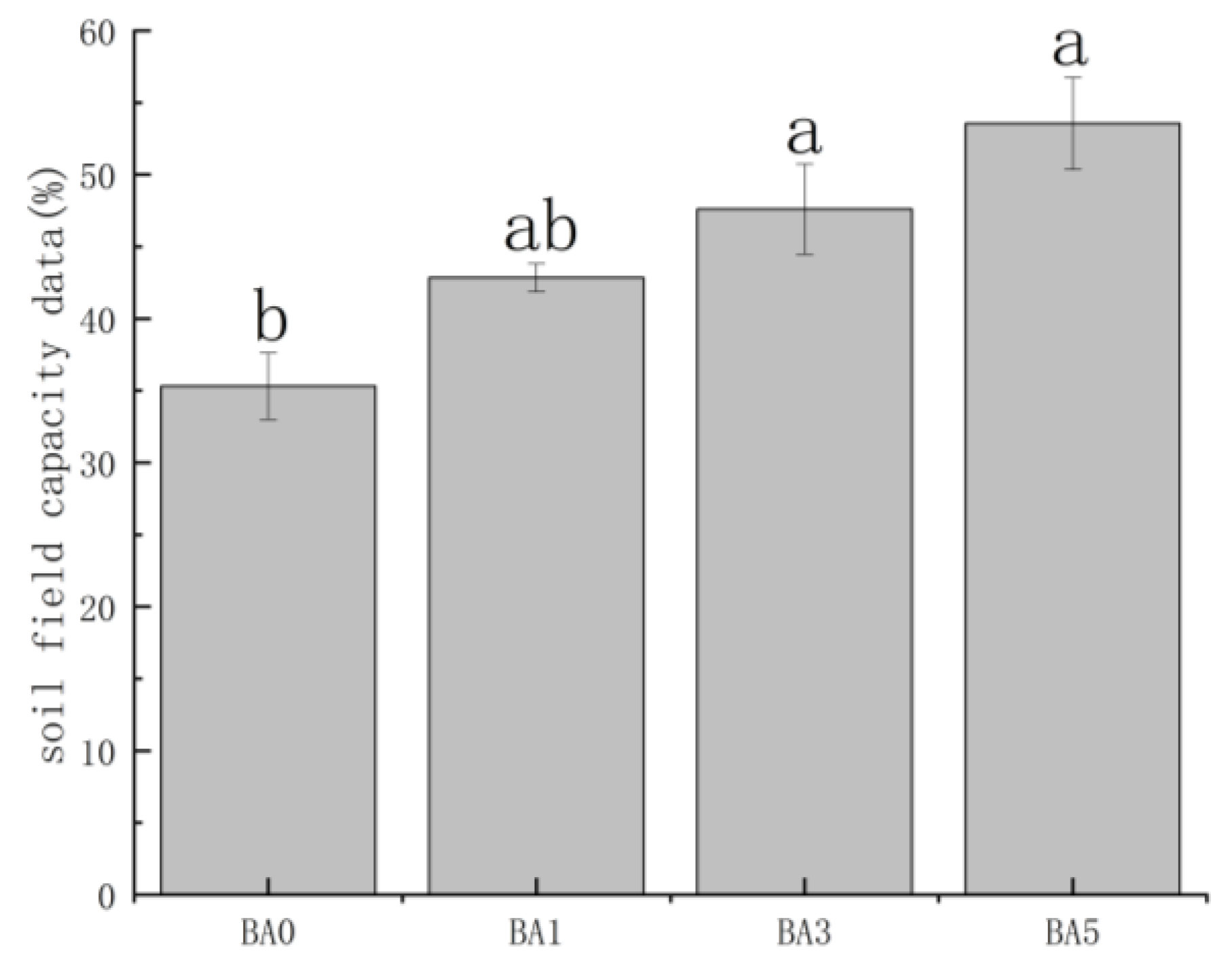
2.3. Effects of Biochar Amendment on Soil Field Capacity
2.4. Effects of Biochar Amendment on Microbial Community Composition
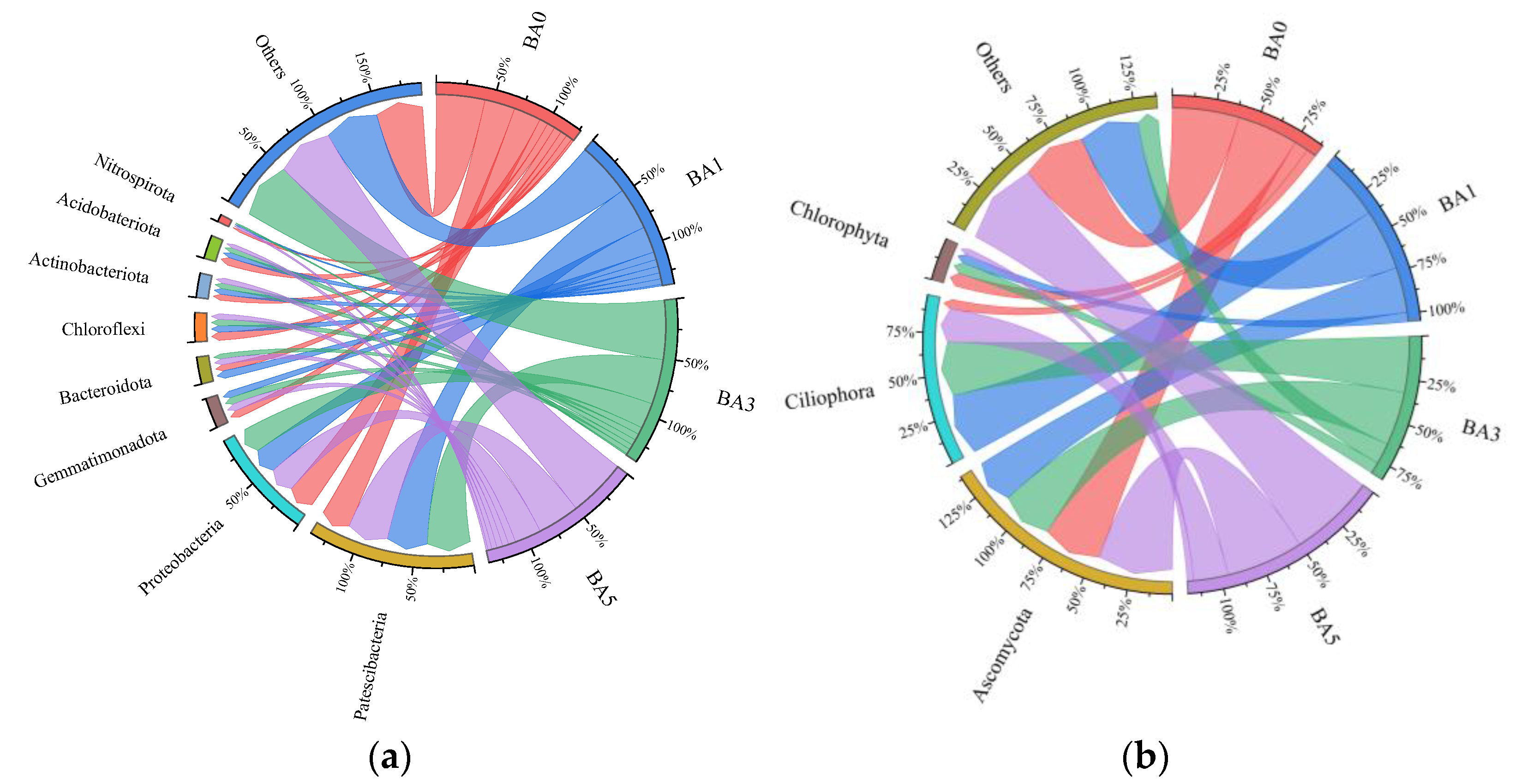
2.4.1. Effect of Biochar Amendment on the Relative Abundance Composition of Microorganisms
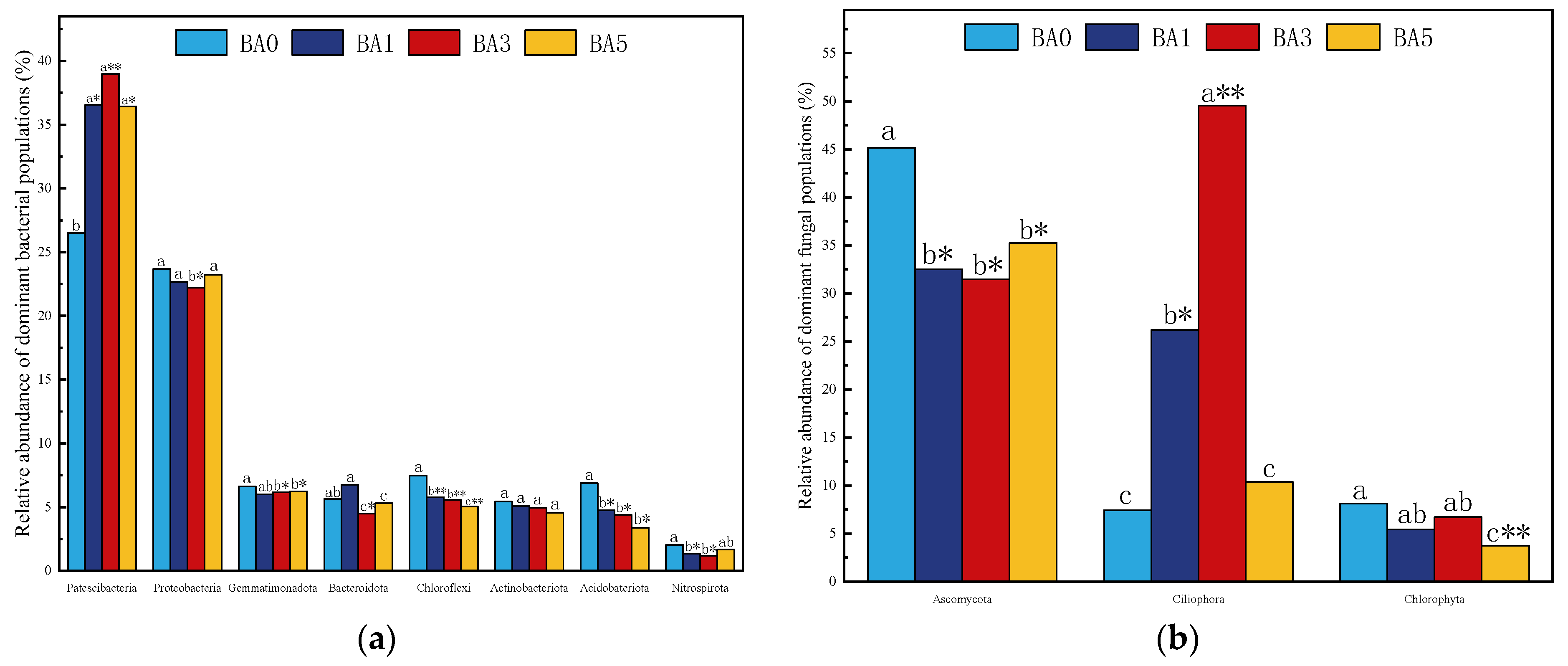
2.4.2. Effect of Biochar Amendment on Dominant Microbial Populations
2.5. Effect of Biochar Amendment on Enzyme Activity
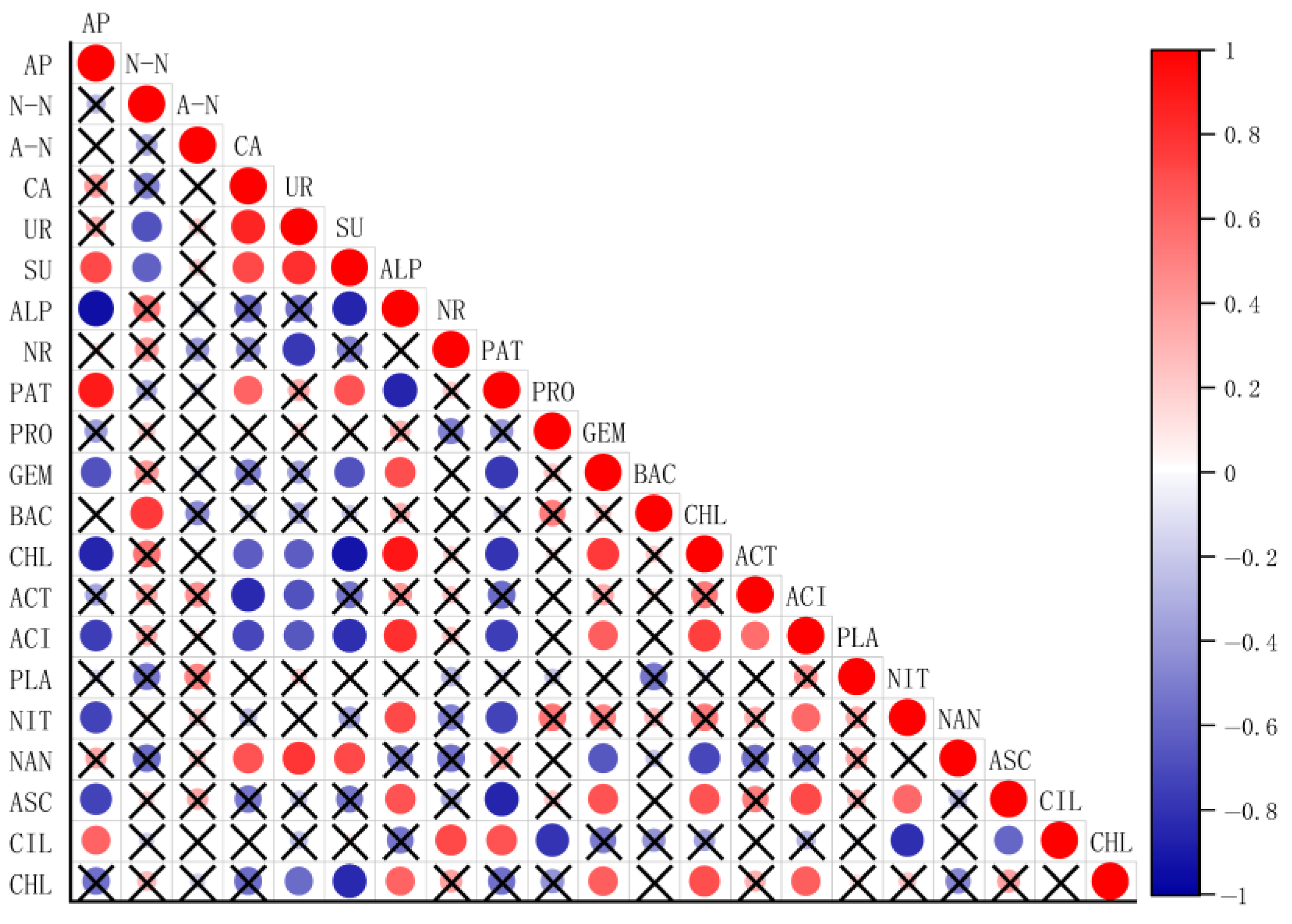
2.6. Correlation Analysis
2.7. Gray Correlation Analysis
3. Discussion
3.1. Effects of Biochar Amendment on Vertical Migration and Concentrations of Soil-Available Phosphorus, Nitrate N, and Ammoniacal N
3.2. Effects of Different Biochar Amendment on Microbial Community Structure
3.3. Effect of Different Biochar Amendment on Enzyme Activity
3.4. Correlation of Soil Nitrogen and Phosphorus Content with Soil Enzyme Activity and Microbial Community After Biochar Application
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Materials
4.2. Experimental Site Description
4.3. Experimental Design and Treatments Application
4.4. Determination of Tomato Growth Indicators
4.5. Gray Relational Analysis Method
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, J.Y.; Tian, W.H.; Jin, C.W. Nitrogen in plants: From nutrition to the modulation of abiotic stress adaptation. Stress Biol. 2022, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Islam, M.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, F.H.; Islam, M.M.; Halder, M.; Hou, E.Q. Phosphorus fertilization is essential for sustaining crop yields on converted natural ecosystems: A global meta-analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 254, 106756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babin, D.; Deubel, A.; Jacquiod, S.; Sorensen, S.J.; Geistlinger, J.; Grosch, R.; Smalla, K. Impact of long-term agricultural management practices on soil prokaryotic communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 129, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, S.M.; Walsh, C.S.; Wallis, A.E.; Ottesen, A.R.; Brown, E.W.; Micallef, S.A. Solanum lycopersicum (tomato) hosts robust phyllosphere and rhizosphere bacterial communities when grown in soil amended with various organic and synthetic fertilizers. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Chen, B.; Song, D. Sustainability evaluation of protected vegetables production in China based on emergy analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 388, 135928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.F.; Ma, Y.; Chenia, H.Y.; Govinden, R.; Luo, J.; Ren, G.D. Biochar-Mediated Control of Phytophthora Blight of Pepper Is Closely Related to the Improvement of the Rhizosphere Fungal Community. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cui, Y.T.; Sun, X.P.; Wang, H.Y.; Teng, X.H. Corn stover biochar increased edible safety of spinach by reducing the migration of mercury from soil to spinach. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes, A.B.; Arbestain, M.C.; Sevilla, M.; Maciá-Agulló, J.A.; Fiol, S.; López, R.; Smernik, R.J.; Aitkenhead, W.P.; Arce, F.; Macias, F. Chemical and structural properties of carbonaceous products obtained by pyrolysis and hydrothermal carbonisation of corn stover. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2010, 48, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, K.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.L.; Han, L.F. Changes in soil properties and CO2 emissions after biochar addition: Role of pyrolysis temperature and aging. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamau, S.; Karanja, N.K.; Ayuke, F.O.; Lehmann, J. Short-term influence of biochar and fertilizer-biochar blends on soil nutrients, fauna and maize growth. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2019, 55, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Li, Y.X.; Xu, Y.; Lu, X.Q. Biochar phosphorus fertilizer effects on soil phosphorus availability. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, Y.C.; Wang, Y.C.; An, W.Q.; Jin, J.; Sun, K.; Wang, X.K. Effects of biochar addition on the abundance, speciation, availability, and leaching loss of soil phosphorus. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, P.P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Wu, Z.; Xiong, Z.Q. Field-aged biochar stimulated N2O production from greenhouse vegetable production soils by nitrification and denitrification. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brtnicky, M.; Mustafa, A.; Hammerschmiedt, T.; Kintl, A.; Trakal, L.; Beesley, L.; Ryant, P.; Omara-Ojungu, C.; Baltazar, T.; Holatko, J. Pre-activated biochar by fertilizers mitigates nutrient leaching and stimulates soil microbial activity. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2023, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.Q.; Ji, Y.J.; He, M.M.; Su, M.M.; Liu, C.L.; Tian, G.M. Simple N Balance Assessment for Optimizing the Biochar Amendment Level in Paddy Soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2014, 45, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.D.; Lu, S.G. Straw and straw biochar differently affect phosphorus availability, enzyme activity and microbial functional genes in an Ultisol. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.H.; Whitman, W.B.; Gundale, M.J.; Chien, C.C.; Chiu, C.Y. Functional response of the soil microbial community to biochar applications. Glob. Change Biol. Bioenergy 2021, 13, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarauer, J.L.; Coleman, M.D. Microbial communities of biochar amended forest soils in northwestern USA. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 188, 104875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.M.; Liu, G.F.; Chen, H.H.; Chen, C.R.; Wang, J.K.; Ai, S.Y.; Wei, D.; Li, D.M.; Ma, B.; Tang, C.X.; et al. Long-term nutrient inputs shift soil microbial functional profiles of phosphorus cycling in diverse agroecosystems. ISME J. 2020, 14, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.X.; He, L.L.; Chen, J.Y.; Lyu, H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yang, L.; Yang, S.M.; Liu, Y.X. Long-Term Successive Biochar Amendments Alter the Composition and α-Diversity of Bacterial Community of Paddy Soil in Rice-Wheat Rotation. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 921766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadad, C.L.M.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Green, S.J.; Uthandi, S.; Foster, J.S. Taxa-specific changes in soil microbial community composition induced by pyrogenic carbon amendments. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanek, S.J.; Lehmann, J. Phosphorus availability to beans via interactions between mycorrhizas and biochar. Plant Soil 2015, 395, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, G.; Zheng, R.; Zhong, M.; Zhu, Y. Effect of biochar on abundance of N-related functional microbial communities in degraded greenhouse soil. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2013, 50, 624–631. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.Y.; Qiu, Y.B.; Yi, F.; Li, J.