The AP2/ERF Gene Family in Camphor Tree: Structure, Evolution, and Transcriptional Response to Epicoccum Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
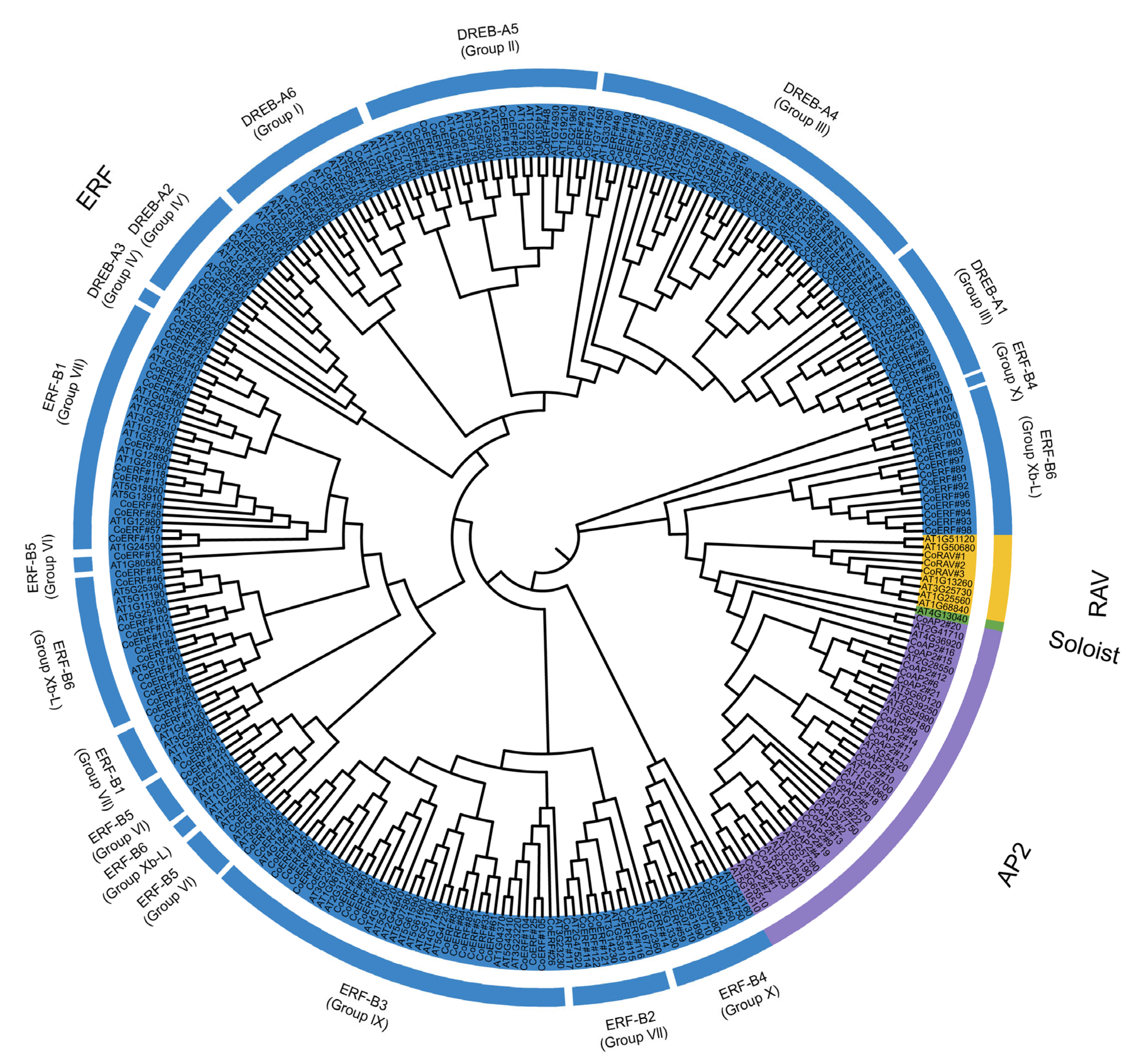
2.1. Identification and Classification of AP2/ERF Transcription Factors in C. officinarum
2.2. Gene Structure and Motif Analysis of AP2/ERF Genes in C. officinarum
2.3. Identification of Cis-Acting Regulatory Elements in CoAP2/ERF Promoters
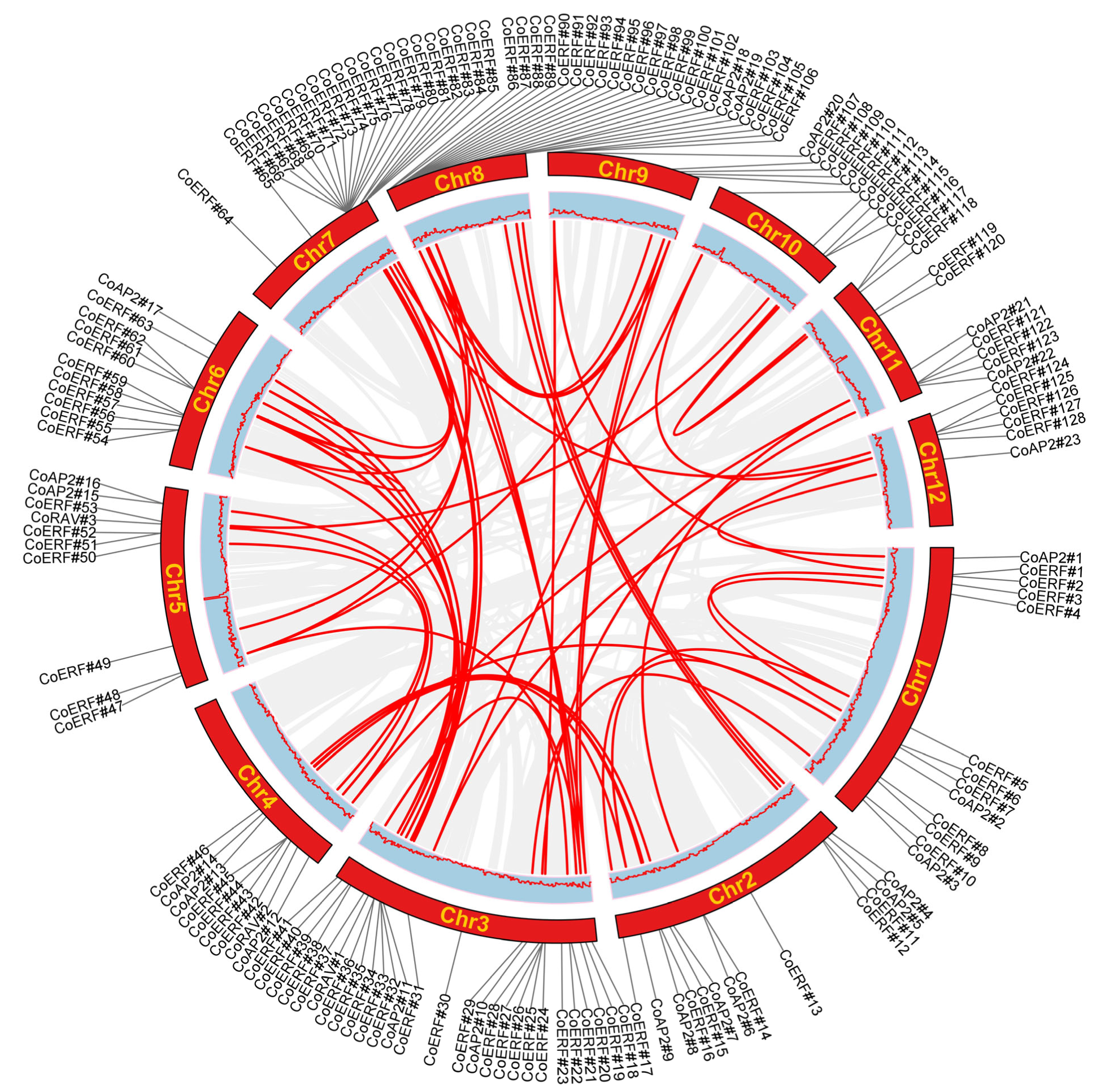
2.4. Collinearity Analysis of CoAP2/ERF Family Genes
2.5. Expression Profiling of CoAP2/ERF Genes During Plant Development
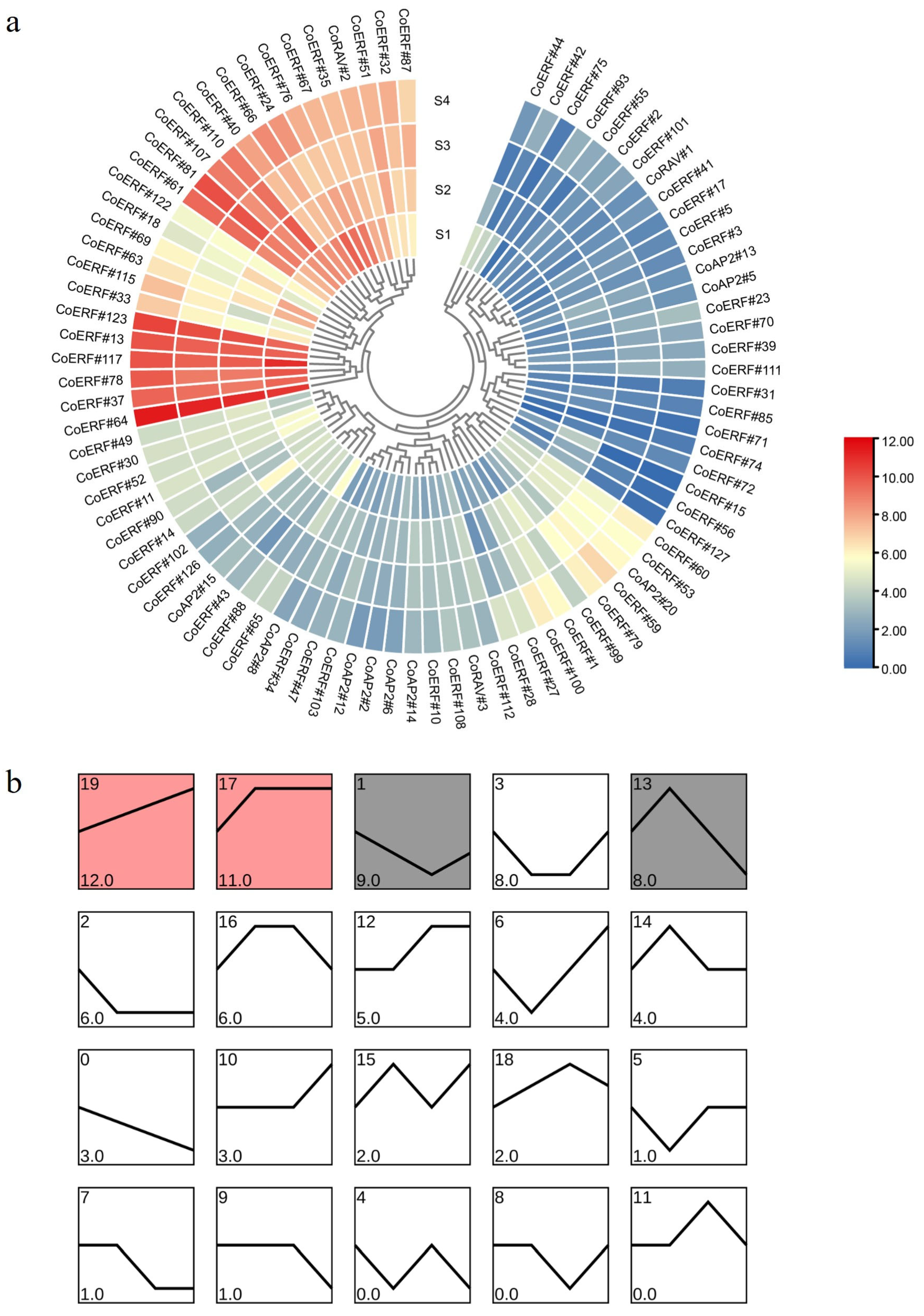
2.6. Expression Profiling of CoAP2/ERF Genes Under E. poaceicola Infection
2.7. qPCR Validation of RNA-Seq Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Infection Assay
4.2. Genome-Wide Identification of CoAP2/ERF Genes
4.3. Phylogenetic Analysis and Classification of the CoAP2/ERF Genes
4.4. Chromosomal Mapping and Collinearity Analyses
4.5. Gene Structure Analysis, Motif Analysis, and Prediction of Cis-Acting Regulatory Elements
4.6. RNA Sequencing
4.7. Expression Analysis of CoAP2/ERF Genes During Plant Development and Under Pathogen Infection
4.8. qPCR Validation of RNA-Seq Data
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, B.; Jin, X.; Zhang, H.; Jin, Z. Transcriptional analysis of metabolic pathways and regulatory mechanisms of essential oil biosynthesis in the leaves of Cinnamomum camphora (L.) Presl. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 598714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wu, F.; Wu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ma, H.; Wu, J. First report of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma asteris’ associated with witches’-broom disease of Cinnamomum camphora in China. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, T.; Song, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Luan, F. First report of leaf spot disease on Cinnamomum camphora (Camphor Tree) caused by Epicoccum poaceicola in China. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Song, Q.; Liu, J.; Yang, Q.; Luan, F.; Li, D. First Report of Anthracnose on Cinnamomum camphora (Camphor tree) Caused by Colletotrichum fioriniae and Colletotrichum siamense in China. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, F. Root rot of Cinnamomum camphora (Linn) presl caused by phytopythium vexans in China. Plants 2023, 12, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, K.; Hou, X.; Xing, G.; Liu, J.; Duan, A.; Xu, Z.; Li, M.; Zhuang, J.; Xiong, A. Advances in AP2/ERF super-family transcription factors in plant. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 750–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Suzuki, K.; Fujimura, T.; Shinshi, H. Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 411–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Raemdonck, D.; Pesquet, E.; Cloquet, S.; Beeckman, H.; Boerjan, W.; Goffner, D.; El Jaziri, M.; Baucher, M. Molecular changes associated with the setting up of secondary growth in aspen. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 2211–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Long, X.; Wu, X.; Ren, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, H. Genome-wide investigation of the AP2/ERF gene family in ginger: Evolution and expression profiling during development and abiotic stresses. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, T.; Xu, X.; Jiang, J.; Li, J. Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of the ERF2 gene family in response to disease resistance against Stemphylium lycopersici in tomato. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Peng, R.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Cai, B.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, F.; Zhu, B.; Fu, X.; Jin, X.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of the putative AP2/ERF family genes in Vitis vinifera. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 123, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riechmann, J.L.; Heard, J.; Martin, G.; Reuber, L.; Jiang, C.; Keddie, J.; Adam, L.; Pineda, O.; Ratcliffe, O.J.; Samaha, R.R.; et al. Arabidopsis transcription factors: Genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science 2000, 290, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, Y.; Liu, Q.; Dubouzet, J.G.; Abe, H.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. DNA-Binding specificity of the ERF/AP2 domain of Arabidopsis DREBs, transcription factors involved in dehydration- and cold-inducible gene expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 290, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukerman, M.J.; Sakai, H. Regulation of flowering time and floral organ identity by a MicroRNA and its APETALA2-like target genes. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2730–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Wang, S.; Ning, K.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Qi, M.; Wang, Q. The APETALA2 transcription factor LsAP2 regulates seed shape in lettuce. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 2463–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrnia, M.; Balazadeh, S.; Zanor, M.I.; Mueller-Roeber, B. EBE, an AP2/ERF transcription factor highly expressed in proliferating cells, affects shoot architecture in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2013, 162, 842–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baillo, E.H.; Kimotho, R.N.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, P. Transcription factors associated with abiotic and biotic stress tolerance and their potential for crops improvement. Genes 2019, 10, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoi, J.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. AP2/ERF family transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1819, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, T.; Yuan, L. ERF gene clusters: Working together to regulate metabolism. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Huang, Z.; Chen, M.; Cao, B.; Zhu, Z.; Lei, J. Systematic analysis of the Capsicum ERF transcription factor family: Identification of regulatory factors involved in the regulation of species-specific metabolites. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.; Munné-Bosch, S. Ethylene response factors: A key regulatory hub in hormone and stress signaling. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandan, R.K.; Kumar, R.; Swain, D.M.; Ghosh, S.; Bhagat, P.K.; Patel, S.; Bagler, G.; Sinha, A.K.; Jha, G. RAV1 family members function as transcriptional regulators and play a positive role in plant disease resistance. Plant J. 2023, 114, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.R.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, U.; Song, I.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Nam, H.G.; Lim, P.O. The RAV1 transcription factor positively regulates leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 3947–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, Y. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals transcriptional regulation and metabolic pathways of terpenoid biosynthesis in developing Cinnamomum camphora leaf cells. Curr. Plant Biol. 2025, 42, 100467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, M.M.; Luscombe, N.M.; Aravind, L.; Gerstein, M.; Teichmann, S.A. Structure and evolution of transcriptional regulatory networks. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2004, 14, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tao, S.; Wei, S.; Ming, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J. The mining and evolutionary investigation of AP2/ERF genes in pear (Pyrus). BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; He, G.; Li, Y.; Yang, G. Evolution of the DEHYDRATION-RESPONSIVE ELEMENT-BINDING PROTEIN subfamily in green plants. Plant Physiol. 2022, 190, 421–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerstens, M.H.; Schranz, M.E.; Bouwmeester, K. Phylogenomic analysis of the APETALA2 transcription factor subfamily across angiosperms reveals both deep conservation and lineage-specific patterns. Plant J. 2020, 103, 1516–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ma, H.; Lin, J. Angiosperm-wide and family-level analyses of AP2/ERF genes reveal differential retention and sequence divergence after whole-genome duplication. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.; An, T.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Gao, H.; Sun, W.; Liao, B.; Jiang, C.; Liu, Z.; Duan, L.; et al. Genomic-wide identification and expression analysis of AP2/ERF transcription factors related to andrographolide biosynthesis in Andrographis paniculata. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 157, 112878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S. Computational analysis of the AP2/ERF family in crops genome. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, L.; Jiang, W. Understanding AP2/ERF transcription factor responses and tolerance to various abiotic stresses in plants: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasserre, E.; Jobet, E.; Llauro, C.; Delseny, M. AtERF38 (At2g35700), an AP2/ERF family transcription factor gene from Arabidopsis thaliana, is expressed in specific cell types of roots, stems and seeds that undergo suberization. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 46, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, M.; Wilson, I.W.; Yang, J.; Buerstenbinder, K.; Llewellyn, D.; Dennis, E.S.; Sauter, M.; Dolferus, R. Arabidopsis RAP2.2: An ethylene response transcription factor that is important for hypoxia survival. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamaitha, M.J.; Yamamoto, R.; Wong, H.L.; Kawasaki, T.; Kawano, Y.; Shimamoto, K. OsRap2.6 transcription factor contributes to rice innate immunity through its interaction with Receptor for Activated Kinase-C 1 (RACK1). Rice 2012, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Nolan, T.M.; Jiang, H.; Yin, Y. AP2/ERF transcription factor regulatory networks in hormone