Distribution and Phylogenetic Diversity of Synechococcus-like Cyanobacteria in the Late Autumn Picophytoplankton of the Kara Sea: The Role of Atlantic and Riverine Water Masses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Environmental Parameters and Chlorophyll “a” Concentration
2.2. Cyanobacteria Abundance, Biomass, and the Contribution to Total Picophytoplankton
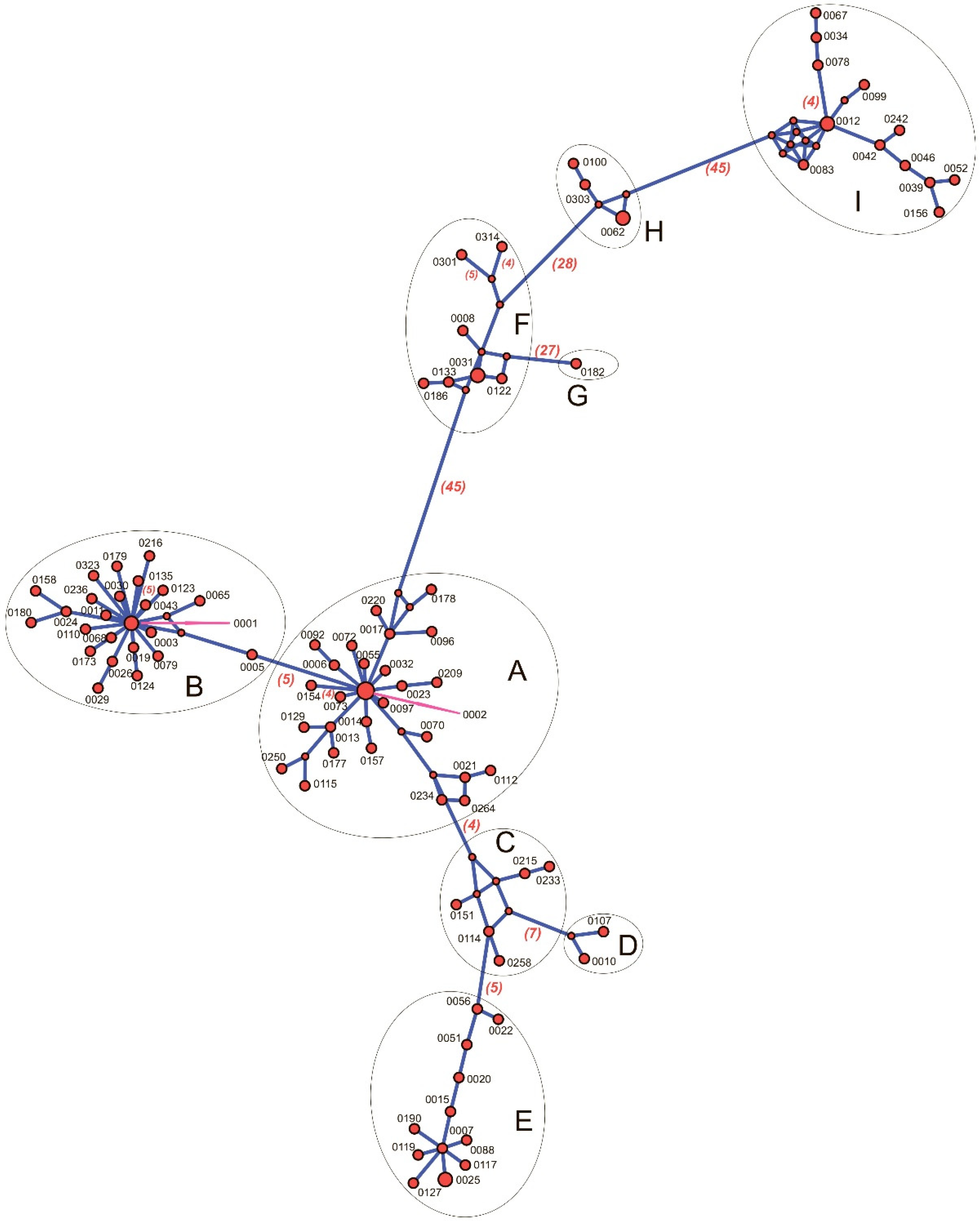
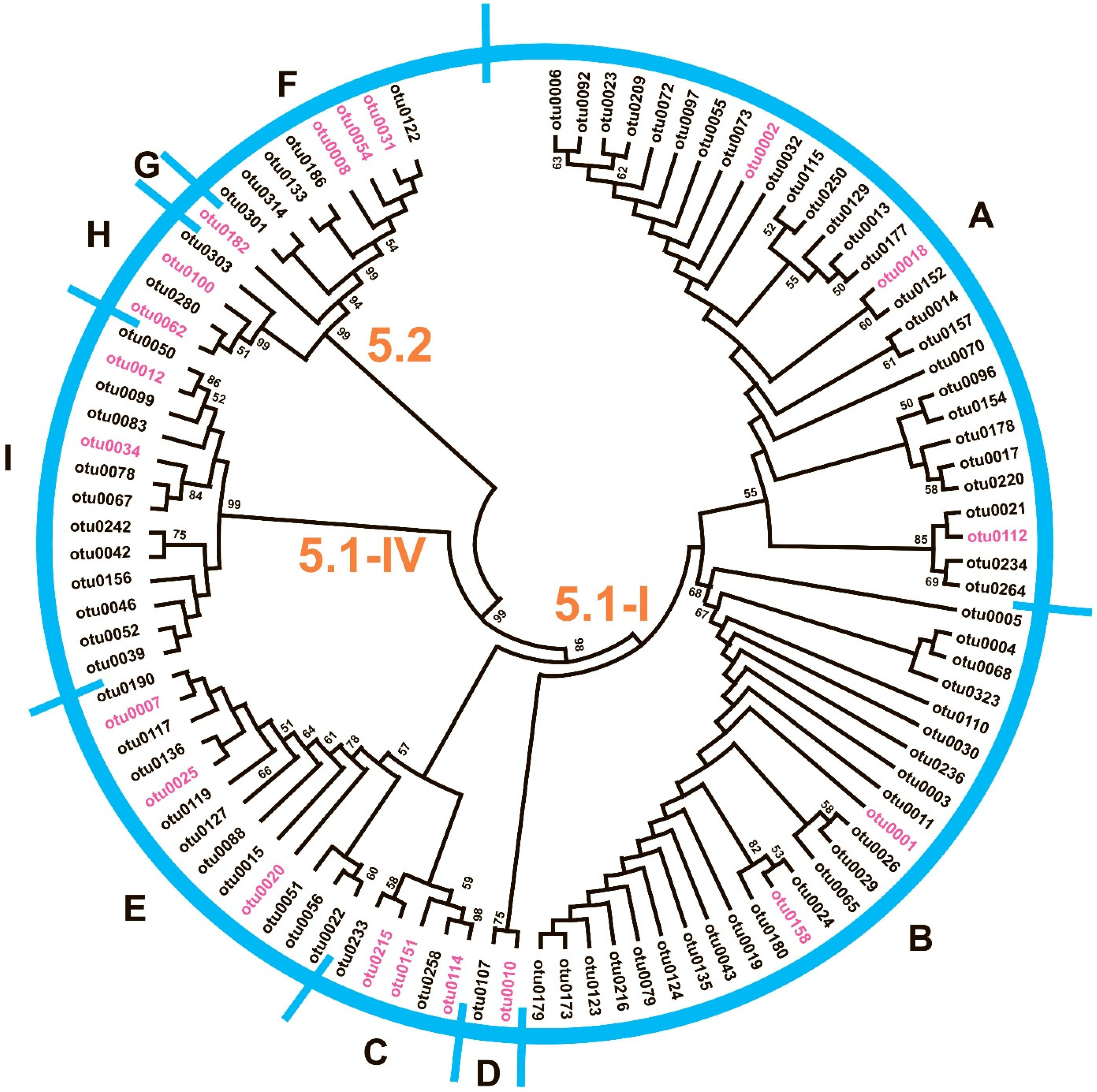
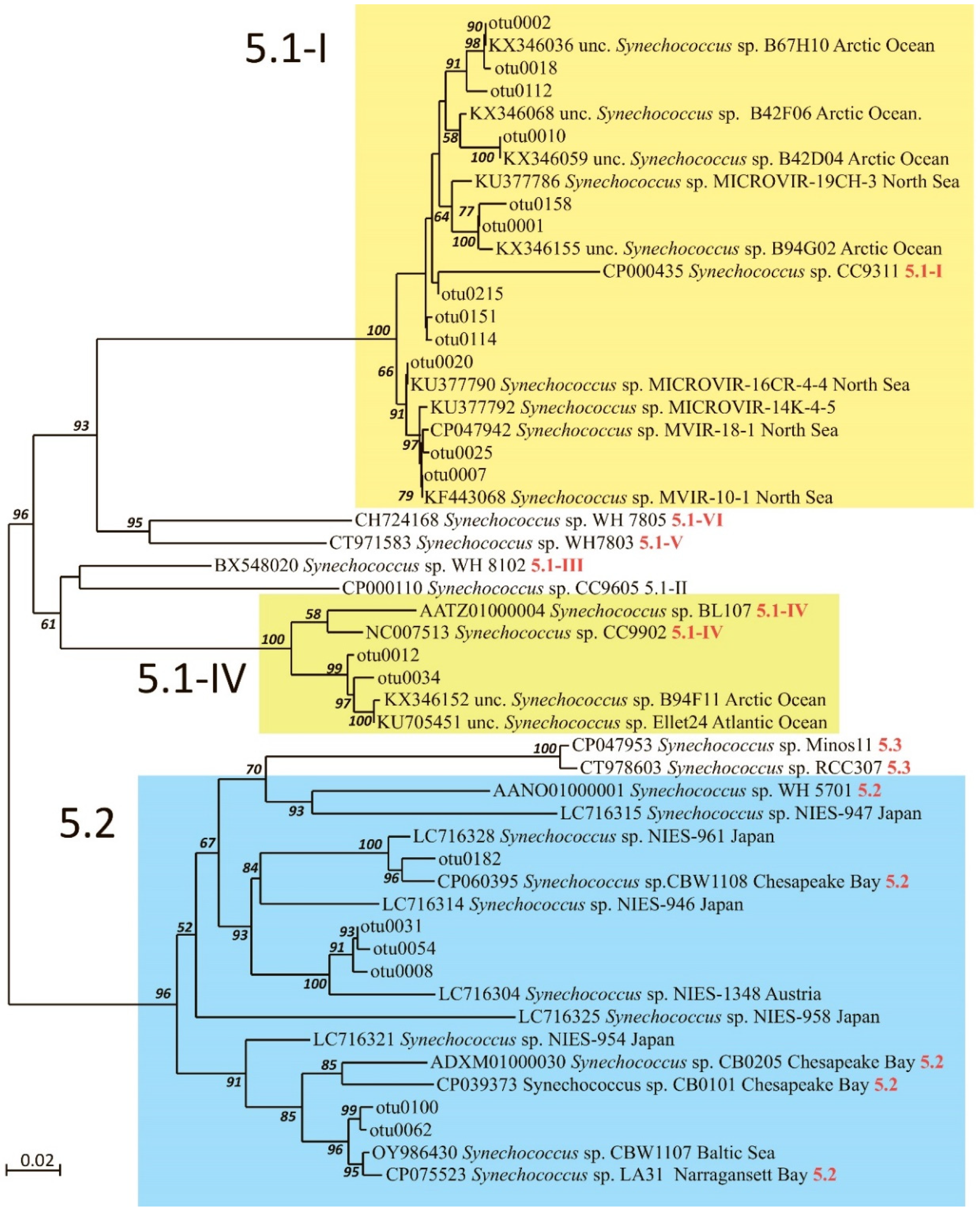
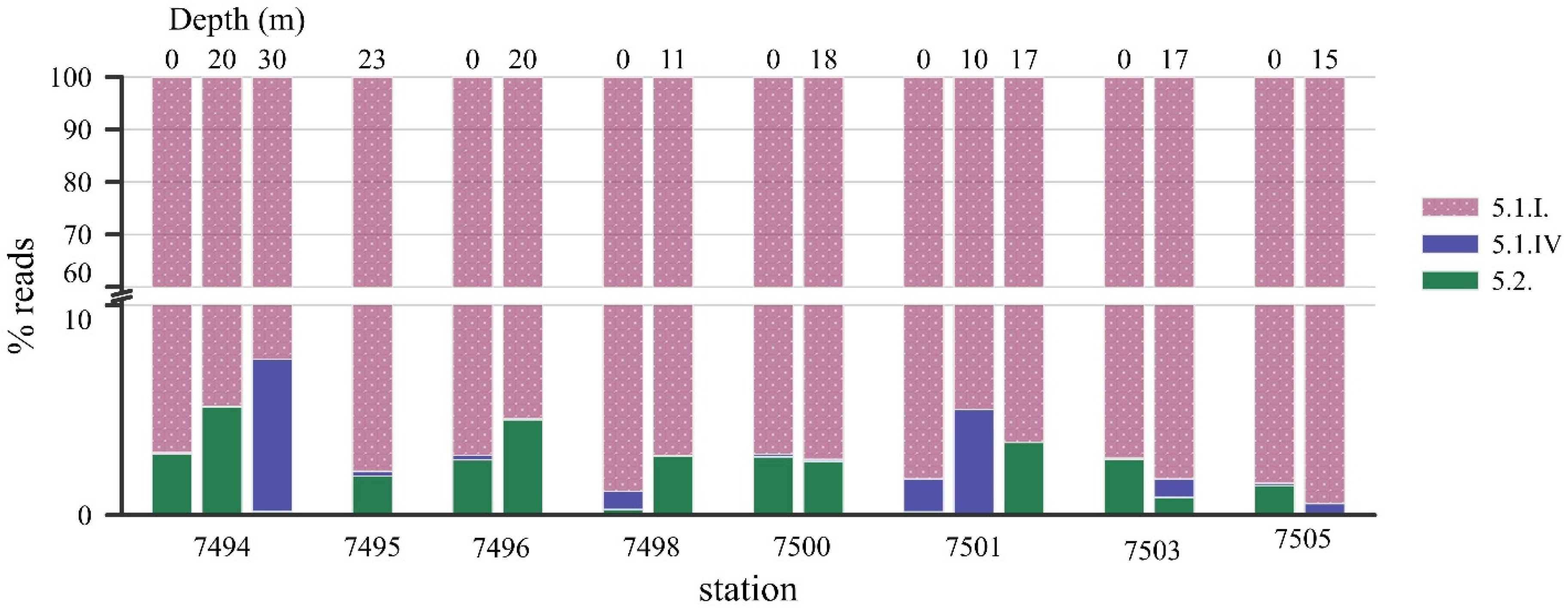
2.3. Synechococcus Phylogenetic Diversity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Water Sample Collection
4.2. Nutrients and Chlorophyll a Concentration
4.3. Total Picophytoplankton and PC Abundance and Biomass
4.4. Determination of Euphotic Depth
4.5. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, Cloning, and Sequencing
4.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gosselin, M.; Levasseur, M.; Wheeler, P.A.; Horner, R.A.; Booth, B.C. New measurements of phytoplankton and ice algal production in the Arctic Ocean. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 1997, 44, 1623–1644q. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, B.C.; Horner, R.A. Microalgae on the Arctic Ocean Section, 1994: Species abundance and biomass. Deep Sea Res. II 1997, 44, 1607–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidov, A.B.; Sukhanova, I.N.; Belevich, T.A.; Flint, M.V.; Gagarin, V.I.; Sergeeva, V.M.; Eremeeva, E.V.; Fedorov, A.V. Size-fractionated surface phytoplankton in the Kara and Laptev seas: Environmental control and spatial variability. Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser. 2021, 664, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partensky, F.; Blanchot, J.; Vaulot, D. Differential distribution and ecology of Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus in oceanic waters: A review. Bull. Inst. Oceanogr. Monaco 1999, 19, 457–476. [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen, M.L.; Doré, H.; Garczarek, L.; Seuthe, L.; Müller, O.; Sandaa, R.A.; Bratbak, G.; Larsen, A. Synechococcus in the Atlantic gateway to the Arctic Ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, A.J.; Moss, J.A.; Pakulski, J.D.; Catala, P.; Joux, F.; Jeffrey, W.H. Microbial diversity in a Pacific Ocean transect from the Arctic to Antarctic circles. Aquat. Microbiol. Ecol. 2005, 41, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwirglmaier, K.; Jardillier, L.; Ostrowski, M.; Mazard, S.; Garczarek, L.; Vaulot, D.; Not, F.; Massana, R.; Ulloa, O.; Scanlan, D.J. Global phylogeography of marine Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus reveals a distinct partitioning of lineages among oceanic biomes. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, M.T.; Kirchman, D.L. Photoheterotrophic microbes in the Arctic Ocean in summer and winter. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 4958–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelou, V.K.; Cottrell, M.T.; Kirchman, D.L. Light stimulated bacterial production and amino acid assimilation by cyanobacteria and other microbes in the North Atlantic Ocean. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5539–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, S.; Ingvaldsen, R.B.; Furevik, T. Arctic warming hotspot in the northern Barents Sea linked to declining sea-ice import. Nat. Clim. Change 2018, 8, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, L.; Vichi, M.; Scoccimarro, E. Sea-ice algal phenology in a warmer Arctic. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.N.; Dieckmann, G.S. (Eds.) Sea Ice, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Carmack, E.; Mclaughlin, F. Towards recognition of physical and geochemical change in Subarctic and Arctic Seas. Prog. Oceanogr. 2011, 90, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proshutinsky, A.; Krishfield, R.; Timmermans, M.L.; Toole, J.; Carmack, E.; McLaughlin, F.; Williams, W.J.; Zimmermann, S.; Itoh, M.; Shimada, K. Beaufort Gyre freshwater reservoir: State and variability from observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, C00A10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mioduchowska, M.; Pawłowska, J.; Mazanowski, K.; Weydmann-Zwolicka, A. contrasting marine microbial communities of the Fram Strait with the first confirmed record of Cyanobacteria Prochlorococcus marinus in the Arctic Region. Biology 2023, 12, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordeev, V.V.; Martin, J.M.; Sidorov, I.S.; Sidorova, M.V. A reassessment of the Eurasian river input of water, sediment, major elements and nutrients to the Arctic Ocean. Am. J. Sci. 1996, 296, 664–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stain, R. Circum Arctic river discharge and its geological record. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2000, 89, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadchiev, A.A.; Izhitskiy, A.S.; Zavialov, P.O.; Kremenetskiy, V.V.; Polukhin, A.A.; Pelevin, V.V.; Toktamysova, Z.M. Structure of the buoyant plume formed by Ob and Yenisei River discharge in the southern part of the Kara Sea during summer and autumn. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 5916–5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadchiev, A.A.; Frey, D.I.; Shchuka, S.A.; Tilinina, N.D.; Morozov, E.G.; Zavialov, P.O. Structure of freshened surface layer in the Kara Sea during icefree periods. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2021, 126, e2020JC016486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanzlick, D.; Aagard, K. Freshwater and Atlantic water in the Kara Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 1980, 85, 4937–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinina, E.O.; Kossova, S.A.; Miroshnikov, A.Y.; Fyaizullina, R.V. Isotope (δD, δ18O) composition and the freshwater input to the Kara Sea. Oceanology 2017, 57, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waleron, M.; Waleron, K.; Vincent, W.F.; Wilmotte, A. Allochthonous inputs of riverine picocyanobacteria to coastal waters in the Arctic Ocean. FEMS Microb. Ecol. 2006, 59, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flombaum, P.; Gallegos, J.L.; Gordillo, R.A.; Rincón, J.; Zabala, L.L.; Jiao, N.; Karl, D.M.; Li, W.K.; Lomas, M.W.; Veneziano, D.; et al. Present and future global distributions of the marine cyanobacteria Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9824–9829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, J.; Jing, H.; Qin, S. Picocyanobacterial Synechococcus in marine ecosystem: Insights from genetic diversity, global distribution, and potential function. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 177, 105622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufresne, A.; Ostrowski, M.; Scanlan, D.; Garczarek, L.; Mazard, S.; Palenik, B.P. Unraveling the genomic mosaic of ubiquitous genus of marine cyanobacteria. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Wang, K.; Huang, S.; Jiao, N.; Chen, F. Distinct patterns of picocyanobacterial communities in winter and summer in the Chesapeake Bay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2955–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, B.; Zehr, J.; Gibson, A.; Campbell, L. Cyanobacterial assimilatory nitrate reductase gene diversity in coastal and oligotrophic marine environments. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 2083–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, A.F.; Penno, S.; Zandbank, K.; Paytan, A.; Huse, S.M.; Welch, D.M. Long term seasonal dynamics of Synechococcus population structure in the Gulf of Aqaba, Northern Red Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, G.; Palenik, B. Synechococcus diversity in the California current as seen by RNA polymerase (rpoC1) gene sequences of isolated strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 4298–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazard, S.; Ostrowski, M.; Partensky, F.; Scanlan, D.J. Multi-locus sequence analysis, taxonomic resolution and biogeography of marine Synechococcus. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Harvey, H.R.; Taylor, K.; Jiao, N.; Chen, F. Novel lineages of Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus in the global oceans. ISME J. 2012, 6, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlgren, N.A.; Rocap, G. Diversity and distribution of marine Synechococcus: Multiple gene phylogenies for consensus classification and development of qPCR assays for sensitive measurement of clades in the ocean. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, F.; Tschoeke, D.A.; Thompson, F.; Thompson, C. Comparative genomics of Synechococcus and proposal of the new genus Parasynechococcus. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komárek, J.; Johansen, J.R.; Šmarda, J.; Strunecký, O. Phylogeny and taxonomy of Synechococcus-like cyanobacteria. Fottea 2020, 20, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, V.W.; Tschoeke, D.A.; Swings, J.; Cosenza, C.A.; Mattoso, M.; Thompson, C.C.; Thompson, F.L. A new genomic taxonomy system for the Synechococcus collective. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 4557–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redfield, A.C.; Ketchum, B.H.; Richards, F.A. The influence of organisms on the composition of seawater. In The Sea; Hill, M.N., Ed.; Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1963; pp. 26–77. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlov, V.K.; Pfirman, S.L. Hydrographic structure and variability of the Kara Sea: Implications for pollutant distribution. Deep Sea Res. Pt. II. 1995, 42, 1369–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, I.N.; Karcher, M.J. Modelling the seasonal variability of circulation and hydrography in the Kara Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 13431–13448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatsepin, A.G.; Morozov, E.G.; Paka, V.T.; Demidov, A.N.; Kondrashov, A.A.; Korzh, A.O.; Kremenetskiy, V.V.; Poyarkov, S.G.; Soloviev, D.M. Circulation in the southwestern part of the Kara Sea in September 2007. Oceanology 2010, 50, 643–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdman, M.; Castenholz, R.W.; Waterbury, J.B.; Rippka, R. Form-genus XIII. Synechococcus. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology; Boone, D.R., Castenholz, R.W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 1, pp. 508–512. [Google Scholar]
- Coello-Camba, A.; Diaz-Rua, R.; Agustí, S. Design and use of a new primer pair for the characterization of the cyanobacteria Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus communities targeting petB gene through metabarcoding approaches. MethodsX 2023, 11, 102444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, Z.V.; Beardall, J.; Flynn, K.J.; Quigg, A.; Rees, T.A.V.; Raven, J.A. Phytoplankton in a changing world: Cell size and elemental stoichiometry. J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, T.R.; Peele, E.R.; Ammerman, J.W.; Harding, L.W., Jr. Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in Chesapeake Bay. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 82, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egge, J.K.; Aksnes, D.L. Silicate as regulating nutrient in phytoplankton competition. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 83, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadchiev, A.; Sedakov, R.; Frey, D.; Gordey, A.; Rogozhin, V.; Zabudkina, Z.; Spivak, E.; Kuskova, E.; Sazhin, A.; Semiletov, I. Intense zonal freshwater transport in the Eurasian Arctic during ice-covered season revealed by in situ measurements. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Wommack, K.E.; Chen, F. Abundance and distribution of Synechococcus spp. and cyanophages in the Chesapeake Bay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7459–7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Cheung, S.; Endo, H.; Suzuki, K.; Liu, H. Latitudinal and vertical variation of Synechococcus assemblage composition along 170 degrees W transect from the South Pacific to the Arctic Ocean. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belevich, T.A.; Ilyash, L.V.; Demidov, A.B.; Flint, M.V. Picophytoplankton distribution at the Ob River section and in the western part of the Kara Sea. Oceanology 2019, 59, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belevich, T.A.; Milyutina, I.A.; Troitsky, A.V.; Flint, M.V. Picophytoplankton in Blagopoluchia Bay (Novaya Zemlya Archipelago) and adjacent part of the Kara Sea. Oceanology 2020, 60, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belevich, T.A.; Demidov, A.B.; Vorob’eva, O.V.; Polukhin, A.A.; Shchuka, S.A.; Eremeeva, E.V.; Flint, M.V. Photoautotrophic picoplankton of the Kara Sea in the middle of summer: Effect of first-year ice retreat on carbon and chlorophyll biomass and primary production. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 202, 106809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belevich, T.A.; Milyutina, I.A.; Demidov, A.B.; Flint, M.V. Spring picophytoplankton of the Kara Sea. Oceanology 2022, 62, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira-Turcq, P.F.; Martin, J.M. Characterization of fine particles by flow cytometry in estuarine and coastal Arctic waters. J. Sea Res. 1998, 39, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belevich, T.A.; Demidov, A.B.; Makkaveev, P.N.; Shchuka, S.A.; Flint, M.V. Picophytoplankton distribution along Khatanga bay-shelf-continental slope environment gradients in the western Laptev Sea. Heliyon 2021, 7, 06224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohm, J.A.; Ahlgren, N.A.; Thomson, Z.J.; Williams, C.; Moffett, J.W.; Saito, M.A.; Webb, E.A.; Rocap, G. Co-occurring Synechococcus ecotypes occupy four major oceanic regimes defined by temperature, macronutrients and iron. ISME J. 2016, 10, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudels, B.; Jones, E.P.; Schauer, U.; Eriksson, P. Atlantic sources of the Arctic Ocean surface and halocline waters. Polar Res. 2004, 23, 181–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wang, K.; Kan, J.; Suzuki, M.T.; Wommack, K.E. Diverse and unique picocyanobacteria in Chesapeake Bay, revealed by 16S-23S rRNA internal transcribed spacer sequences. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2239–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Wang, K.; Kan, J.; Bachoon, D.S.; Lu, J.; Lau, S.; Campbell, L. Phylogenetic diversity of Synechococcus in the Chesapeake Bay revealed by Rilbulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase (RuBisCO) large subunit gene (rbcL) sequences. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 36, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xia, X.; Partensky, F.; Garczarek, L.; Suzuki, K.; Guo, C.; Cheung, S.Y.; Liu, H. Phylogeography and pigment type diversity of Synechococcus cyanobacteria in surface waters of the northwestern Pacific Ocean. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Vidyarathna, N.K.; Palenik, B.; Lee, P.; Liu, H. Comparison of the seasonal variations of Synechococcus assemblage structures in estuarine waters and coastal waters of Hong Kong. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 7644–7655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belevich, T.A.; Milyutina, I.A.; Troitsky, A.V. Picocyanobacteria in estuaries of three Siberian rivers and adjacent shelves of Russian Arctic Seas: Genetic diversity and distribution. Diversity 2023, 15, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverkamp, T.; Acinas, S.G.; Doeleman, M.; Stomp, M.; Huisman, J.; Stal, L.J. Diversity and phylogeny of Baltic Sea picocyanobacteria inferred from their ITS and phycobiliprotein operons. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucich, D.; Xu, Y.; Sosa, A.