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Fu, Q.; Fu, X.H.; Yao, Z.Y.; Dai, Z.M.; Qiu, Y.P.; et al. Biochar dose-dependent impacts on soil bacterial and fungal diversity across the globe. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elad, Y.; Cytryn, E.; Harel, Y.M.; Lew, B.; Graber, E.R. The Biochar Effect: Plant resistance to biotic stresses. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2011, 50, 335–349. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.X.; Xiao, Q.; Cheng, H.Y.; Shi, B.J.; Shen, Y.F.; Li, S.Q. Seasonal dynamics of soil microbial activity after biochar addition in a dryland maize field in North-Western China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 104, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Shah, J.J.F. Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry and Ecological Theory. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 313–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, N.; Li, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, G.W.; Ma, L.J.; Min, W.; Ye, J.; Hou, Z.N. Effects of biochar on soil microbial community composition and activity in drip-irrigated desert soil. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2016, 72, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadem, A.; Raiesi, F. Response of soil alkaline phosphatase to biochar amendments: Changes in kinetic and thermodynamic characteristics. Geoderma 2019, 337, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ali, A.; Su, J.F.; Li, K.; Hu, R.Z.; Wang, Z. Microbial-induced calcium carbonate precipitation: Influencing factors, nucleation pathways, and application in waste water remediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokharel, P.; Ma, Z.L.; Chang, S.X. Biochar increases soil microbial biomass with changes in extra- and intracellular enzyme activities: A global meta-analysis. Biochar 2020, 2, 65–79, Erratum in Biochar 2021, 3, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintala, R.; Schumacher, T.E.; McDonald, L.M.; Clay, D.E.; Malo, D.D.; Papiernik, S.K.; Clay, S.A.; Julson, J.L. Phosphorus Sorption and Availability from Biochars and Soil/Biochar Mixtures. CLEAN-Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; DeLuca, T.H. Rangeland application of biochar and rotational grazing interact to influence soil and plant nutrient dynamics. Geoderma 2022, 408, 115572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troy, S.M.; Lawlor, P.G.; Flynn, C.J.O.; Healy, M.G. The Impact of Biochar Addition on Nutrient Leaching and Soil Properties from Tillage Soil Amended with Pig Manure. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, V.; Hussain, N.; Husk, B.R.; Whalen, J.K. Biochar-induced soil stability influences phosphorus retention in a temperate agricultural soil. Geoderma 2019, 351, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.T.; Sun, Y.Q.; Fan, B.Q.; Zhang, S.; Bolan, N.S.; Chen, Q.; Tsang, D.C.W. Fe/Al (hydr)oxides engineered biochar for reducing phosphorus leaching from a fertile calcareous soil. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar effects on soil biota—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, M.; Van Zwieten, L.; Bashir, S.; Younas, A.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Chhajro, M.A.; Kubar, K.A.; Ali, U.; Rana, M.S.; Mehmood, M.A.; et al. A concise review of biochar application to agricultural soils to improve soil conditions and fight pollution. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 228, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, F.; Zhang, D.-L.; Yi, W.-M. Effect of Biochar Structure on Adsorption Characteristics of Ammonia Nitrogen. Huanjing Kexue 2019, 40, 5421–5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, X.; Liu, H.; Zhai, L.; Ren, T.; Wang, H. Temporal fluctuations of impacts of corn-stover biochar on nutrients and microbial community structure in a neutral paddy soil. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 719–728. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhao, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H. Effect of biochar amendment on bacterial community structure and diversity in straw-amended soils. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2017, 37, 712–720. [Google Scholar]
- Rillig, M.C.; Wagner, M.; Salem, M.; Antunes, P.M.; George, C.; Ramke, H.G.; Titirici, M.M.; Antonietti, M. Material derived from hydrothermal carbonization: Effects on plant growth and arbuscular mycorrhiza. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 45, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.B.; Gao, X.; Wang, D.B.; Guo, L.; Wang, D.K.; Xu, S.G. Effects of Different Biochar Application Rates on Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Diversity of Tobacco. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2018, 33, 224–232. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Zheng, J.; Qu, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Pan, G. Consistent increase in abundance and diversity but variable change in community composition of bacteria in topsoil of rice paddy under short term biochar treatment across three sites from South China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 91, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chang, Z.Z.; Xue, X.M.; Yu, J.G.; Shi, X.X.; Ma, L.Q.; Li, H.B. Biochar decreases nitrogen oxide and enhances methane emissions via altering microbial community composition of anaerobic paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolton, M.; Harel, Y.M.; Pasternak, Z.; Graber, E.R.; Elad, Y.; Cytryn, E. Impact of Biochar Application to Soil on the Root-Associated Bacterial Community Structure of Fully Developed Greenhouse Pepper Plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 4924–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Whalen, J.K.; Thomas, B.W.; Sachdeva, V.; Deng, H.Y. Physico-chemical properties and microbial responses in biochar-amended soils: Mechanisms and future directions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 206, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollivier, J.; Töwe, S.; Bannert, A.; Hai, B.; Kastl, E.M.; Meyer, A.; Su, M.X.; Kleineidam, K.; Schloter, M. Nitrogen turnover in soil and global change. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 78, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, R.L.; Pieterse, C.M.J.; Bakker, P. The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, V.L.; Fansler, S.J.; Smith, J.L.; Bolton, H. Reconciling apparent variability in effects of biochar amendment on soil enzyme activities by assay optimization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.L.; Yin, B.Y.; Zhang, J.R.; Zhou, S.S.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xu, J.Z.; Liang, B.W. Exogenous melatonin alleviates apple replant disease by regulating rhizosphere soil microbial community structure and nitrogen metabolism. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 884, 163830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.Y.; Gong, J.R.; Li, X.B.