Transcriptional Regulation of the Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase (PAL) Gene Family in Mulberry Under Chitosan-Induced Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. A Map of Grouped TFs via Known Cis-Elements in PAL Promoter Regions
2.2. Identifying Conserved Motifs in the Promoter Regions of PAL Genes
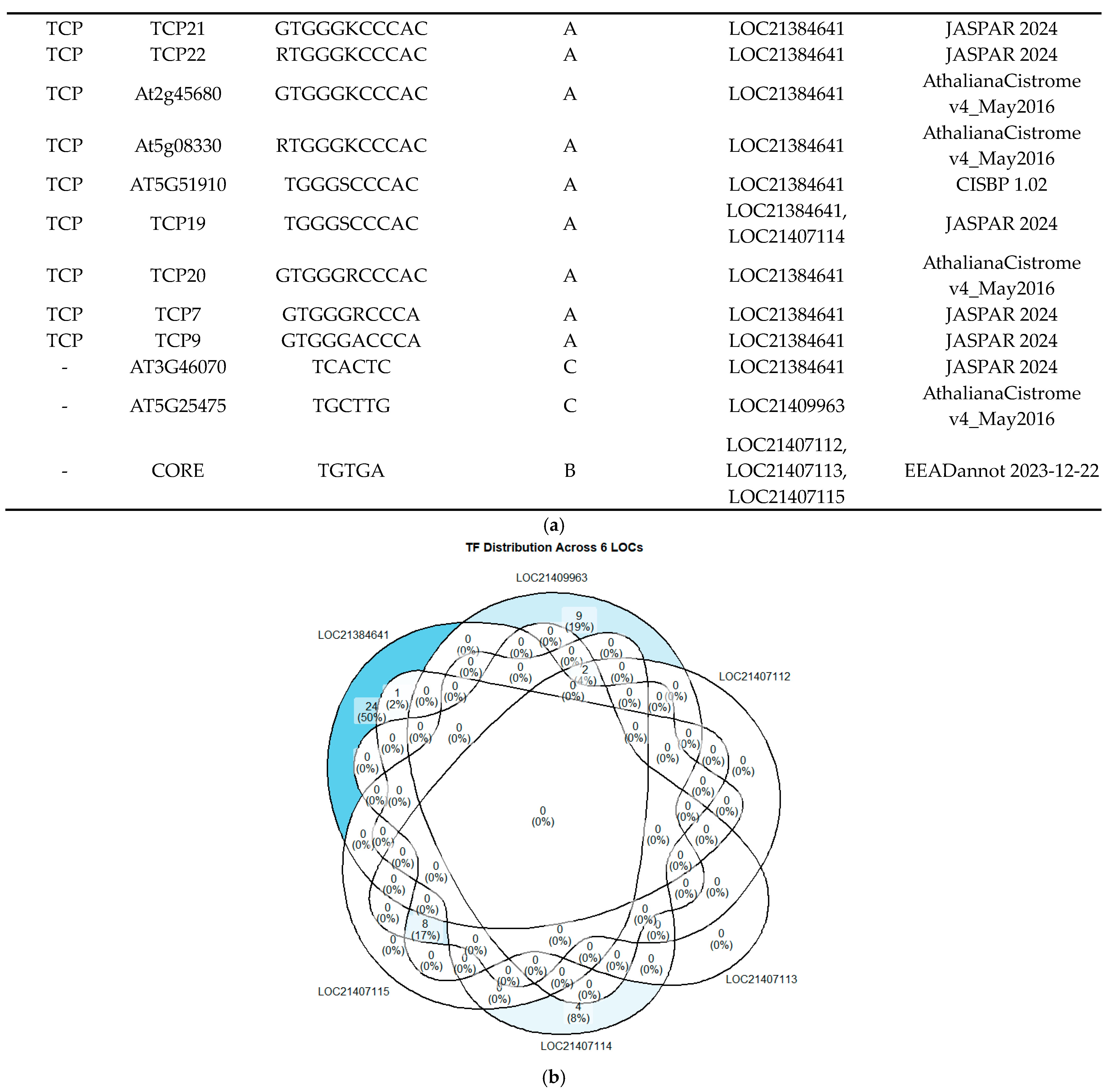
2.3. In Silico Exploration for TF Candidates in PAL Promoter Conserved Motifs
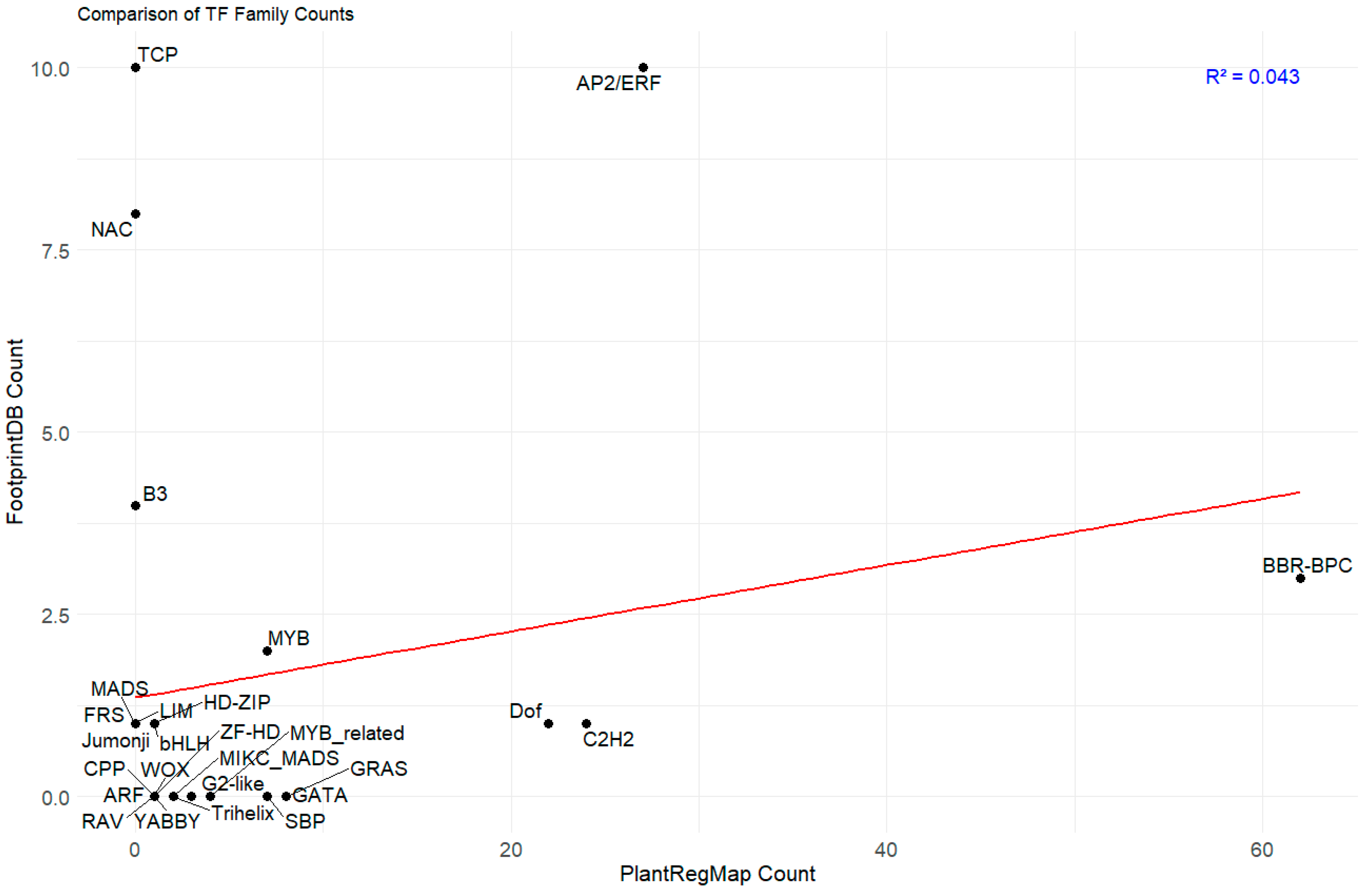
2.4. Correlation Study of TFBS Predictions by PlantRegMap and FootprintDB in PAL Promoters
2.5. Transcriptional Response of Candidate Regulators of PALs Under Conditions That Alter PAL Expression
3. Discussion
3.1. A Complex Regulatory Network Involving AP2/ERF, BBR-BPC, and Other TF Families Controls PAL Gene Expression
3.2. NAC083 Acts as an Activator in PAL Expression in Chitosan Application
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identifying Known Binding Sites and Conserved Sequence Motifs in Mulberry PAL Gene Promoters
4.2. Assessment of Candidate TFs Regulating PAL via Motifs and Database Correlation Analysis
4.3. Plant Sample Collection and RNA Extraction
4.4. cDNA Synthesis and Preparation of the Library for High-Throughput Sequencing
4.5. De Novo Transcriptome Assembly and Identifying Expression Differences
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AP2/ERF | Apetala2/Ethylene-Responsive Factor |
| BBR-BPC | Bar-domain and BPC-domain containing proteins |
| bHLH | basic Helix-Loop-Helix |
| bp | base pairs |
| BS | binding sites |
| C2H2 | Cys2/His2 |
| cDNA | complementary DNA |
| Dof | DNA-binding with one finger |
| FPKM | Fragments Per Kilobase of transcript per Million mapped reads |
| FN | full-nutrient |
| GATA | GATA binding factor |
| GRAS | GAI, RGA, and SCR |
| HD-ZIP | Homeodomain-leucine zipper |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| MADS | MCM1, AGAMOUS, DEFICIENS, and SRF |
| MEME | Multiple EM for Motif Elicitation |
| MIKC | MADS-box, Intervening, Keratin-like, and C-terminal |
| MYB | Myeloblastosis |
| NAC | NAM, ATAF, and CUC |
| PAL | Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PR1 | pathogenesis-related protein 1 |
| SBP | Squamosa promoter-binding protein |
| TF | Transcription Factor |