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, R.; Jiao, N.; Chen, F. Complete genome sequences of Chesapeake Bay Synechococcus strains CBW1002 and CBW1006 isolated in Winter. Genome Biol. Evol. 2021, 13, evab009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F. Picocyanobacteria in the Chesapeake Bay: Isolation, diversity, and adaptation. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kawachi, M. Potential genetic diversity of Synechococcus-related strains maintained in the Microbial Culture Collection of the National Institute for Environmental Studies, Japan. Microb. Resour. Syst. 2022, 38, 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Belevich, T.A.; Milyutina, I.A.; Vorob’eva, O.V.; Troitsky, A.V. The rDNA diversity, interseasonal dynamic, and functional role of cyanobacteria Synechococcus in the Sub-Arctic White Sea. Plants 2024, 13, 3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karl, D.M.; Bailiff, M.D. The measurement and distribution of dissolved nucleic acids in aquatic environments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 34, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFlaun, M.; Paul, J.; Jeffrey, W. Distribution and molecular weight of dissolved DNA in subtropical estuarine and oceanic environments. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1987, 38, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cokelet, E.D.; Tervalon, N.; Bellingham, J.G. Hydrography of the West Spitsbergen Current, Svalbard Branch: Autumn 2001. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 2008, 113, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatsepin, A.G.; Kremenetskiy, V.V.; Kubryakov, A.A.; Stanichny, S.V.; Soloviev, D.M. Propagation and transformation of waters of the surface desalinated layer in the Kara Sea. Oceanology 2015, 55, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, U.; Loeng, H.; Rudels, B.; Ozhigin, V.K.; Dieck, W. Atlantic Water flow through the Barents and Kara Seas. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2002, 49, 2281–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karcher, M.; Kulakov, M.; Pivovarov, S.; Schauer, U.; Kauker, F.; Schlitzer, R. Atlantic Water flow to the Kara Sea—Comparing model results with observations. In Proceeding in Marine Science, Siberian River Run-Off in the Kara Sea: Characterisation, Quantification, Variability and Environmental Significance; Stein, R., Fahl, R., Futterer, K., Galimov, E., Eds.; Proceedings in Marine Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 47–69. [Google Scholar]
- Grasshoff, K.; Kremling, K.; Ehrhardt, M. (Eds.) Methods of Seawater Analysis, 3rd ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 1999; p. 577. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, T.R.; Maita, Y.; Lalli, C.M. A Manual of Chemical and Biological Methods for Seawater Analysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; p. 173. [Google Scholar]