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhang, W.Y.; Li, Y.; Song, L.Y.; Zhang, S.Q.; Dong, J.J.; Baoyin, T.T. Phosphorus application promoted the sequestration of orthophosphate within soil microorganisms and regulated the soil solution P supply in a temperate grassland in northern China: A 31P NMR study. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 227, 105612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.L.; Xu, C.S.; He, H.H.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, G.S. Effect of Biochar on Soil Enzyme Activity & the Bacterial Community and Its Mechanism. Huanjing Kexue 2021, 42, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| Treatment | Available Phosphorus (mg·kg−1) | Nitrate N (mg·kg−1) | Ammonium N (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BA0 | 1.2 ± 0.0060 b | 15 ± 1.2 a | 0.042 ± 0.0050 a |
| BA1 | 1.4 ± 0.043 a | 16 ± 0.11 a | 0.035 ± 0.0010 a |
| BA3 | 1.4 ± 0.021 a | 12 ± 0.15 b | 0.042 ± 0.011 a |
| BA5 | 1.4 ± 0.034 a | 11 ± 0.13 b | 0.046 ± 0.0040 a |
| BA0 | 1.2 ± 0.0060 b | 15 ± 1.2 a | 0.042 ± 0.0050 a |
| Treatment | Catalase Enzyme | Urease Enzyme | Sucrase | Alkaline Phosphatase | Nitrate Reductase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BA0 | 6.32 ± 0.08 b | 0.24 ± 0.02 b | 43.00 ± 0.63 c | 0.38 ± 0.01 a | 0.45 ± 0.02 b |
| BA1 | 6.45 ± 0.07 ab | 0.24 ± 0.01 b | 54.25 ± 2.12 b ** | 0.29 ± 0.02 b ** | 0.57 ± 0.03 a |
| BA3 | 6.51 ± 0.29 ab | 0.27 ± 0.01 b | 56.55 ± 1.00 b ** | 0.26 ± 0.02 c ** | 0.59 ± 0.07 a * |
| BA5 | 6.78 ± 0.14 a * | 0.35 ± 0.02 a ** | 68.22 ± 1.20 a ** | 0.25 ± 0.02 c ** | 0.27 ± 0.04 c ** |
| Indicators | Catalase Enzyme | Urease Enzyme | Sucrase | Alkaline Phosphatase | Nitrate Reductase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| catalase enzyme | 1.00 | ||||
| urease enzyme | 0.83 | 1.00 | |||
| sucrase | 0.69 | 0.82 | 1.00 | ||
| alkaline phosphatase | 0.49 | 0.55 | 0.86 | 1.00 | |
| nitrate reductase | 0.46 | 0.78 | 0.49 | 0.08 | 1.00 |
| mean value of correlation coefficient | 0.62 | 0.59 | 0.72 | 0.50 | 0.45 |
| weighting factor | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 0.20 |
| Treatment | SEI Affiliation Value | Soil Enzyme Index (SEI) | Soil Enzyme Index Ranking | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalase Enzyme | Urease Enzyme | Sucrase | Alkaline Phosphatase | Nitrate Reductase | |||
| BA0 | 0.35 | 0.39 | 0.37 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.49 | 4 |
| BA1 | 0.56 | 0.39 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 0.65 | 0.62 | 1 |