| TFBS | Transcription Factor Binding Site |
| TPM | Transcripts Per Million |
| WOX | WUSCHEL-related homeobox |
| Y1H | yeast one-hybrid |
| ZF-HD | Zinc finger-homeodomain |
References
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wei, W.; Zhang, X. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals key genes involved in the biosynthesis of anthocyanins in Brassica rapa. Plant Sci. 2020, 297, 110521. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Butelli, E.; Alseekh, S.; Tohge, T.; Rallapalli, G.; Luo, J.; Kawar, P.G.; Hill, L.; Santino, A.; Fernie, A.R.; et al. Multi-level engineering facilitates the production of phenylpropanoid compounds in tomato. Nat. Commun. 2015, 26, 8635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tikunov, Y.; Schouten, R.E.; Marcelis, L.F.; Visser, R.G.; Bovy, A. Anthocyanin biosynthesis and degradation mechanisms in Solanaceous vegetables: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 687994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Gu, M.; Lai, Z.; Fan, B.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.H.; Yu, J.Q.; Chen, Z. Functional analysis of the Arabidopsis PAL gene family in plant growth, development, and response to environmental stress. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 1526–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrázová, A.; Belay, S.A.; Eliášová, A.; Perez-Delgado, C.; Kaducová, M.; Betti, M.; Vega, J.M.; Paľove-Balang, P. Expression, activity of phenylalanine-ammonia-lyase and accumulation of phenolic compounds in Lotus japonicus under salt stress. Biologia 2017, 72, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Hwang, B.K. An important role of the pepper phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene (PAL1) in salicylic acid-dependent signalling of the defence response to microbial pathogens. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, S.; Soliman, M.M.; Althobaiti, F.; Albattal, S.B.; Dar, M.R.; Inam, M.; Khan, A.K.; Elshehawi, A.; Mujahid, H. Impacts of Ficus Religiosa-loaded chitosan nanoparticles against indomethacin induced peptic ulcer in rats: Promising therapy with enhanced bioavailability and gastro-protective activity. Toxicol. Res. 2025, 14, tfaf034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubis, M.; Gana, A.; Maysarah, S.; Ginting, M.H.S.; Harahap, M.B. Production of bioplastic from jackfruit seed starch (Artocarpus heterophyllus) reinforced with microcrystalline cellulose from cocoa pod husk (Theobroma cacao L.) Using glycerol as plasticizer. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 309, p. 012100. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Jia, K.P.; Lian, H.L.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Yang, H.Q. Jasmonic acid enhancement of anthocyanin accumulation is dependent on phytochrome A signaling pathway under far-red light in Arabidopsis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 454, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraj, T.A.; Fu, J.; Raza, M.A.; Zhu, C.; Shen, Q.; Xu, D.; Wang, Q. Transcriptional factors regulate plant stress responses through mediating secondary metabolism. Genes 2020, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; He, Q.; Gao, P.; Tian, P.; et al. The COP1-bbxs-HY5-PIF4 regulatory module regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple skin. Plant Physiol. 2021, 187, 2432–2448. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Pan, J.; Lou, D.; Hu, Y.; Yu, D. The bhlh transcription factors MYC2, MYC3, and MYC4 are required for jasmonate-mediated inhibition of flowering in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2022, 10, 1461–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Duan, G.; Li, C.; Liu, L.; Han, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C. The crosstalks between jasmonic acid and other plant hormone signaling highlight the involvement of jasmonic acid as a core component in plant response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 10, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lin-Wang, K.; Espley, R.V.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, P.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Stmyb44 is a key regulator of the biosynthesis of phenolic acids and flavonols that contribute to pest and disease resistance in potato. Plant Sci. 2023, 332, 111627. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yang, B.; Sun, S.; Peng, L.; Wang, Z. Indole-3-acetate beta-glucosyltransferase osiaglu regulates seed vigour through mediating crosstalk between auxin and abscisic acid in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 18, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Bender, Y.; Boyle, K.; Fobert, P.R. Plant BBR/BPC transcription factors: Unlocking multilayered regulation in development, stress and immunity. Plant Mol. Biol. 2023, 112, 675–694. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, K.; Yokota, A.; Shibata, D. Transcription factors of Lotus: Regulation of isoflavonoid biosynthesis requires coordinated changes in transcription factor activity. Plant Physiol. 2017, 159, 531–545. [Google Scholar]
- Dubos, C.; Kelemen, Z.; Sebastian, A.; Bülow, L.; Huep, G.; Xu, W.; Grain, D.; Salsac, F.; Brousse, C.; Lepiniec, L.; et al. Integrating bioinformatic resources to predict transcription factors interacting with cis-sequences conserved in co-regulated genes. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakpenthai, A.; Apodiakou, A.; Whitcomb, S.J.; Hoefgen, R. In silico analysis of cis-elements and identification of transcription factors putatively involved in the regulation of the OAS cluster genes SDI1 and SDI2. Plant J. 2022, 110, 1286–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Feng, Q.; Lu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, A.; Tian, Q.; Zhan, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, T.; et al. Pan-genome analysis highlights the extent of genomic variation in cultivated and wild rice. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theune, M.L.; Blom, J.; van Dijk, A.D.; Koning-Boucoiran, C.F.; van der Vlugt, R.A.; Westerhof, J.H.; Schijlen, E.G. The tomato yellow leaf curl virus resistance genes Ty-1 and Ty-3 are allelic and code for DFDGD-class RNA-dependent RNA polymerases. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008475. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, X.; Mao, P.; Gao, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z.; et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the WRKY transcription factor family in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) under abiotic stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 829365. [Google Scholar]