- Holm-Hansen, O.; Riemann, B. Chlorophyll-a determination: Improvements in methodology. OIKOS 1978, 30, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verity, P.G.; Robertson, C.Y.; Tronzo, C.R.; Andrews, M.G.; Nelson, J.R.; Sieracki, M.E. Relationship between cell volume and the carbon and nitrogen content of marine photosynthetic nanoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 1434–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuRand, M.D.; Olson, R.J.; Chisholm, S.W. Phytoplankton population dynamics at the Bermuda Atlantic time-series station in the Sargasso Sea. Deep-Sea Res. II 2001, 48, 1983–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrand, H.; Dürselen, C.-D.; Kirschtel, D.; Pollingher, U.; Zohary, T. Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J. Phycol. 1999, 5, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidov, A.B.; Kopelevich, O.V.; Mosharov, S.A.; Sheberstov, S.V.; Vazyulya, S.V. Modelling Kara Sea phytoplankton primary production: Development and skill assessment of regional algorithms. J. Sea Res. 2017, 125, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selivanova, E.A.; Ignatenko, M.E.; Yatsenko-Stepanova, T.N.; Plotnikov, A.O. Diatom assemblages of the brackish Bolshaya Samoroda River (Russia) studied via light microscopy and DNA metabarcoding. Protistology 2019, 13, 215–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzhetsky, A.; Nei, M. A simple method for estimating and testing minimum-evolution trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1992, 9, 945–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Suleski, M.; Sanderford, M.; Sharma, S.; Tamura, K. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 12 for adaptive and green computing. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2024, 41, msae263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11030–11035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast Model Selection for Accurate Phylogenetic Estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, F. Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 1989, 123, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandelt, H.; Forster, P.; Röhl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. POPART: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rantanen, M.; Karpechko, A.Y.; Lipponen, A.; Nordling, K.; Hyvärinen, O.; Ruosteenoja, K.; Vihma, T.; Laaksonen, A. The Arctic has warmed nearly four times faster than the globe since 1979. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

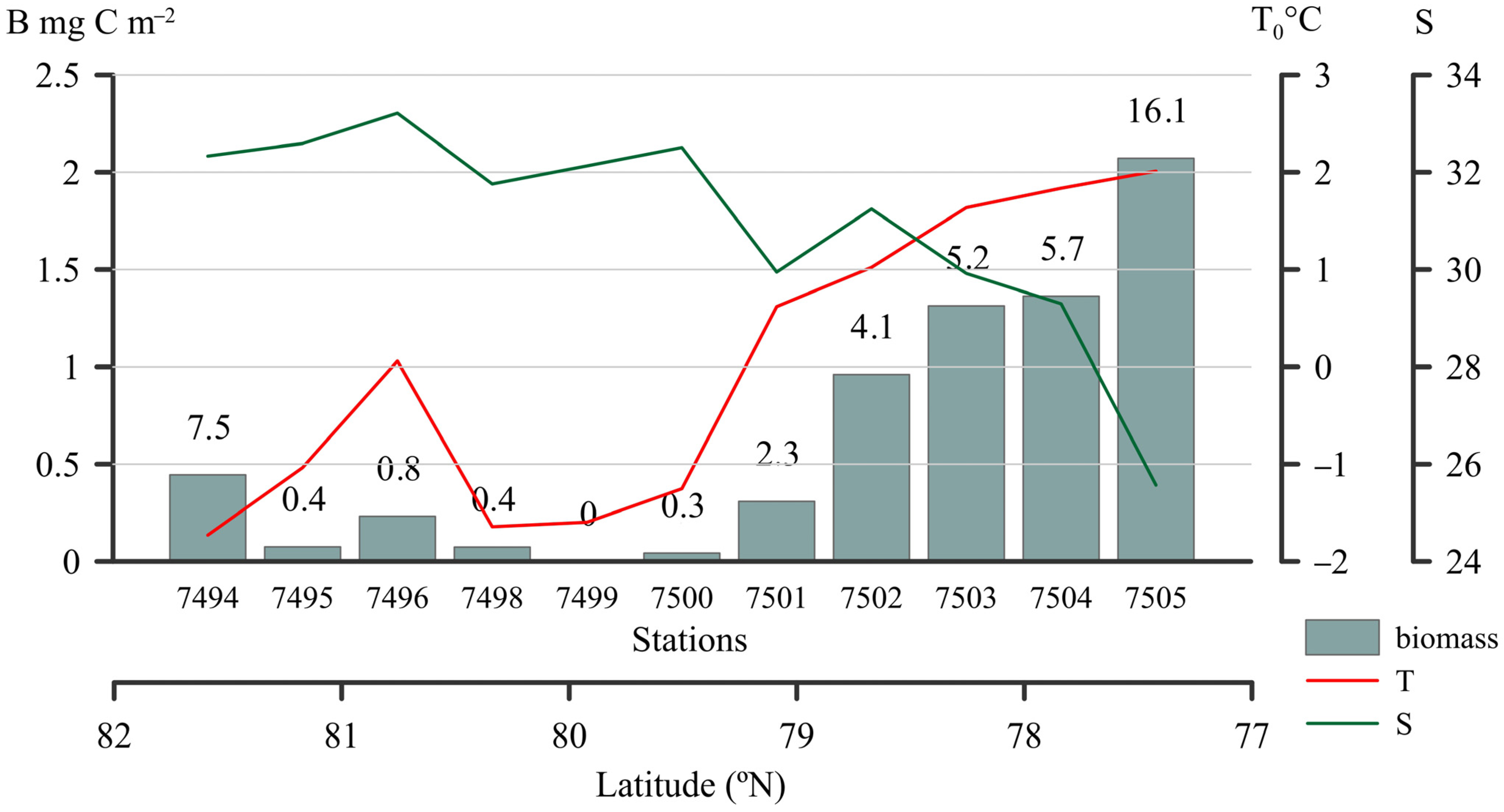
| Station | H | Zeu | Surface | Chltot | Chlpico | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 °C | S0 | PO43– | Si(OH)4 | DIN | |||||
| 7494 | 1652 | 40 | −1.7 | 32.3 | 0.09 | 0.46 | 0.49 | 0.15 | 0.02 |
| 7495 | 490 | 29 | −1.0 | 32.6 | 0.08 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.05 |
| 7496 | 176 | 34 | 0.1 | 33.2 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.05 |
| 7498 | 196 | 43 | −1.6 | 31.8 | 0.11 | 0.31 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.04 |
| 7499 | 233 | 47 | −1.6 | 32.1 | 0.11 | 0.46 | 0.32 | 0.10 | 0.04 |
| 7500 | 83 | 64 | −1.3 | 32.5 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.03 |
| 7501 | 292 | 20 | 0.6 | 29.9 | 0.13 | 3.54 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.05 |
| 7502 | 230 | 23 | 1.0 | 31.2 | 0.12 | 1.49 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0.05 |