and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zheng, R.; Peng, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhu, X.; Xie, K.; Su, Q.; Huang, R.; Zhan, S.; Peng, D.; et al. Bioinformatic assessment and expression profiles of the AP2/ERF superfamily in the Melastoma dodecandrum genome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, G.H.; Wan, J.; Kim, H.J.; Nguyen, X.C.; Chung, W.S.; Hong, J.C.; Stacey, G. Ethylene-responsive element-binding factor 5, ERF5, is involved in chitin-induced innate immunity response. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2012, 25, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lin, H.; Wang, X.; Bi, B.; Gao, Y.; Shao, L.; Zhang, R.; Liang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Genome and whole-genome resequencing of Cinnamomum camphora elucidate its dominance in subtropical urban landscapes. BMC Biol. 2023, 21, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, J.; Bar-Joseph, Z. STEM: A tool for the analysis of short time series gene expression data. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Classification | Characteristics | No. |
|---|---|---|
| AP2 subfamily | one AP2/ERF domain | 1 |
| two AP2/ERF domains | 22 | |
| ERF subfamily | one AP2/ERF domain | 127 |
| two AP2/ERF domains | 1 | |
| RAV subfamily | B3 domain | 3 |
| Total | 154 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, J.; He, J.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, C.; Zeng, R.; Wan, H. The AP2/ERF Gene Family in Camphor Tree: Structure, Evolution, and Transcriptional Response to Epicoccum Infection. Plants 2025, 14, 2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172694
Hou J, He J, Liu Y, Xiao Z, Zhang H, Xiao C, Zeng R, Wan H. The AP2/ERF Gene Family in Camphor Tree: Structure, Evolution, and Transcriptional Response to Epicoccum Infection. Plants. 2025; 14(17):2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172694
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Jiexi, Jinrui He, Yiran Liu, Zhufei Xiao, Haiyan Zhang, Changlong Xiao, Rong Zeng, and Hongjian Wan. 2025. "The AP2/ERF Gene Family in Camphor Tree: Structure, Evolution, and Transcriptional Response to Epicoccum Infection" Plants 14, no. 17: 2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172694
APA StyleHou, J., He, J., Liu, Y., Xiao, Z., Zhang, H., Xiao, C., Zeng, R., & Wan, H. (2025). The AP2/ERF Gene Family in Camphor Tree: Structure, Evolution, and Transcriptional Response to Epicoccum Infection. Plants, 14(17), 2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172694