- de Boer, C.G.; Vaishnav, E.D.; Sadeh, R.; Abeyta, E.L.; Friedman, N.; Regev, A. Deciphering eukaryotic gene-regulatory logic with 100 million random promoters. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Wysocka, J. Deciphering the multi-scale, quantitative cis-regulatory code. Mol. Cell 2023, 83, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, T.; Guo, S.; Hu, J.; Zhan, Y. Ectopic expression of aenac83, a NAC transcription factor from Abelmoschus esculentus, inhibits growth and confers tolerance to salt stress in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, H.M.; He, J.; Arshad, M.B.; Wang, M. Characterization of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase genes in soybean: Genomic insights and expression analysis under abiotic stress tolerance. Plant Stress 2025, 10, 100896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D587–D592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Yang, D.C.; Meng, Y.Q.; Jin, J.; Gao, G. Plantregmap: Charting functional regulatory maps in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D1104–D1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Moreira, B.; Sebastian, A. Footprintdb: Analysis of plant cis-regulatory elements, transcription factors, and binding interfaces. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1482, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sebastian, A.; Contreras-Moreira, B. Footprintdb: A database of transcription factors with annotated cis elements and binding interfaces. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Dusa, A. Ggvenndiagram: A ‘ggplot2’ Implement of Venndiagram, version 1.5.2.; R package: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Posit Team. Rstudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; Posit Software; PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Mccarthy, D.; Ritchie, M.; Robinson, M.; Smyth, G.; Hall, E. Edger: Differential Analysis of Sequence Read Count Data User’s Guide; R Package: Vienna, Austria, 2020; pp. 1–121. [Google Scholar]

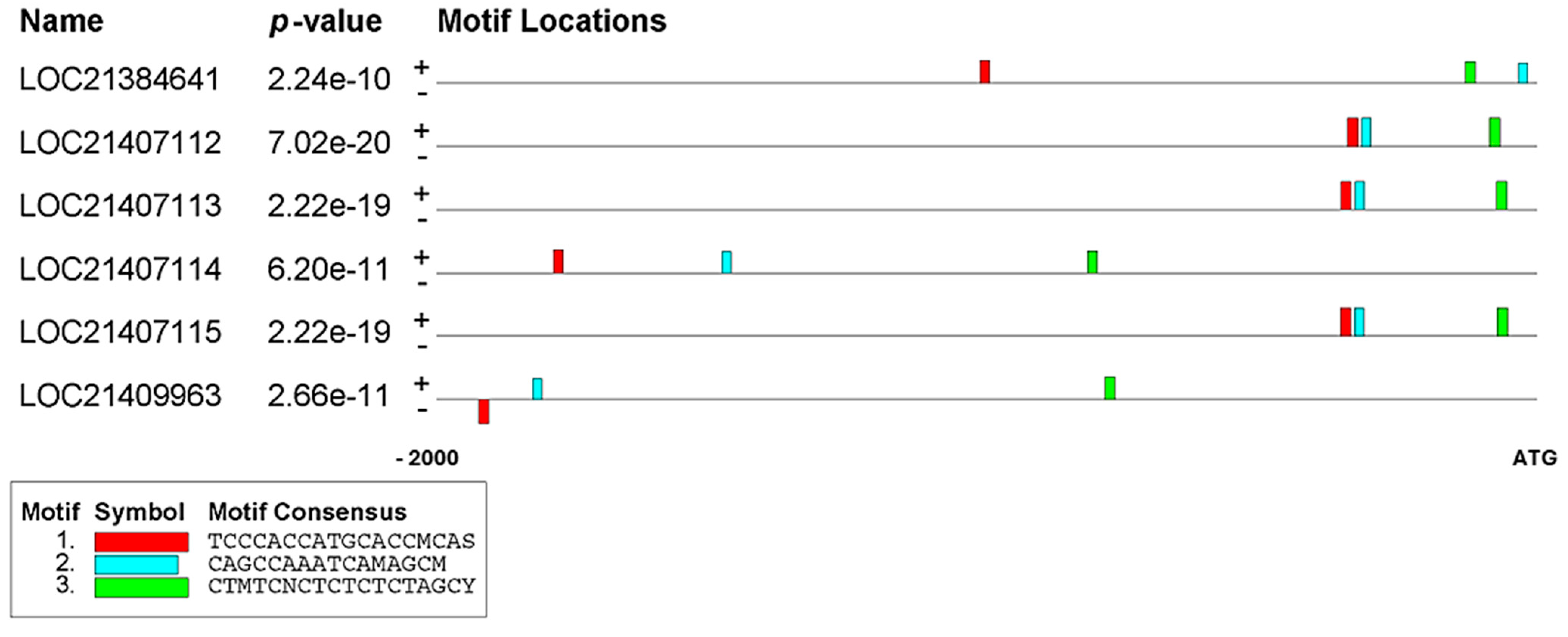


| Motif | A | B | C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motif Seq Logo |  TCCCACCATGCACCMCAS TCCCACCATGCACCMCAS |  CAGCCAAATCAMAGCM CAGCCAAATCAMAGCM |  CTMTCNCTCTCTCTAGCY CTMTCNCTCTCTCTAGCY | |
| LOC21384641 | Matched | TCCCTCTGTGGGGCCCAC (+) | CACGCAAACCAAAGCA (+) | CTAGCACTCTATGTAGCT (+) |
| Location | −1012 | −32 | −129 | |