| 7503 | 104 | 21 | 1.6 | 29.9 | 0.10 | 3.13 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.05 |
| 7504 | 120 | 22 | 1.8 | 29.3 | 0.14 | 5.37 | 0.1 | 0.13 | 0.05 |
| 7505 | 72 | 24 | 2.0 | 25.6 | 0.16 | 11.99 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.03 |
| A | C | B | D | E | I | G | F | Within Clades | Number of OTUs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.012 | 29 | ||||||||
| C | 0.029 | 0.009 | 5 | |||||||
| B | 0.031 | 0.030 | 0.011 | 25 | ||||||
| D | 0.034 | 0.033 | 0.036 | 0.010 | 2 | |||||
| E | 0.040 | 0.025 | 0.047 | 0.041 | 0.009 | 13 | ||||
| I | 0.166 | 0.161 | 0.164 | 0.160 | 0.168 | 0.013 | 13 | |||
| G | 0.169 | 0.177 | 0.179 | 0.174 | 0.170 | 0.173 | - | 1 | ||
| F | 0.170 | 0.177 | 0.175 | 0.178 | 0.173 | 0.175 | 0.098 | 0.017 | 8 | |
| H | 0.174 | 0.174 | 0.176 | 0.170 | 0.162 | 0.156 | 0.126 | 0.111 | 0.006 | 4 |
| Data | Location | Cells mL−1 | % | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kara Sea | ||||
| September 2017 | Shelf, Ob estuary | 190–240 | 0.2–11 | [48] |
| September 2017 | Northwest | 20 | – | [49] |
| July 2019 | Northwest | 20–70 | – | [50] |
| June 2021 | Western area | 8–16 | 0.2–2 | [51] |
| October 2022 | Shelf, continental slope | 2–88 | 0.3–16 | This study |
| Laptev Sea | ||||
| September 1991 | Lena River delta | 1000–30,000 | – | [52] |
| September 2017 | Continental slope, shelf, Khatanga estuary | 20–1250 | 1–26 | [53] |
| Beaufort Sea | ||||
| September 2002 | Shelf, Mackenzie estuary | 215–2400 | [22] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belevich, T.A.; Milyutina, I.A.; Demidov, A.B.; Vorob’eva, O.V.; Polukhin, A.A.; Shchuka, S.A.; Troitsky, A.V. Distribution and Phylogenetic Diversity of Synechococcus-like Cyanobacteria in the Late Autumn Picophytoplankton of the Kara Sea: The Role of Atlantic and Riverine Water Masses. Plants 2025, 14, 2614. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172614
Belevich TA, Milyutina IA, Demidov AB, Vorob’eva OV, Polukhin AA, Shchuka SA, Troitsky AV. Distribution and Phylogenetic Diversity of Synechococcus-like Cyanobacteria in the Late Autumn Picophytoplankton of the Kara Sea: The Role of Atlantic and Riverine Water Masses. Plants. 2025; 14(17):2614. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172614
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelevich, Tatiana A., Irina A. Milyutina, Andrey B. Demidov, Olga V. Vorob’eva, Alexander A. Polukhin, Sergey A. Shchuka, and Aleksey V. Troitsky. 2025. "Distribution and Phylogenetic Diversity of Synechococcus-like Cyanobacteria in the Late Autumn Picophytoplankton of the Kara Sea: The Role of Atlantic and Riverine Water Masses" Plants 14, no. 17: 2614. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172614
APA StyleBelevich, T. A., Milyutina, I. A., Demidov, A. B., Vorob’eva, O. V., Polukhin, A. A., Shchuka, S. A., & Troitsky, A. V. (2025). Distribution and Phylogenetic Diversity of Synechococcus-like Cyanobacteria in the Late Autumn Picophytoplankton of the Kara Sea: The Role of Atlantic and Riverine Water Masses. Plants, 14(17), 2614. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172614