| BA3 | 0.37 | 0.42 | 0.58 | 0.22 | 0.39 | 0.53 | 3 |
| BA5 | 0.38 | 0.29 | 0.59 | 0.43 | 0.68 | 0.61 | 2 |
| Soil Index | Ej | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| AP | 0.9022 | 0.0739 |
| N-N | 0.8594 | 0.1062 |
| A-N | 0.8604 | 0.1054 |
| Patescibacteria | 0.9024 | 0.0737 |
| Gemmatimonadota | 0.9294 | 0.0533 |
| Bacteroidota | 0.9124 | 0.0662 |
| Chloroflexi | 0.9243 | 0.0572 |
| Acidobateriota | 0.9539 | 0.0348 |
| Nitrospirota | 0.9506 | 0.0373 |
| Ascomycota | 0.9383 | 0.0466 |
| Ciliophora | 0.8153 | 0.1395 |
| Urease enzyme | 0.9370 | 0.0476 |
| Sucrase | 0.8802 | 0.0904 |
| Alkaline phosphatase | 0.9099 | 0.0680 |
| Treatment | WGCD | WO |
|---|---|---|
| BA0 | 0.8123 | 4 |
| BA1 | 0.8666 | 2 |
| BA3 | 0.8638 | 3 |
| BA5 | 0.8747 | 1 |
| Types | Sequencing Region | Name of Primer | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16S bacterium | V3-V4 | 341F | CCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG |
| 806R | GGACTACHVGGGTATCTAAT | ||
| ITS Fungal | ITS2 | ITS3_KYO2 | GATGAAGAACGYAGYRAA |
| ITS4 | TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Chang, T.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, D. Corn Stover Biochar Amendment Enhances Nitrogen and Phosphorus Transformations, Microbial Community Diversity, and Enzyme Activities in Agricultural Soil. Plants 2025, 14, 2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172787
Li B, Zhang J, Chang T, Wu Q, Zheng H, Zhang D. Corn Stover Biochar Amendment Enhances Nitrogen and Phosphorus Transformations, Microbial Community Diversity, and Enzyme Activities in Agricultural Soil. Plants. 2025; 14(17):2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172787
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Baihui, Jie Zhang, Tingting Chang, Qianqian Wu, Hanyu Zheng, and Dong Zhang. 2025. "Corn Stover Biochar Amendment Enhances Nitrogen and Phosphorus Transformations, Microbial Community Diversity, and Enzyme Activities in Agricultural Soil" Plants 14, no. 17: 2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172787
APA StyleLi, B., Zhang, J., Chang, T., Wu, Q., Zheng, H., & Zhang, D. (2025). Corn Stover Biochar Amendment Enhances Nitrogen and Phosphorus Transformations, Microbial Community Diversity, and Enzyme Activities in Agricultural Soil. Plants, 14(17), 2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172787