| E-value | 9.54 × 10−9 | 5.06 × 10−8 | 1.73 × 10−8 | |
| LOC21407112 | Matched | TCCCACCATGCACCCCAG (+) | CAGCCAAATCACAGCC (+) | CTCTCCCTCTCTCTAGCT (+) |
| Location | −343 | −317 | −85 | |
| E-value | 2.73 × 10−12 | 7.20 × 10−11 | 4.17 × 10−12 | |
| LOC21407113 | Matched | TCCCACCATGCACCCCAG (+) | CAGCCAAATCACAGCC (+) | CTCTCTCTCTCTCTAGCT (+) |
| Location | −355 | −329 | −72 | |
| E-value | 2.73 × 10−12 | 7.20 × 10−11 | 1.38 × 10−11 | |
| LOC21407114 | Matched | TCACACACTGCCCCACAC (+) | CAGCCAAAAGAAGGCC (+) | CCAACCCTGTCACTAGCC (+) |
| Location | −1787 | −1480 | −816 | |
| E-value | 5.09 × 10−9 | 2.74 × 10−8 | 1.52 × 10−8 | |
| LOC21407115 | Matched | TCCCACCATGCACCCCAG (+) | CAGCCAAATCACAGCC (+) | CTCTCTCTCTCTCTAGCT (+) |
| Location | −356 | −330 | −71 | |
| E-value | 2.73 × 10−12 | 7.20 × 10−11 | 1.38 × 10−11 | |
| LOC21409963 | Matched | TTCCCACATGCACCACAC (−) | CCGCCAGAGCTCAGCA (+) | CTCTTGCTCTCGCAAGCC (+) |
| Location | −1922 | −1824 | −784 | |
| E-value | 3.63 × 10−9 | 3.53 × 10−8 | 6.66 × 10−9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rakpenthai, A.; Watanabe, M.; Wongkaew, A.; Nakasathien, S. Transcriptional Regulation of the Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase (PAL) Gene Family in Mulberry Under Chitosan-Induced Stress. Plants 2025, 14, 2783. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172783
Rakpenthai A, Watanabe M, Wongkaew A, Nakasathien S. Transcriptional Regulation of the Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase (PAL) Gene Family in Mulberry Under Chitosan-Induced Stress. Plants. 2025; 14(17):2783. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172783
Chicago/Turabian StyleRakpenthai, Apidet, Mutsumi Watanabe, Arunee Wongkaew, and Sutkhet Nakasathien. 2025. "Transcriptional Regulation of the Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase (PAL) Gene Family in Mulberry Under Chitosan-Induced Stress" Plants 14, no. 17: 2783. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172783
APA StyleRakpenthai, A., Watanabe, M., Wongkaew, A., & Nakasathien, S. (2025). Transcriptional Regulation of the Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase (PAL) Gene Family in Mulberry Under Chitosan-Induced Stress. Plants, 14(17), 2783. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172783








